Missing Data Generation Method Based on Flow Model and Its Application in Remaining Life Prediction
-
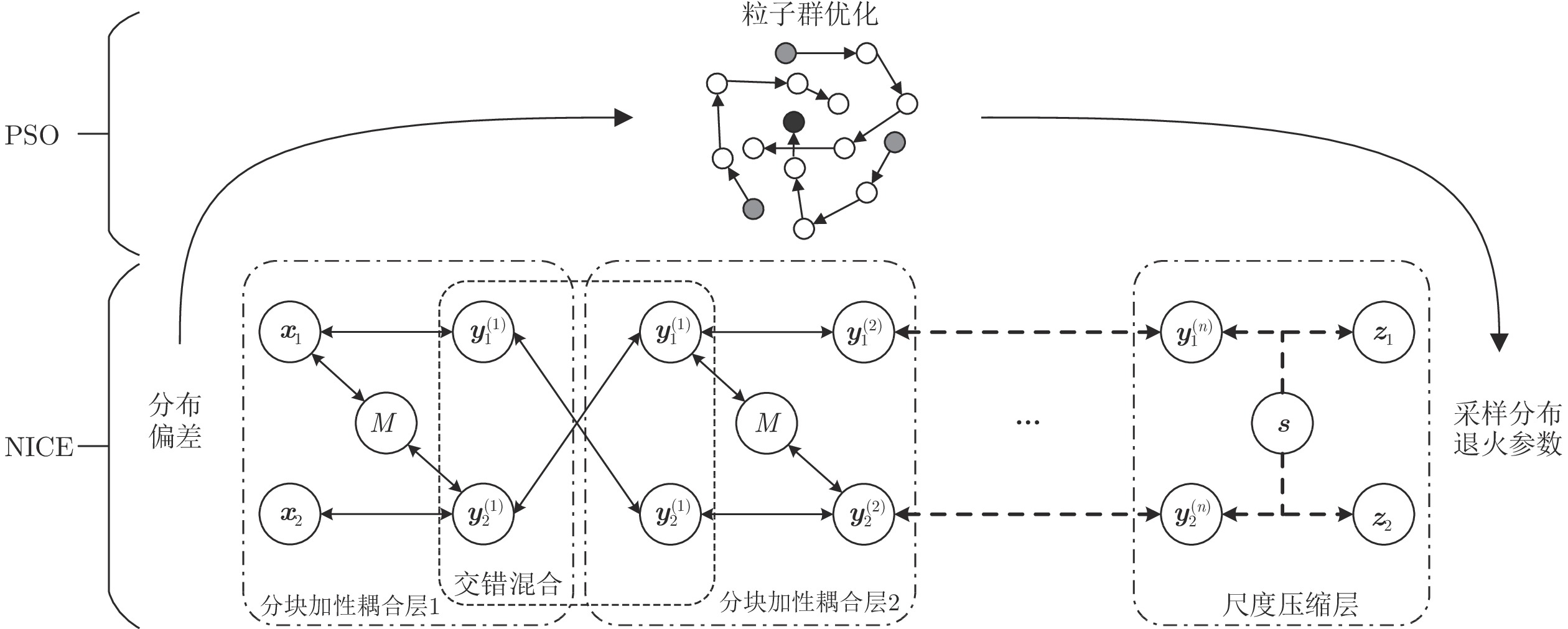
摘要: 针对缺失数据生成模型精度低和训练速度慢的问题, 本文基于流模型框架提出了一种改进非线性独立成分估计(Nonlinear independent components estimation, NICE)的缺失时间序列生成方法. 该方法依靠流模型框架生成模型精度高、训练过程速度快的优势, 并结合粒子群优化算法(Particle swarm optimization, PSO) 优化NICE生成网络采样的退火参数, 训练学习监测数据的真实分布, 从而实现对数据缺失部分的最优填补. 为进一步拓宽所提方法的应用范围, 利用基于流模型的缺失数据生成方法得到的生成数据, 通过建立融合注意力机制的双向长短时记忆网络(Bidirectional long short-term memory with attention, Bi-LSTM-Att)的退化设备预测模型, 实现设备剩余寿命的准确预测. 最后, 通过锂电池退化数据的实例研究, 验证了该方法的有效性和潜在应用价值.Abstract: Aiming at the problems of low accuracy and slow training speed of the missing data generation model, this paper proposes a missing time series generation method based on the flow model framework, which improves the nonlinear independent components estimation (NICE). The method relies on the flow model framework. The advantages of the high accuracy of the generative model and the fast training process are combined with the particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm to optimize the annealing parameters of the NICE generation network sampling, and the training and learning to monitor the real distribution of the data, so as to achieve the most optimal part of the missing data. In order to further broaden the application scope of the proposed method, this paper uses the generated data obtained by the missing data generation method based on the flow model, and establishes a bidirectional long short-term memory network (Bidirectional long short-term memory with attention, Bi-LSTM-Att) degradation device prediction model to achieve accurate prediction of the remaining life of the device. Finally, the effectiveness and potential application value of the proposed method are verified through a case study of lithium battery degradation data.
-
表 1 CS2_37构造的原始数据和不同缺失率下的训练数据
Table 1 Original data constructed by CS2_37 and training data with different missing rates
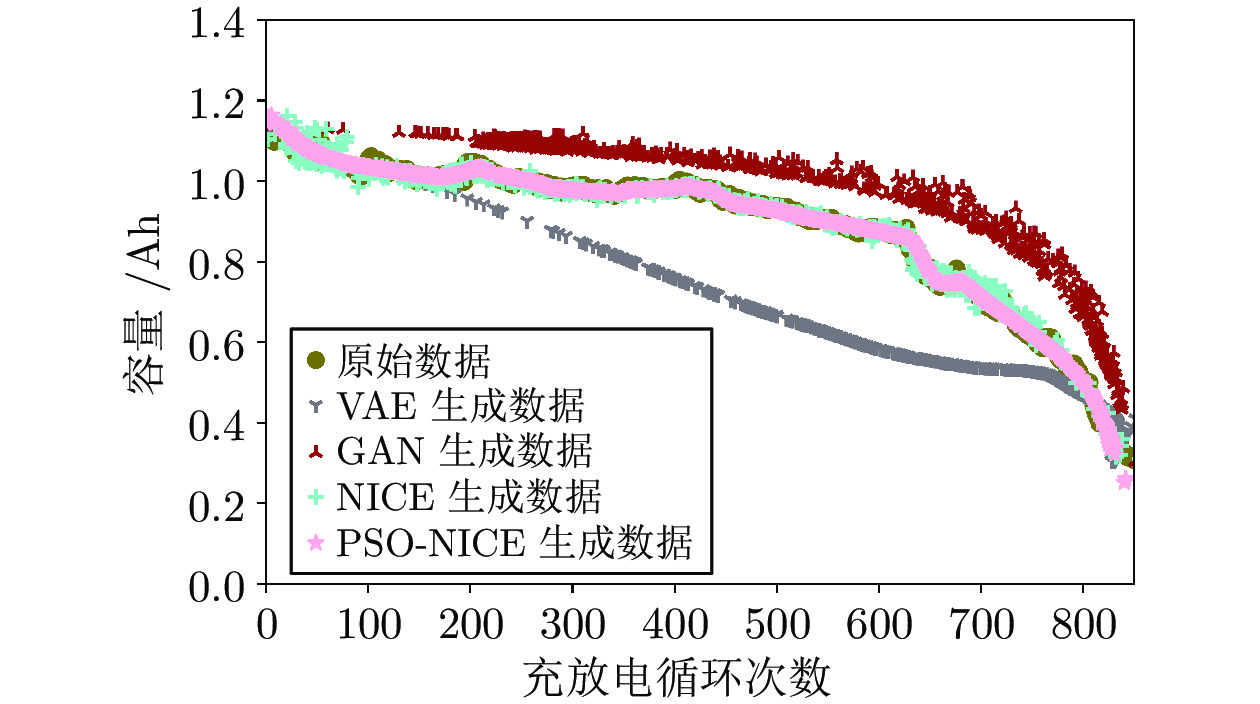
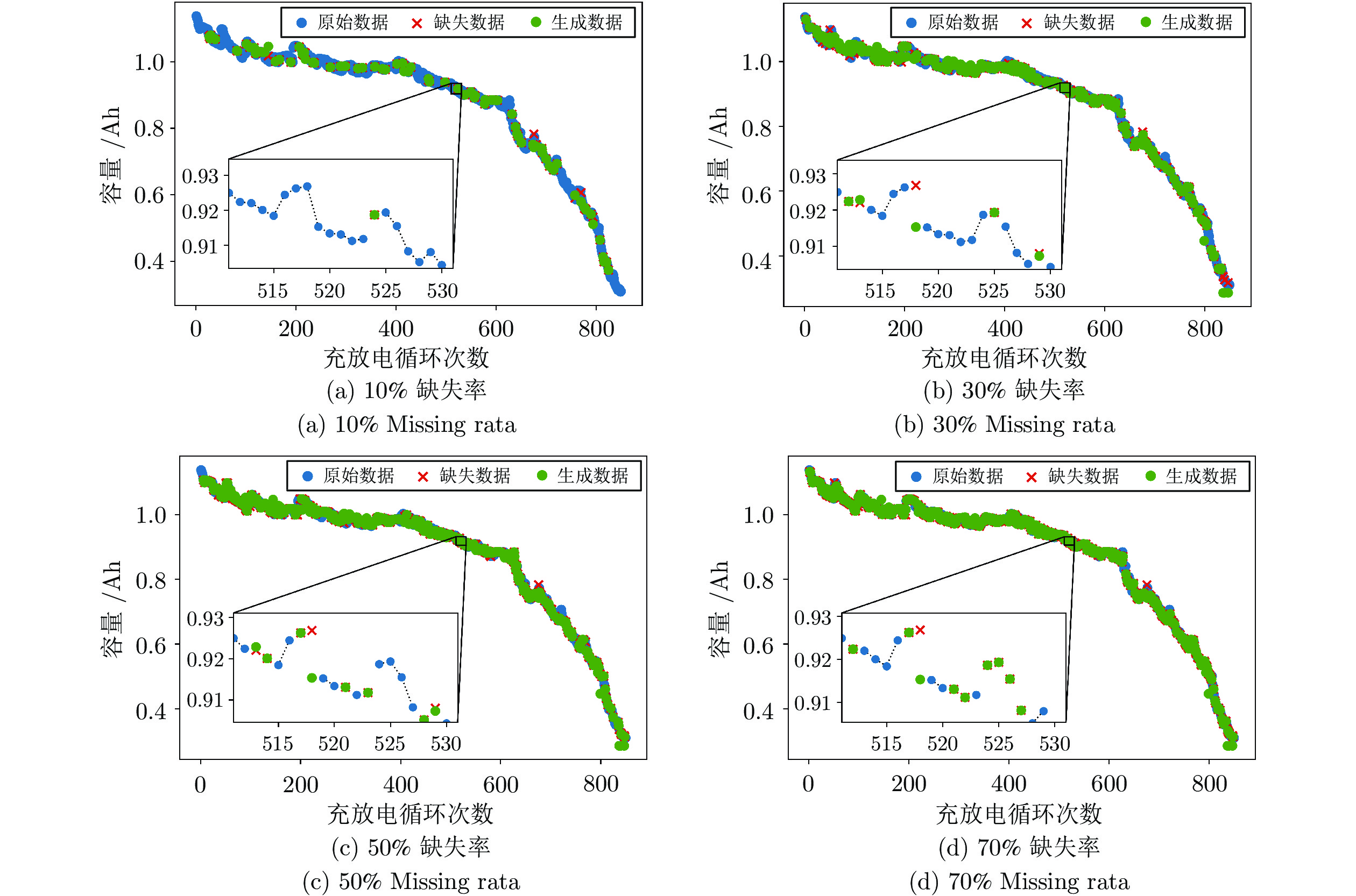
数据类型 缺失率 样本数量 原始数据 0 850 缺失数据 10% 771 30% 643 50% 513 70% 438 表 2 CS2数据集构造RUL预测的训练样本和验证样本
Table 2 CS2 dataset constructs training samples and validation samples for RUL prediction
样本类型 样本组成 样本量 训练样本 CS2_35 851 CS2_36 944 CS2_38 991 CS2_37 (0$\sim$600) 600 验证样本 CS2_37 (601$\sim$1006) 406 表 3 不同缺失率下的PSO-NICE模型参数
Table 3 PSO-NICE model parameters with different missing rates
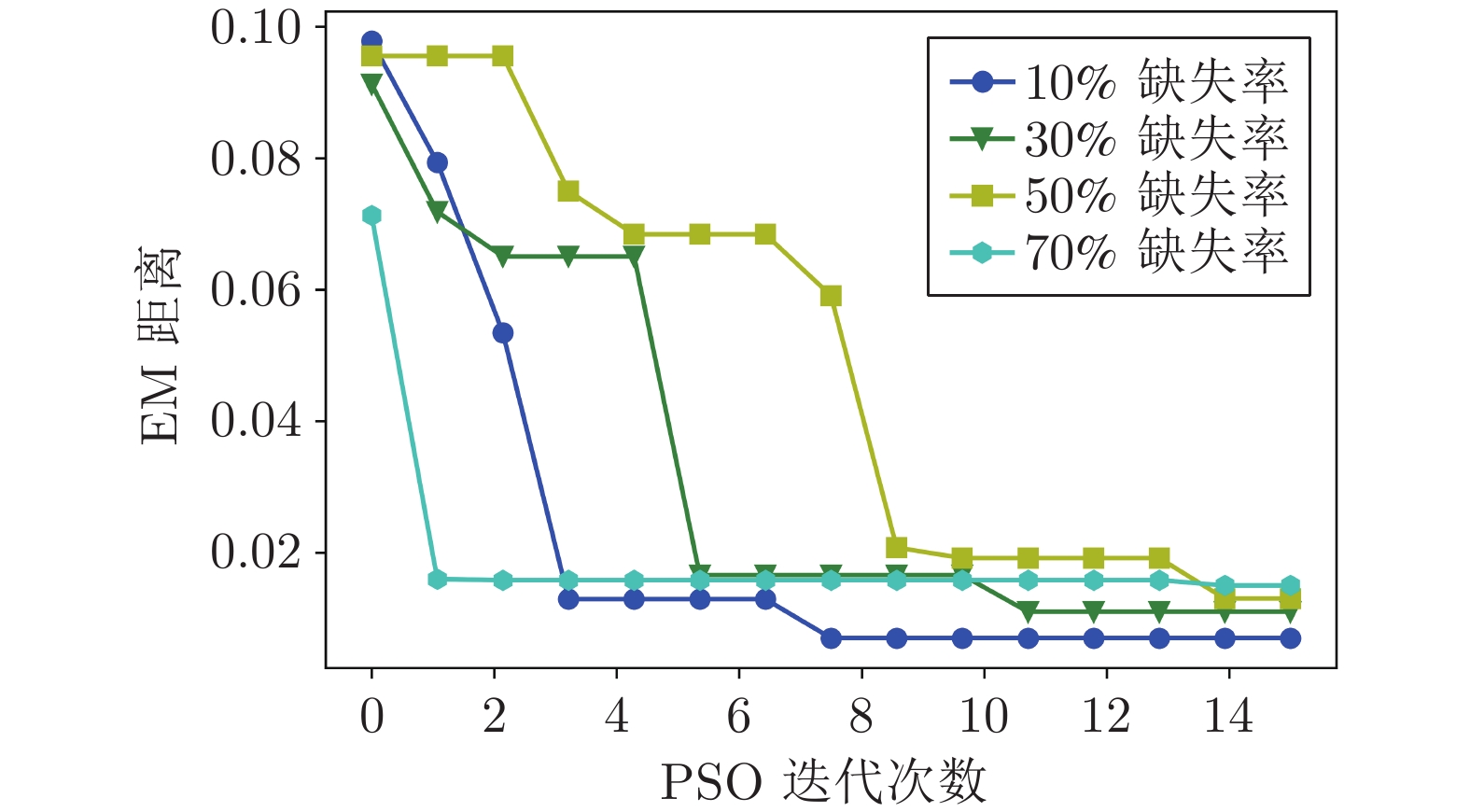
训练数据缺失率 样本剩余量 分块加性耦合层数 耦合层数 每层神经元 批处理量 NICE迭代次数 粒子维度大小 粒子群大小 PSO迭代次数 10% 771 16 5 1000 128 1000 2 2 15 30% 643 14 5 1000 64 1000 2 2 15 50% 513 12 5 1000 64 1000 2 2 15 70% 438 10 5 1000 64 1000 2 2 15 表 4 不同缺失率下各方法生成样本与完整样本的EM距离
Table 4 The EM distance between generation sample and the complete sample under different missing rates
缺失率 不处理 VAE GAN NICE PSO-NICE DCGAN-KS[11] 10% 0.081 0.064 0.056 0.012 0.007 0.024 30% 0.218 0.175 0.159 0.014 0.011 0.049 50% 0.357 0.282 0.207 0.024 0.013 0.072 70% 0.431 0.397 0.284 0.028 0.015 0.122 表 5 现有常用预测网络的参数
Table 5 Parameters of existing common prediction networks
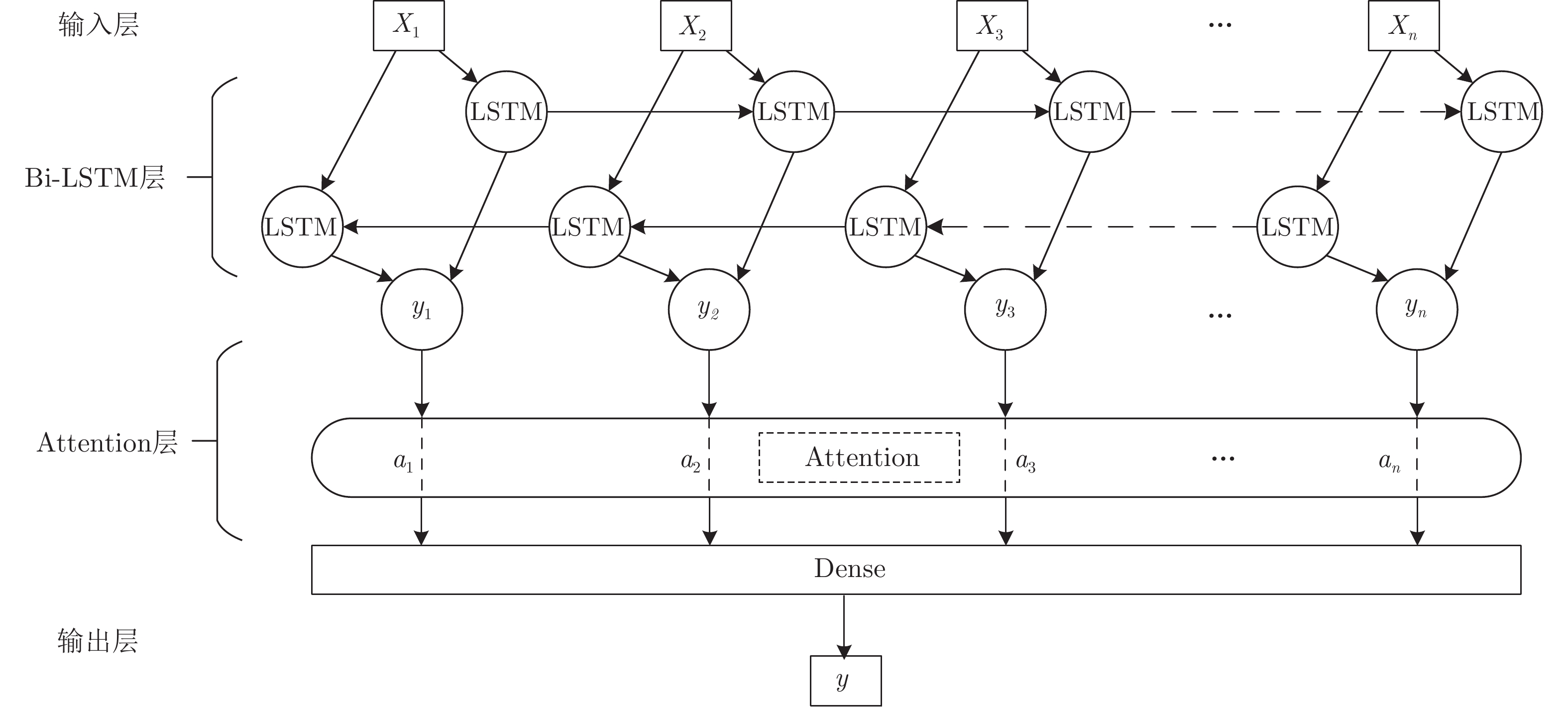
预测网络 网络层数 每层单元数 Attention单元数 全连接层数 每层神经元个数 随机种子 批处理量 迭代次数 RNN 1 64 0 1 1 3 16 4 GRU 1 64 0 1 1 0 16 5 LSTM 1 64 0 1 1 0 16 5 Bi-LSTM 2 64 0 1 1 0 16 5 Bi-LSTM-Att 2 64 1 1 1 0 16 5 表 6 不同预测方法的效果评估
Table 6 Effectiveness evaluation of different forecasting methods
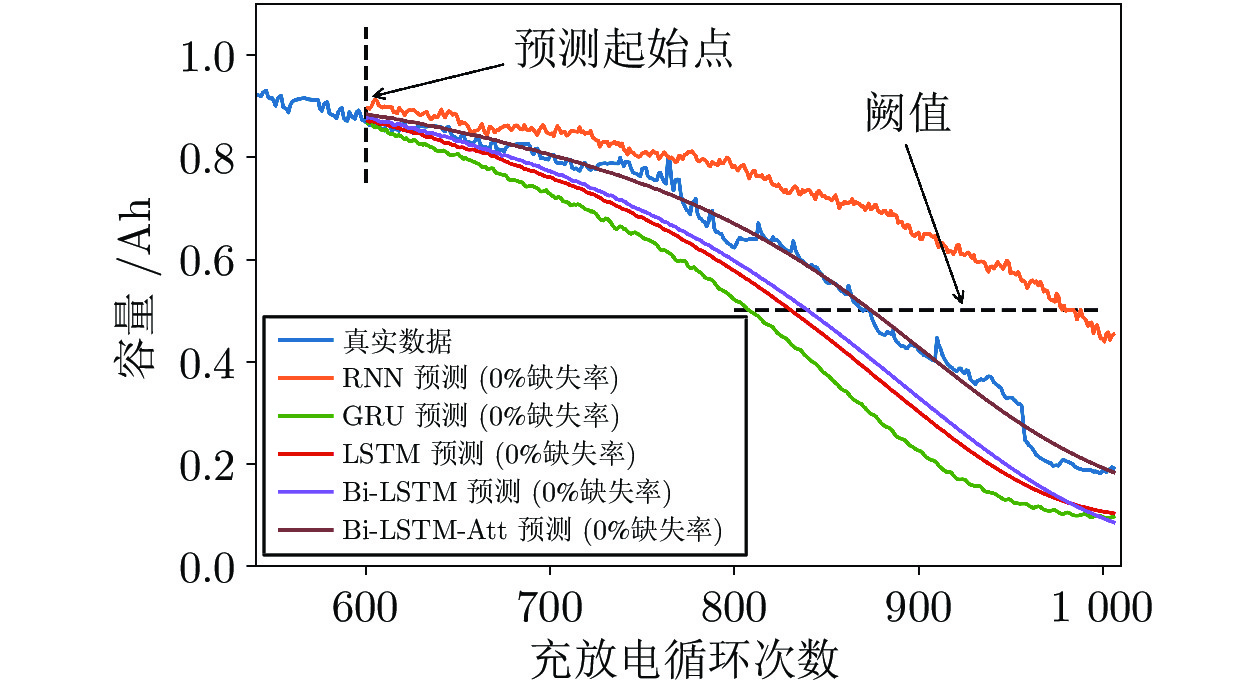
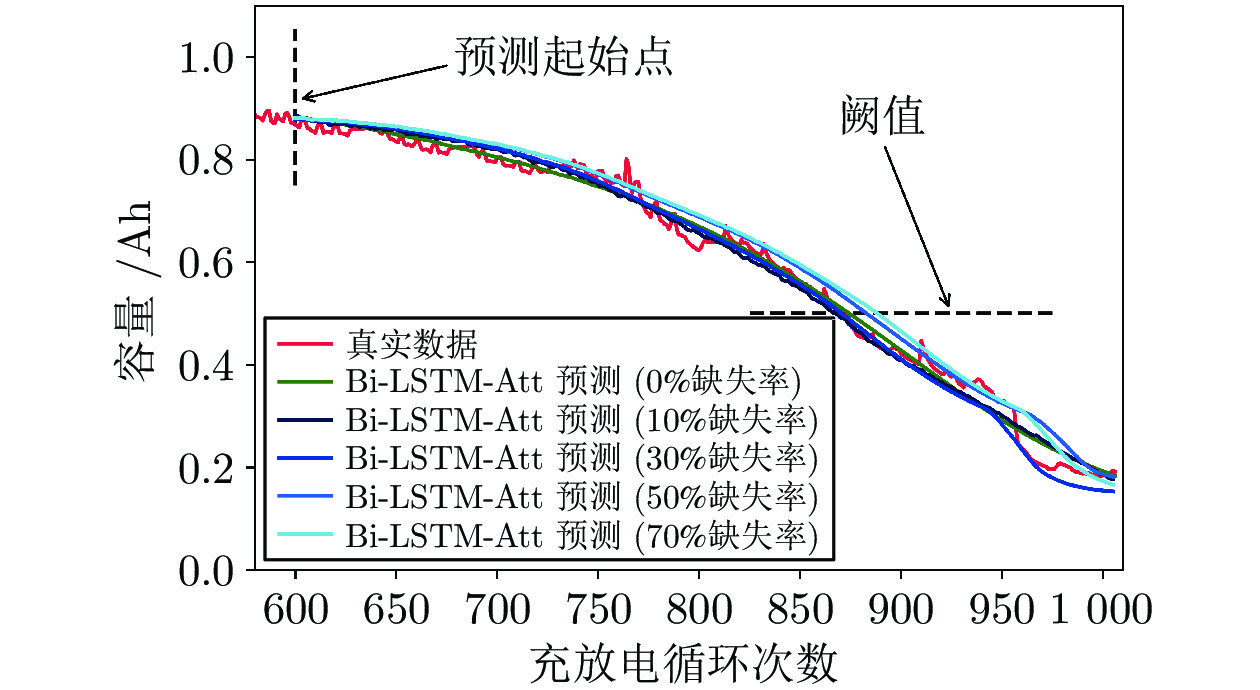
预测方法 缺失率 RMSE $R^2$ 运行时间 (秒) RNN 0% 0.1679 –0.77041 14 GRU 0.1376 0.72191 15 LSTM 0.0902 0.8713 15 Bi-LSTM 0.0746 0.9114 17 Bi-LSTM-Att 0% 0.0213 0.9907 26 10% 0.022 0.99 30% 0.0224 0.9898 50% 0.0328 0.978 70% 0.0424 0.9632 表 7 不同缺失率填补后Bi-LSTM-Att重复预测量化结果
Table 7 Quantification results of Bi-LSTM-Att repeated prediction after imputation with different missing rates
缺失率 预测均值 95%置信区间 0% 0.0213 [0.0379, 0.0468] 10% 0.0215 [0.0460, 0.0493] 30% 0.0294 [0.0526, 0.0657] 50% 0.0300 [0.0428, 0.1024] 70% 0.0468 [0.0560, 0.1054] -
[1] Si X S, Wang W, Hu C H, et al. Remaining useful life estimation–a review on the statistical data driven approaches. European Journal of Operational Research, 2011, 213(1): 1-14 doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2010.11.018 [2] 周东华, 魏慕恒, 司小胜. 工业过程异常检测、寿命预测与维修决策的研究进展. 自动化学报, 2013, 39(6): 711-722Zhou Dong-Hua, Wei Mu-Heng, Si Xiao-Sheng. A survey on anomaly detection, life prediction and maintenance decision for industrial processes. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(6): 711-722 [3] 董青, 郑建飞, 胡昌华, 李冰, 牟含笑. 基于两阶段自适应Wiener过程的剩余寿命预测方法. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(2):539-553Dong Qing, Zheng Jian-Fei, Hu Chang-Hua, Li Bing, Mu Han-Xiao. Remaining useful life prognostic method based on two-stage adaptive Wiener process. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(2): 539-553 [4] Zheng J F, Si X S, Hu C H, et al. A nonlinear prognostic model for degrading systems with three-source variabilit. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2016, 65(2): 736-750 doi: 10.1109/TR.2015.2513044 [5] Saha B, Goebel K. Battery Data Set, NASA ames prognostics data repository[Online], available: https://ti.arc.nasa.gov/tech/dash/groups/pcoe/prognostic-data-repository/, December 23, 2022 [6] Pecht M, Osterman M. Battery Research Data, Center for Advanced Life Cycle Engineering (CALCE) [Online], available: https://web.calce.umd.edu/batteries/data.html, December 23, 2022 [7] 杜党波, 张伟, 胡昌华, 周志杰, 司小胜, 张建勋. 含缺失数据的小波-卡尔曼滤波故障预测方法. 自动化学报, 2014, 40(10):2115--2125Du Dang-Bo, Zhang Wei, Hu Chang-Hua, Zhou Zhi-Jie, Si Xiao-Sheng, Zhang Jian-Xun. A failure prognosis method based on wavelet-Kalmanfiltering with missing data. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(10): 2115-2125 [8] 裴洪, 胡昌华, 司小胜, 张建勋, 庞哲楠, 张鹏. 基于机器学习的设备剩余寿命预测方法综述. 机械工程学报, 2019, 55(8):1-13 doi: 10.3901/JME.2019.08.001Pei Hong, Hu Chang-Hua, Si Xiao-Sheng, Zhang Jian-Xun, Pang Zhe-Nan, Zhang Peng. Overview of machine learning-based equipment remaining life prediction methods. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2019, 55(8): 1-13 doi: 10.3901/JME.2019.08.001 [9] 胡铭菲, 左信, 刘建伟. 深度生成模型综述. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(1):40-74 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190866Hu Ming-Fei, Liu Jian-Wei, Zuo Xin. Survey on deep generate model. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(1):40-74 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190866 [10] Yoon J, Jordon J, Schaar M. Gain: missing data imputation using generative adversarial nets. In: Proceedings of the Machine Learning Research. Stockholm, Sweden, PMLR, 2018: 5689−5698 [11] 张晟斐, 李天梅, 胡昌华, 杜党波, 司小胜. 基于深度卷积生成对抗网络的缺失数据生成方法及其在剩余寿命预测中的应用. 航空学报, 2022, 43(8):441-455 doi: 10.7527/j.issn.1000-6893.2022.8.hkxb202208032Zhang Sheng-Fei, Li Tian-Mei, Hu Chang-Hua, Du Dang-Bo, Si Xiao-Sheng. Deep convolutional generative adversarial network based missing data generation method and its application in remaining useful life prediction. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2022, 43(8):441-455 doi: 10.7527/j.issn.1000-6893.2022.8.hkxb202208032 [12] Nazabal A, Olmos P M, Ghahramani Z, et al. Handling incomplete heterogeneous data using vaes. Pattern Recognition, 2020, 107: 107501 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2020.107501 [13] Dinh L, Krueger D, Bengio Y. Nice: non-linear independent components estimation. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1410.8516, 2014 [14] Dinh L, Sohl-Dickstein J, Bengio S. Density estimation using real nvp. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1605.08803, 2016 [15] Kingma D P, Dhariwal P. Glow: generative flow with invertible 1x1 convolutions. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1807.03039, 2018 [16] Prenger R, Valle R, Catanzaro B. Waveglow: a flow-based generative network for speech synthesis. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing. Brighton, UK, IEEE, 2019: 3617−3621 [17] Ge L, Liao W, Wang S, et al. Modeling daily load profiles of distribution network for scenario generation using flow-based generative network. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 77587-77597 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2989350 [18] 薛阳, 杨艺宁, 廖文龙, 杨德昌. 基于非线性独立成分估计的分布式光伏窃电数据增强方法. 电力系统自动化, 2022, 46(2):171-179Xue Yang, Yang Yi-Ning, Liao Wen-Long, Yang De-Chang. Distributed photovoltaic power stealing data enhancement method based on nonlinear independent component estimation. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2022, 46(2):171-179 [19] Su Jian-Lin. NICE: basic concept and implementation of flow model [Online], available: https://spaces.ac.cn/archives/5776, December 23, 2022 [20] 余海燕, 陈京京, 邱航, 王永, 王若凡. 嵌套删失数据期望最大化的高斯混合聚类算法.自动化学报, 2021, 47(6):1302-1314 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190081Yu Hai-Yan, Chen Jing-Jing, Qiu Hang, Wang Yong, Wang Ruo-Fan. Adapted expectation maximization algorithm for Gaussian mixture clustering with censored data. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(6): 1302-1314 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190081 -




 下载:
下载: