Robust Weighted Heterogeneous Feature Ensemble Prediction Model of Temperature in Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Process
-
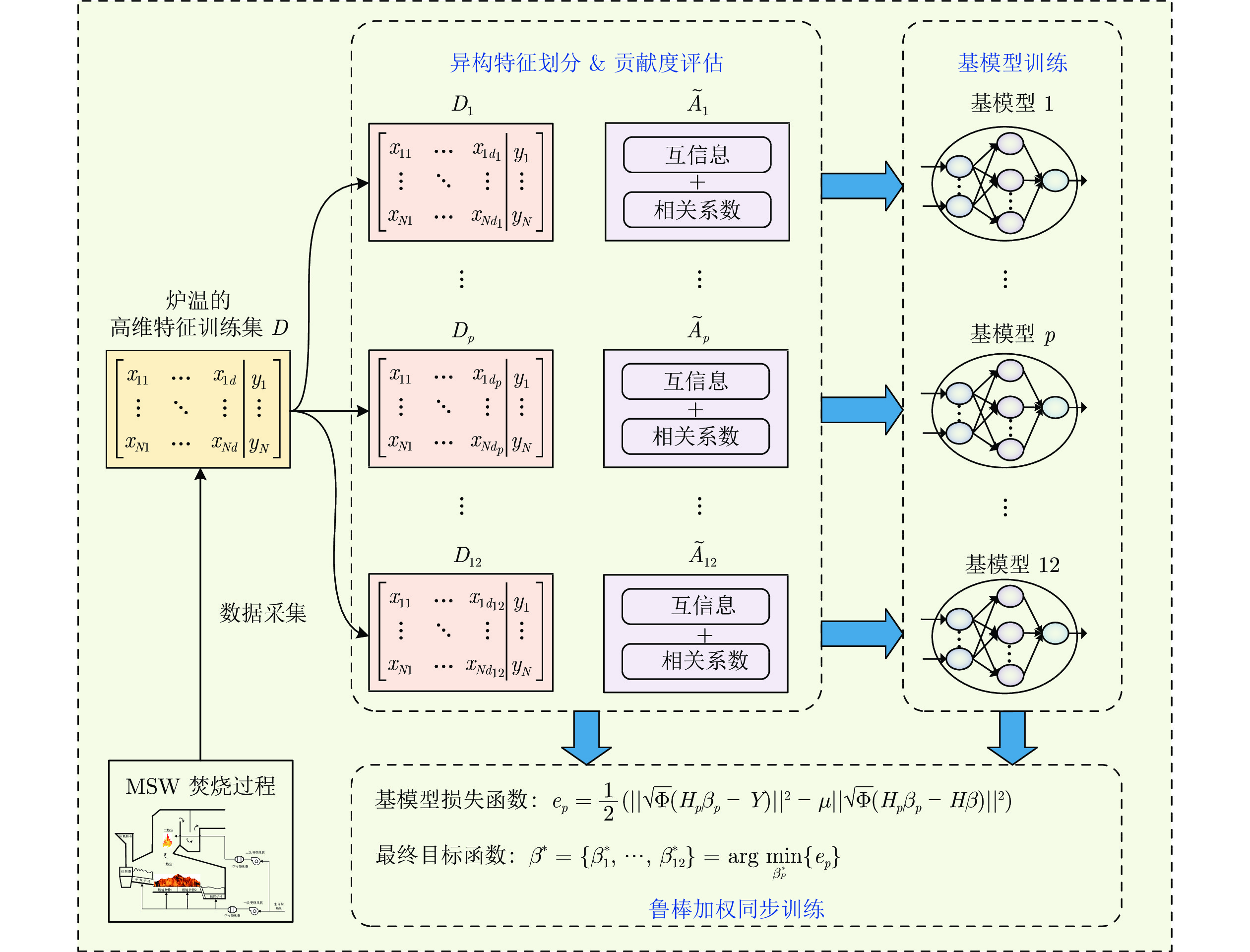
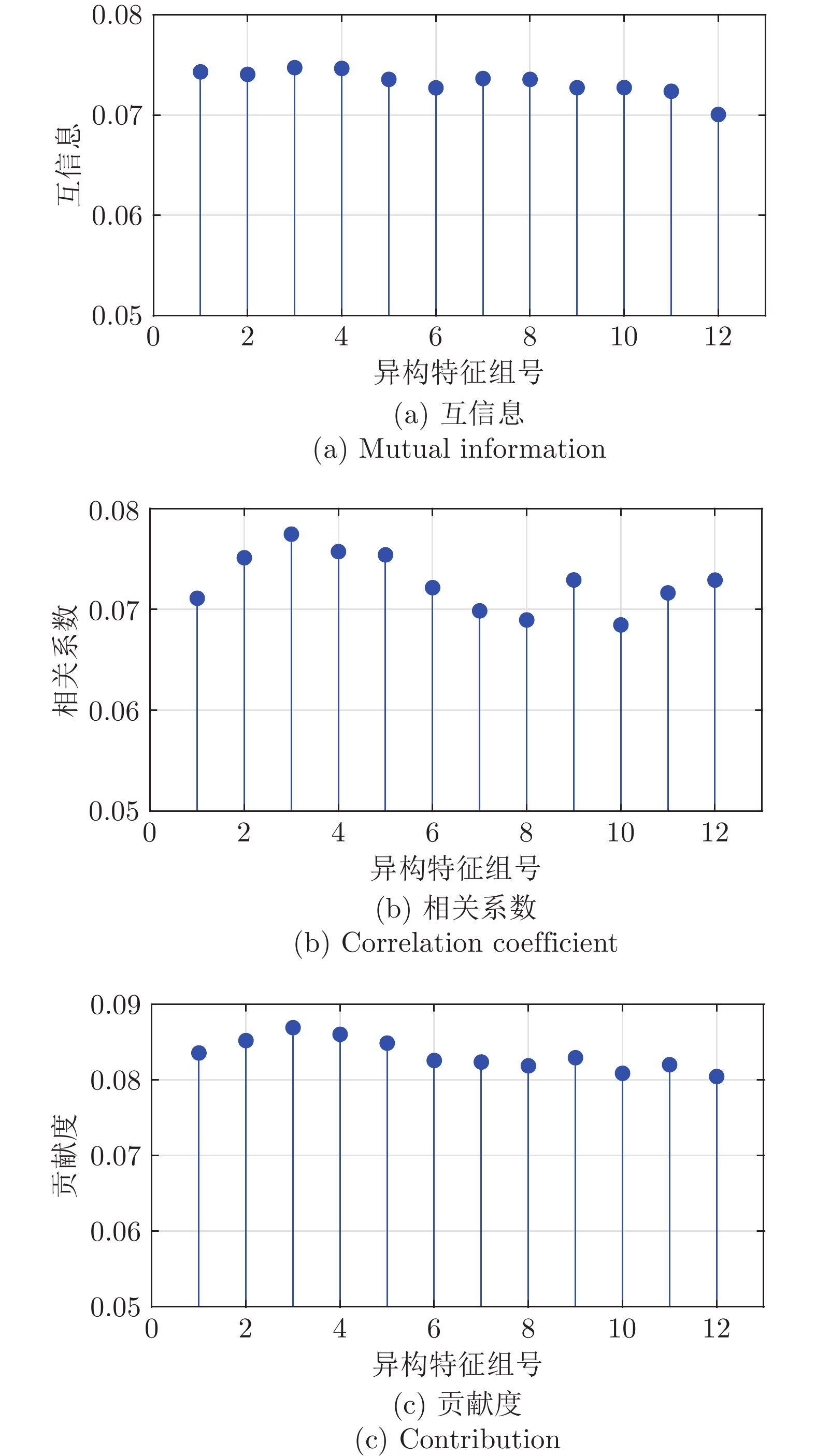
摘要: 针对城市固体废物(Municipal solid waste, MSW)焚烧过程, 数据具有异常值和特征变量维度高时, 炉温预测模型的准确性和泛化能力欠缺的挑战性问题, 提出一种鲁棒加权异构特征集成建模方法, 用于建立城市固体废物焚烧过程炉温预测模型. 首先, 依据焚烧过程机理将高维特征变量划分为异构特征集合, 并采用互信息和相关系数综合评估每组异构特征集合的贡献度; 其次, 采用基于混合t分布的鲁棒随机配置网络(Stochastic configuration network, SCN)构建基模型, 同时确定训练样本的惩罚权重; 最后, 设计一种鲁棒加权负相关学习(Negative correlation learning, NCL)策略, 实现基模型的鲁棒同步训练. 使用国内某城市固体废物焚烧厂的炉温历史数据, 对该方法进行测试. 测试结果表明, 该方法建立的炉温预测模型在准确性和泛化能力方面具有优势.Abstract: Aiming at the challenging problems of the deficient accuracy and generalization ability of the furnace temperature prediction model when the municipal solid waste (MSW) incineration process data has abnormal values and high dimensionality of feature variables, a robust weighted heterogeneous feature ensemble modeling method is proposed to establish the furnace temperature prediction model of the municipal solid waste incineration process. Firstly, the high dimensional feature variables are divided into heterogeneous feature sets according to the incineration process mechanism, and the contribution of each heterogeneous feature set is evaluated by the mutual information and correlation coefficient. Secondly, a robust stochastic configuration network (SCN) with the t mixture distribution is employed to construct base models, and penalty weights of training samples are determined at the same time. Finally, the robust weighted negative correlation learning (NCL) strategy is used to realize the synchronous training of base models. Comparative experiments are carried out using the historical furnace temperature data of a municipal solid waste incineration plant in China. The results show that the furnace temperature prediction model established by the proposed method performs more favourably in accuracy and generalization.
-
表 1 在不同异常值比例下, 各集成炉温预测模型的测试RMSE (均值$\pm$标准差) (℃)
Table 1 Test RMSE of each ensemble furnace temperature prediction model under different percentages of abnormal value (mean $\pm$ standard deviation) (℃)
异常值比例 (%) Mt-RSCNE DNNE SCNE MoGL-SCNE BESCN 0 16.3 $\pm$ 0.06 18.0 $\pm$ 0.24 16.4 $\pm$ 0.06 17.1 $\pm$ 0.12 17.1 $\pm$ 0.13 10 16.6 $\pm$ 0.06 18.1 $\pm$ 0.23 16.9 $\pm$ 0.11 17.2 $\pm$ 0.14 17.2 $\pm$ 0.20 20 16.6 $\pm$ 0.06 19.6 $\pm$ 0.26 18.0 $\pm$ 0.10 18.6 $\pm$ 0.12 17.9 $\pm$ 0.22 表 2 在不同异常值比例下, 各集成炉温预测模型的测试MAE (均值$\pm$标准差) (℃)
Table 2 Test MAE of each ensemble furnace temperature prediction model under different percentages of abnormal value (mean $\pm$ standard deviation) (℃)
异常值比例 (%) Mt-RSCNE DNNE SCNE MoGL-SCNE BESCN 0 12.9 $\pm$ 0.06 14.4 $\pm$ 0.23 13.0 $\pm$ 0.07 13.8 $\pm$ 0.12 13.8 $\pm$ 0.13 10 13.1 $\pm$ 0.06 14.3 $\pm$ 0.22 13.3 $\pm$ 0.10 13.5 $\pm$ 0.12 13.7 $\pm$ 0.15 20 13.1 $\pm$ 0.05 15.6 $\pm$ 0.21 14.4 $\pm$ 0.09 15.3 $\pm$ 0.13 14.6 $\pm$ 0.19 A1 炉温预测模型过程变量明细
A1 Process variable details of furnace temperature prediction model
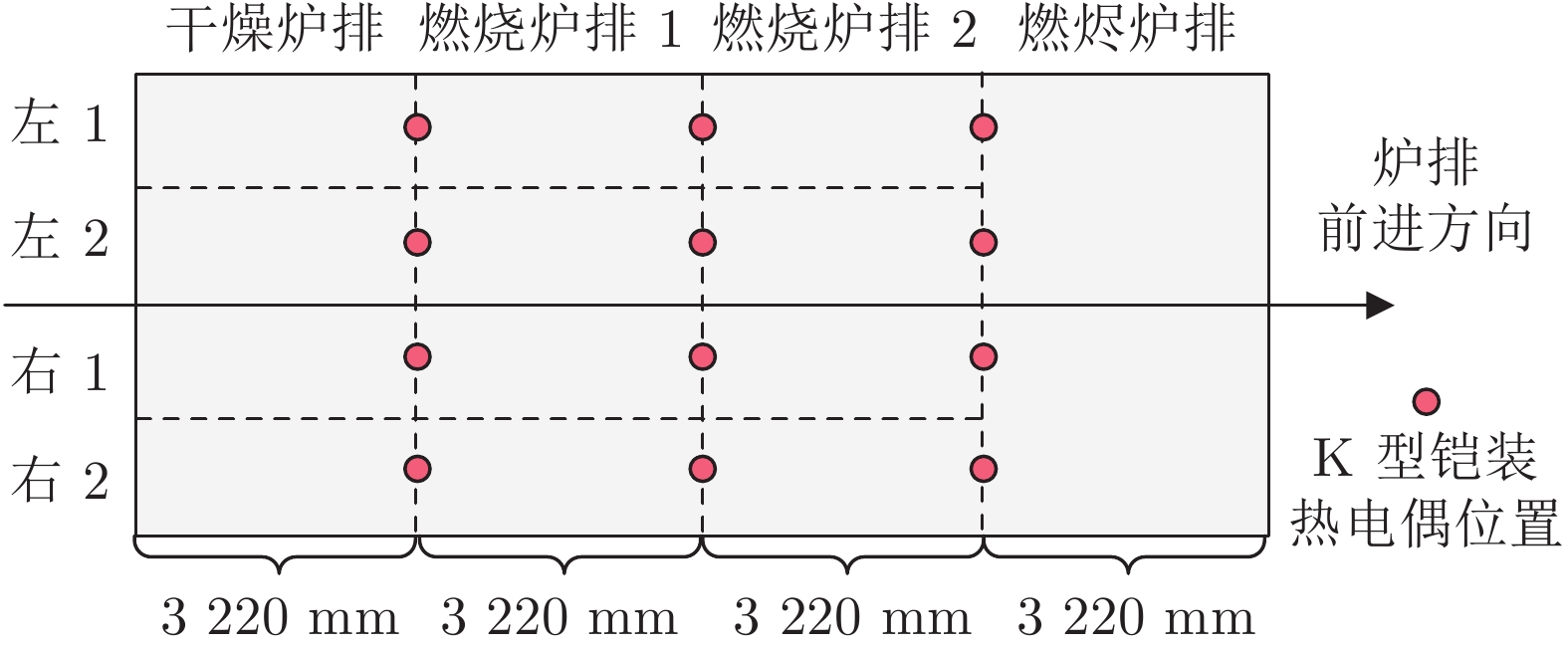
序号 名称 单位 1 干燥炉排左内侧速度 % 2 干燥炉排左外侧速度 % 3 干燥炉排右内侧速度 % 4 干燥炉排右外侧速度 % 5 燃烧炉排1左内侧速度 % 6 燃烧炉排1左外侧速度 % 7 燃烧炉排1右内侧速度 % 8 燃烧炉排1右外侧速度 % 9 燃烧炉排2左内侧速度 % 10 燃烧炉排2左外侧速度 % 11 燃烧炉排2右内侧速度 % 12 燃烧炉排2右外侧速度 % 13 干燥炉排左1空气流量 ${\rm {km^3N/h} }$ 14 干燥炉排右1空气流量 ${\rm {km^3N/h} }$ 15 干燥炉排左2空气流量 ${\rm {km^3N/h} }$ 16 干燥炉排右2空气流量 ${\rm {km^3N/h} }$ 17 燃烧段炉排左1-1段空气流量 ${\rm {km^3N/h} }$ 18 燃烧段炉排右1-1段空气流量 ${\rm {km^3N/h} }$ 19 燃烧段炉排左1-2段空气流量 ${\rm {km^3N/h} }$ 20 燃烧段炉排右1-2段空气流量 ${\rm {km^3N/h} }$ 21 燃烧段炉排左2-1段空气流量 ${\rm {km^3N/h} }$ 22 燃烧段炉排右2-1段空气流量 ${\rm {km^3N/h} }$ 23 燃烧段炉排左2-2段空气流量 ${\rm {km^3N/h} }$ 24 燃烧段炉排右2-2段空气流量 ${\rm {km^3N/h} }$ 25 二次风流量 ${\rm {km^3N/h} }$ 26 一次风机出口空气压力 kPa 27 干燥段炉排左内侧温度 ℃ 28 干燥段炉排左外侧温度 ℃ 29 干燥段炉排右内侧温度 ℃ 30 干燥段炉排右外侧温度 ℃ 31 燃烧段炉排1左内侧温度 ℃ 32 燃烧段炉排1左外侧温度 ℃ 33 燃烧段炉排1右内侧温度 ℃ 34 燃烧段炉排1右外侧温度 ℃ 35 燃烧段炉排2左内侧温度 ℃ 36 燃烧段炉排2左外侧温度 ℃ 37 燃烧段炉排2右内侧温度 ℃ 38 燃烧段炉排2右外侧温度 ℃ 39 干燥段炉排进口空气温度 ℃ 40 燃烧段炉排进口空气温度 ℃ 41 一次风加热器出口空气温度 ℃ 42 炉温(当前值) ℃ 43 炉温(预测值) ℃ -
[1] Zhao X G, Jiang G W, Li A, Li Y. Technology, cost, a performance of waste-to-energy incineration industry in China. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2016, 55(3): 115-130 [2] Cheng H F, Hu Y A. Municipal solid waste (MSW) as a renewable source of energy: Current and future practices in China. Bioresource Technology, 2010, 101(11): 3816-3824 doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2010.01.040 [3] Nzihou A, Themelis N J, Kemiha M, Benhamou Y. Dioxin emissions from municipal solid waste incinerators (MSWIs) in France. Waste Management, 2012, 32(12): 2273-2277 doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2012.06.016 [4] Ding H X, Tang J, Qiao J F. Dynamic modeling of multi-input and multi-output controlled object for municipal solid waste incineration process. Applied Energy, 2023, 339(1): Article No. 120982 [5] Alobaid F, Al-Maliki W A K, Lanz T, Haaf M, Brachthauser A, Epple B, et al. Dynamic simulation of a municipal solid waste incinerator. Energy, 2018, 149(4): 230-249 [6] He H J, Meng X, Tang J, Qiao J F. A novel self-organizing TS fuzzy neural network for furnace temperature prediction in MSWI process. Neural computing and applications, 2022, 34(12): 9759-9776 [7] 丁海旭, 汤健, 夏恒, 乔俊飞. 基于TS-FNN的城市固废焚烧过程MIMO被控对象建模. 控制理论与应用, 2022, 39(8): 1529-1540 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2022.10524Ding Hai-Xu, Tang Jian, Xia Heng, Qiao Jun-Fei. Modeling of MIMO controlled object in municipal solid waste incineration process based on TS-FNN. Control Theory & Applications, 2022, 39(8): 1529-1540 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2022.10524 [8] Scardapane S, Wang D H. Randomness in neural networks: an overview. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 2017, 7(2): 1-18 [9] Wang D H, Li M. Stochastic configuration networks: fundamentals and algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2017, 47(10): 3346-3479 [10] Lu J, Ding J L. A novel stochastic configuration network with iterative learning using privileged information and its application. Information Sciences, 2022, 613(10): 953-965 [11] Wang Q, Hong Q, Wu S, Dai W. Multitarget stochastic configuration network and applications. IEEE Transactions on Artificial Intelligence, 2023, 4(2): 338-348 doi: 10.1109/TAI.2022.3162570 [12] 代伟, 李德鹏, 杨春雨, 马小平. 一种随机配置网络的模型与数据混合并行学习方法. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(10): 2427-2437 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190411Dai Wei, Li Da-Peng, Yang Chun-Yu, Ma Xiao-Ping. A model and data hybrid parallel learning method for stochastic configuration networks. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(10): 2427-2437 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190411 [13] Wang D H, Li M. Robust stochastic configuration networks with kernel density estimation for uncertain data regression. Information Sciences, 2017, 412(10): 210-222 [14] Li M, Huang C Q, Wang D H. Robust stochastic configuration networks with maximum correntropy criterion for uncertain data regression. Information Sciences, 2019, 473(4): 73-86 [15] Lu J, Ding J L. Mixed-distribution based robust stochastic configuration networks for prediction interval construction. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2020, 16(8): 5099-5109 doi: 10.1109/TII.2019.2954351 [16] Yan A J, Guo J C, Wang D H. Robust stochastic configuration networks based on Student’s-t mixture distribution. Information Sciences, 2022, 607(8): 493-505 [17] Zaman E A K, Mohamed A, Ahmad A. Feature selection for online streaming high-dimensional data: A state-of-the-art review. Applied Soft Computing, 2022, 127(9): Article No. 109355 [18] Chandrashekar G, Sahin F. A survey on feature selection methods. Computers and Electrical Engineering, 2014, 40(12): 16-28 [19] Wang D H, Cui C H. Stochastic configuration networks ensemble with heterogeneous features for large-scale data analytics. Information Sciences, 2017, 417(31): 55-71 [20] Liu Y, Yao X. Simultaneous training of negatively correlated neural networks in an ensemble. IEEE Transactions On Systems, Man, and Cybernetics—Part B: Cybernetics, 1999, 29(6): 716-725 doi: 10.1109/3477.809027 [21] Zhuang J B, Tang J, Aljerf L. Comprehensive review on mechanism analysis and numerical simulation of municipal solid waste incineration process based on mechanical grate. Fuel, 2022, 320(4): 1-20 [22] Xia Z, Shan P, Chen C, Du H, Huang J, Bai L. A two-fluid model simulation of an industrial moving grate waste incinerator. Waste Management, 2020, 104(1): 183-191 [23] Alhamdoosh M, Wang D H. Fast decorrelated neural network ensembles with random weightInformation Sciences, 2014, 264(11): 104-117 [24] Lu J, Ding J L, Dai X, Chai T Y. Ensemble stochastic configuration networks for estimating prediction intervals: A simultaneous robust training algorithm and its application.IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2020, 31(12): 5426-5440 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2020.2967816 -





 下载:
下载: