Fractional-order Terminal Sliding-mode Control of MIMO Systems With Unmatched Uncertainties
-
摘要: 针对一类非匹配不确定多输入多输出(Multi-input multi-output, MIMO)系统提出一种分数阶终端滑模控制(Fractional-order terminal sliding-mode, FOTSM)策略, 使系统输出收敛到零而非其邻域. 该方法解除传统反步法控制律设计中, 虚拟控制增益右伪逆矩阵必须存在的严苛限制; 对系统不确定性的假设不局限于慢时变和H2范数有界型扰动, 分析控制增益存在摄动情况下系统的控制问题. 分数阶终端滑模面及其控制律的设计使得虚拟和实际控制信号连续, 削弱抖振现象, 利用自适应滑模切换增益技术解决由控制增益矩阵摄动引起的代数环问题. 最后, 仿真分析验证所提方法的正确性和优越性.Abstract: This paper proposes a fractional-order terminal sliding-mode control (FOTSM) for multi-input multi-output (MIMO) systems with unmatched uncertainties to force the outputs to converge to the equilibrium point rather than their neighborhoods. The control method breaks through the limitation in traditional back-stepping control that the right Moore-Penrose pseudo inverse of the gain matrix of the virtual control signal must exist. The proposed control method can deal with uncertainties, which are not limited to being slow time-varying or H2 norm-bounded. Besides, the method can apply to the system with uncertain control gain. Meanwhile, an adaptive sliding mode control law is designed to compensate for the uncertainties caused by the gain matrix variation and attenuate the switching gain's amplitude. The smooth virtual and actual control signals can be obtained thanks to the fractional-order sliding mode control method, which eliminates the chattering in the MIMO systems with unmatched uncertainties. Finally, simulations demonstrate the correctness and superiority of the proposed control method.
-
表 1 控制器主要设计参数
Table 1 The design parameters of the controllers
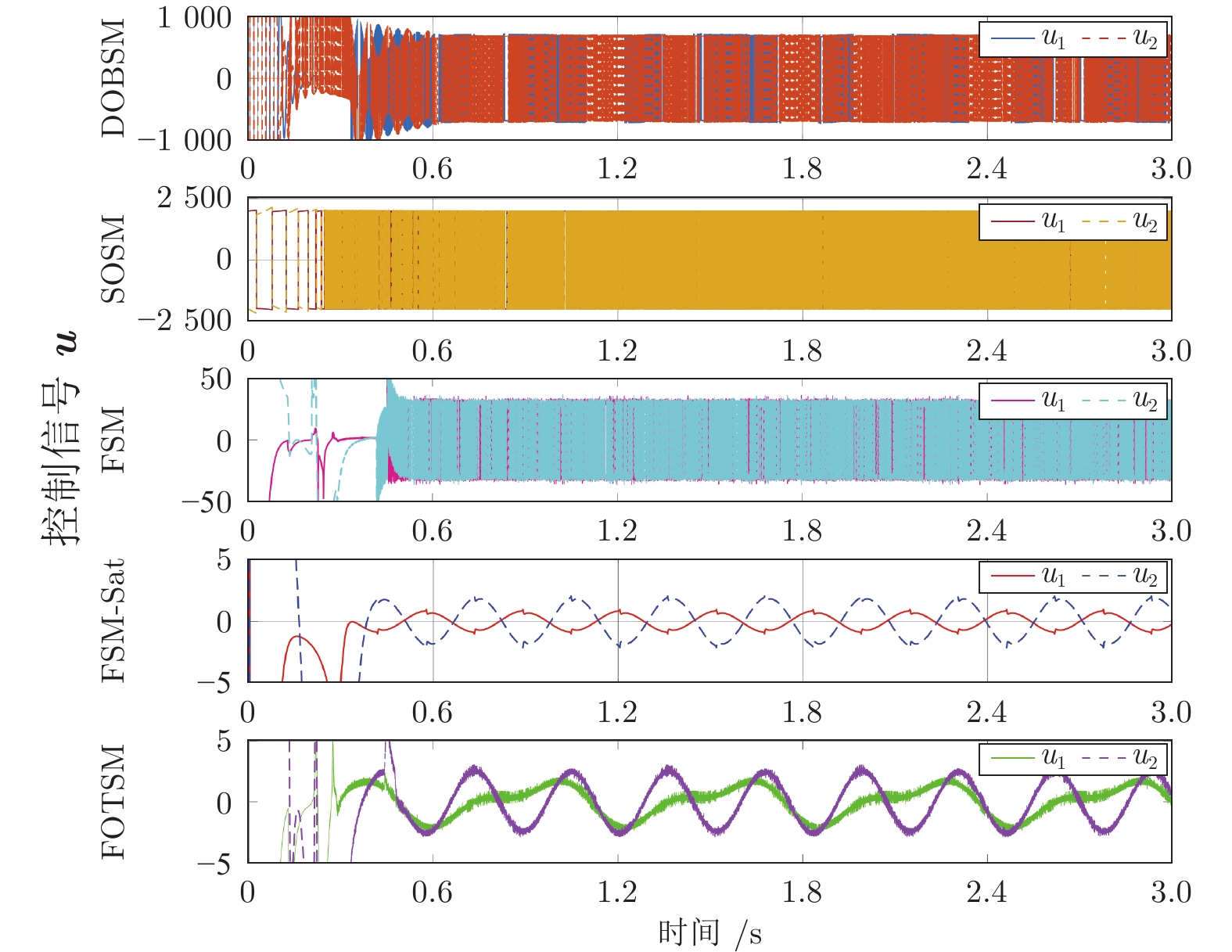
控制方法 控制器参数 DOBSM $c_1=c_2=10, k_1=k_2=700$, $l_1=l_2=10$ SOSM $c=60, k=2\;000$ FSM ${\boldsymbol{C} }_{1}={\rm{diag}}\{60,60\}$, ${\boldsymbol{C} }_{2}={\rm{diag}}\{150,170\}$, $p=5, q=3$ FSM-Sat ${\boldsymbol{C} }_{1}={\rm{diag}}\{60,60\}$, ${\boldsymbol{C} }_{2}={\rm{diag}}\{150,170\}$, $\delta=1/8$, $p=5,q=3$ 表 2 不同控制方法性能对比
Table 2 Performance comparison of the five methods
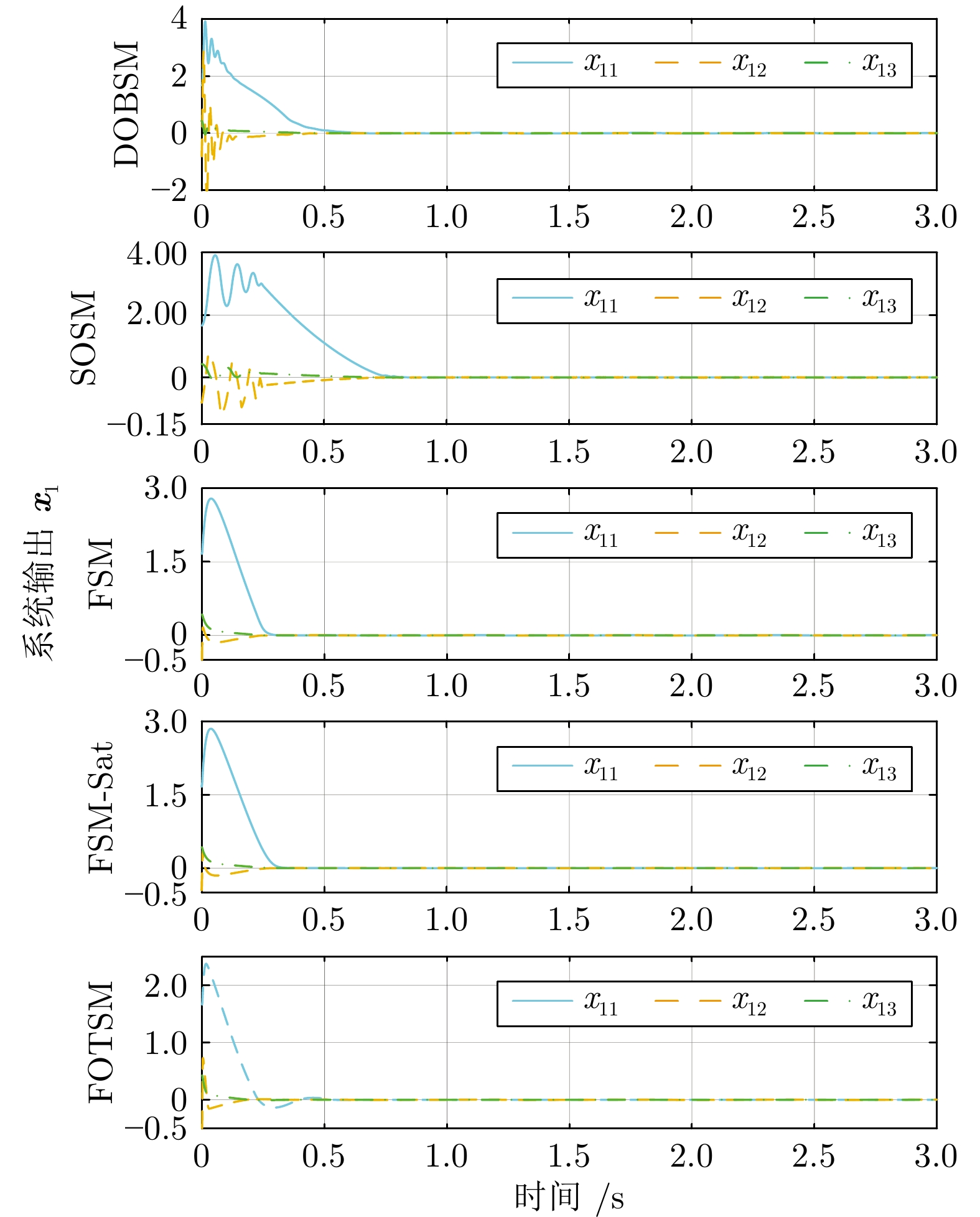
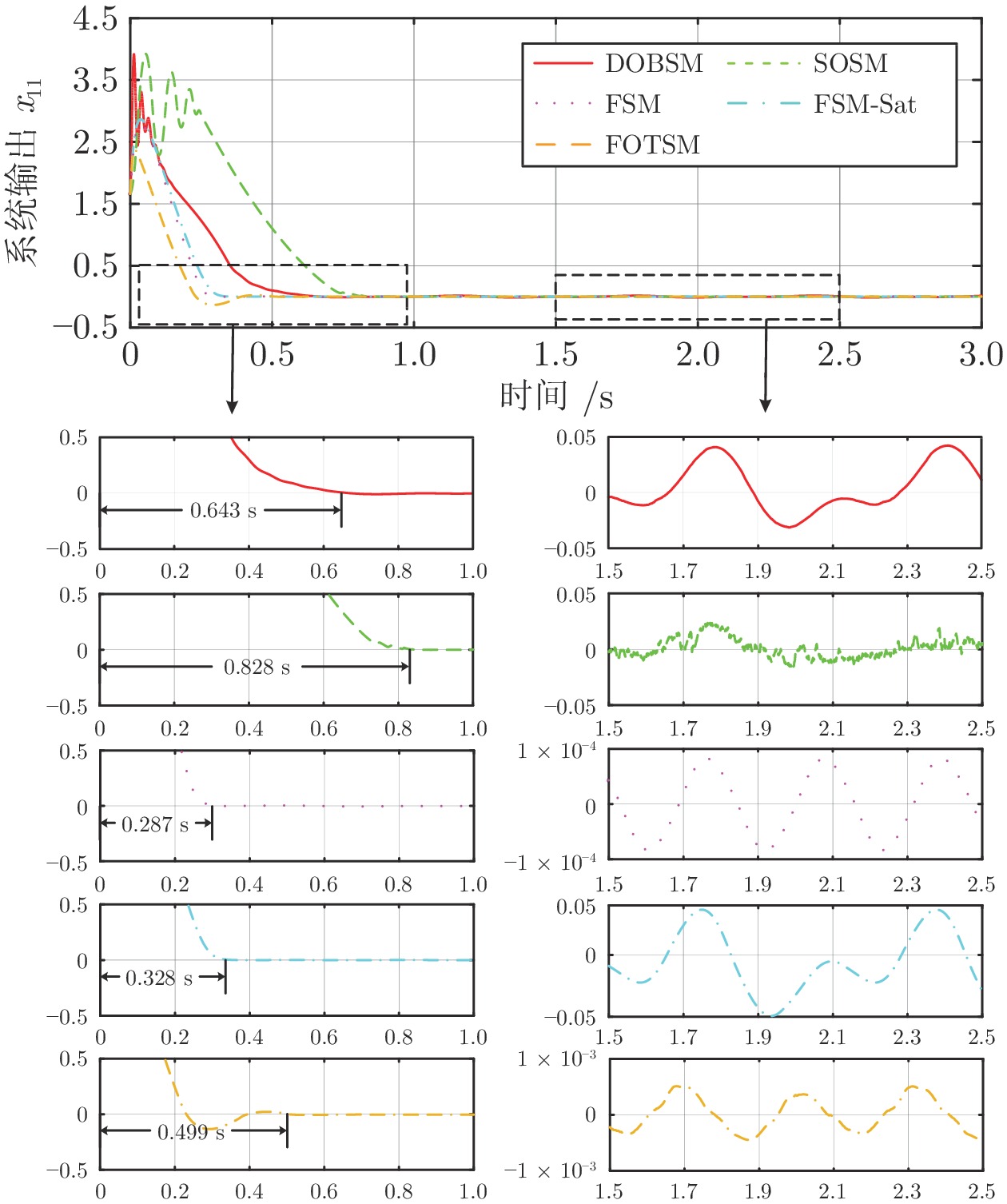
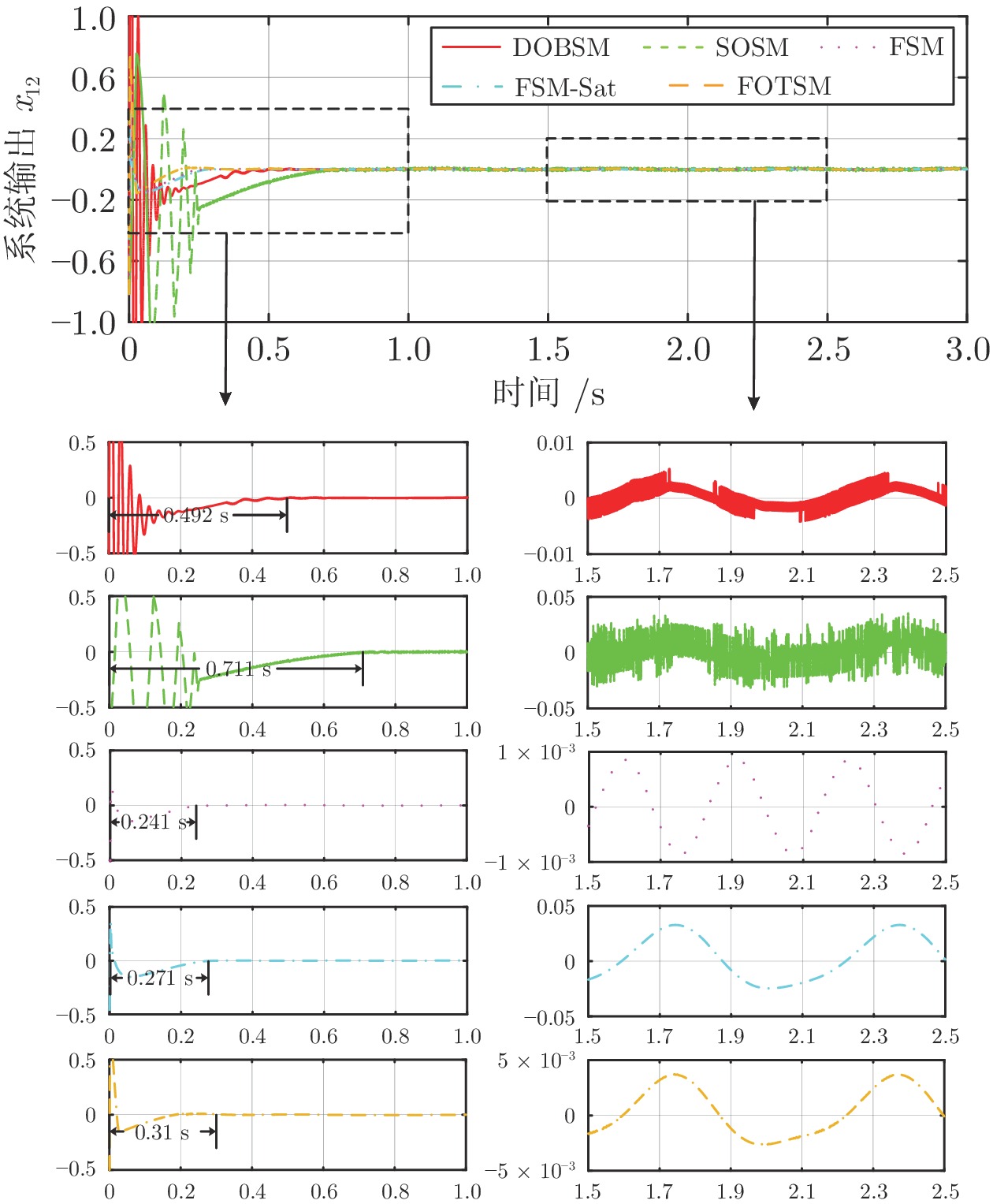
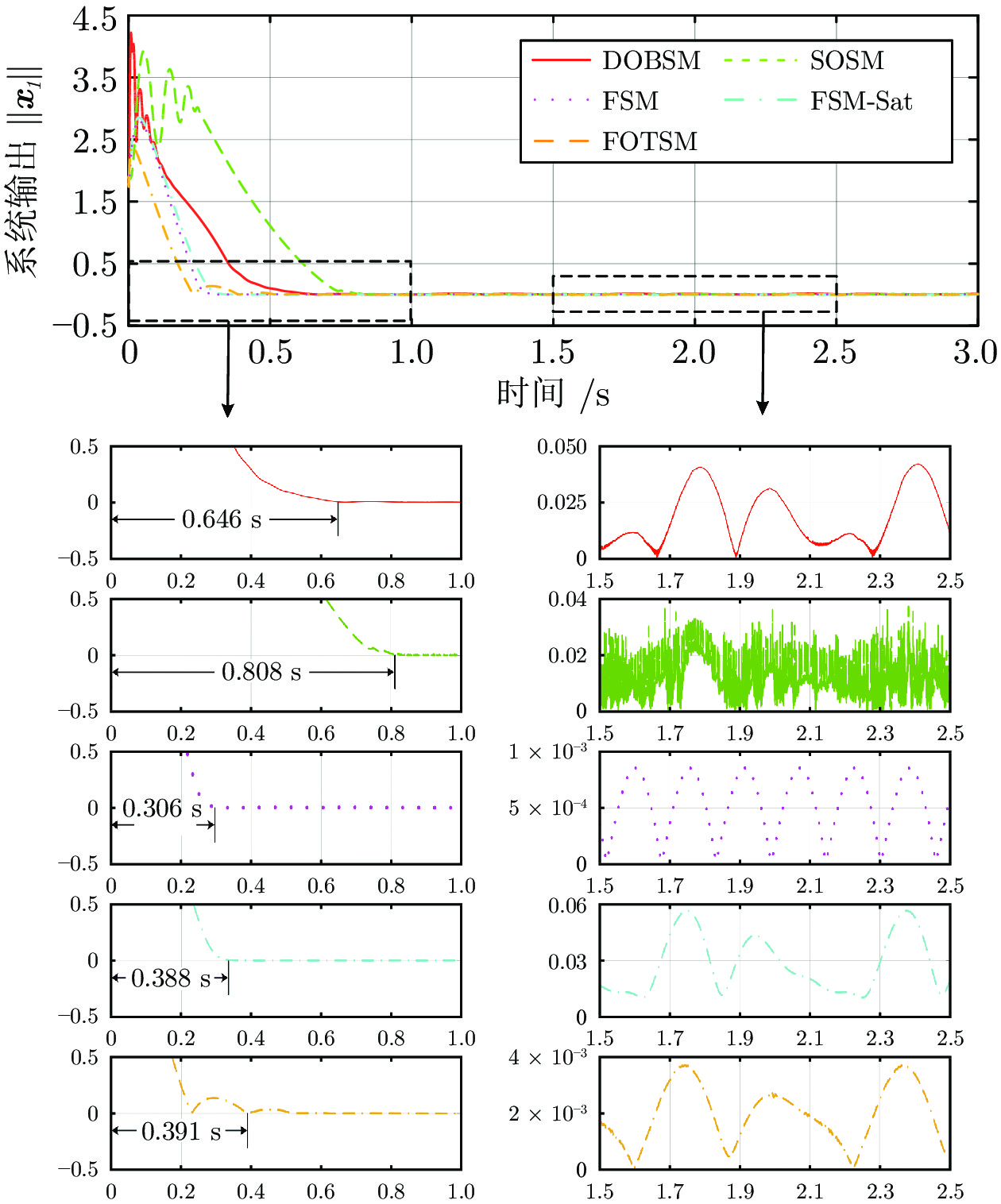
控制方法 收敛速度 控制精度 控制信号 DOBSM 较快 $\leq0.05$ 不连续, 抖振 SOSM 较快 $\leq0.04$ 不连续, 抖振 FSM 快 $\leq 1\times10^{-3}$ 不连续, 抖振 FSM-Sat 快 $\leq0.06$ 连续 FOTSM 快 $\leq4\times10^{-3}$ 连续 -
[1] Yu X H, Feng Y, Man Z H. Terminal sliding mode control-an overview. IEEE Open Journal of the Industrial Electronics Society, 2021, 2: 36-52 doi: 10.1109/OJIES.2020.3040412 [2] Feng Y, Yu X H, Man Z H. Non-singular terminal sliding mode control of rigid manipulators. Automatica, 2002, 38(12): 2159-2167 doi: 10.1016/S0005-1098(02)00147-4 [3] Feng Y, Zhou M H, Han Q L, Han F L, Cao Z W, Ding S L. Integral-type sliding-mode control for a class of mechatronic systems with gain adaptation. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2020, 16(8): 5357-5368 doi: 10.1109/TII.2019.2954550 [4] Mu C X, He H B. Dynamic behavior of terminal sliding mode control. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2018, 65(4): 3480-3490 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2017.2764842 [5] 游星星, 杨道文, 郭斌, 刘凯, 佃松宜, 朱雨琪. 基于观测器和指定性能的非线性系统事件触发跟踪控制. 自动化学报, DOI: 10.16383/j.aas.c210387You Xing-Xing, Yang Dao-Wen, Guo Bin, Liu Kai, Dian Song-Yi, Zhu Yu-Qi. Event-triggered tracking control for a class of nonlinear systems with observer and prescribed performance. Acta Automatica Sinica, DOI: 10.16383/j.aas.c210387 [6] Hou H Z, Yu X H, Xu L, Rsetam K, Cao Z W. Finite-time continuous terminal sliding mode control of servo motor systems. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2020, 67(7): 5647-5656 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2019.2931517 [7] Yang J, Yu X H, Zhang L, Li S H. A Lyapunov-based approach for recursive continuous higher order nonsingular terminal sliding-mode control. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2021, 66(9): 4424-4431 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2020.3047145 [8] Zhou M H, Cheng S W, Feng Y, Xu W, Wang L K, Cai W. Full-order terminal sliding-mode-based sensorless control of induction motor with gain adaptation. IEEE Journal of Emerging and Selected Topics in Power Electronics, 2022, 10(2): 1978-1991 doi: 10.1109/JESTPE.2021.3081863 [9] Du H B, Chen X P, Wen G H, Yu X H, Lü J H. Discrete-time fast terminal sliding mode control for permanent magnet linear motor. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2018, 65(12): 9916-9927 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2018.2815942 [10] 李繁飙, 黄培铭, 阳春华, 廖力清, 桂卫华. 基于非线性干扰观测器的飞机全电刹车系统滑模控制设计. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(11): 2557-2569 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c201041Li Fan-Biao, Huang Pei-Ming, Yang Chun-Hua, Liao Li-Qing, Gui Wei-Hua. Sliding mode control design of aircraft electric brake system based on nonlinear disturbance observer. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(11): 2557-2569 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c201041 [11] Man Z H, Paplinski A P, Wu H R. A robust MIMO terminal sliding mode control scheme for rigid robotic manipulators. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1994, 39(12): 2464-2469 doi: 10.1109/9.362847 [12] 史宏宇, 冯勇. 感应电机高阶终端滑模磁链观测器的研究. 自动化学报, 2012, 38(2): 288-294 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2012.00288Shi Hong-Yu, Feng Yong. High-order terminal sliding mode flux observer for induction motors. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2012, 38(2): 288-294 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2012.00288 [13] Cao J H, Xie S Q, Das R. MIMO sliding mode controller for gait exoskeleton driven by pneumatic muscles. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2018, 26(1): 274-281 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2017.2654424 [14] Rehman F U, Mufti M R, Din S U, Afzal H, Qureshi M I, Khan D M. Adaptive smooth super-twisting sliding mode control of nonlinear systems with unmatched uncertainty. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 177932-177940 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3027194 [15] Castanos F, Fridman L. Analysis and design of integral sliding manifolds for systems with unmatched perturbations. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2006, 51(5): 853-858 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2006.875008 [16] Li S H, Yang J, Chen W H, Chen X S. Generalized extended state observer based control for systems with mismatched uncertainties. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2012, 59(12): 4792-4802 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2011.2182011 [17] Zhang X Y, Xiao L F, Li H F. Robust control for switched systems with unmatched uncertainties based on switched robust integral sliding mode. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 138396-138405 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3012462 [18] Yang J, Li S H, Yu X H. Sliding-mode control for systems with mismatched uncertainties via a disturbance observer. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2013, 60(1): 160-169 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2012.2183841 [19] 侯利民, 王龙洋, 王怀震. 基于NDOB的匹配/非匹配不确定性系统滑模控制(英文). 自动化学报, 2017, 43(7): 1257-1264 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.e160014Hou L M, Wang L Y, Wang H Z. SMC for systems with matched and mismatched uncertainties and disturbances based on NDOB. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(7): 1257-1264 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.e160014 [20] 李强, 方一鸣, 李建雄, 马壮. 非匹配不确定性下连铸结晶器振动位移系统准滑模控制. 控制与决策, 2020, 35(7): 1615-1622Li Qiang, Fang Yi-Ming, Li Jian-Xiong, Ma Zhuang. Quasi-sliding mode control for mold vibration displacement system with unmatched uncertainties. Control and Decision, 2020, 35(7): 1615-1622 [21] Ding S H, Li S H. Second-order sliding mode controller design subject to mismatched term. Automatica, 2017, 77: 388-392 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2016.07.038 [22] Salihbegovic A. Robust internal-loop compensator based sliding mode control of nonlinear systems in the presence of mismatched disturbances. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 50492-50502 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2910725 [23] Zhu W H. Comments on "Robust tracking control for rigid robotic manipulators". IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2000, 45(8): 1577-1580 doi: 10.1109/9.871778 [24] 王艳敏, 冯勇, 夏红伟, 申立群. 多输入不确定系统的平滑非奇异终端滑模控制. 控制与决策, 2015, 30(1): 161-165Wang Yan-Min, Feng Yong, Xia Hong-Wei, Shen Li-Qun. Smooth nonsingular terminal sliding mode control of uncertain multi-input systems. Control and Decision, 2015, 30(1): 161-165 [25] Kao Y G, Ma S, Xia H W, Wang C H, Liu Y L. Integral sliding mode control for a kind of impulsive uncertain reaction-diffusion systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2023, 68(2): 1154-1160 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2022.3149865 [26] 沈智鹏, 张晓玲. 基于非线性增益递归滑模的船舶轨迹跟踪动态面自适应控制. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(10): 1833-1841 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c170198Shen Zhi-Peng, Zhang Xiao-Ling. Recursive sliding-mode dynamic surface adaptive control for ship trajectory tracking with nonlinear gains. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(10): 1833-1841 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c170198 [27] Feng Y, Zhou M H, Zheng X M, Han F L, Yu X H. Full-order terminal sliding-mode control of MIMO systems with unmatched uncertainties. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2018, 355(2): 653-674 doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2017.10.034 [28] Ma Z Q, Liu Z X, Huang P F, Kuang Z A. Adaptive fractional-order sliding mode control for admittance-based telerobotic system with optimized order and force estimation. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2022, 69(5): 5165-5174 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2021.3078385 [29] Long B, Lu P J, Chong K T, Rodriguez J, Guerrero J M. Robust fuzzy-fractional-order nonsingular terminal sliding-mode control of LCL-type grid-connected converters. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2022, 69(6): 5854-5866 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2021.3094411 [30] Lin D, Liao X Z, Dong L, Yang R C, Yu S S, Iu H H C, et al. Experimental study of fractional-order RC circuit model using the Caputo and Caputo-Fabrizio derivatives. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2021, 68(3): 1034-1044 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2020.3040556 [31] 王智伟, 李鹏瀚, 刘鑫, 王文倬, 柯贤波, 李征. 基于分数阶滑模控制的双馈风电系统次同步振荡抑制方法. 中国电机工程学报, DOI: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.221357Wang Zhi-Wei, Li Peng-Han, Liu Xin, Wang Wen-Zhuo, Ke Xian-Bo, Li Zheng. Suppression method of subsynchronous oscillation in DFIG-based wind power system based on fractional-order sliding mode control. Proceedings of the CSEE, DOI: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.221357 [32] 赵希梅, 王超, 金鸿雁. 基于NDO的永磁同步电动机自适应分数阶滑模控制. 中国机械工程, 2023, 34(9): 1093−1099Zhao Xi-Mei, Wang Chao, Jin Hong-Yan. Adaptive fractional order sliding mode control for permanent magnet synchronous motor based on NDO. Chinese Mechanical Engineering, 2023, 34(9): 1093−1099 [33] Lin X P, Liu J X, Liu F G, Liu Z, Gao Y B, Sun G H. Fractional-order sliding mode approach of buck converters with mismatched disturbances. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2021, 68(9): 3890-3900 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2021.3092138 [34] Zhang X F, Huang W K, Wang Q G. Robust H∞ adaptive sliding mode fault tolerant control for T-S fuzzy fractional order systems with mismatched disturbances. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2021, 68(3): 1297-1307 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2020.3039850 [35] Levant A, Shustin B. Quasi-continuous MIMO sliding-mode control. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2018, 63(9): 3068-3074 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2017.2778251 [36] Utkin V, Lewis F L, Guldner J, Ge S S, Shi J X. Sliding Mode Control in Electro-Mechanical Systems. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2009. [37] Yang J, Li S H, Su J Y, Yu X H. Continuous nonsingular terminal sliding mode control for systems with mismatched disturbances. Automatica, 2013, 49(7): 2287-2291 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2013.03.026 [38] Aghababa M P. Design of a chatter-free terminal sliding mode controller for nonlinear fractional-order dynamical systems. International Journal of Control, 2013, 86(10): 1744-1756 doi: 10.1080/00207179.2013.796068 [39] Tang Y G, Zhang X Y, Zhang D L, Zhao G, Guan X P. Fractional order sliding mode controller design for antilock braking systems. Neurocomputing, 2013, 111: 122-130 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2012.12.019 [40] Bhat S P, Bernstein D S. Finite-time stability of continuous autonomous systems. SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization, 2000, 38(3): 751-766 doi: 10.1137/S0363012997321358 [41] Zak M. Terminal attractors for addressable memory in neural networks. Physics Letters A, 1988, 133(1-2): 18-22 doi: 10.1016/0375-9601(88)90728-1 [42] Sun G H, Ma Z Q, Yu J Y. Discrete-time fractional order terminal sliding mode tracking control for linear motor. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2018, 65(4): 3386-3394 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2017.2748045 [43] Edwards C, Spurgeon S K. Sliding Mode Control: Theory and Applications. London: CRC Press, 1998. -




 下载:
下载: