Sliding Mode Swing Angle Control for a Hydraulic Roofbolter Based on Improved Extended State Observer
-
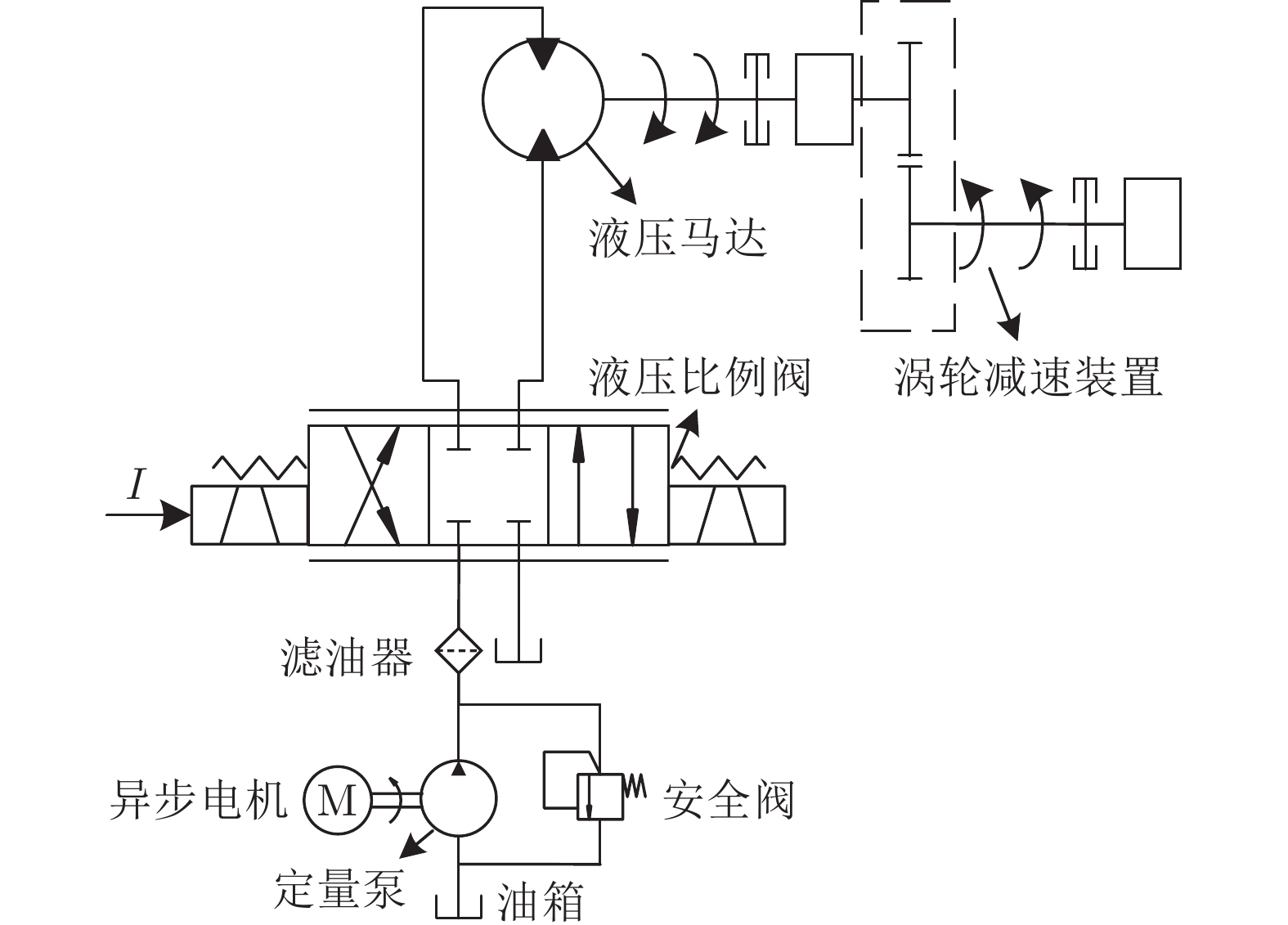
摘要: 液压锚杆钻机摆角系统固有的死区、干扰和时变参数严重影响其动态和稳态性能. 为解决该问题, 通过融合动态面方法、滑模方法和扩展状态观测器, 提出一种基于改进非线性扩展状态观测器的液压锚杆钻机自适应滑模摆角控制方法. 首先, 引入一种死区补偿方法, 建立摆角系统的死区补偿模型. 其次, 为提高系统的抗扰动能力和抑制噪声, 设计一种改进的非线性扩展状态观测器. 此外, 构造一种自适应滑模控制律, 这其中, 基于性能函数和动态面方法设计一种新型的滑模面, 以提高控制精度; 随后, 设计一种新的滑模趋近律, 以提高系统滑模响应速度和消除滑模抖振. 进一步, 分别设计估计误差自适应律和参数自适应律以补偿扰动估计误差和抑制时变参数的影响. 最后, 通过将所提出的控制方法与8种控制方法进行比较, 验证其有效性.Abstract: The inherent dead-zone, disturbance and time-varying parameters deteriorate dynamic and steady-state performances of swing angle system for a hydraulic roofbolter. To address the issue, by fusing dynamic surface method, sliding mode method and extended state observer, this paper proposes an adaptive sliding mode swing angle control method for a hydraulic roofbolter based on an improved nonlinear extended state observer. First, a dead-zone compensation method is introduced, thus a swing angle system is modeled after compensating dead-zone. Secondly, in order to improve the anti-disturbance capability of swing angle system and suppress noise, an improved nonlinear extended state observer is designed. In addition, an adaptive novel sliding mode control law is constructed, in which a novel sliding mode surface is designed based on performance function and dynamic surface method to improve the control accuracy. Subsequently, a novel sliding mode reaching law is designed to improve the response speed and eliminate sliding mode chattering. Further, an estimation error adaptation law and parameter adaptation laws are designed to compensate the disturbance estimation error and suppress the influence of time-varying parameters, respectively. Finally, the effectiveness of the proposed control method is verified by comparing it with eight control methods.
-
Key words:
- Hydraulic roofbolter /
- sliding mode control /
- extended state observer /
- adaptation law
-
表 1 控制性能指标
Table 1 Control performance indexes
控制器 性能指标 MAAE (rad) MEAE (rad) SDAE (rad) ITAE MAACI (mA) MEACI (mA) SDACI (mA) ITACI 所提控制器 0.00069 0.00021 0.00016 0.0088 6.8388 1.4815 1.3499 59.2616 对比控制器 0.02610 0.00650 0.00600 0.2600 14.3389 3.5546 3.3775 143.1829 表 2 控制性能指标
Table 2 Control performance indexes
控制器 性能指标 MAAE (rad) MEAE (rad) SDAE (rad) ITAE MAACI (mA) MEACI (mA) SDACI (mA) ITACI 所提控制器 0.00069 0.00021 0.00016 0.0088 6.8388 1.4815 1.3499 59.2616 对比控制器 0.02460 0.00640 0.00570 0.2565 12.9016 3.3578 3.0065 134.3130 表 3 控制性能指标
Table 3 Control performance indexes
控制器 性能指标 MAAE (rad) MEAE (rad) SDAE (rad) ITAE MAACI (mA) MEACI (mA) SDACI (mA) ITACI 所提控制器 0.00069 0.00021 0.00016 0.0088 6.8388 1.4815 1.3499 59.2616 对比控制器 0.00930 0.00230 0.00190 0.0914 12.1356 2.9717 2.4346 118.8676 表 4 控制性能指标
Table 4 Control performance indexes
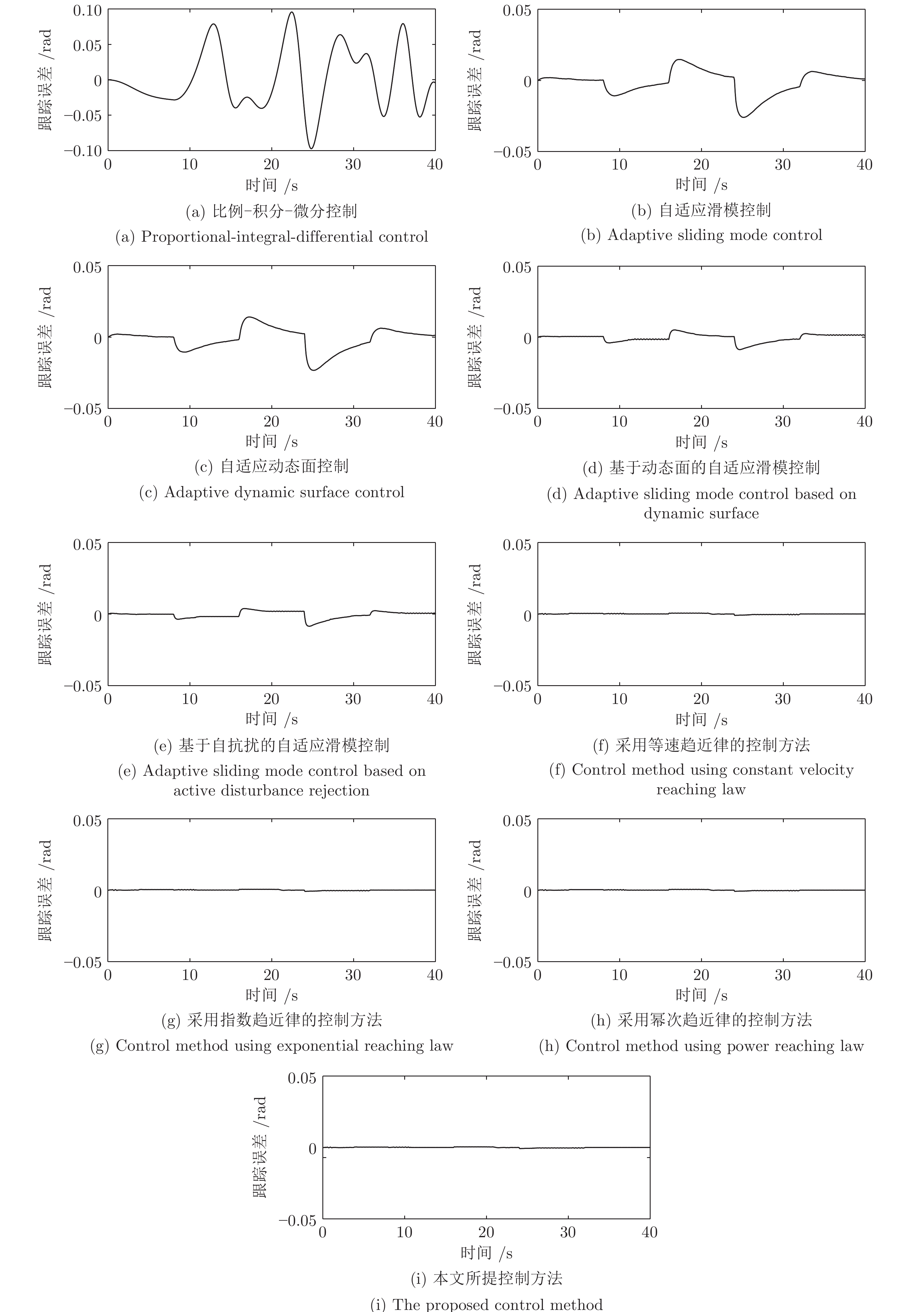
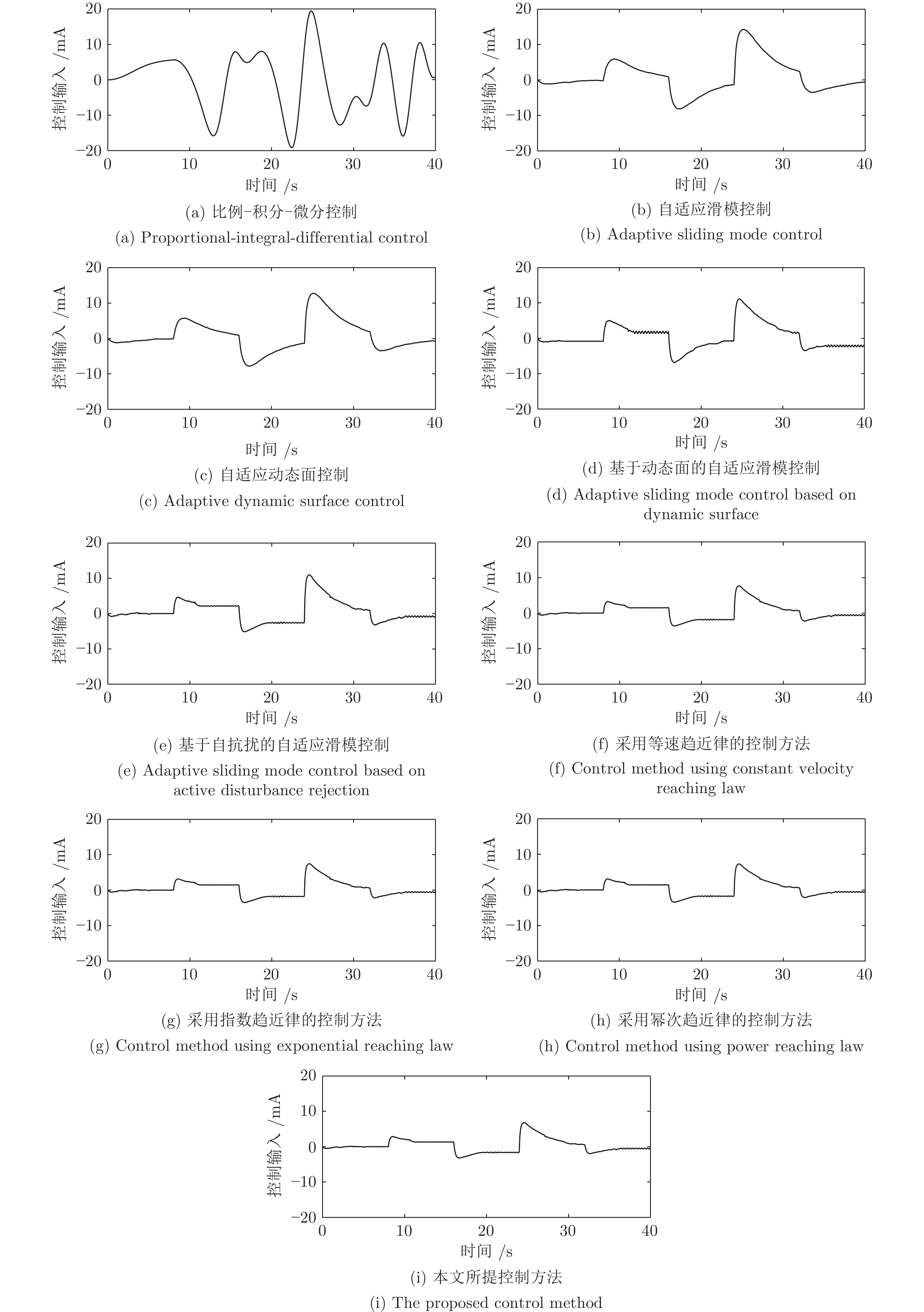
控制器 性能指标 MAAE (rad) MEAE (rad) SDAE (rad) ITAE MAACI (mA) MEACI (mA) SDACI (mA) ITACI 1) 0.09580 0.06850 0.10790 2.7303 19.4312 13.6954 21.5717 546.0658 2) 0.02600 0.00650 0.00610 0.2594 14.3092 3.5663 3.3437 142.6516 3) 0.02320 0.00610 0.00540 0.2420 12.7854 3.3276 2.9794 133.1030 4) 0.00860 0.00210 0.00170 0.0847 11.2366 2.7516 2.2543 110.0626 5) 0.00840 0.00180 0.00170 0.0735 11.0303 2.3896 2.1772 95.5833 6) 0.00091 0.00029 0.00022 0.0115 7.7212 1.6727 1.5240 66.9083 7) 0.00084 0.00026 0.00021 0.0106 7.5006 1.6249 1.4805 64.9966 8) 0.00077 0.00024 0.00019 0.0097 7.3682 1.5962 1.4544 63.8496 9) 0.00069 0.00021 0.00016 0.0088 6.8388 1.4815 1.3499 59.2616 -
[1] Kang H P, Lin J, Fan M J. Investigation on support pattern of a coal mine roadway within soft rocks a case study. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2015, 140: 31-40 doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2015.01.003 [2] 郭一楠, 陆希望, 张振, 巩敦卫. 变频泵控锚杆钻臂摆角动态滑模自适应控制. 控制理论与应用, 2019, 36(10): 1768-1775 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2019.80600Guo Yi-Nan, Lu Xi-Wang, Zhang Zhen, Gong Dun-Wei. Dynamic sliding-mode adaptive control for the rotation angle of an anchor-hole drilling arm driven by a variable-frequency pump. Control Theory & Applications, 2019, 36(10): 1768-1775 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2019.80600 [3] Bessa W M, de Paula A S, Savi M A. Sliding mode control with adaptive fuzzy dead-zone compensation for uncertain chaotic systems. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2012, 70(3): 1989-2001 doi: 10.1007/s11071-012-0591-z [4] Li S, Ding L, Gao H B, Liu Y J, Huang L, Deng Z Q. Adaptive fuzzy finite-time tracking control for nonstrict full states constrained nonlinear system with coupled dead-zone input. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2020, 52(2): 1138-1149 [5] Dai K Y, Zhu Z C, Shen G, Tang Y, Li X, Wang W, et al. Adaptive force tracking control of electrohydraulic systems with low load using the modified LuGre friction model. Control Engineering Practice, 2022, 125: Article No. 105213 [6] Guo Q, Zhang Y, Celler B G, Su S W. State-constrained control of single-rod electrohydraulic actuator with parametric uncertainty and load disturbance. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2018, 26(6): 2242-2249 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2017.2753167 [7] Jiang Y X, Sun Q L, Zhang X L, Chen Z Q. Pressure regulation for oxygen mask based on active disturbance rejection control. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2017, 64(8): 6402-6411 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2017.2677323 [8] Guo Q, Yin J M, Yu T, Jiang D. Saturated adaptive control of an electrohydraulic actuator with parametric uncertainty and load disturbance. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2017, 64(10): 7930-7941 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2017.2694352 [9] Guo Y N, Zhang Z, Liu Q Y, Nie Z, Gong D W. Decoupling-based adaptive sliding-mode synchro-position control for a dual-cylinder driven hydraulic support with different pipelines. ISA Transactions, 2022, 123: 357-371 doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2021.05.013 [10] Liu J X, Gao Y B, Su X J, Wack M, Wu L G. Disturbance-observer based control for air management of pem fuel cell systems via sliding mode technique. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2019, 27(3): 1129-1138 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2018.2802467 [11] Liu J X, Wu L G, Wu C W, Luo W S, Franquelo L G. Event-triggering dissipative control of switched stochastic systems via sliding mode. Automatica, 2019, 103: 261-273 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2019.01.029 [12] Mishra J P, Li C J, Jalili M, Yu X H. Robust second-order consensus using a fixed-time convergent sliding surface in multiagent systems. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2020, 50(2): 846-855 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2018.2875362 [13] Li P, Zhu G L. Robust internal model control of servo motor based on sliding mode control approach. ISA Transactions, 2019, 93: 199-208 doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2019.03.021 [14] Sun X J, Zhang Q L. Admissibility analysis for interval type-2 fuzzy descriptor systems based on sliding mode control. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2019, 49(8): 3032-3040 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2018.2837890 [15] Guo Y N, Cheng W, Gong D W, Zhang Y, Zhang Z, Xue G H. Adaptively robust rotary speed control of an anchor-hole driller under varied surrounding rock environments. Control Engineering Practice, 2019, 86: 24-36 doi: 10.1016/j.conengprac.2019.02.002 [16] Yang X B, Zheng X L, Chen Y H. Position tracking control law for an electro-hydraulic servo system based on backstepping and extended differentiator. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2018, 23(1): 132-140 doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2017.2746142 [17] Chen G R, Wang J Z, Wang S K, Zhao J B, Shen W. The separate meter in separate meter out control system using dual servo valves based on indirect adaptive robust dynamic surface control. Journal of Systems Science & Complexity, 2019, 32(2): 109-128 [18] 韩京清. 自抗扰控制技术 — 估计补偿不确定因素的控制技术. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2008.Han Jing-Qing. Active Disturbance Rcjection Control Technique — The Technique for Estimating and Compensating the Uncertaintics. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2008. [19] 王东委, 富月. 基于高阶观测器和干扰补偿控制的模型预测控制方法. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(6): 1220-1228 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c180697Wang Dong-Wei, Fu Yue. Model predict control method based on higher-order observer and disturbance compensation control. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(6): 1220-1228 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c180697 [20] Guo Y N, Zhang Z, Gong D W, Lu X W, Zhang Y, Cheng W. Optimal active-disturbance-rejection control for propulsion of anchor-hole drillers. Science China Information Sciences, 2021, 64(5): 1-3 [21] 李繁飙, 黄培铭, 阳春华, 廖力清, 桂卫华. 基于非线性干扰观测器的飞机全电刹车系统滑模控制设计. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(11): 2558-2569 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c201041Li Fan-Biao, Huang Pei-Ming, Yang Chun-Hua, Liao Li-Qing, Gui Wei-Hua. Sliding mode control design of aircraft electric brake system based on nonlinear disturbance observer. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(11): 2558-2569 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c201041 [22] Won D, Kim W, Tomizuka M. High-gain-observer-based integral sliding mode control for position tracking of electrohydraulic servo systems. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2017, 22(6): 2695-2704 doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2017.2764110 [23] Zhu L K, Wang Z B, Liu Y Q, Song W L. Sliding-mode dynamic surface control for MDF continuous hot pressing hydraulic system. In: Proceedings of the Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC). Yinchuan, China: IEEE, 2016. 2509−2514 [24] Yao J Y, Deng W X. Active disturbance rejection adaptive control of hydraulic servo systems. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2017, 64(10): 8023-8032 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2017.2694382 [25] Yang G C. Dual extended state observer-based backstepping control of electro-hydraulic servo systems with time-varying output constraints. Transactions of the Institute of Measurement and Control, 2020, 42(5): 1070−1080 [26] Shen W, Huang H L, Wang J H. Robust backstepping sliding mode controller investigation for a port plate position servo system based on an extended states observer. Asian Journal of Control, 2019, 21(1): 302-311 doi: 10.1002/asjc.1885 [27] Du H, Shi J J, Chen J D, Zhang Z Z, Feng X Y. High-gain observer-based integral sliding mode tracking control for heavy vehicle electro-hydraulic servo steering systems. Mechatronics, 2021, 74(2): Article No. 102484 [28] Zou Q. Extended state observer-based finite time control of electro hydraulic system via sliding mode technique. Asian Journal of Control, 2022, 24(5): 2311-2327 doi: 10.1002/asjc.2638 [29] Shi S, Li J, Li Y, Fang Y. Backstepping sliding mode control for electro-hydraulic servo system with input saturation via an extended state observer. Journal of Computational Information Systems, 2014, 10(5): 1955-1963 [30] Ma Q K, Wang X Y, Yuan F, Tao J F, Liu P. Research on feed-forward PIDD2 control for hydraulic continuous rotation motor electro-hydraulic servo system with long pipeline. In: Proceedings of the UKACC 11th International Conference on Control (CONTROL). Belfast, UK: IEEE, 2016. 1−6 [31] Merritt H E. Hydraulic Control Systems. New York: Wily, 1967. [32] Bessa W M, Dutra M S, Kreuzer E. Sliding mode control with adaptive fuzzy dead-zone compensation of an electro-hydraulic servo-system. Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems, 2010, 58(1): 3-16 [33] He Y D, Wang J Z, Hao R J. Adaptive robust dead-zone compensation control of electro-hydraulic servo systems with load disturbance rejection. Journal of Systems Science & Complexity, 2015, 28(2): 341-359 [34] Hu C X, Yao B, Wang Q F. Adaptive robust precision motion control of systems with unknown input dead-zones: A case study with comparative experiments. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2011, 58(6): 2454-2464 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2010.2066535 [35] Lewis F L, Tim W K, Wang L Z, Li Z X. Deadzone compensation in motion control systems using adaptive fuzzy logic control. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 1999, 7(6): 731-742 doi: 10.1109/87.799674 [36] Zhang Z, Guo Y N, Gong D W, Zhu S. Hybrid extended state observer-based integral sliding mode control of the propulsion for a hydraulic roofbolter. Control Engineering Practice, 2022, 126: Article No. 105260 [37] Baghestan K, Rezaei S M, Talebi H A, Zareinejad M. Robust force control in a novel electro-hydraulic structure using polytopic uncertainty representation. ISA Transactions, 2014, 53(6): 1873–1880 doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2014.08.002 [38] Yao J Y, Jiao Z X, Ma D W. Extended-state-observer-based output feed back nonlinear robust control of hydraulic systems with backstepping. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2014, 61(11): 6285-6293 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2014.2304912 [39] Qi X H, Li J, Xia Y Q, Wan H. On stability for sampled-data nonlinear adrc-based control system with application to the ball-beam problem. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2018, 355(17): 8537-8553 doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2018.09.002 [40] Li J, Qi X H, Xia Y Q, Pu F, Chang K. Frequency domain stability analysis of nonlinear active disturbance rejection control system. ISA Transactions, 2015, 56: 188-195 doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2014.11.009 [41] 刘金琨. 滑模变结构控制 MATLAB 仿真. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2015.Liu Jin-Kun. Sliding Mode Control Design and MATLAB Simulation. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2015. [42] Polyakov, A. Nonlinear feedback design for fixed-time stabilization of linear control systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2012, 57(8): 2106-2110 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2011.2179869 [43] Zhang Z, Guo Y N, Gong D W, Liu J X. Global integral sliding-mode control with improved nonlinear extended state observer for rotary tracking of a hydraulic roofbolter. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, DOI: 10.1109/TMECH.2022.3203517 [44] Lyapunov A M. The general problem of the stability of motion. International Journal of Control, 1992, 55(3): 531-534 doi: 10.1080/00207179208934253 -




 下载:
下载: