-
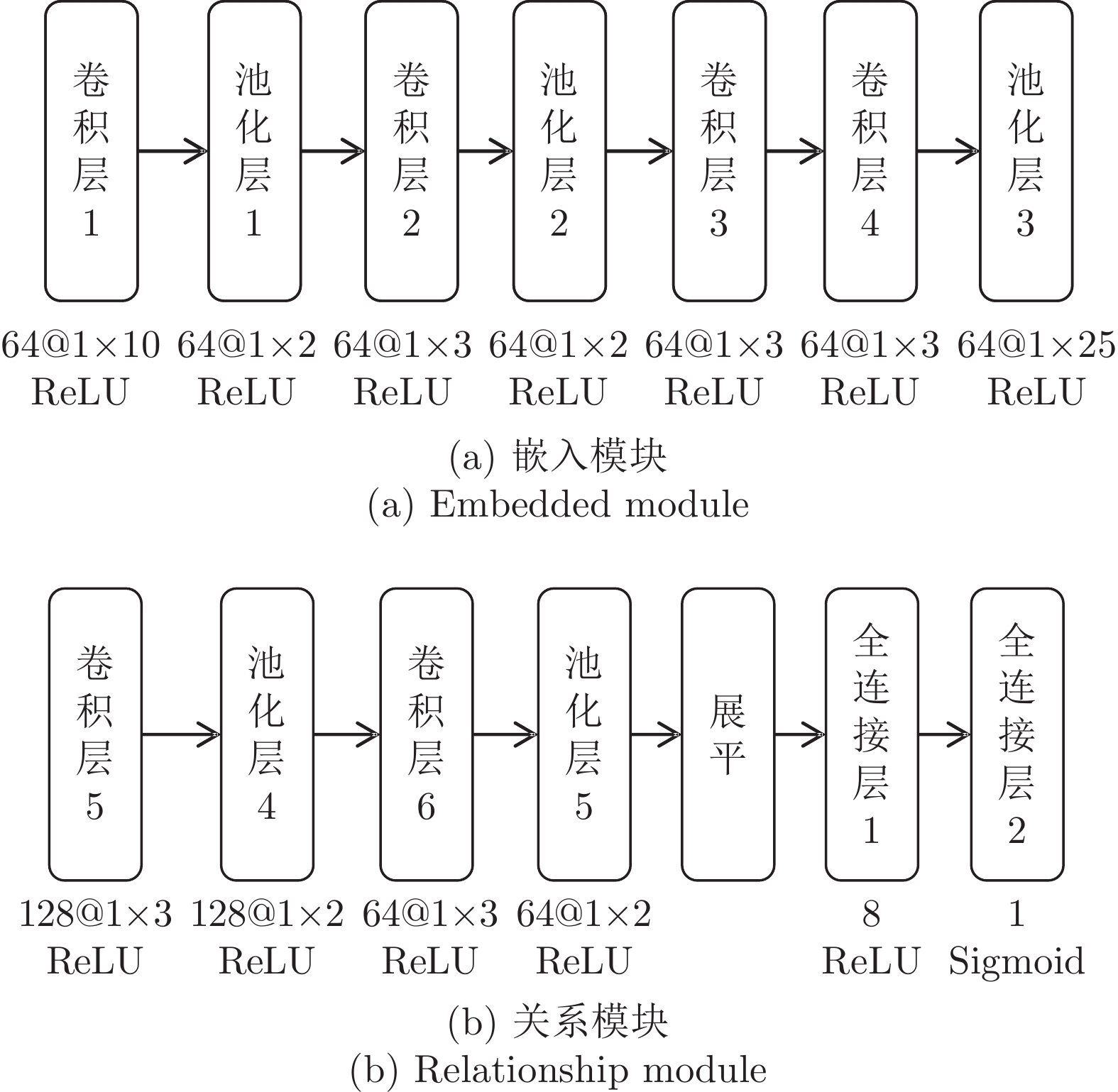
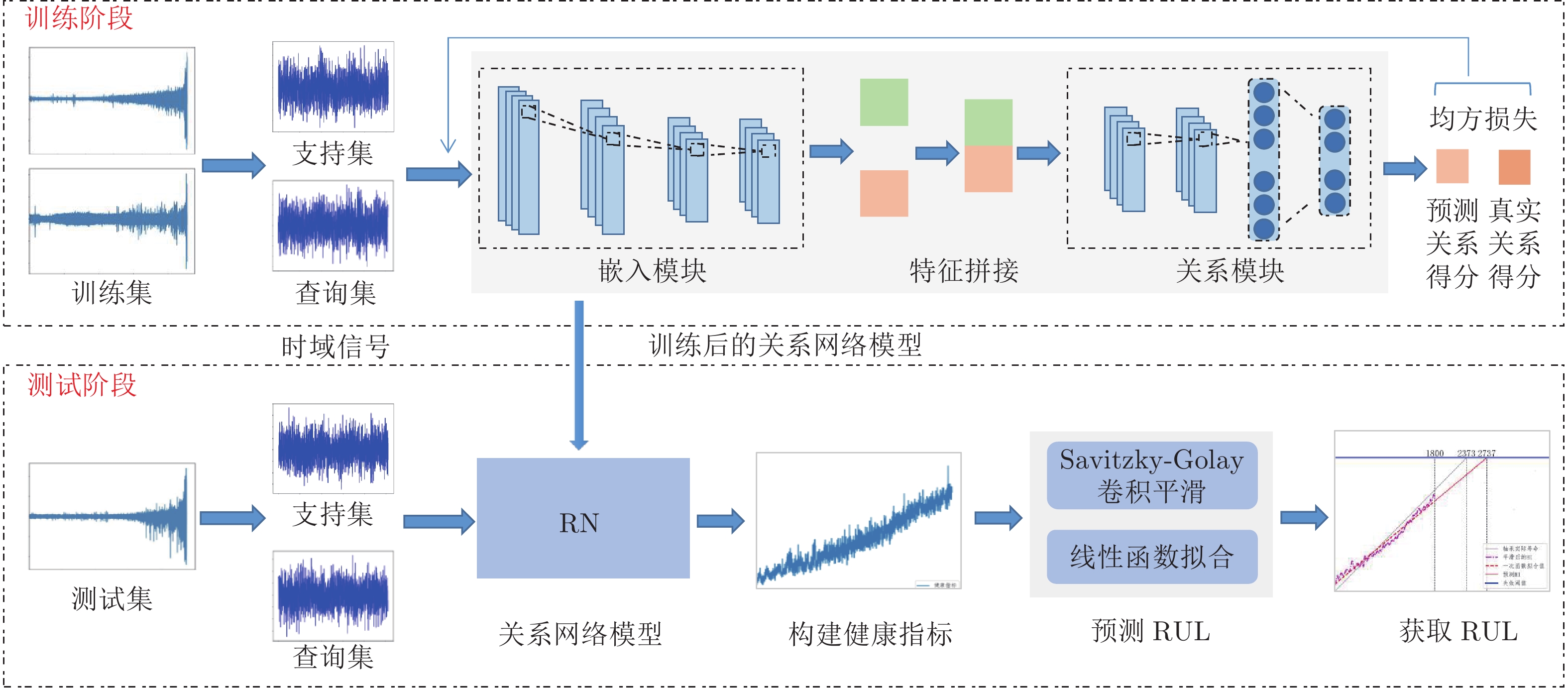
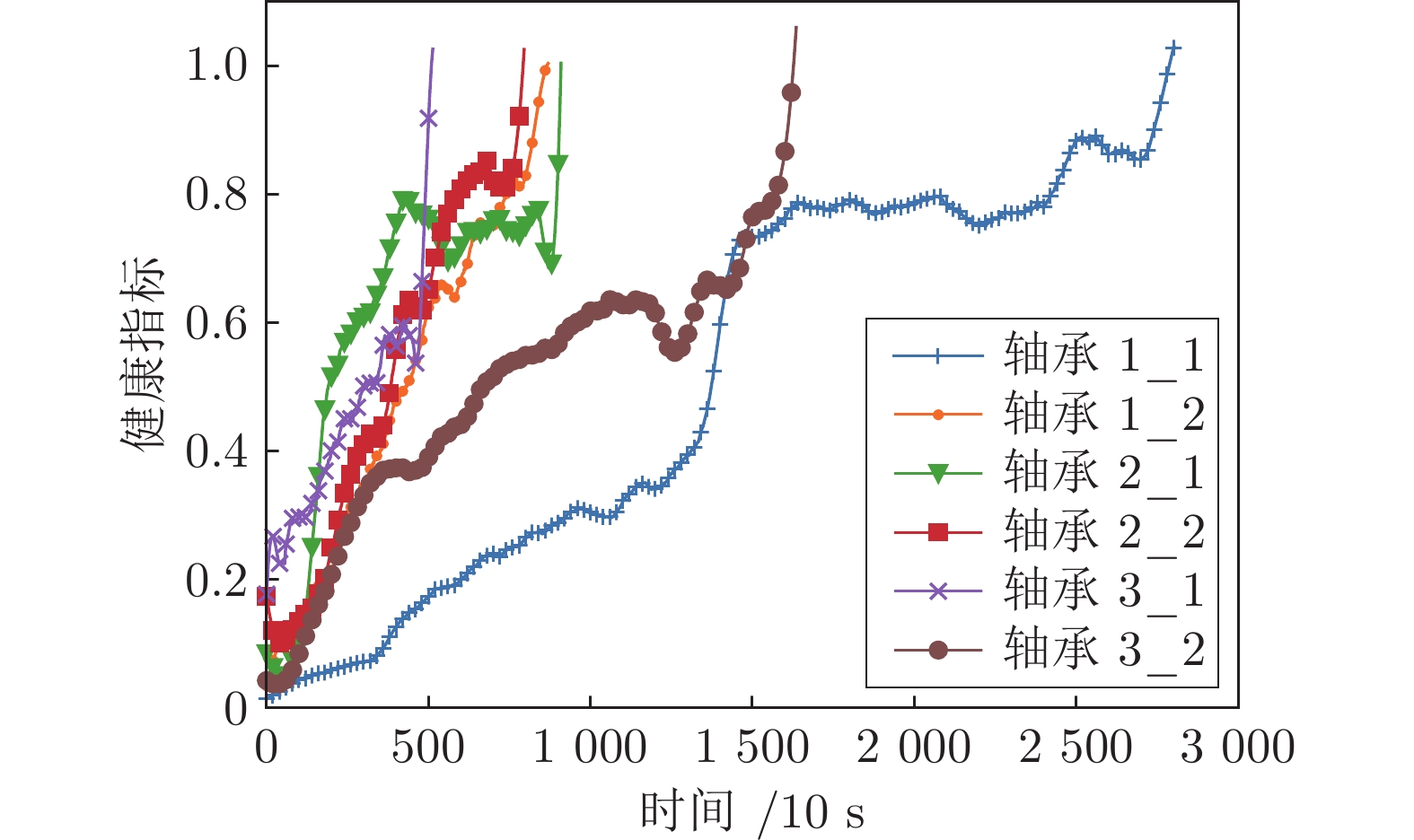
摘要: 针对轴承全寿命周期数据获取困难、训练样本少的问题, 提出一种基于关系网络的轴承剩余使用寿命(Remaining useful life, RUL)预测方法. 关系网络是一种基于度量的元学习方法, 在少量训练样本下, 具有快速学习新任务的优点. 设计了一种基于关系网络的轴承健康评估模型, 利用关系网络的嵌入模块提取轴承状态特征, 利用关系模块度量轴承状态特征之间的相似性, 基于相似性构建轴承健康指标(Health indicator, HI); 对健康指标进行Savitzky-Golay滤波平滑处理, 降低振荡对预测结果的影响; 最后利用线性函数对健康指标进行拟合, 得到轴承RUL预测值. 为验证所提方法的有效性, 在PHM2012轴承实测数据集上进行实验. 结果表明, 所得健康指标能够反映轴承的退化趋势, 所得RUL预测结果与空间卷积长短期记忆神经网络 (Convolutional long short-term memory neural network, ConvLSTM)、Transformer、循环神经网络(Recurrent neural network, RNN)、卷积神经网络(Convolutional neural network, CNN) + 长短期记忆网络 (long short-term memory network, LSTM )、编码器−解码器(Encoder-decoder) + 注意力机制 (Attention mechanism)方法相比, 误差百分比分别减少了1.67%, 3.40%, 9.02%, 13.71%, 30.48%. 该方法在少量训练样本的基础上可以取得较好的预测结果, 具有一定的应用价值.Abstract: To solve the problems of difficult acquisition of bearing life cycle data and few training samples, this study proposes a prediction method of bearing remaining useful life (RUL) based on a relation network. A relation network is a meta-learning method based on metric learning. It has the advantage of learning new tasks quickly with a few training samples. A bearing health assessment model based on relation network is designed. The embedded module of the relation network is used to extract the bearing state features, the relational module is used to measure the similarity between the bearing state features, and the health indicator (HI) of bearing is constructed based on the similarity. The health indicators were smoothed by Savitzky-Golay filter to reduce the impact of oscillation on the prediction results. Finally, the linear function is used to fit the health index, and the predicted value of bearing RUL is obtained. To verify the effectiveness of the proposed method, experiments are conducted on the measured bearing dataset of PHM2012. The results show that the obtained health indicators can reflect the degradation trend of the bearing. Compared with ConvLSTM (convolutional long short-term memory neural network), Transformer, RNN (recurrent neural network), CNN + LSTM (convolutional neural network + long short-term memory network), encoder-decoder + attention mechanism methods, the error percentages of the obtained RUL prediction results are reduced by 1.67%, 3.40%, 9.02%, 13.71%, and 30.48%, respectively. This method can obtain better prediction results based on a few training samples and has a certain application value.
-
Key words:
- Bearing /
- remaining useful life (RUL) /
- health indicator (HI) /
- relation network /
- meta-learning
-
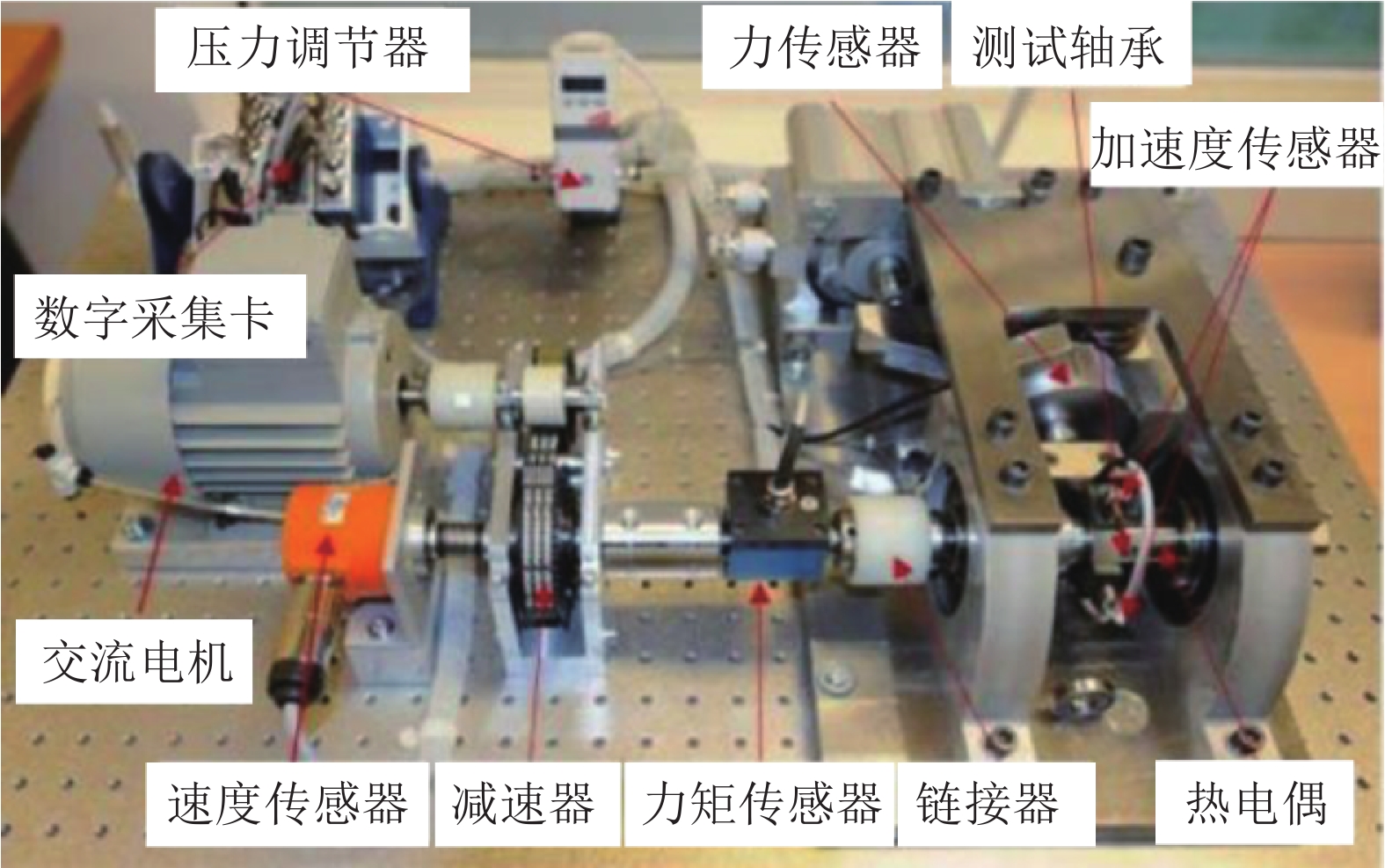
表 1 PHM2012轴承数据集
Table 1 PHM2012 bearing dataset
工况 工况1 工况2 工况3 训练集 轴承1_1 轴承2_1 轴承3_1 轴承1_2 轴承2_2 轴承3_2 轴承1_5 轴承2_4 轴承1_6 轴承2_5 轴承1_7 轴承2_7 测试集 轴承1_3 轴承2_3 轴承3_3 轴承1_4 轴承2_6 表 2 不同模型参数量对比
Table 2 Comparison of different model parameters
方法 参数量 (k) 本文方法 78.61 ConvLSTM 220.50 Transformer 6461.44 CNN+LSTM 1136.64 表 3 轴承RUL预测结果
Table 3 Bearing RUL prediction results
轴承 当前时刻 (10 s) 真实寿命 (10 s) 预测寿命 (10 s) 本文方法 (%) 文献 [13] (%) 文献 [28] (%) 文献 [11] (%) 文献 [29] (%) 文献 [12] (%) 轴承1_3 1801 573 937 −63.53 33.68 74.17 74.17 54.73 7.62 轴承1_4 1138 290 338 −16.55 47.24 −0.69 −0.69 38.69 −157.71 轴承2_3 1201 753 1005 −33.46 −32.80 61.36 61.36 75.53 81.24 轴承2_6 571 129 131 −1.55 8.52 0.78 0.78 17.87 24.92 轴承3_3 351 82 77 6.09 7.32 1.22 1.22 2.93 2.09 平均误差 — — — 24.24 25.91 27.64 33.26 37.95 54.72 -
[1] 雷亚国, 贾峰, 孔德同, 林京, 邢赛博. 大数据下机械智能故障诊断的机遇与挑战. 机械工程学报, 2018, 54(5): 94-104 doi: 10.3901/JME.2018.05.094Lei Ya-Guo, Jia Feng, Kong De-Tong, Lin Jing, Xing Sai-Bo. Opportunities and challenges of machinery intelligent fault diagnosis in big data era. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2018, 54(5): 94-104 doi: 10.3901/JME.2018.05.094 [2] 赵志宏, 李乐豪, 杨绍普, 李晴. 一种无监督的轴承健康指标及早期故障检测方法. 中国机械工程, 2022, 33(10): 1234-1243 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2022.10.013Zhao Zhi-Hong, Li Le-Hao, Yang Shao-Pu, Li Qing. An unsupervised bearing health indicator and early fault detection method. China Mechanical Engineering, 2022, 33(10): 1234-1243 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2022.10.013 [3] 刘建昌, 权贺, 于霞, 何侃, 李镇华. 基于参数优化VMD和样本熵的滚动轴承故障诊断. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(3): 808-819Liu Jian-Chang, Quan He, Yu Xia, He Kan, Li Zhen-Hua. Rolling bearing fault diagnosis based on parameter optimization VMD and sample entropy. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(3): 808-819 [4] 康守强, 邢颖怡, 王玉静, 王庆岩, 谢金宝, Mikulovich V I. 基于无监督深度模型迁移的滚动轴承寿命预测方法. 自动化学报, DOI: 10.16383/j.aas.c200890Kang Shou-Qiang, Xing Ying-Yi, Wang Yu-Jing, Wang Qing-Yan, Xie Jin-Bao, Mikulovich V I. Rolling bearing life prediction based on unsupervised deep model transfer. Acta Automatica Sinica, DOI: 10.16383/j.aas.c200890 [5] Jouin M, Gouriveau R, Hissel D, Péra M C, Zerhouni N. Particle filter-based prognostics: Review, discussion and perspectives. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2016, 72-73: 2-31 doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2015.11.008 [6] Jouin M, Gouriveau R, Hissel D, Péra M C, Zerhouni N. Degradations analysis and aging modeling for health assessment and prognostics of PEMFC. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2016, 148: 78-95 [7] Ali J B, Chebel-Morello B, Saidi L, Malinowski S, Fnaiech F. Accurate bearing remaining useful life prediction based on Weibull distribution and artificial neural network. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2015, 56-57: 150-172 doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2014.10.014 [8] Yang H B, Sun Z, Jiang G D, Zhao F, Mei X S. Remaining useful life prediction for machinery by establishing scaled-corrected health indicators. Measurement, 2020, 163: Article No. 108035 [9] Hong S, Zhou Z, Zio E, Hong K. Condition assessment for the performance degradation of bearing based on a combinatorial feature extraction method. Digital Signal Processing, 2014, 27: 159-166 doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2013.12.010 [10] Hinton G E, Osindero S, Teh Y W. A fast learning algorithm for deep belief nets. Neural Computation, 2006, 18(7): 1527-1554 doi: 10.1162/neco.2006.18.7.1527 [11] Guo L, Li N P, Jia F, Lei Y G, Lin J. A recurrent neural network based health indicator for remaining useful life prediction of bearings. Neurocomputing, 2017, 240: 98-109 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2017.02.045 [12] Chen Y H, Peng G L, Zhu Z Y, Li S J. A novel deep learning method based on attention mechanism for bearing remaining useful life prediction. Applied Soft Computing, 2020, 86: Article No. 105919 [13] 王久健, 杨绍普, 刘永强, 文桂林. 一种基于空间卷积长短时记忆神经网络的轴承剩余寿命预测方法. 机械工程学报, 2021, 57(21): 88-95 doi: 10.3901/JME.2021.21.088Wang Jiu-Jian, Yang Shao-Pu, Liu Yong-Qiang, Wen Gui-Lin. A method of bearing remaining useful life estimation based on convolutional long short-term memory neural network. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2021, 57(21): 88-95 doi: 10.3901/JME.2021.21.088 [14] 康守强, 周月, 王玉静, 谢金宝, Mikulovich V I. 基于改进SAE和双向LSTM的滚动轴承RUL预测方法. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(9): 2327-2336Kang Shou-Qiang, Zhou Yue, Wang Yu-Jing, Xie Jin-Bao, Mikulovich V I. RUL prediction method of a rolling bearing based on improved SAE and Bi-LSTM. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(9): 2327-2336 [15] 李凡长, 刘洋, 吴鹏翔, 董方, 蔡奇, 王哲. 元学习研究综述. 计算机学报, 2021, 44(2): 422-446Li Fan-Chang, Liu Yang, Wu Peng-Xiang, Dong Fang, Cai Qi, Wang Zhe. A survey on recent advances in meta-learning. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2021, 44(2): 422-446 [16] Koch G, Zemel R, Salakhutdinov R. Siamese neural networks for one-shot image recognition. In: Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning. Lille, France: JMLR, 2015. [17] Vinyals O, Blundell C, Lillicrap T, Kavukcuoglu K, Wierstra D. Matching networks for one shot learning. In: Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Barcelona, Spain: ACM, 2016. 3637−3645 [18] Snell J, Swersky K, Zemel R. Prototypical networks for few-shot learning. In: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach, USA: ACM, 2017. 4080−4090 [19] Sung F, Yang Y X, Zhang L, Xiang T, Torr P H S, Hospedales T M. Learning to compare: Relation network for few-shot learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 1199−1208 [20] Bishay M, Zoumpourlis G, Patras I. TARN: Temporal attentive relation network for few-shot and zero-shot action recognition. In: Proceedings of the 30th British Machine Vision Conference. Cardiff, UK: BMVC, 2019. Article No. 154 [21] 王晓茹, 张珩. 基于注意力机制和图卷积的小样本分类网络. 计算机工程与应用, 2021, 57(19): 164-170Wang Xiao-Ru, Zhang Heng. Relation network based on attention mechanism and graph convolution for few-shot learning. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2021, 57(19): 164-170 [22] Wu J Y, Zhao Z B, Sun C, Yan R Q, Chen X F. Few-shot transfer learning for intelligent fault diagnosis of machine. Measurement, 2020, 166: Article No. 108202 [23] 吕枫, 王义, 阮胡林, 秦毅, 王平. 深度嵌入关系空间下齿轮箱标记样本扩充及其半监督故障诊断方法. 仪器仪表学报, 2021, 42(2): 55-65Lv Feng, Wang Yi, Ruan Hu-Lin, Qin Yi, Wang Ping. Labeled sample augmentation based on deep embedding relation space for semi-supervised fault diagnosis of gearbox. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2021, 42(2): 55-65 [24] Savitzky A, Golay M J E. Smoothing and differentiation of data by simplified least squares procedures. Analytical Chemistry, 1964, 36(8): 1627-1639 doi: 10.1021/ac60214a047 [25] Nectoux P, Gouriveau R, Medjaher K, Ramasso E, Morello B, Zerhouni N, et al. PRONOSTIA: An experimental platform for bearings accelerated degradation tests. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Prognostics and Health Management. Denver, USA: IEEE, 2012. 1−8 [26] Soualhi A, Medjaher K, Zerhouni N. Bearing health monitoring based on hilbert–huang transform, support vector machine, and regression. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2015, 64(1): 52-62 doi: 10.1109/TIM.2014.2330494 [27] Singleton R K, Strangas E G, Aviyente S. Extended kalman filtering for remaining-useful-life estimation of bearings. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2015, 62(3): 1781-1790 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2014.2336616 [28] 周哲韬, 刘路, 宋晓, 陈凯. 基于Transformer模型的滚动轴承剩余使用寿命预测方法. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2023, 49(2): 430-443Zhou Zhe-Tao, Liu Lu, Song Xiao, Chen Kai. Remaining useful life prediction method of rolling bearing based on transformer model. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2023, 49(2): 430-443 [29] Hinchi A Z, Tkiouat M. Rolling element bearing remaining useful life estimation based on a convolutional long-short-term memory network. Procedia Computer Science, 2018, 127: 123-132 doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2018.01.106 -





 下载:
下载: