Research on False Data Injection Attack Detection in Power System Based on Improved Multi Layer Extreme Learning Machine
-
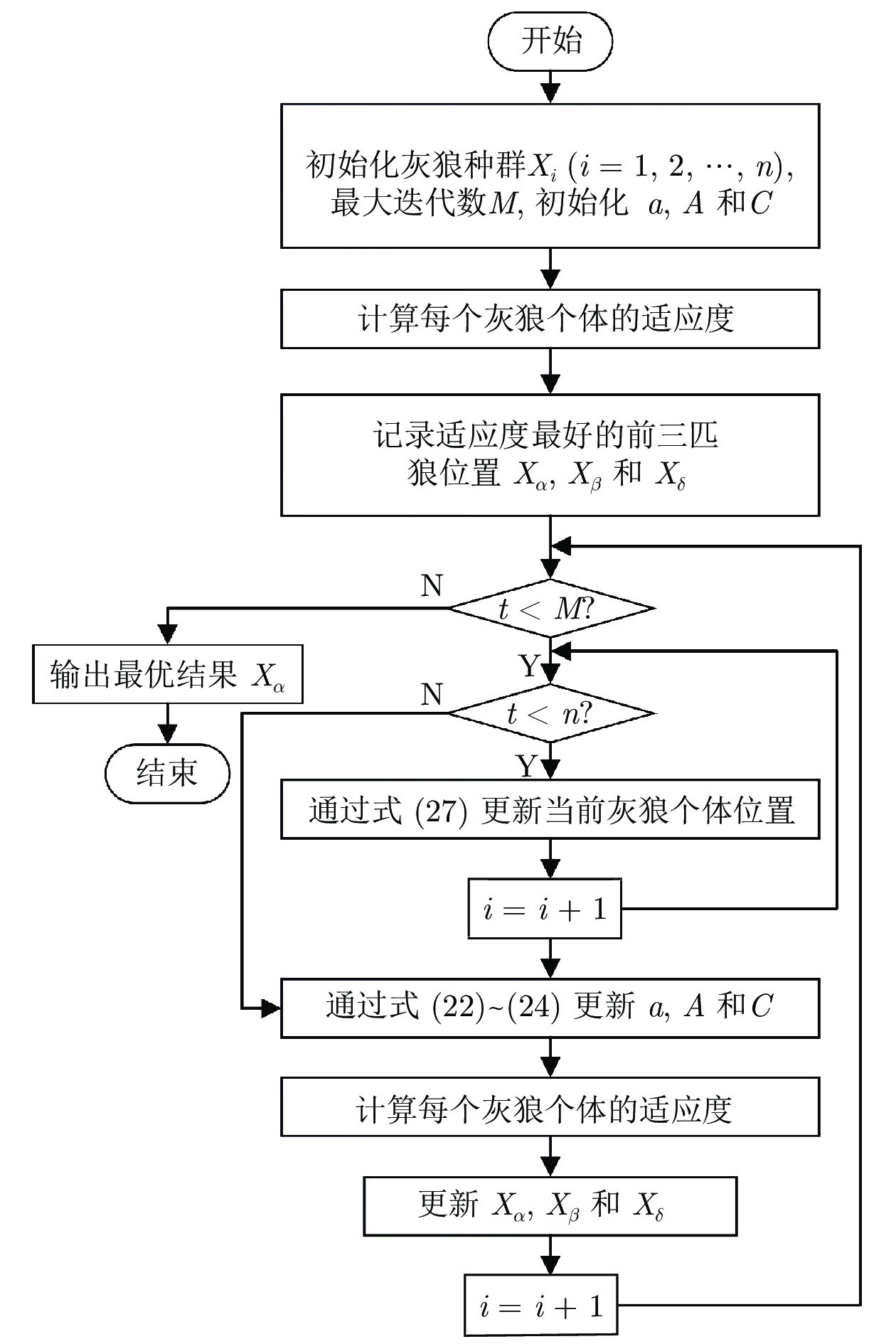
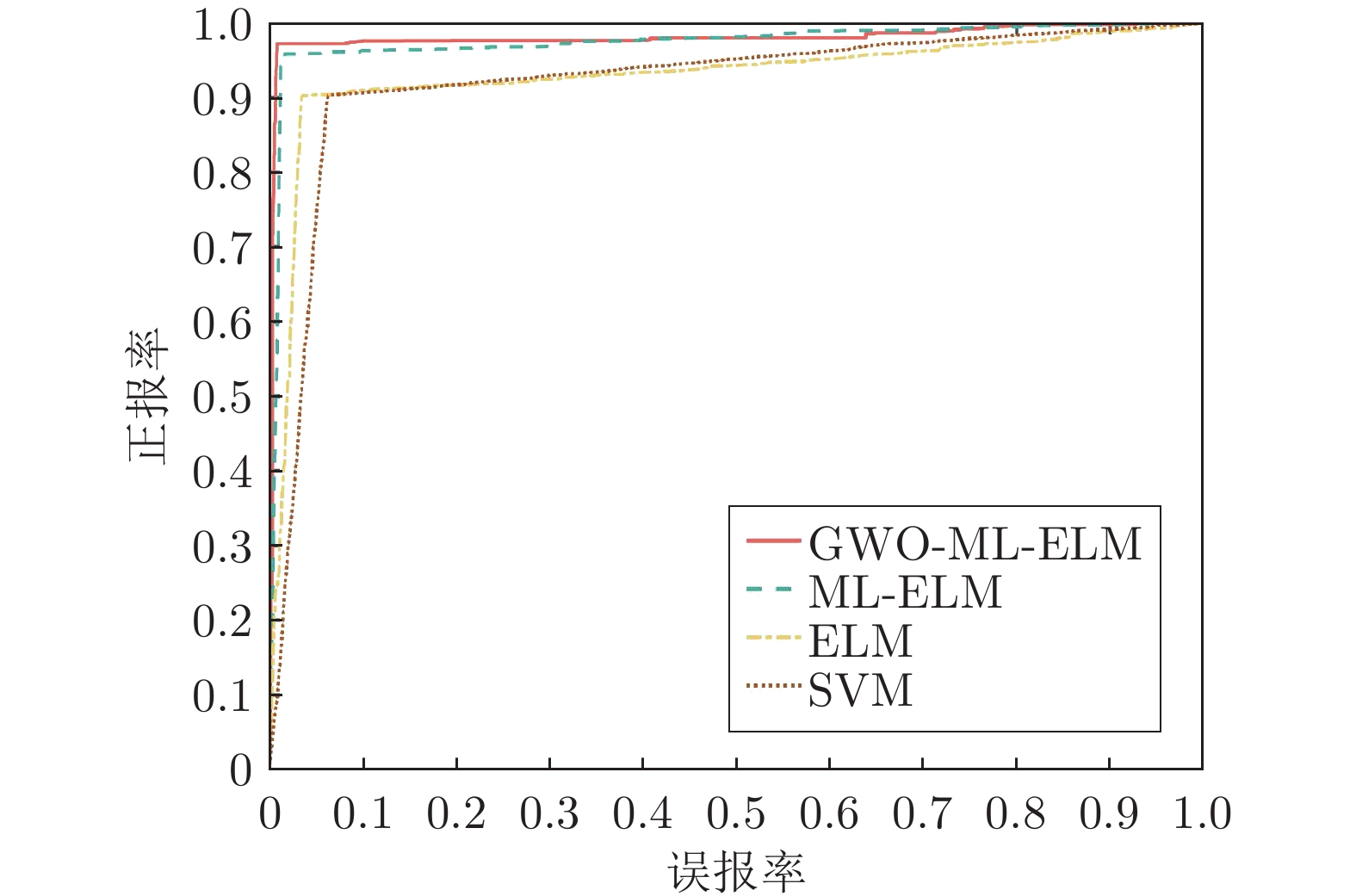
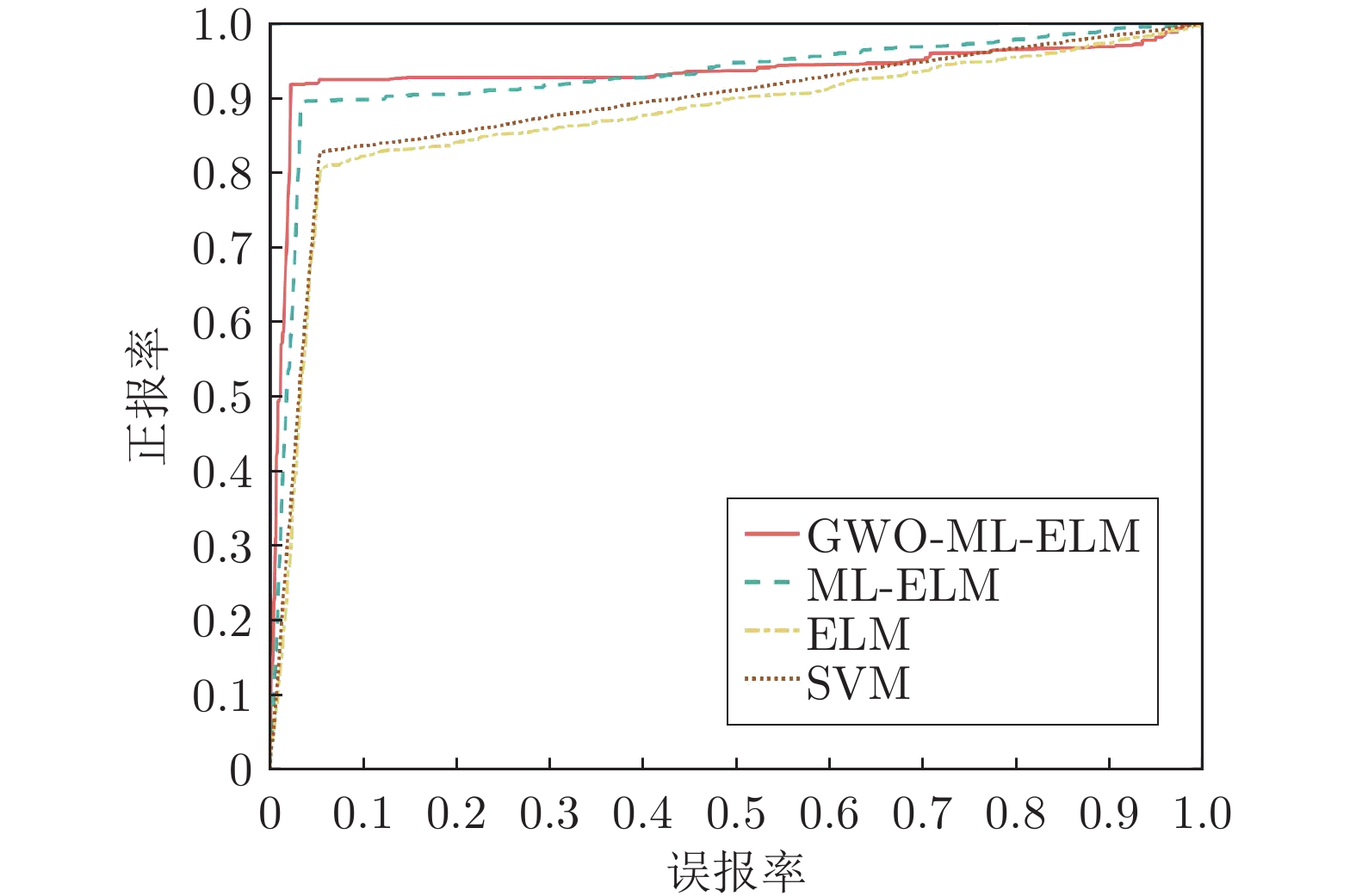
摘要: 虚假数据注入攻击(False data injection attacks, FDIA)严重威胁了电力信息物理系统(Cyber-physical system, CPS)的状态估计, 而目前大多数检测方法侧重于攻击存在性检测, 无法获取准确的受攻击位置. 故本文提出了一种基于灰狼优化(Gray wolf optimization, GWO)多隐层极限学习机(Multi layer extreme learning machine, ML-ELM)的电力信息物理系统虚假数据注入攻击检测方法. 所提方法将攻击检测看作是一个多标签二分类问题, 不仅将用于特征提取与分类训练的极限学习机由单隐层变为多隐层, 以解决极限学习机特征表达能力有限的问题, 且融入了具有强全局搜索能力的灰狼优化算法以提高多隐层极限学习机分类精度和泛化性能. 进而自动识别系统各个节点状态量的异常, 获取受攻击的精确位置. 通过在不同场景下对IEEE-14和57节点测试系统上进行大量实验, 验证了所提方法的有效性, 且分别与极限学习机、未融入灰狼优化的多隐层极限学习机以及支持向量机(Support vector machine, SVM)相比, 所提方法具有更精确的定位检测性能.Abstract: False data injection attacks (FDIA) seriously threaten the state estimation of power cyber-physical system (CPS). At present, most detection methods focus on the detection of attack existence, and can not obtain the accurate attacked location. Therefore, this paper proposes a false data injection attack detection method for power cyber-physical system based on gray wolf optimized multi layer extreme learning machine (ML-ELM). The proposed method regards attack detection as a multilabel binary classification problem. It not only changes the extreme learning machine used for feature extraction and classification training from single hidden layer to multi hidden layer to solve the problem of limited feature expression ability of extreme learning machine, but also integrates the gray wolf optimization (GWO) algorithm with strong global search ability to improve the classification accuracy and generalization performance of multi layer extreme learning machine. Furthermore, it automatically identify the abnormal state variables of each node of the system, and obtain the accurate attacked location. Through a large number of experiments on IEEE-14 and 57 node test systems in different scenarios, the effectiveness of the proposed method is verified, and the proposed method has more accurate positioning and detection performance than the extreme learning machine, the multi layer extreme learning machine without gray wolf optimization and the support vector machine (SVM), respectively.
-
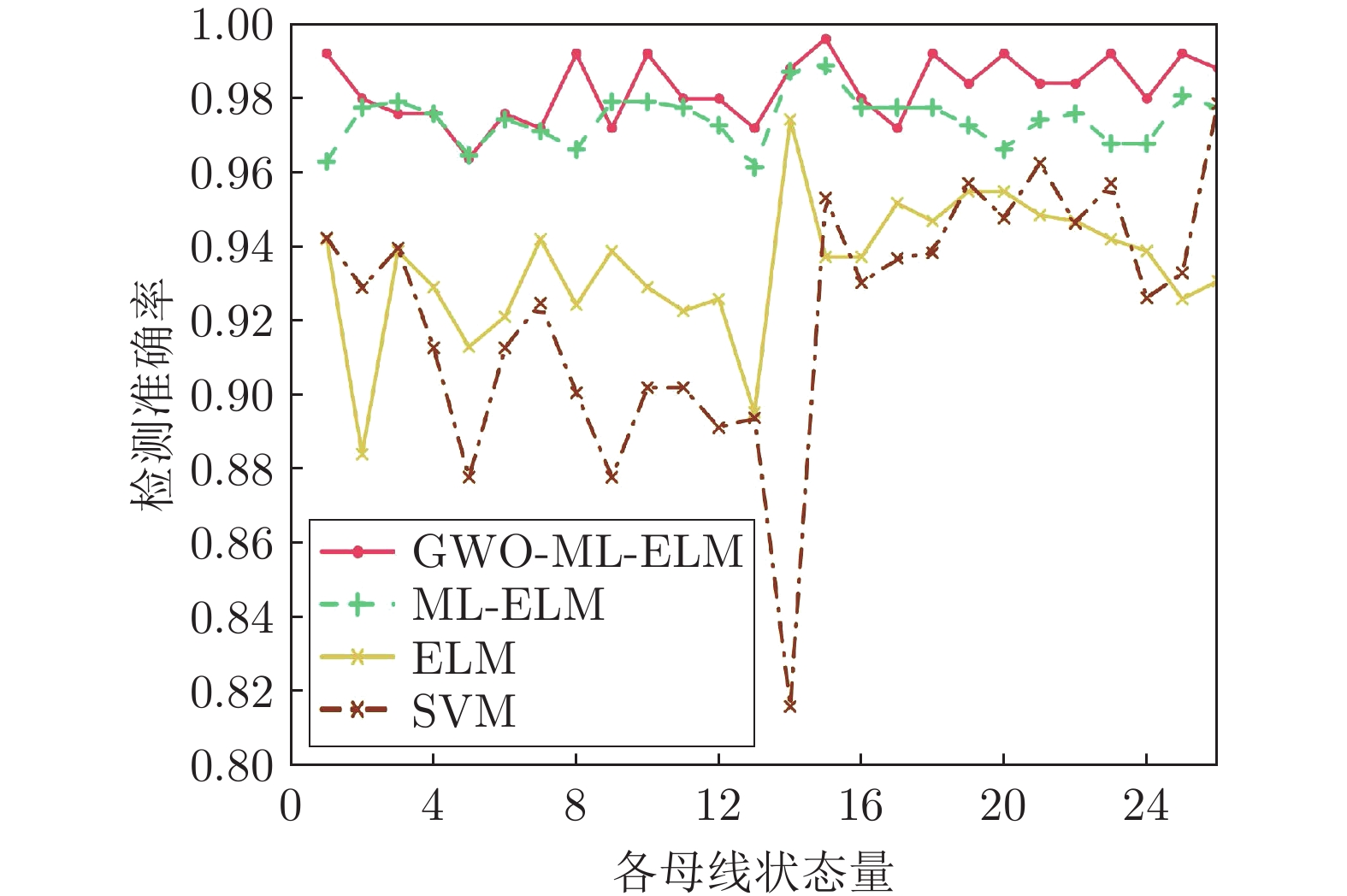
表 1 IEEE-14节点系统性能评估指标结果
Table 1 Performance evaluation index results for IEEE 14-bus system
总线 指标 GWO-ML-ELM ML-ELM ELM SVM 14节点 精度 0.9881 0.9774 0.9499 0.9133 召回率 0.9717 0.9571 0.9020 0.9023 F1值 0.9798 0.9671 0.9253 0.9078 表 2 IEEE-57节点系统性能评估指标结果
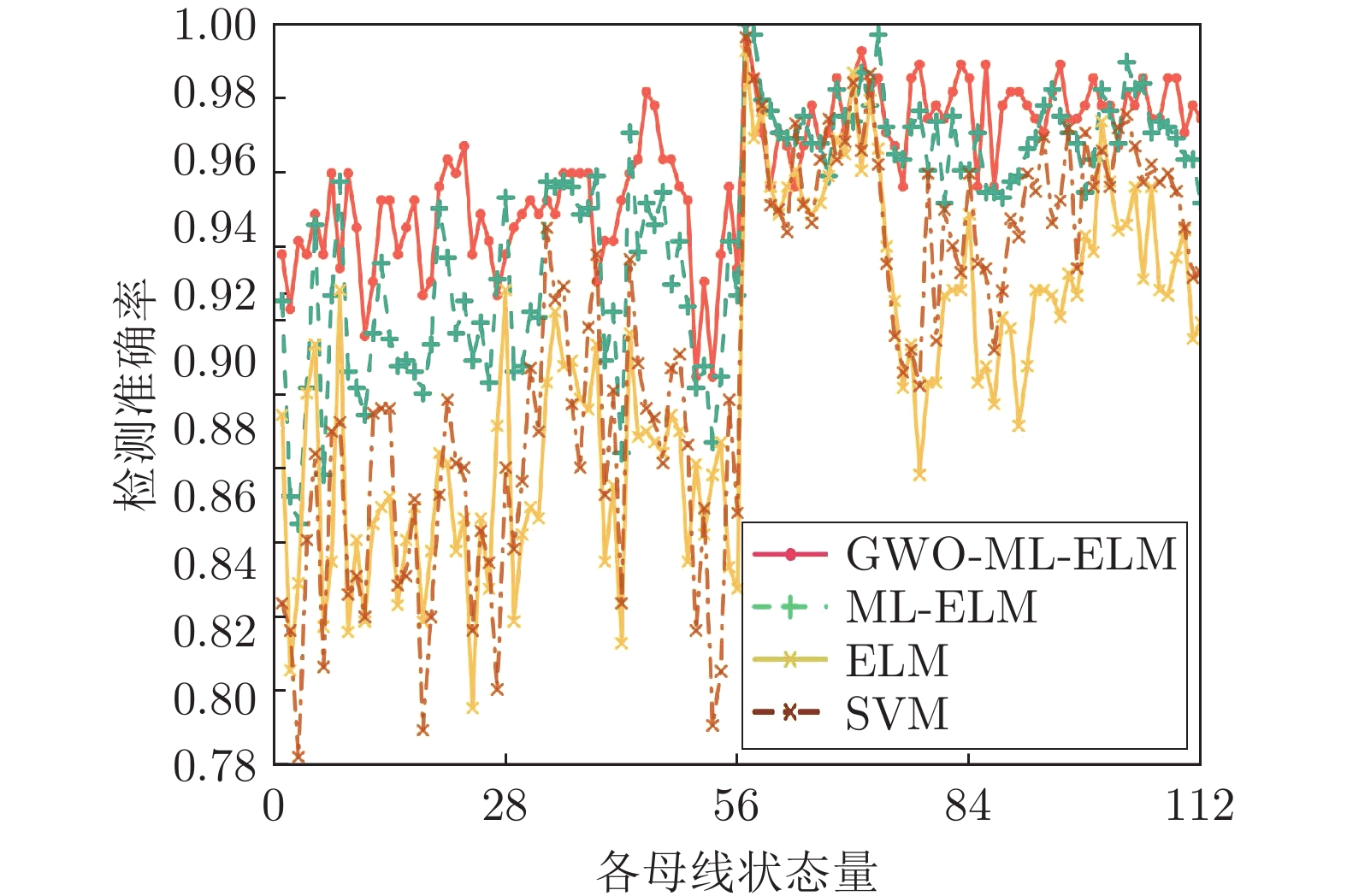
Table 2 Performance evaluation index results for IEEE 57-bus system
总线 指标 GWO-ML-ELM ML-ELM ELM SVM 57节点 精度 0.9524 0.9314 0.8857 0.8940 召回率 0.9181 0.8946 0.8068 0.8273 F1值 0.9349 0.9126 0.8444 0.8594 -
[1] 臧海祥, 郭镜玮, 黄蔓云, 卫志农, 孙国强, 俞文帅. 基于深度迁移学习的时变拓扑下电力系统状态估计. 电力系统自动化, 2021, 45(24): 49−56Zang Hai-Xiang, Guo Jing-Wei, Huang Man-Yun, Wei Zhi-Nong, Sun Guo-Qiang, Yu Wen-Shuai. State estimation for power systems with time-varying topology based on deep transfer learning. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2021, 45(24): 49−56 [2] 秦博雅, 刘东. 电网信息物理系统分析与控制的研究进展与展望. 中国电机工程学报, 2020, 40(18): 5816−5827Qin Bo-Ya, Liu Dong. Research progresses and prospects on analysis and control of cyber-physical system for power grid. Journal of Chinese Electrical Engineering Science, 2020, 40(18): 5816−5827 [3] Ding D, Han Q L, Ge X, Wang J. Secure state estimation and control of cyber-physical systems: A survey. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2021, 51(1): 176−190 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2020.3041121 [4] Liu Z, Wang L. Leveraging network topology optimization to strengthen power grid resilience against cyber-physical attacks. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2020, 12(2): 1552−1564 [5] 刘莉, 翟登辉, 姜新丽. 电力系统不良数据检测与辨识方法的现状与发展. 电力系统保护与控制, 2010, 38(5): 143−147 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3415.2010.05.036Liu Li, Zhai Deng-Hui, Jiang Xin-Li. Current situation and development of the methods on bad-data detection and identification of power system. Power System Protection and Control, 2010, 38(5): 143−147 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3415.2010.05.036 [6] Liu Y, Ning P, Reiter M K. False data injection attacks against state estimation in electric power grids. ACM Transactions on Information and System Security (TISSEC), 2011, 14(1): 1−33 [7] Yan J J, Yang G H, Wang Y. Dynamic reduced-order observer-based detection of false data injection attacks with application to smart grid systems. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2022, 18(10): 6712−6722 doi: 10.1109/TII.2022.3144445,tobepublished [8] Jorjani M, Seifi H, Varjani A Y. A graph theory-based approach to detect false data injection attacks in power system AC state estimation. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2021, 17(4): 2465−2475 doi: 10.1109/TII.2020.2999571 [9] 朱杰, 张葛祥. 基于历史数据库的电力系统状态估计欺诈性数据防御. 电网技术, 2016, 40(6): 1772−1777Zhu Jie, Zhang Ge-Xiang. Defense against false data in power system state estimation based on historical database. Power System Technology, 2016, 40(6): 1772−1777 [10] Zhao J, Zhang G, Scala M L, Zhao Y D, Chen C, Wang J. Short-term state forecasting-aided method for detection of smart grid general false data injection attacks. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2017, 8(4): 1580−1590 doi: 10.1109/TSG.2015.2492827 [11] 罗小元, 潘雪扬, 王新宇, 关新平. 基于自适应 Kalman 滤波的智能电网假数据注入攻击检测. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(12): 2960−2971 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190636Luo Xiao-Yuan, Pan Xue-Yang, Wang Xin-Yu, Guan Xin-Ping. Detection of false data injection attack in smart grid via adaptive kalman filtering. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(12): 2960−2971 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190636 [12] 刘鑫蕊, 常鹏, 孙秋野. 基于 XGBoost 和无迹卡尔曼滤波自适应混合预测的电网虚假数据注入攻击检测. 中国电机工程学报, 2021, 41(16): 5462−5476Liu Xin-Rui, Chang Peng, Sun Qiu-Ye. Grid false data injection attacks detection based on xgboost and unscented kalman filter adaptive hybrid prediction. Journal of Chinese Electrical Engineering Science, 2021, 41(16): 5462−5476 [13] Zhang Y, Wang J, Chen B. Detecting false data injection attacks in smart grids: A semi-supervised deep learning approach. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2021, 12(1): 623−634 doi: 10.1109/TSG.2020.3010510 [14] 李元诚, 曾婧. 基于改进卷积神经网络的电网假数据注入攻击检测方法. 电力系统自动化, 2019, 43(20): 97−104 doi: 10.7500/AEPS20180919001Li Yuan-Cheng, Zeng Jing. Detection method of false data injection attack on power grid based on improved convolutional neural network. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2019, 43(20): 97−104 doi: 10.7500/AEPS20180919001 [15] Ashrafuzzaman M, Das S, Chakhchoukh Y, Shiva S, Sheldon F T. Detecting stealthy false data injection attacks in the smart grid using ensemble-based machine learning.Computers and Security, 2020, 97: Article No. 101994 [16] Wu T, Xue W, Wang H, Chung C Y, Wang G, Peng J, et al. Extreme learning machine-based state reconstruction for automatic attack filtering in cyber physical power system. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2021, 17(3): 1892−1904 doi: 10.1109/TII.2020.2984315 [17] Wang S, Bi S, Zhang Y J A. Locational detection of the false data injection attack in a smart grid: A multilabel classification approach. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 7(9): 8218−8227 doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.2983911 [18] 徐睿, 梁循, 齐金山, 李志宇, 张树森. 极限学习机前沿进展与趋势. 计算机学报, 2019, 42(7): 1640−1670Xu Rui, Liang Xun, Qi Jin-Shan, Li Zhi-Yu, Zhang Shu-Sen. Advances and trends in extreme learning machine. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2019, 42(7): 1640−1670 [19] Mirjalili S, Mirjalili S M, Lewis A. Grey wolf optimizer. Advances in Engineering Software, 2014, 69: 46−61 doi: 10.1016/j.advengsoft.2013.12.007 [20] Deng R, Xiao G, Lu R, Liang H, Vasilakos A V. False data injection on state estimation in power systems — Attacks, impacts, and defense: A survey. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2016, 13(2): 411−423 [21] James J Q, Hou Y, Li V O K. Online false data injection attack detection with wavelet transform and deep neural networks. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2018, 14(7): 3271−3280 doi: 10.1109/TII.2018.2825243 [22] Wu T, Chung C Y, Kamwa I. A fast state estimator for systems including limited number of pmus. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2017, 32(6): 4329−4339 doi: 10.1109/TPWRS.2017.2673857 [23] 冯晓萌, 孙秋野, 王冰玉, 高嘉文. 基于蠕虫传播和 FDI 的电力信息物理协同攻击策略. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(10): 2429−2441 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190574Feng Xiao-Meng, Sun Qiu-Ye, Wang Bing-Yu, Gao Jia-Wen. The coordinated cyber physical power attack strategy based on worm propagation and false data injection. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(10): 2429−2441 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190574 [24] Tu C M, He X, Liu X, Li P. Cyber-attacks in PMU-based power network and countermeasures. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 65594−65603 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2878436 [25] Huang G B, Zhu Q Y, Siew C K. Extreme learning machine: Theory and applications. Neurocomputing, 2006, 70(1/3): 489−501 [26] Xue D B, Jing X R, Liu H Q. Detection of false data injection attacks in smart grid utilizing ELM-based OCON framework. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 31762−31773 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2902910 [27] Huang G B, Zhou H, Ding X, Zhang R. Extreme learning machine for regression and multiclass classification. IEEE Transactions on Systems Man, and Cybernetics, Part B (Cybernetics), 2012, 42(2): 513−529 doi: 10.1109/TSMCB.2011.2168604 [28] Kasun L, Zhou H, Huang G B, Vong C M. Representational learning with elms for big data. IEEE Intelligent Systems, 2013, 28(6): 31−34 [29] Hou G, Xuan M, Zhang Y. A new method for intrusion detection using manifold learning algorithm. Telkomnika Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering, 2013, 11(12): 7339−7343 [30] Yadav S, Shukla S. Analysis of k-fold cross-validation over hold-out validation on colossal datasets for quality classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE 6th International Conference on Advanced Computing (IACC). Bhimavaram, India: IEEE, 2016. 78−83 [31] 王琦, 邰伟, 汤奕, 倪明. 面向电力信息物理系统的虚假数据注入攻击研究综述. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(1): 72−83Wang Qi, Tai Wei, Tang Yi, Ni Ming. A review on false data injection attack toward cyber-physical power system. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(1): 72−83 -





 下载:
下载: