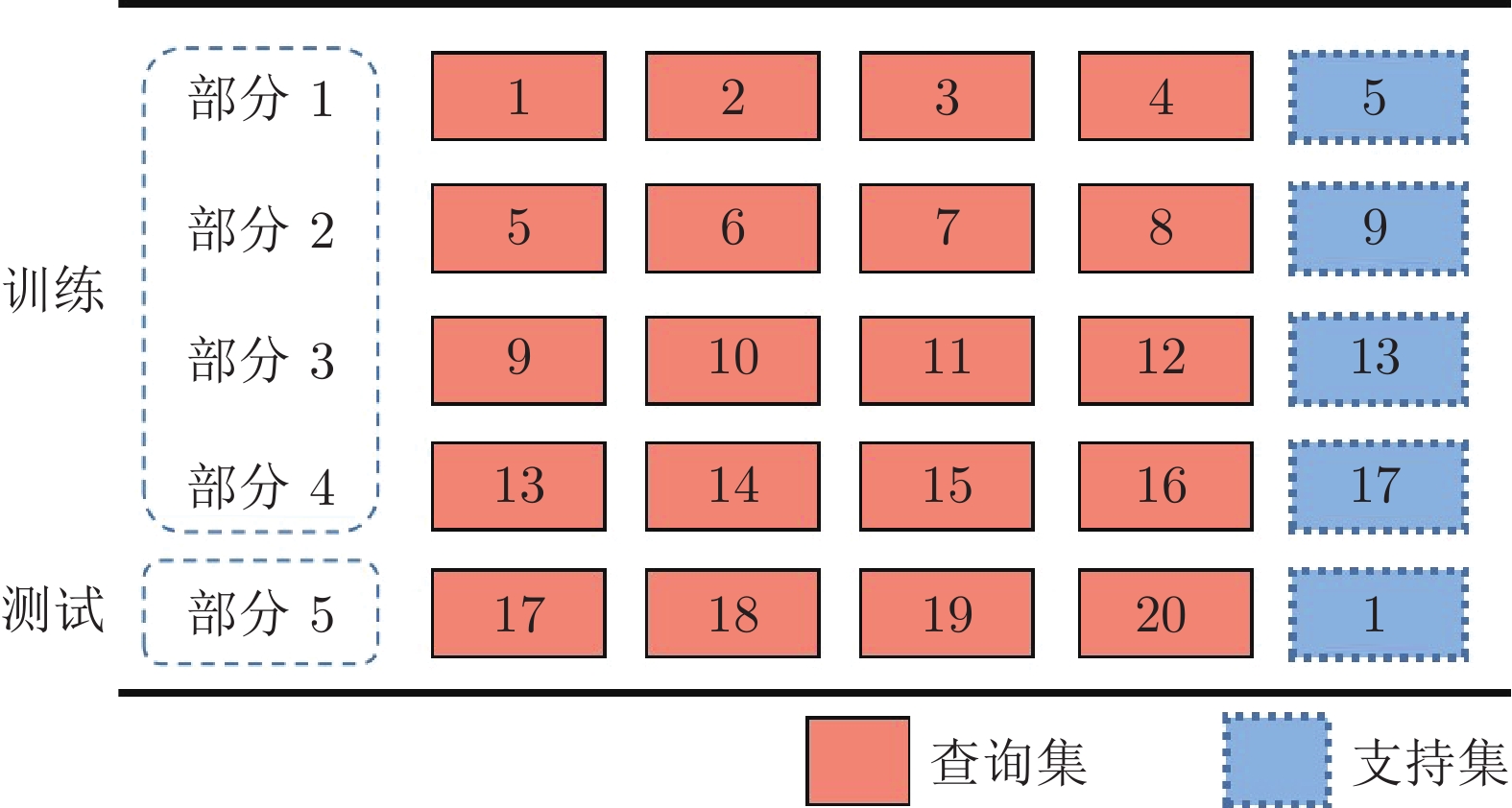
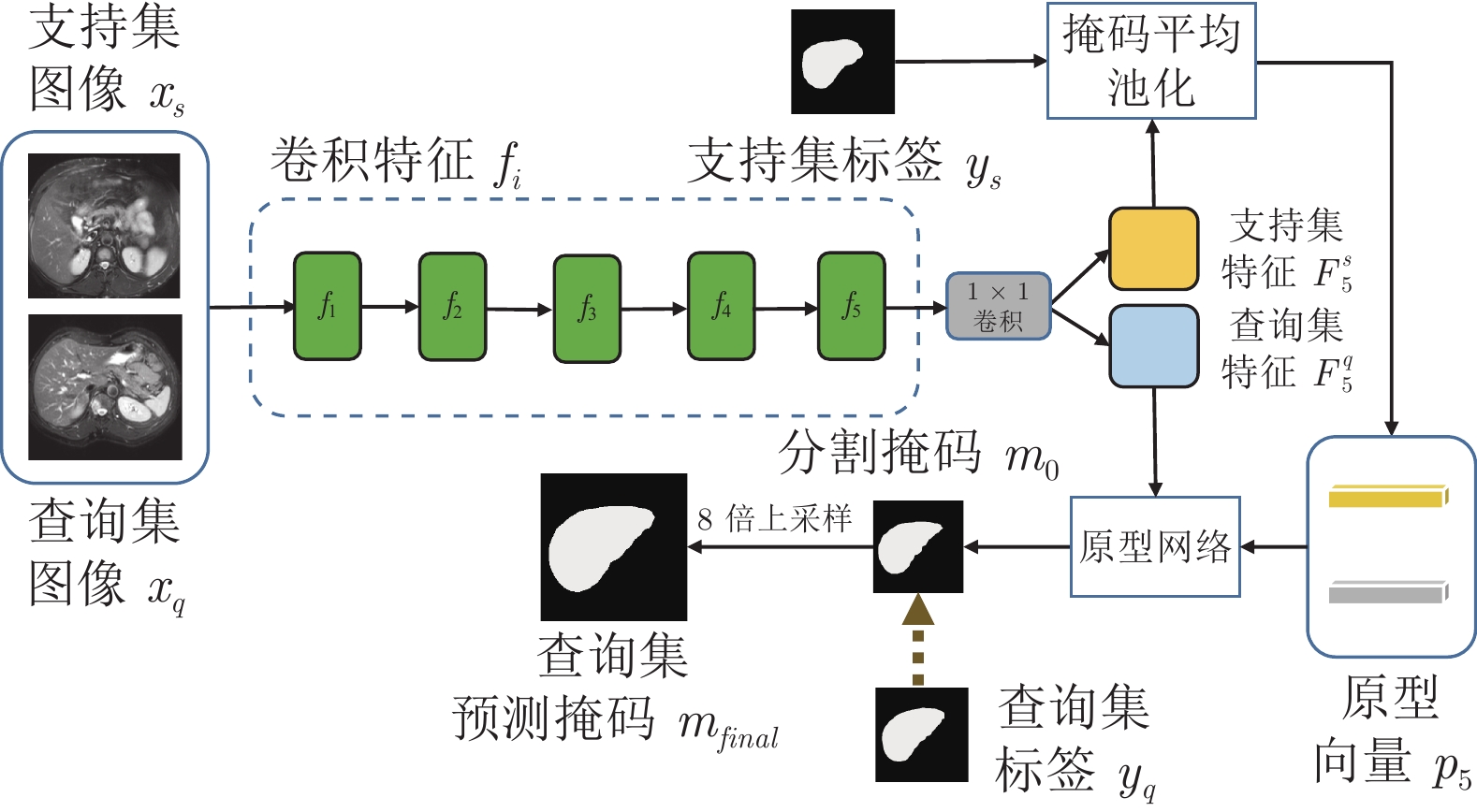
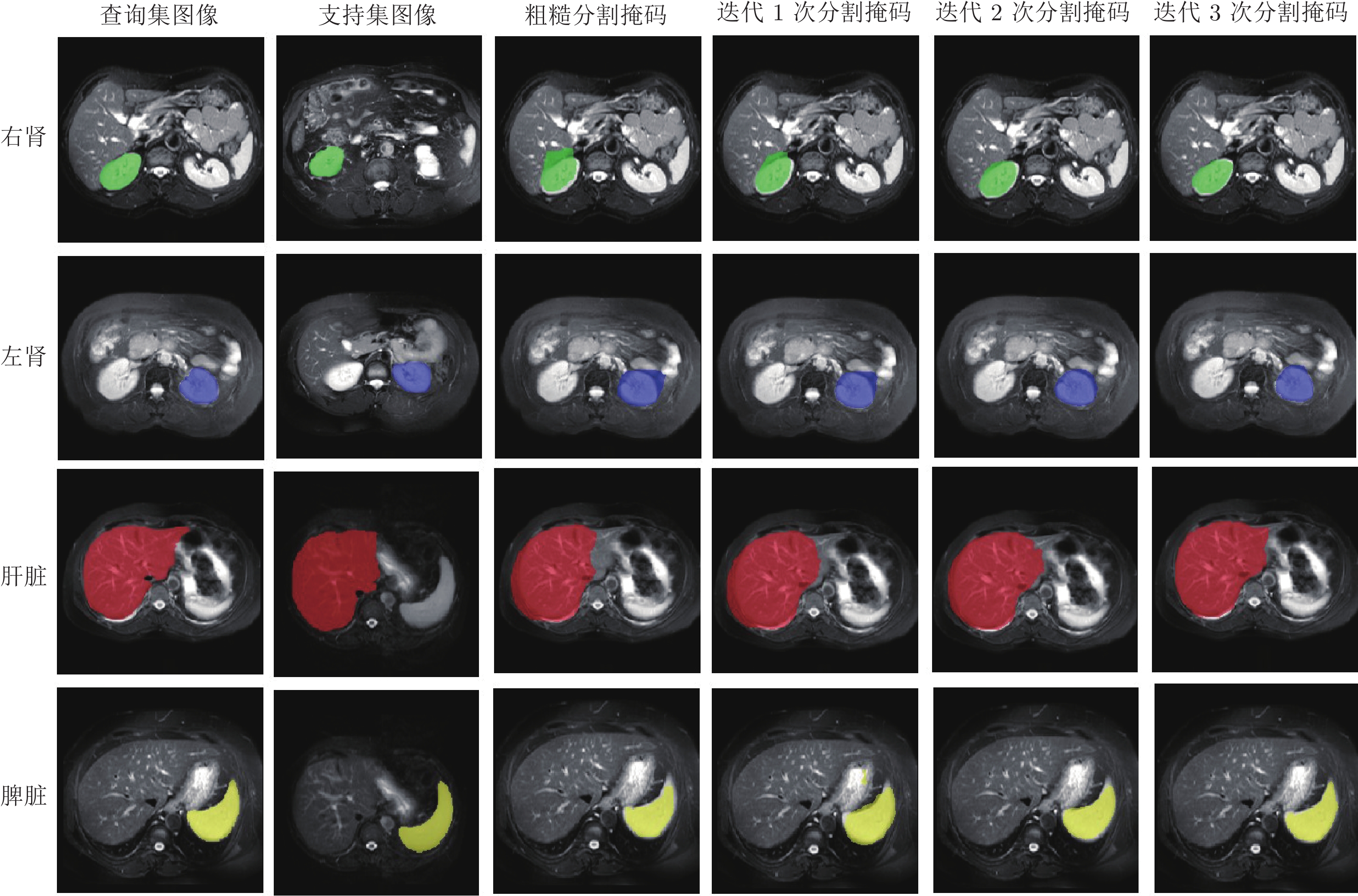
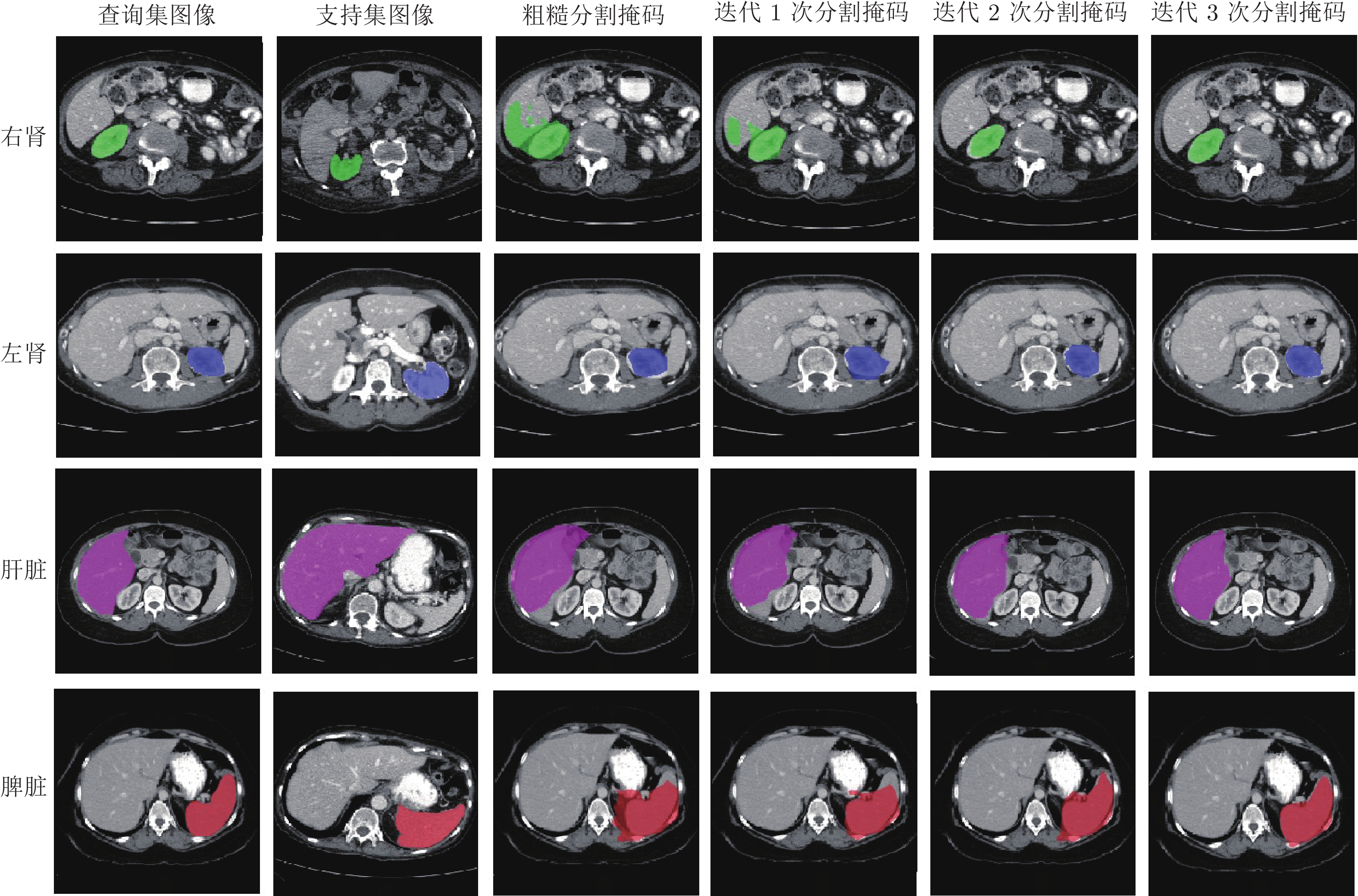
-
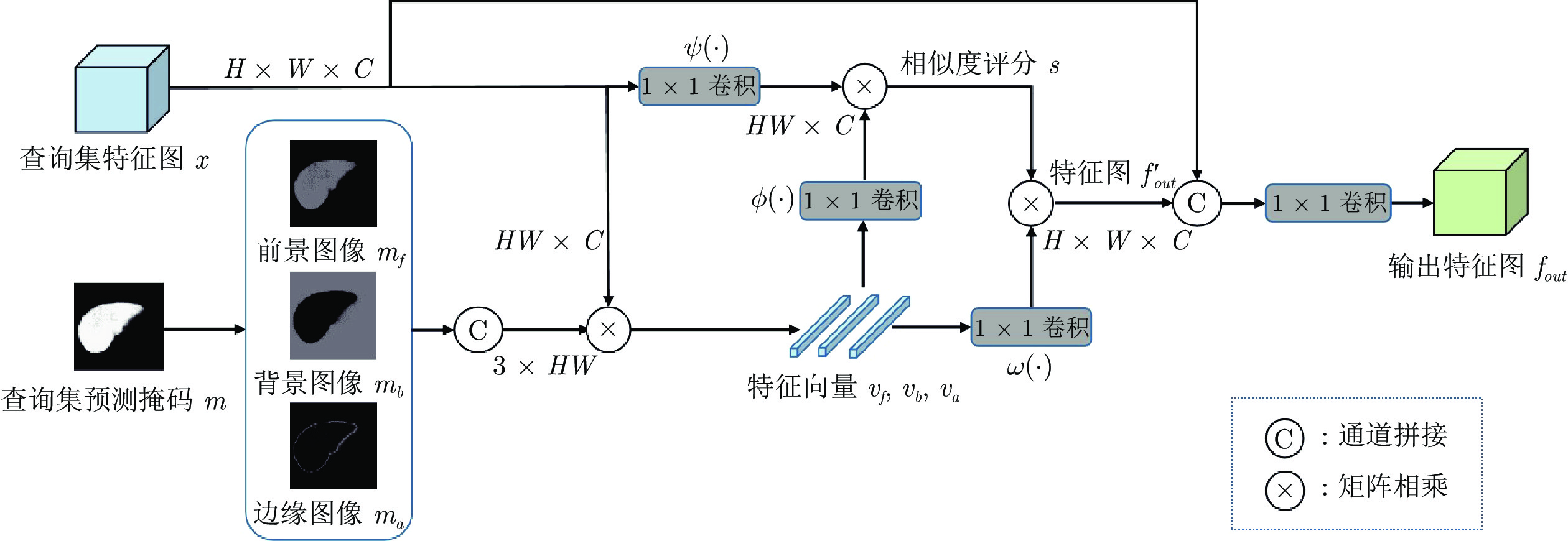
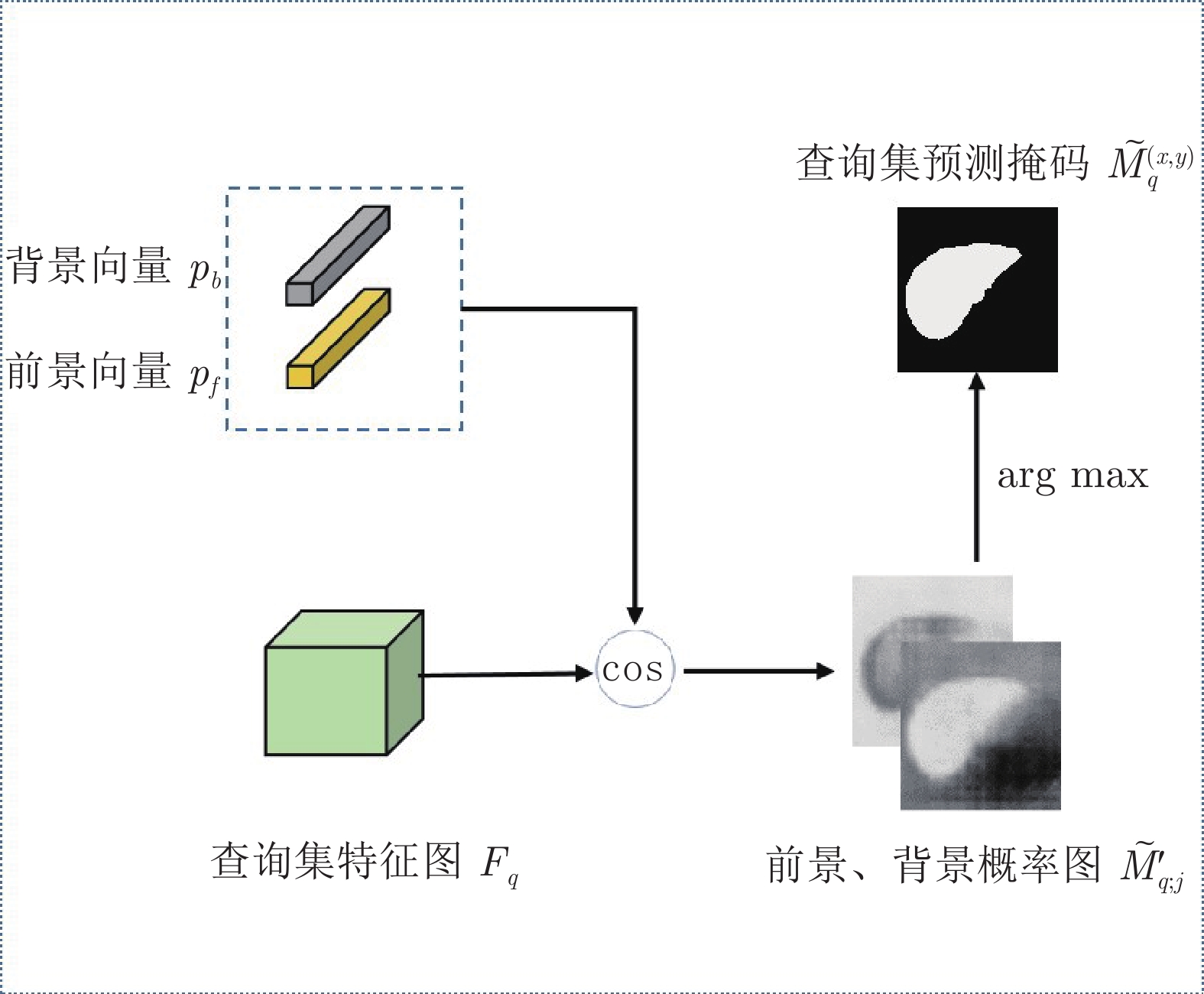
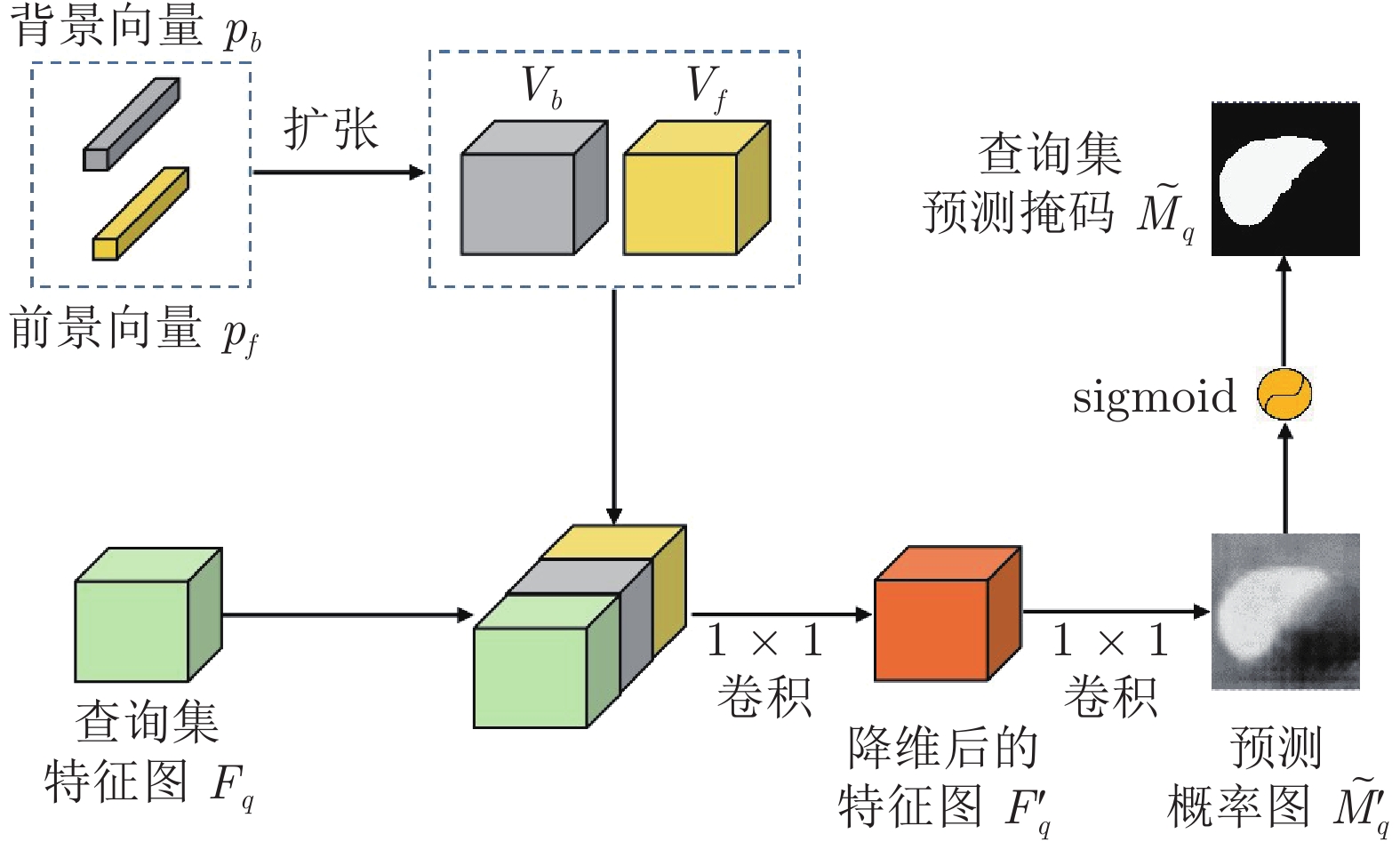
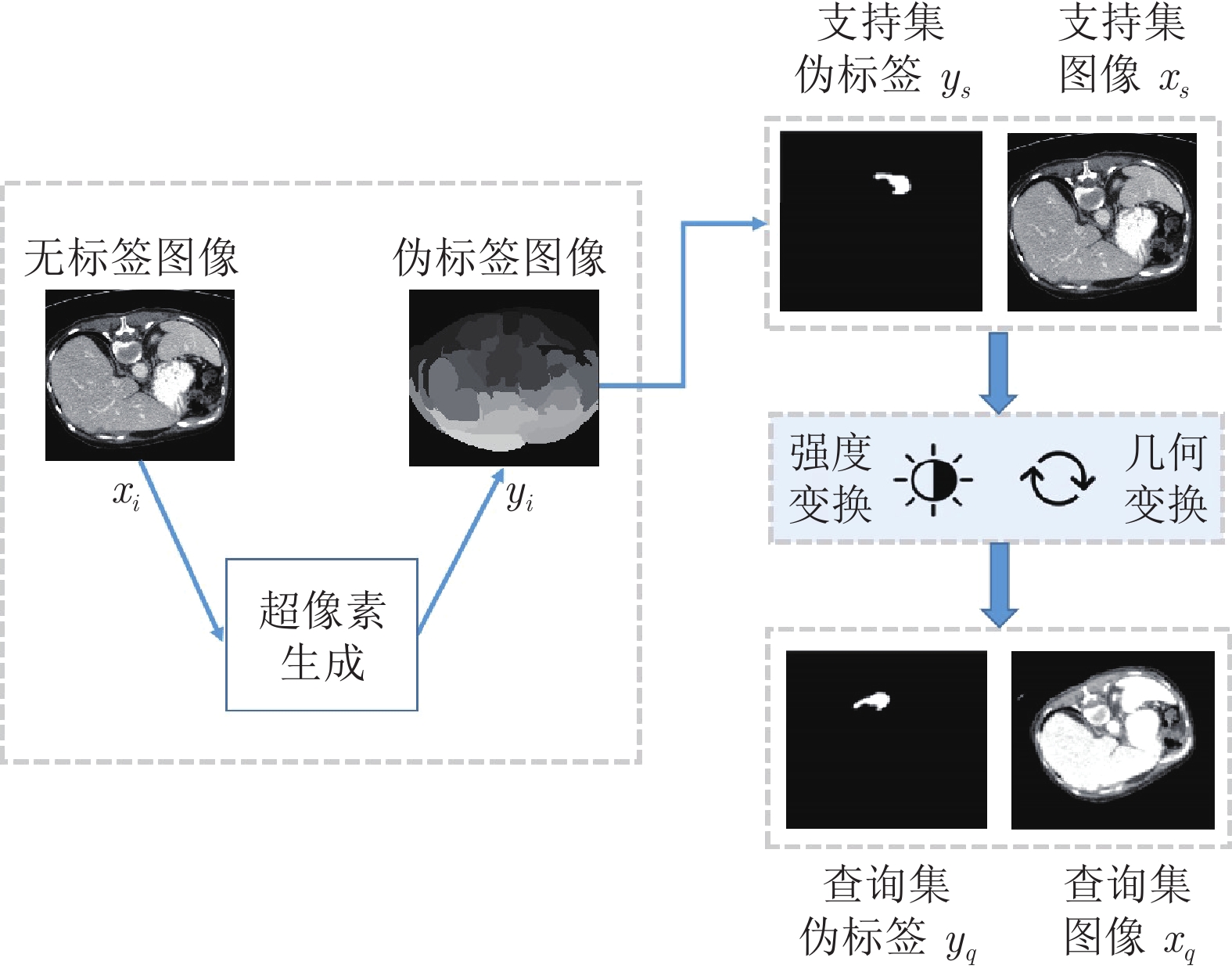
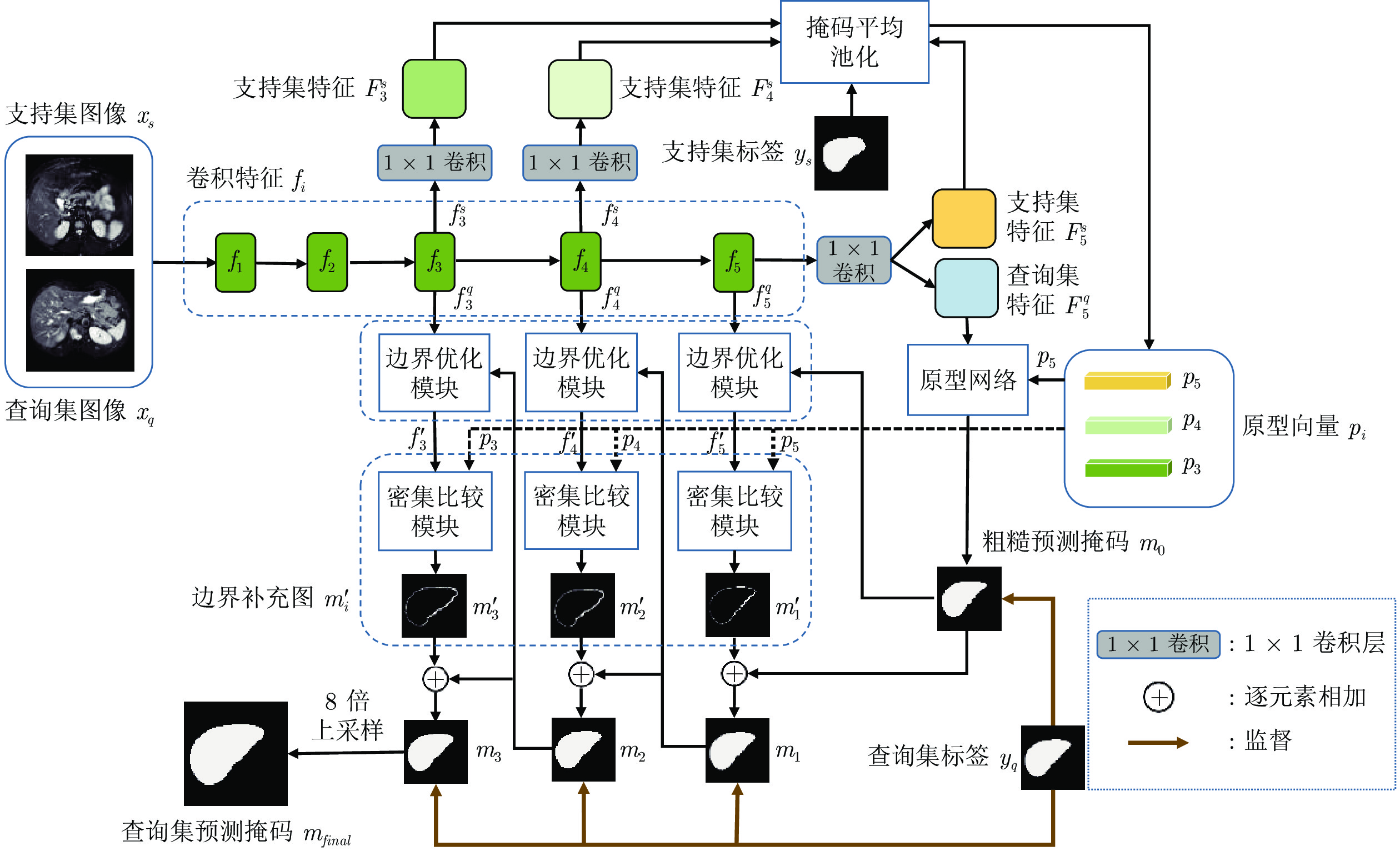
摘要: 精准的医学图像自动分割是临床影像学诊断和影像三维重建的重要基础. 但医学图像数据的目标对象间对比度差异小、受器官运动影响大, 加之标注样本规模小, 因此在小样本下建立高性能的医学分割模型仍是目前的难点问题. 针对主流原型学习小样本分割网络对医学图像边界分割性能差的问题, 提出一种迭代边界优化的小样本分割网络(Iterative boundary refinement based few-shot segmentation network, IBR-FSS-Net). 以双分支原型学习的小样本分割框架为基础, 引入类别注意力机制和密集比较模块(Dense comparison module, DCM), 对粗分割掩码进行迭代优化, 引导分割模型在多次迭代学习过程中关注边界, 从而提升边界分割精度. 为进一步克服医学图像训练样本少且多样性不足问题, 使用超像素方法生成伪标签, 扩充训练数据以提升模型泛化性. 在ABD-MR和ABD-CT医学图像分割公共数据集上进行实验, 与现有多种先进的医学图像小样本分割方法进行对比分析和消融实验. 实验结果表明, 该方法有效提升了未见医学类别的分割性能.Abstract: Accurate automatic segmentation of medical images is an important basis for clinical imaging diagnosis and 3D image reconstruction. However, medical image data has small contrast differences between target objects, is greatly affected by organ movement, and the scale of labeled samples is small. Therefore, it is still a difficult problem to establish a high-performance medical segmentation model under few samples. In view of the poor performance of the mainstream prototype learning few-shot segmentation network for medical image boundary segmentation, an iterative boundary refinement based few-shot segmentation network (IBR-FSS-Net) is proposed. Based on the few-shot segmentation framework of dual-branch prototype learning, the category attention mechanism and dense comparison module (DCM) are introduced to iteratively refine the coarse segmentation mask, and guide the segmentation model to focus on the boundary during multiple iterative learning processes, thereby improving the boundary segmentation accuracy. In order to further overcome the problem of few training samples and insufficient diversity of medical images, this paper uses the super-pixel method to generate pseudo-labels and expand the training data to improve the generalization of the model. Experiments on the mainstream ABD-MR and ABD-CT medical image segmentation public datasets are done, we conduct extensive comparative analysis and ablation experiments with various existing advanced medical image few-shot segmentation methods. The results show that our method effectively improves the segmentation performance of unseen medical categories.1) 本文责任编委 XXX Recommended by Associate Editor BIAN Wei
-
表 1 ABD-CT和ABD-MR数据集上, 不同方法的Dice系数值 (%)
Table 1 Dice coefficient values with different models on ABD-CT and ABD-MR datasets (%)
方法 ABD-CT ABD-MR 脾脏 左肾 右肾 肝脏 平均值 脾脏 左肾 右肾 肝脏 平均值 SE-Net 0.23 32.83 14.34 0.27 11.91 51.80 62.11 61.32 27.43 50.66 PANet 25.59 32.34 17.37 38.42 29.42 50.90 53.45 38.64 42.26 46.33 SSL-ALPNet 60.25 63.34 54.82 73.65 63.02 67.02 73.63 78.39 73.05 73.02 GCN-DE 56.53 68.13 75.50 46.77 61.73 60.63 76.07 83.03 49.47 67.30 RP-Net 69.85 70.48 70.00 79.62 72.48 76.35 81.40 85.78 73.51 79.26 ADNet — — — — — 75.92 75.28 83.28 80.81 78.82 PoissonSeg 52.33 50.11 47.02 58.74 52.05 52.85 50.58 53.57 61.03 54.51 AAS-DCL 66.36 64.71 69.95 71.61 68.16 74.86 76.90 83.75 69.94 76.36 IBR-FSS-Net 71.73 73.78 72.02 78.13 73.92 75.12 82.19 85.64 75.89 79.71 表 2 不同组件组合方式的Dice系数值 (%)
Table 2 Dice coefficient values with different component combinations (%)
组合方式 脾脏 左肾 右肾 肝脏 平均值 Baseline 62.33 63.65 66.87 64.18 64.26 Baseline+Concat 60.62 65.55 68.53 66.56 65.32 Baseline+BRM 66.63 72.10 74.83 69.17 70.68 Baseline+3Concat 61.20 68.72 70.38 66.95 66.81 Baseline+3BRM 75.12 82.19 85.64 75.89 79.71 表 3 不同边界优化模块数量的Dice系数值 (%)
Table 3 Dice coefficient values with different number of boundary refinement modules (%)
组件 脾脏 左肾 右肾 肝脏 平均值 Baseline 62.33 63.65 66.87 64.18 64.26 Baseline+BRM 66.63 72.10 74.83 69.17 70.68 Baseline+2BRM 69.88 79.98 82.12 73.56 76.39 Baseline+3BRM 75.12 82.19 85.64 75.89 79.71 Baseline+4BRM 68.57 77.23 78.82 69.60 73.56 Baseline+5BRM 64.13 70.55 72.69 66.42 68.45 表 4 不同特征提取网络的Dice系数值 (%)
Table 4 Dice coefficient values with different feature extraction networks (%)
骨干网络 脾脏 左肾 右肾 肝脏 平均值 VGG-16 52.09 63.83 64.48 57.88 59.57 U-Net 69.66 78.94 80.46 72.15 75.30 Res U-Net 71.82 78.24 81.10 73.41 76.14 Attention U-Net 73.96 79.14 83.51 73.60 77.55 ResNet50 71.23 78.19 82.57 73.68 76.42 ResNet101 75.12 82.19 85.64 75.89 79.71 表 5 不同度量网络组合方式的Dice系数值 (%)
Table 5 Dice coefficient values with different combination of metric networks (%)
度量网络组合方式 脾脏 左肾 右肾 肝脏 平均值 Prototypical-Net 70.92 80.61 83.70 74.48 77.43 DCM 71.53 81.36 83.44 74.81 77.79 DCM+Prototypical-Net 72.97 81.49 83.68 74.83 78.24 Prototypical-Net+DCM 75.12 82.19 85.64 75.89 79.71 表 6 ABD-CT和ABD-MR数据集上, 与其他少标注样本下医学图像分割方法对比的Dice系数值 (%)
Table 6 Dice coefficient values with other medical segmentation models in case of less annotated sample on ABD-CT and ABD-MR datasets (%)
方法(比例) ABD-CT ABD-MR 脾脏 左肾 右肾 肝脏 平均值 脾脏 左肾 右肾 肝脏 平均值 MagicNet (30%) 91.42 86.19 84.64 93.89 89.04 — — — — — CVCL (部分) 95.40 94.60 94.60 96.70 95.33 — — — — — C-CAM (0%) — — — — — 74.16 81.00 84.75 72.68 78.15 IBR-FSS-Net (5%) 71.73 73.78 72.02 78.13 73.92 75.12 82.19 85.64 75.89 79.71 -
[1] Zhang B, Zhang L, Zhang L, Karray F. Retinal vessel extraction by matched filter with first-order derivative of Gaussian. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 2010, 40(4): 438−445 doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2010.02.008 [2] Vinyals O, Blundell C, Lillicrap T, Wierstra D. Matching networks for one shot learning. In: Proceedings of the PMLR on Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Barcelona, Spain: PMLR, 2016. 3637–3645 [3] Finn C, Abbeel P, Levine S. Model-agnostic meta-learning for fast adaptation of deep networks. In: Proceedings of the PMLR on International Conference on Machine Learning. Sydney, Australia: PMLR, 2017. 1126−1135 [4] Sung F, Yang Y, Zhang L, Tao X, Philip H S T, Timothy M. Learning to compare: Relation network for few-shot learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE on Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 1199− 1208 [5] Li G, Jampani V, Sevilla-Lara L, Sun D, Kim J, Kim J. Adaptive prototype learning and allocation for few-shot segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE on Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Virtual Event: IEEE, 2021. 8334−8343 [6] Yu Q, Dang K, Tajbakhsh N, Terzopoulos D, Ding X. A location-sensitive local prototype network for few-shot medical image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE on Image Processing. Anchorage, USA: IEEE, 2021. 262−266 [7] 孙君梅, 葛青青, 李秀梅, 赵宝奇. 具有边界增强功能的医学图像分割网络. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(5): 1643−1652 doi: 10.11999/JEIT210784Sun Jun-Mei, Ge Qing-Qing, Li Xiu-Mei, Zhao Bao-Qi. A medical image segmentation network with boundary enhancement. Journal of Electronics, 2022, 44(5): 1643−1652 doi: 10.11999/JEIT210784 [8] Yuan Y, Chen X, Wang J. Object-contextual representations for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Virtual Event: Springer, 2020. 23−28, 173−190 [9] Kim T, Lee H, Kim D. UACANet: Uncertainty augmented context attention for polyp segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on ACM International Conference on Multimedia. Chengdu, China: ACM, 2021. 2167−2175 [10] Zhang C, Lin G, Liu F, Rui Y, She C. CANet: Class-agnostic segmentation networks with iterative refinement and attentive few-shot learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 5217−5226 [11] Ouyang C, Biffi C, Chen C, Kart T, Qiu H, Rueckert D. Self-supervision with super-pixels: Training few-shot medical image segmentation without annotation. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Virtual Event: Springer, 2020. 762−780 [12] Tang H, Liu X, Sun S, Yan X, Xie X. Recurrent mask refinement for few-shot medical image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE on International Conference on Computer Vision. Seoul, South Korea: IEEE, 2021. 3918−3928 [13] Fan D P, Ji G P, Zhou T, Chen G, Fu H, Shen J, et al. PRANet: Parallel reverse attention network for polyp segmentation. In: Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention. Lima, Peru: Springer, 2020. 263− 273 [14] Shaban A, Bansal S, Liu Z, Essa I, Byron B. One-shot learning for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference. London, UK: BMVA, 2017. 1−12 [15] Wang K, Liew J H, Zou Y, Zhou D, Feng J. PANet: Few-shot image semantic segmentation with prototype alignment. In: Proceedings of the IEEE on International Conference on Computer Vision. Seoul, South Korea: IEEE, 2019. 9197−9206 [16] Tian Z, Zhao H, Shu M, Yang Z, Li R, Jia J. Prior guided feature enrichment network for few-shot segmentation. Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 44(2): 1050−1065 [17] Zhang G, Kang G, Yang Y, Wei Y. Few-shot segmentation via cycle-consistent transformer. In: Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Montreal, Canada: NeurIPS, 2021. 21984−21996 [18] Roy A G, Siddiqui S, Polsterl S, Navab N, Wachinger C. “Squeeze & Excite” guided few-shot segmentation of volumetric images. Medical Image Analysis, 2020, 59: Article No. 101587 [19] Sun L, Li C, Ding X, Huang Y, Chen Z, Wang G, et al. Few-shot medical image segmentation using a global correlation network with discriminative embedding. Computers in Biology an Medicine, 2022, 140: Article No. 105067 [20] Tang H, Liu X, Sun S, Yan X, Xie X. Recurrent mask refinement for few-shot medical image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE on International Conference on Computer Vision. Montreal, Canada: IEEE, 2021. 3918−3928 [21] Hansen S, Gautam S, Jenssen R, Kampffmeyer M. Anomaly detection-inspired few-shot medical image segmentation through self-supervision with super-voxels. Medical Image Analysis, 2022, 78: Article No. 102385 [22] Shen X, Zhang G, Lai H, Luo J, Lu J. PoissonSeg: Semi-supervised few-shot medical image segmentation via Poisson learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine. Houston, USA: IEEE, 2021. 1513− 1518 [23] Wu H, Xiao F, Liang C. Dual contrastive learning with anatomical auxiliary supervision for few-shot medical image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Tel Aviv, Israel: Springer, 2022. 417−434 [24] Chen D, Bai Y, Shen W, Li Q, Yu L, Wang Y. MagicNet: Semi-supervised multi-organ segmen-tation via magic-cube partition and recovery. In: Proceedings of the IEEE on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Oxford, UK: IEEE, 2023. 23869−23878 [25] Liu P, Zheng G. Context-aware voxel-wise contrastive learning for label efficient multi-organ segmentation. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Singapore: Springer, 2022. 653− 662 [26] Chen Z, Tian Z, Zhu J, Li C, Du S. C-CAM: Causal cam for weakly supervised semantic segmentation on medical image. In: Proceedings of the IEEE on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 11676−11685 [27] Chen S, Tan X, Wang B, Hu X. Reverse attention for salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 234−250 [28] 陈琼, 杨永, 黄田琳, 冯媛. 新型全向立体视觉系统设计. 数据与计算发展前沿, 2022, 3(6): 17−34Chen Qiong, Yang Yong, Huang Tian-Lin, Feng Yuan. A survey on few-shot image semantic segmentation. Frontiers of Data and Computing, 2022, 3(6): 17−34 [29] Snell J, Swersky K, Zemel R. Prototypical networks for few-shot learning. In: Proceedings of the Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach, USA: NeurIPS, 2017. 4080–4090 [30] Landman B, Xu Z, Igelsias J, Styner M, Langerak T, Klein A. Miccai multi-atlas labeling beyond the cranial vault-workshop and challenge. In: Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2015. 1–12 [31] Kavur A E, Gezer N S, Baris M, Aslan S, Conze P H, Groza V. Chaos challenge-combined (CT-MR) healthy abdominal organ segmentation. Medical Image Analysis, 2021, 69: Article No. 101950 [32] Irving B. MaskSLIC: Regional super-pixel generation with application to local pathology characterisation in medical images. In: Proceedings of the IEEE on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. Article No. 9518 [33] Lin T Y, Maire M, Belongie S, Hays J, Perona P, Ramanan D, et al. Microsoft COCO: Common objects in context. In: Proceed-ings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Zurich, Switzerland: Springer, 2014. 740−755 [34] Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations. San Diego, USA: ICLR, 2015. 1−14 [35] Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-assisted Intervention. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2015. 234−241 [36] Xiao X, Lian S, Luo Z, Li S. Weighted Res U-Net for high-quality retina vessel segmentation. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Information Technology in Medicine and Education. Hangzhou, China: IEEE, 2018. 327−331 [37] Oktay O, Schlemper J, Folgoc L L, Lee M, Heinrich M, Misawa K. Attention U-Net: Learning where to look for the pancreas. In: Proceedings of the IEEE on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. Atricle No. 3999 [38] Kervadec H, Bouchtiba J, Desrosiers C, Granger E, Dolz J, Ayed I B. Boundary loss for highly unbalanced segmentation. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Imaging With Deep Learning. Shanghai, China: PMLR, 2019. 285− 296 -




 下载:
下载: