A Review on Robotized Automated Lay-up Technology for Composite Material Manufacturing
-
摘要: 碳纤维增强复合材料(Carbon fiber-reinforced composite, CFRC)因具有轻质高强、耐腐蚀、耐冲击等优越性能, 在生产生活中的应用已越来越广泛, 然而复材产品的生产制造仍是劳动密集性产业, 主要依靠人工. 机械臂自上世纪50年代进入工业生产中以来, 极大提高了生产效率和质量, 然而目前机械臂在复材产品制造中的应用是少见的, 主要集中在机械臂形式的自动铺丝(Automated fiber placement, AFP)中. 复材产品制造工艺繁琐, 将复合材料铺放在模具上是复材产品制造过程中的一个重要环节, 本文称之为“铺层”, 使用机械臂完成复合材料自动铺层将是未来复材产品制造自动化、智能化发展的一个关键方向. 本文将机械臂进行复合材料自动铺层操作分为两种主要形式: 铺片和铺带(丝), 通过案例调研和分析, 归纳总结现有的设计理念和技术方法, 提出未来发展趋势, 以期对机械臂的应用和研究、复材产品的智能化制造和工业4.0的发展形成参考.Abstract: Carbon fiber-reinforced composite (CFRC) has been widely used in production and life because of its superior properties such as light weight and high strength, corrosion resistance and impact resistance. However, the manufacturing of composite products is still a labor-intensive industry, mainly relying on manual labor. Since the robot arm entered the industrial production in the 1950s, it has greatly improved the production efficiency and quality, however, the current application of robot arm in the manufacturing of composite products is rare, mainly focusing on the robot arm form of automated fiber placement (AFP). The manufacturing process of composite products is tedious, and laying the composite material on the mold is an important part of the manufacturing process of composite products, which we call “lay-up”, and the use of robot arm to complete the automated lay-up operation will be a key direction for the future automation and intelligent development of the manufacturing of composite products. This paper offers a thorough examination of automated lay-up operation for robot arm, and categorizes them into two primary types: Lay-up sheets and lay-up tapes (fibers). Through case study and analysis of existing design concepts and technical methods, this paper identifies trend and suggests future development direction. The insights are of significant value for application and research related to robot arm, intelligent manufacturing of composite products, and the progression of Industry 4.0.
-
表 1 机械臂在传统工业场景和复材产品制造场景应用特点对比
Table 1 Comparison of the application characteristics of robot arm in traditional industrial scenario and composite products manufacturing scenario
对比 特点 传统工业场景 复材产品制造场景 喷涂 点焊 搬运 装配 铺片 铺带(丝) 相同之处 重复定位精度 高 位置跟踪要求 高 不同之处 操作是否接触 否 是 是 是 是 是 操作材料特性 气体 高温 硬质 硬质 柔软粘性 柔软粘性 是否需要加热 否 是 否 否 是 是 是否有接触力 否 否 是 是 是 是 末端构造 喷嘴 焊钳 夹持 各类工具 夹持悬垂拾取 专有铺放头 表 2 不同拾取原理的优劣对比
Table 2 Comparison of the advantages and disadvantages of different pick-up principles
拾取原理 对材料的损坏程度 成本 实现难度 易操作性 针刺 高 低 低 高 低温 中 中 中 中 真空吸取 无 高 中 中 表 3 单机械臂铺层研究案例对比
Table 3 Comparison of single robot arm lay-up study cases
研究机构 研究重点 路径规划 运动规划 工艺参数 系统软件 使用的机械臂 相关文献 德国宇航中心 全过程自动化 基于视觉生成 系统生成 未知 独立开发 KUKA [45−46, 71−72] 汉堡科技大学 工艺流程优化 未知 未知 未知 未知 ABB [73−76] 慕尼黑工业大学 全过程自动化 人类专家设计 控制器生成 人类专家设计 CFK-Tex.Office KUKA KR-500 [32−34, 77] 布里斯托大学 铺放自动化 未知 未知 人类专家设计 未知 ABB [62] 德国宇航中心 全过程自动化 系统生成 系统生成 未知 独立开发 KUKA [78−79] 南丹麦大学 铺放自动化 基于模拟方法 系统生成 未知 独立开发 KUKA KR-360 [60, 80−84] 表 4 多机械臂协同铺层研究案例对比
Table 4 Comparison of multi-robot arms collaborative lay-up study cases
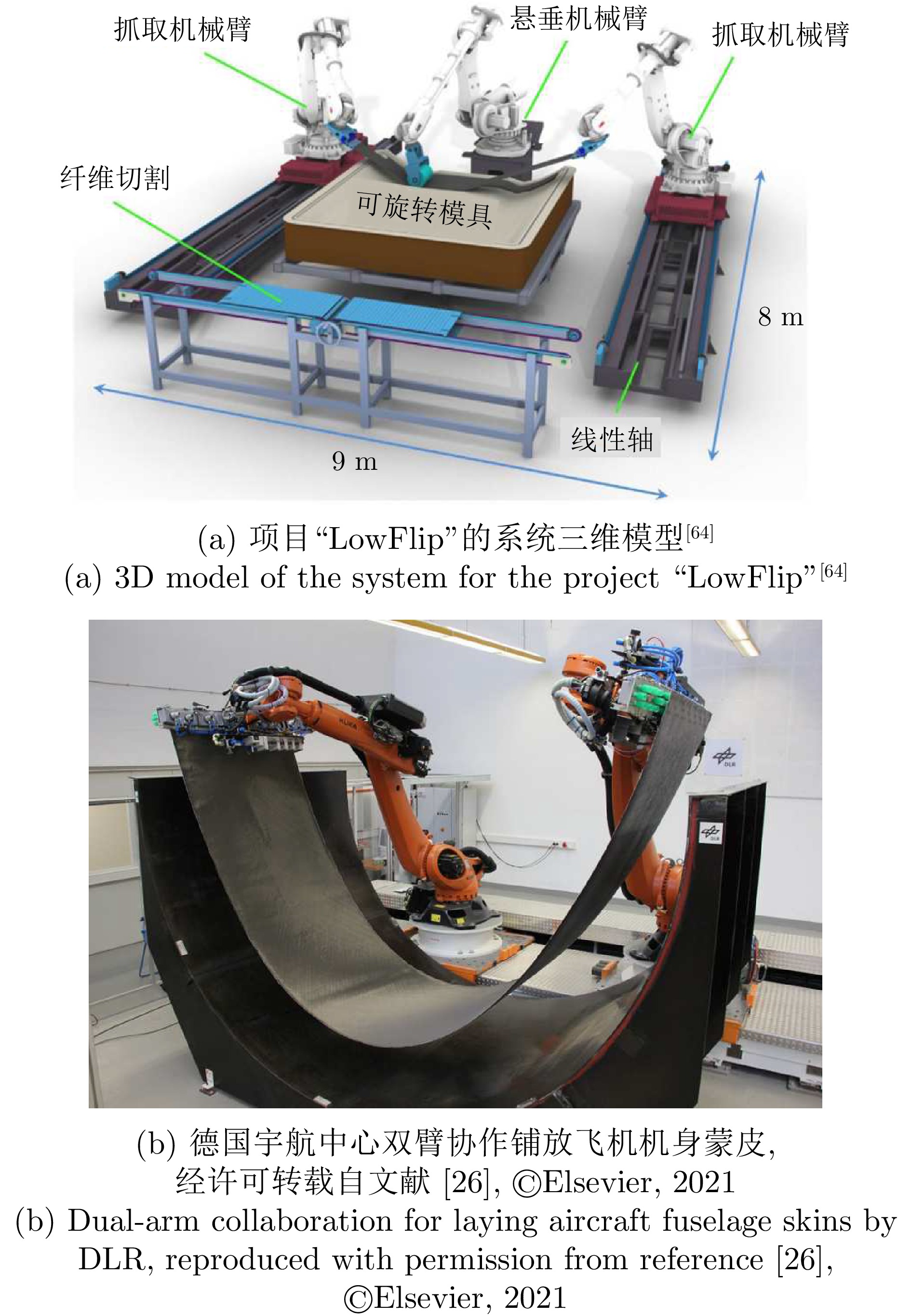
研究机构 机械臂数量 研究内容 路径规划 运动规划 系统软件 使用的机械臂 相关文献 南卡罗莱纳大学 3 路径规划 运动规划 算法生成 控制器生成 独立开发 KUKA-iiwa [85−87, 89−91] 斯图加特大学 3 系统搭建 路径规划 人类专家设计 系统生成 独立开发 ABB [64, 92] 德国宇航中心 2 系统搭建 路径规划 算法生成 系统生成 独立开发 KUKA-KR270 [93−101] 空客集团 2 系统搭建 末端开发 人类专家设计 系统生成 独立开发 KUKA [41−42, 106] 林雪平大学 2 技术验证 末端开发 未知 未知 未知 KUKA-KR10, ABB [107−108] 慕尼黑工业大学 2 系统搭建 路径规划 算法生成 系统生成 独立开发 Staubli, KUKA [24] 思克莱德大学 1 技术验证 人类专家设计 系统生成 独立开发 KUKA-KR6 [110] 维也纳技术大学 2 技术验证 人类专家设计 系统生成 未知 自制 [111−112] 表 5 铺带(丝)头中采用的切割方式对比
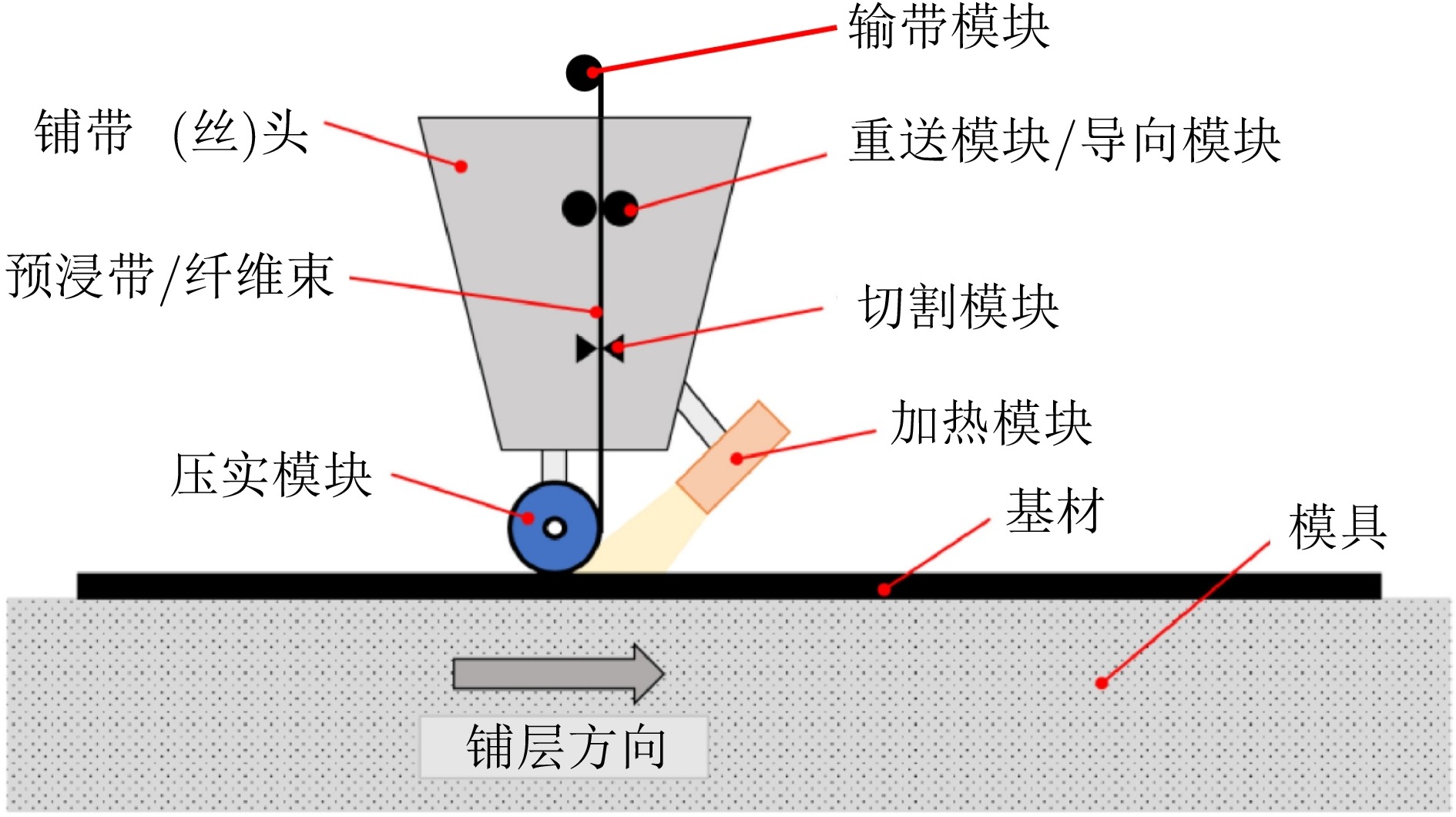
Table 5 Comparison of cutting methods used in tape (fiber) lay-up heads
切割方式 成本 优点 缺点 机械道具切割 低 结构简单, 切割效率高, 适用于多种复杂环境,
维修更换比较方便难以控制切割深度且切口毛糙, 损伤预浸料,
无法保证切口质量激光切割 较高 切割效率高, 非接触式切割, 产品边缘光滑平整,
激光对位精准, 切割精度高温度较高, 使复合材料发生变质且
切割深度不易控制水喷射切割 低 设备结构简单, 操作容易, 工作机构具有喷头体积小、
后坐力小、移动方便、生产效率高等特点给整个铺带环境带来大量污染液体,
影响复合材料成型, 铺带工作不便超声波切割 较高 切割效率高, 切口平整; 合适的切割速度、
切割深度满足不同工况下的切割易受负载、温度等因素影响, 引起谐振频率、
等效阻抗等参数漂移变化表 6 铺带(丝)头中采用的加热方式对比
Table 6 Comparison of heating methods used in tape (fiber) lay-up heads
加热方式 成本 优点 缺点 电阻丝加热 低 加热均匀, 实现简单 热损失大, 功率密度低, 使用寿命短 激光加热 高 激光加热效率高, 响应快 温度难以控制, 容易产生局部过热 热风加热 低 温度场均匀, 调节范围广 加热升温时间长, 热效率较低 红外加热 高 热效率高, 加热均匀, 响应速度快 辐射面存在一定限制, 温度场不均匀 表 7 路径规划方法对比
Table 7 Comparison of path planning methods
分类 方法 优点 缺点 参考路径生成 自然路径法 可以避免纤维起皱, 轨迹可铺放性良好 计算量大, 仅适用于低曲率表面 定角度路径法 原理及计算过程简单 仅适用于整体曲率波动较小的曲面 变角度路径法 能够自适应芯模曲面不规则情况 算法计算量大 路径密化 等距偏置算法 算法简单, 能够覆盖整个芯模表面 在复杂表面上可能存在间隙和重叠 等角度算法 算法实现简单, 适应各种复杂构件 易存在间隙和重叠 关键技术 研究内容 研究目标 轨迹规划 根据构件3D表面设计相应路径规划算法, 自适应生成铺放轨迹 满足构件结构的方向性、铺放顺序和铺叠层数要求 铺放路径覆盖 根据曲面上相邻路径的间距, 对铺丝路径的覆盖性进行检验与优化 实现对模具的满覆盖、不重叠, 满足空隙容差 边界处理 根据构件的边界轮廓信息, 设计边界处理算法, 控制边缘和角部的铺放方式与形态 确保铺放边界质量和表面光洁度 后置处理 数控代码生成、代码优化与合成、加工仿真技术等 机器人能够识别执行的指令 表 9 现有自动化缺陷检测技术优劣对比
Table 9 Comparison of the advantages and disadvantages of existing automated defect detection technologies
-
[1] 林刚, CINTE21. 构建“硬科技”优势——2021全球碳纤维复合材料市场报告. 纺织科学研究, 2022, 33(5): 46−66Lin Gang, CINTE21. Building a “hard technology” advantage-global carbon fibre composites market report 2021. Textile Science Research, 2022, 33(5): 46−66 [2] 中国电子学会. 中国机器人产业发展报告(2022年), 世界机器人大会, 中国, 2022.Chinese Institute of Electronics. China Robotics Industry Development Report (2022), World Robot Conference, China, 2022. [3] 亿欧智库. 2022中国工业机器人市场研究报告. 机器人产业, 2022, (4): 83−95 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-0182.2022.04.014EqualOcean. 2022 China industrial robotics market research report. Robot Industry, 2022, (4): 83−95 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-0182.2022.04.014 [4] Lei T, Rong Y M, Wang H, Huang Y, Li M. A review of vision-aided robotic welding. Computers in Industry, 2020, 123: Article No. 103326 doi: 10.1016/j.compind.2020.103326 [5] Sun Y W, Jia J J, Xu J T, Chen M S, Niu J B. Path, feedrate and trajectory planning for free-form surface machining: A state-of-the-art review. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2022, 35(8): 12−29 doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2021.06.011 [6] Urhal P, Weightman A, Diver C, Bartolo P. Robot assisted additive manufacturing: A review. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2019, 59: 335−345 doi: 10.1016/j.rcim.2019.05.005 [7] Cong Y, Chen R H, Ma B T, Liu H S, Hou D D, Yang C G. A comprehensive study of 3-D vision-based robot manipulation. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2023, 53(3): 1682−1698 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2021.3108165 [8] 秦方博, 徐德. 机器人操作技能模型综述. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(8): 1401−1418Qin Fang-Bo, Xu De. Review of robot manipulation skill models. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(8): 1401−1418 [9] 曾超, 杨辰光, 李强, 戴诗陆. 人−机器人技能传递研究进展. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(10): 1813−1828Zeng Chao, Yang Chen-Guang, Li Qiang, Dai Shi-Lu. Research progress on human-robot skill transfer. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(10): 1813−1828 [10] 齐志刚, 黄攀峰, 刘正雄, 韩冬. 空间冗余机械臂路径规划方法研究. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(6): 1103−1110Qi Zhi-Gang, Huang Pan-Feng, Liu Zheng-Xiong, Han Dong. Research on path planning method of spatial redundant manipulator. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(6): 1103−1110 [11] Chutima P. A comprehensive review of robotic assembly line balancing problem. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 2022, 33(1): 1−34 doi: 10.1007/s10845-020-01641-7 [12] Rajak D K, Pagar D D, Menezes P L, Linul E. Fiber-reinforced polymer composites: Manufacturing, properties, and applications. Polymers, 2019, 11(10): Article No. 1667 doi: 10.3390/polym11101667 [13] Elkington M, Ward C, Sarkytbayev A. Automated composite draping: A review. In: Proceedings of the SAMPE Seattle 2017. Seattle, USA: SAMPE North America, 2017. [14] Björnsson A, Jonsson M, Johansen K. Automated material handling in composite manufacturing using pick-and-place systems——A review. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2018, 51: 222−229 doi: 10.1016/j.rcim.2017.12.003 [15] Lukaszewicz D H J A, Ward C, Potter K D. The engineering aspects of automated prepreg layup: History, present and future. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2012, 43(3): 997−1009 doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2011.12.003 [16] Brasington A, Sacco C, Halbritter J, Wehbe R, Harik R. Automated fiber placement: A review of history, current technologies, and future paths forward. Composites Part C: Open Access, 2021, 6: Article No. 100182 doi: 10.1016/j.jcomc.2021.100182 [17] Zhang W X, Liu F, Jiang T, Yi M H, Chen W Q, Ding X L. Overview of current design and analysis of potential theories for automated fibre placement mechanisms. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2022, 35(4): 1−13 doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2021.04.018 [18] Chen J P, Fu K K, Li Y. Understanding processing parameter effects for carbon fibre reinforced thermoplastic composites manufactured by laser-assisted automated fibre placement (AFP). Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2021, 140: Article No. 106160 doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2020.106160 [19] de Campos A A, Henriques E, Magee C L. Technological improvement rates and recent innovation trajectories in automated advanced composites manufacturing technologies: A patent-based analysis. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2022, 238: Article No. 109888 doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2022.109888 [20] Soares B A R, Henriques E, Ribeiro I, Freitas M. Cost analysis of alternative automated technologies for composite parts production. International Journal of Production Research, 2019, 57(6): 1797−1810 doi: 10.1080/00207543.2018.1508903 [21] Jayasekara D, Lai N Y G, Wong K H, Pawar K, Zhu Y D. Level of automation (LOA) in aerospace composite manufacturing: Present status and future directions towards industry 4.0. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 2022, 62: 44−61 doi: 10.1016/j.jmsy.2021.10.015 [22] Potter K, Ward C. Draping processes for composites manufacture. Advances in Composites Manufacturing and Process Design. Amsterdam: Woodhead Publishing, 2015. 93−109 [23] Cevotec. Composite tank reinforcements [Online], available: https://www.cevotec.com/industries-applications/fpp-composite-tanks/, July 29, 2023 [24] Michl F, Coquel M. Fully-automated production of complex CFRP parts using fibre-patch-preforming technology. JEC Com posites Magazine, 2014, 87: 108−110 [25] Malhan R K, Shembekar A V, Kabir A M, Bhatt P M, Shah B, Zanio S, et al. Automated planning for robotic layup of composite prepreg. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2021, 67: Article No. 102020 doi: 10.1016/j.rcim.2020.102020 [26] Larsen L, Kim J. Path planning of cooperating industrial robots using evolutionary algorithms. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2021, 67: Article No. 102053 doi: 10.1016/j.rcim.2020.102053 [27] Khodunov A A, Bogachev V V, Borodulin A S. Advances in tailored fiber placement technology. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2021, 1990: Article No. 012041 [28] Lindback J E, Björnsson A, Johansen K. New automated composite manufacturing process: Is it possible to find a cost effective manufacturing method with the use of robotic equipment? In: Proceedings of the 5th International Swedish Production Symposium. Linkoping, Sweden: 2012. 523−531 [29] Kordi M T, Husing M, Corves B. Development of a multifunctional robot end-effector system for automated manufacture of textile preforms. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics. Zurich, Switzerland: IEEE, 2007. 1−6 [30] Reinhart G, Straßer G. Flexible gripping technology for the automated handling of limp technical textiles in composites industry. Production Engineering, 2011, 5(3): 301−306 doi: 10.1007/s11740-011-0306-1 [31] Reinhart G, Strassr G, Ehinger C. Highly flexible automated manufacturing of composite structures consisting of limp carbon fibre textiles. SAE International Journal of Aerospace, 2010, 2(1): 181−187 [32] Angerer A, Ehinger C, Hoffmann A, Reif W, Reinhart G. Design of an automation system for preforming processes in aerospace industries. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Automation Science and Engineering. Trieste, Italy: IEEE, 2011. 557−562 [33] Ehinger C, Reinhart G. Robot-based automation system for the flexible preforming of single-layer cut-outs in composite industry. Production Engineering, 2014, 8(5): 559−565 doi: 10.1007/s11740-014-0546-y [34] Reinhart G, Ehinger C. Novel robot-based end-effector design for an automated preforming of limb carbon fiber textiles. In: Proceedings of the 1st Conference of the German Academic Society for Production Engineering (WGP). Berlin, Germany: Springer, 2013. 131−142 [35] Löchte C, Kunz H, Schnurr R, Dietrich F, Raatz A, Dilger K, et al. Form-flexible handling technology for automated preforming. In: Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Composite Materials. Montreal, Canada: Concordia University, 2013. [36] Löchte C, Kunz H, Schnurr R, Langhorst S, Dietrich F, Raatz A, et al. Form-flexible handling and joining technology (FormHand) for the forming and assembly of limp materials. Procedia CIRP, 2014, 23: 206−211 doi: 10.1016/j.procir.2014.10.086 [37] Kunz H, Löchte C, Dietrich F, Raatz A, Fischer F, Dröder K, et al. Novel form-flexible handling and joining tool for automated preforming. Science and Engineering of Composite Materials, 2015, 22(2): 199−213 doi: 10.1515/secm-2013-0326 [38] Dröder K, Dietrich F, Löchte C, Hesselbach J. Model based design of process-specific handling tools for workpieces with many variants in shape and material. CIRP Annals, 2016, 65(1): 53−56 doi: 10.1016/j.cirp.2016.04.109 [39] Apmann H. Automatic Handling of CFRP-material for Frame and Stringer Production, SAE Technical Paper 2008-01-2289, SAE, USA, 2008. [40] Apmann H, Hemmen A, Herkt M. Automatic Handling of Carbon Fiber Preforms for CFRP Parts in Aerospace, SAE Technical Paper 2012-01-1864, SAE, USA, 2012. [41] Apmann H, Busse M, Du J Y, Köhnke P. Automated manufacture of fibre metal laminates to achieve high rate of production. Lightweight Design Worldwide, 2017, 10(4): 28−33 [42] Ucan H, Apmann H, Graßl G, Krombholz C, Fortkamp K, Nieberl D, et al. Production technologies for lightweight structures made from fibre-metal laminates in aircraft fuselages. CEAS Aeronautical Journal, 2019, 10(2): 479−489 doi: 10.1007/s13272-018-0330-3 [43] Ucan H, Scheller J, Nguyen C, Nieberl D, Beumler T, Haschenburger A, et al. Automated, quality assured and high volume oriented production of fiber metal laminates (FML) for the next generation of passenger aircraft fuselage shells. Science and Engineering of Composite Materials, 2019, 26(1): 502−508 doi: 10.1515/secm-2019-0031 [44] Braun G, Buchheim A, Fischer F, Gerngross T. Handgeführter Endeffektor Für Die Automatisierte Handhabung von Textilen Zuschnitten, DLR-IB 435-2013/88, Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt e.V. (DLR), Germany, 2013. [45] Kuehnel M, Schuster A, Buchheim A, Gergross T, Kupke M. Automated near-net-shape preforming of carbon fiber reinforced thermoplastics (CFRTP). In: Proceedings of the Paper for the I.C.S of the JEC Europe 2014. Paris, France: 2014. [46] Kuhnel M, Schuster A, Rähtz C, Kupke M. Near net shape thermoplastic preforming with continuously automated cutting and robotic pick and place processes. In: Proceedings of the International Conference and Exhibition on Thermoplastic Composites. Bremen, Germany: 2016. [47] Vistein M, Faber J, Schmidt-Eisenlohr C, Reiter D. Automated handling of auxiliary materials using a multi-kinematic gripping system. Procedia Manufacturing, 2019, 38: 1276−1283 doi: 10.1016/j.promfg.2020.01.220 [48] Gunnarsson G G, Nielsen O W, Schlette C, Petersen H G. Fast and simple interacting models of drape tool and ply material for handling free hanging, pre-impregnated carbon fibre material. In: Proceedings of the 15th Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics. Porto, Portugal: Springer, 2018. 1−25 [49] Fleischer J, Förster F, Crispieri N V. Intelligent gripper technology for the handling of carbon fiber material. Production Engineering, 2014, 8(6): 691−700 doi: 10.1007/s11740-014-0549-8 [50] Förster F, Ballier F, Coutandin S, Defranceski A, Fleischer J. Manufacturing of textile preforms with an intelligent draping and gripping system. Procedia CIRP, 2017, 66: 39−44 doi: 10.1016/j.procir.2017.03.370 [51] Wirth B, Coutandin S, Fleischer J. Disturbance force estimation for a low pressure suction gripper based on differential pressure analysis. In: Proceedings of the Annals of Scientific Society for Assembly, Handling and Industrial Robotics. Berlin, Germany: Springer, 2020. 263−273 [52] Wirth B, Schwind T, Friedmann M, Fleischer J. Automated stack singulation for technical textiles using sensor supervised low pressure suction grippers. In: Proceedings of the Annals of Scientific Society for Assembly, Handling and Industrial Robotics 2022. Cham, Germany: Springer, 2022. 329−340 [53] Brink M, Ohlendorf J H, Thoben K D. Development of a handling system with integrated sensors for textile preforms using additive manufacturing. Procedia Manufacturing, 2018, 24: 114−119 doi: 10.1016/j.promfg.2018.06.016 [54] Björnsson A, Jonsson M, Eklund D, Lindbäck J E, Björkman M. Getting to grips with automated prepreg handling. Production Engineering, 2017, 11: 445−453 doi: 10.1007/s11740-017-0763-2 [55] Brinker J, Prause I, Kosse P, Früh H C, Printz S, Henke C, et al. Automated handling and draping of reinforcing textiles-challenges and developments. New Advances in Mechanisms, Mechanical Transmissions and Robotics. Cham, Germany: Springer, 2017. 485−493 [56] Brinker J, Paris J, Müller M, Hüsing M, Corves B. Mechanism type synthesis approach for automated handling and multiaxial draping of reinforcing textiles. New Trends in Mechanism and Machine Science: Theory and Industrial Applications. Cham, Germany: Springer, 2017. 523−532 [57] Brinker J, Müller M, Paris J, Husing M, Corves B. Mechanism design for automated handling and multiaxial draping of reinforcing textiles. In: Proceedings of the ASME International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference. Charlotte, USA: ASME, 2016. Article No. V05BT07A040 [58] Corves B, Brinker J, Prause I, Hüsing M, Abbas B, Krieger H, et al. AutoHD——Automated handling and draping of reinforcing textiles. In: Proceedings of the Conference on Mechanisms, Transmissions and Applications. Cham, Germany: Springer, 2015. 301−309 [59] Wang B W. Design and Development of a Soft Robotic Gripper for Fabric Material Handling [Master thesis], University of Windsor, Canada, 2020. [60] Krogh C, Jakobsen J, Sherwood J A. Development of a computationally efficient fabric model for optimization of gripper trajectories in automated composite draping. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1810.07619, 2018. [61] Elkington M, Bloom D, Ward C, Chatzimichali A, Potter K. Hand layup: Understanding the manual process. Advanced Manufacturing: Polymer & Composites Science, 2015, 1(3): 138−151 [62] Elkington M, Ward C, Potter K D. Automated layup of sheet prepregs on complex moulds. Journal of Advanced Materials, 2016, 3 : 70−84 [63] Elkington M, Almas E, Ward-Cherrier B, Pestell N, Lloyd J, Ward C, et al. Real time defect detection during composite layup via tactile shape sensing. Science and Engineering of Composite Materials, 2021, 28(1): 1−10 doi: 10.1515/secm-2021-0001 [64] Szcesny M, Heieck F, Carosella S, Middendorf P, Sehrschön H, Schneiderbauer M. The advanced ply placement process——An innovative direct 3D placement technology for plies and tapes. Advanced Manufacturing: Polymer & Composites Science, 2017, 3(1): 2−9 [65] Richrath M, Franke J, Ohlendorf J H, Thoben K D. Effector for automated direct textile placement in rotor blade production. Lightweight Design Worldwide, 2017, 10(5): 42−47 doi: 10.1007/s41777-017-0039-8 [66] Schouterden G, Cramer J, Demeester E, Kellens K. Development of a membrane-shaped MR-based composite draping tool. Procedia CIRP, 2019, 86: 167−172 doi: 10.1016/j.procir.2020.01.048 [67] Denkena B, Schmidt C, Werner S, Schwittay D. Development of a shape replicating draping unit for continuous layup of unidirectional non-crimp fabrics on complex surface geometries. Journal of Composites Science, 2021, 5(4): Article No. 93 doi: 10.3390/jcs5040093 [68] Helber F, Amann A, Carosella S, Middendorf P. Intrinsic fibre heating: A novel approach for automated dry fibre placement. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2018, 460: Article No. 012064 [69] Björnsson A, Lindback J E, Johansen K. Automated removal of prepreg backing paper——A sticky problem. In: Proceedings of the SAE 2013 AeroTech Congress & Exhibition. New York, USA: SAE International, 2013. [70] Bruns C, Micke-Camuz M, Bohne F, Raatz A. Process design and modelling methods for automated handling and draping strategies for composite components. CIRP Annals, 2018, 67(1): 1−4 doi: 10.1016/j.cirp.2018.04.014 [71] Schuster A, Larsen L, Fischer F, Glück R, Schneyer S, Kühnel M, et al. Smart manufacturing of thermoplastic CFRP skins. Procedia Manufacturing, 2018, 17: 935−943 doi: 10.1016/j.promfg.2018.10.147 [72] Beyrle M, Endraß M, Kühnel M, Schuster A, Stefani T, Glück R, et al. Automated production and joining of high performance structures out of carbon fiber reinforced thermoplastics. In: Proceedings of the Composites and Advanced Materials Expo. Orlando, USA: 2017. [73] Roth F, Eschen H, Schüppstuhl T. The loop gripper: A soft gripper for honeycomb materials. Procedia Manufacturing, 2021, 55: 160−167 doi: 10.1016/j.promfg.2021.10.023 [74] Eschen H, Harnisch M, Schuppstühl T. Flexible and automated production of sandwich panels for aircraft interior. Procedia Manufacturing, 2018, 18: 35−42 doi: 10.1016/j.promfg.2018.11.005 [75] Eschen H, Kalscheuer F, Schüppstuhl T. Optimized process chain for flexible and automated aircraft interior production. Procedia Manufacturing, 2020, 51: 535−542 doi: 10.1016/j.promfg.2020.10.075 [76] Kalscheuer F, Eschen H, Schüppstuhl T. Towards semi automated pre-assembly for aircraft interior production. In: Proceedings of the Annals of Scientific Society for Assembly, Handling and Industrial Robotics 2021. Cham, Germany: Springer, 2022. 203−213 [77] Angerer A, Ehinger C, Hoffmann A, Reif W, Reinhart G, Strasser G. Automated cutting and handling of carbon fiber fabrics in aerospace industries. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Automation Science and Engineering. Toronto, Canada: IEEE, 2010. 861−866 [78] Gerngross T, Nieberl D. Automated manufacturing of large, three-dimensional CFRP parts from dry textiles. CEAS Aeronautical Journal, 2016, 7(2): 241−257 doi: 10.1007/s13272-016-0184-5 [79] Nägele L, Macho M, Angerer A, Hoffmann A, Vistein M, Schönheits M, et al. A backward-oriented approach for offline programming of complex manufacturing tasks. In: Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Automation, Robotics and Applications (ICARA). Queenstown, New Zealand: IEEE, 2015. 124−130 [80] Ellekilde L P, Wilm J, Nielsen O W, Krogh C, Kristiansen E, Gunnarsson G G, et al. Design of automated robotic system for draping prepreg composite fabrics. Robotica, 2021, 39(1): 72−87 doi: 10.1017/S0263574720000193 [81] Serpina G G G, Petersen H G. Mathematical modeling of a highly underactuated tool for draping fiber plies on double curved molds. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Xi'an, China: IEEE, 2021. 1666−1672 [82] Krogh C, Glud J A, Jakobsen J. Modeling of prepregs during automated draping sequences. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2017, 1896: Article No. 030036 [83] Krogh C, Glud J A, Jakobsen J. Modeling the robotic manipulation of woven carbon fiber prepreg plies onto double curved molds: A path-dependent problem. Journal of Composite Materials, 2019, 53(15): 2149−2164 doi: 10.1177/0021998318822722 [84] Krogh C, Sherwood J A, Jakobsen J. Generation of feasible gripper trajectories in automated composite draping by means of optimization. Advanced Manufacturing: Polymer & Composites Science, 2019, 5(4): 234−249 [85] Malhan R K, Kabir A M, Shembekar A V, Shah B, Gupta S K, Centea T. Hybrid cells for multi-layer prepreg composite sheet layup. In: Proceedings of the IEEE 14th International Conference on Automation Science and Engineering (CASE). Munich, Germany: IEEE, 2018. 1466−1472 [86] Malhan R K, Kabir A M, Shah B, Centea T, Gupta S K. Automated prepreg sheet placement using collaborative robotics. In: Proceedings of the North America Society for the Advancement of Material and Process Engineering (SAMPE) Long Beach Conference. Long Beach, USA: SAMPE, 2018. [87] Malhan R K, Kabir A M, Shah B, Gupta S K. Identifying feasible workpiece placement with respect to redundant manipulator for complex manufacturing tasks. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Montreal, Canada: IEEE, 2019. 5585−5591 [88] Malhan R K, Kabir A M, Shah B, Centea T, Gupta S K. Determining feasible robot placements in robotic cells for composite prepreg sheet layup. In: Proceedings of the ASME 14th International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference. Erie, USA: ASME, 2019. Article No. V001T02A025 [89] Manyar O M, Desai J, Deogaonkar N, Joesph R J, Malhan R, McNulty Z, et al. A simulation-based grasp planner for enabling robotic grasping during composite sheet layup. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Xi'an, China: IEEE, 2021. 930−937 [90] Malhan R K, Joseph R J, Shembekar A V, Kabir A M, Bhatt P M, Gupta S K. Online grasp plan refinement for reducing defects during robotic layup of composite prepreg sheets. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Paris, France: IEEE, 2020. 11500−11507 [91] Malhan R K, Thakar S, Kabir A M, Rajendran P, Bhatt P M, Gupta S K. Generation of configuration space trajectories over semi-constrained cartesian paths for robotic manipulators. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2023, 20(1): 193−205 doi: 10.1109/TASE.2022.3144673 [92] Helber F, Carosella S, Middendorf P. Multi-robotic composite production of complex and large-scaled components for the automotive industry. In: Proceedings of the Advances in Automotive Production Technology——Theory and Application. Berlin, Germany: Springer, 2021. 369−376 [93] Krebs F, Larsen L, Braun G, Dudenhausen W. Design of a multifunctional cell for aerospace CFRP production. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2016, 85: 17−24 doi: 10.1007/s00170-014-6022-1 [94] Tekles N, Reiner M, Krebs F. Model-based elastic deformation compensation for a multi-robot work cell. In: Proceedings of the IEEE 15th International Conference on Control and Automation (ICCA). Edinburgh, UK: IEEE, 2019. 530−536 [95] Tekles N, Krebs F, Reiner M. Inverse model command shaper for a flexible gantry robot. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Vancouver, Canada: IEEE, 2017. 1636−1642 [96] Eckardt M, Buchheim A, Gerngross T. Investigation of an automated dry fiber preforming process for an aircraft fuselage demonstrator using collaborating robots. CEAS Aeronautical Journal, 2016, 7(3): 429−440 doi: 10.1007/s13272-016-0199-y [97] Schuster A, Kupke M, Larsen L. Autonomous manufacturing of composite parts by a multi-robot system. Procedia Manufacturing, 2017, 11: 249−255 doi: 10.1016/j.promfg.2017.07.238 [98] Brandt L, Eckardt M. Automated handling and positioning of large dry carbon fibre cut-pieces with cooperating robots in rear pressure bulkhead production. In: Proceedings of the CEAS Conference. Bucharest, Romania: CEAS, 2017. [99] Schuster A, Frommel C, Deden D, Brandt L, Eckardt M, Glück R, et al. Simulation based draping of dry carbon fibre textiles with cooperating robots. Procedia Manufacturing, 2019, 38: 505−512 doi: 10.1016/j.promfg.2020.01.064 [100] Deden D, Frommel C, Glück R, Larsen L, Malecha M, Schuster A. Towards a fully automated process chain for the lay-up of large carbon dry-fibre cut pieces using cooperating robots. In: Proceedings of the SAMPE Europe Conference. Nantes, France: SAMPE, 2019. [101] Frommel C, Krebs F, Haase T, Vistein M, Schuster A, Larsen L, et al. Automated manufacturing of large composites utilizing a process orchestration system. Procedia Manufacturing, 2020, 51: 470−477 doi: 10.1016/j.promfg.2020.10.066 [102] Larsen L, Kim J, Kupke M. Intelligent path panning towards collision-free cooperating industrial robots. In: Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Informatics in Control. Vienna, Austria: SciTePress, 2014. [103] Angerer A, Hoffmann A, Larsen L, Vistein M, Kim J, Kupke M, et al. Planning and execution of collision-free multi-robot trajectories in industrial applications. In: Proceedings of the 47th International Symposium on Robotics. Munich, Germany: VDE, 2016. 1−7 [104] Larsen L, Pham V L, Kim J, Kupke M. Collision-free path planning of industrial cooperating robots for aircraft fuselage production. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2015. 2042−2047 [105] Larsen L, Kaspar M, Schuster A, Vistein M, Kim J, Kupke M. Full automatic path planning of cooperating robots in industrial applications. In: Proceedings of the 13th IEEE Conference on Automation Science and Engineering (CASE). Xi'an, China: IEEE, 2017. 523−530 [106] Vistein M, Deden D, Glück R, Schneyer S. Automated production of large fibre metal laminate aircraft structure parts. Procedia Manufacturing, 2019, 38: 1300−1307 doi: 10.1016/j.promfg.2020.01.160 [107] Björnsson A, Jonsson M, Johansen K. Automation of composite manufacturing using off-the-shelf solutions, three cases from the aerospace industry. In: Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Composite Materials. Copenhagen, Denmark: Aalborg University, 2015. [108] Björnsson A, Lindback J E, Eklund D, Jonsson M. Low-cost automation for prepreg handling-two cases from the aerospace industry. SAE International Journal of Materials and Manufacturing, 2016, 9(1): 68−74 [109] Zhang X W, Chi X F, Ji C C. Discrete path planning of carbon fiber patch placement with complex surface. Textile Research Journal, 2023, 93(17−18): 4010−4022 doi: 10.1177/00405175231169045 [110] Yang M M, Yu L J, Wong C B, Mineo C, Yang E F, Bomphray I, et al. A cooperative mobile robot and manipulator system (Co-MRMS) for transport and lay-up of fibre plies in modern composite material manufacture. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2022, 119: 1249−1265 doi: 10.1007/s00170-021-08342-2 [111] Flixeder S, Glück T, Kugi A. Force-based cooperative handling and lay-up of deformable materials: Mechatronic design, modeling, and control of a demonstrator. Mechatronics, 2017, 47: 246−261 doi: 10.1016/j.mechatronics.2016.10.003 [112] Hartl-Nesic C, Glück T, Kugi A. Surface-based path following control: Application of curved tapes on 3-D objects. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2021, 37(2): 615−626 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2020.3033721 [113] Belhaj M, Dodangeh A, Hojjati M. Experimental investigation of prepreg tackiness in automated fiber placement. Composite Structures, 2021, 262: Article No. 113602 doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2021.113602 [114] Zhao F H, Liu Z Q, Chen R F, Hao Y, Ma Z H. The effect of temperature field on the characteristics of carbon fiber reinforced thermoplastic composites in the laying and shaping process. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2022, 121: 7569−7589 doi: 10.1007/s00170-022-09795-9 [115] de Sá Rodrigues J, Gonçalves P T, Pina L, Gomes de Almeida F. Modelling the heating process in the transient and steady state of an in situ tape-laying machine head. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing, 2022, 6(1): Article No. 8 doi: 10.3390/jmmp6010008 [116] Zhang P, Sun R L, Zhao X Y, Hu L J. Placement suitability criteria of composite tape for mould surface in automated tape placement. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2015, 28(5): 1574−1581 doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2015.06.002 [117] 赵尧旭. 热塑性复合材料机器人铺放设备及工艺研究 [硕士学位论文], 哈尔滨工业大学, 中国, 2019.Zhao Yao-Xu. Research on Robotic Placement Machine and Placement Process of Thermoplastic Composite [Master thesis], Harbin Institute of Technology, China, 2019. [118] 解五一. 复合材料自动铺带机器人设计及铺带过程控制 [硕士学位论文], 武汉大学, 中国, 2019.Xie Wu-Yi. Design of Automatic Composite Tape Laying Robot and Process Control of Taping [Master thesis], Wuhan University, China, 2019. [119] Han Z Y, Hu F C, Lu H, Fu H Y. Design of ultrasonic cutting bench for automatic tape laying machine. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2014, 552: 80−85 doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.552.80 [120] Grimshaw M N, Grant C M C G, Diaz C M J M L. Advanced technology tape laying for affordable manufacturing of large composite structures. In: Proceedings of the 46th International SAMPE Symposium. Long Beach, USA: SAMPE, 2001. 2484−2494 [121] Budelmann D, Detampel H, Schmidt C, Meiners D. Interaction of process parameters and material properties with regard to prepreg tack in automated lay-up and draping processes. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2019, 117: 308−316 doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2018.12.001 [122] Ren S L, Lu H, Wang Y Z, Fu H Y. Development of PLC-based tension control system. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2007, 20(3): 266−271 doi: 10.1016/S1000-9361(07)60043-0 [123] Izco L, Isturiz J, Motilva M. High Speed Tow Placement System for Complex Surfaces with Cut/Clamp/ & Restart Capabilities at 85 m/min (3350 IPM), SAE Technical Paper 2006-01-3138, Aerospace Manufacturing and Automated Fastening Conference and Exhibition, USA, 2006. [124] Denkena B, Schmidt C, Weber P. Automated fiber placement head for manufacturing of innovative aerospace stiffening structures. Procedia Manufacturing, 2016, 6: 96−104 doi: 10.1016/j.promfg.2016.11.013 [125] Singh Y, Singh J, Sharma S, Sharma A, Singh Chohan J. Process parameter optimization in laser cutting of coir fiber reinforced epoxy composite——A review. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2022, 48: 1021−1027 doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2021.06.344 [126] Liu X L, Han Z Y, Zhao Z Y, Sun S Z. Thermal analysis of cylindrical molds using thermoplastic composite during robotic fiber placement. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2021, 1765: Article No. 012023 [127] 蒋威, 周悦, 杨飞, 黄志高, 陈诚, 周华民. 红外辅助自动纤维铺放工艺对连续玻璃纤维增强聚丙烯复合材料结构与性能影响. 复合材料学报, 2023, 40(4): 2015−2025Jiang Wei, Zhou Yue, Yang Fei, Huang Zhi-Gao, Chen Cheng, Zhou Hua-Min. Infrared-assisted automated fiber placement process on the structure and properties of continuous glass fiber reinforced polypropylene composites. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2023, 40(4): 2015−2025 [128] 杨宇. 门式六通道纤维铺放系统的研究与装备实现 [硕士学位论文], 武汉理工大学, 中国, 2019.Yang Yu. Research and Equipment Realization of Gantry Type Six-channel Fiber Laying System [Master thesis], Wuhan University of Technology, China, 2019. [129] Sabido A M. Development of an Automated Fiber Placement Process for the Fabrication of Thermoplastic Composite Laminates [Master thesis], University of South Carolina, USA, 2019. [130] Zhang W X, Liu F, Lv Y X, Ding X L. Modelling and layout design for an automated fibre placement mechanism. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2020, 144: Article No. 103651 doi: 10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2019.103651 [131] Hauber D E, Langone R J, Martin J P, Miller S F, Pasanen M J. Composite Tape Laying Apparatus and Method, U.S. Patent 7063118, June 2006 [132] Mischler P L, Tingley M C, Hoffmann K. Compaction Roller for A Fiber Placement Machine, U.S. Patent 7810539, October 2010 [133] 王磊. 纱架与铺丝头一体化纤维铺放系统研究 [硕士学位论文], 哈尔滨工业大学, 中国, 2015.Wang Lei. Research on Integration Technique of Creels and Fiber Placment Head for Automated Fiber Placement Machine [Master thesis], Harbin Institute of Technology, China, 2015. [134] Liu F, Zhang W X, Shang J F, Yi M H, Wang S R, Ding X L. A planar underactuated compaction mechanism with self-adaptability for automated fiber placement heads. Aerospace, 2022, 9(10): Article No. 586 doi: 10.3390/aerospace9100586 [135] Saboukhi A. Designing and Implementing a Small-size Automated Fiber Placement (AFP) Head Capable of Depositing Thermoset Layers on V-shape Structures [Master thesis], Concordia University, Canada, 2023. [136] Li L N, Xu D, Wang X G, Tan M. A survey on path planning algorithms in robotic fibre placement. In: Proceedings of the 27th Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC). Qingdao, China: IEEE, 2015. 4704−4709 [137] Rousseau G, Wehbe R, Halbritter J, Harik R. Automated fiber placement path planning: A state-of-the-art review. Computer-Aided Design & Applications, 2018, 16(2): 172−203 [138] Shinno N, Shigematsu T. Method for Controlling Tape Affixing Direction of Automatic Tape Affixing Apparatus, U.S. Patent 5041179, August 1991 [139] 尹书云. 自由型面自动铺丝线型规划约束研究 [硕士学位论文], 武汉理工大学, 中国, 2013.Yin Shu-Yun. Research on Constraint for Fibers Arrangement Pattern Planning in Auto Fiber Placement on Free-surface [Master thesis], Wuhan University of Technology, China, 2013. [140] Zhang J F, Xu D L, Wang Z H. Modeling approach for fiber placement routes on complex surface. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2014, 686: 560−566 doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.686.560 [141] Xiao H, Han W, Tang W B, Duan Y G. An efficient and adaptable path planning algorithm for automated fiber placement based on meshing and multi guidelines. Materials, 2020, 13(18): Article No. 4209 doi: 10.3390/ma13184209 [142] Hély C, Birglen L, Xie W F. Feasibility study of robotic fibre placement on intersecting multi-axial revolution surfaces. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2017, 48: 73−79 doi: 10.1016/j.rcim.2017.02.005 [143] Qu W W, Gao J X, Yang D, He R M, Yang Q, Cheng L, et al. Automated fiber placement path generation method based on prospective analysis of path performance under multiple constraints. Composite Structures, 2021, 255: Article No. 112940 doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2020.112940 [144] 张鹏, 尹来容, 周振华, 黄龙. 基于近似测地线的分层次自动铺带轨迹规划方法. 机械工程学报, 2020, 56(23): 226−238 doi: 10.3901/JME.2020.23.226Zhang Peng, Yin Lai-Rong, Zhou Zhen-Hua, Huang Long. A multi-level trajectory planning method based on quasi-geodesic for automated tape placement. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2020, 56(23): 226−238 doi: 10.3901/JME.2020.23.226 [145] Punera D, Mukherjee P. Recent developments in manufacturing, mechanics, and design optimization of variable stiffness composites. Journal of Reinforced Plastics and Composites, 2022, 41(23−24): 917−945 doi: 10.1177/07316844221082999 [146] Parnas L, Oral S, Ceyhan Ü. Optimum design of composite structures with curved fiber courses. Composites Science and Technology, 2003, 63(7): 1071−1082 doi: 10.1016/S0266-3538(02)00312-3 [147] IJsselmuiden S T, Abdalla M M, Gurdal Z. Optimization of variable-stiffness panels for maximum buckling load using lamination parameters. AIAA Journal, 2010, 48(1): 134−143 doi: 10.2514/1.42490 [148] Blom A W, Tatting B F, Hol J M A M, Gürdal Z. Fiber path definitions for elastically tailored conical shells. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2009, 40(1): 77−84 doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2008.03.011 [149] 李玥华, 富宏亚, 韩振宇, 韩德东. 两类非可展曲面零件自动纤维铺放变角度轨迹规划算法. 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 2013, 25(10): 1523−1529Li Yue-Hua, Fu Hong-Ya, Han Zhen-Yu, Han De-Dong. Variable-angle trajectory planning algorithm for automated fiber placement of two non-developable surfaces. Journal of Computer-Aided Design & Computer Graphics, 2013, 25(10): 1523−1529 [150] 李玥华. 热塑性预浸丝变角度铺放及其轨迹规划的研究 [博士学位论文], 哈尔滨工业大学, 中国, 2013.Li Yue-Hua. Research on Thermoplastic Towpreg Variable Angle Placement and Trajectory Planning [Ph.D. dissertation], Harbin Institute of Technology, China, 2013. [151] Shirinzadeh B, Cassidy G, Oetomo D, Alici G, Ang Jr M H. Trajectory generation for open-contoured structures in robotic fibre placement. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2007, 23(4): 380−394 doi: 10.1016/j.rcim.2006.04.006 [152] Schueler K, Miller J, Hale R. Approximate geometric methods in application to the modeling of fiber placed composite structures. Journal of Computing and Information Science in Engineering, 2004, 4(3): 251−256 doi: 10.1115/1.1736685 [153] Zhu Y J, Yao K Z. Optimization path planning algorithm based on STL file reconstruction for automated fiber placement. In: Proceedings of the Chinese Intelligent Systems Conference. Singapore: Springer, 2019. 379−387 [154] Li L, Wang X G, Xu D, Tan M. A placement path planning algorithm based on meshed triangles for carbon fiber reinforce composite component with revolved shape. International Journal on Control Systems and Applications, 2014, 1(1): 23−32 [155] 王小平, 周宇, 刘付国. 三角网格面自动铺丝定角度路径规划算法. 南京航空航天大学学报, 2020, 52(3): 378−387Wang Xiao-Ping, Zhou Yu, Liu Fu-Guo. Fixed-angle method for automatic fiber placement on triangular mesh surface. Journal of Nanjing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics, 2020, 52(3): 378−387 [156] Bruyneel M, Zein S. A modified fast marching method for defining fiber placement trajectories over meshes. Computers & Structures, 2013, 125: 45−52 [157] 刘志强, 顾献安, 郭昊, 奚浩, 王明强, 李军利. 碳纤维螺旋桨自动铺放成形轨迹规划方法. 中国机械工程, 2020, 31(17): 2079−2084 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2020.17.010Liu Zhi-Qiang, Gu Xian-An, Guo Hao, Xi Hao, Wang Ming-Qiang, Li Jun-Li. A trajectory planning method for automatic placement of carbon n fiber screw propellers. China Mechanical Engineering, 2020, 31(17): 2079−2084 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2020.17.010 [158] 赵安安, 何大亮, 王晗, 郭俊刚, 柯映林. 复杂曲面上的自动铺放路径规划方法. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2022, 48(4): 595−601Zhao An-An, He Da-Liang, Wang Han, Guo Jun-Gang, Ke Ying-Lin. Automatic paving path planning method on complex surfaces. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2022, 48(4): 595−601 [159] Yan L, Chen Z C, Shi Y Y, Mo R. An accurate approach to roller path generation for robotic fibre placement of free-form surface composites. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2014, 30(3): 277−286 doi: 10.1016/j.rcim.2013.10.007 [160] Wang P Y, Li Y, Wang X F, Xiao J. Research on fiber placement trajectory design algorithm for the free-form surface with given ply orientation information. Polymers and Polymer Composites, 2011, 19(2−3): 203−208 doi: 10.1177/0967391111019002-323 [161] Qu W W, He R M, Wang Q, Cheng L, Yang D, Gao J X, et al. Algorithms for constructing initial and offset path of automated fiber placement for complex double-curved surfaces. Applied Composite Materials, 2021, 28(3): 855−875 doi: 10.1007/s10443-021-09901-2 [162] Lu J R, Xu H J, Jiang Z H, Li K M, Hu J. Design of a composite truncated elliptical rotary shell based on variable-angle trajectories. Composite Structures, 2022, 294: Article No. 115772 doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2022.115772 [163] Scheirer N, Holland S D, Krishnamurthy A. Fiber layup generation on curved composite structures. Computer-Aided Design, 2021, 136: Article No. 103031 doi: 10.1016/j.cad.2021.103031 [164] Xu K, Hao X Z, Lin J M. Automated fibre placement path generation for complex surfaces via digital image deconvolution algorithm. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2022, 163: Article No. 107246 doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2022.107246 [165] Wang K, Wang X P, Gan J Q, Jiang S K. A general method of trajectory generation based on point-cloud structures in automatic fibre placement. Composite Structures, 2023, 314: Article No. 116976 doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2023.116976 [166] 张洋, 钟翔屿, 包建文. 先进树脂基复合材料自动丝束铺放技术研究现状及发展方向. 航空制造技术, 2013, 56(23): 131−136 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-833X.2013.23.026Zhang Yang, Zhong Xiang-Yu, Bao Jian-Wen. Research status and future trend of automated fiber placement technology for advanced polymer matrix composites. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology, 2013, 56(23): 131−136 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-833X.2013.23.026 [167] Oromiehie E, Prusty B G, Compston P, Rajan G. The influence of consolidation force on the performance of AFP manufactured laminates. In: Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Composite Materials. Xi'an, China: Chinese Society for Composite Materials, 2017. 1−11 [168] 徐志明. 复合材料自动铺放技术的研究进展及其工艺特点分析. 电气自动化, 2018, 40(1): 88−91Xu Zhi-Ming. Research progress of automatic placement of composite materials and analysis of its technological characters. Electrical Automation, 2018, 40(1): 88−91 [169] Khan M A, Mitschang P, Schledjewski R. Parametric study on processing parameters and resulting part quality through thermoplastic tape placement process. Journal of Composite Materials, 2013, 47(4): 485−499 doi: 10.1177/0021998312441810 [170] 刘林, 文立伟, 李勇, 肖军. 基于PMAC随动控制模式下自动铺带切割的研究. 宇航材料工艺, 2007, 37(5): 46−49 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2330.2007.05.012Liu Lin, Wen Li-Wei, Li Yong, Xiao Jun. Research on tape-cutting for automated tape laying based on tracking control mode of PMAC. Aerospace Materials & Technology, 2007, 37(5): 46−49 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2330.2007.05.012 [171] Gao J C, Pashkevich A, Caro S. Optimization of the robot and positioner motion in a redundant fiber placement workcell. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2017, 114: 170−189 doi: 10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2017.04.009 [172] FarzanehKaloorazi M, Bonev I A, Birglen L. Simultaneous path placement and trajectory planning optimization for a redundant coordinated robotic workcell. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2018, 130: 346−362 doi: 10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2018.08.022 [173] Zhang X M, Xie W F, Hoa S V. Semi-offline trajectory synchronized algorithm of the cooperative automated fiber placement system. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2018, 51: 53−62 doi: 10.1016/j.rcim.2017.11.015 [174] Hassan M, Liu D K, Xu D L. A two-stage approach to collaborative fiber placement through coordination of multiple autonomous industrial robots. Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems, 2019, 95: 915−933 [175] He K, Nie H P, Yan C. The intelligent composite panels manufacturing technology based on tape-laying automatic system. Procedia CIRP, 2016, 56: 610−613 doi: 10.1016/j.procir.2016.10.120 [176] Yao Y X. Adaptive Position/Force Control and Calibration of Robotic Manipulators as Applied to Automated Composite Tape-laying [Ph.D. dissertation], The University of Wisconsin-Madison, USA, 1988. [177] Jiang J X, He Y X, Wang H, Ke Y L. Modeling and experimental validation of compaction pressure distribution for automated fiber placement. Composite Structures, 2021, 256: Article No. 113101 doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2020.113101 [178] Shirinzadeh B, Hui Tan B, Tronche D. Planning and simulation for robotic fibre placement. In: Proceedings of the 30th International Symposium on Robotics. Tokyo, Japan: International Federation of Robotics, 1999. 161−168 [179] 朱珮旗, 樊红日, 钱波. 复合材料自动铺丝软件技术研究与应用综述. 软件工程与应用, 2022, 11(6): 1521−1533 doi: 10.12677/SEA.2022.116157Zhu Pei-Qi, Fan Hong-Ri, Qian Bo. Review of research and application about composite automated fibre placement software technology. Software Engineering and Applications, 2022, 11(6): 1521−1533 doi: 10.12677/SEA.2022.116157 [180] Shirinzadeh B, Alici G, Foong C W, Cassidy G. Fabrication process of open surfaces by robotic fibre placement. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2004, 20(1): 17−28 doi: 10.1016/S0736-5845(03)00050-4 [181] Shirinzadeh B, Wei Foong C, Hui Tan B. Robotic fibre placement process planning and control. Assembly Automation, 2000, 20(4): 313−320 doi: 10.1108/01445150010353242 [182] Druiff P P, Ma K, Visrolia A, Arruda M, Palardy-Sim M, Bolduc S, et al. A smart interface for machine learning based data-driven automated fibre placement. In: Proceedings of the Composites and Advanced Materials Expo. Dallas, USA: 2021. [183] Wanigasekara C, Oromiehie E, Swain A, Prusty B G, Nguang S K. Machine learning-based inverse predictive model for AFP based thermoplastic composites. Journal of Industrial Information Integration, 2021, 22: Article No. 100197 doi: 10.1016/j.jii.2020.100197 [184] Zimmerling C, Poppe C, Stein O, Kärger L. Optimisation of manufacturing process parameters for variable component geometries using reinforcement learning. Materials & Design, 2022, 214: Article No. 110423 [185] Croft K, Lessard L, Pasini D, Hojjati M, Chen J H, Yousefpour A. Experimental study of the effect of automated fiber placement induced defects on performance of composite laminates. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2011, 42(5): 484−491 doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2011.01.007 [186] Halbritter A, Harper R. Big parts demand big changes to the fiber placement status quo. In: Proceedings of the SME Composites Manufacturing. Mesa, USA: 2012. [187] Juarez P D, Gregory E D. In situ thermal inspection of automated fiber placement for manufacturing induced defects. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2021, 220 : Article No. 109002 [188] Harik R, Saidy C, Williams S J, Gurdal Z, Grimsley B. Automated fiber placement defect identity cards: Cause, anticipation, existence, significance, and progression. In: Proceedings of the SAMPE 2018 Technical Conference and Exhibition. Long Beach, USA: SAMPE, 2018. [189] Shadmehri F, Ioachim O, Pahud O, Brunel J E, Landry A, Hoa S V, et al. Laser-vision inspection system for automated fiber placement (AFP) process. In: Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Composite Materials. Copenhagen, Denmark: Aalborg University, 2015. [190] Rudberg T, Cemenska J. Incorporation of laser projectors in machine cell controller reduces ply boundary inspection time, on-part course identification and part probing. SAE International Journal of Aerospace, 2012, 5(1): 74−78 doi: 10.4271/2012-01-1886 [191] Rudberg T, Nielson J, Henscheid M, Cemenska J. Improving AFP cell performance. SAE International Journal of Aerospace, 2014, 7(2): 317−321 doi: 10.4271/2014-01-2272 [192] Juarez P D, Cramer K E, Seebo J P. Advances in in situ inspection of automated fiber placement systems. In: Proceedings of the SPIE 9861, Thermosense: Thermal Infrared Applications XXXVIII. Baltimore, USA: SPIE, 2016. Article No. 986109 [193] Denkena B, Schmidt C, Völtzer K, Hocke T. Thermographic online monitoring system for automated fiber placement processes. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2016, 97: 239−243 doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2016.04.076 [194] Yadav N, Oswald-Tranta B, Gürocak M, Galic A, Adam R, Schledjewski R. In-line and off-line NDT defect monitoring for thermoplastic automated tape layup. NDT & E International, 2023, 137: Article No. 102839 [195] Chen H Z, Zhang Z J, Yin W L, Wang Q, Li Y F, Zhao C Y. Surface defect characterization and depth identification of CFRP material by laser line scanning. NDT & E International, 2022, 130: Article No. 102657 [196] Cemenska J, Rudberg T, Henscheid M. Automated in-process inspection system for AFP machines. SAE International Journal of Aerospace, 2015, 8(2): 303−309 doi: 10.4271/2015-01-2608 [197] 马少博. 复合材料自动铺放过程表层缺陷检测与识别方法研究 [硕士学位论文], 南京航空航天大学, 中国, 2020.Ma Shao-Bo. Surface Defect Inspection Technology of Automated Fiber Placement Manufacturing Process [Master thesis], Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, China, 2020. [198] Tang Y P, Wang Q, Wang H, Li J X, Ke Y L. A novel 3D laser scanning defect detection and measurement approach for automated fibre placement. Measurement Science and Technology, 2021, 32(7): Article No. 075201 [199] Tang Y P, Wang Q, Cheng L, Li J X, Ke Y L. An in-process inspection method integrating deep learning and classical algorithm for automated fiber placement. Composite Structures, 2022, 300: Article No. 116051 doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2022.116051 [200] Nguyen D H, Sun X C, Tretiak I, Valverde M A, Kratz J. Automatic process control of an automated fibre placement machine. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2023, 168: Article No. 107465 doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2023.107465 [201] Tao Y C, Jia S H, Duan Y G, Zhang X H. An online detection method for composite fibre tow placement accuracy. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part B: Journal of Engineering Manufacture, 2016, 230(9): 1614−1621 doi: 10.1177/0954405416640189 [202] Chen M J, Jiang M, Liu X L, Wu B L. Intelligent inspection system based on infrared vision for automated fiber placement. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation (ICMA). Changchun, China: IEEE, 2018. 918−923 [203] 蔡志强. 基于图像处理的纤维铺放缺陷检测研究 [硕士学位论文], 南京航空航天大学, 中国, 2017.Cai Zhi-Qiang. Research on Defect Detection Based on Image Processing for AFP [Master thesis], Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, China, 2017. [204] Sacco C, Radwan A B, Harik R, Van Tooren M. Automated fiber placement defects: Automated inspection and characterization. In: Proceedings of the SAMPE 2018 Technical Conference and Exhibition. Long Beach, USA: SAMPE, 2018. [205] Sacco C. Machine Learning Methods for Rapid Inspection of Automated Fiber Placement Manufactured Composite Structures [Master thesis], University of South Carolina, USA, 2019. [206] Zambal S, Heindl C, Eitzinger C, Scharinger J. End-to-end defect detection in automated fiber placement based on Artificially generated data. In: Proceedings of the SPIE 11172, Fourteenth International Conference on Quality Control by Artificial Vision. Mulhouse, France: SPIE, 2019. 371−378 [207] Meister S, Möller N, Stüve J, Groves R M. Synthetic image data augmentation for fibre layup inspection processes: Techniques to enhance the data set. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 2021, 32(6): 1767−1789 doi: 10.1007/s10845-021-01738-7 [208] Manyar O M, Cheng J Y, Levine R, Krishnan V, Barbič J, Gupta S K. Physics informed synthetic image generation for deep learning-based detection of wrinkles and folds. Journal of Computing and Information Science in Engineering, 2023, 23(3): Article No. 030903 [209] Szarski M, Chauhan S. An unsupervised defect detection model for a dry carbon fiber textile. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 2022, 33(7): 2075−2092 doi: 10.1007/s10845-022-01964-7 [210] Schmidt C, Hocke T, Denkena B. Artificial intelligence for non-destructive testing of CFRP prepreg materials. Production Engineering, 2019, 13(5): 617−626 doi: 10.1007/s11740-019-00913-3 [211] Zhang Y D, Wang W, Liu Q, Guo Z H, Ji Y C. Research on defect detection in automated fiber placement processes based on a multi-scale detector. Electronics, 2022, 11(22): Article No. 3757 doi: 10.3390/electronics11223757 [212] 柯岩, 傅云, 周玮珠, 朱伟东. 基于Transformer的复合材料多源图像实例分割网络. 红外与激光工程, 2023, 52(2): Article No. 20220338Ke Yan, Fu Yun, Zhou Wei-Zhu, Zhu Wei-Dong. Transformer-based multi-source images instance segmentation network for composite materials. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2023, 52(2): Article No. 20220338 [213] Rath J E, Graupner R, Schüppstuhl T. Processing strategies for dieless forming of fiber-reinforced plastic composites. Machines, 2023, 11(3): Article No. 365 doi: 10.3390/machines11030365 [214] Priyadharshini M, Balaji D, Bhuvaneswari V, Rajeshkumar L, Sanjay M R, Siengchin S. Fiber reinforced composite manufacturing with the aid of artificial intelligence——A state-of-the-art review. Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering, 2022, 29(7): 5511−5524 doi: 10.1007/s11831-022-09775-y [215] Yadav N, Schledjewski R. Review of in-process defect monitoring for automated tape laying. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2023, 173: Article No. 107654 doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2023.107654 [216] Cong Y, Tian D Y, Feng Y, Fan B J, Yu H B. Speedup 3-D texture-less object recognition against self-occlusion for intelligent manufacturing. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2019, 49(11): 3887−3897 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2018.2851666 [217] Manyar O M, Kanyuck A, Deshkulkarni B, Gupta S K. Visual servo based trajectory planning for fast and accurate sheet pick and place operations. In: Proceedings of the ASME 17th International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference. West Lafayette, USA: ASME, 2022. Article No. V001T04A019 [218] Döbrich O, Brauner C. Machine vision system for digital twin modeling of composite structures. Frontiers in Materials, 2023, 10: Article No. 1154655 doi: 10.3389/fmats.2023.1154655 [219] Glück R, Korber M. Automated control and simulation of dynamic robot teams in the domain of CFK production. arXiv: 2210.11213, 2022. [220] Manyar O M, McNulty Z, Nikolaidis S, Gupta S K. Inverse reinforcement learning framework for transferring task sequencing policies from humans to robots in manufacturing applications. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). London, UK: IEEE, 2023. 849−856 [221] Si W Y, Wang N, Li Q C, Yang C G. A framework for composite layup skill learning and generalizing through teleoperation. Frontiers in Neurorobotics, 2022, 16: Article No. 840240 doi: 10.3389/fnbot.2022.840240 -




 下载:
下载: