Multi-plan Collaborative Rescheduling of High-speed Train Operation Considering the Utilization of Rolling Stock and Arrival and Departure Tracks
-
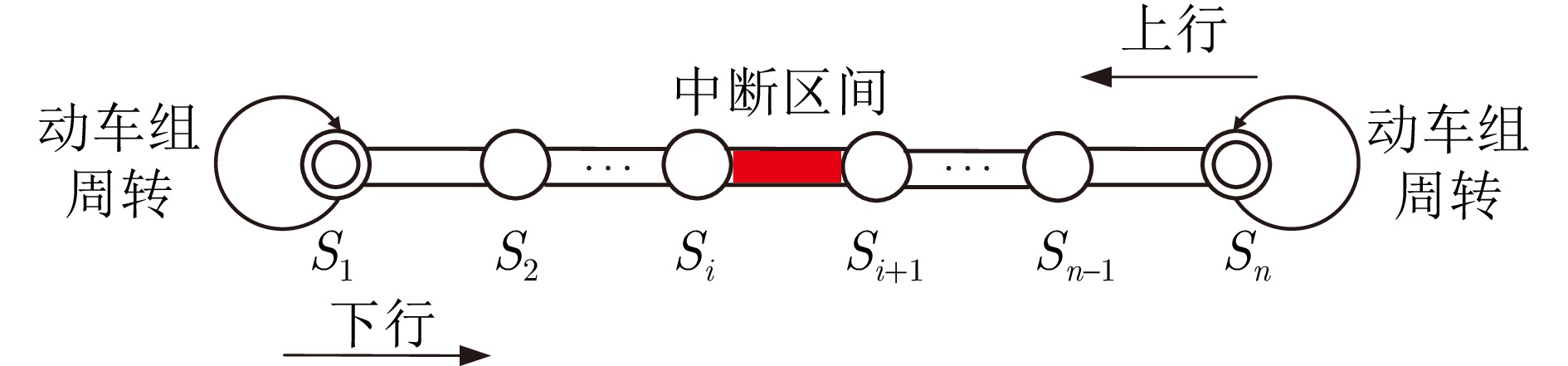
摘要: 随着我国高速铁路快速发展, “八纵八横”高铁路网加密成型, 呈现出运行环境复杂、行车密度高及长交路跨线运营等典型特征. 一旦遭受大风、红光带、接触网挂异物和设备故障等突发事件, 则将导致列车偏离运行计划, 进而影响到发线运用和动车组(Eletric multiple units, EMU)周转计划. 如何在调整运行图的同时保证动车组和到发线运用的可行性是提高列车运行调整效率的关键. 针对区间双向中断场景下到发线运用冲突和动车组接续计划失效问题, 采用取消列车、变更列车到发时刻、更换到发线、备用动车组接续等策略对运行图、动车组和到发线运用计划进行调整. 基于事件−活动网络建立考虑动车组接续和到发线运用的列车运行协同调整模型, 设计两阶段求解方法对模型求解. 运用京津城际实际数据对模型和方法进行仿真验证, 结果表明相比于先到先服务(First come, first served, FCFS)策略, 多计划协同调整策略能有效降低列车晚点时间. 与整体求解方法相比, 两阶段求解方法能够保证模型求得解的质量且有效提高模型求解效率.Abstract: With the rapid development of high-speed railways in China, the “eight vertical and eight horizontal” high-speed railway network has become denser, presenting typical characteristics such as complex operating environments, high train densities, and long-distance cross-line operations. Once facing sudden events as strong winds, red light bands, foreign objects on overhand lines and equipment failures, trains will deviate from the operating plan, which in turn affects the departure line operation and electric multiple units (EMUs) turnover plan. Ensuring the feasibility of EMUs and departure line operations while adjusting timetable is crucial to improving the efficiency of train operation adjustments. To address departure line operations conflicts and EMU connection plans failure under the scenario of bidirectional interruptions between sections, strategies as canceling trains, changing train departure times, switching departure lines, backup EMU connections are employed to adjust timetable, EMUs, and departure line operation plans. A train operation coordination adjustment model considering EMU connections and departure line operations is established based on event-activity network, a two-stage solving method is designed to solve the model. The model and method are validated using actual data from Beijing-Tianjin intercity railway, the results show that compared to “first come, first served (FCFS)” strategy, multi-plan coordination adjustment method can effectively reduce train delay time. Compared with overall solving method, the two-stage solving method can ensure the model solution quality and effectively improve the model solving efficiency.
-
表 1 决策变量定义
Table 1 Definition of decision variables
序号 决策变量 含义 类型 1 $ x_{e} $ 事件$e $发生的实际时刻 整数 2 $ y_{t} $ 列车$t $是否被取消运行 0-1 3 $ \varphi_{a} $ 列车停站活动a是否发生 0-1 4 $ \lambda_{a} $ 两列车之间的顺序活动 0-1 5 $ \theta_{t,\;s}^{p} $ 列车$t $在$s $站是否占用p股道 0-1 6 $ \delta_{t_{e},\;t_{f}}^{p} $ 两列车是否占用相同到发线$p $ 0-1 表 2 参数定义
Table 2 Definition of parameters
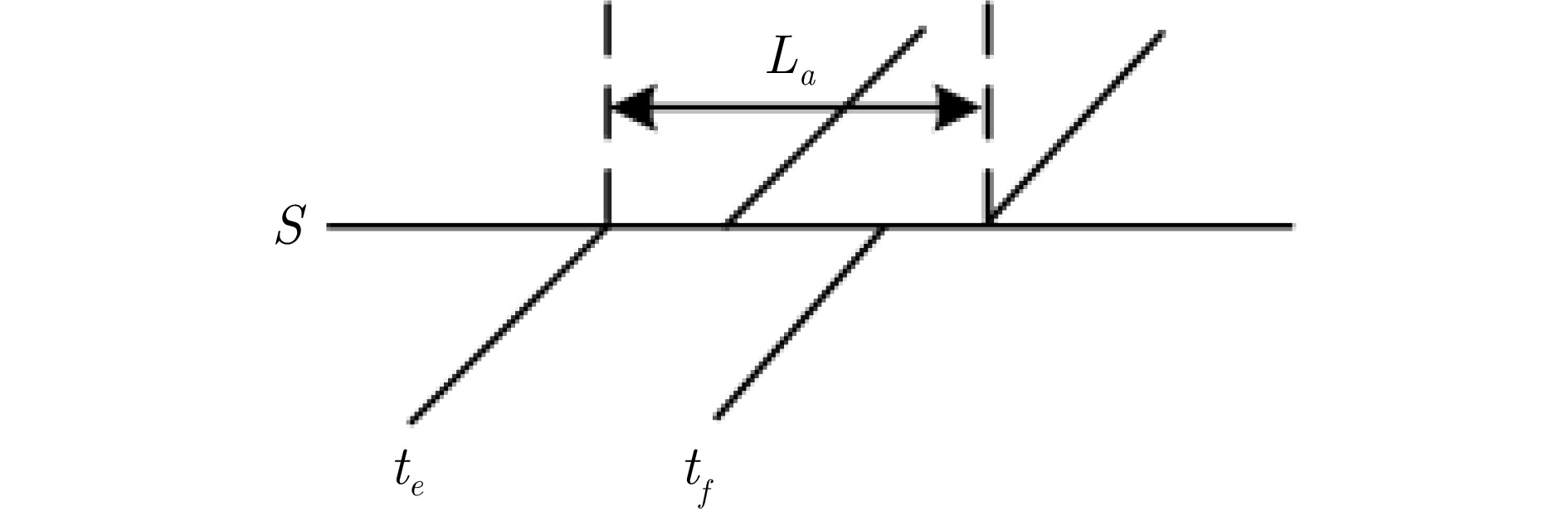
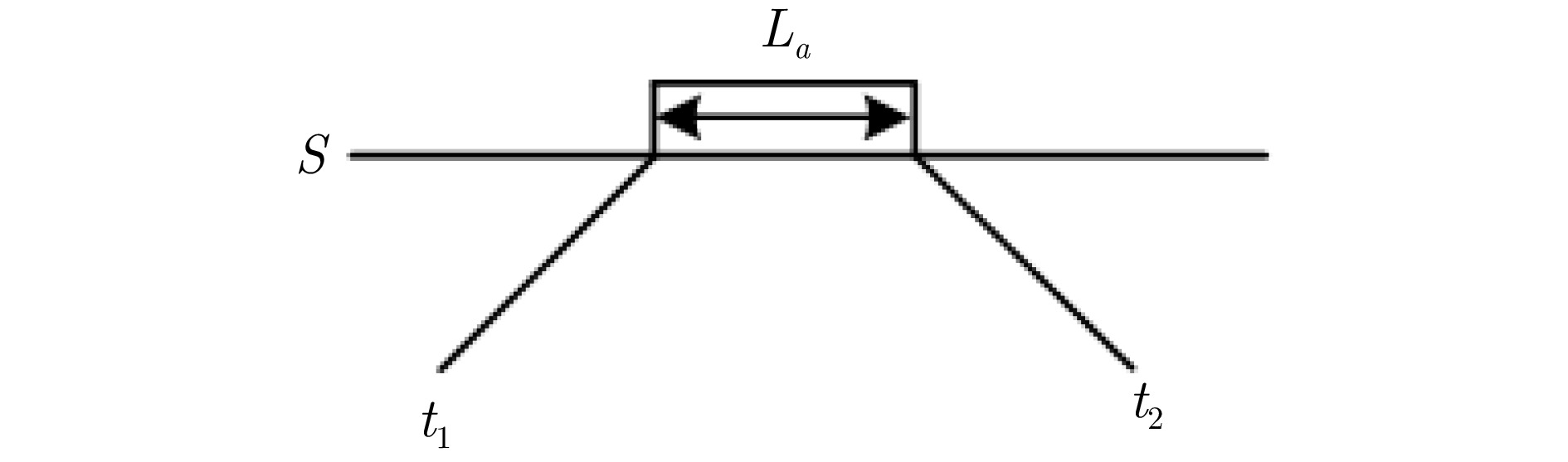
序号 参数 定义 1 $T $ 列车集合, $t \in T$ 2 $S $ 车站集合, $s \in S$ 3 $P $ 车站股道集合, $ p\in P$ 4 $E $ 事件集合, $ e \in E $ 5 ${{E}} _{{\mathrm{origin}}}^{{\mathrm{dep}}} $ 始发站列车的出发事件 6 $A $ 活动集合, $a \in A$ 7 $ {{A}}_{{\mathrm{rol}}} $ 动车组接续活动集合 8 $ {{t}}_{{{e}}} $ 与事件$e $相关联的列车 9 $ {{p}}_{{{e}}} $ 事件$e $计划发生时刻 10 $M $ 足够大的正整数 11 $ \omega _{1} $, $ \omega _{2} $, $ \omega _{3} $ 目标函数惩罚系数 12 ${{L}}_{{a}} $ 活动$a $最小间隔时间 表 3 相关参数取值
Table 3 Values of relative parameters
序号 参数 取值 1 列车最小停站时间${L}_{a} $ 2 min 2 同向列车最小到发间隔${L}_{a} $ 3 min 3 占用相同股道列车最小安全间隔${L}_{a} $ 2 min 4 动车组最小接续时间${L}_{a} $ 15 min 5 北京南站备用动车组 9 列 6 滨海站备用动车组 3 列 7 $M $ 1 440 min 8 $ \omega_{1} $ 1 000 9 $ \omega_{2} $ 1 10 $ \omega_{3} $ 1 表 4 调整后列车运行计划
Table 4 The rescheduled train plans
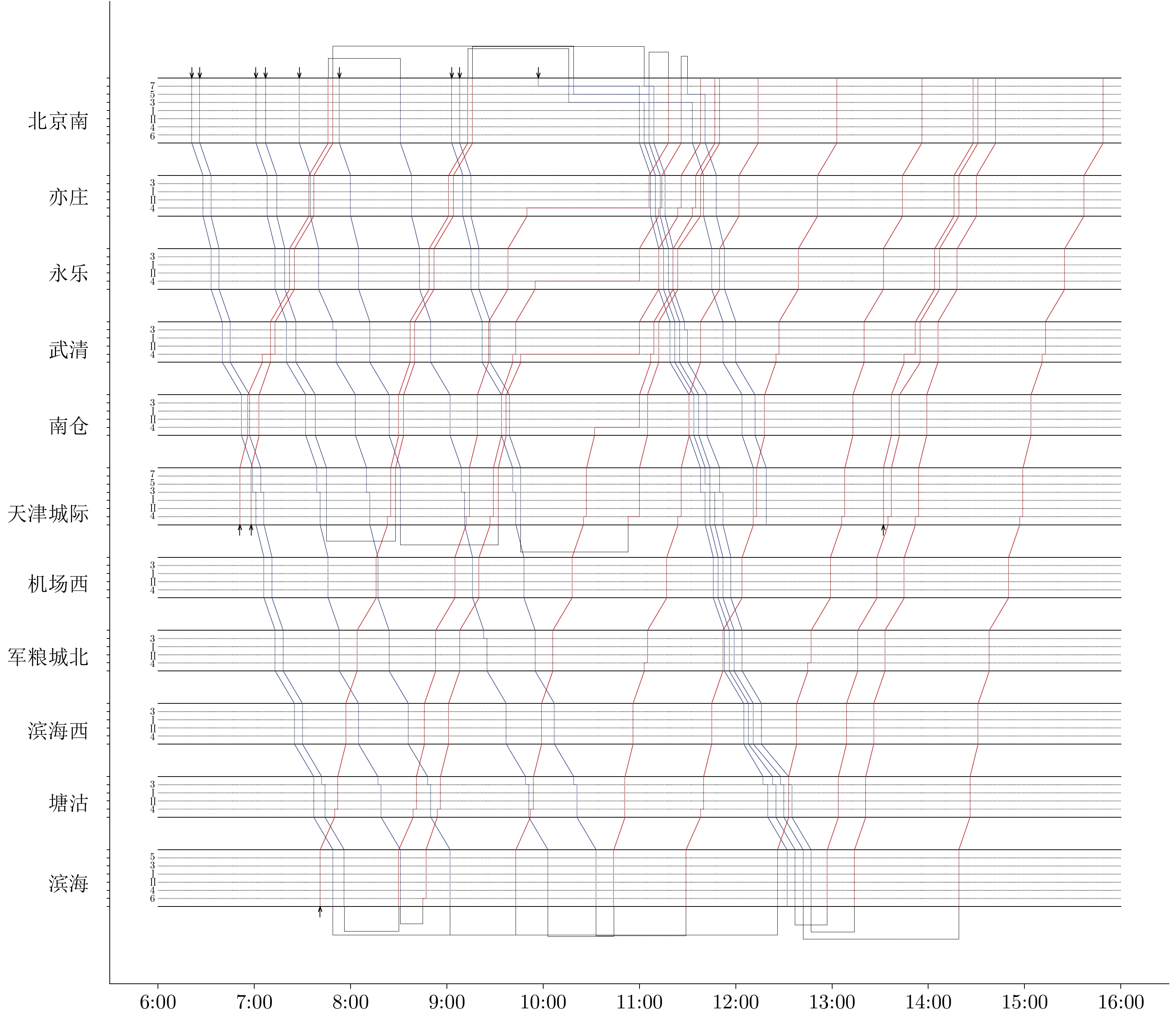
列车编号 始发时刻 终到时刻 停站方案 后续列车 D1 06:21 07:17 51111511113 U3 D2 06:26 07:29 51111711133 U5 D3 07:01 08:04 51111711133 U6 D4 07:07 07:45 (07:37) 311117 U4 D5 07:28 09:02 (08:37) 311313 (7)11133 U8 D6 07:53 08:31 (08:23) 311113 U7 D7 08:31 10:03 (09:41) 311113 (7)13133 U9 D8 09:03 10:33 (10:06) 311113 (7)11133 U11 D9 09:08 09:46 (09:38) 311113 U10 D10 11:09 (09:25) 12:42 (10:28) 511113 (5)11135 U16(−) D11 11:33 (09:46) 12:11 (10:16) 311113 — D12 11:00 (09:57) 12:32 (11:00) 7(5) 11113 (5)11135 −(U12) D13 11:03 (10:16) 12:37 (11:23) 3(5) 1111511135 U13 D14 11:09 (10:52) 12:47 (12:02) 7(5) 11313 (7)11(3)133U14 D15 11:41 (11:30) 12:19 (12:00) 5(3) 11113 — U1 06:51 07:49 (07:33) 424226 D10 (D6) U2 06:58 07:46 (07:28) 422226 D7 U3 07:41 09:13 (08:44) 44222422226 D13 (D8) U4 08:28 (08:25) 09:16 (08:55) 422226 D14 U5 08:30 11:18 (09:33) 6422242224 (2)6D11 U6 08:47 (08:45) 11:26 (09:55) 442224244 (2)4(2)6D15 U7 09:32 (09:30) 11:38 (10:00) 424(2)24(2)4 −(D13) U8 09:43 11:47 (10:53) 4422244 (2)424(2)4— U9 10:44 12:14 (11:47) 42242422226 — U10 11:00 (10:53) 11:50 (11:23) 422226 — U11 11:29 13:03 (12:39) 64222424226 — U12 12:26 13:56 (13:29) 62242422226 — U13 12:57 14:31 (13:52) 4222242 (4)2226 — U14 13:14 14:42 (14:09) 62222422226 — U15 13:32 14:28 (14:14) 424226 — U16 14:19 15:49 (15:22) 62222424226 — 表 5 不同中断场景下考虑不同策略的列车运行调整
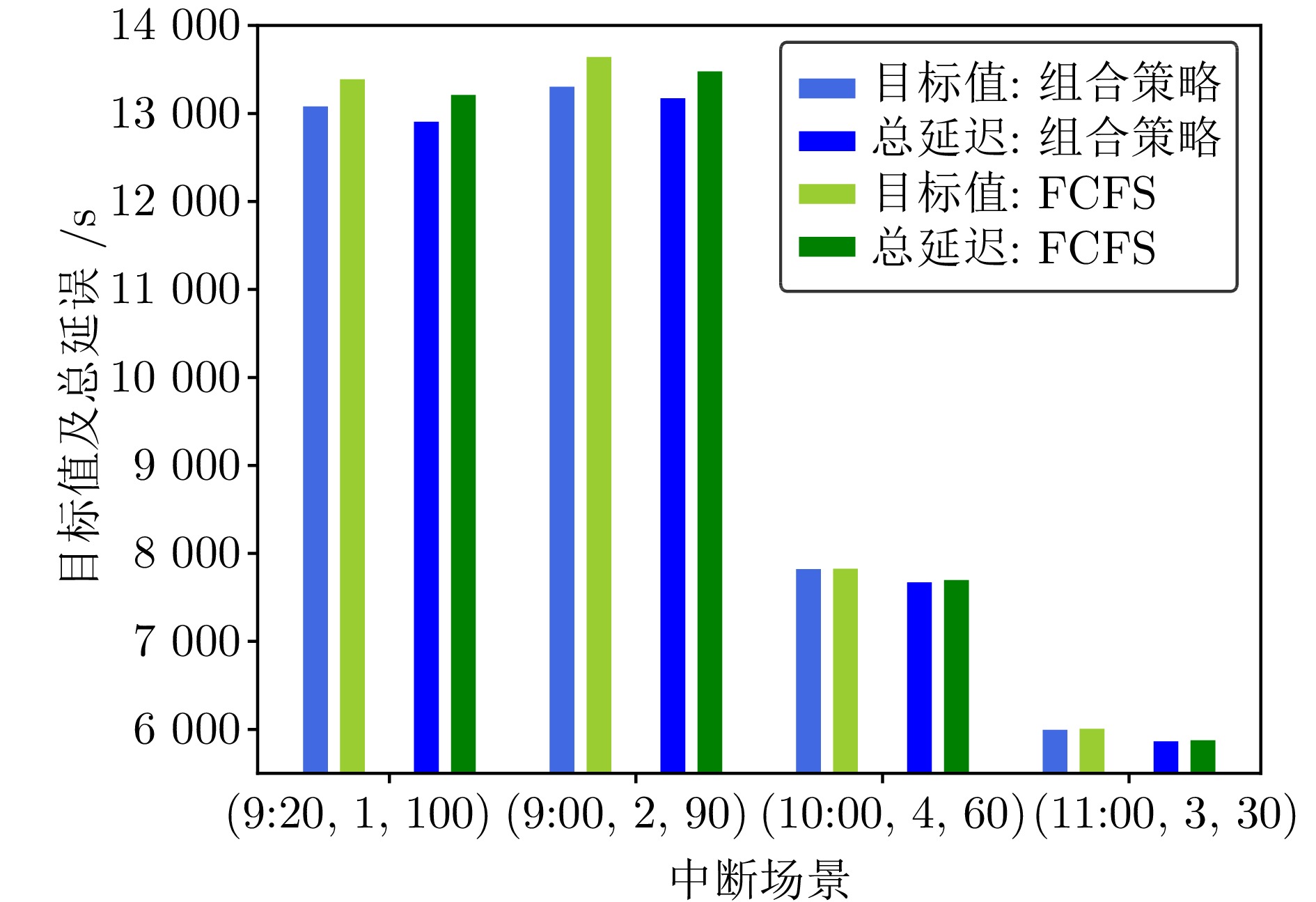
Table 5 Train reschedule considering different strategies under different interruption scenarios
中断场景 策略 目标值 $ P^{{\mathrm{o}}} $(%) 求解时间(s) 取消列车数量(列) 列车总延误时间(s) $ P^{{\mathrm{d}}} $ (%) (9:20, 1, 100) 组合策略 13 080 2.35 159.0 0 12 905 2.37 (9:20, 1, 100) FCFS 13 388 47.3 0 13 211 (9:00, 2, 90) 组合策略 13 303 2.55 361.0 0 13 173 2.31 (9:00, 2, 90) FCFS 13 642 73.8 0 13 478 (10:00, 4, 60) 组合策略 7 821 0.06 17.0 0 7 671 0.33 (10:00, 4, 60) FCFS 7 826 6.9 0 7 696 (11:00, 3, 30) 组合策略 5 994 0.21 3.0 0 5 864 0.21 (11:00, 3, 30) FCFS 6 007 2.7 0 5 876 表 6 各中断场景下整体求解结果
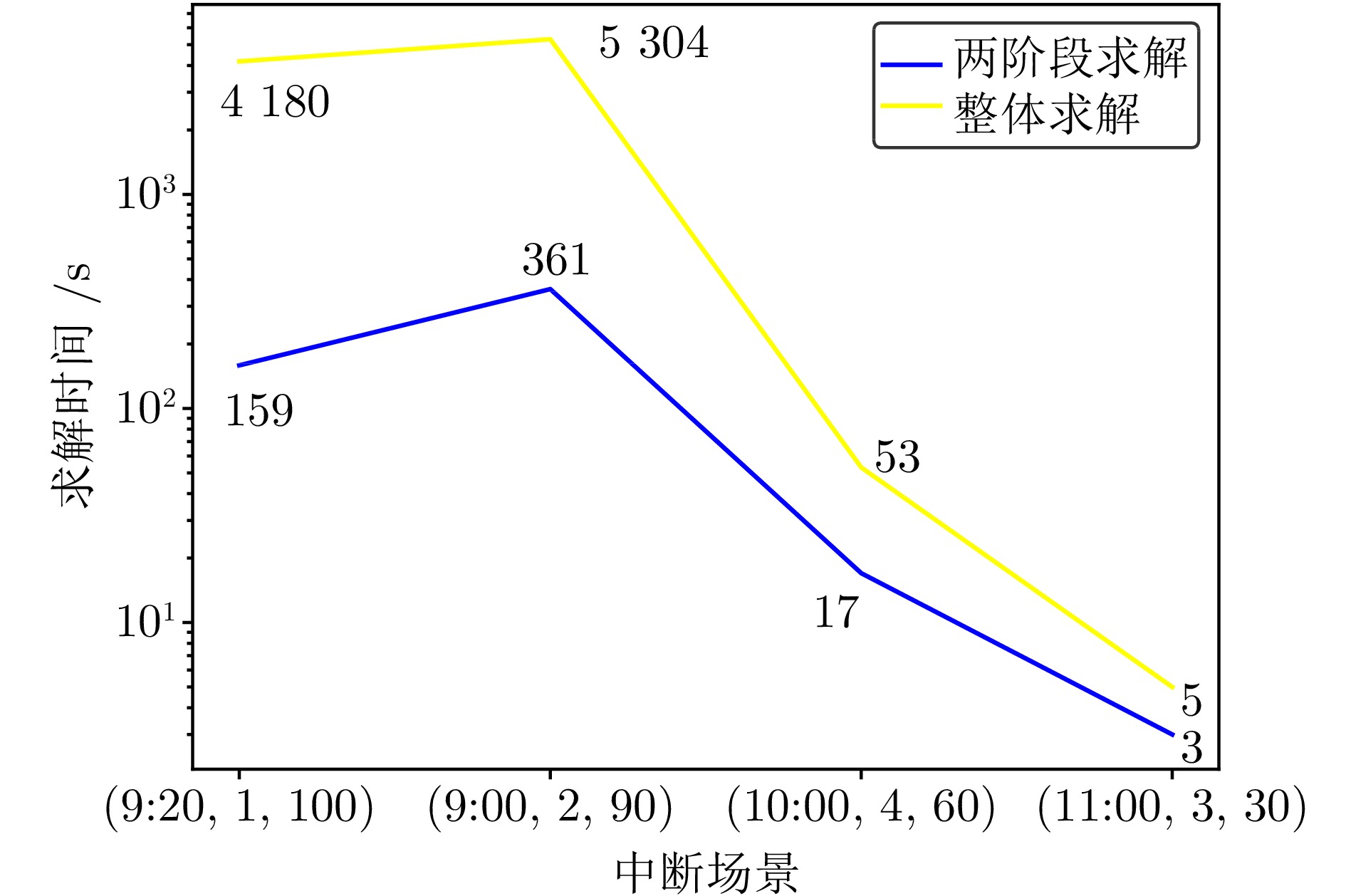
Table 6 The overall solution results under each interruption scenario
中断场景 求解方法 目标值 求解时间(s) 取消列车数量(列) 总延误时间(s) (9:20, 1, 100) 整体求解 12 382 4 180 0 12 362 (9:00, 2, 90) 整体求解 12 453 5 304 0 12 269 (10:00, 4, 60) 整体求解 7 510 53 0 7 395 (11:00, 3, 30) 整体求解 5 896 5 0 5 786 表 7 不同权重系数下模型求解结果对比
Table 7 Comparison of solution results under different weight coefficients
$ \omega_{1} $ $ \omega_{2} $ $ \omega_{3} $ 目标值 取消列车数(列) 总延误时间(s) 求解时间(s) 1 1 1 12 819 0 12 723 330.0 1 10 1 127 865 0 12 767 425.0 1 100 1 1 278 215 0 12 767 359.5 1 1 000 1 12 796 015 0 12 795 314.0 10 1 1 12 819 0 12 723 326.0 100 1 1 12 819 0 12 723 319.0 1 000 1 1 12 819 0 12 726 307.0 1 1 10 17 214 3 17 064 251.8 1 1 100 18 130 3 17 223 227.0 1 1 1 000 25 463 3 19 585 605.7 -
[1] 宁滨, 董海荣, 郑伟, 荀径, 高士根, 王洪伟, 等. 高速铁路运行控制与动态调度一体化的现状与展望. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(12): 2208−2217Ning Bin, Dong Hai-Rong, Zheng Wei, Xun Jing, Gao Shi-Gen, Wang Hong-Wei, et al. Integration of train control and online rescheduling for high-speed railways: Challenges and future. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(12): 2208−2217 [2] 林鹏, 田宇, 袁志明, 张琦, 董海荣, 宋海锋, 等. 高速铁路信号系统运维分层架构模型研究. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(1): 152−161Lin Peng, Tian Yu, Yuan Zhi-Ming, Zhang Qi, Dong Hai-Rong, Song Hai-Feng, et al. Operation and maintenance of high-speed railway signaling system: Hierarchical structure model. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(1): 152−161 [3] 刘昊俣, 贺诗波, 陈积明. 数据驱动的高速铁路强风报警自适应解除策略. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(12): 2242−2250Liu Hao-Yu, He Shi-Bo, Chen Ji-Ming. Data-driven adaptive adjustment strategy for strong wind alarm in high-speed railway. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(12): 2242−2250 [4] Zhou M, Dong H R, Liu X, Zhang H J, Wang F Y. Integrated timetable rescheduling for multidispatching sections of high-speed railways during large-scale disruptions. IEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems, 2022, 9(2): 366−375 doi: 10.1109/TCSS.2021.3069754 [5] Zhu Y Q, Goverde R M P. Dynamic and robust timetable rescheduling for uncertain railway disruptions. Journal of Rail Transport Planning and Management, 2020, 15: Article No. 100196 [6] Veelenturf L P, Kidd M P, Cacchiani V, Kroon L G, Toth P. A railway timetable rescheduling approach for handling large-scale disruptions. Transportation Science, 2016, 50(3): 841−862 doi: 10.1287/trsc.2015.0618 [7] Reynolds E, Maher S J. A data-driven, variable-speed model for the train timetable rescheduling problem. Computers & Operations Research, 2022, 142: Article No. 105719 [8] Zhan S G, Kroon L G, Zhao J, Peng Q Y. A rolling horizon approach to the high speed train rescheduling problem in case of a partial segment blockage. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 2016, 95: 32−61 doi: 10.1016/j.tre.2016.07.015 [9] 吴兴堂, 杨明坤, 王洪伟, 周敏, 吕金虎, 董海荣. 面向负载均衡的高铁路网列车开行方案优化方法. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(2): 492−503Wu Xing-Tang, Yang Ming-Kun, Wang Hong-Wei, Zhou Min, Lv Jin-Hu, Dong Hai-Rong. Load-balancing oriented line plan optimization for a high-speed railway network. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(2): 492−503 [10] Meng X L, Wang Y H, Xiang W L, Jia L M. An integrated model for train rescheduling and station track assignment. IET Intelligent Transport Systems, 2021, 15(1): 17−30 doi: 10.1049/itr2.12001 [11] Zhang H M, Li S K, Wang Y H, Yang L X, Gao Z Y. Collaborative real-time optimization strategy for train rescheduling and track emergency maintenance of high-speed railway: A Lagrangian relaxation-based decomposition algorithm. Omega, 2021, 102: Article No. 102371 doi: 10.1016/j.omega.2020.102371 [12] Meng L Y, Zhou X S. Simultaneous train rerouting and rescheduling on an N-track network: A model reformulation with network-based cumulative flow variables. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2014, 67: 208−234 doi: 10.1016/j.trb.2014.05.005 [13] Lu G Y, Ning J, Liu X B, Nie Y. Train platforming and rescheduling with flexible interlocking mechanisms: An aggregate approach. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 2022, 159: Article No. 102622 doi: 10.1016/j.tre.2022.102622 [14] Yang L X, Qi J G, Li S K, Gao Y. Collaborative optimization for train scheduling and train stop planning on high-speed railways. Omega, 2016, 64: 57−76 doi: 10.1016/j.omega.2015.11.003 [15] Zhang H M, Li S K, Wang Y H, Wang Y H, Yang L X. Real-time optimization strategy for single-track high-speed train rescheduling with disturbance uncertainties: A scenario-based chance-constrained model predictive control approach. Computers & Operations Research, 2021, 127: Article No. 105135 [16] 彭其渊, 宁佳, 鲁工圆. 大型高铁客运站到发线运用调整模型及算法. 铁道学报, 2019, 41(1): 10−19Peng Qi-Yuan, Ning Jia, Lu Gong-Yuan. Model and algorithm for train platform scheme rescheduling at large high-speed railway station. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2019, 41(1): 10−19 [17] Liu X, Zhou M, Dong H R, Wu X T, Li Y D, Wang F Y. ADMM-based joint rescheduling method for high-speed railway timetabling and platforming in case of uncertain perturbation. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2023, 152: Article No. 104150 doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2023.104150 [18] Zhou H S, Qi J G, Yang L X, Shi J G, Pan H C, Gao Y. Joint optimization of train timetabling and rolling stock circulation planning: A novel flexible train composition mode. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2022, 162: 352−385 doi: 10.1016/j.trb.2022.06.007 [19] Hoogervorst R, Dollevoet T, Maróti G, Huisman D. A variable neighborhood search heuristic for rolling stock rescheduling. EURO Journal on Transportation and Logistics, 2021, 10: Article No. 100032 doi: 10.1016/j.ejtl.2021.100032 [20] Wang Y H, Zhao K Q, D'Ariano A, Niu R, Li S K, Luan X J. Real-time integrated train rescheduling and rolling stock circulation planning for a metro line under disruptions. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2021, 152: 87−117 doi: 10.1016/j.trb.2021.08.003 [21] 周晓昭, 张琦, 许伟, 王涛, 宋鹏飞. 考虑动车组接续的列车运行图智能调整方法. 铁道学报, 2018, 40(8): 19−27Zhou Xiao-Zhao, Zhang Qi, Xu Wei, Wang Tao, Song Peng-Fei. Intelligent adjustment method for train operation diagram with consideration of motor train set connection. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2018, 40(8): 19−27 [22] 史峰, 魏堂建, 周文梁, 罗湘. 考虑动车组周转和到发线运用的高速铁路列车运行图优化方法. 中国铁道科学, 2012, 33(2): 107−114Shi Feng, Wei Tang-Jian, Zhou Wen-Liang, Luo Xiang. Optimization method for train diagram of high-speed railway considering the turnover of multiple units and the utilization of arrival-departure tracks. China Railway Science, 2012, 33(2): 107−114 [23] 史常庆. 基于动车组接续优化的高速铁路列车运行图调整研究. [硕士学位论文], 西南交通大学, 中国, 2015.Shi Chang-Qing. High-speed Railway Train Diagram Adjustment Based on Train-set Connection Optimization [Master thesis], Southwest Jiaotong University, China, 2015. [24] 占曙光. 考虑动车组接续的高速铁路列车运行实时调整. 交通运输工程与信息学报, 2020, 18(2): 1−9, 38 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4747.2020.02.001Zhan Shu-Guang. Real-time high speed train rescheduling considering the multiple units connecting. Journal of Transportation Engineering and Information, 2020, 18(2): 1−9, 38 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4747.2020.02.001 [25] 石敏涵, 吕红霞, 倪少权, 吕苗苗. 考虑要素协同的高铁列车运行图双层优化模型. 交通运输工程与信息学报, 2022, 20(2): 125−135Shi Min-Han, Lv Hong-Xia, Ni Shao-Quan, Lv Miao-Miao. Bilevel optimization model for high-speed railway train operation diagram considering multifactor cooperation. Journal of Transportation Engineering and Information, 2022, 20(2): 125−135 [26] 王斌, 黄玲, 郑亚晶, 张鲁生. 动车组周转和到发线运用方案的综合优化研究. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2018, 18(3): 175−181Wang Bin, Huang Ling, Zheng Ya-Jing, Zhang Lu-Sheng. Comprehensive optimization for turnover of multiple units and utilization of arrival-departure track. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2018, 18(3): 175−181 -




 下载:
下载: