Domain Adaptive Object Detection Based on Attention Mechanism and Cycle Domain Triplet Loss
-
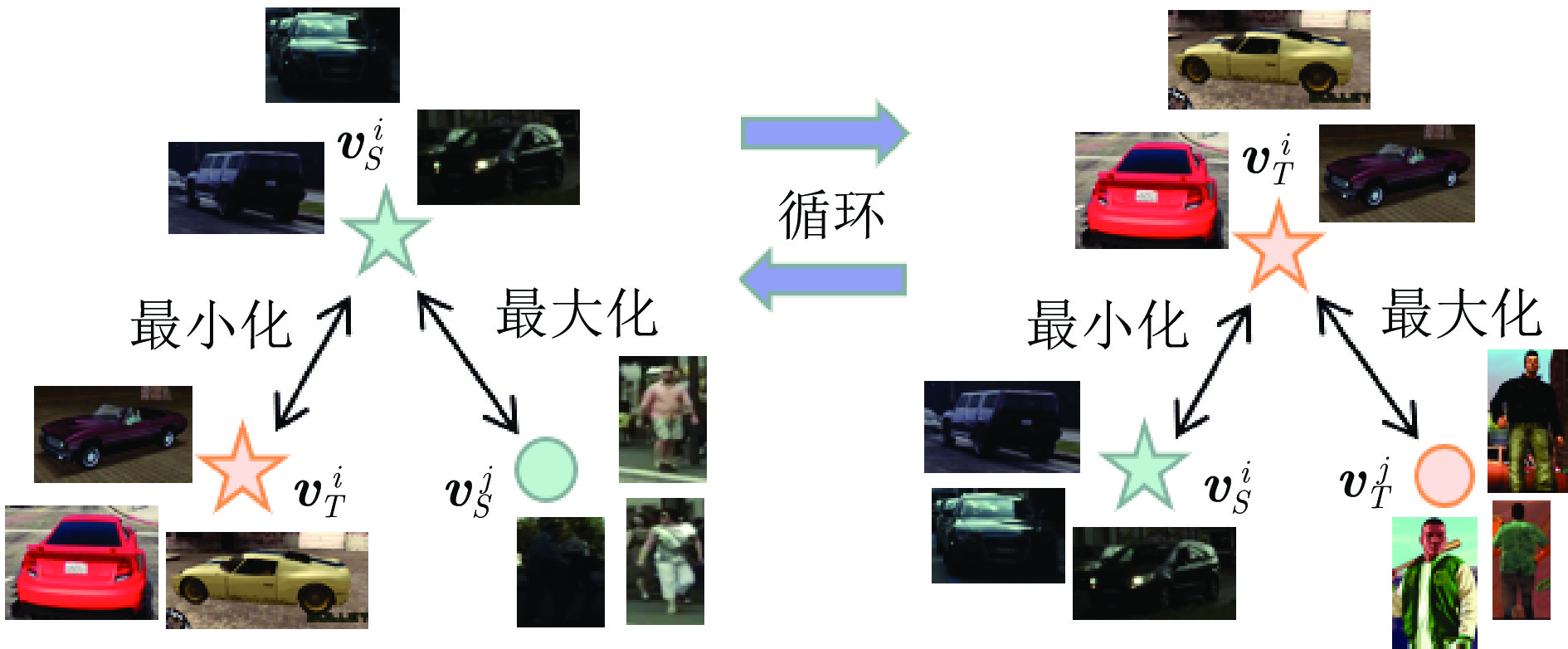
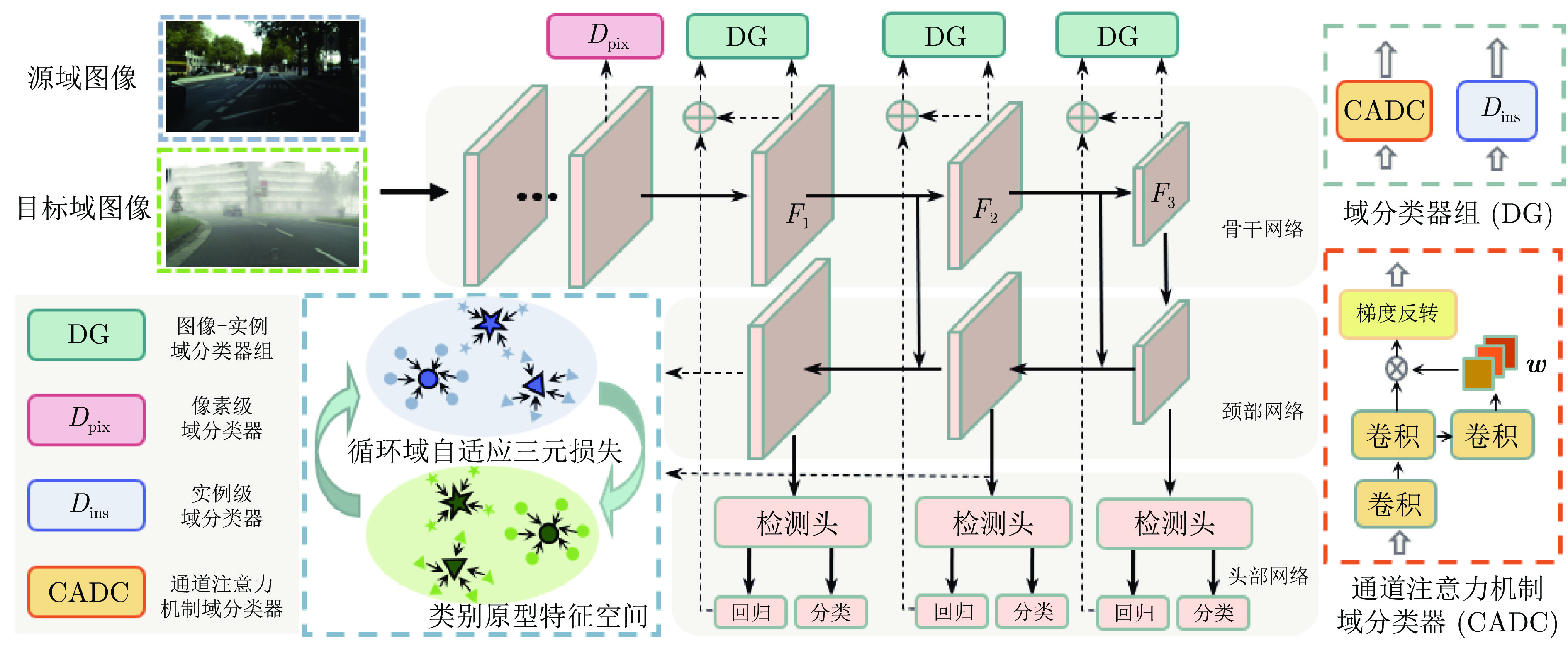
摘要: 目前大多数深度学习算法都依赖于大量的标注数据并欠缺一定的泛化能力. 无监督域自适应算法能提取到已标注数据和未标注数据间隐式共同特征, 从而提高算法在未标注数据上的泛化性能. 目前域自适应目标检测算法主要为两阶段目标检测器设计. 针对单阶段检测器中无法直接进行实例级特征对齐导致一定数量域不变特征的缺失, 提出结合通道注意力机制的图像级域分类器加强域不变特征提取. 此外, 对于域自适应目标检测中存在类别特征的错误对齐引起的精度下降问题, 通过原型学习构建类别中心, 设计了一种基于原型的循环域三元损失(Cycle domain triplet loss, CDTL)函数, 从而实现原型引导的精细类别特征对齐. 以单阶段目标检测算法作为检测器, 并在多种域自适应目标检测公共数据集上进行实验. 实验结果证明该方法能有效提升原检测器在目标域的泛化能力, 达到比其他方法更高的检测精度, 并且对于单阶段目标检测网络具有一定的通用性.Abstract: Most current deep learning algorithms rely heavily on large amounts of annotated data and exist deficiency in generalization ability. The unsupervised domain adaptation algorithm can extract the common implicit invariant features from the labeled data and unlabeled data, so that the algorithm can achieve good generalization performance on the unlabeled data. At present, domain adaptation object detection algorithms are mainly designed as two-stage object detectors. For the one-stage object detectors, the difficulty of explicit aligning instance-level features leads to the absence of a number of domain invariant features. In this paper, an image-level domain classifier combined with channel attention mechanism is proposed to strengthen domain invariant feature extraction. In addition, to address the issue of reduced accuracy caused by inaccurate alignment of category features in domain adaptive object detection, a prototype based cycle domain triplet loss (CDTL) function was designed to construct category centers through prototype learning, thereby we can achieve precise category feature alignment guided by prototypes. One-stage object detection algorithms are used as detectors, and experiments are conducted on various domain adaptive object detection public datasets. The experimental results show that our method can effectively improve the generalization ability of the original detector on the target domain and achieves higher detection accuracy than other methods. Meanwhile, the experiment on different detector indicate our method is universal for the one-stage object detection network.
-
表 1 不同方法在CityScapes→FoggyCityScapes数据集上的对比实验结果(%)
Table 1 The results of different methods on the CityScapes→FoggyCityScapes dataset (%)
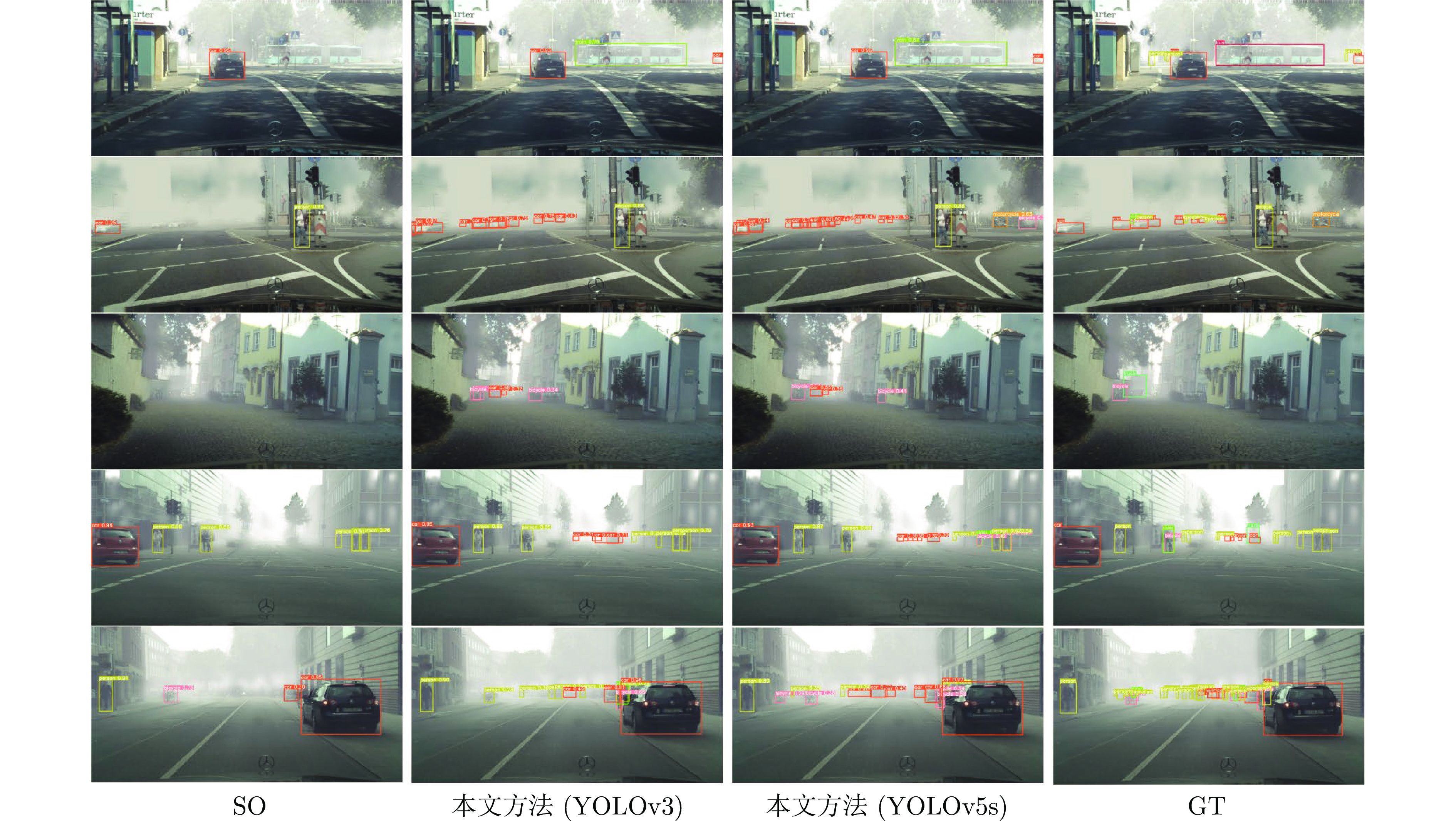
方法 检测器 person rider car truck bus motor bike train mAP mGP DAF[10] Faster R-CNN 25.0 31.0 40.5 22.1 35.3 20.0 27.1 20.2 27.7 38.8 SWDA[11] Faster R-CNN 29.9 42.3 43.5 24.5 36.2 30.0 35.3 32.6 34.3 70.0 C2F[14] Faster R-CNN 34.0 46.9 52.1 30.8 43.2 34.7 37.4 29.9 38.6 79.1 CAFA[16] Faster R-CNN 41.9 38.7 56.7 22.6 41.5 24.6 35.5 26.8 36.0 81.9 ICCR-VDD[21] Faster R-CNN 33.4 44.0 51.7 33.9 52.0 34.2 36.8 34.7 40.0 — MeGA[20] Faster R-CNN 37.7 49.0 52.4 25.4 49.2 34.5 39.0 46.9 41.8 91.1 DAYOLO[28] YOLOv3 29.5 27.7 46.1 9.1 28.2 12.7 24.8 4.5 36.1 61.0 本文方法(v3) YOLOv3 34.0 37.2 55.8 31.4 44.4 22.3 30.8 50.7 38.3 83.9 MS-DAYOLO[31] YOLOv4 39.6 46.5 56.5 28.9 51.0 27.5 36.0 45.9 41.5 68.6 A-DAYOLO[32] YOLOv5 32.8 35.7 51.3 18.8 34.5 11.8 25.6 16.2 28.3 — S-DAYOLO[34] YOLOv5 42.6 42.1 61.9 23.5 40.5 24.4 37.3 39.5 39.0 69.9 本文方法(v5) YOLOv5s 30.9 37.4 53.3 23.8 39.5 24.2 29.9 35.0 34.3 83.8 注: “—”表示该方法没有进行此实验; (v3)表示检测器为YOLOv3; (v5)表示检测器为YOLOv5s; 加粗数值表示对比实验中的最佳结果. 表 2 不同方法在SunnyDay→DuskRainy数据集上的对比实验结果(%)
Table 2 The results of different methods on the SunnyDay→DuskRainy dataset (%)
方法 检测器 bus bike car motor person rider truck mAP $\Delta{\rm{mAP}}$ DAF[10] Faster R-CNN 43.6 27.5 52.3 16.1 28.5 21.7 44.8 33.5 5.2 SWDA[11] Faster R-CNN 40.0 22.8 51.4 15.4 26.3 20.3 44.2 31.5 3.2 ICCR-VDD[21] Faster R-CNN 47.9 33.2 55.1 26.1 30.5 23.8 48.1 37.8 9.5 本文方法(v3) YOLOv3 50.1 24.9 70.7 24.2 39.1 19.0 53.2 40.2 7.4 本文方法(v5) YOLOv5s 46.2 22.1 68.2 16.5 34.8 17.5 50.5 36.5 9.4 注: $\Delta {\rm{mAP}}$表示mAP的涨幅程度. 表 3 不同方法在SunnyDay→NightRainy数据集上的对比实验结果(%)
Table 3 The results of different methods on the SunnyDay→NightRainy dataset (%)
方法 检测器 bus bike car motor person rider truck mAP $\Delta {\rm{mAP}}$ DAF[10] Faster R-CNN 23.8 12.0 37.7 0.2 14.9 4.0 29.0 17.4 1.1 SWDA[11] Faster R-CNN 24.7 10.0 33.7 0.6 13.5 10.4 29.1 17.4 1.1 ICCR-VDD[21] Faster R-CNN 34.8 15.6 38.6 10.5 18.7 17.3 30.6 23.7 7.4 本文方法(v3) YOLOv3 45.0 8.2 51.1 4.0 20.9 9.6 37.9 25.3 5.1 本文方法(v5) YOLOv5s 40.7 9.3 45.0 0.6 12.8 9.2 32.5 21.5 4.7 表 4 KITTI→CityScapes和Sim10k→CityScapes数据集上的对比实验结果(%)
Table 4 The results of different methods on KITTI→CityScapes and Sim10k→CityScapes datasets (%)
表 5 CityScapes→FoggyCityScapes数据集上基于YOLOv3的消融实验结果(%)
Table 5 The results of ablation experiment on CityScapes→FoggyCityScapes dataset based on YOLOv3 (%)
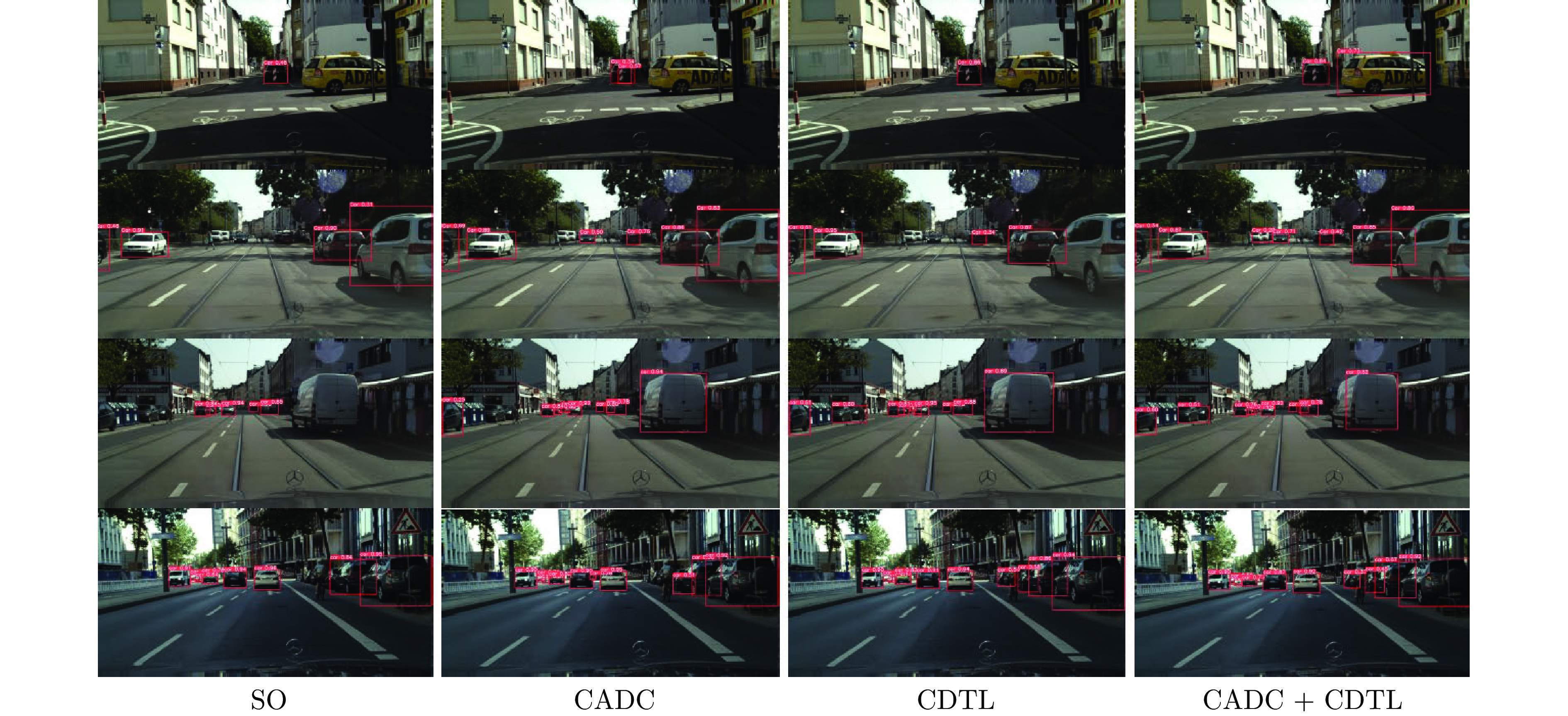
方法 person rider car truck bus motor bike train mAP SO 29.8 35.0 44.7 20.4 32.4 14.8 28.3 21.6 28.4 CADC 34.4 38.0 54.7 24.4 45.0 21.2 32.1 49.1 37.2 CDTL 31.1 38.0 46.7 28.9 34.5 23.4 27.8 13.7 30.5 CADC + CDTL 34.0 37.2 55.8 31.4 44.4 22.3 30.8 50.7 38.3 Oracle 34.9 38.8 55.9 25.3 45.0 22.6 33.4 49.1 40.2 表 6 CityScapes→FoggyCityScapes数据集上基于YOLOv5s的消融实验结果(%)
Table 6 The results of ablation experiment on CityScapes→FoggyCityScapes dataset based on YOLOv5s (%)
方法 person rider car truck bus motor bike train mAP SO 26.9 33.1 39.9 8.9 21.1 11.3 24.8 4.9 21.4 CADC 32.6 37.1 52.7 26.8 38.1 23.0 38.1 32.6 34.1 CDTL 29.7 36.7 43.2 13.1 25.5 17.1 28.7 13.1 26.2 CADC + CDTL 30.9 37.4 53.3 23.8 39.5 24.2 29.9 35.0 34.3 Oracle 34.8 37.9 57.5 24.4 42.7 23.1 33.2 40.8 36.8 表 7 SunnyDay→DuskRainy数据集上基于YOLOv3的消融实验结果(%)
Table 7 The results of ablation experiment on SunnyDay→DuskRainy dataset based on YOLOv3 (%)
方法 bus bike car motor person rider truck mAP SO 43.7 14.3 68.4 12.0 31.5 10.9 48.7 32.8 CADC 50.0 22.6 70.8 23.2 38.4 18.7 53.5 39.6 CDTL 45.4 20.1 69.2 15.2 34.8 17.2 47.8 35.7 CADC + CDTL 50.1 24.9 70.7 24.2 39.1 19.0 53.2 40.2 表 8 SunnyDay→DuskRainy数据集上基于YOLOv5s的消融实验结果(%)
Table 8 The results of ablation experiment on SunnyDay→DuskRainy dataset based on YOLOv5s (%)
方法 bus bike car motor person rider truck mAP SO 37.2 8.4 63.8 5.5 23.7 7.9 43.4 27.1 CADC 45.6 22.1 68.2 16.6 34.5 15.4 50.1 35.9 CDTL 41.6 13.1 65.5 7.6 29.7 10.2 44.9 30.4 CADC + CDTL 46.2 22.1 68.2 16.5 34.8 17.5 50.5 36.5 表 9 SunnyDay→NightRainy数据集上基于YOLOv3的消融实验结果(%)
Table 9 The results of ablation experiment on SunnyDay→NightRainy dataset based on YOLOv3 (%)
方法 bus bike car motor person rider truck mAP SO 39.2 5.1 44.2 0.2 14.8 6.9 30.7 20.2 CADC 44.4 8.1 50.9 0.6 20.2 11.3 38.3 24.8 CDTL 40.4 8.2 45.8 0.6 16.2 7.2 33.4 21.7 CADC + CDTL 45.0 8.2 51.1 4.0 20.9 9.6 37.9 25.3 表 10 SunnyDay→NightRainy数据集上基于YOLOv5s的消融实验结果(%)
Table 10 The results of ablation experiment on SunnyDay→NightRainy dataset based on YOLOv5s (%)
方法 bus bike car motor person rider truck mAP SO 25.4 3.2 36.3 0.2 9.1 4.4 20.8 14.2 CADC 38.7 8.3 42.7 0.3 12.3 6.4 32.0 20.1 CDTL 34.3 6.2 44.2 0.5 11.2 8.7 30.3 19.3 CADC + CDTL 40.7 9.3 45.0 0.6 12.8 9.2 32.5 21.5 表 11 KITTI→CityScapes和Sim10k→CityScapes数据集上的对比实验结果(%)
Table 11 The results of different methods on KITTI→CityScapes and Sim10k→CityScapes datasets (%)
方法 KITTI Sim10k YOLOv3 SO 59.6 58.5 CADC 60.5 59.6 CDTL 60.5 60.8 CADC + CDTL 61.1 59.8 Oracle 64.7 64.7 YOLOv5s SO 54.0 53.1 CADC 59.5 58.6 CDTL 59.0 60.3 CADC + CDTL 60.0 59.0 Oracle 65.9 65.9 表 12 本文方法在VOC→Clipart1k上的实验(%)
Table 12 The experiment of our method on VOC→Clipart1k (%)
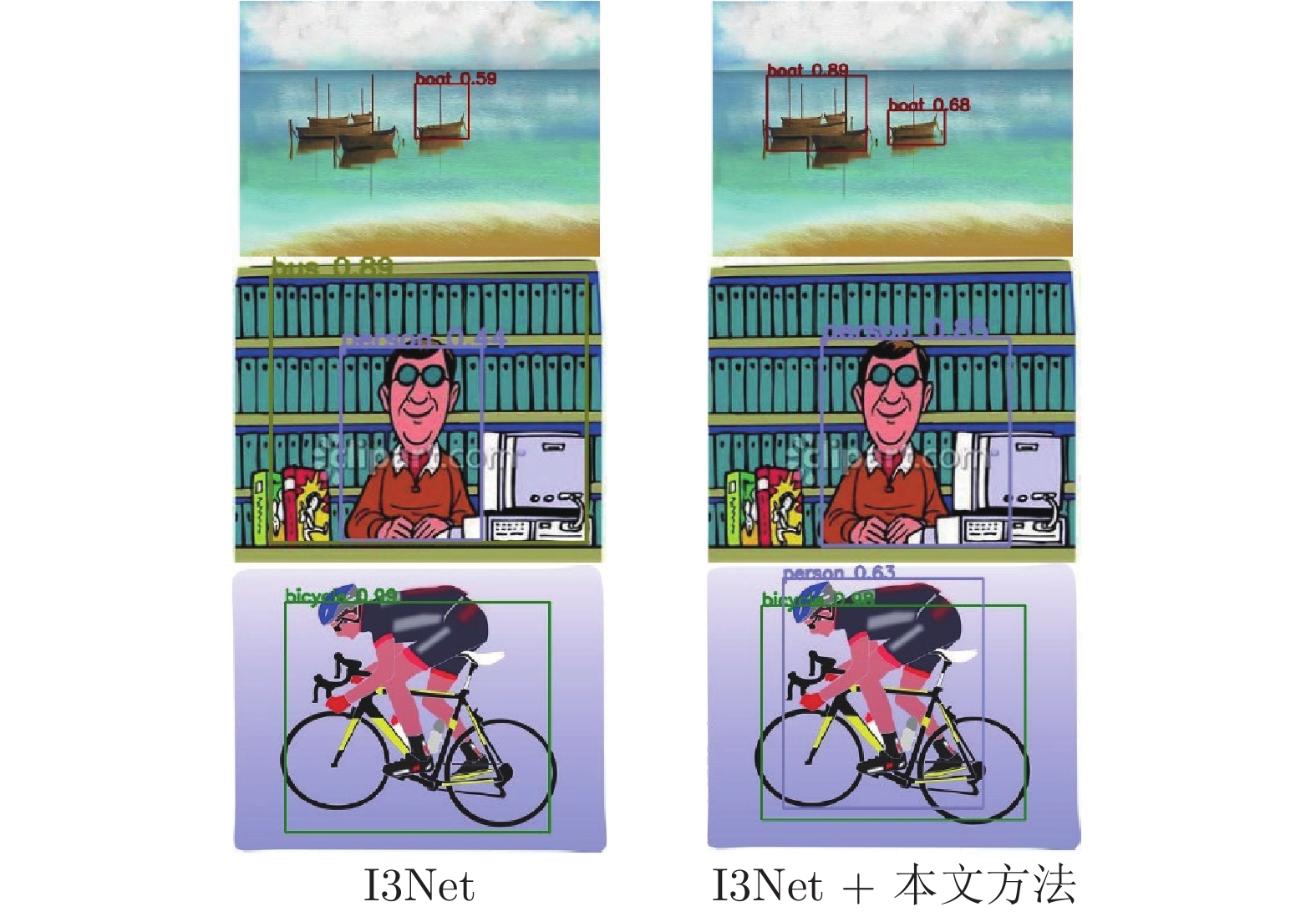
方法 aero bcycle bird boat bottle bus car cat chair cow table dog hrs bike prsn plnt sheep sofa train tv mAP I3Net 23.7 66.2 25.3 19.3 23.7 55.2 35.7 13.6 37.8 35.5 25.4 13.9 24.1 60.3 56.3 39.8 13.6 34.5 56.0 41.8 35.1 I3Net + CDTL 23.3 61.6 27.8 17.1 24.7 54.3 39.8 12.3 41.4 34.1 32.2 15.5 27.6 77.9 57.0 37.4 5.50 31.3 51.8 47.8 36.0 I3Net + CDTL + ${\rm{CADC}}^*$ 31.2 60.4 31.8 19.4 27.0 63.3 40.7 13.7 41.1 38.4 27.2 18.0 25.5 67.8 54.9 37.2 15.5 36.4 54.8 47.8 37.6 表 13 本文方法在VOC→Comic2k上的实验(%)
Table 13 The experiment of our method on VOC→Comic2k (%)
方法 bike bird car cat dog person mAP I3Net 44.9 17.8 31.9 10.7 23.5 46.3 29.2 I3Net + CDTL 43.7 15.1 31.5 11.7 18.6 46.9 27.9 I3Net + CDTL + CADC* 47.8 16.0 33.8 15.1 24.4 43.5 30.1 表 14 本文方法在VOC→Watercolor2k上的实验(%)
Table 14 The experiment of our method on VOC→Watercolor2k (%)
方法 bike bird car cat dog person mAP I3Net 81.3 49.6 43.6 38.2 31.3 61.7 51.0 I3Net + CDTL 79.5 47.2 41.7 33.5 35.4 60.3 49.6 I3Net + CDTL + CADC* 84.1 45.3 46.6 32.9 31.4 61.4 50.3 表 15 像素级对齐对网络的影响(%)
Table 15 The impact of pixel alignment to network (%)
方法 检测器 C→F K→C S→C CDTL + CADC YOLOv3 35.9 59.8 58.4 CDTL + CADC + $D_{{\rm{pixel}}}$ YOLOv3 37.2 60.5 59.6 CDTL + CADC YOLOv5s 32.7 58.9 56.8 CDTL + CADC + $D_{{\rm{pixel}}}$ YOLOv5s 34.1 59.5 58.6 表 16 通道注意力域分类器中损失函数的选择
Table 16 The choice of loss function in channel attention domain classifier
检测器 $F_1$ $F_2$ $F_3$ mAP (%) YOLOv3/v5s CE CE CE 35.8/32.7 YOLOv3/v5s CE CE FL 36.4/33.2 YOLOv3/v5s CE FL FL 37.2/34.1 YOLOv3/v5s FL FL FL 37.0/33.5 -
[1] Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Lake Tahoe, USA: NIPS, 2012. 1106−1114 [2] Bottou L, Bousquet O. The tradeoffs of large scale learning. In: Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: Curran Associates Inc., 2007. 161−168 [3] Shen J, Qu Y R, Zhang W N, Yu Y. Wasserstein distance guided representation learning for domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the 32nd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. New Orleans, USA: AAAI, 2018. 4058−4065 [4] 皋军, 黄丽莉, 孙长银. 一种基于局部加权均值的领域自适应学习框架. 自动化学报, 2013, 39(7): 1037−1052Gao Jun, Huang Li-Li, Sun Chang-Yin. A local weighted mean based domain adaptation learning framework. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(7): 1037−1052 [5] Ganin Y, Ustinova E, Ajakan H, Germain P, Larochelle H, Laviolette F, et al. Domain-adversarial training of neural networks. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2016, 17(1): 2096−2030 [6] Goodfellow I, Pouget-Abadie J, Mirza M, Xu B, Warde-Farley D, Ozair S, et al. Generative adversarial networks. Communications of the ACM, 2020, 63(11): 139−144 doi: 10.1145/3422622 [7] 郭迎春, 冯放, 阎刚, 郝小可. 基于自适应融合网络的跨域行人重识别方法. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(11): 2744−2756Guo Ying-Chun, Feng Fang, Yan Gang, Hao Xiao-Ke. Cross-domain person re-identification on adaptive fusion network. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(11): 2744−2756 [8] 梁文琦, 王广聪, 赖剑煌. 基于多对多生成对抗网络的非对称跨域迁移行人再识别. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(1): 103−120Liang Wen-Qi, Wang Guang-Cong, Lai Jian-Huang. Asymmetric cross-domain transfer learning of person re-identification based on the many-to-many generative adversarial network. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(1): 103−120 [9] Ren S Q, He K M, Girshick R, Sun J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In: Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Montreal, Canada: MIT Press, 2015. 91−99 [10] Chen Y H, Li W, Sakaridis C, Dai D X, Van Gool L. Domain adaptive faster R-CNN for object detection in the wild. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 3339−3348 [11] Saito K, Ushiku Y, Harada T, Saenko K. Strong-weak distribution alignment for adaptive object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 6949−6958 [12] Lin T Y, Goyal P, Girshick R, He K M, Dollar P. Focal loss for dense object detection. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(2): 318−327 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2858826 [13] Shen Z Q, Maheshwari H, Yao W C, Savvides M. SCL: Towards accurate domain adaptive object detection via gradient detach based stacked complementary losses. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1911.02559, 2019. [14] Zheng Y T, Huang D, Liu S T, Wang Y H. Cross-domain object detection through coarse-to-fine feature adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 13763−13772 [15] Xu C D, Zhao X R, Jin X, Wei X S. Exploring categorical regularization for domain adaptive object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 11721−11730 [16] Hsu C C, Tsai Y H, Lin Y Y, Yang M H. Every pixel matters: Center-aware feature alignment for domain adaptive object detector. In: Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Glasgow, UK: Springer, 2020. 733−748 [17] Chen C Q, Zheng Z B, Ding X H, Huang Y, Dou Q. Harmonizing transferability and discriminability for adapting object detectors. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 8866−8875 [18] Zhu J Y, Park T, Isola P, Efros A A. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 2242−2251 [19] Deng J H, Li W, Chen Y H, Duan L X. Unbiased mean teacher for cross-domain object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Nashville, USA: IEEE, 2021. 4089−4099 [20] Xu M H, Wang H, Ni B B, Tian Q, Zhang W J. Cross-domain detection via graph-induced prototype alignment. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 12352−12361 [21] Wu A M, Liu R, Han Y H, Zhu L C, Yang Y. Vector-decomposed disentanglement for domain-invariant object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Montreal, Canada: IEEE, 2021. 9322−9331 [22] Chen C Q, Zheng Z B, Huang Y, Ding X H, Yu Y Z. I.3Net: Implicit instance-invariant network for adapting one-stage object detectors. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. IEEE, 2021. 12576−12585 [23] 李威, 王蒙. 基于渐进多源域迁移的无监督跨域目标检测. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(9): 2337−2351Li Wei, Wang Meng. Unsupervised cross-domain object detection based on progressive multi-source transfer. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(9): 2337−2351 [24] Rodriguez A L, Mikolajczyk K. Domain adaptation for object detection via style consistency. In: Proceedings of the 30th British Machine Vision Conference. Cardiff, UK: BMVA Press, 2019. [25] Liu W, Anguelov D, Erhan D, Szegedy C, Reed S, Fu C Y, et al. SSD: Single shot MultiBox detector. In: Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Springer, 2016. 21−37 [26] Redmon J, Divvala S, Girshick R, Farhadi A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 779−788 [27] Yolov8 [Online], available: https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov8, February 15, 2023 [28] Zhang S Z, Tuo H Y, Hu J, Jing Z L. Domain adaptive YOLO for one-stage cross-domain detection. In: Proceedings of the 13th Asian Conference on Machine Learning. PMLR, 2021. 785−797 [29] Redmon J, Farhadi A. YOLOv3: An incremental improvement. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1804.02767, 2018. [30] Hnewa M, Radha H. Integrated multiscale domain adaptive YOLO. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2023, 32: 1857−1867 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2023.3255106 [31] Bochkovskiy A, Wang C Y, Liao H Y M. YOLOv4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detection. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2004.10934, 2020. [32] Vidit V, Salzmann M. Attention-based domain adaptation for single-stage detectors. Machine Vision and Applications, 2022, 33(5): Article No. 65 doi: 10.1007/s00138-022-01320-y [33] YOLOv5 [Online], available: https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5, November 28, 2022 [34] Li G F, Ji Z F, Qu X D, Zhou R, Cao D P. Cross-domain object detection for autonomous driving: A stepwise domain adaptative YOLO approach. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles, 2022, 7(3): 603−615 doi: 10.1109/TIV.2022.3165353 [35] Hu J, Shen L, Sun G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 7132−7141 [36] Wang Q L, Wu B G, Zhu P F, Li P H, Zuo W M, Hu Q H. ECA-Net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 11531−11539 [37] Lee H, Kim H E, Nam H. SRM: A style-based recalibration module for convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Seoul, South Korea: IEEE, 2019. 1854−1862 [38] Wang M Z, Wang W, Li B P, Zhang X, Lan L, Tan H B, et al. InterBN: Channel fusion for adversarial unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Multimedia. Virtual Event: ACM, 2021. 3691−3700 [39] Ding S Y, Lin L, Wang G R, Chao H Y. Deep feature learning with relative distance comparison for person re-identification. Pattern Recognition, 2015, 48(10): 2993−3003 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2015.04.005 [40] Snell J, Swersky K, Zemel R. Prototypical networks for few-shot learning. In: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2017. 4080−4090 [41] He K M, Fan H Q, Wu Y X, Xie S N, Girshick R. Momentum contrast for unsupervised visual representation learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 9726−9735 [42] Cordts M, Omran M, Ramos S, Rehfeld T, Enzweiler M, Benenson R, et al. The cityscapes dataset for semantic urban scene understanding. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 3213−3223 [43] Sakaridis C, Dai D X, Van Gool L. Semantic foggy scene understanding with synthetic data. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2018, 126(9): 973−992 doi: 10.1007/s11263-018-1072-8 [44] Yu F, Chen H F, Wang X, Xian W Q, Chen Y Y, Liu F C, et al. Bdd100K: A diverse driving dataset for heterogeneous multitask learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 2633−2642 [45] Geiger A, Lenz P, Stiller C, Urtasun R. Vision meets robotics: The KITTI dataset. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2013, 32(11): 1231−1237 doi: 10.1177/0278364913491297 [46] Johnson-Roberson M, Barto C, Mehta R, Sridhar S N, Rosaen K, Vasudevan R. Driving in the matrix: Can virtual worlds replace human-generated annotations for real world tasks? In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Singapore: IEEE, 2017. 746−753 [47] Everingham M, Van Gool L, Williams C K I, Winn J, Zisserman A. The Pascal visual object classes (VOC) challenge. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2010, 88(2): 303−338 doi: 10.1007/s11263-009-0275-4 [48] Inoue N, Furuta R, Yamasaki T, Aizawa K. Cross-domain weakly-supervised object detection through progressive domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 5001−5009 -




 下载:
下载: