Research on a Latency Upper-bound Analysis Model Based on Network Calculus in Time-sensitive Networking
-
摘要: 时间敏感网络(Time-sensitive networking, TSN)作为一种新兴工业通信技术, 能够为工业控制业务提供高可靠及确定性时延保障. 针对时间敏感网络在工业场景中广泛采用的时间感知整形(Time-aware shaper, TAS)机制, 提出一种基于网络演算的时延上界分析模型, 对多节点组网下端到端时延上界进行定量分析, 用以评估门控 (Gate control list, GCL)设置是否满足业务服务质量(Quality of service, QoS)需求, 有助于简化多节点组网场景下门控设置复杂度. 模型仿真部分对影响端到端时延的主要因素进行了对比分析, 并通过OMNeT++ 实时仿真验证了所提出时延上界分析模型的有效性.Abstract: As an emerging technology of industrial communication, time-sensitive networking (TSN) can provide high reliability and deterministic latency guarantee for industrial control traffics. This article proposes a latency upper-bound analysis model based on network calculus for time-aware shaper (TAS) widely used in TSN. The proposed model gives an explicit analysis for upper-bound of the end-to-end latency under multiple TSN-node networking scenarios, which can be used to evaluate the quality of service (QoS)-guarantee performance of the current gate control list (GCL) setting, as well as to help to simplify the complexity of GCL setting. In the model simulation part, the main factors affecting the end-to-end latency are compared and analyzed, and the validity of the latency upper-bound given by the proposed model is verified with OMNeT++.
-
表 1 基本参数符号
Table 1 Basic parameter symbols
符号 符号含义 $f$ 业务流 $p_f$ 业务流优先级 $T_f$ 业务流到达周期 $M$ 队列集合 $p_m$ 队列优先级 $T_m$ 队列门控周期 $T_{\rm GCL}$ GCL超周期 $G_m(t)$ 门控状态 $t^{o, i}$ 第$i$个门控窗口的开启时间 $t^{c, i}$ 第$i$个门控窗口的关闭时间 $l^{\max}$ 数据帧的最大长度 $C_{\rm out}$ 数据帧出队时的转发速率 $\overline{L}^{i}$ 门控窗口的保证服务时隙 $o^{j, i}$ 不同门控窗口之间的相对偏移量 $S^{i}$ 最大等待时间 $t_{up}$ 时延分布值上界 表 2 仿真参数设定
Table 2 Simulation parameters setting
参数 大小 数据帧长度 400 Bytes 发送速率 1 Gb/s 链路传播时延 0.1 μs 交换机处理时延 5 μs 表 3 业务流信息定义
Table 3 The traffic information definition
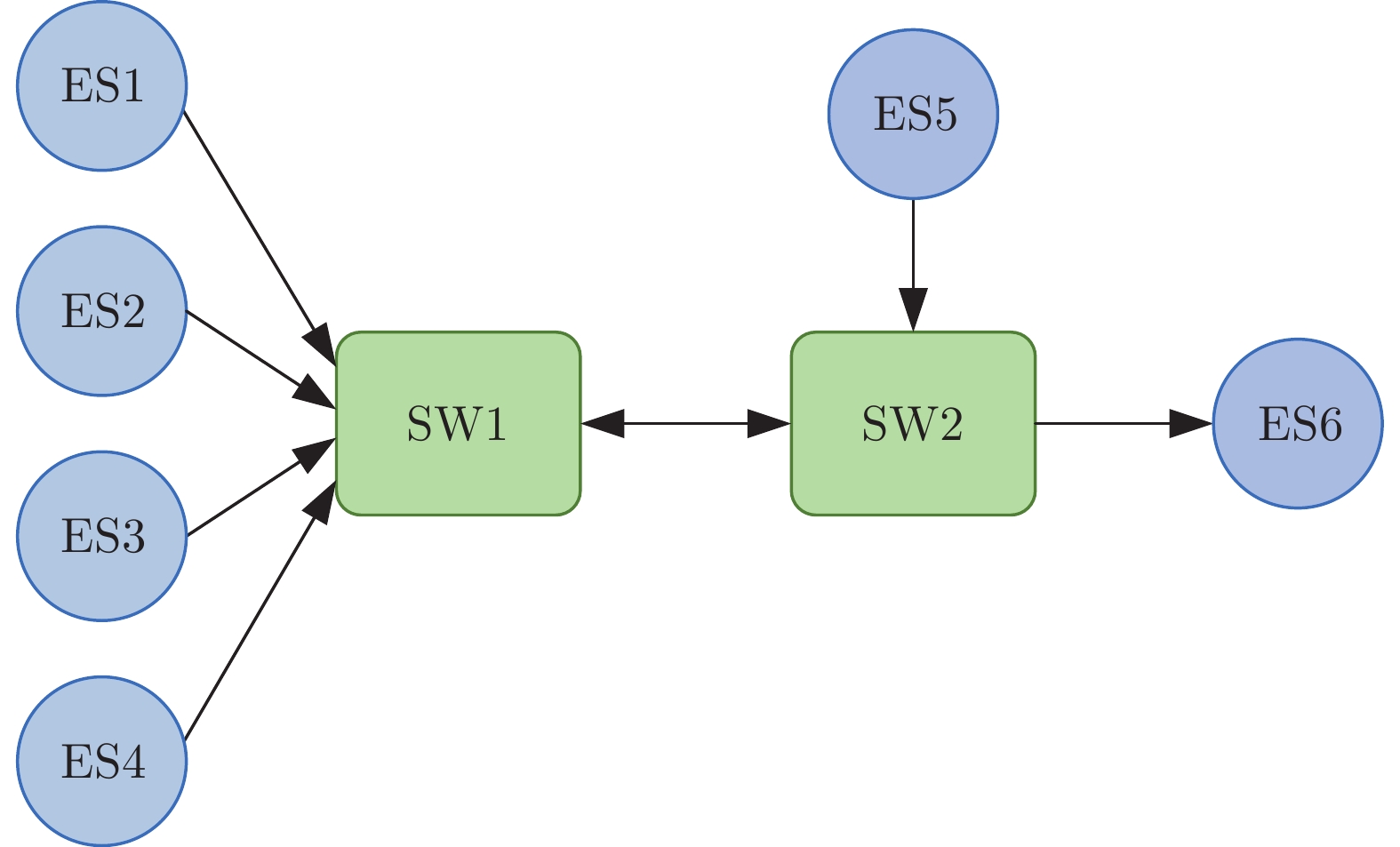
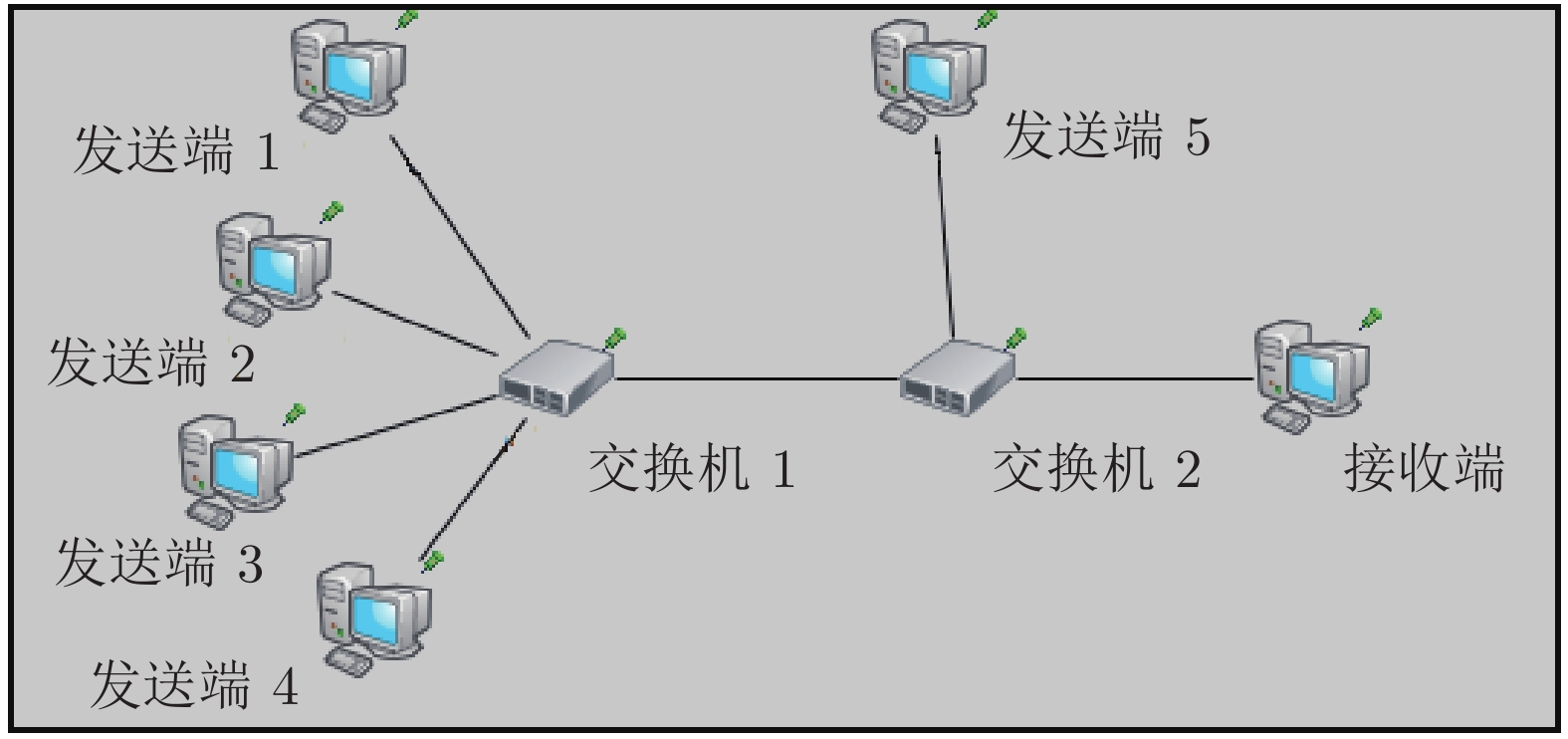
业务流 发送源端 周期T (μs) 到达时间$t_0$(μs) 高优先级 ES1 100 40 ES2 80 ES5 20 表 4 SW1的GCL定义
Table 4 The GCL definition of SW1
交换机 优先级队列 组别 初始门控开闭时间(μs) 门控周期(μs) 开 关 SW1 高 1 20 60 150 2 20 60 3 20 60 4 20 70 5 10 50 中 1 45 80 150 2 60 95 3 40 75 4 55 90 5 35 70 低 1 10 25 150 2 5 20 3 15 30 4 10 25 5 0 15 表 5 SW2的GCL定义
Table 5 The GCL definition of SW2
交换机 优先级队列 组别 初始门控开闭时间(μs) 门控周期(μs) 开 关 SW2 高 1 60 100 150 2 60 100 3 60 100 4 60 110 5 50 90 中 1 45 70 150 2 35 60 3 50 75 4 45 70 5 35 60 低 1 95 110 150 2 100 115 3 90 105 4 105 120 5 85 100 表 6 各交换机WCD的上界
Table 6 The upper-bound of WCD at each switch
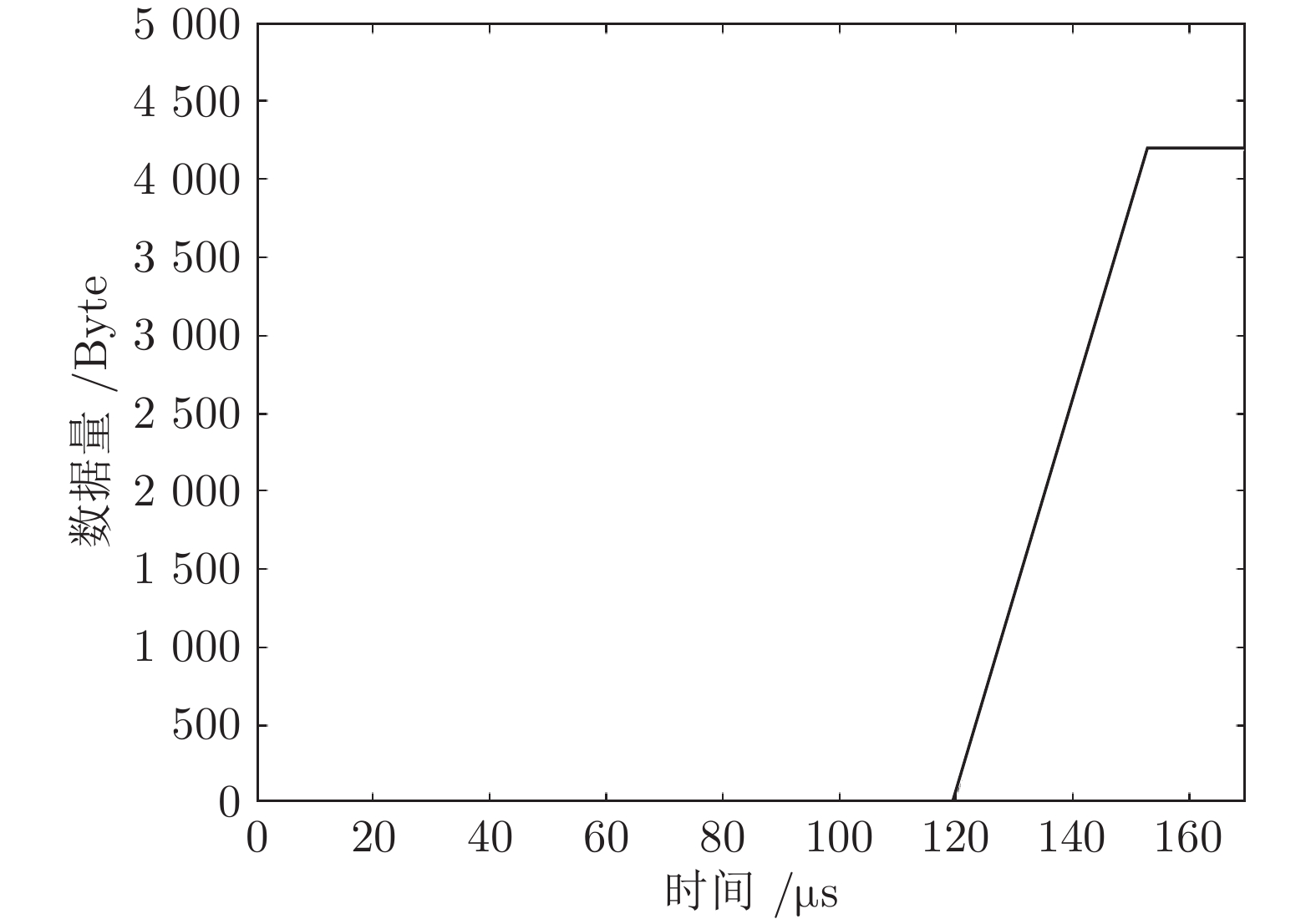
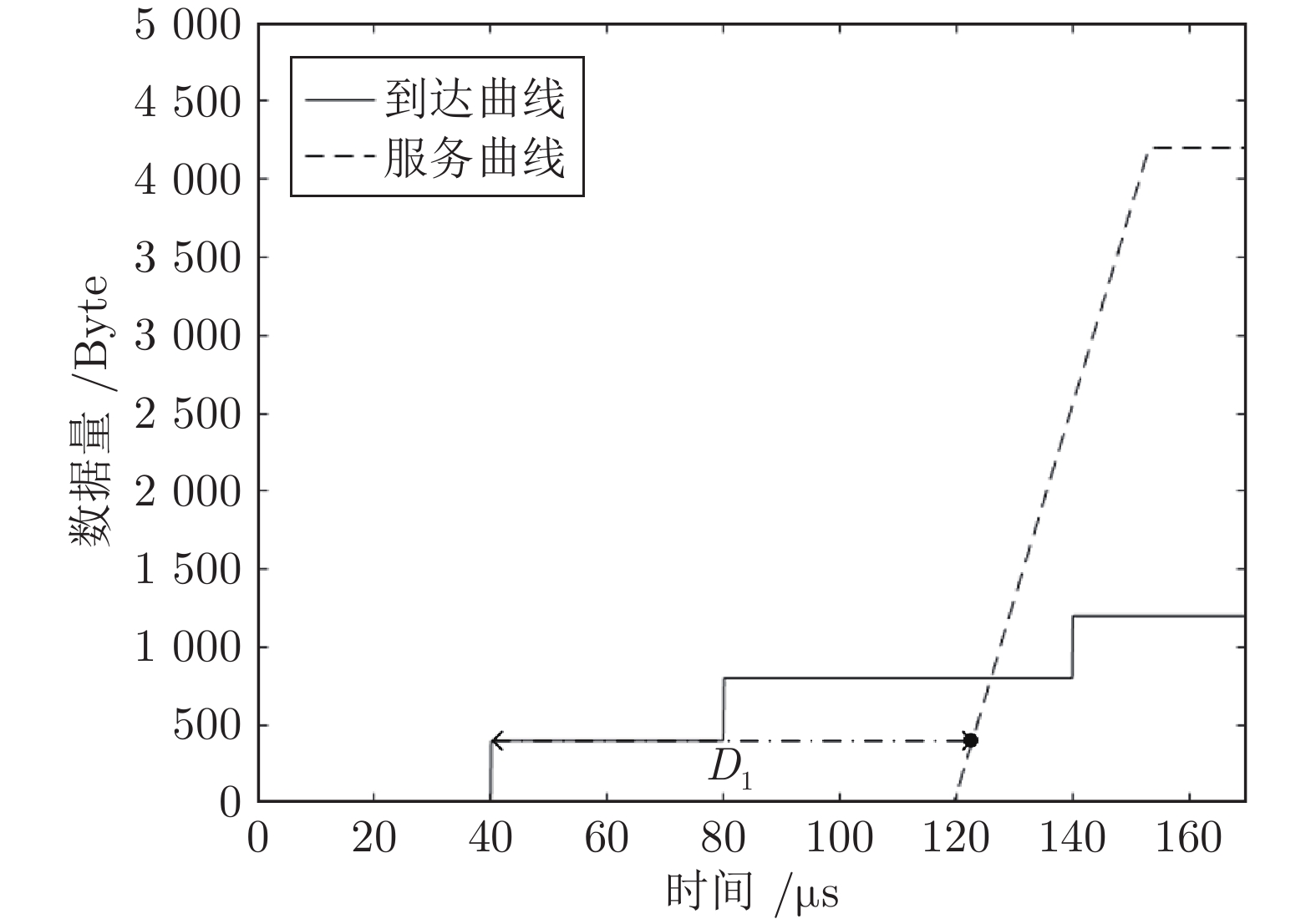
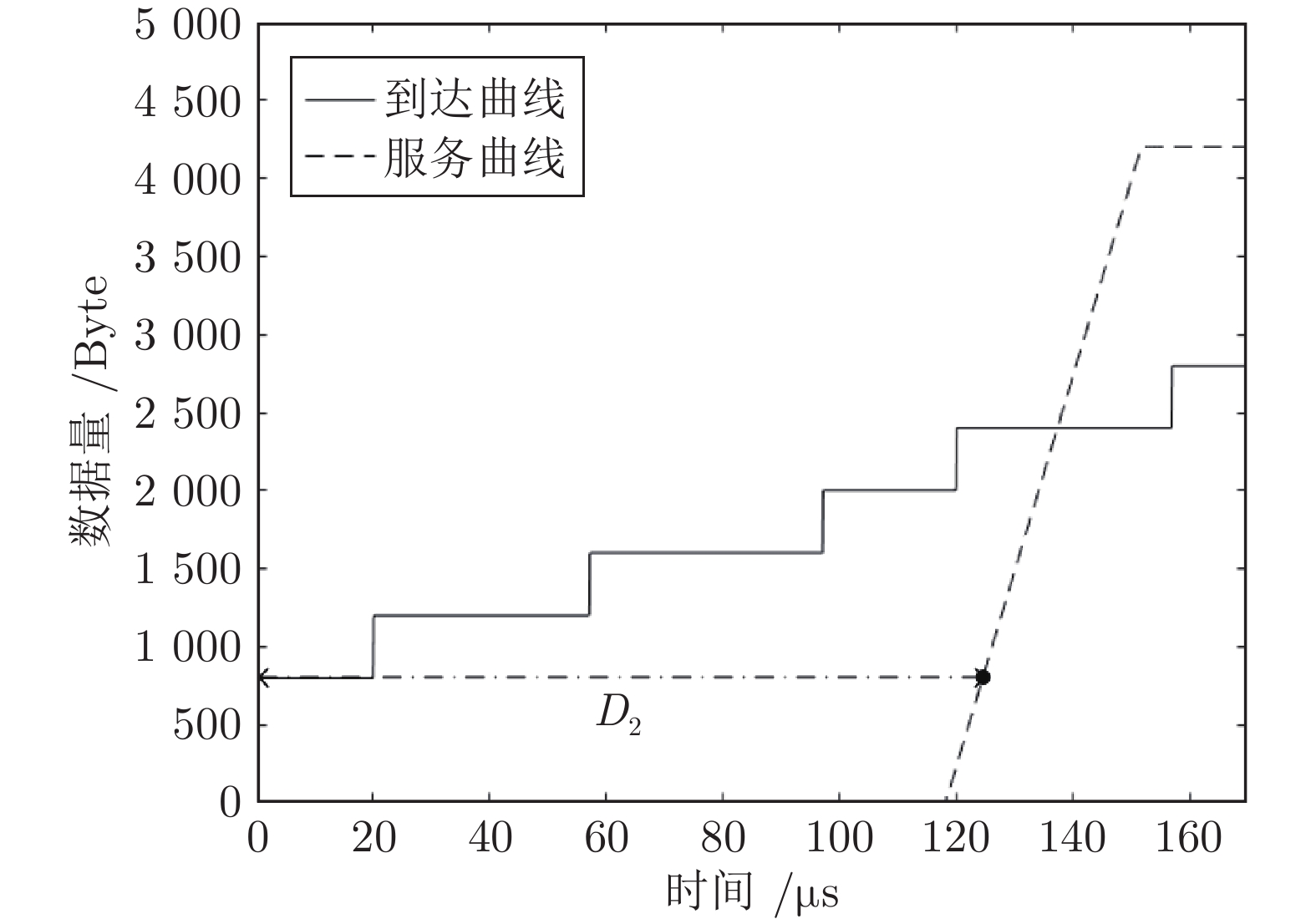
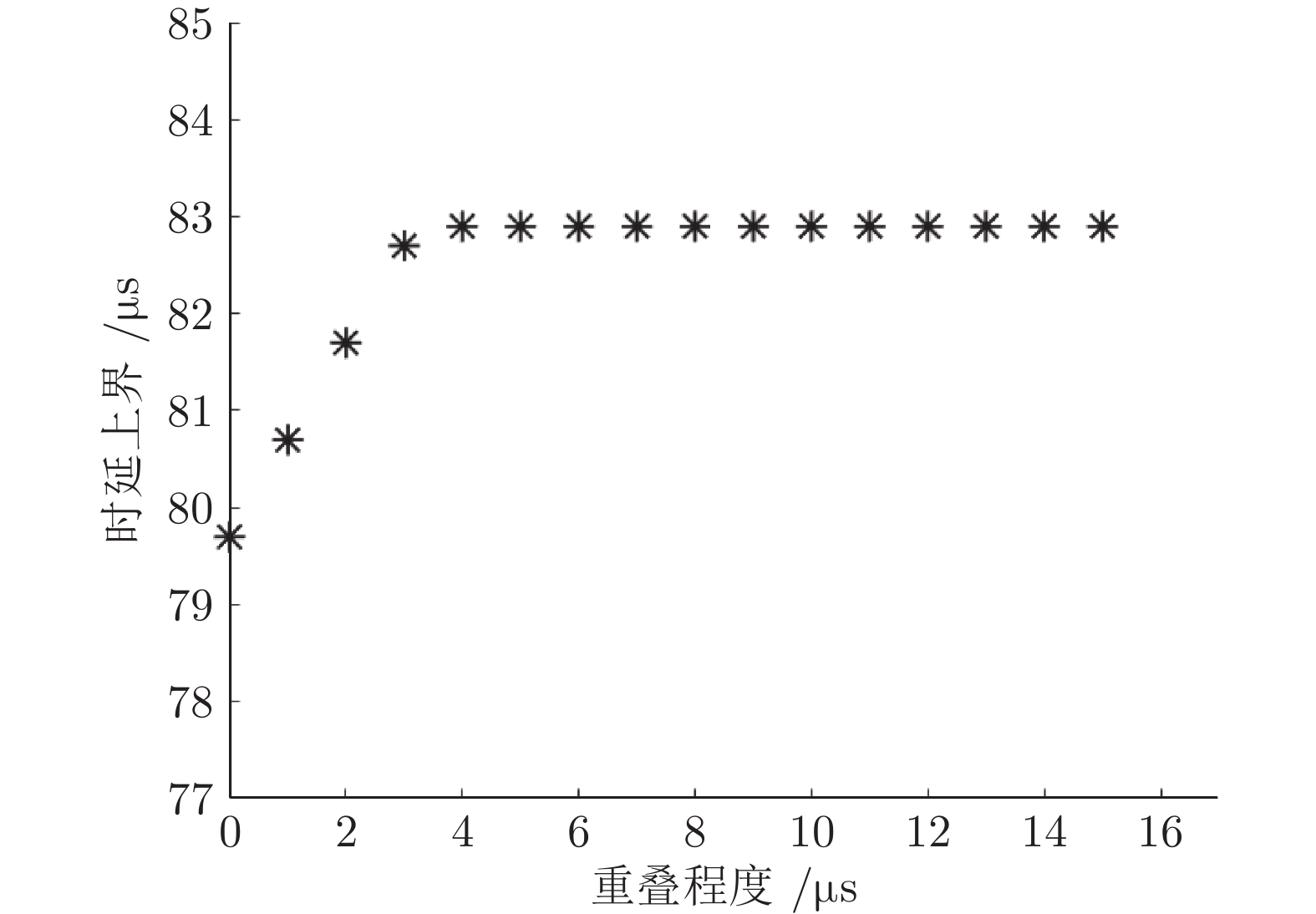
业务流 组别 WCD的上界(μs) SW1 SW2 高优先级 1 82.9 124.7 2 76.5 119.7 3 82.9 126.1 4 72.9 114.7 5 82.9 124.7 表 7 组别1各交换机内部时延
Table 7 The internal delay of each switch in the group 1
交换机 交换机内部时延(μs) 时延上界 处理时延 总时延$t_{\mathrm{SW}}$ SW1 82.9 5 87.9 SW2 124.7 5 129.7 表 8 中、低优先级业务流参数配置
Table 8 The parameter configuration of the medium and low priority traffic
业务流 发送源端 周期T (μs) 到达时间$t_0$ (μs) 中优先级 ES3 150 40 低优先级 ES4 200 15 -
[1] 关新平, 陈彩莲, 杨博, 华长春, 吕玲, 朱善迎. 工业网络系统的感知−传输−控制一体化: 挑战和进展. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(1): 25−36Guan Xin-Ping, Chen Cai-Lian, Yang Bo, Hua Chang-Chun, Lv Ling, Zhu Shan-Ying. Towards the integration of sensing, transmission and control for industrial network systems: Challenges and recent developments. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(1): 25-36 [2] 蔡岳平, 姚宗辰, 李天驰. 时间敏感网络标准与研究综述. 计算机学报, 2021, 44(7): 1378−1397 doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2020.01378Cai Yue-Ping, Yao Zong-Chen, Li Tian-Chi. A survey on time-sensitive networking: Standards and state-of-the-art. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2021, 44(7): 1378−1397 doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2020.01378 [3] 聂宏蕊, 李绍胜, 刘勇. 时间敏感网络中基于IEEE 802.1Qch标准的优化调度机制. 通信学报, 2022, 43(9): 12−26Nie Hong-Rui, Li Shao-Sheng, Liu Yong. Optimized scheduling mechanism based on IEEE 802.1Qch standard in time-sensitive networking. Journal on Communications, 2022, 43(9): 12−26 [4] 时间敏感网络白皮书, 中国电子技术标准化研究院, 2020.Time-sensitive Networking White Paper, China Electronics Standardization Institute, 2020. [5] 李宗辉, 杨思琪, 喻敬海, 邓仰东, 万海. 时间敏感网络中确定性传输技术综述. 软件学报, 2022, 33(11): 4334−4355 doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.006524Li Zong-Hui, Yang Si-Qi, Yu Jing-Hai, Deng Yang-Dong, Wan Hai. State-of-the-art survey on deterministic transmission technologies in time-sensitive networking. Journal of Software, 2022, 33(11): 4334−4355 doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.006524 [6] 张彤, 冯佳琦, 马延滢, 渠思源, 任丰原. 时间敏感网络流量调度综述. 计算机研究与发展, 2022, 59(4): 747−764 doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.20210203Zhang Tong, Feng Jia-Qi, Ma Yan-Ying, Qu Si-Yuan, Ren Feng-Yuan. Survey on traffic scheduling in time-sensitive networking. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2022, 59(4): 747−764 doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.20210203 [7] Maile L, Hielscher K S, German R. Network calculus results for TSN: An introduction. In: Proceedings of the Information Communication Technologies Conference (ICTC). Nanjing, China: IEEE, 2020. 131−140 [8] Hu H, Li Q, Xiong H G, Fang B W. The delay bound analysis based on network calculus for asynchronous traffic shaping under parameter inconsistency. In: Proceedings of the IEEE 20th International Conference on Communication Technology (ICCT). Nanjing, China: IEEE, 2020. 908−915 [9] Axer P, Thiele D, Ernst R, Diemer J. Exploiting shaper context to improve performance bounds of ethernet AVB networks. In: Proceedings of the 51st ACM/EDAC/IEEE Design Automation Conference (DAC). San Francisco, CA, USA: IEEE, 2014. 1−6 [10] Mohammadpour E, Stai E, Mohiuddin M, Boudec J Y L. Latency and backlog bounds in time-sensitive networking with credit based shapers and asynchronous traffic shaping. In: Proceedings of the 30th International Teletraffic Congress (ITC 30). Vienna, Austria: IEEE, 2018. 1−6 [11] Cao J Y, Cuijpers P J L, Bril R J, Lukkien J J. Tight worst-case response-time analysis for ethernet AVB using eligible intervals. In: Proceedings of the IEEE World Conference on Factory Communication Systems (WFCS). Aveiro, Portugal: IEEE, 2016. 1−8 [12] Queck R. Analysis of ethernet AVB for automotive networks using network calculus. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Vehicular Electronics and Safety (ICVES 2012). Istanbul, Turkey: IEEE, 2012. 61−67 [13] Zhao L X, Pop P, Gong Z J, Fang B W. Improving latency analysis for flexible window-based GCL scheduling in TSN networks by integration of consecutive nodes offsets. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(7): 5574−5584 doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3031932 [14] Zhao L X, Xiong H G, Zheng Z, Li Q. Improving worst-case latency analysis for rate-constrained traffic in the time-triggered ethernet network. IEEE Communications Letters, 2014, 18(11): 1927−1930 doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2014.2358233 [15] Zhao L X, Pop P, Li Q, Chen J Y, Xiong H G. Timing analysis of rate-constrained traffic in TTEthernet using network calculus. Real-Time Systems, 2017, 53(2): 254−287 doi: 10.1007/s11241-016-9265-0 [16] Zhao L X, Pop P, Craciunas S S. Worst-case latency analysis for IEEE 802.1Qbv time sensitive networks using network calculus. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 41803−41815 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2858767 [17] IEEE Standard for Local and Metropolitan Area Networks —— Bridges and Bridged Networks-amendment 25: Enhancements for Scheduled Traffic, IEEE Standard 802.1 Qbv, 2015. [18] Cruz R L. A calculus for network delay. I. Network elements in isolation. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1991, 37(1): 114−131 doi: 10.1109/18.61109 [19] Parekh A K, Gallager R G. A generalized processor sharing approach to flow control in integrated services networks: The single-node case. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 1993, 1(3): 344−357 doi: 10.1109/90.234856 [20] Chang C S. On deterministic traffic regulation and service guarantees: A systematic approach by filtering. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1998, 44(3): 1097−1110 doi: 10.1109/18.669173 [21] Boudec J L, Thiran P. Network Calculus: A Theory of Deterministic Queuing Systems for the Internet. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 2001. [22] 张晓楠. 基于随机网络演算的网络流量性能测量与分析[硕士学位论文], 北京邮电大学, 中国, 2021.Zhang Xiao-Nan. Measurement and Analysis of Traffic Network Performance Based on Stochastic Network Calculus [Master thesis], Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, China, 2021. [23] 李明辉. 基于网络演算的网络建模方法研究[硕士学位论文], 西南交通大学, 中国, 2007.Li Ming-Hui. Research on Network Modeling Based on Network Calculus [Master thesis], Southwest Jiaotong University, China, 2007. [24] 施金豆. 边缘网络业务性能分析模型和时延确定性传输算法研究[硕士学位论文], 南京邮电大学, 中国, 2021.Shi Jin-Dou. Research on Service Performance Analysis Model and Delay Deterministic Transmission Algorithm of Edge Networks [Master thesis], Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, China, 2021. [25] Vojnovic M, Boudec J Y L. Stochastic analysis of some expedited forwarding networks. In: Proceedings of the Twenty-first Annual Joint Conference of the IEEE Computer and Communications Societies. New York, USA: IEEE, 2002. 1004−1013 [26] Do Y, Kim M, Kim J, Jeon J. Method and analysis for the improvement of preemption performance in IEEE 802.1 TSN. In: Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Ubiquitous Information Management and Communication (IMCOM). Seoul, South Korea: IEEE, 2023. 1−8 [27] Integration of 5G With Time-Sensitive Networking for Industrial Communications, 5G-ACIA, 2021. [28] Paulon J V M, Souza B J O, Endler M. Exploring data collection on bluetooth mesh networks. Ad Hoc Networks, 2022, 130: 102809 doi: 10.1016/j.adhoc.2022.102809 [29] 张林波, 刘彤. OMNeT++ 与无线通信网络仿真. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学出版社, 2020. 18−23Zhang Lin-Bo, Liu Tong. OMNeT++ and Wireless Communication Network Simulation. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology Press, 2020. 18−23 -




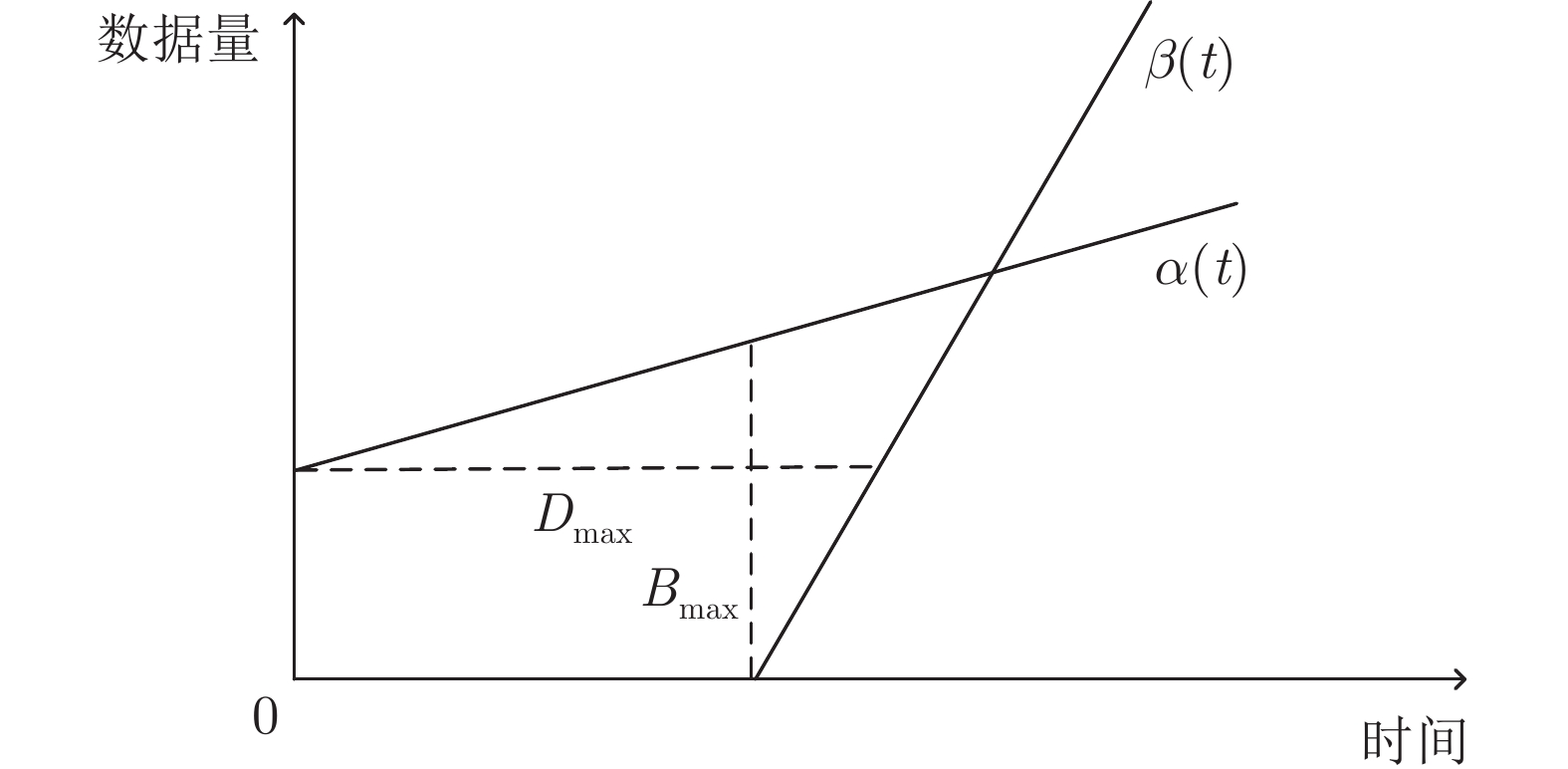
 下载:
下载: