A Survey of Real-time Transmission Scheduling Algorithms for Industrial Wireless Network
-
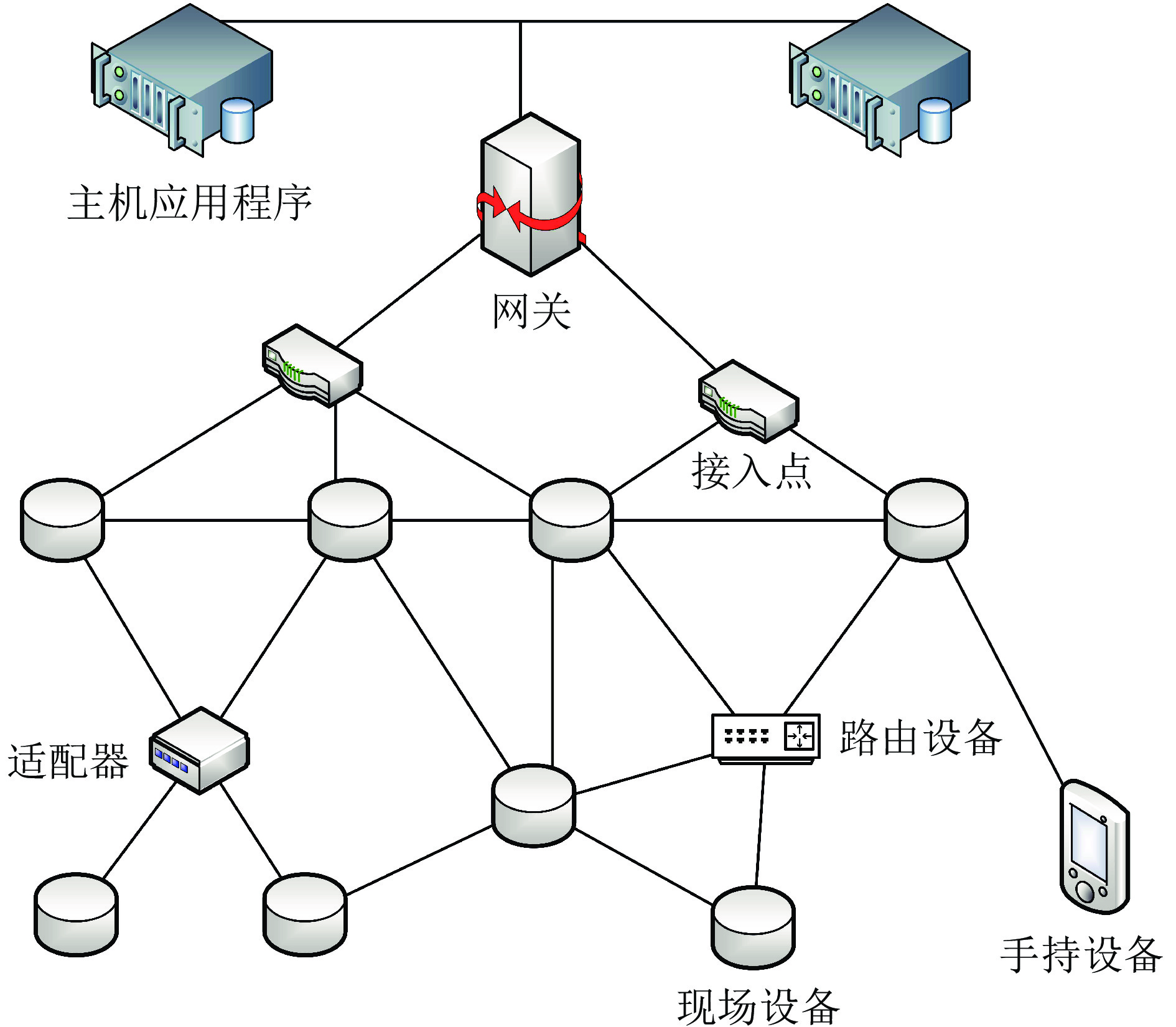
摘要: 无线网络是工业物联网中一种具有良好前景的网络互联技术. 它的应用为工业现场设备部署提供了极大便利, 使设备摆脱了线缆的束缚, 从而在空间上选点更为灵活, 同时能够节省线材和人力等方面的成本. 然而, 无线通信易受环境噪声影响, 尤其是在复杂电磁干扰的工业环境中, 易导致无线传输的时延增大和数据丢失. 这些问题对于传输实时性要求较高的工业控制系统是非常不利的因素. 为了提高无线网络在工业环境中数据传输的实时性, 学者们设计了多种传输调度算法, 以提高无线通信的实时性和可靠性, 从而满足工业应用的需求. 综述了工业无线网络传输调度算法的研究现状, 对其发展历程、问题定义、评价指标、分类方法和现有标准等方面进行了全面总结, 详细阐述了具有代表性的调度算法的工作原理, 并指出了未来的研究方向.Abstract: The wireless network provides great convenience for the deployment of industrial devices, gets rid of the shackles of cables, makes the deployment of devices more flexible, and saves the cost of materials and manpower, which is the development trend of the industrial internet of things. However, since wireless communication is susceptible to interference, especially in the industrial environment with complex electromagnetic interference, it is easy to lead to increased delay and data loss in wireless transmission, which is a disadvantage for industrial control systems that require high real-time transmission. In order to improve the real-time performance of data transmission in wireless networks in industrial environments, researchers have designed a variety of industrial wireless network transmission scheduling algorithms to improve the real-time and reliability of wireless communication to meet the industrial application requirements. This paper reviews the current researches of transmission scheduling algorithms for industrial wireless network, and comprehensively summarizes the development history, problem definitions, evaluation metrics, classification methods and existing standards, and elaborates the working principles of representative scheduling algorithms in detail, and points out the future research direction.
-
Key words:
- Industrial wireless networks /
- transmission scheduling /
- real-time /
- reliability
-
表 1 工业无线网络标准和调度算法发展概况
Table 1 Overview of the development standards and scheduling algorithms for industrial wireless network
年份 标准 集中式 分布式 2008—2010 WirelessHART、WIA-PA TSMP、Bit DRAND 2011 ISA-100.11a C-LLF Tinka 2012—2013 IEEE 802.15.4e TASA、RT-WiFi DeTAS、GCSA 2014 6TiSCH、WIA-FA SA、PSO、MinMax — 2015 — SSEvent、OLS Orchestra 2016 — LDF Wave 2017—2018 LoRaWAN、5G OBSSA、TDMH — 2019 — SM、Autobahn DIVA、TESLA、DiGs 2020 — w-SHARP OST 2021 WiFi 7 RLSchedule OSCAR、ATRIA、$ A^{3} $ 2022—2023 — SmartHART EDSF 表 2 工业无线标准对比
Table 2 Comparison of industrial wireless standards
标准 物理层 多路径 TDMA 介质访问 IEEE 802.15.4 IEEE 802.15.4控制层 $ \times $ $ \times $ CSMA/CA WirelessHART IEEE 802.15.4物理层 $ \surd $ 基于TDMA的时隙信道跳频 IEEE 802.15.4控制层 时隙信道跳频 ISA100.11a IEEE 802.15.4物理层 $ \surd $ 基于CSMA的慢跳频 IEEE 802.15.4控制层 混合跳频 WIA-PA/FA IEEE 802.15.4物理层 $ \surd $ 时隙跳频 IEEE 802.15.4物理层 自适应跳频 自适应频率切换 IEEE 802.15.4e IEEE 802.15.4物理层 $ \surd $ 基于TDMA的时隙信道跳频 TSCH、DSME、LLDN 工业5G 5G NR物理层 $ \surd $ 正交频分多址 5G NR物理层 WiFi 7 IEEE 802.11物理层 $ \surd $ 正交频分多址 CSMA/CA 表 3 调度优化算法比较
Table 3 Comparison of scheduling optimization algorithms
算法 方法 算法复杂度 DDPA 非线性规划 $ \text{O}\left( N\log{N}\right) $ C-LLF 凸优化 $ \text{O}\left(N^{2}\right) $ RS 凸优化 $ \text{O}\left( N\log{N}\right) $ SA、PSO 集群智能优化算法 $ \text{O}\left( N\log{N}\right) $ DLSA 非线性规划 $ \text{O}\left({N^{3}}/\log{N} \right) $ MLS 迭代 $ \text{O}\left( N\log{N}\right) $ 表 4 经典算法调度方式比较
Table 4 Comparison of classical algorithm scheduling modes
调度算法 网络模型 管理模式 支持多跳 数据流 信道 投递率 延迟 能耗 DiGs 网状 分布式 是 周期流 多信道 $ \surd $ $ \surd $ $ \surd $ DistributedHART 网状 分布式 是 周期流和事件流 多信道 $ \surd $ $ \surd $ $ \surd $ ALICE 树形 分布式 是 周期流 多信道 $ \surd $ $ \surd $ $ \surd $ OST 树形 分布式 是 周期流 多信道 $ \surd $ $ \surd $ $ \surd $ DIVA 网状 分布式 是 周期流 多信道 $ \surd $ Wave 树状 分布式 是 周期流 多信道 $ \surd $ OLS 树状 集中式 是 事件流 多信道 $ \surd $ DDPA 网状 集中式 是 事件流 多信道 $ \surd $ LDF 树状 集中式 否 周期流 多信道 $ \surd $ $ \surd $ SA、PSO 树状 集中式 是 事件流 单信道 $ \surd $ GCSA 树状 分布式 是 周期流 单信道 $ \surd $ TASA 树状 集中式 是 周期流 多信道 $ \surd $ $ \surd $ OBSSA 网状 集中式 是 周期流和事件流 多信道 $ \surd $ SM 树状 集中式 是 周期流和事件流 多信道 $ \surd $ DRAND 网状 分布式 是 周期流 多信道 $ \surd $ $ \surd $ Tinka 网状 分布式 是 周期流 多信道 $ \surd $ DeTAS 网状 分布式 是 周期流 多信道 $ \surd $ Orchestra 网状 分布式 是 周期流 多信道 $ \surd $ $ \surd $ $ \surd $ TSMP 网状 集中式 是 周期流和事件流 多信道 $ \surd $ $ \surd $ $ \surd $ C-LLF 树状 集中式 是 周期流 多信道 $ \surd $ TDMH 网状 集中式 是 周期流 多信道 $ \surd $ Ergen 网状 集中式 是 周期流 多信道 $ \surd $ MinMax 树状 集中式 是 周期流 多信道 $ \surd $ RS 网状 集中式 是 周期流 多信道 TESLA 树状 分布式 是 周期流 多信道 $ \surd $ $ \surd $ $ \surd $ JiTS 树状 分布式 是 周期流 单信道 $ \surd $ SSEvent 网状 集中式 是 周期流和事件流 多信道 $ \surd $ Bit 网状 集中式 是 周期流 多信道 $ \surd $ $ \surd $ $ \surd $ SRDR 网状 集中式 是 周期流 多信道 $ \surd $ $ \surd $ $ \surd $ Hierarchic 树状 集中式 是 周期流和事件流 多信道 $ \surd $ $ \surd $ CCA 网状 集中式 是 周期流和事件流 单信道 $ \surd $ $ \surd $ $ \surd $ RLSchedule 树状 集中式 是 周期流 多信道 $ \surd $ $ \surd $ $ \surd $ OSCAR 网状 分布式 是 周期流 多信道 $ \surd $ $ \surd $ $ \surd $ EDSF 树状 分布式 是 周期流 多信道 $ \surd $ $ \surd $ $ \surd $ -
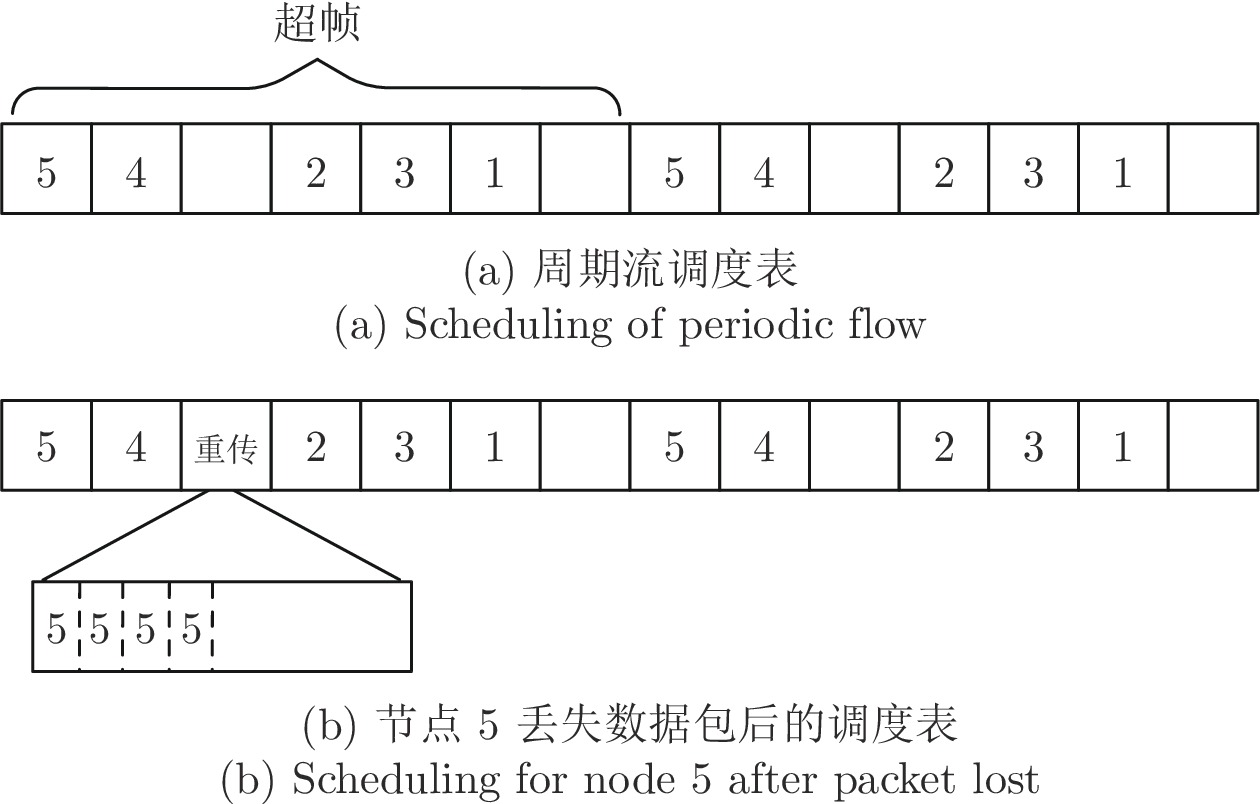
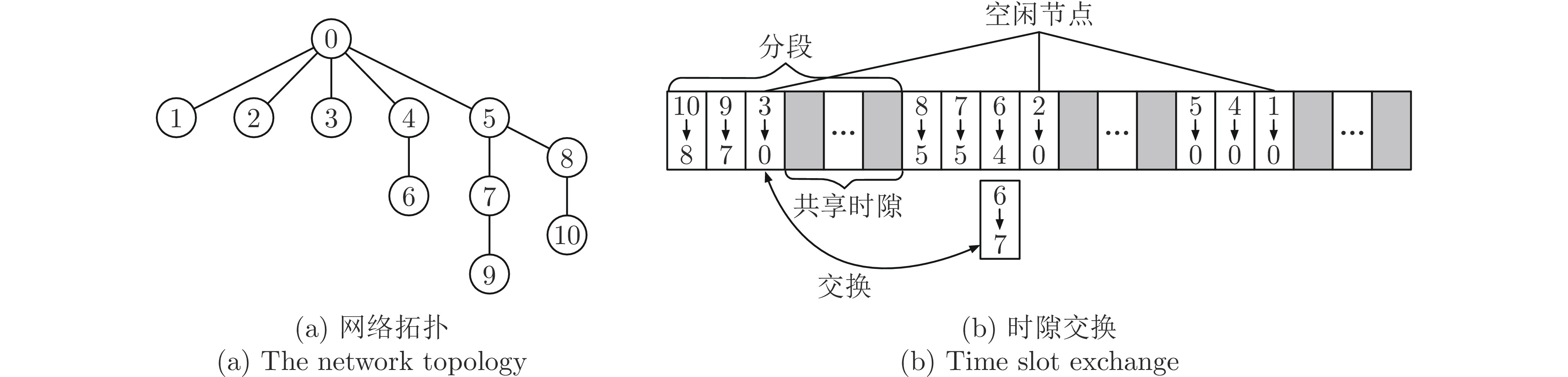
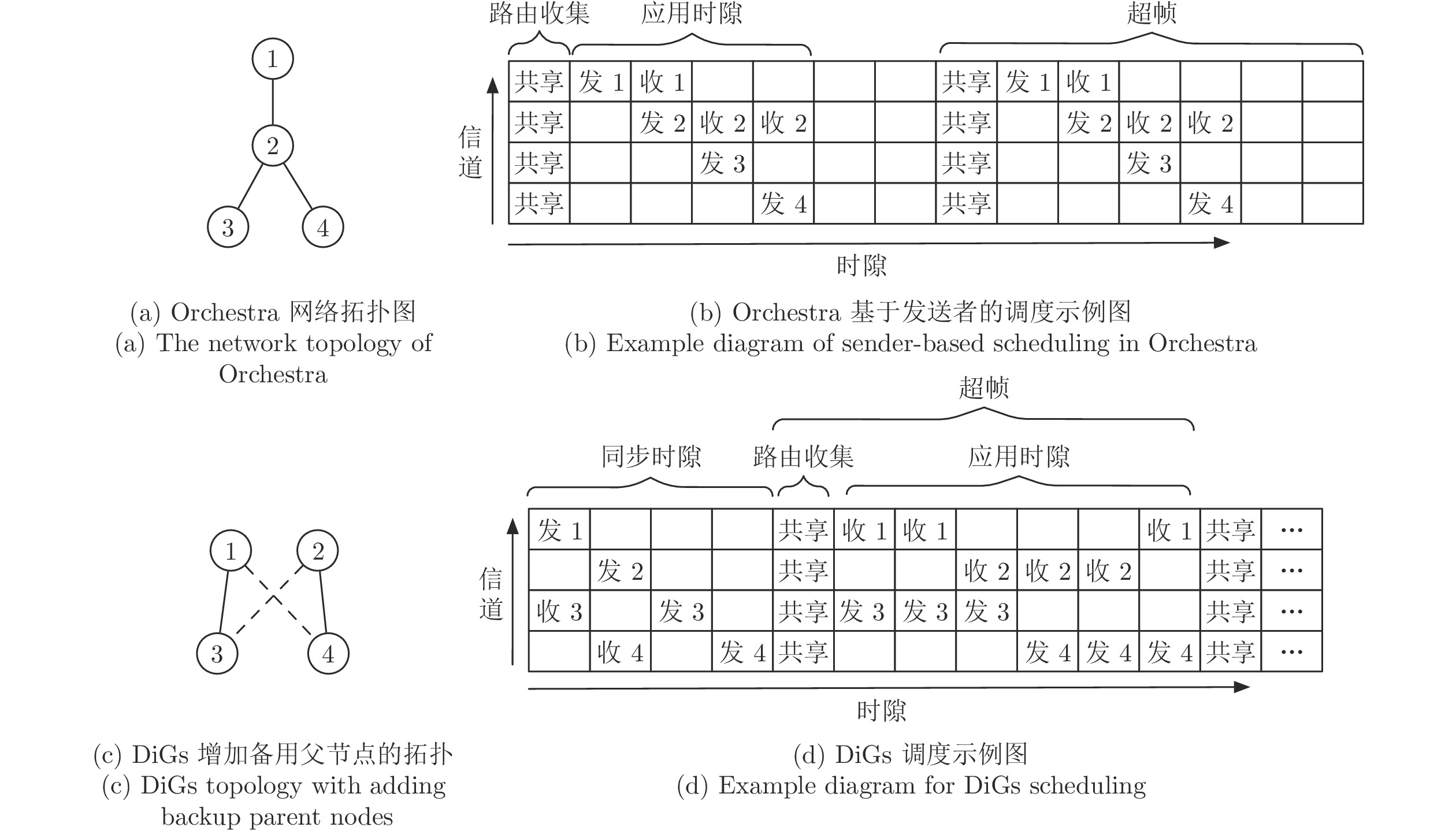
[1] Venkata P M, Abusayeed S, Sanjay M. Distributed graph routing for wirelesshart networks. Association for Computing Machinery, 2018, 27(4): 1669−1682 [2] Wu C J, Dolvara G, Abusayeed S, Mo S. Maximizing network lifetime of wirelesshart networks under graph routing. In: Proceedings of the IEEE First International Conference on Internet-of-Things Design and Implementation. Berlin, Germany: IEEE, 2016. 176–186 [3] He Y, Guo X Z, Zheng X L, Yu Z H, Zhang J, Jiang H T, et al. Cross-technology communication for the Internet of Things: A survey. ACM Computing Surveys, 2022, 55(5): 1−29 [4] Daniele P, Martin H. Multipath fading in wireless sensor networks: Measurements and interpretation. In: Proceedings of the International Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing Conference. Amman, Jordan: IEEE, 2006. 1039–1044 [5] Krijn L, Jan H F. The capture effect in fm receivers. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 1976, 24(5): 531−539 doi: 10.1109/TCOM.1976.1093327 [6] Federico F, Marco Z, Lothar T, Olga S. Efficient network flooding and time synchronization with glossy. In: Proceedings of the 10th ACM/IEEE International Conference on Information Processing in Sensor Networks. Chicago, USA: IEEE, 2011. 73–84 [7] Luís M B, Fernando J V, António S L. Survey on the characterization and classification of wireless sensor networks applications. IEEE Communications Surveys Tutorials, 2014, 16(4): 1860−1890 doi: 10.1109/COMST.2014.2320073 [8] 张晓玲, 梁炜, 于海斌, 封锡盛. 无线传感器网络传输调度方法综述. 通信学报, 2012, 33(5): 143−156 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-436X.2012.05.019Zhang Xiao-Ling, Liang Wei, Yu Hai-Bin, Feng Xi-Sheng. Survey of transmission scheduling methods in wireless sensor networks. Journal on Communications, 2012, 33(5): 143−156 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-436X.2012.05.019 [9] Liu K, Nael A G, Kyoung D K. JiTS: Just-in-time scheduling for real-time sensor data dissemination. In: Proceedings of the Fourth Annual IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications. Pisa, Italy: IEEE, 2006. 42–46 [10] Tengfei C, Thomas W, Xavier V, Pedro H G. Constructive interference in 802.15.4: A tutorial. IEEE Communications Surveys Tutorials, 2019, 21(1): 217−237 doi: 10.1109/COMST.2018.2870643 [11] Zhang K W, Shi Y, Karnouskos S, Sauter T, Fang H Z, Colombo A W. Advancements in industrial cyber-physical systems: An overview and perspectives. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2022, 19(1): 716−729 [12] Brummet R, Hossain M K, Chipara O, Herman T, Goddard S. WARP: On-the-fly program synthesis for agile, real-time, and reliable wireless networks. In: Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Information Processing in Sensor Networks. Nashville, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, 2021. 254–267 [13] Romain J, Marco Z, Huang P C, Jan B, Lothar T. End-to-end real-time guarantees in wireless cyber-physical systems. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Real-Time Systems Symposium. Porto, Portugal: IEEE, 2016. 167–178 [14] Chen Y, Zhang H W, Nathan F, Wang L Y, George Y. Probabilistic per-packet real-time guarantees for wireless networked sensing and control. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2018, 14(5): 2133−2145 doi: 10.1109/TII.2018.2795567 [15] Kayan H, Nunes M, Rana O, Burnap P, Perera C. Cybersecurity of industrial cyber-physical systems: A review. ACM Computing Surveys, 2022, 54(11): 1−35 [16] Shen W, Zhang T T, Mikael G. Prioritymac: A priority-enhanced mac protocol for critical traffic in industrial wireless sensor and actuator networks. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2014, 10(1): 824−835 doi: 10.1109/TII.2013.2280081 [17] Adil M, Menon V G, Balasubramanian V, Alotaibi S R, Song H, Jin Z p, et al. Survey: Self-Empowered wireless sensor networks security taxonomy, challenges and future research directions. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2023, 23(18): 20519−20535 doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2022.3216824 [18] Milanez G, Vieira M, Vieira L, Nacif J. VariBan: A variable bandwidth channel allocation algorithm for IEEE 802.15. 4e-based networks. Computer Networks, 2023, 231: Article No. 109774 doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2023.109774 [19] Wang Q, Jiang J. Comparative examination on architecture and protocol of industrial wireless sensor network standards. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, 2016, 18(3): 2179−2219 [20] Sinem C E, Pravin V. TDMA scheduling algorithms for wireless sensor networks. Wireless Networks, 2010, 16: 985−997 doi: 10.1007/s11276-009-0183-0 [21] Simon D, Beshr A N, Olaf L, Thomas W. Orchestra: Robust mesh networks through autonomously scheduled TSCH. In: Proceedings of the 13th ACM Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems. Seoul, South Korea: Association for Computing Machinery, 2015. 337–350 [22] Dominik B, Fabian M, Marco Z, Sebastian T. Control-guided communication: Efficient resource arbitration and allocation in multi-hop wireless control systems. IEEE Control Systems Letters, 2020, 4(1): 127−132 doi: 10.1109/LCSYS.2019.2922188 [23] Bang A O, Rao U P, Kaliyar P, Conti M. Assessment of routing attacks and mitigation techniques with RPL control messages: A survey. ACM Computing Surveys, 2022, 55(2): 1−36 [24] Javan N T, Sabaei M, Hakami V. Adaptive channel hopping for IEEE 802.15. 4 TSCH-based networks: A dynamic bernoulli bandit approach. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(20): 23667−23681 doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3110720 [25] Diego D, Thomas W, Xavier V, Pascal T. 6TiSCH: Deterministic IP-enabled industrial internet (of things). IEEE Communications Magazine, 2014, 25(12): 1−36 [26] Gutierrez J A, Naeve M, Callaway E, Bourgeois M. IEEE 802.15.4: A developing standard for low-power low-cost wireless personal area networks. ACM Transactions on Internet of Things, 2001, 15(5): 12−19 [27] Wireless LAN Medium Access Control (MAC) and Physical Layer (PHY) Specifications, IEEE Standard 802.11, Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1997. [28] Foundation H C. WirelessHART Specification 75: TDMA Data-Link Layer, HART Communication Foundation Standard, HART Communication Foundation, Australia, 2008. [29] ISA-100.11 a-2011 Wireless Systems for Industrial Automation: Process Control and Related Applications, Process Control and Related Applications Standard, International Society of Automation, USA, 2011. [30] 802.15. 4e-2012——IEEE Standard for Local and Metropolitan Area Networks——Part 15.4: Low-Rate Wireless Personal Area Networks (LR-WPANs), IEEE Standard Association, IEEE Standards Association, USA, 2012. [31] Moon S, Park H, Chwa H S, Park K. AdaptiveHART: An adaptive real-time mAC protocol for industrial internet-of-things. IEEE Systems Journal, 2022, 16(3): 4849−4860 doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2022.3171962 [32] Chilukuri S, Gupta A, Sai P, Hemanth S. SmartHART: A priority-aware scheduling and routing scheme for ⅡoT networks using deep reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Communication Systems and Networks. Bangalore, India: IEEE, 2023. 452–456 [33] Liang W, Zheng M, Zhang J L, Shi H G, Yu H B, Yang Y T, et al. WIA-FA and its applications to digital factory: A wireless network solution for factory automation. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2019, 107(6): 1053−1073 doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2019.2897627 [34] Wun C J, Junhee L. Performance evaluation of IEEE 802.15.4e DSME MAC protocol for wireless sensor networks. In: Proceedings of the First IEEE Workshop on Enabling Technologies for Smartphone and Internet of Things. Seoul, South Korea: IEEE, 2012. 452–456 [35] Gianluca C, Lucia S, Adriano V, Claudio Z. On the performance of IEEE 802.11e wireless infrastructures for soft-real-time industrial applications. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2010, 6(3): 425−437 doi: 10.1109/TII.2010.2052058 [36] Michal S, Martin M, Zdenek H. Experiments for real-time communication contracts in IEEE 802.11e EDCA networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Workshop on Factory Communication Systems. Dresden, Germany: IEEE, 2008. 89–92 [37] Junyoung H, Jiman H, Yookun C. Earq: Energy aware routing forreal-time and reliable communication in wireless industrial sensornetworks. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2009, 5(1): 3−11 doi: 10.1109/TII.2008.2011052 [38] Wei Y H, Leng Q, Han S, Aloysius K M, Zhang W L. Rt-WiFi: Real-time high-speed communication protocol for wireless cyber-physical control applications. In: Proceedings of the IEEE 34th Real-Time Systems Symposium. Vancouver, Canada: IEEE, 2013. 140–149 [39] Tian G S, Seyit C, Tian Y C. A deadline-constrained 802.11MAC protocol with QoS differentiation for soft real-time control. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2016, 12(2): 544−554 doi: 10.1109/TII.2016.2520398 [40] Lucia S, Gianluca C, Stefano S, Adriano V, Claudio Z. Enhancing communication determinism in WiFi networks for softreal-time industrial applications. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2009, 13(2): 866−876 [41] Leng Q, Wei Y H, Han S, Aloysius K, Zhang W L. Improving control performance by minimizing jitter in RT-WiFi networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Real-Time Systems Symposium. Rome, Italy: IEEE, 2014. 63–73 [42] Seijo O, Val I, Fernandez J L. w-SHARP: Implementation of a high-performance wireless time-sensitive network for low latency and ultra-low cycle time industrial applications. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2020, 17(5): 3651−3662 [43] Yun Z L, Wu P, Zhou S L, Mok A K, Mark N, Han S. RT-WiFi on software-defined radio: Design and implementation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE 28th Real-Time and Embedded Technology and Applications Symposium. Milano, Italy: IEEE, 2022. 254–266 [44] Morgado A, Huq K M S, Mumtaz S. A survey of 5G technologies: Regulatory, standardization and industrial perspectives. Digital Communications and Networks, 2018, 4(2): 87−97 doi: 10.1016/j.dcan.2017.09.010 [45] Garcia-Rodriguez A, Lopez-Perez D, Galati-Giordano L. IEEE 802.11 be: WiFi 7 strikes back. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2021, 59(4): 102−108 doi: 10.1109/MCOM.001.2000711 [46] Azzino T, Ropitault T, Zorzi M. Scheduling the data transmission interval in IEEE 802.11 ad: A reinforcement learning approach. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Computing, Networking and Communications. Big Island, USA: IEEE, 2020. 602–607 [47] Chen C, Li J C, Balasubramaniam V, Wu Y Q, Zhang Y R, Wan S H. Contention resolution in WiFi 6-enabled Internet of Things based on deep learning. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(7): 5309−5320 doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3037774 [48] Cheng C Y, Li C Y, Chiu C H. An experience driven design for IEEE 802.11ac rate adaptation based on reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM 2021-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications. Vancouver, Canada: IEEE, 2021. 1–10 [49] Sha M, Dolvara G, Wu C J, Lu C Y. Empirical study and enhancements of industrial wireless sensor actuator network protocols. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2017, 4(3): 696−704 doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2017.2653362 [50] Abusayeed S, Chengjie W, Paras B T, Xu Y, Fu Y, Lu C Y. Near optimal rate selection for wireless control systems. IEEE Real-Time and Embedded Technology and Applications Symposium, 2012, 13(45): 231−240 [51] Pablo S, Zhang H B, Johansson M. Deadline-constrained transmission scheduling and data evacuation in wirelesshart networks. In: Proceedings of the European Control Conference. Budapest, Hungary: IEEE, 2009. 4320–4325 [52] Venkata P M, Dali I, Mahbubur R, Abusayeed S. A utilization-based approach for schedulability analysis in wireless control systems. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Industrial Internet. Bellevue, USA: IEEE, 2008. 49–58 [53] 王恒, 朱元杰, 杨杭, 王平. 基于优先级分类的工业无线网络确定性调度算法. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(2): 373−384Wang Heng, Zhu Yuan-Jie, Yang Hang, Wang Ping. Deterministic scheduling algorithm with priority classification for industrial wireless networks. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(2): 373−384 [54] Felix D, Zhang T T, Mikael G. End-to-end reliability-aware scheduling for wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2016, 12(2): 758−767 doi: 10.1109/TII.2014.2382335 [55] Alharbi N, Mackenzie L, Pezaros D. Enhancing graph routing algorithm of industrial wireless sensor networks using the covariance-matrix adaptation evolution strategy. Sensors, 2022, 22(19): Article No. 7462 doi: 10.3390/s22197462 [56] Park M, Paek J. On-demand scheduling of command and responses for low-power multihop wireless networks. Sensors, 2021, 21(3): 738−753 doi: 10.3390/s21030738 [57] Abusayeed S, Xu Y, Lu C Y, Chen Y X. End-to-end communication delay analysisin industrial wireless networks. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2015, 64(5): 1361−1374 doi: 10.1109/TC.2014.2322609 [58] Abusayeed S, Dolvara G, Paras T, Mo S, Lu C Y. Schedulability analysis under graph routing in wirelesshart networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Real-Time Systems Symposium. San Antonio, USA: IEEE, 2015. 165–174 [59] Song H, Zhu X M, Aloysius K M, Chen D J, Nixon M. Reliable and real-time communication in industrial wireless meshnetworks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Real-Time and Embedded Technology and Applications Symposiumn. Chicago, USA: IEEE, 2011. 3–12 [60] Terraneo F, Polidori P, Leva A, Fornaciari W. TDMA-MAC: Real-time and multi-hop in the same wireless mac. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Real-Time Systems Symposium. Nashville, USA: IEEE, 2018. 277–287 [61] Yu G, Tian H, Lin M G, Xu J H. Spatiotemporal delay control for low-duty-cycle sensor networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Real-Time Systems Symposium. Washington DC, USA: IEEE, 2009. 127–137 [62] Kiszka J, Wagner B. RT-Net: A flexible hard real-time networking framework. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Emerging Technologies and Factory Automation. Prague, Czech Republic: IEEE, 2005. 449–456 [63] Kang X H, Wang W N, José J, Ying L. On the performance of largest-deficit-first for scheduling real-time traffic in wireless networks. ACM Transactions on Networking, 2016, 24(1): 72−84 doi: 10.1109/TNET.2014.2360365 [64] Abusayeed S, You X, Lu C Y, Chen Y X. Real-time scheduling for wirelesshart networks. In: Proceedings of the 31st IEEE Real-Time Systems Symposium. San Diego, USA: IEEE, 2010. 150–159 [65] Harms O, Landsiedel O. MASTER: Long-term stable routing and scheduling in low-power wireless networks. In: Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Distributed Computing in Sensor Systems. Marina del Rey, USA: IEEE, 2020. 86–94 [66] Harms O, Landsiedel O. Opportunistic routing and synchronous transmissions meet TSCH. In: Proceedings of the IEEE 46th Conference on Local Computer Networks. Edmonton, Canada: IEEE, 2021. 107–114 [67] Chilukuri S, Piao G, Lugones D. Deadline-aware TDMA scheduling for multihop networks using reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the IFIP Networking Conference. Espoo, Finland: IEEE, 2021. 1–9 [68] Chilukuri S, Pesch D. RECCE: Deep reinforcement learning for joint routing and scheduling in time-constrained wireless networks. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 32053−32063 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3047711 [69] Paulo T. Event-triggered real-time scheduling of stabilizing control tasks. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2007, 52(9): 1680−1685 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2007.904277 [70] Wang X F, Michael D L. Self-triggered feedback control systems with finite-gain l2 stability. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2009, 54(3): 452−467 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2009.2012973 [71] Lunze J, Lehmann D. A state-feedback approach to event-based control. Automatica, 2010, 46(1): 211−215 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2009.10.035 [72] Jin X, Saifullah A, Lu C Y, Zeng P. Real-time scheduling for event-triggered and time-triggered flows in industrial wireless sensor-actuator networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM IEEE Conference on Computer Communications. Paris, France: IEEE, 2019. 1684–1692 [73] Hong S Y, Han X B, Sharon H G. Online data link layer scheduling in wireless networked control systems. In: Proceedings of the 27th Euromicro Conference on Real-Time Systems. Lund, Sweden: IEEE, 2015. 57–65 [74] Li B, Nie L S, Wu C J, Humberto G, Lu C Y. Incorporating emergency alarms in reliable wireless process control. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Cyber-Physical System. Seattle, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, 2015. 218–227 [75] Xia C Q, Xi J, Kong L H, Zeng P. Scheduling for emergency tasks in industrial wireless sensor networks. Sensors, 2017, 17(7): Article No. 1674 doi: 10.3390/s17071674 [76] Jin X, Kong F X, Kong L H, Wang H H, Xia C Q. A hierarchical data transmission framework for industrial wireless sensor and actuator networks. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2017, 13(4): 2019−2029 doi: 10.1109/TII.2017.2685689 [77] Kristofer S J P, Lance D. TSMP: Time synchronized mesh protocol. In: Proceedings of the IASTED Distributed Sensor Networks. Crete, Greece: IEEE, 2008. 391–398 [78] Dimitri B. Nonlinear Programming: 3nd Edition. Athena Scientific. Nashua: Athena Scientific, 2016. 97–123 [79] Hou I H, Borkar V, Kumar P R. A theory of QoS for wireless. In: Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM. Rio de Janeiro, Brazil: IEEE, 2009. 486–494 [80] Ma Y H, Guo J L, Wang Y B, Chakrabarty A, Ahn H J, Lu C Y. Optimal dynamic scheduling of wireless networked control systems. In: Proceedings of the 10th ACM/IEEE International Conference on Cyber-Physical Systems. Montreal, Canada: Association for Computing Machinery, 2019. 77–89 [81] Saifullah A, Xu Y, Lu C Y, Chen Y X. Real-time scheduling for wirelesshart networks. In: Proceedings of the Real-time Systems Symposium. San Diego, USA: IEEE, 2011. 150–159 [82] Karadag G, Iqbal M S, Coleri S. Optimal power control, scheduling, and energy harvesting for wireless networked control systems. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(3): 1789−1801 doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2020.3042792 [83] Yang G K, Myung J L. Scheduling multi-channel and multi-timeslot in time constrained wireless sensor networks via simulated annealing and particle swarm optimization. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2014, 52(1): 122−129 doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2014.6710073 [84] Thong H, Fabrice T, Won J H. On the interest of opportunistic anycast scheduling for wireless low power lossy networks. Computer Communications, 2017, 104: 55−66 doi: 10.1016/j.comcom.2016.06.001 [85] Iqbal M S, Sadi Y, Coleri S. Minimum length scheduling for discrete-rate full-duplex wireless powered communication networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2022, 21(1): 135−148 doi: 10.1109/TWC.2021.3094138 [86] Zoppi S, Champati J P, Gross J, Kellerer W. Scheduling of wireless edge networks for feedback-based interactive applications. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2022, 70(5): 3295−3309 doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2022.3163761 [87] Palattella M, Accettura N, Dohler M, Grieco L, Boggia G. Traffic aware scheduling algorithm for reliable low-power multi-hop IEEE 802.15.4e networks. In: Proceedings of the 23rd IEEE International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications. Sydney, Australia: IEEE, 2012. 327–332 [88] Wu C J, Gunatilaka D, Sha M, Lu C Y. Real-time wireless routing for industrial internet of things. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Internet-of-Things Design and Implementation. Orlando, USA: IEEE, 2018. 261–266 [89] Jonsson M, Kunert K. Towards reliable wireless industrial communication with real-time guarantees. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2009, 5(4): 429−442 doi: 10.1109/TII.2009.2031921 [90] Yang D, Xu Y Z, Wang H C, Zheng T, Zhang H, Zhang H K, et al. Assignment of segmented slots enabling reliable real-time transmission in industrial wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2015, 62(6): 3966−3977 [91] Munir S, Lin S, Hoque E, Shahriar S M. Addressing burstiness for reliable communicationand latency bound generation in wireless sensor networks. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Information Processing in Sensor Networks. Stockholm, Sweden: Association for Computing Machinery, 2010. 303–314 [92] Gamba G, Tramarin F, Willigt A. Retransmission strategies for cyclic polling over wireless channels in the presence of interference. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2009, 6(3): 405−415 [93] Shi H, Zheng M, Liang W. AODR: An automatic on-demand retransmission scheme for WIA-FA networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(6): 6094−6107 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3076988 [94] Venkata P M, Abusayeed S, Sanjay M. A distributed real-time scheduling system for industrial wireless networks. ACM Transactions on Embedded Computing Systems, 2021, 20(5): 1−28 [95] Rekik S, Baccour N, Jmaiel M, Drira K, Grieco L. Autonomous and traffic-aware scheduling for tsch networks. Computer Networks, 2018, 135: 201−212 doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2018.02.023 [96] Shi J Y, Sha M, Yang Z C. Distributed graph routing and scheduling for industrial wireless sensor-actuator networks. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2019, 27(4): 1669−1682 doi: 10.1109/TNET.2019.2925816 [97] Kim S, Kim H S, Kim C. ALICE: Autonomous link-based cell scheduling for TSCH. In: Proceedings of the 18th ACM/IEEE International Conference on Information Processing in Sensor Networks. Montreal, Canada: Association for Computing Machinery, 2019. 121–132 [98] Jeong S, Paek J, Kim H S, Bahk S. TESLA: Traffic-aware elastic slotframe adjustment in TSCH networks. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 130468−130483 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2940457 [99] Jeong S, Kim H S, Paek J, Bahk S. OST: On-demand tsch scheduling with traffic-awareness. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Communications. Toronto, Canada: IEEE, 2020. 69–78 [100] Cheng X, Sha M. Autonomous traffic-aware scheduling for industrial wireless sensor-actuator networks. Association for Computing Machinery, 2021, 19(2): 1−25 [101] Osman M, Nabki F. OSCAR: An optimized scheduling cell allocation algorithm for convergecast in IEEE 802.15. 4e TSCH networks. Sensors, 2021, 21(7): Article No. 2493 doi: 10.3390/s21072493 [102] Kim S, Kim H S, Kim C. A3: Adaptive autonomous allocation of TSCH slots. In: Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Information Processing in Sensor Networks. Nashville, USA : Association for Computing Machinery, 2021. 299–314 [103] Rhee I, Warrier A, Min J, Xu L. DRAND: Distributed randomized tdma scheduling for wireless ad hoc networks. In: Proceedings of the 7th ACM International Symposium On Mobile Ad Hoc Networking And Computing. Florence, Italy: Association for Computing Machinery, 2006. 190–201 [104] Tinka A, Watteyne T, Kristofer S J, Bayen A M. A decentralized scheduling algorithm for time synchronized channel hopping. In: Proceedings of Ad Hoc Networks Second International Conference. Victoria, Canada: Springer, 2010. 201–216 [105] Bilgili A K. DIVA: A distributed divergecast scheduling algorithm for IEEE 802.15.4e TSCH networks. Wireless Networks, 2019, 25(2): 625−635 [106] Modekurthy V P, Saifullah A, Madria S. Distributedhart: A distributed real-time scheduling system for wirelesshart networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Real-Time and Embedded Technology and Applications Symposium. Montreal, Canada: IEEE, 2019. 216–227 [107] Kang H, Zhao Y N, Mei F. A graph coloring based tdma scheduling algorithm for wireless sensor networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 2013, 72(2): 1005−1022 doi: 10.1007/s11277-013-1052-9 [108] Abusayeed S, Xu Y, Lu C Y, Chen Y X. Distributed channel allocation protocolsfor wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2014, 25(9): 2264−2274 doi: 10.1109/TPDS.2013.185 [109] Nicola A, Palattella M R, Gennaro B, Alfredo G, Mischa D. Decentralized traffic aware scheduling for multi-hop low power lossy networks in the internet of things. In: Proceedings of the IEEE 14th International Symposium on “A World of Wireless, Mobile and Multimedia Networks”. Madrid, Spain: IEEE, 2013. 1–6 [110] Soua R, Minet P, Livolant E. Wave: A distributed scheduling algorithm for convergecast in IEEE 802.15.4e TSCH networks. European Transactions on Telecommunications, 2016, 27(4): 557−575 [111] Emiliano S, Paolo F, Fernandes C D, Stefano R, Pasetti M, Alessandra F, et al. EDSF: Efficient distributed scheduling function for IETF 6TiSCH-based industrial wireless networks. Mobile Networks and Applications, 2022, 27(6): 2244−2253 doi: 10.1007/s11036-022-02004-7 [112] Marco Z, Luca M, Silvia S. Synchronous transmissions in low-power wireless: A survey of communication protocols and network services. ACM Computing Surveys, 2020, 53(6): 1−39 [113] Jonathan O, Yang F, Sam M, Danny H. Zero-wire: A deterministic and low-latency wireless bus through symbol-synchronous transmission of optical signals. In: Proceedings of the 18th Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems. Virtual Event: Association for Computing Machinery, 2020. 164–178 [114] Matteo T, Gabriel G, Timofei I, Manuel M J, Pietro P G. The wireless control bus: Enabling efficient multi-hop event-triggered control with concurrent transmissions. ACM Transactions on Cyber-Physical Systems, 2022, 6(1): 1−25 [115] Lorawan 1.1 specification [Online], available: https://lora-alliance.org/resource_hub/lorawan-specification-v1-1, October 11, 2017 [116] Luca L, Filippo B, Lucia L B. Rt-loRa: A medium access strategy to support real-time flows over LoRa-based networks for industrial IoT applications. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(6): 10812−10823 doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2942776 [117] Quy L H, Hoon O. A real-time lora protocol using logical frame partitioning for periodic and aperiodic data transmission. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(16): 15401−15412 doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2022.3162019 [118] Emiliano S, Paolo F, Fernandes C D, Stefano R, Pasetti M, Alessandra F, et al. Lorawan range extender for industrial IoT. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2019, 16(8): 5607−5616 -




 下载:
下载: