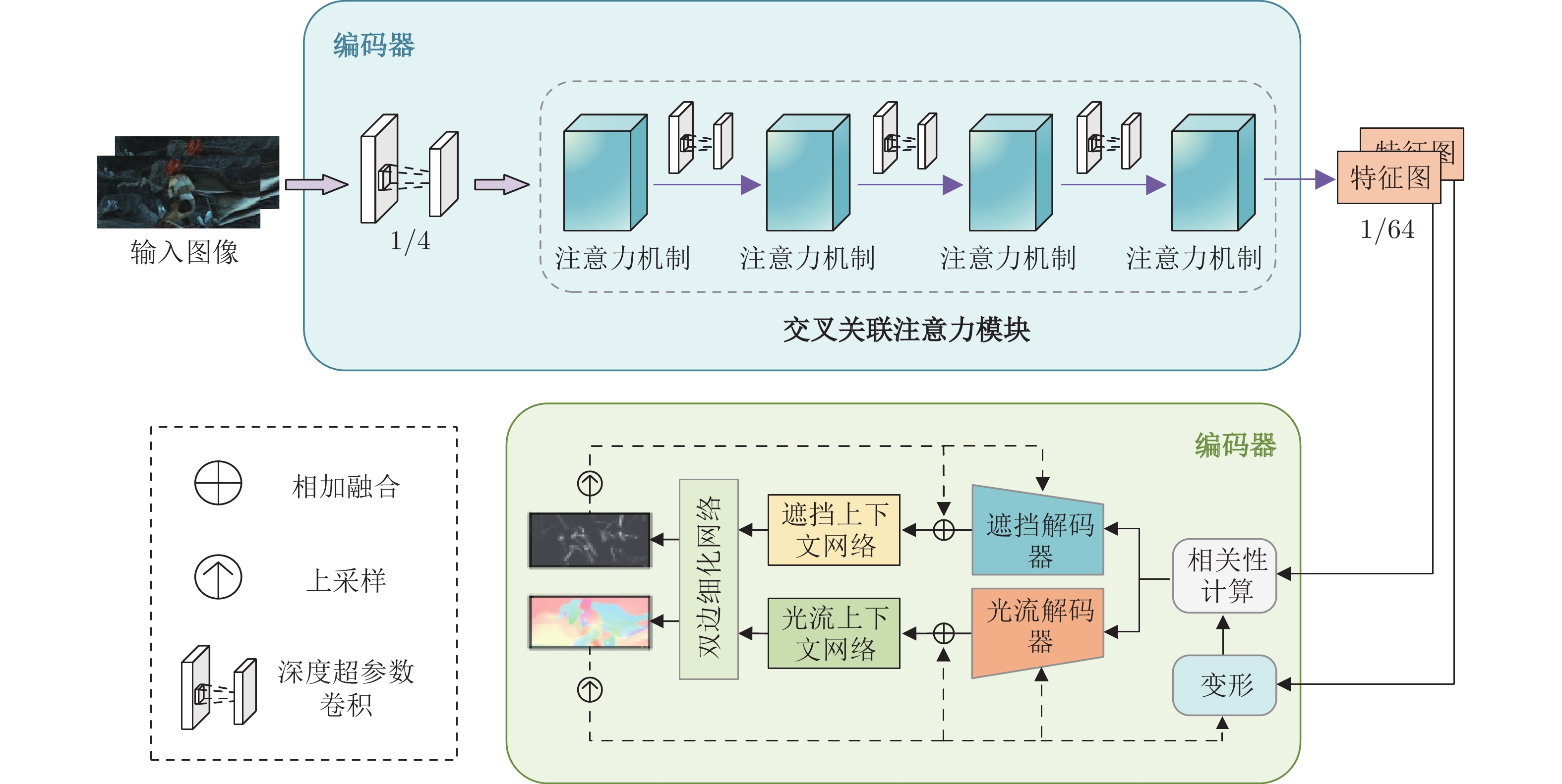
Large Displacement Optical Flow Estimation Jointing Depthwise Over-parameterized Convolution and Cross Correlation Attention
-
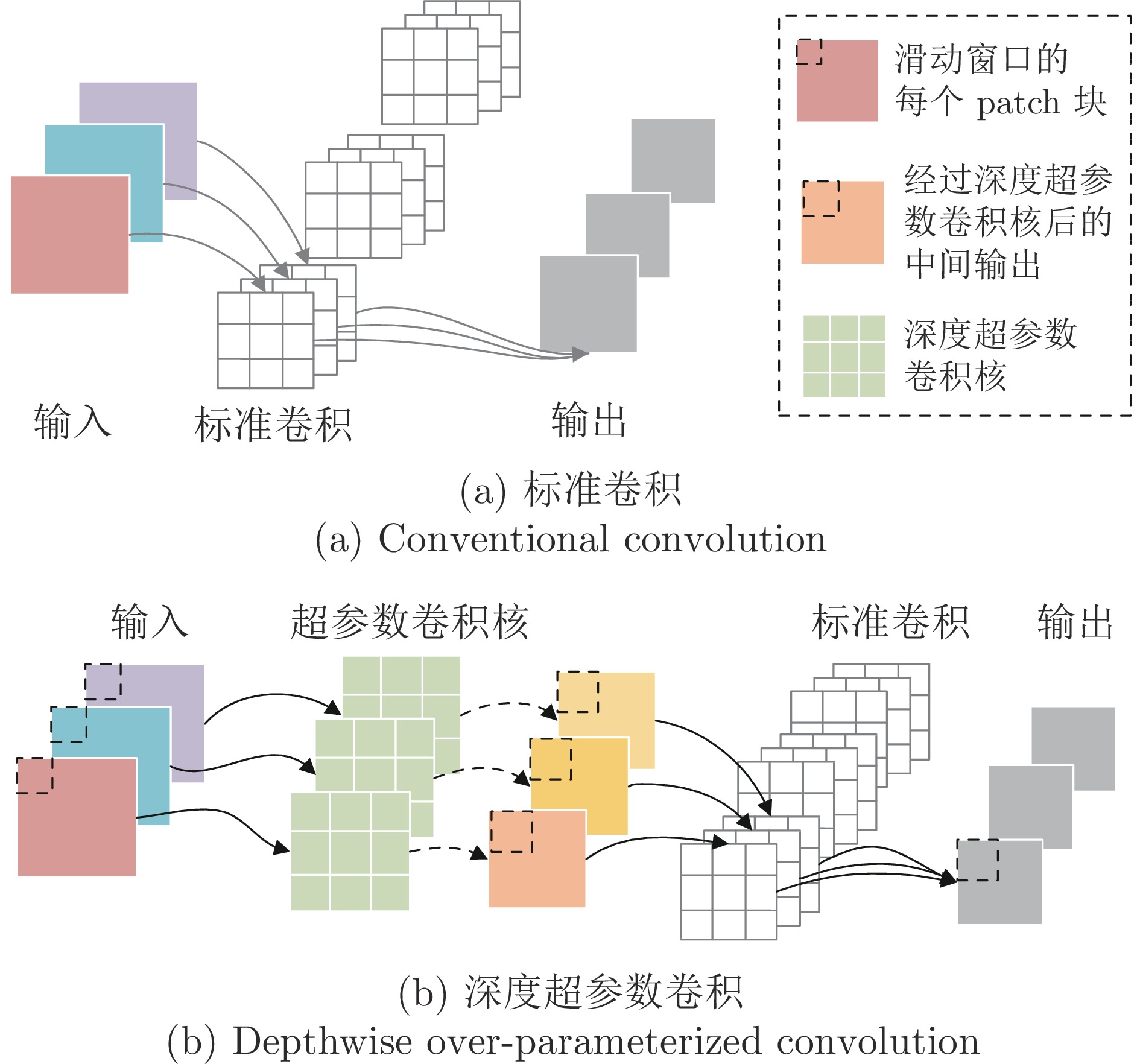
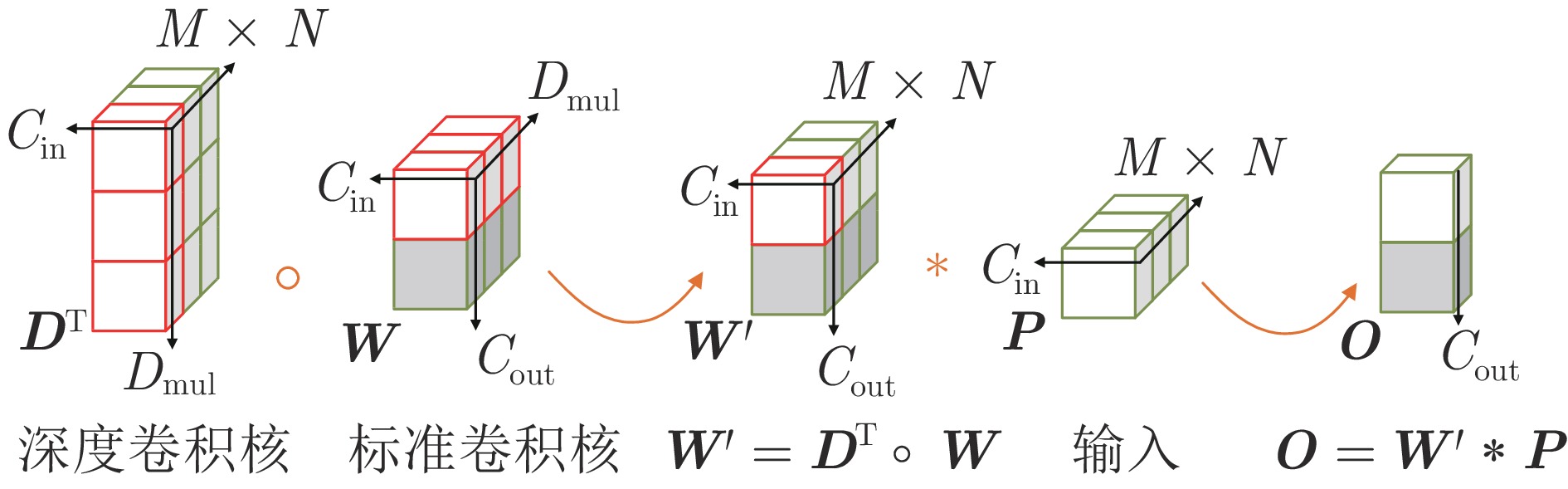
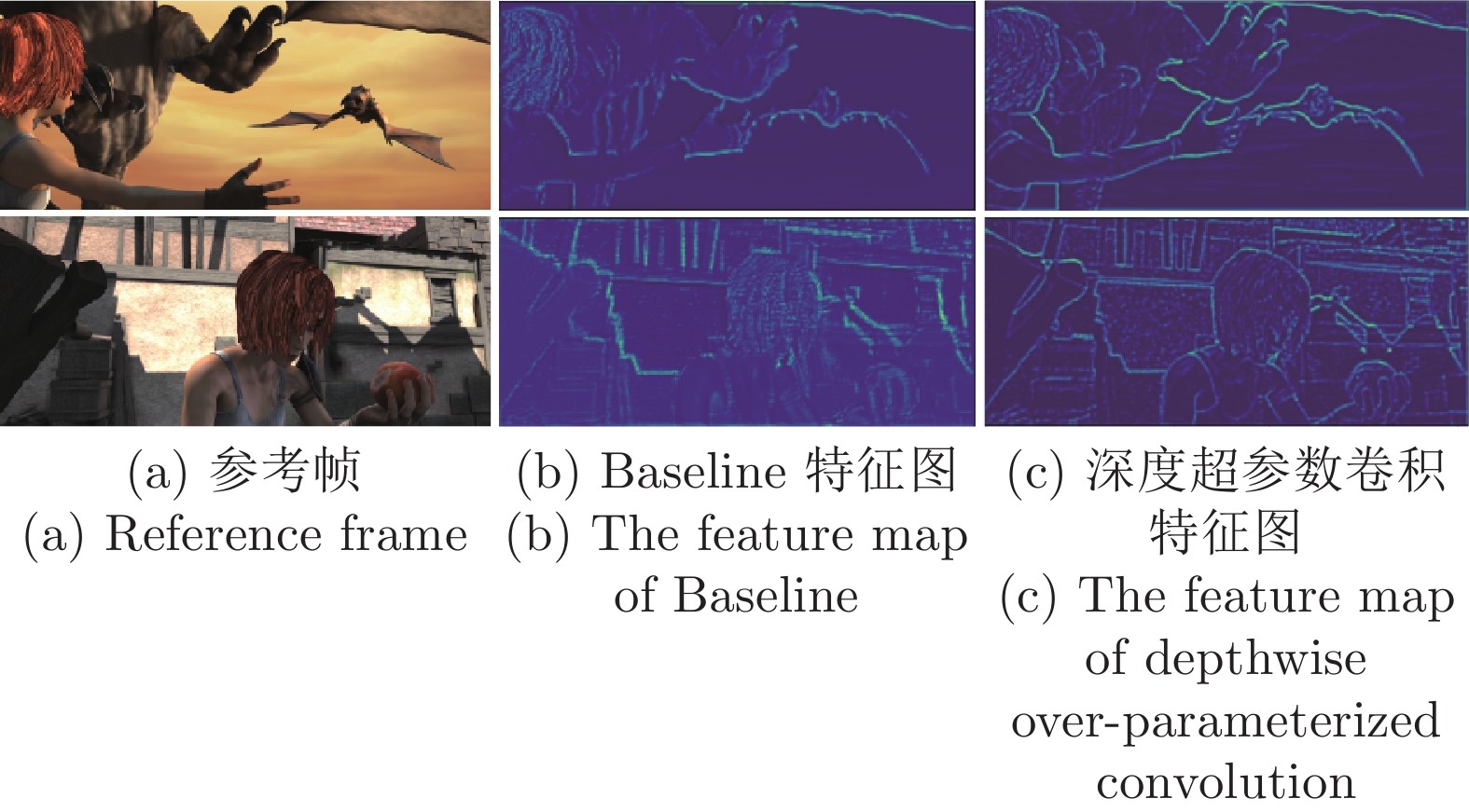
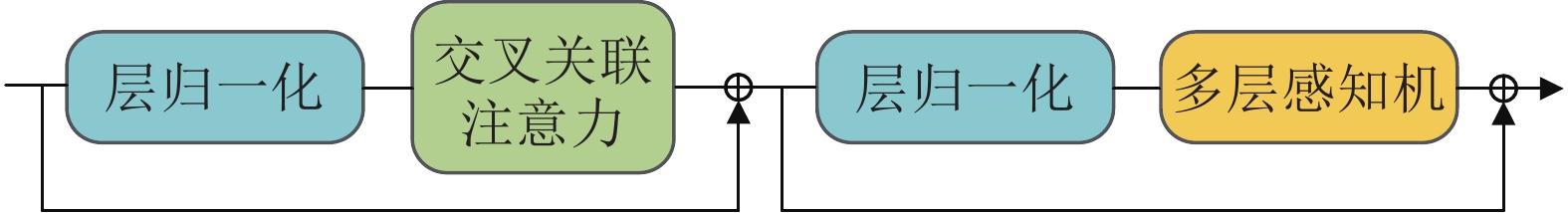
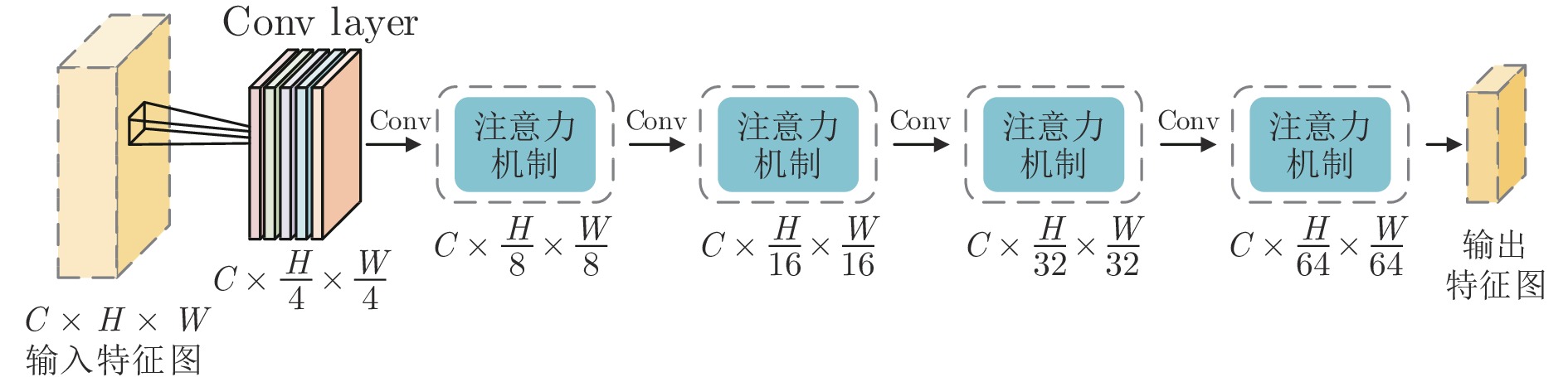
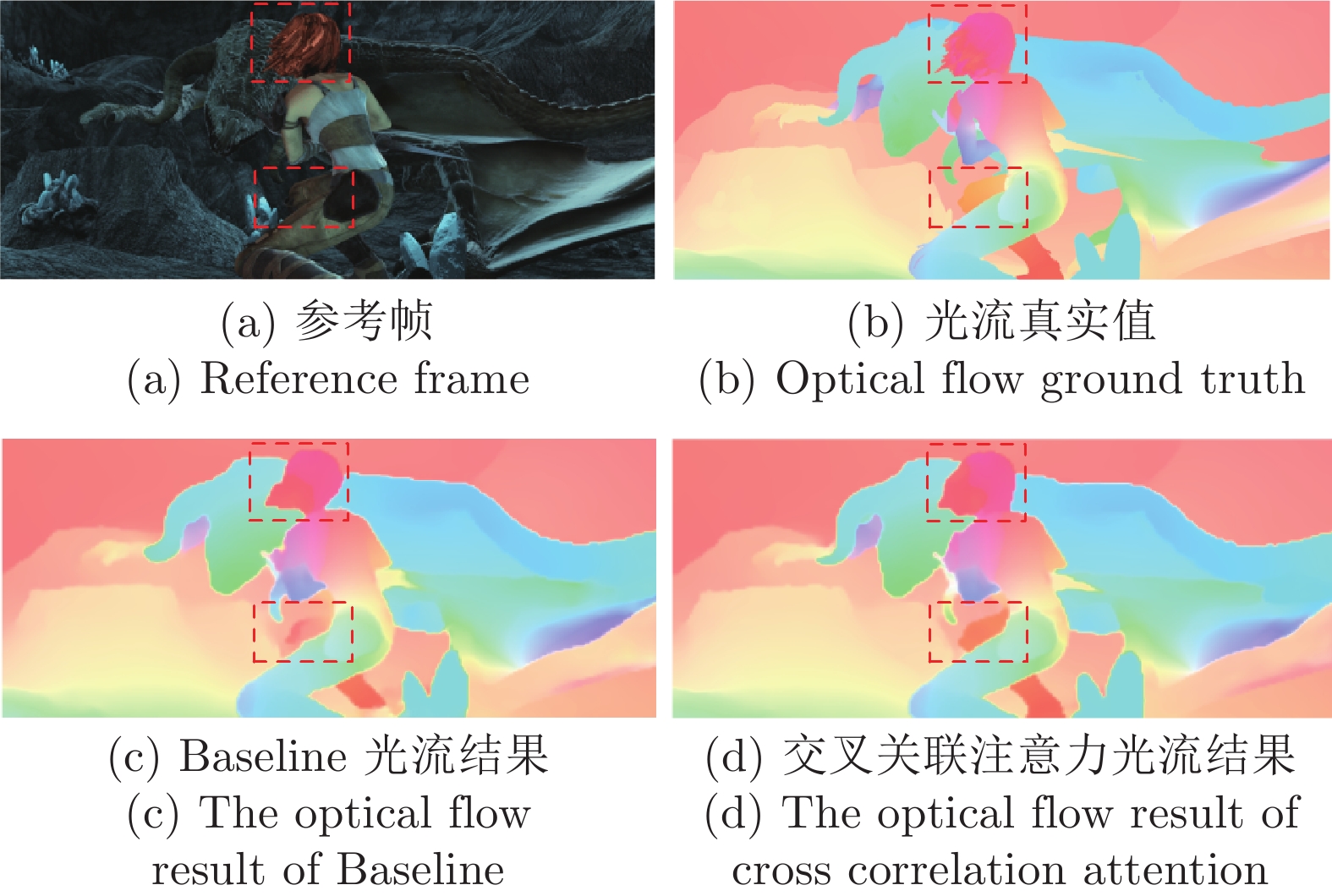
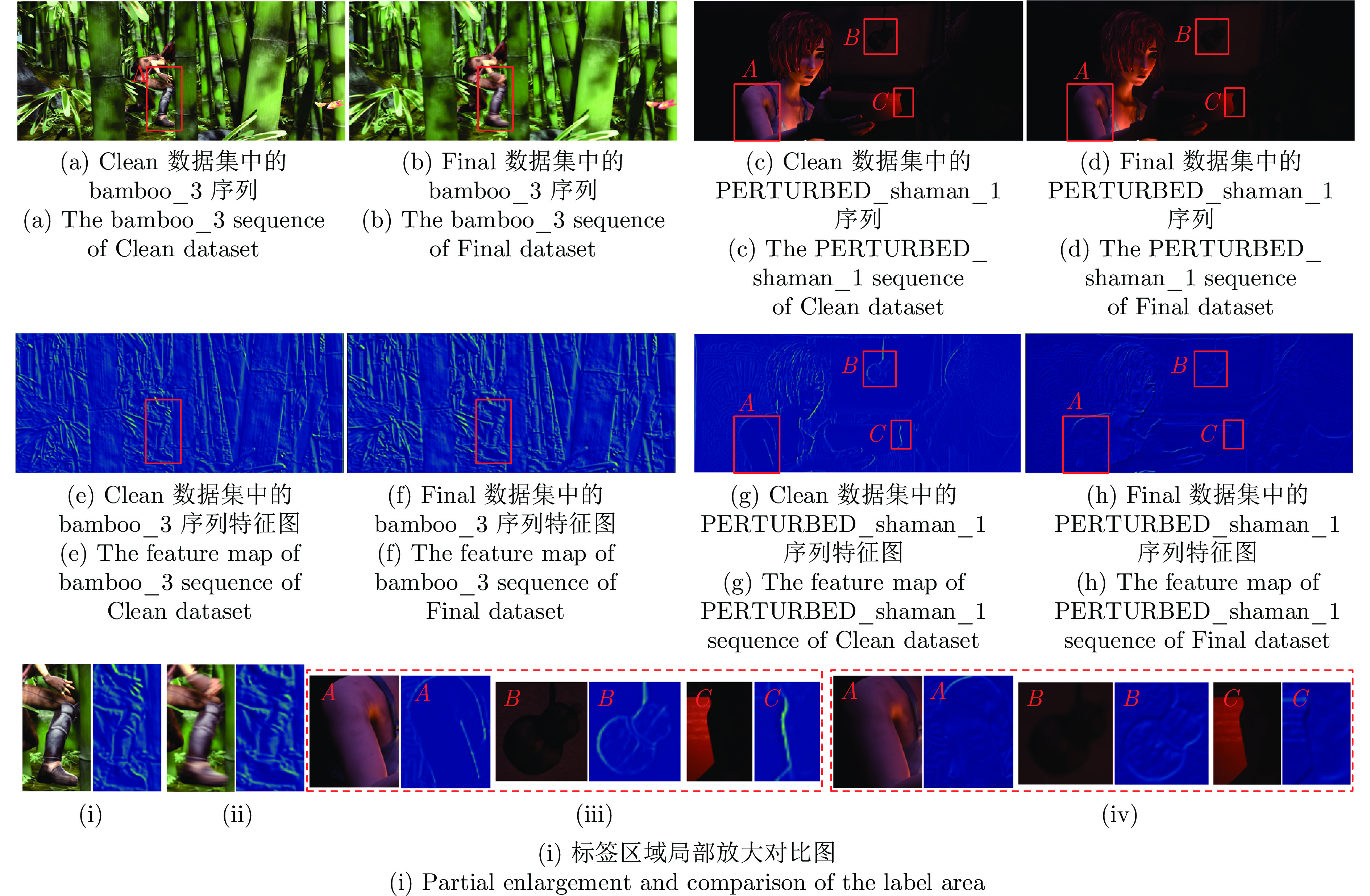
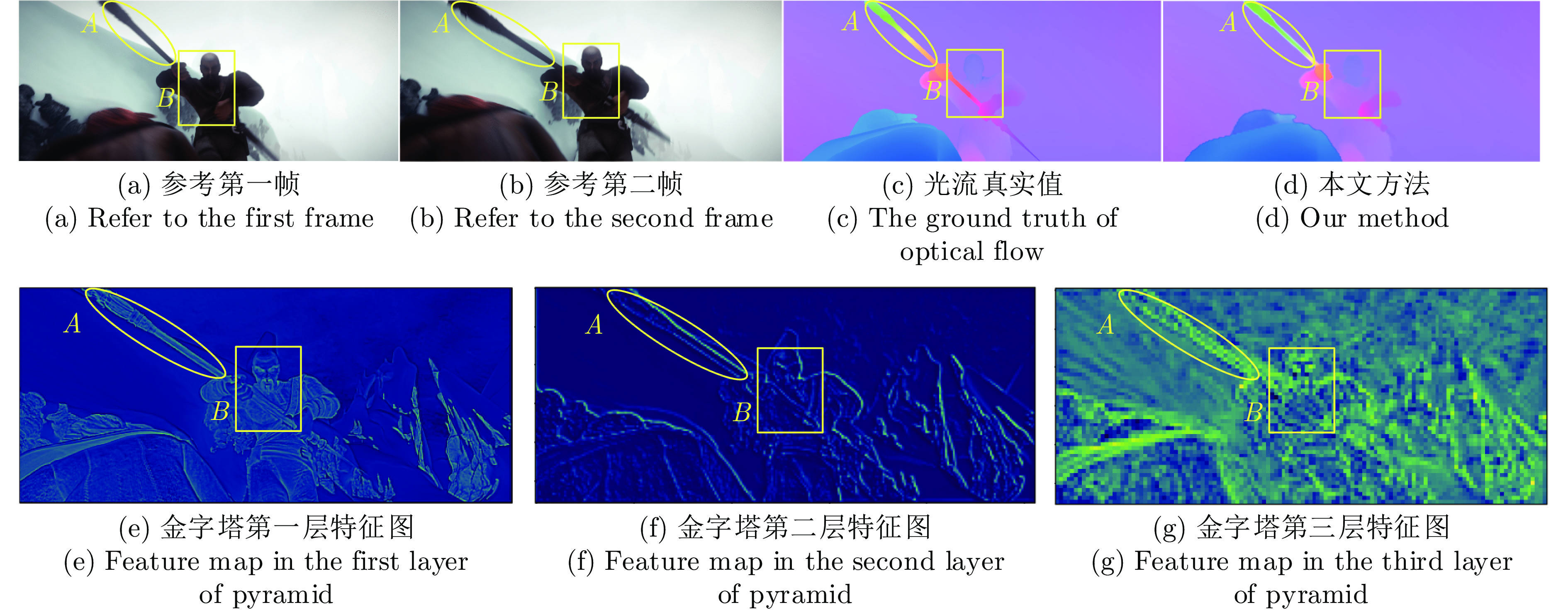
摘要: 针对现有深度学习光流估计模型在大位移场景下的准确性和鲁棒性问题, 提出了一种联合深度超参数卷积和交叉关联注意力的图像序列光流估计方法. 首先, 通过联合深层卷积和标准卷积构建深度超参数卷积以替代普通卷积, 提取更多特征并加快光流估计网络训练的收敛速度, 在不增加网络推理量的前提下提高光流估计的准确性; 然后, 设计基于交叉关联注意力的特征提取编码网络, 通过叠加注意力层数获得更大的感受野, 以提取多尺度长距离上下文特征信息, 增强大位移场景下光流估计的鲁棒性; 最后, 采用金字塔残差迭代模型构建联合深度超参数卷积和交叉关联注意力的光流估计网络, 提升光流估计的整体性能. 分别采用MPI-Sintel和KITTI测试图像集对本文方法和现有代表性光流估计方法进行综合对比分析, 实验结果表明本文方法取得了较好的光流估计性能, 尤其在大位移场景下具有更好的估计准确性与鲁棒性.Abstract: To improve the computation accuracy and robustness of deep-learning based optical flow models under large displacement scenes, we propose an optical flow estimation method jointing depthwise over-parameterized convolution and cross correlation attention. First, we construct a depthwise over-parameterized convolution model by combining the common convolution and depthwise convolution, which extracts more features and accelerates the convergence speed of optical flow network. This improves the optical flow accuracy without increasing computation complexity. Second, we exploit a feature extraction encoder based on cross correlation attention network, which extracts multi-scale long distance context feature information by stack the attention layers to obtain a larger receptive field. This improves the robustness of optical flow estimation under large displacement scenes. Finally, a pyramid residual iteration network by combing cross correlation attention and depthwise over-parameterized convolution is presented to improve the overall performance of optical flow estimation. We compare our method with the existing representative approaches by using the MPI-Sintel and KITTI datasets. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method shows better optical flow estimation performance, especially achieves better computation accuracy and robustness under large displacement areas.
-
表 1 MPI-Sintel数据集图像序列光流估计结果 (pixels)
Table 1 Optical flow calculation results of image sequences in MPI-Sintel dataset (pixels)
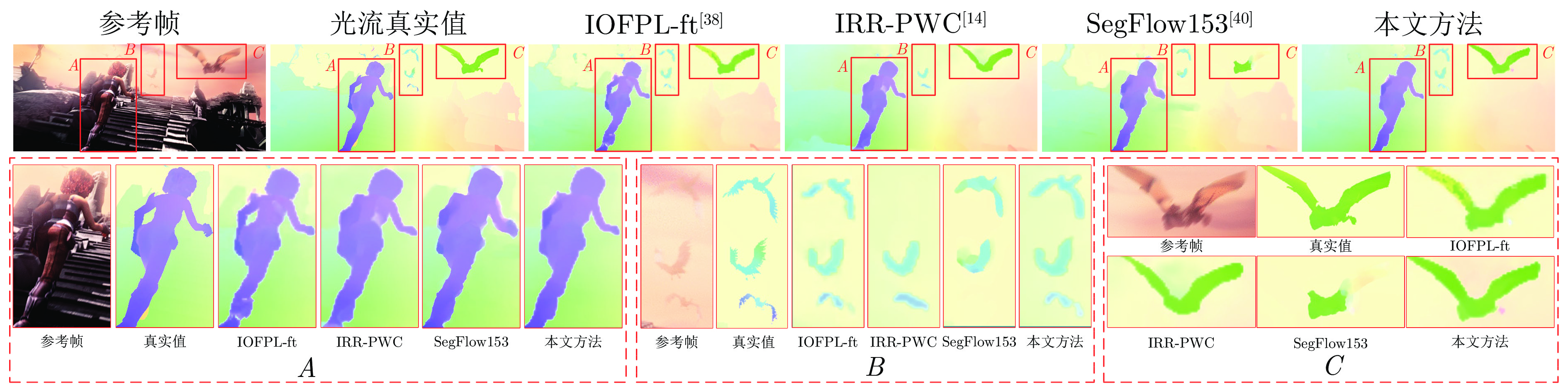
对比方法 Clean Final All Matched Unmatched All Matched Unmatched IRR-PWC[14] 3.844 1.472 23.220 4.579 2.154 24.355 PPAC-HD3[36] 4.589 1.507 29.751 4.599 2.116 24.852 LiteFlowNet2[37] 3.483 1.383 20.637 4.686 2.248 24.571 IOFPL-ft[38] 4.394 1.611 27.128 4.224 1.956 22.704 PWC-Net[25] 4.386 1.719 26.166 5.042 2.445 26.221 HMFlow[39] 3.206 1.122 20.210 5.038 2.404 26.535 SegFlow153[40] 4.151 1.246 27.855 6.191 2.940 32.682 SAMFL[41] 4.477 1.763 26.643 4.765 2.282 25.008 本文方法 2.763 1.062 16.656 4.202 2.056 21.696 表 2 MPI-Sintel数据集运动边缘与大位移指标对比结果 (pixels)
Table 2 Comparison results of motion edge and large displacement index in MPI-Sintel dataset (pixels)
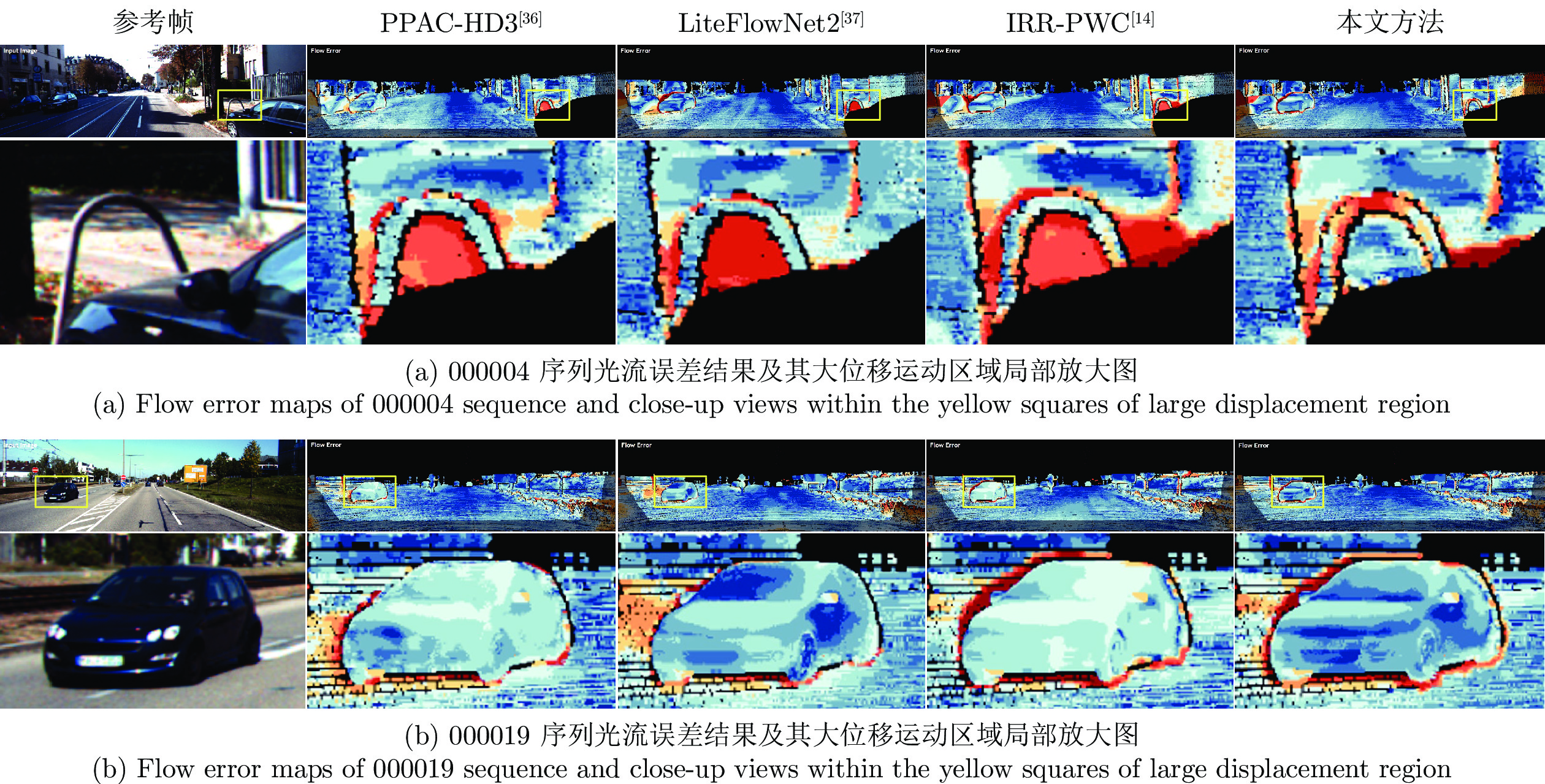
对比方法 Clean Final ${d}_{0\text{-}10}$ ${d}_{10\text{-}60}$ ${d}_{60\text{-}140}$ ${s}_{0\text{-}10}$ ${s}_{10\text{-}40}$ ${s}_{40+}$ ${d}_{0\text{-}10}$ ${d}_{10\text{-}60}$ ${d}_{60\text{-}140}$ ${s}_{0\text{-}10}$ ${s}_{10\text{-}40}$ ${s}_{40+}$ IRR-PWC[14] 3.509 1.296 0.721 0.535 1.724 25.430 4.165 1.843 1.292 0.709 2.423 28.998 PPAC-HD3[36] 2.788 1.340 1.068 0.355 1.289 33.624 3.521 1.702 1.637 0.617 2.083 30.457 LiteFlowNet2[37] 3.293 1.263 0.629 0.597 1.772 21.976 4.048 1.899 1.473 0.811 2.433 29.375 IOFPL-ft[38] 3.059 1.421 0.943 0.391 1.292 31.812 3.288 1.479 1.419 0.646 1.897 27.596 PWC-Net[25] 4.282 1.657 0.674 0.606 2.070 28.793 4.636 2.087 1.475 0.799 2.986 31.070 HMFlow[39] 2.786 0.957 0.584 0.467 1.693 20.470 4.582 2.213 1.465 0.926 3.170 29.974 SegFlow153[40] 3.072 1.143 0.656 0.486 2.000 27.563 4.969 2.492 2.119 1.201 3.865 36.570 SAMFL[41] 3.946 1.623 0.811 0.618 1.860 29.995 4.208 1.846 1.449 0.893 2.587 29.232 本文方法 2.772 0.854 0.443 0.541 1.621 16.575 3.884 1.660 1.292 0.753 2.381 25.715 表 3 KITTI2015数据集计算结果 (%)
Table 3 Calculation results in KITTI2015 dataset (%)
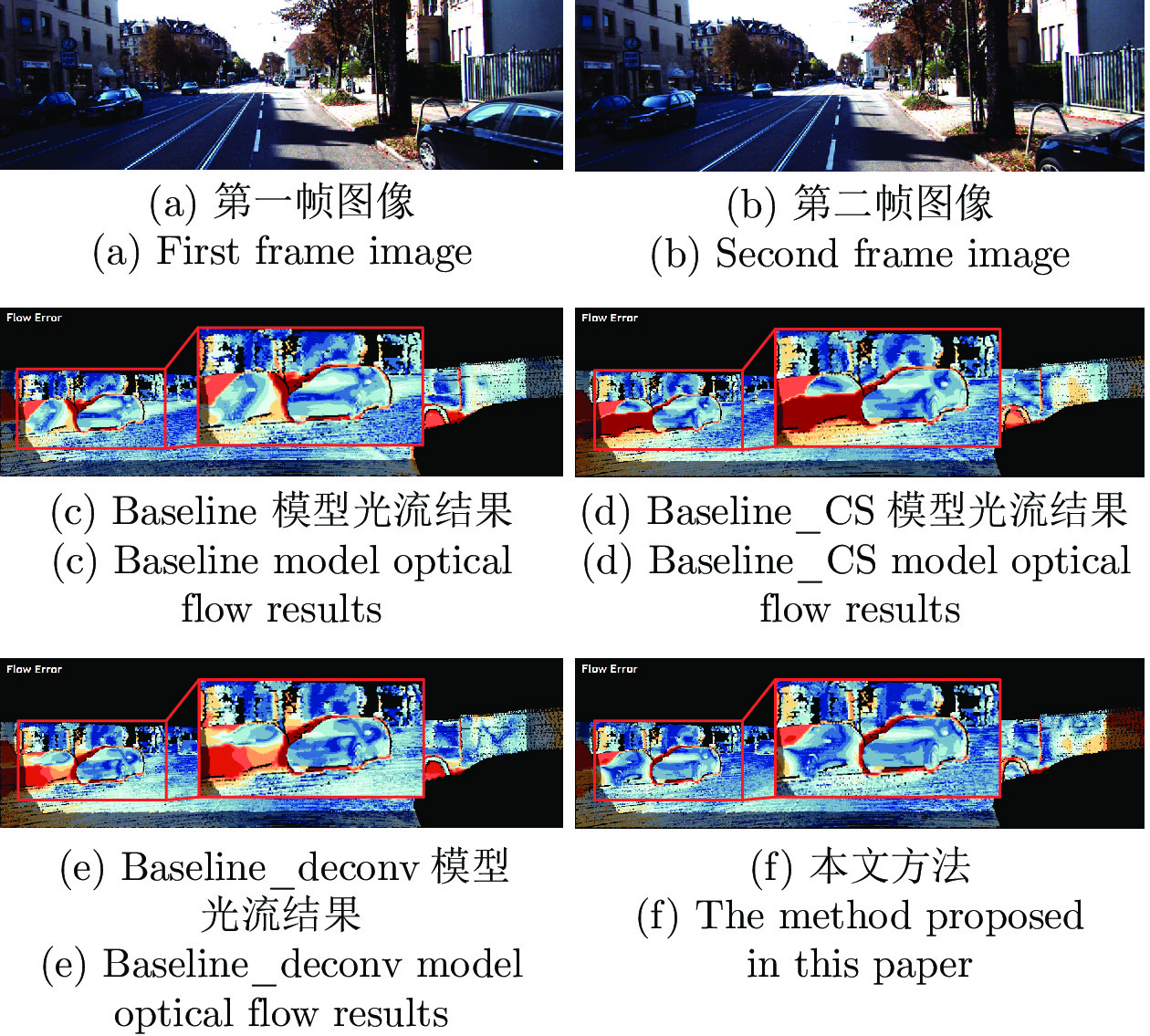
表 4 MPI-Sintel数据集上消融实验结果对比 (pixels)
Table 4 Comparison of ablation experiment results in MPI-Sintel dataset (pixels)
消融模型 All Matched Unmatched $s_{10\text{-}40}$ $s_{40+}$ Baseline 3.844 1.472 23.220 1.724 25.430 Baseline_CS 2.892 1.070 17.765 1.662 17.460 Baseline_deconv 3.621 1.461 21.272 1.659 23.482 Full model 2.763 1.062 16.656 1.621 16.575 表 5 KITTI2015数据集上消融实验结果对比
Table 5 Comparison of ablation experiment results in KITTI2015 dataset
消融模型 $Fl\text{-}bg $ (%) $Fl\text{-}fg $ (%) $Fl\text{-}all $ (%) 训练时间(min) Baseline 7.68 7.52 7.65 621 Baseline_CS 7.74 7.58 7.71 690 Baseline_deconv 7.28 7.30 7.29 632 Full model 7.43 6.65 7.30 616 -
[1] 张骄阳, 丛爽, 匡森. n比特随机量子系统实时状态估计及其反馈控制. 自动化学报, 2024, 50(1): 42−53Zhang Jiao-Yang, Cong Shuang, Kuang Sen. Real-time state estimation and feedback control for n-qubit stochastic quantum systems. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2024, 50(1): 42−53 [2] 张伟, 黄卫民. 基于种群分区的多策略自适应多目标粒子群算法. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(10): 2585−2599 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c200307Zhang Wei, Huang Wei-Min. Multi-strategy adaptive multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm based on swarm partition. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(10): 2585−2599 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c200307 [3] 张芳, 赵东旭, 肖志涛, 耿磊, 吴骏, 刘彦北. 单幅图像超分辨率重建技术研究进展. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(11): 2634−2654 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c200777Zhang Fang, Zhao Dong-Xu, Xiao Zhi-Tao, Geng Lei, Wu Jun, Liu Yan-Bei. Research progress of single image super-resolution reconstruction technology. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(11): 2634−2654 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c200777 [4] 杨天金, 侯振杰, 李兴, 梁久祯, 宦娟, 郑纪翔. 多聚点子空间下的时空信息融合及其在行为识别中的应用. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(11): 2823−2835 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190327Yang Tian-Jin, Hou Zhen-Jie, Li Xing, Liang Jiu-Zhen, Huan Juan, Zheng Ji-Xiang. Recognizing action using multi-center subspace learning-based spatial-temporal information fusion. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(11): 2823−2835 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190327 [5] 闫梦凯, 钱建军, 杨健. 弱对齐的跨光谱人脸检测. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(1): 135−147 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c210058Yan Meng-Kai, Qian Jian-Jun, Yang Jian. Weakly aligned cross-spectral face detection. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(1): 135−147 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c210058 [6] 郭迎春, 冯放, 阎刚, 郝小可. 基于自适应融合网络的跨域行人重识别方法. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(11): 2744−2756 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c220083Guo Ying-Chun, Feng Fang, Yan Gang, Hao Xiao-Ke. Cross-domain person re-identification on adaptive fusion network. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(11): 2744−2756 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c220083 [7] Horn B K P, Schunck B G. Determining optical flow. Artificial Intelligence, 1981, 17(1−3): 185−203 doi: 10.1016/0004-3702(81)90024-2 [8] Sun D Q, Roth S, Black M J. Secrets of optical flow estimation and their principles. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). San Francisco, USA: IEEE, 2010. 2432−2439 [9] Menze M, Heipke C, Geiger A. Discrete optimization for optical flow. In: Proceedings of the 37th German Conference Pattern Recognition (GCPR). Aachen, Germany: Springer, 2015. 16−28 [10] Chen Q F, Koltun V. Full flow: Optical flow estimation by global optimization over regular grids. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 4706−4714 [11] Dosovitskiy A, Fischer P, Ilg E, Häusser P, Hazirbas C, Golkov V. FlowNet: Learning optical flow with convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Santiago, Chile: IEEE, 2015. 2758−2766 [12] Ranjan A, Black M J. Optical flow estimation using a spatial pyramid network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 2720−2729 [13] Amiaz T, Lubetzky E, Kiryati N. Coarse to over-fine optical flow estimation. Pattern Recognition, 2007, 40(9): 2496−2503 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2006.09.011 [14] Hur J, Roth S. Iterative residual refinement for joint optical flow and occlusion estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 5754−5763 [15] Tu Z G, Xie W, Zhang D J, Poppe R, Veltkamp R C, Li B X, et al. A survey of variational and CNN-based optical flow techniques. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 2019, 72: 9−24 doi: 10.1016/j.image.2018.12.002 [16] Zhang C X, Ge L Y, Chen Z, Li M, Liu W, Chen H. Refined TV-L1 optical flow estimation using joint filtering. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2020, 22(2): 349−364 doi: 10.1109/TMM.2019.2929934 [17] Dalca A V, Rakic M, Guttag J, Sabuncu M R. Learning conditional deformable templates with convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: Curran Associates Inc., 2019. Article No. 32 [18] Chen J, Lai J H, Cai Z M, Xie X H, Pan Z G. Optical flow estimation based on the frequency-domain regularization. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2021, 31(1): 217−230 doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2020.2974490 [19] Zhai M L, Xiang X Z, Lv N, Kong X D. Optical flow and scene flow estimation: A survey. Pattern Recognition, 2021, 114: Article No. 107861 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2021.107861 [20] Zach C, Pock T, Bischof H. A duality based approach for realtime TV-L1 optical flow. In: Proceedings of the 29th DAGM Symposium on Pattern Recognition. Heidelberg, Germany: Springer, 2007. 214−223 [21] Zhao S Y, Zhao L, Zhang Z X, Zhou E Y, Metaxas D. Global matching with overlapping attention for optical flow estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 17571−17580 [22] Li Z W, Liu F, Yang W J, Peng S H, Zhou J. A survey of convolutional neural networks: Analysis, applications, and prospects. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2022, 33(12): 6999−7019 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3084827 [23] Han J W, Yao X W, Cheng G, Feng X X, Xu D. P-CNN: Part-based convolutional neural networks for fine-grained visual categorization. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 44(2): 579−590 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2933510 [24] Ilg E, Mayer N, Saikia T, Keuper M, Dosovitskiy A, Brox T. FlowNet 2.0: Evolution of optical flow estimation with deep networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 1647−1655 [25] Sun D Q, Yang X D, Liu M Y, Kautz J. PWC-Net: CNNs for optical flow using pyramid, warping, and cost volume. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 8934−8943 [26] Wang Z G, Chen Z, Zhang C X, Zhou Z K, Chen H. LCIF-Net: Local criss-cross attention based optical flow method using multi-scale image features and feature pyramid. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 2023, 112: Article No. 116921 doi: 10.1016/j.image.2023.116921 [27] Teed Z, Deng J. RAFT: Recurrent all-pairs field transforms for optical flow. In: Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Glasgow, UK: Springer, 2020. 402−419 [28] Han K, Xiao A, Wu E H, Guo J Y, Xu C J, Wang Y H. Transformer in transformer. In: Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Montreal, Canada: NIPS, 2021.15908−15919 [29] Jiang S H, Campbell D, Lu Y, Li H D, Hartley R. Learning to estimate hidden motions with global motion aggregation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Montreal, Canada: 2021. 9752−9761 [30] Xu H F, Zhang J, Cai J F, Rezatofighi H, Tao D C. GMFlow: Learning optical flow via global matching. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 8111−8120 [31] Cao J M, Li Y Y, Sun M C, Chen Y, Lischinski D, Cohen-Or D, et al. DO-Conv: Depthwise over-parameterized convolutional layer. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2022, 31: 3726−3736 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2022.3175432 [32] Dong X Y, Bao J M, Chen D D, Zhang W M, Yu N H, Yuan L, et al. CSWin transformer: A general vision transformer backbone with cross-shaped windows. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 12114−12124 [33] Huang Z L, Wang X G, Huang L C, Huang C, Wei Y C, Liu W Y. CCNet: Criss-cross attention for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Seoul, Korea (South): IEEE, 2019. 603−612 [34] Butler D J, Wulff J, Stanley G B, Black M J. A naturalistic open source movie for optical flow evaluation. In: Proceedings of the 12th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Florence, Italy: Springer, 2012. 611−625 [35] Menze M, Geiger A. Object scene flow for autonomous vehicles. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Boston, USA: IEEE, 2015. 3061−3070 [36] Wannenwetsch A S, Roth S. Probabilistic pixel-adaptive refinement networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 11639−11648 [37] Hui T W, Tang X O, Loy C C. A lightweight optical flow CNN——Revisiting data fidelity and regularization. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2021, 43(8): 2555−2569 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2020.2976928 [38] Hofinger M, Bulò S R, Porzi L, Knapitsch A, Pock T, Kontschieder P. Improving optical flow on a pyramid level. In: Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Glasgow, UK: Springer, 2020. 770−786 [39] Yu S H J, Zhang Y M, Wang C, Bai X, Zhang L, Hancock E R. HMFlow: Hybrid matching optical flow network for small and fast-moving objects. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR). Milan, Italy: IEEE, 2021. 1197−1204 [40] Chen J, Cai Z M, Lai J H, Xie X H. Efficient segmentation-based PatchMatch for large displacement optical flow estimation. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2019, 29(12): 3595−3607 doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2018.2885246 [41] Zhang C X, Zhou Z K, Chen Z, Hu W M, Li M, Jiang S F. Self-attention-based multiscale feature learning optical flow with occlusion feature map prediction. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2022, 24: 3340−3354 doi: 10.1109/TMM.2021.3096083 [42] Lu Z H, Xie H T, Liu C B, Zhang Y D. Bridging the gap between vision transformers and convolutional neural networks on small datasets. In: Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New Orleans, USA: 2022. 14663−14677 -




 下载:
下载: