Trajectory Planning for Overhead Crane With Double Spherical Pendulum and Varying Cable Length Effect
-
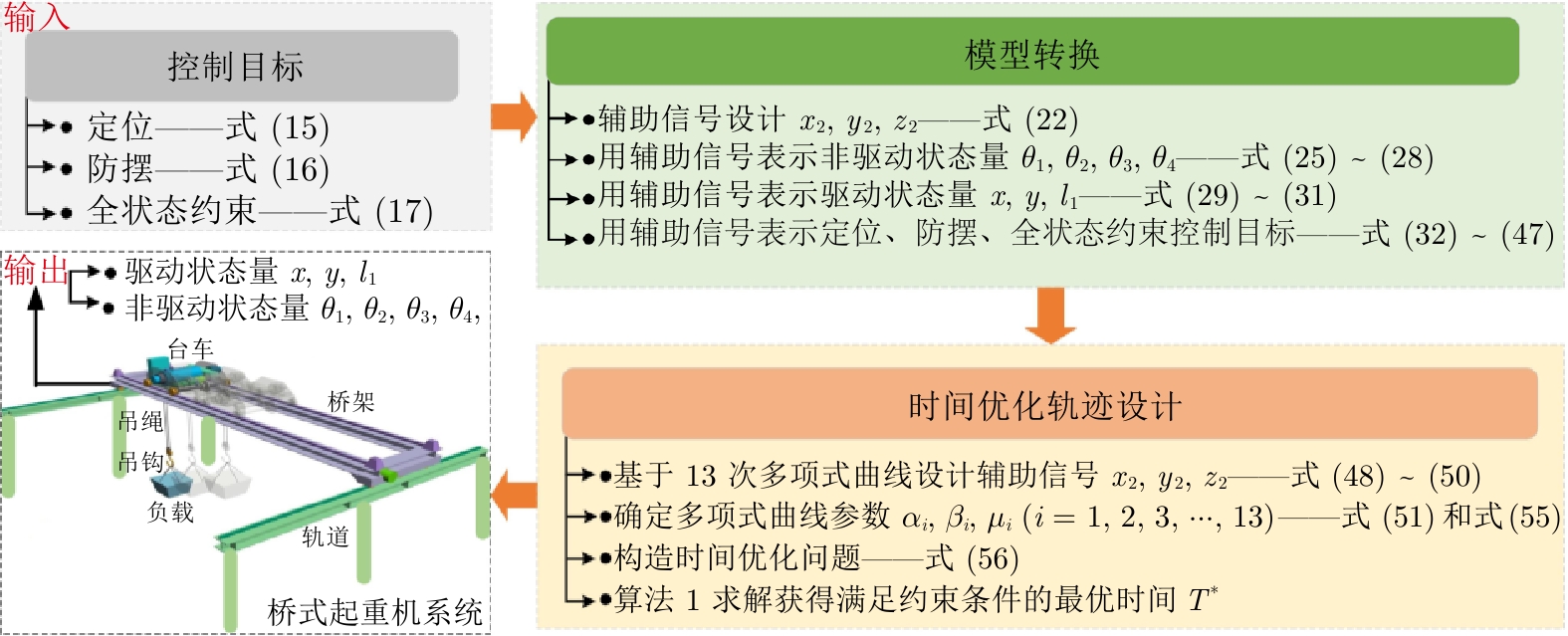
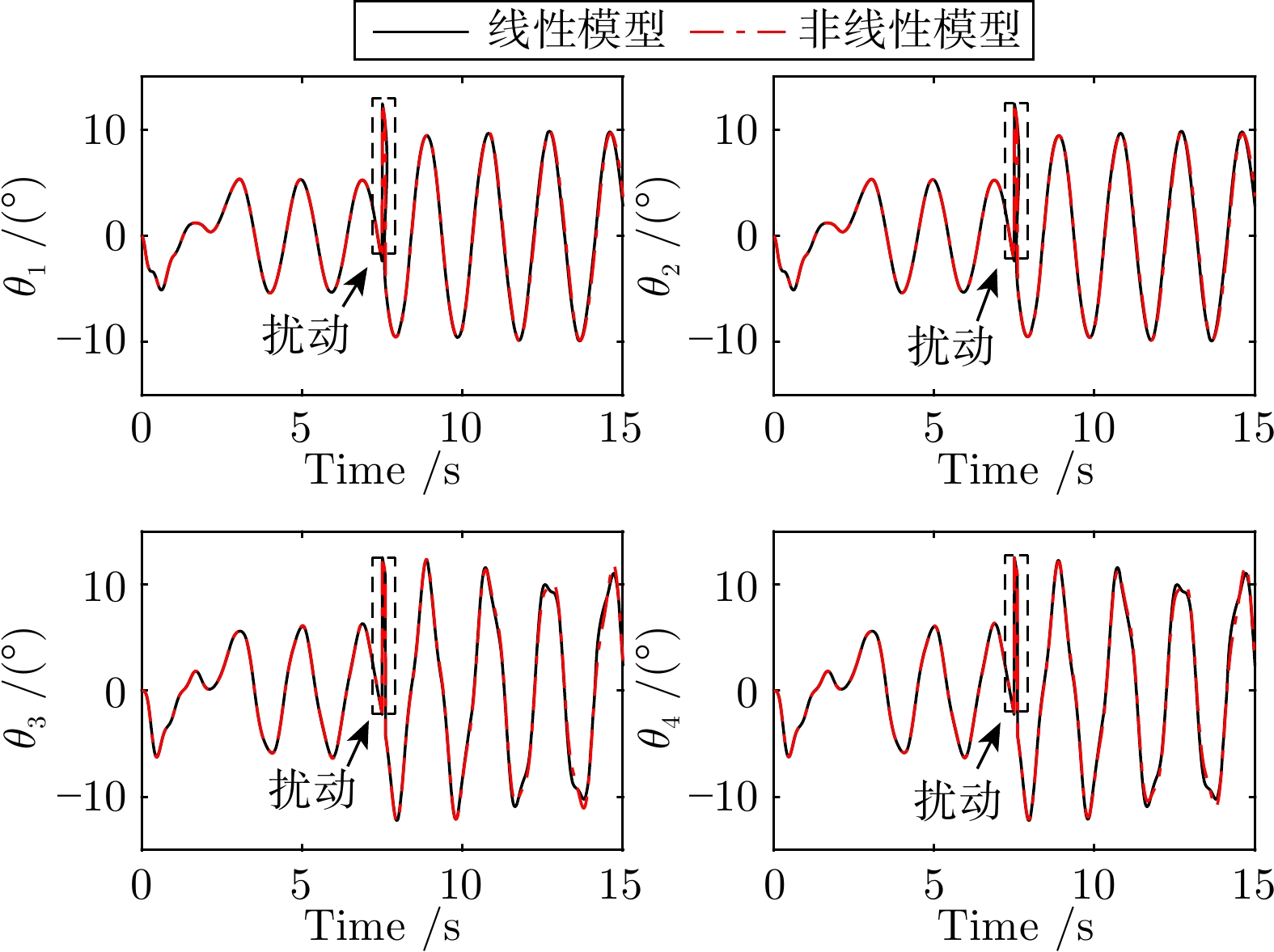
摘要: 带有双球面摆和变绳长效应的桥式起重机具有多输入多输出以及欠驱动的动力学特性, 目前仍缺乏有效的控制策略. 在台车移动、桥架移动、负载升降同步作业过程中, 吊钩和负载两级球面摆动特性更为复杂, 各状态量之间的非线性耦合关系更强, 桥式起重机的防摆控制更具挑战性. 不仅如此, 现有方法无法保证桥式起重机系统全状态量的暂态控制性能. 为解决上述问题, 提出一种基于多项式的优化轨迹规划方法. 首先, 在未进行近似简化的前提下, 使用拉格朗日方法建立带有双球面摆和变绳长效应的7自由度 (Seven degree-of-freedom, 7-DOF) 桥式起重机的精确动力学模型. 在此基础上, 构造一组包含各状态量的辅助信号, 将施加在台车、桥架、绳长以及吊钩、负载摆动上的约束转化为对辅助信号的约束, 从而将桥式起重机的轨迹规划问题转化为与辅助信号相关的时间优化问题, 并使用二分法求解. 该轨迹规划方法不仅缩短了吊运时间, 而且确保了全状态量满足约束条件. 最后, 仿真结果证明了动力学模型的准确性和轨迹规划方法的有效性.Abstract: Due to the multi-input multi-output and underactuated dynamic characteristics, the overhead crane with double spherical pendulum and varying cable length effect still lacks efficient control approaches. During the simultaneous operation of trolley moving, bridge moving and payload hoisting/lowing, the double spherical pendulum of hook and payload is more complex, and the nonlinear coupling characteristics of various state variables are stronger. It makes anti-swing control of overhead crane much more challenging. Moreover, the existing control methods cannot guarantee the desired transient control performance of the overhead crane system. To address the abovementioned issues, this paper proposes a novel polynomial-based optimal trajectory planning approach. Firstly, an accurate dynamic model for seven degree-of-freedom (7-DOF) overhead crane with double spherical pendulum and varying cable length effects is established by Lagrangian method without any simplifications. Based on this, a group of auxiliary signals containing various states are constructed. Then, the constraints imposed on the trolley/bridge moving, cable length varying, hook/payload swing are equivalently transformed to some new constraints on the auxiliary signals. Therefore, the trajectory planning problem of the overhead crane is transformed into a time optimization problem related to the auxiliary signals and solved by using the bisection method. The proposed trajectory planner not only makes transportation time as short as possible, but also ensures that full-states constraints are satisfied. At last, the simulation results prove the accuracy of the dynamic model and the effectiveness of the trajectory planning method.
-
表 1 本文与桥式起重机相关工作的比较
Table 1 Comparison between our work and the relevant work about overhead crane
自由度 参考文献 台车移动 桥架移动 变绳长 吊钩摇摆 负载摇摆 2 [7−8] $\checkmark$ $\times$ $\times$ $\times$ $\checkmark$ 3 [9−11] $\checkmark$ $\times$ $\times$ $\checkmark$ $\checkmark$ 3 [12−14] $\checkmark$ $\times$ $\checkmark$ $\times$ $\checkmark$ 4 [15−17] $\checkmark$ $\times$ $\checkmark$ $\checkmark$ $\checkmark$ 4 [18−19] $\checkmark$ $\checkmark$ $\times$ $\times$ $\checkmark$ 5 [20−21] $\checkmark$ $\checkmark$ $\checkmark$ $\times$ $\checkmark$ 6 [22−24] $\checkmark$ $\checkmark$ $\times$ $\checkmark$ $\checkmark$ 7 本文 $\checkmark$ $\checkmark$ $\checkmark$ $\checkmark$ $\checkmark$ 表 2 系统参数
Table 2 System parameters
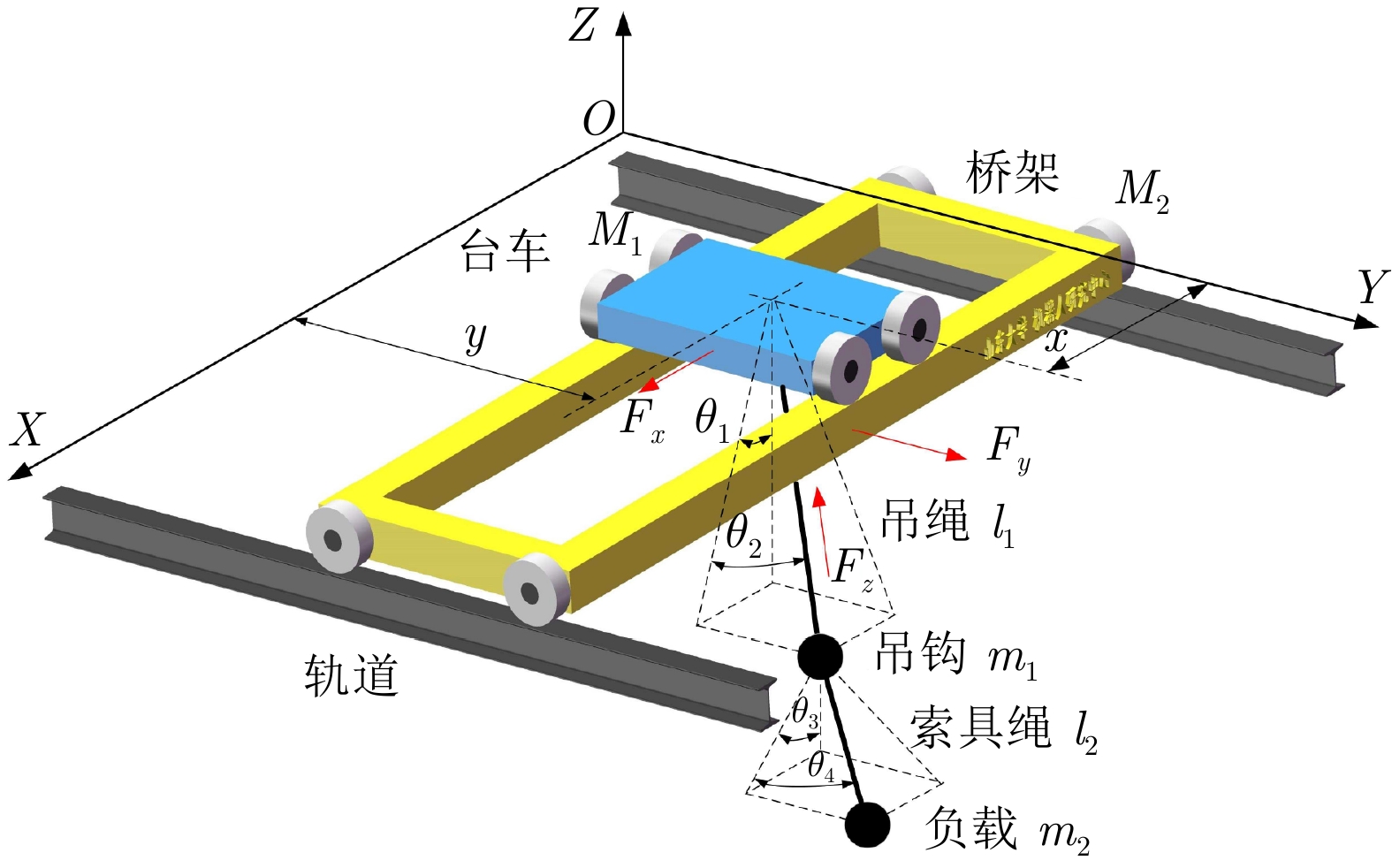
参数 物理意义 单位 $M_1$ 台车质量 kg $M_2$ 台车和桥架质量之和 kg $m_1,m_2$ 吊钩、负载质量 kg $x,y$ 台车、桥架位移 m $l_1,l_2$ 吊绳、索具绳长度 m $\theta_1,\theta_2,\theta_3,\theta_4$ 吊钩、负载三维空间摆角 ° $F_x,F_y,F_z$ 台车、桥架、吊绳驱动力 N $g$ 重力加速度 m/s2 表 3 量化指标对比结果
Table 3 Comparison results of quantitative indices
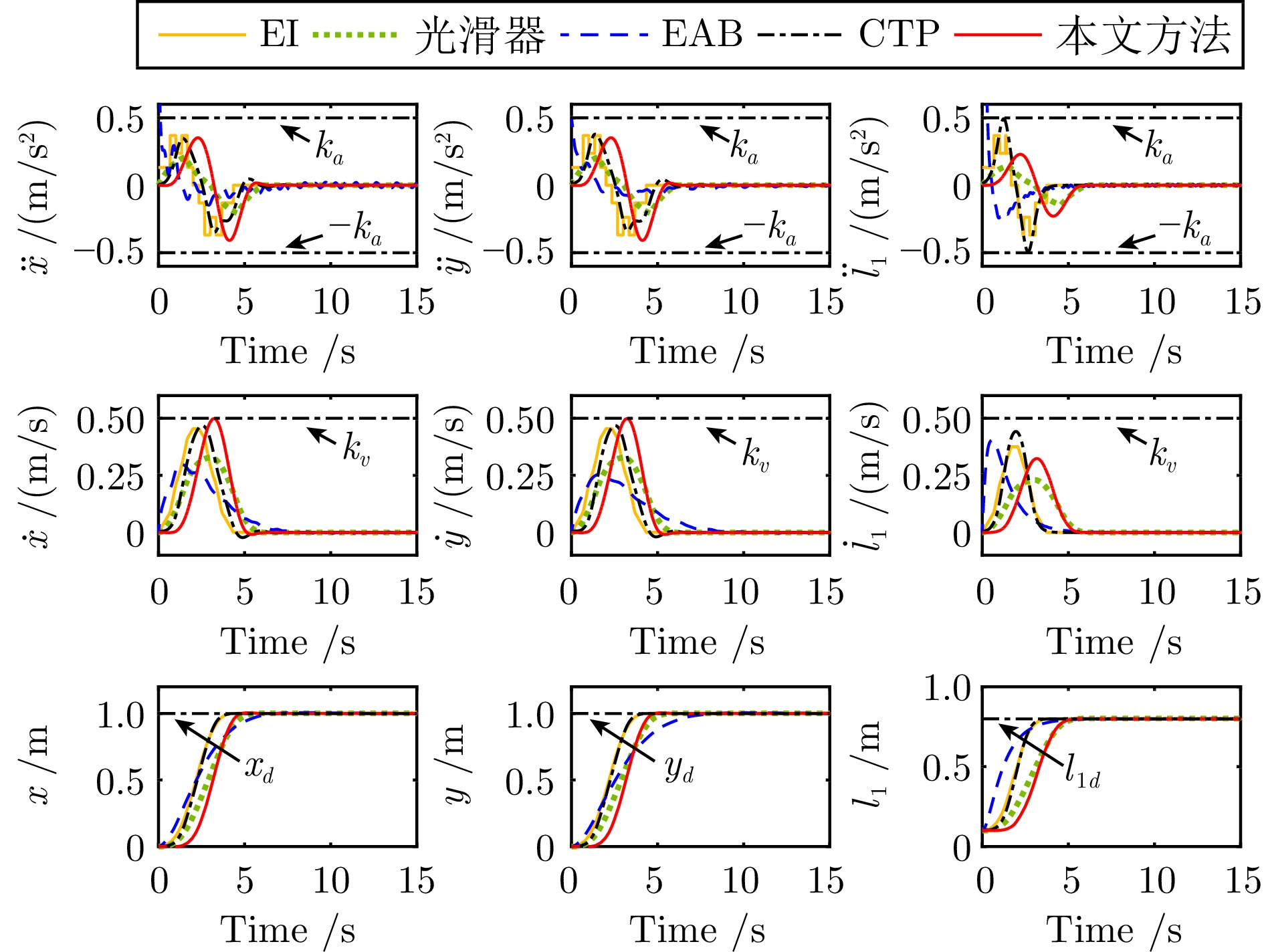
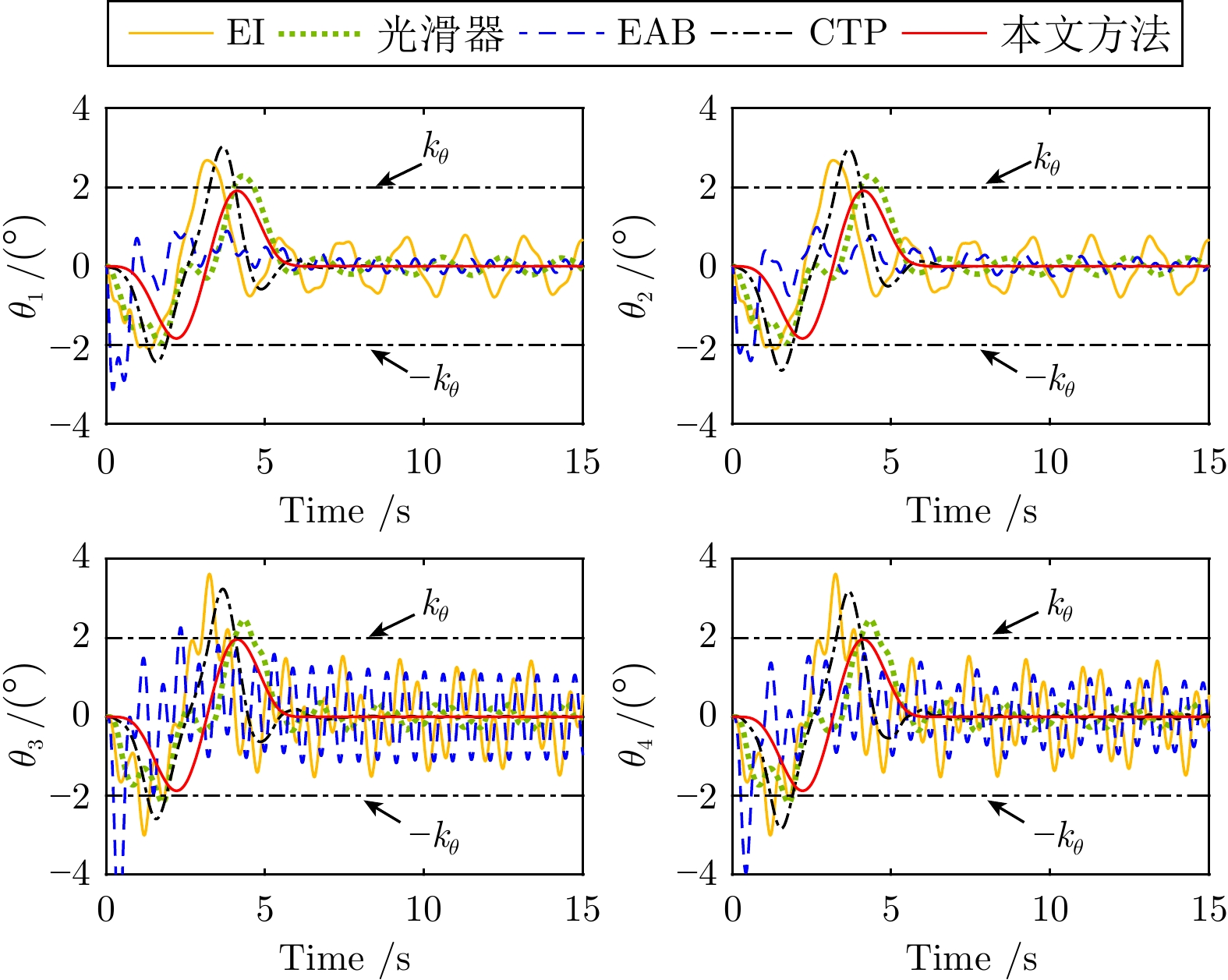
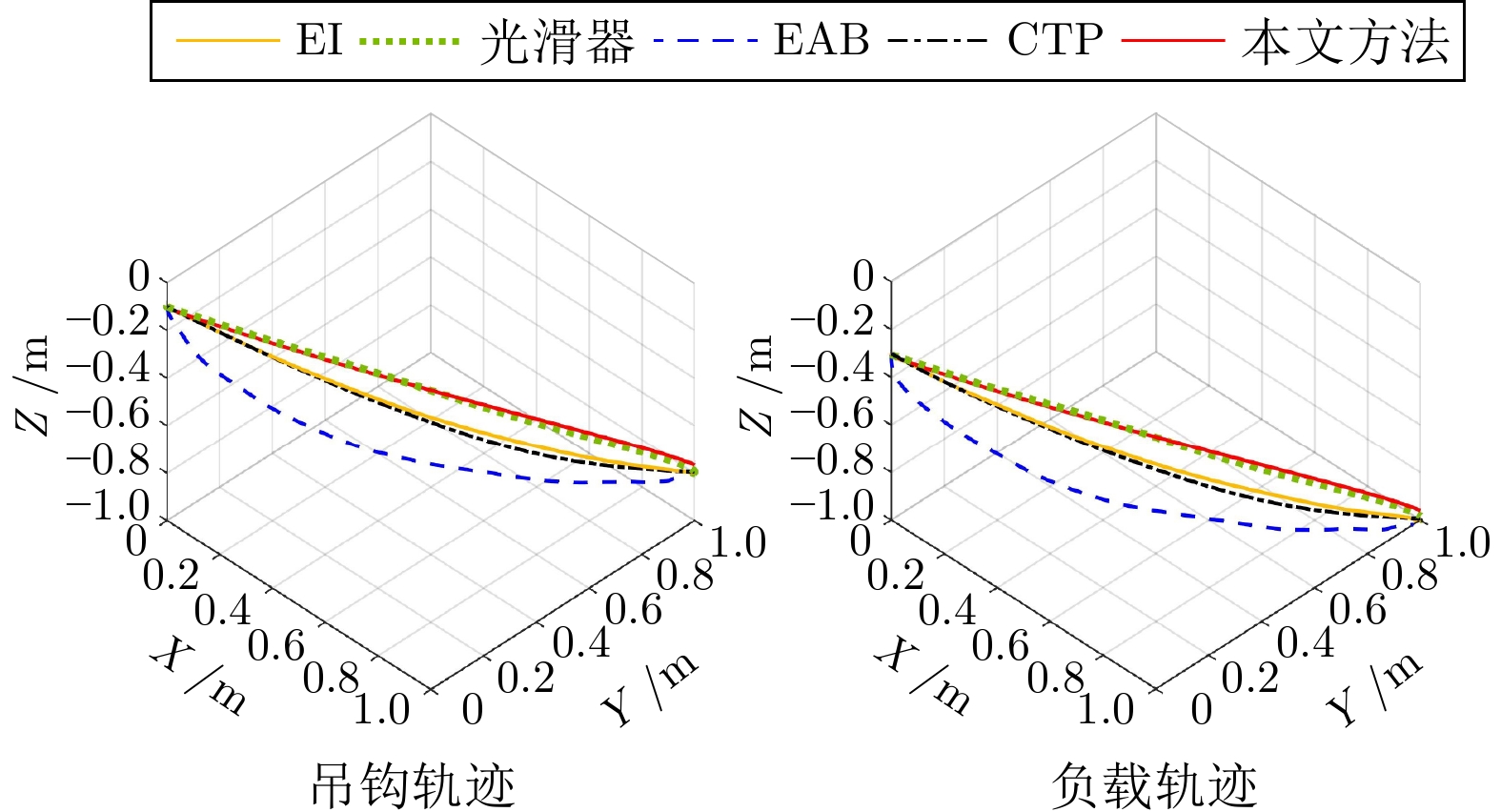
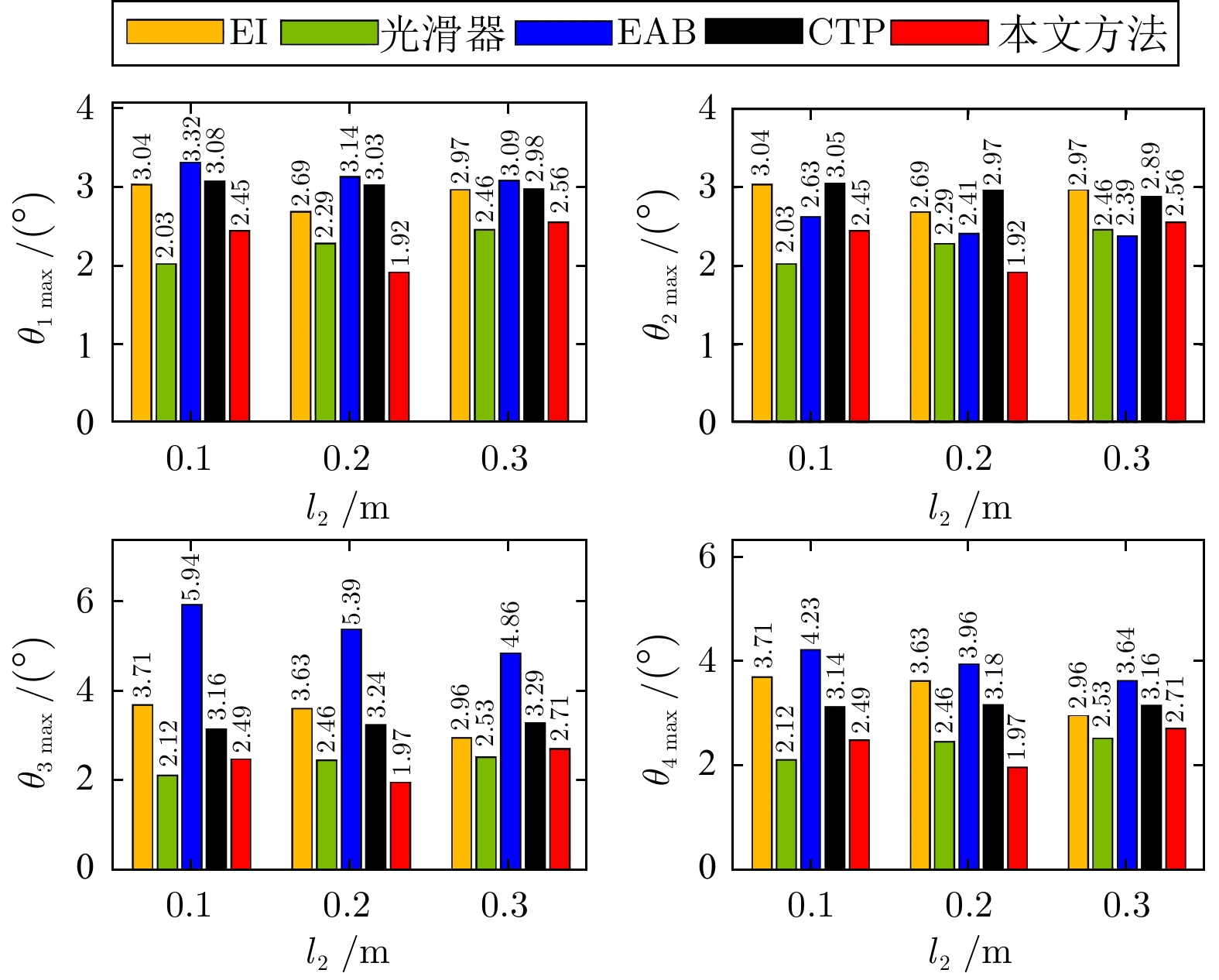
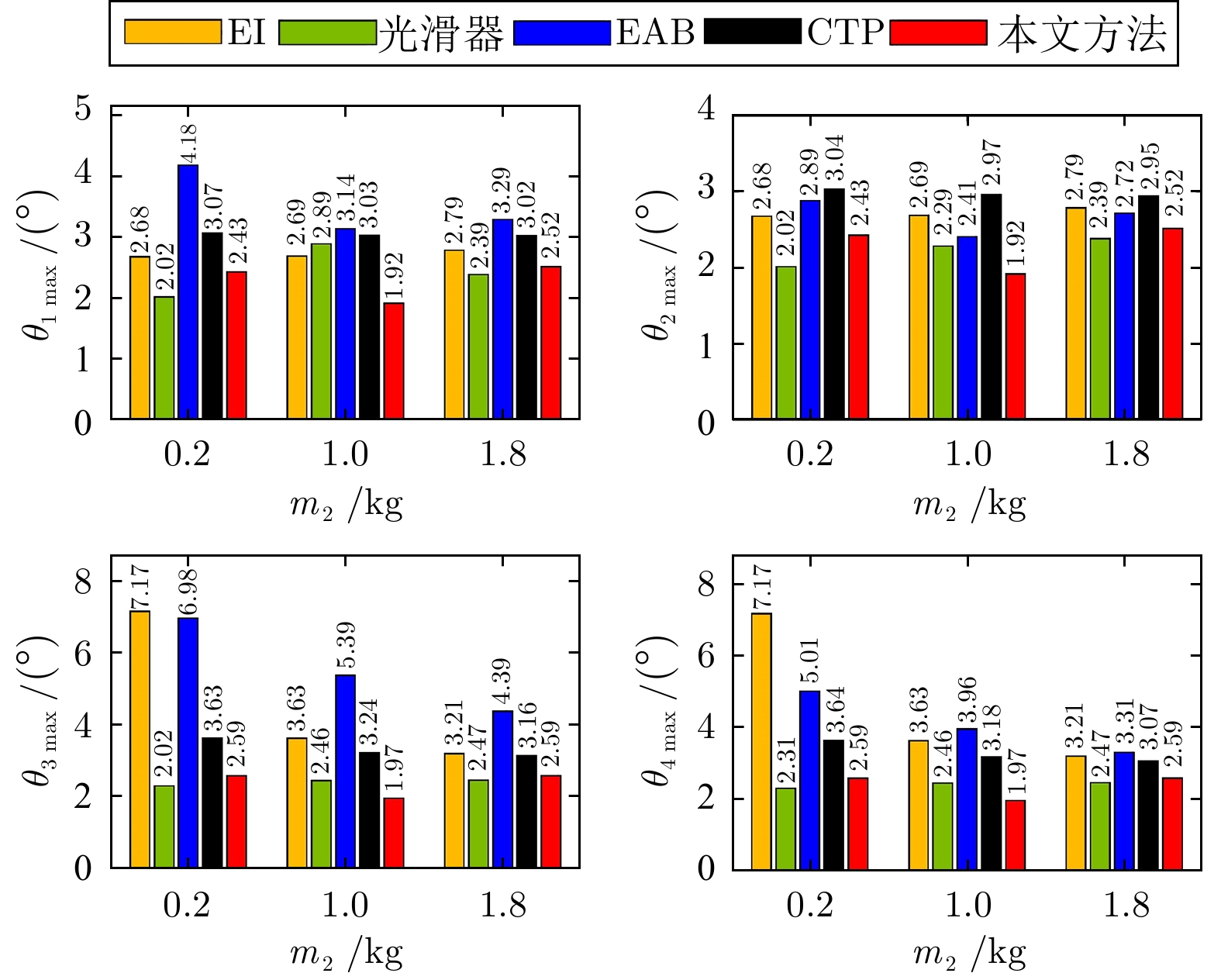
控制方法 $t_s\;({\rm{s}})$ ${\theta _{1\max }}\; (^\circ)$ ${\theta _{1\,{\rm{res} } } } \;(^\circ )$ ${\theta _{3\max }}\;(^\circ)$ ${\theta _{3\,{\rm{res} } } }\;(^\circ )$ EI $>15.00$ 2.69 0.79 3.63 1.46 光滑器 $>15.00$ 2.29 0.23 2.46 0.35 EAB $>15.00$ 3.14 0.22 5.39 1.21 CTP 4.82 3.03 0.01 3.24 0.02 本文方法 4.91 1.92 0 1.97 0 -
[1] 曹海昕, 郝运嵩, 林静正, 卢彪, 方勇纯. 绳长时变情况下轮胎式集装箱起重机非线性防摆控制算法. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(8): 1876−1884Cao Hai-Xin, Hao Yun-Song, Lin Jing-Zheng, Lu Biao, Fang Yong-Chun. Nonlinear anti-swing control for rubber tyre container gantry crane with rope length variation. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(8): 1876−1884 [2] Li G, Ma X, Li Z, Guo P J, Li Y B. Kinematic coupling-based trajectory planning for rotary crane system with double-pendulum effects and output constraints. Journal of Field Robotics, 2023, 40(2): 289−305 doi: 10.1002/rob.22130 [3] 魏萃, 柴天佑, 贾瑶, 王良勇. 补偿信号法驱动的Pendubot自适应平衡控制. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(6): 1146−1156Wei Cui, Chai Tian-You, Jia Yao, Wang Liang-Yong. Compensation signal driven adaptive balance control of the Pendubot. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(6): 1146−1156 [4] 武宪青, 徐可心, 张益波. 基于输出反馈的欠驱动TORA系统的有界输入控制. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(1): 200−204Wu Xian-Qing, Xu Ke-Xin, Zhang Yi-Bo. Output-based feedback control of underactuated TORA systems by bounded inputs. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(1): 200−204 [5] 王岳, 孙宁, 吴易鸣, 梁潇, 陈鹤, 方勇纯. 深海起重机系统的实时轨迹规划方法. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(12): 2761−2770Wang Yue, Sun Ning, Wu Yi-Ming, Liang Xiao, Chen He, Fang Yong-Chun. Real-time motion planning of deep sea-oriented flexible crane systems. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(12): 2761−2770 [6] Ouyang H M, Zhao B Q, Zhang G M. Enhanced-coupling nonlinear controller design for load swing suppression in three-dimensional overhead cranes with double-pendulum effect. ISA Transactions, 2021, 115: 95−107 doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2021.01.009 [7] Zhang S Z, He X X, Zhu H Y, Li X C, Liu X G. PID-like coupling control of underactuated overhead cranes with input constraints. Mechanical Systems & Signal Processing, 2022, 178: Article No. 109274 [8] Zhu X, Wang N. Hairpin RNA genetic algorithm based ANFIS for modeling overhead cranes. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2022, 165: Article No. 108326 doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2021.108326 [9] 陈鹤, 方勇纯, 孙宁, 钱彧哲. 基于伪谱法的双摆吊车时间最优消摆轨迹规划策略. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(1): 153−160Chen He, Fang Yong-Chun, Sun Ning, Qian Yu-Zhe. Pseudo-spectral method based time optimal anti-swing trajectory planning for double pendulum crane systems. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(1): 153−160 [10] Mar R, Goyal A, Nguyen V, Yang T L, Singhose W. Combined input shaping and feedback control for double-pendulum systems. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2017, 85: 267−277 doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2016.08.012 [11] Chen H, Sun N. Nonlinear control of underactuated systems subject to both actuated and unactuated state constraints with experimental verification. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2020, 67(9): 7702−7714 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2019.2946541 [12] Sun N, Fang Y C. Nonlinear tracking control of underactuated cranes with load transferring and lowering: Theory and experimentation. Automatica, 2014, 50(9): 2350−2357 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2014.07.023 [13] Shen P, Schatz J, Caverly R J. Passivity-based adaptive trajectory control of an underactuated 3-DOF overhead crane. Control Engineering Practice, 2021, 112: Article No. 104834 doi: 10.1016/j.conengprac.2021.104834 [14] Kim J, Lee D, Kiss B, Kim D. An adaptive unscented Kalman filter with selective scaling (AUKF-SS) for overhead cranes. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2021, 68(7): 6131−6140 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2020.2996150 [15] Lu B, Fang Y C, Sun N. Enhanced-coupling adaptive control for double-pendulum overhead cranes with payload hoisting and lowering. Automatica, 2019, 101: 241−251 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2018.12.009 [16] Shi H T, Yao F X, Yuan Z, Tong S H, Tang Y H, Han G. Research on nonlinear coupled tracking controller for double pendulum gantry cranes with load hoisting/lowering. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2022, 108(1): 223−238 doi: 10.1007/s11071-021-07185-6 [17] Zhang W, Chen H, Yao X Y, Li D L. Adaptive tracking of double pendulum crane with payload hoisting/lowering. Automation in Construction, 2022, 141: Article No. 104368 doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2022.104368 [18] Chwa D. Sliding-mode-control-based robust finite-time antisway tracking control of 3-D overhead cranes. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2017, 64(8): 6775−6784 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2017.2701760 [19] Zhang M H, Zhang Y F, Chen H, Cheng X G. Model-independent PD-SMC method with payload swing suppression for 3D overhead crane systems. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2019, 129: 381−393 doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2019.04.046 [20] Maghsoudi M J, Mohamed Z, Sudin S, Buyamin S, Jaafar H I, Ahmad S M. An improved input shaping design for an efficient sway control of a nonlinear 3D overhead crane with friction. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2017, 92: 364−378 doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2017.01.036 [21] Maghsoudi M J, Ramli L, Sudin S, Mohamed Z, Husain A R, Wahid H. Improved unity magnitude input shaping scheme for sway control of an underactuated 3D overhead crane with hoisting. Mechanical Systems & Signal Processing, 2019, 123: 466−482 [22] Gao T T, Huang J, Singhose W. Eccentric-load dynamics and oscillation control of industrial cranes transporting heterogeneous loads. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2022, 172: Article No. 104800 doi: 10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2022.104800 [23] Ouyang H M, Zhao B Q, Zhang G M. Swing reduction for double-pendulum three-dimensional overhead cranes using energy-analysis-based control method. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2021, 31(9): 4184−4202 doi: 10.1002/rnc.5466 [24] Zhao B Q, Ouyang H M, Iwasaki M. Motion trajectory tracking and sway reduction for double-pendulum overhead cranes using improved adaptive control without velocity feedback. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2022, 27(5): 3648−3659 doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2021.3126665 [25] Li G, Ma X, Li Z, Li Y B. Optimal trajectory planning strategy for underactuated overhead crane with pendulum-sloshing dynamics and full-state constraints. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2022, 109: 815−835 doi: 10.1007/s11071-022-07480-w [26] Li G, Ma X, Li Z, Li Y B. Time-polynomial-based optimal trajectory planning for double-pendulum tower crane with full-state constraints and obstacle avoidance. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2023, 28(2): 919−932 doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2022.3210536 [27] 孙宁, 方勇纯, 钱彧哲. 带有状态约束的双摆效应吊车轨迹规划. 控制理论与应用, 2014, 31(7): 974−980Sun Ning, Fang Yong-Chun, Qian Yu-Zhe. Motion planning for cranes with double pendulum effects subject to state constraints. Control Theory and Applications, 2014, 31(7): 974−980 [28] Hou M X, Cao H R, Li Q, Shi J H. Industry-oriented method for dynamic force identification in peripheral milling based on FSC-LSQR using acceleration signals. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2022, 121: 7793−7809 doi: 10.1007/s00170-022-09697-w [29] 欧阳慧珉, 王健, 张广明, 梅磊, 邓歆. 基于新型滑模算法的双摆旋转起重机消摆跟踪控制. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(7): 1344−1353Ouyang Hui-Min, Wang Jian, Zhang Guang-Ming, Mei Lei, Deng Xin. Tracking and anti-sway control for double-pendulum rotary cranes using novel sliding mode algorithm. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(7): 1344−1353 [30] Shi H T, Li R R, Bai X T, Zhang Y X, Min L G, Wang D, et al. A review for control theory and condition monitoring on construction robots. Journal of Field Robotics, 2023, 40(4): 934−954 doi: 10.1002/rob.22156 [31] Zhang M H, Ma X, Chai H, Rong X W, Tian X C, Li Y B. A novel online motion planning method for double-pendulum overhead cranes. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2016, 85: 1079−1090 doi: 10.1007/s11071-016-2745-x [32] Yang T, Sun N, Chen H, Fang Y C. Motion trajectory-based transportation control for 3-D boom cranes: Analysis, design, and experiments. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2018, 66(5): 3636−3646 -




 下载:
下载: