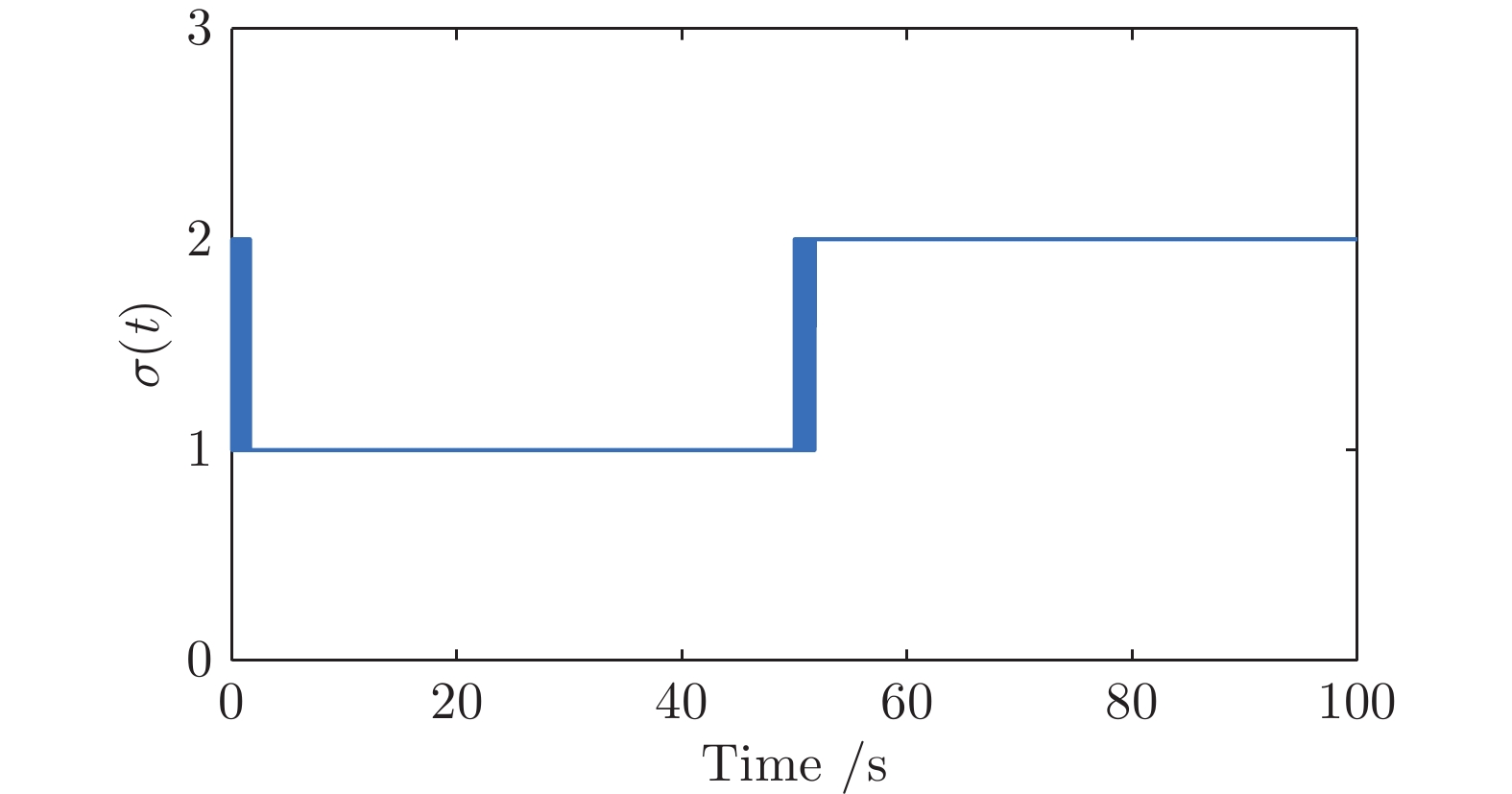
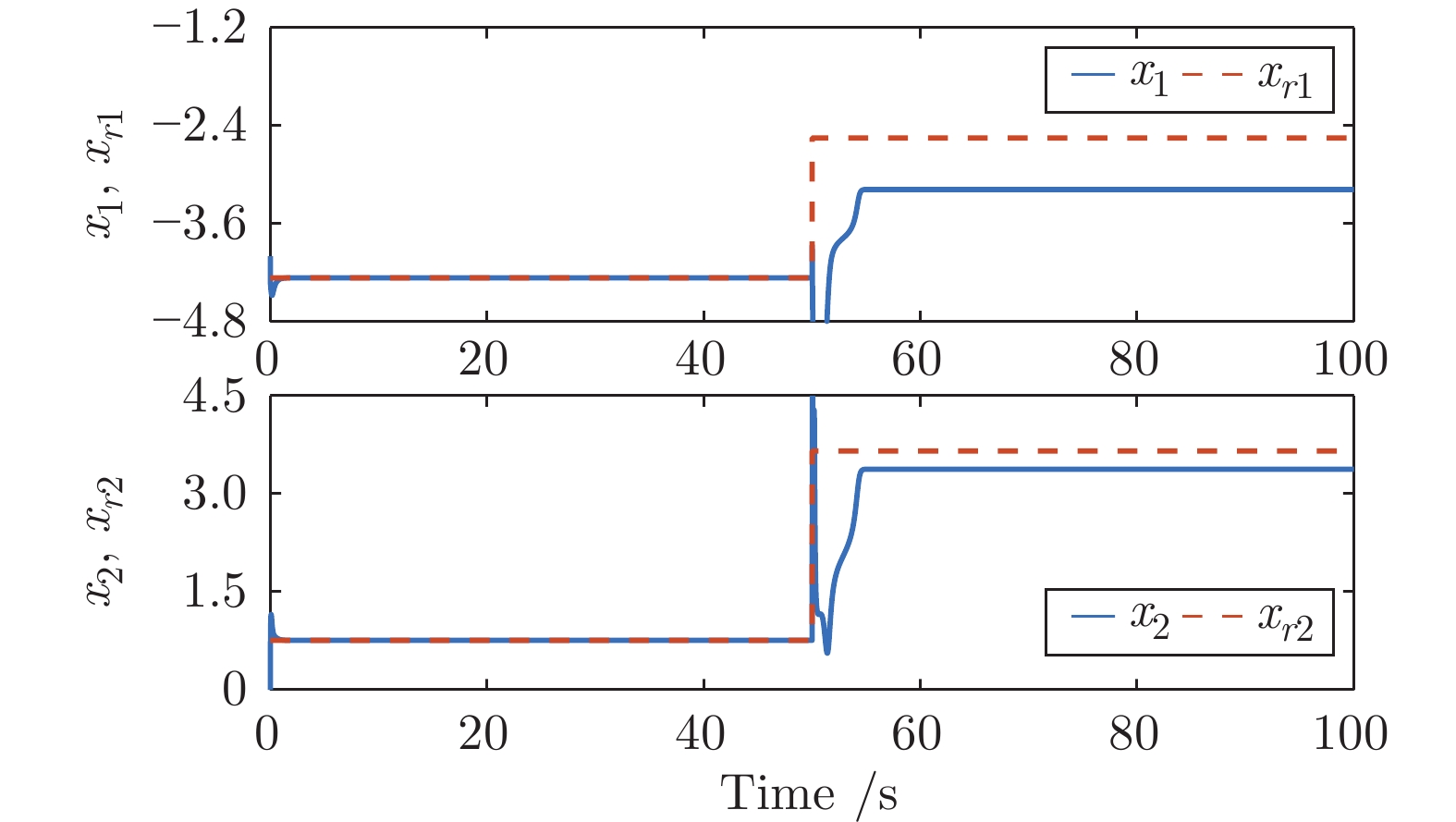
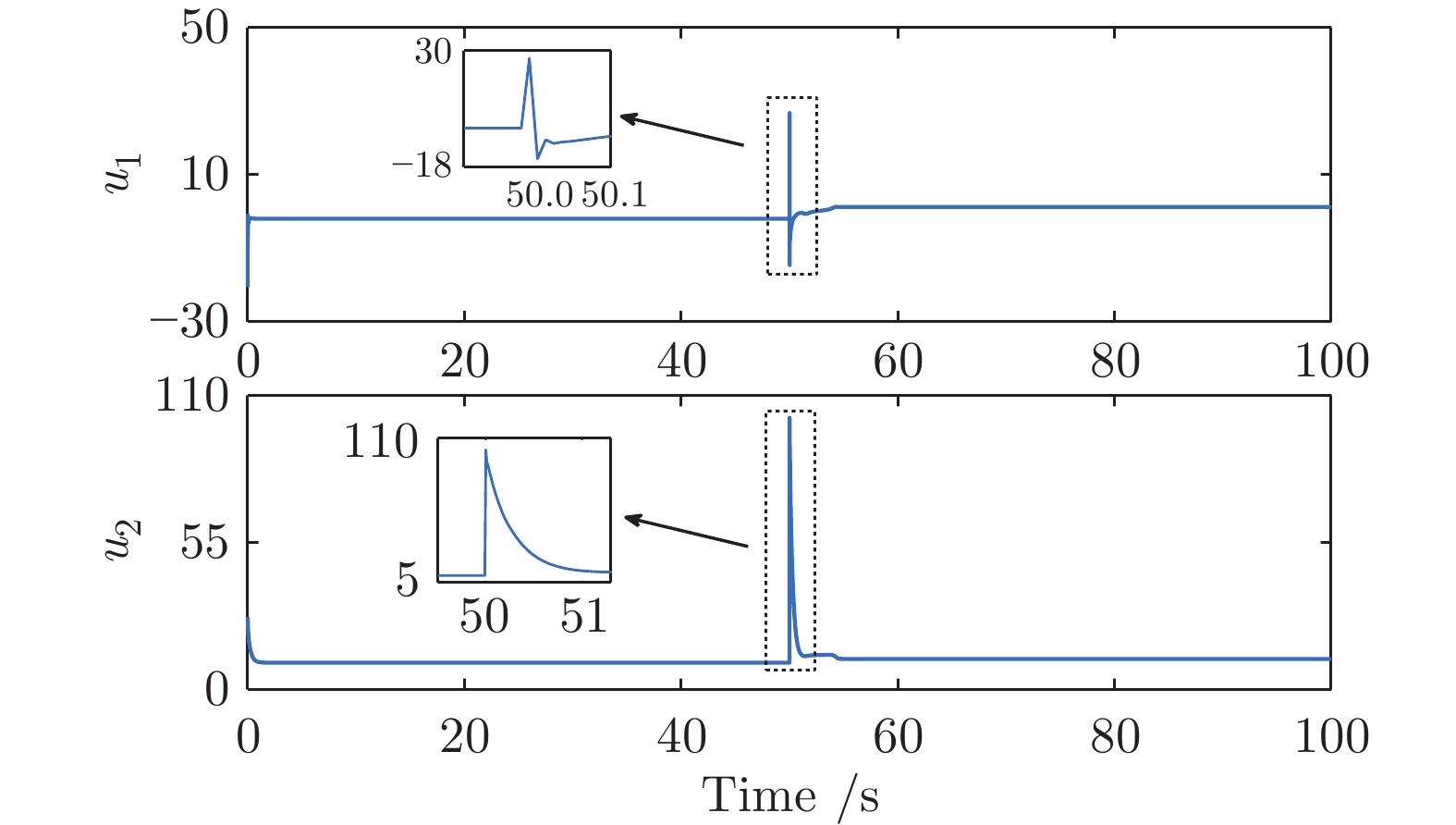
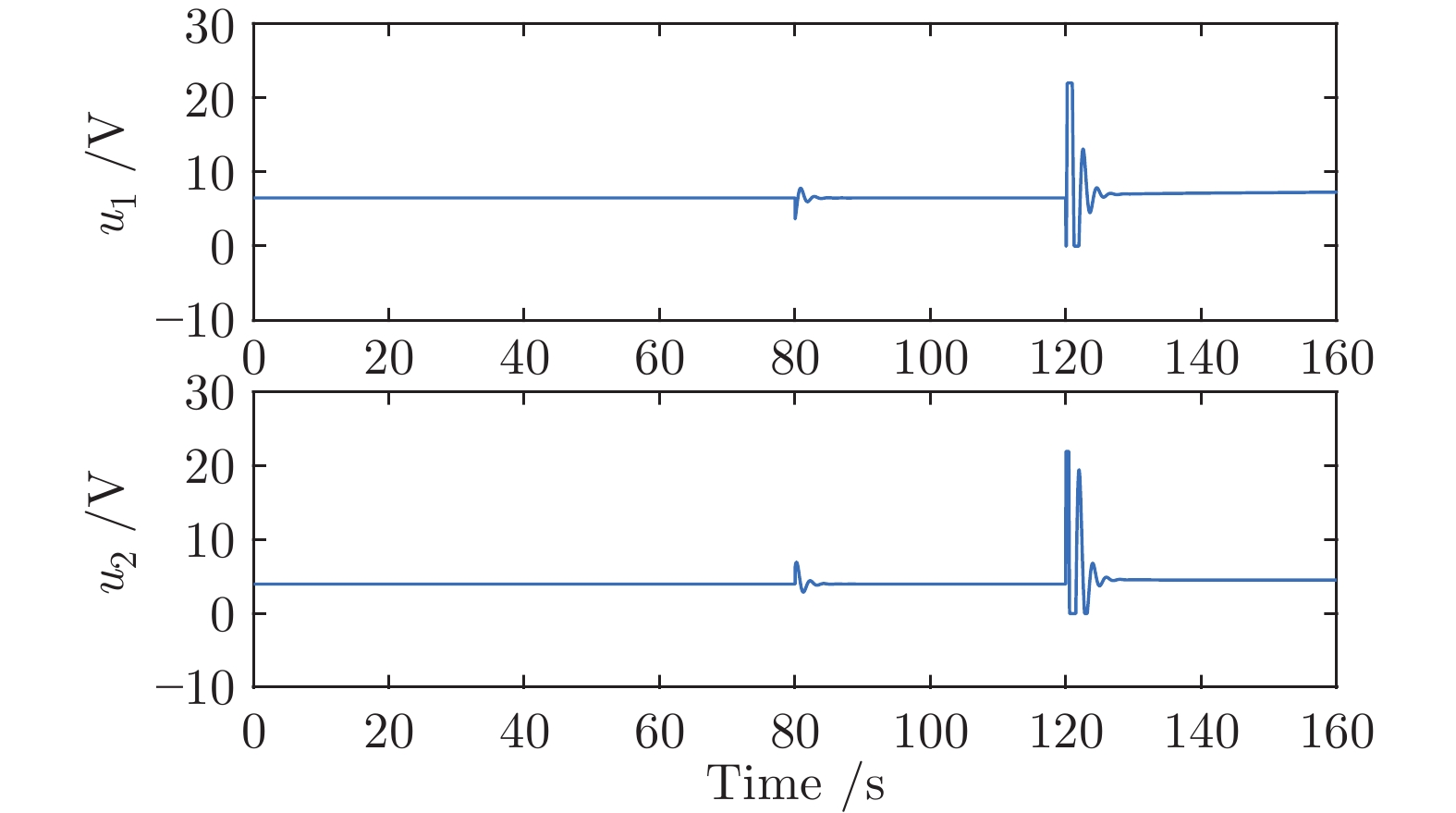
-
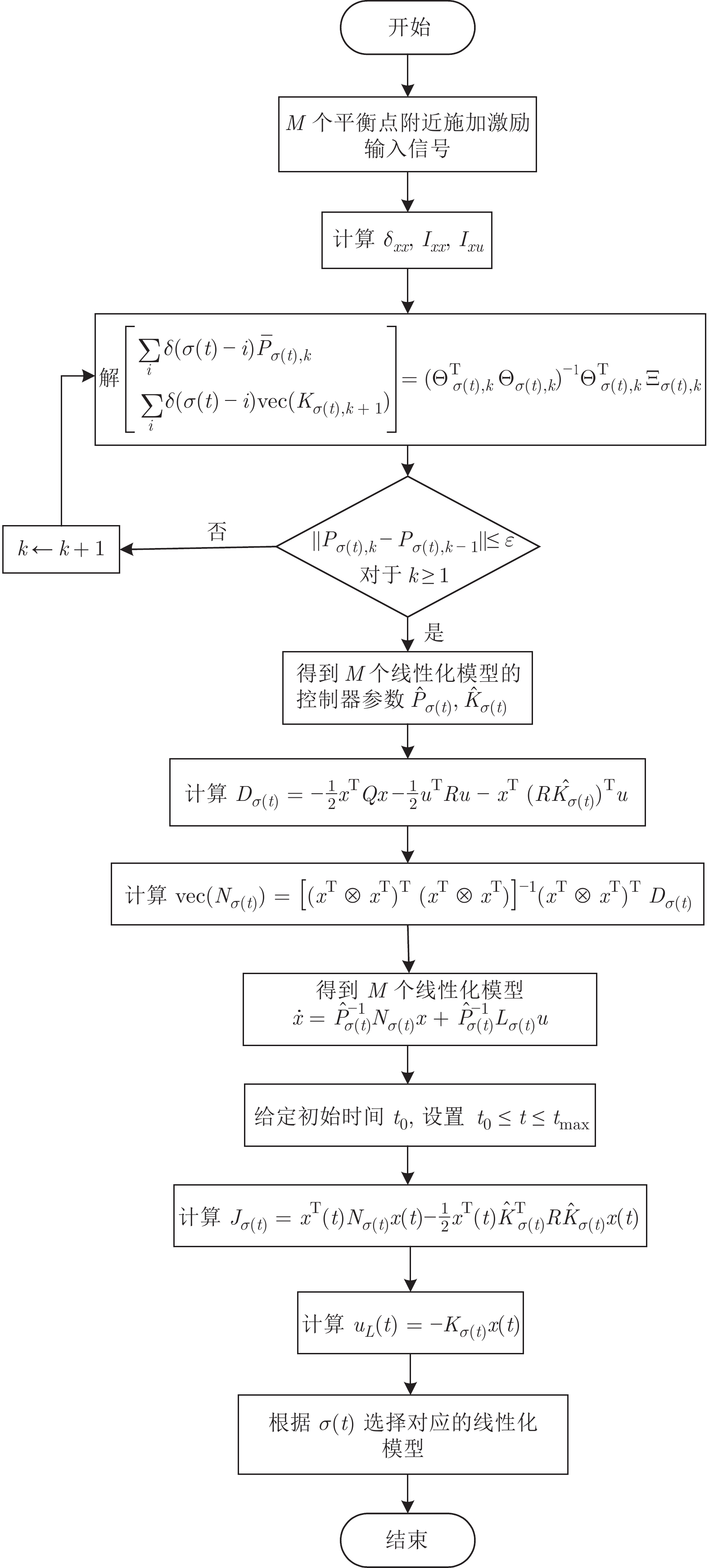
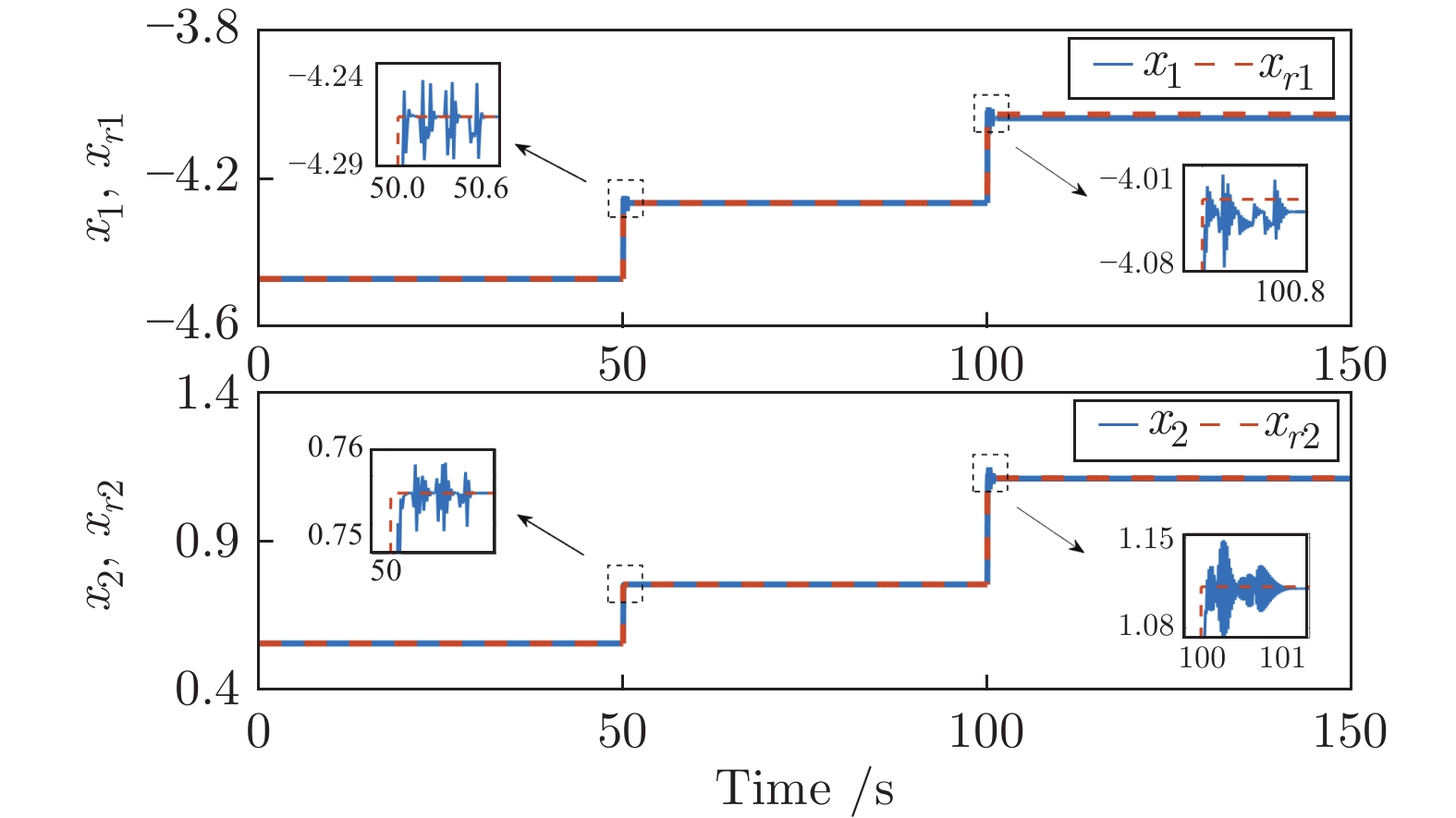
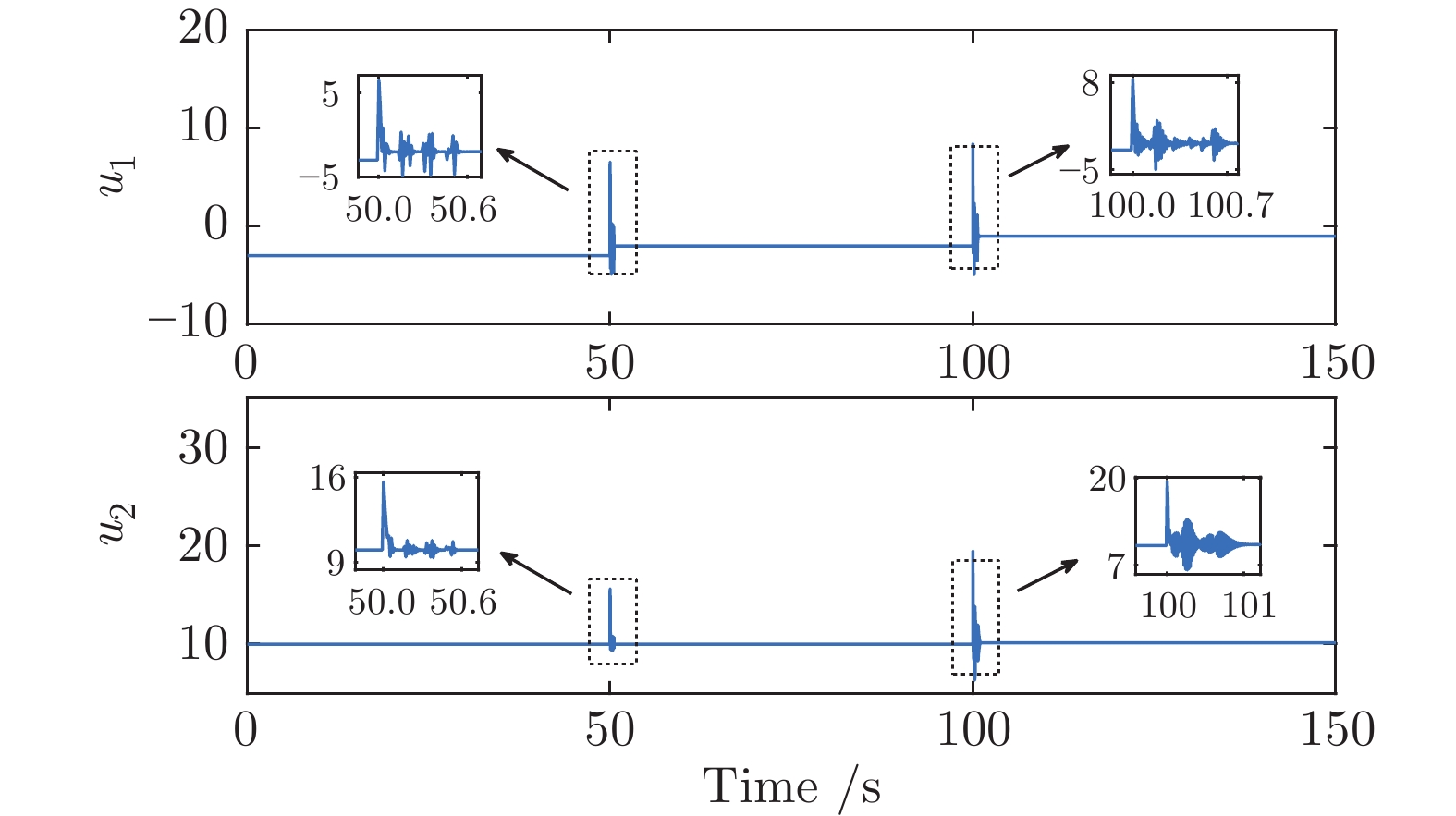
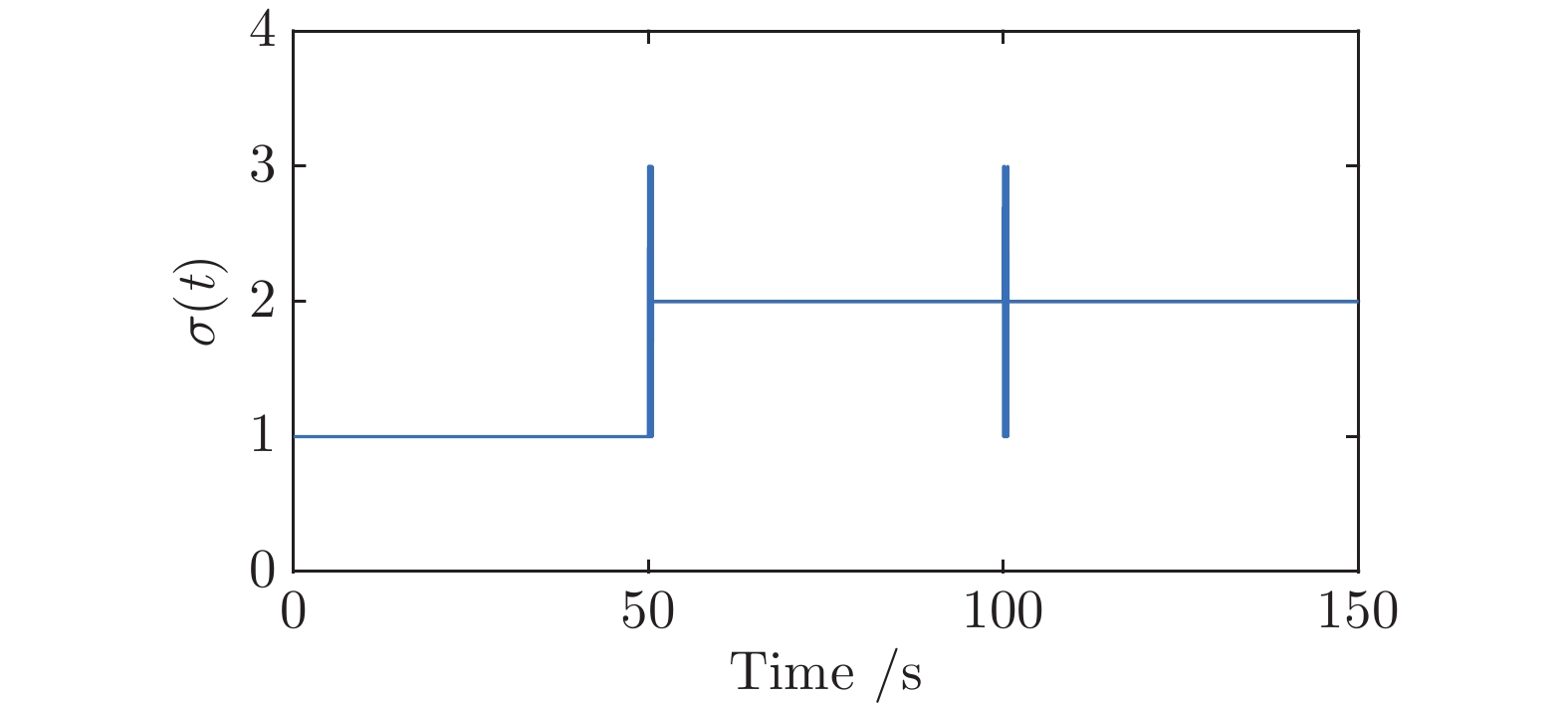
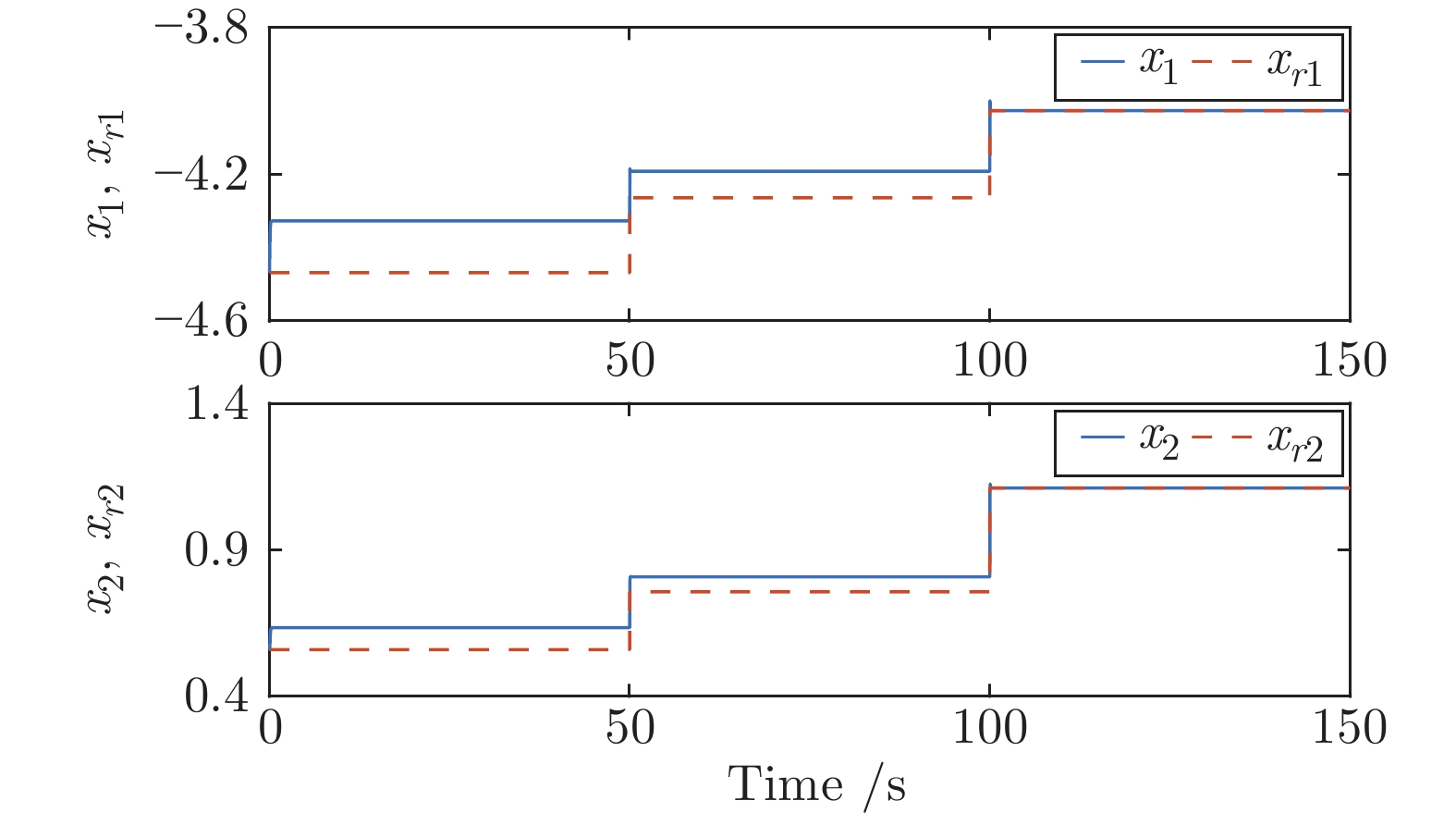
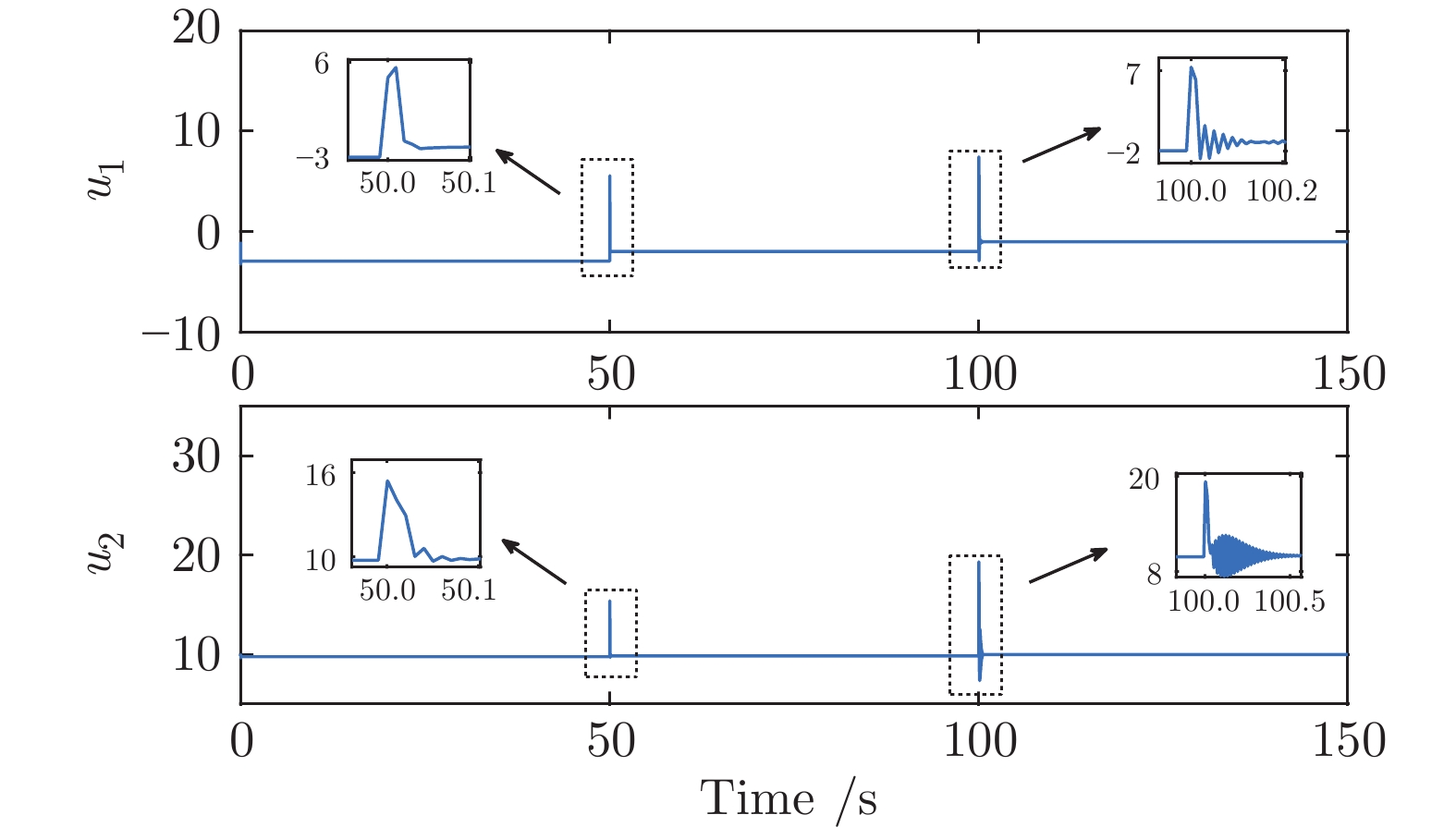
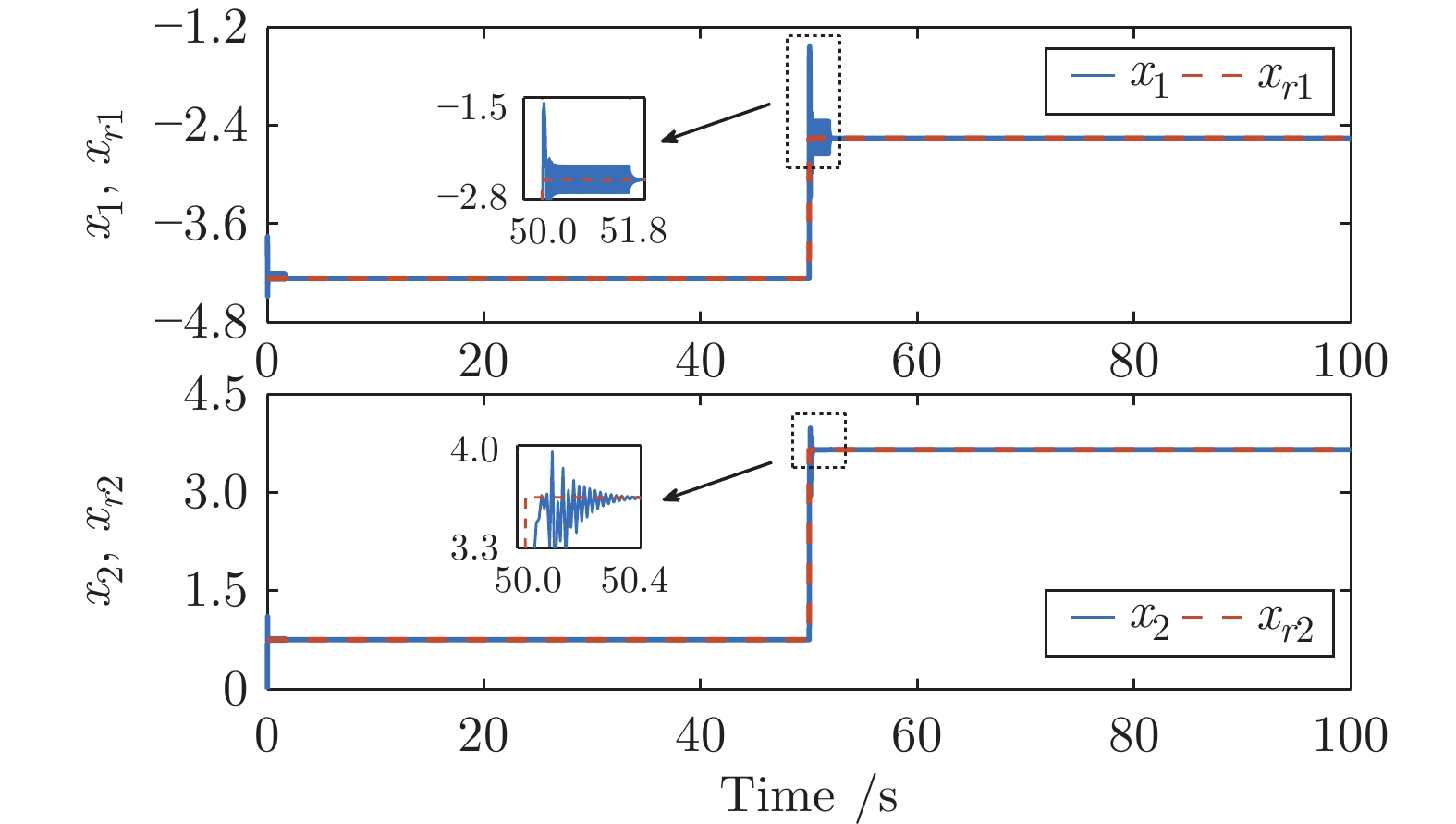
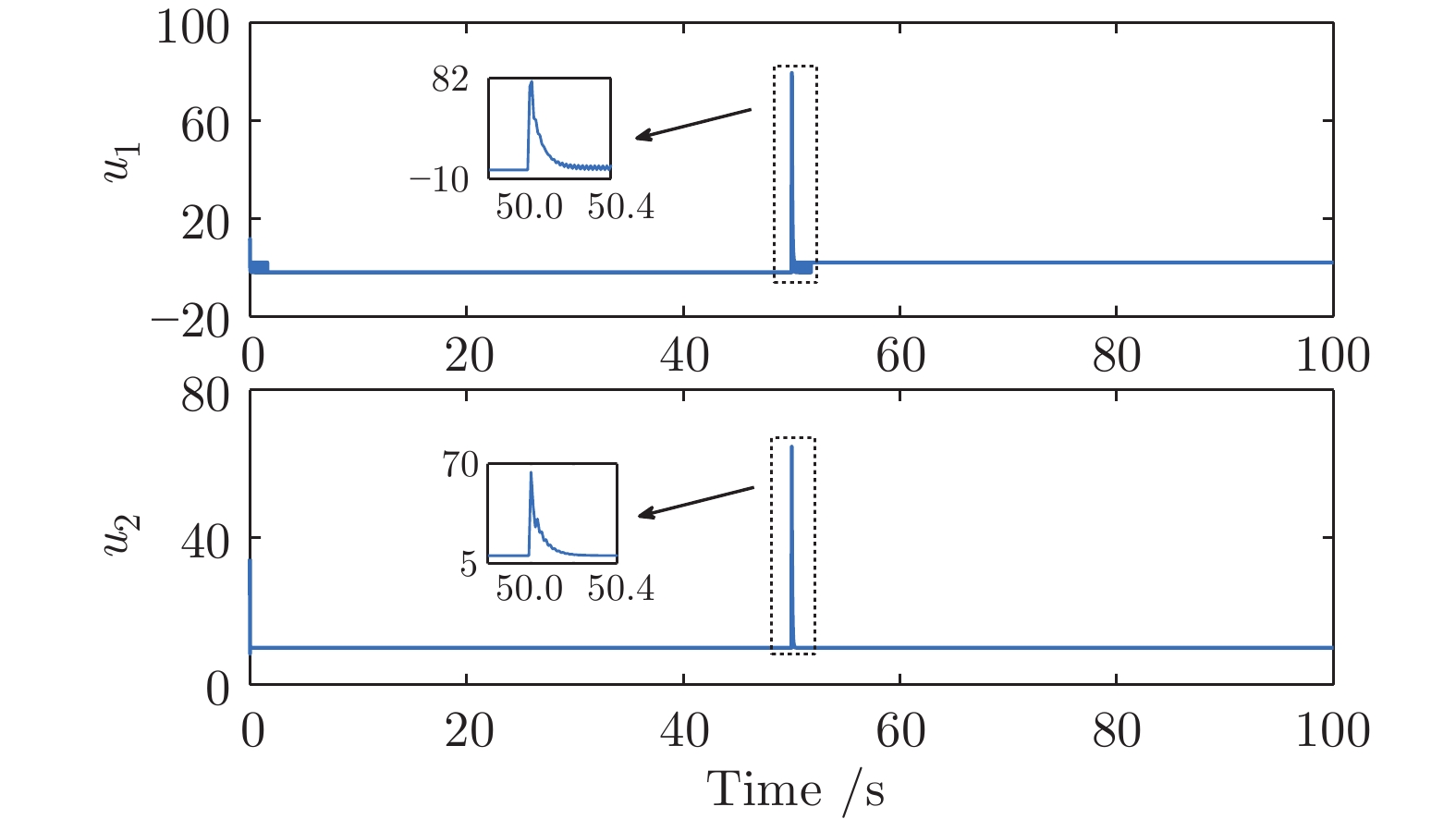
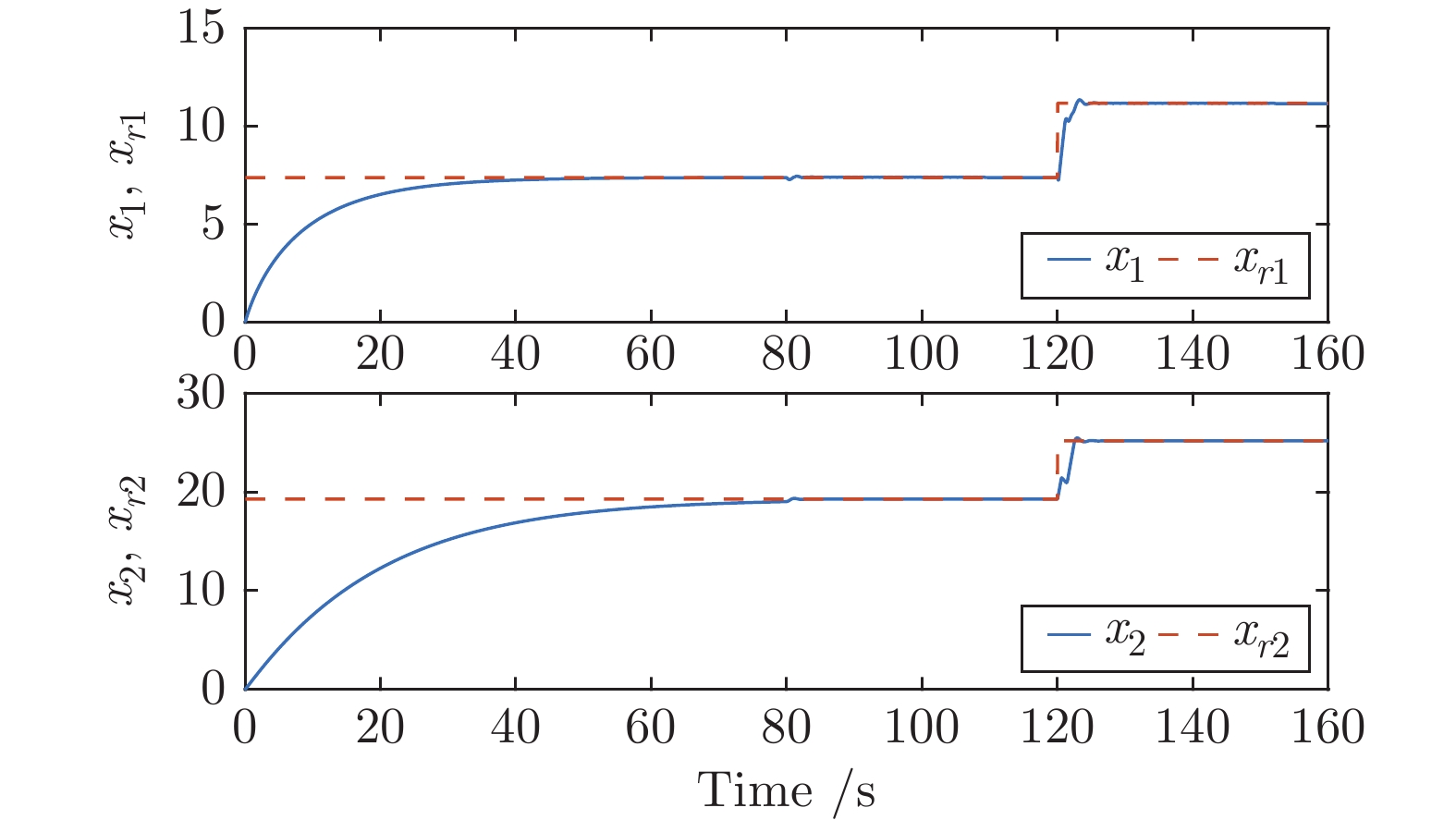
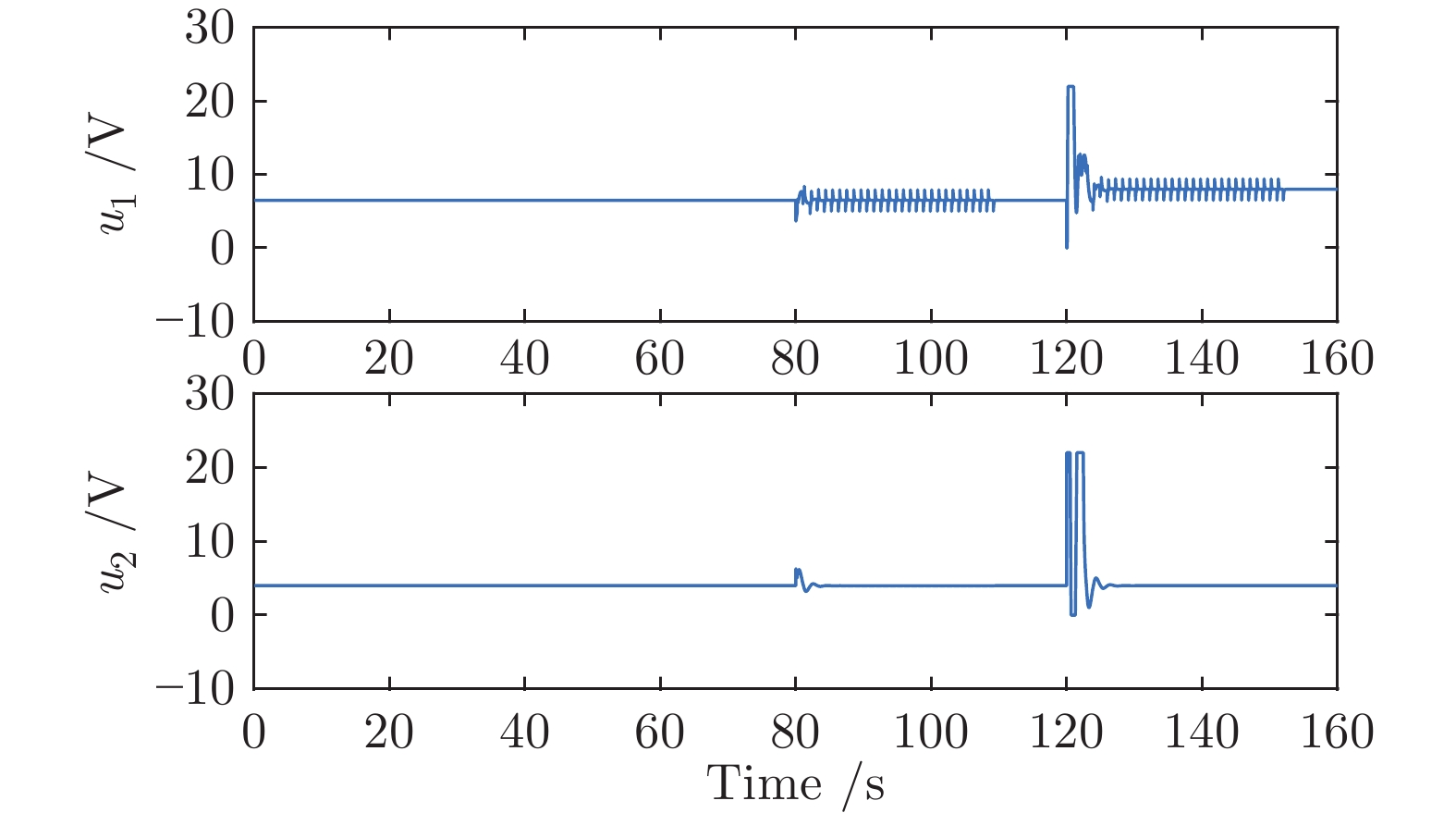
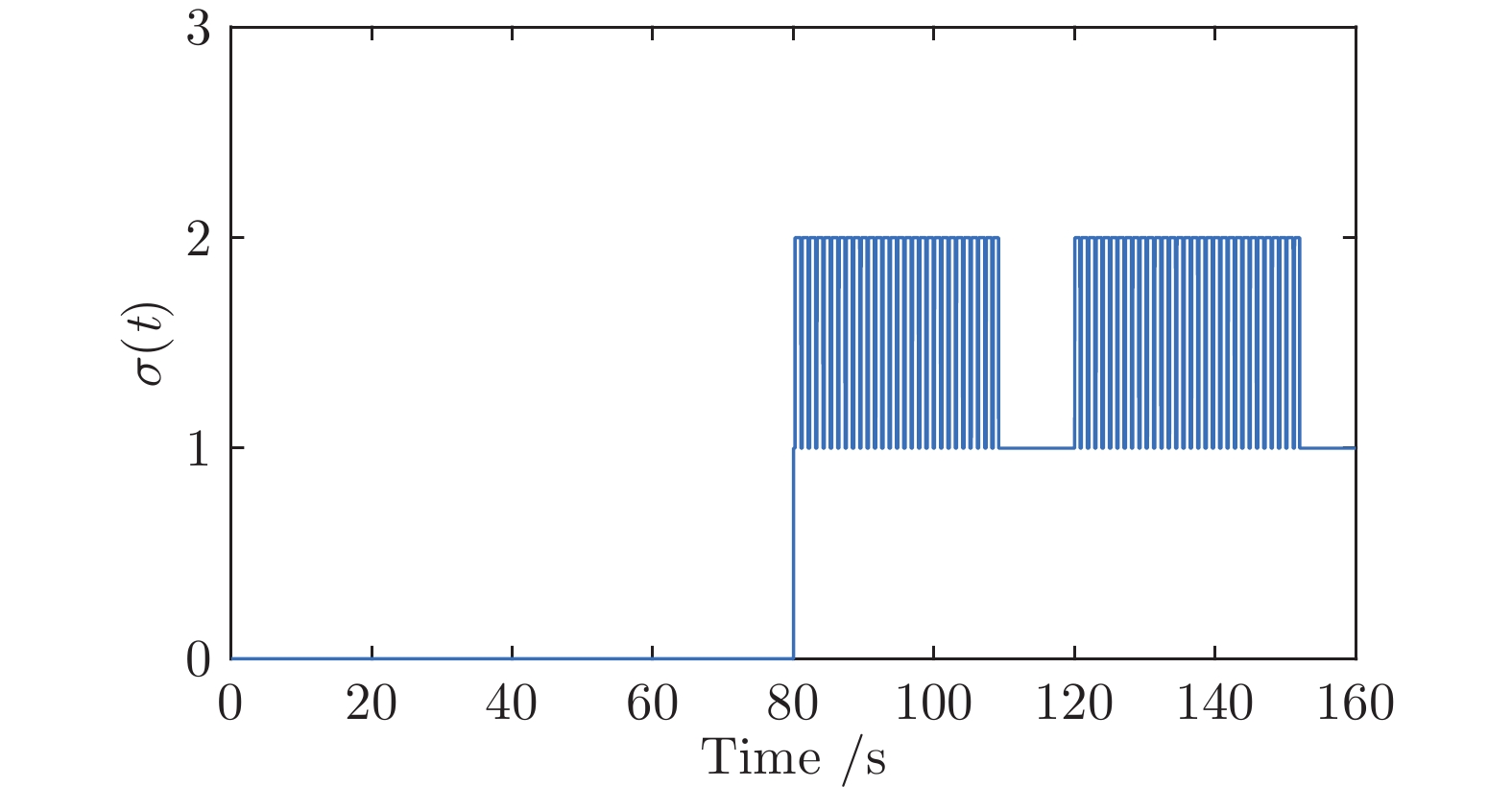
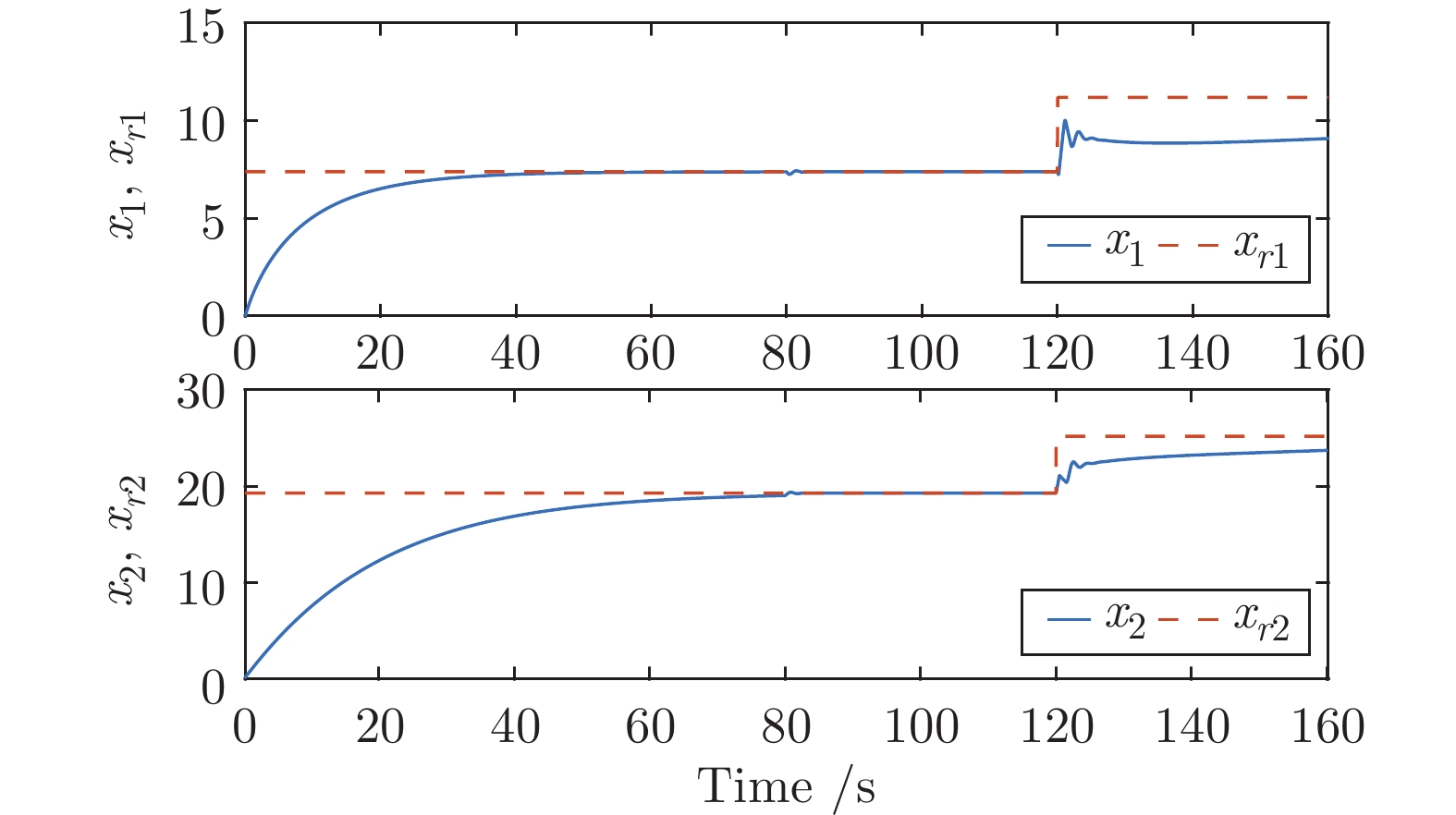
摘要: 针对具有未知动态和M个平衡点的连续时间非线性系统, 将线性自适应最优切换控制器和未建模动态补偿器相结合, 基于嵌入转换技术和近似动态规划思想, 提出一种自适应最优切换控制方法. 首先在非线性系统的M个平衡点建立M个线性化模型, 当模型参数已知时, 提出由线性最优切换控制器、切换准则、未建模动态补偿器以及非线性系统组成的控制系统结构; 当模型参数未知时, 在每个平衡点附近采集输入和状态数据, 利用黎卡提方程的迭代求解公式、最小二乘方法、极小值原理以及二次规划技术得到非线性系统的自适应最优切换控制器和最优切换序列; 最后进行仿真实验, 实验结果验证了所提方法的有效性、优越性和实际可应用性.Abstract: In this paper, for continuous-time nonlinear systems with unknown dynamics and M equilibrium points, based on embedding-transformation and approximate dynamic programming, an adaptive optimal switching control method is proposed by combining a linear adaptive optimal switching controller and an unmodeled dynamic compensator. Firstly, M linearized models are established at M equilibrium points of the nonlinear system. When the model parameters are known, a control system structure consisting of a linear optimal switching controller, a switching mechanism, an unmodeled dynamic compensator, and the nonlinear system is proposed. When the model parameters are unknown, the input and state data are collected at the neighborhood of each equilibrium point. Then the adaptive optimal switching controller and optimal switching sequence are obtained by using the iterative Riccati equation, least square method, minimum principle, and quadratic programming. Finally, simulations are conducted, and the results verify the effectiveness, superiority and applicability of the proposed method.
-
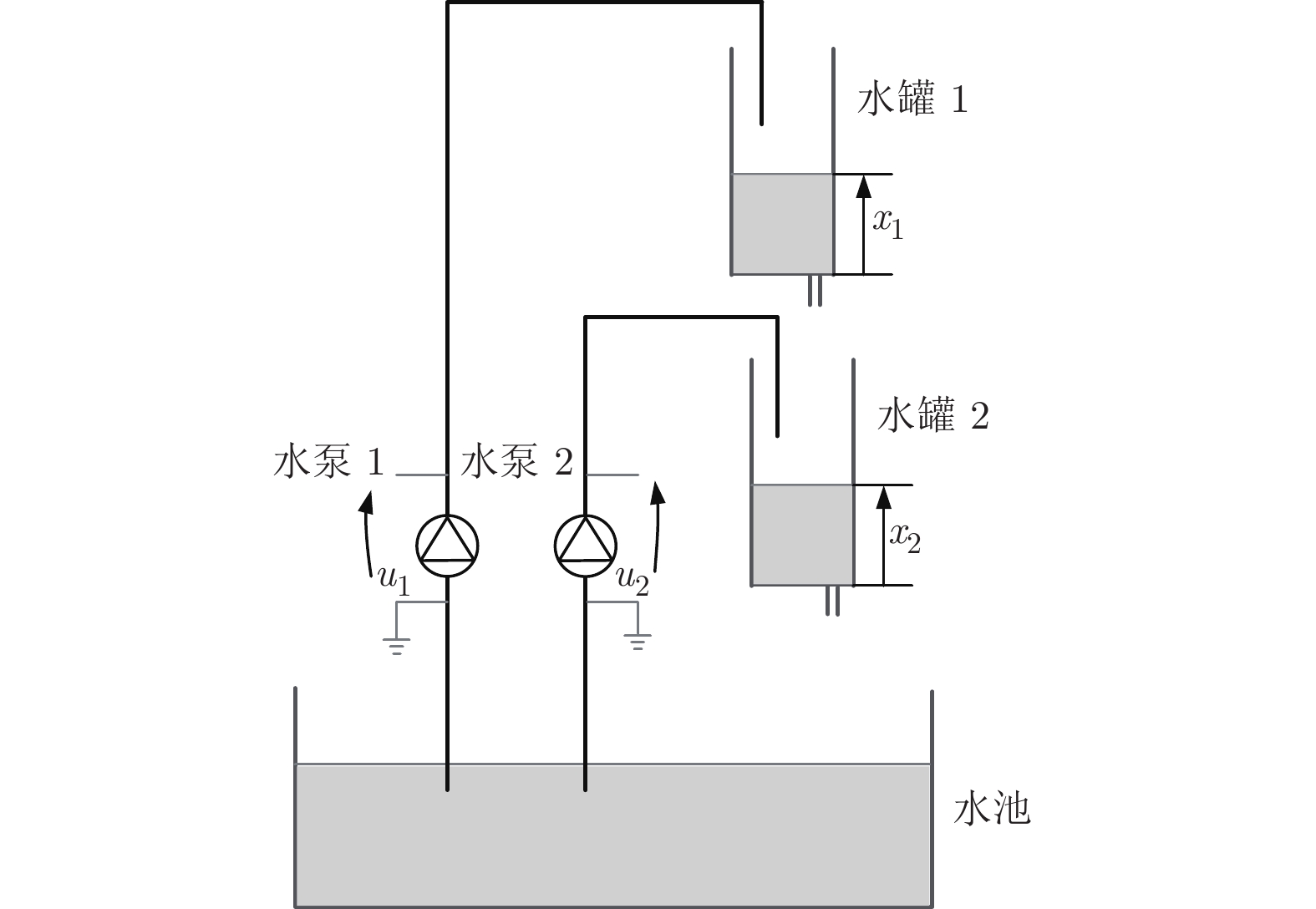
表 1 模型中涉及的符号含义及取值
Table 1 The symbol meaning and value involved in the model
符号 含义 取值 $K_{p1}$ 水泵1增益 $3.3$ $K_{p2}$ 水泵2增益 $3.3$ $A_{o1}$ 漏水孔1的横截面积 $0.1781\;\text{cm}^{2}$ $A_{o2}$ 漏水孔2的横截面积 $0.1781\;\text{cm}^\text{2}$ $A_{t1}$ 水罐1的横截面积 $15.5179\;\text{cm}^\text{2}$ $A_{t2}$ 水罐2的横截面积 $15.5179\;\text{cm}^\text{2}$ $g$ 重力加速度 $981\;\text{cm/s}^2$ -
[1] Lei J, Khalil H K. Feedback linearization for nonlinear systems with time-varying input and output delays by using high-gain predictors. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2016, 61(8): 2262-2268 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2015.2491719 [2] Wu Y Q, Isidori A, Lu R Q, Khalil H K. Performance recovery of dynamic feedback-linearization methods for multivariable nonlinear systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2020, 65(4): 1365-1380 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2019.2924176 [3] Wang N, Tao F, Fu Z, Song S. Adaptive fuzzy control for a class of stochastic strict feedback high-order nonlinear systems with full-state constraints. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2022, 52(1): 205-213 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2020.2996635 [4] Fu Z, Wang N, Song S, Wang T. Adaptive fuzzy finite-time tracking control of stochastic high-order nonlinear systems with a class of prescribed performance. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2022, 30(1): 88-96 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2020.3032776 [5] Banks S P, Cimen T. Nonlinear optimal tracking control with application to super-tankers for autopilot design. Automatica, 2004, 40(11): 1845-1863 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2004.05.015 [6] Fu Y, Chai T Y. Neural-network-based nonlinear adaptive dynamical decoupling control. IEEE transactions on neural networks, 2007, 18(3): 921-925 doi: 10.1109/TNN.2007.891588 [7] Fu Y, Chai T Y. Self-tuning control with a filter and a neural compensator for a class of nonlinear systems. IEEE transactions on neural networks and learning systems, 2013, 24(5): 837-843 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2013.2238638 [8] Chai T Y, Zhang Y J, Wang H, Su C Y, Sun J. Data-based virtual unmodeled dynamics driven multivariable nonlinear adaptive switching control. IEEE transactions on neural networks, 2011, 22(12): 2154-2172 doi: 10.1109/TNN.2011.2167685 [9] Jia Y, Chai T Y. A data-driven dual-rate control method for a heat exchanging process. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2017, 64(5): 4158-4168 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2016.2608878 [10] Tan C, Tao G, Qi R Y, Yang H. A direct MRAC based multivariable multiple-model switching control scheme. Automatica, 2017, 84: 190-198 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2017.07.020 [11] Narendra K S, Cheng X. Adaptive control of discrete-time systems using multiple models. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2000, 45(9): 1669-1686 doi: 10.1109/9.880617 [12] Fu Y, Chai T Y. Nonlinear multivariable adaptive control using multiple models and neural networks. Automatica, 2007, 43(6): 1101-1110 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2006.12.010 [13] Kuipers M, Ioannou P. Multiple model adaptive control with mixing. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2010, 55(8): 1822-1836 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2010.2042345 [14] Han Z, Narendra K S. New concepts in adaptive control using multiple models. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2012, 57(1): 78-89 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2011.2152470 [15] Huang M, Wang X, Wang Z L. Multiple model adaptive control for a class of linear-bounded nonlinear systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2015, 60(1): 271-276 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2014.2323161 [16] Chaudhuri B, Majumder R, Pal B C. Application of multiple-model adaptive control strategy for robust damping of interarea oscillations in power system. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2004, 12(5): 727-736 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2004.833409 [17] Karimi A, Landau I D. Robust adaptive control of a flexible transmission system using multiple models. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2000, 8(2): 321-331 doi: 10.1109/87.826803 [18] Chai T Y, Zhai L F, Yue H. Multiple models and neural networks based decoupling control of ball mill coal-pulverizing systems. Journal of Process Control, 2011, 21(3): 351-366 doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2010.11.007 [19] Ghaffarzdeh H, Mehrizi-Sani A. Mitigation of subsynchronous resonance induced by a type III wind system. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 2020, 11(3): 1717-1727 doi: 10.1109/TSTE.2019.2938014 [20] Leon A E, Amodeo S J, Mauricio J M. Enhanced compensation filter to mitigate subsynchronous oscillations in series-compensated DFIG-based wind farms. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 2021, 36(6): 3805-3814 doi: 10.1109/TPWRD.2021.3049318 [21] Wu G Y, Sun J, Chen J. Optimal linear quadratic regulator of switched systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2019, 64(7): 2898-2904 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2018.2872204 [22] Kleinman D. On an iterative technique for Riccati equation computations. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1968, 13(1): 114-115 doi: 10.1109/TAC.1968.1098829 [23] Jiang Z P, Jiang Y. Computational adaptive optimal control for continuous-time linear systems with completely unknown dynamics. Automatica, 2012, 48(10): 2699-2704 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2012.06.096 [24] Fu Y, Chen W, Fu J, A new optimal tracking controller of linear strongly coupled systems and its applications, IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2022, 69(3): 1387-1391 doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2021.3122434 -




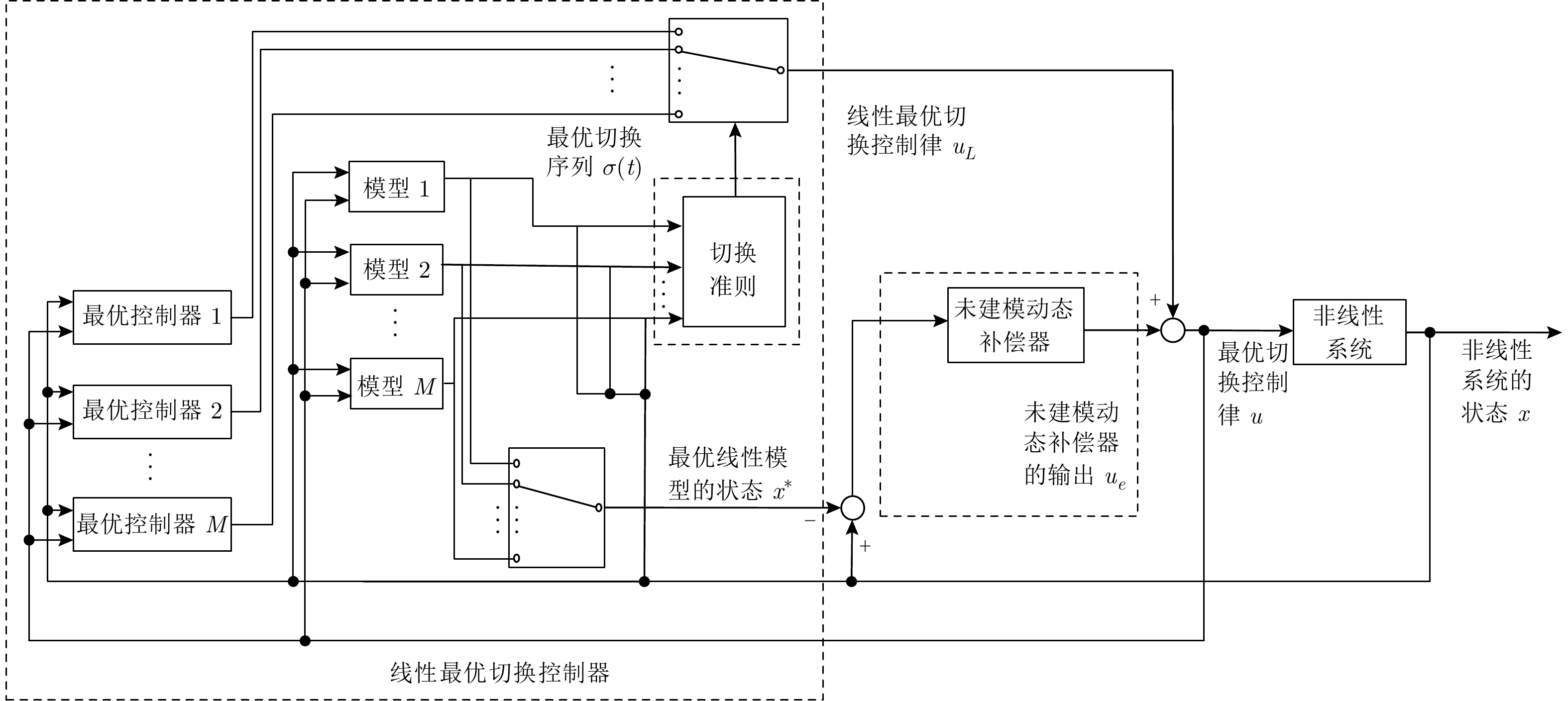
 下载:
下载: