-
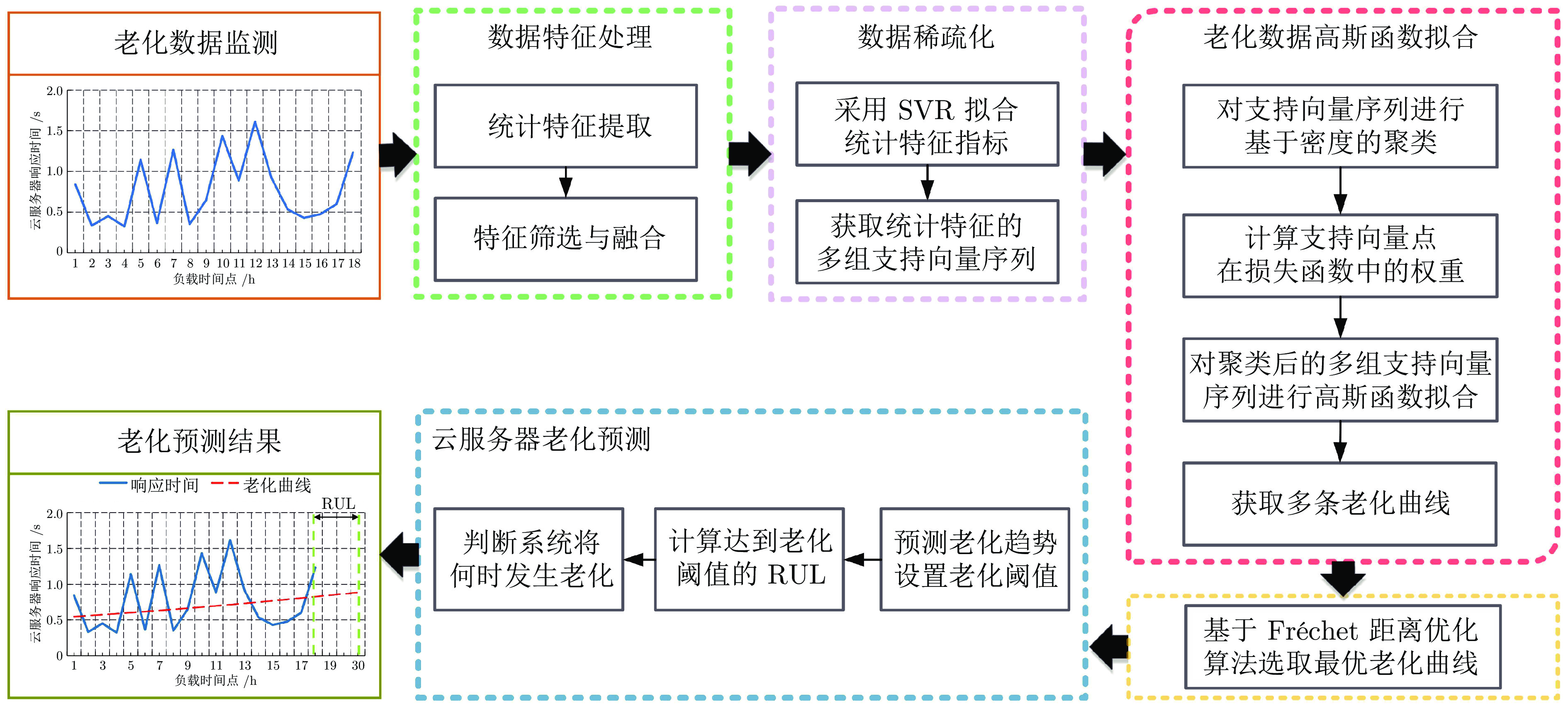
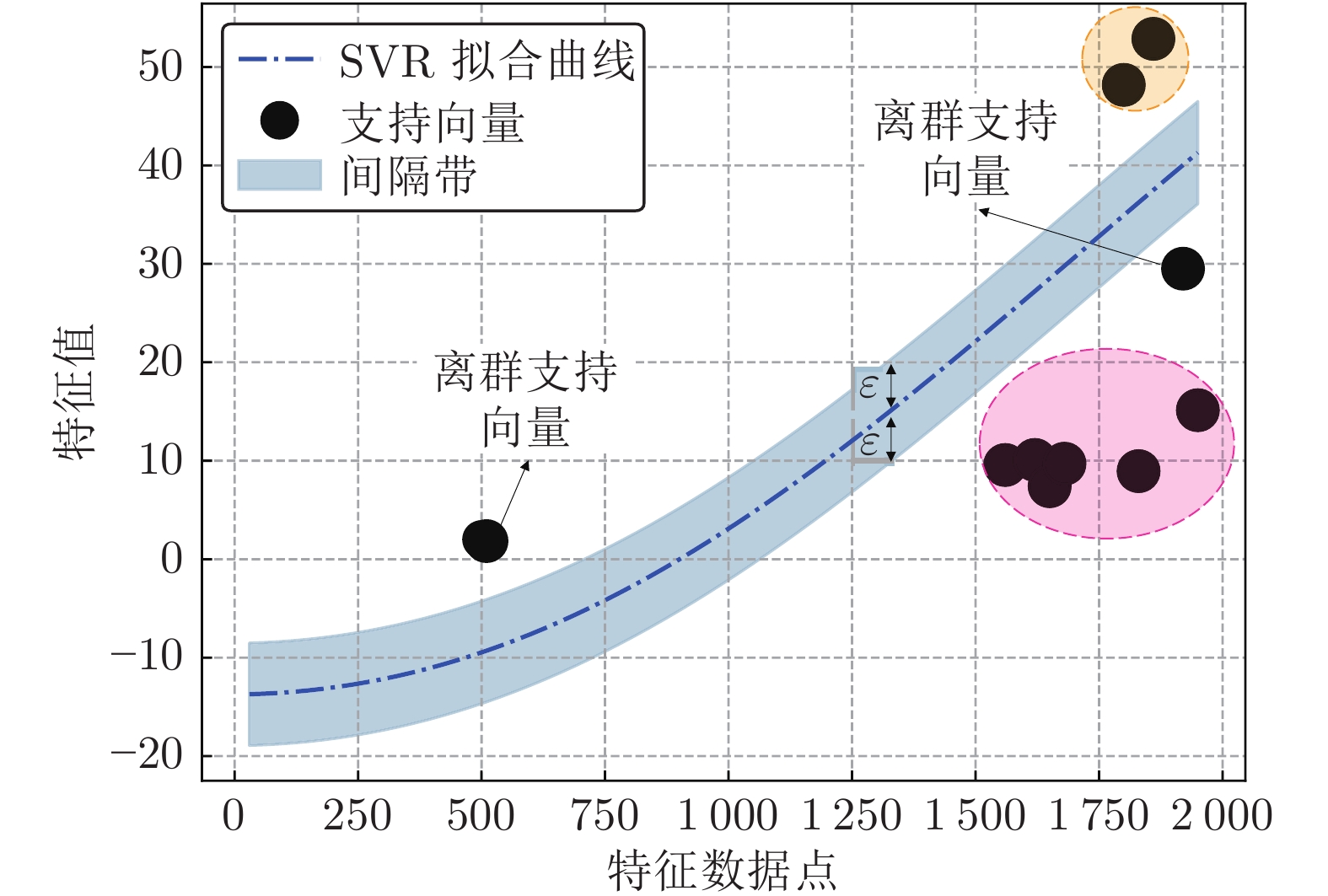
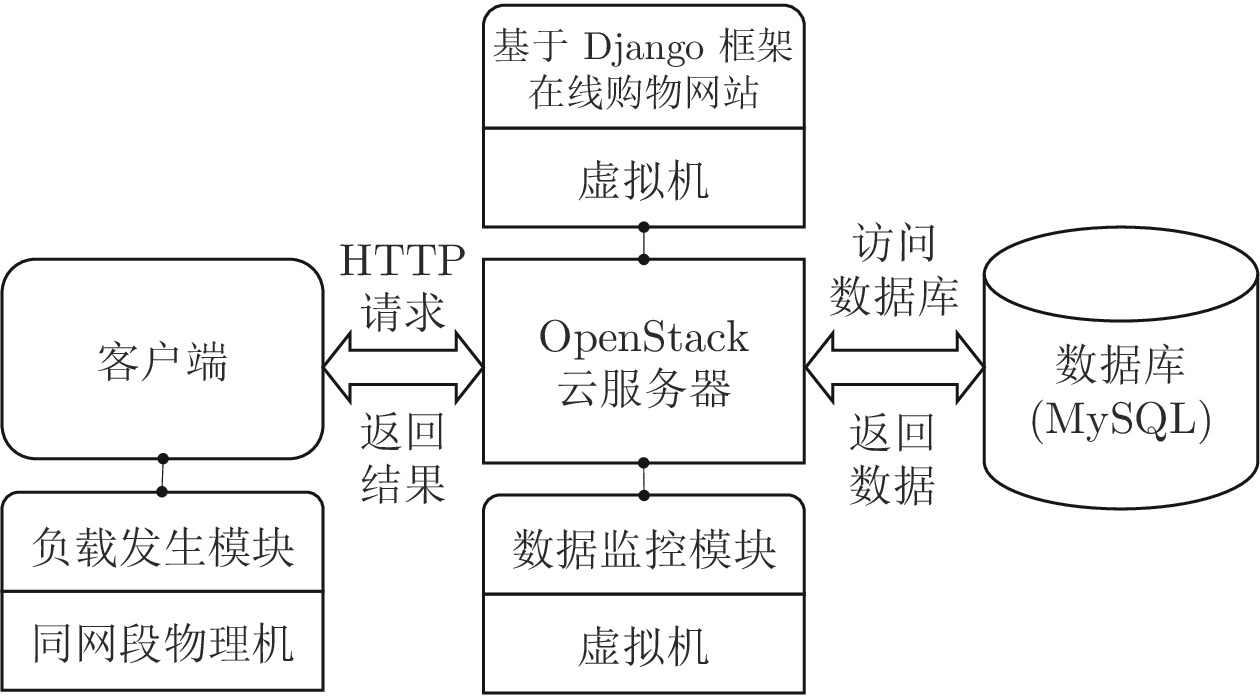
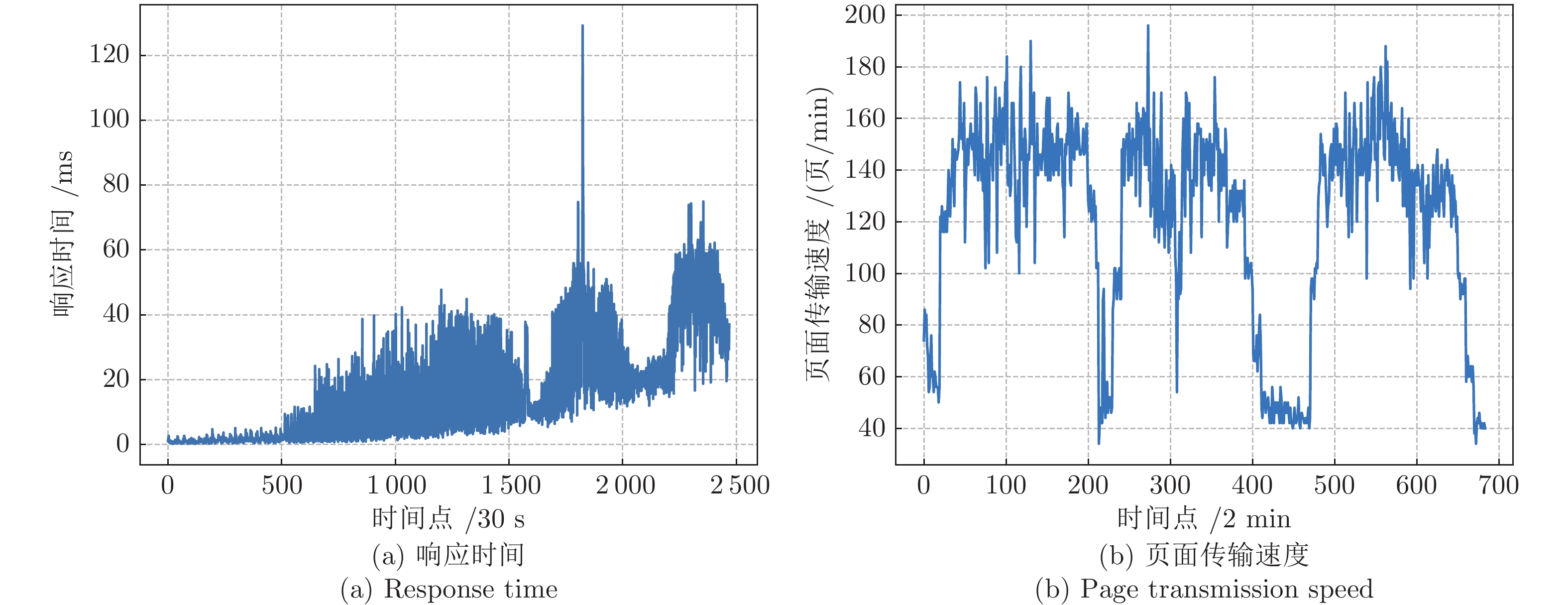
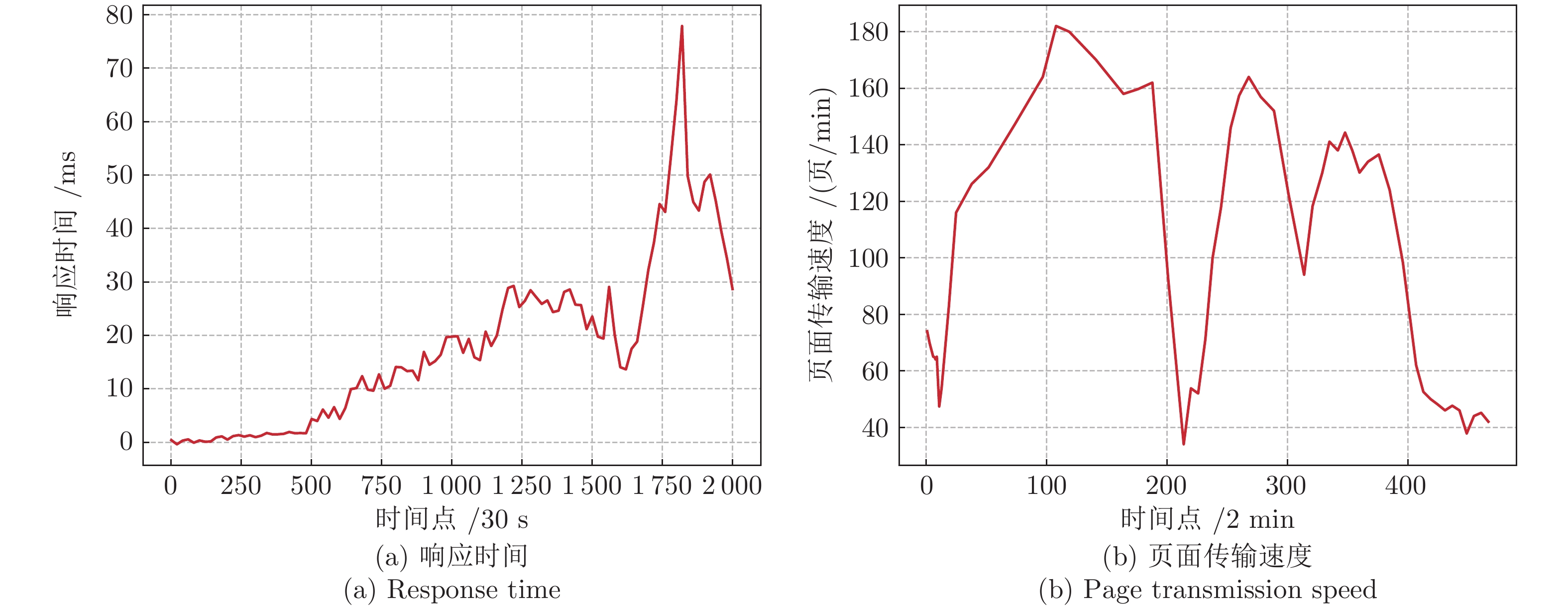
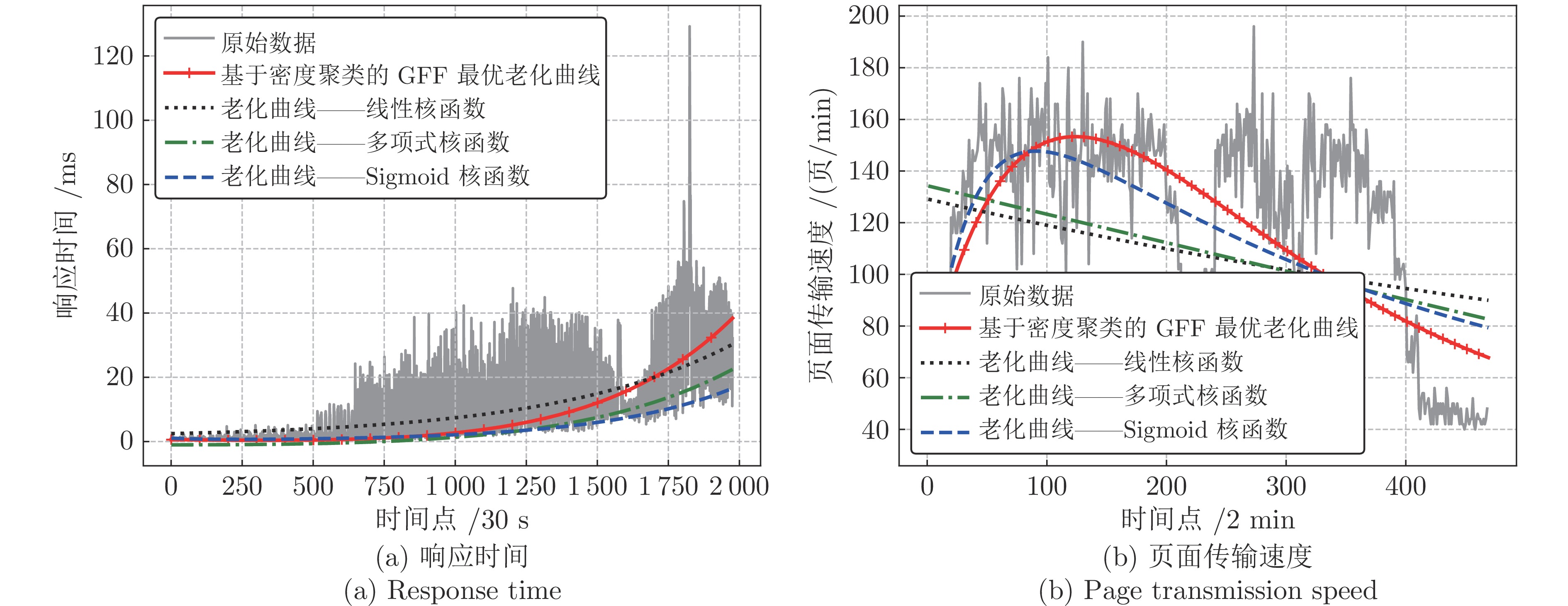
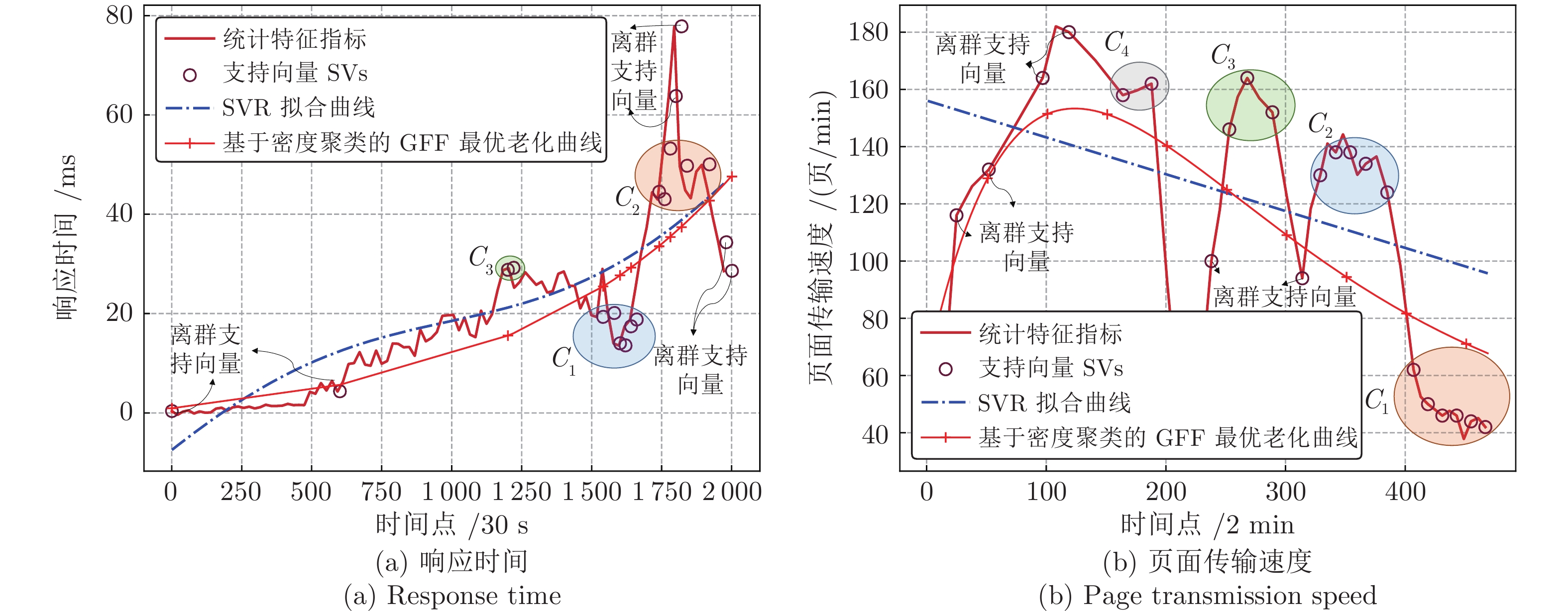
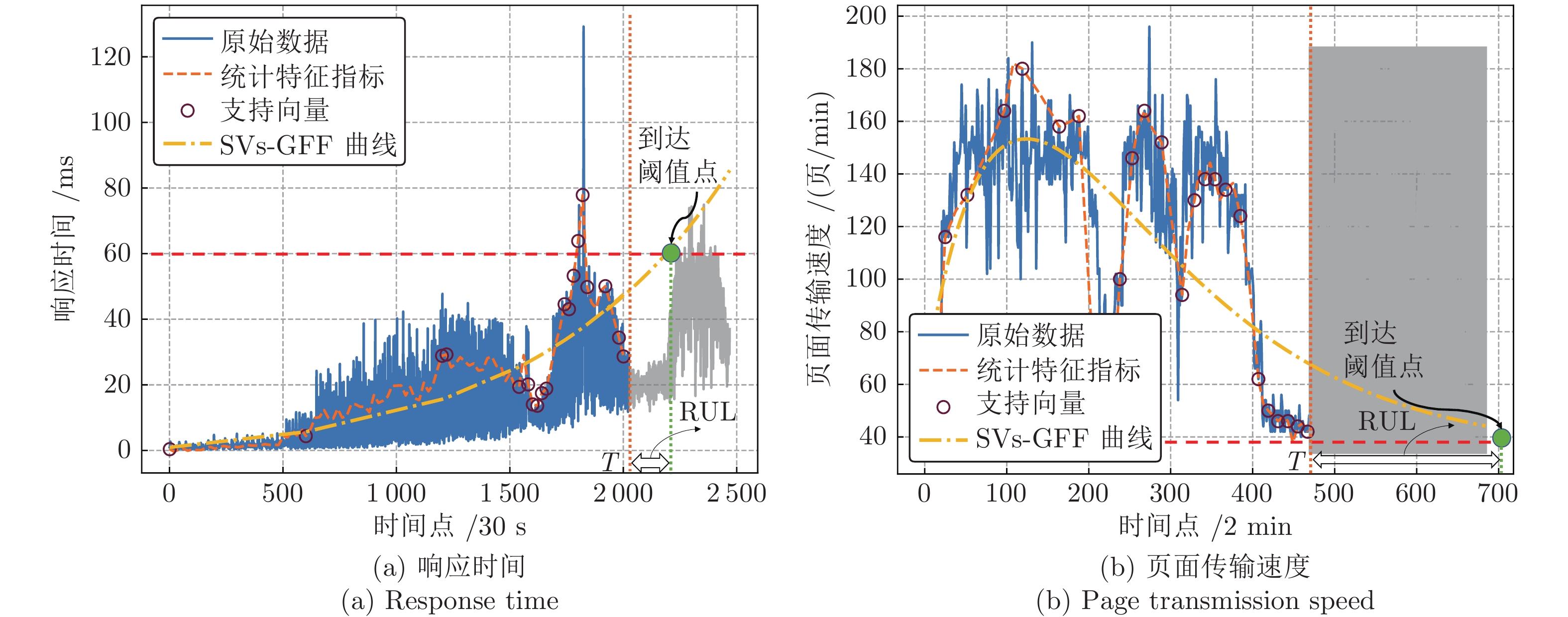
摘要: 针对云服务器中存在软件老化现象, 将造成系统性能衰退与可靠性下降问题, 借鉴剩余使用寿命(Remaining useful life, RUL)概念, 提出基于支持向量和高斯函数拟合(Support vectors and Gaussian function fitting, SVs-GFF)的老化预测方法. 首先, 提取云服务器老化数据的统计特征指标, 并采用支持向量回归(Support vector regression, SVR)对统计特征指标进行数据稀疏化处理, 得到支持向量(Support vectors, SVs)序列数据; 然后, 建立基于密度聚类的高斯函数拟合(Gaussian function fitting, GFF)模型, 对不同核函数下的支持向量序列数据进行老化曲线拟合, 并采用Fréchet距离优化算法选取最优老化曲线; 最后, 基于最优老化曲线, 评估系统到达老化阈值前的RUL, 以预测系统何时发生老化. 在OpenStack云服务器4个老化数据集上的实验结果表明, 基于RUL和SVs-GFF的云服务器老化预测方法与传统预测方法相比, 具有更高的预测精度和更快的收敛速度.Abstract: Aiming at the problem that software aging in cloud servers will cause system performance degradation and reliability descending, a software aging prediction method based on support vectors (SVs) and Gaussian function fitting (SVs-GFF) with the use of the concept of remaining useful life (RUL) is proposed. Firstly, the statistical characteristic indexes of aging data on a cloud server are extracted, and then support vector regression (SVR) is used to sparse the data of statistical characteristic indexes into support vector sequences. Then, the Gaussian function fitting (GFF) model based on density clustering is established to fit the aging curves of support vector sequence data under different kernel functions, and the Fréchet distance optimization algorithm is used to select the optimal aging curve. Finally, based on the optimal aging curve, the remaining useful life before the system reaches the aging threshold is evaluated to predict when software aging occurs. The experiment results on four aging data sets of an OpenStack cloud server show that, the proposed cloud server aging prediction method based on remaining useful life and SVs-GFF has higher accuracy and faster convergence speed compared with traditional prediction methods.
-
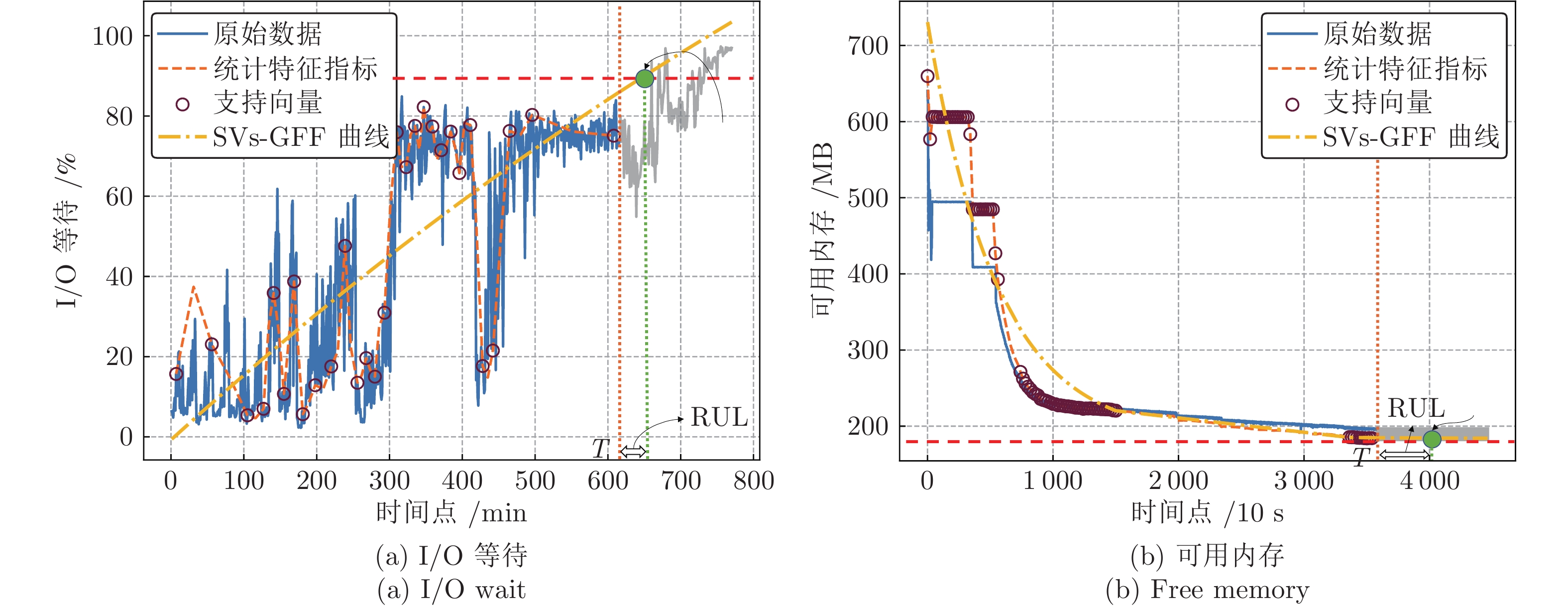
表 1 老化曲线拟合RMSE对比 (%)
Table 1 Comparison of aging curve fitting RMSE (%)
拟合方法 响应时间集 页面传输速度集 基于密度聚类的GFF 21.598 47.129 SVR 57.334 114.239 表 2 不同预测方法的参数设置
Table 2 Parameter setting of different prediction methods
预测方法 参数设置 SVs-GFF 高斯函数中$\alpha$、$\beta$、$\sigma$和$\gamma$的初始值: 0, 寻优方法: 最小二乘法, SVR中正则化参数: 1.0, 距离阈值$\varepsilon$: 0.5 SVR 正则化参数: 1, 核函数: RBF GFF 高斯函数中$\alpha$、$\beta$、$\sigma$和$\gamma$的初始值: 0, 寻优方法: 最小二乘法 PF 基于PF模型更新指数模型参数, 老化特征值$\alpha$: 1.979, 指数模型参数$b$: 0.00271 , $c$: −0.1697 , 白噪声标准差$d$: −0.06942 ANN 神经元数: [输入层: 30, 隐藏层1: 64, 隐藏层2: 64, 隐藏层3: 32, 输出层: 1 ], 激活函数: ReLU, 迭代次数: 100 LSTM 神经元数: [输入层: 10, 隐藏层1: 32, 隐藏层2: 32, 隐藏层3: 16, 输出层: 1 ], 激活函数: ReLU, 迭代次数: 100 Markov 基于Markov模型更新指数模型参数, 指数模型参数的初始值: 0 表 3 预测性能比较
Table 3 Comparison of prediction performances
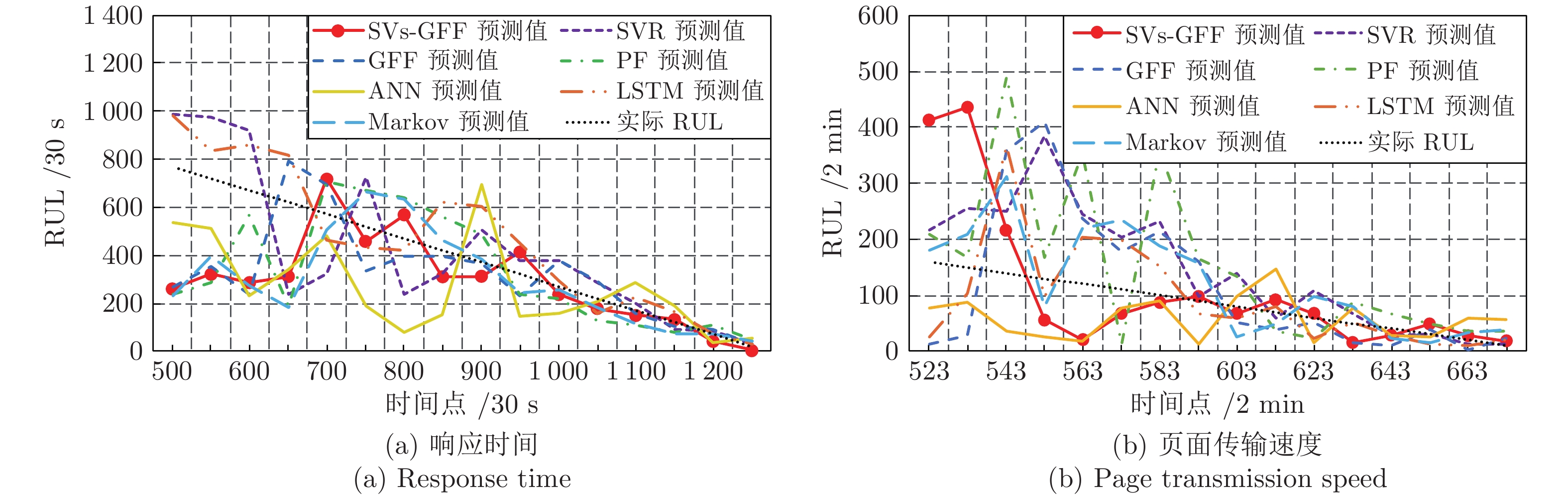
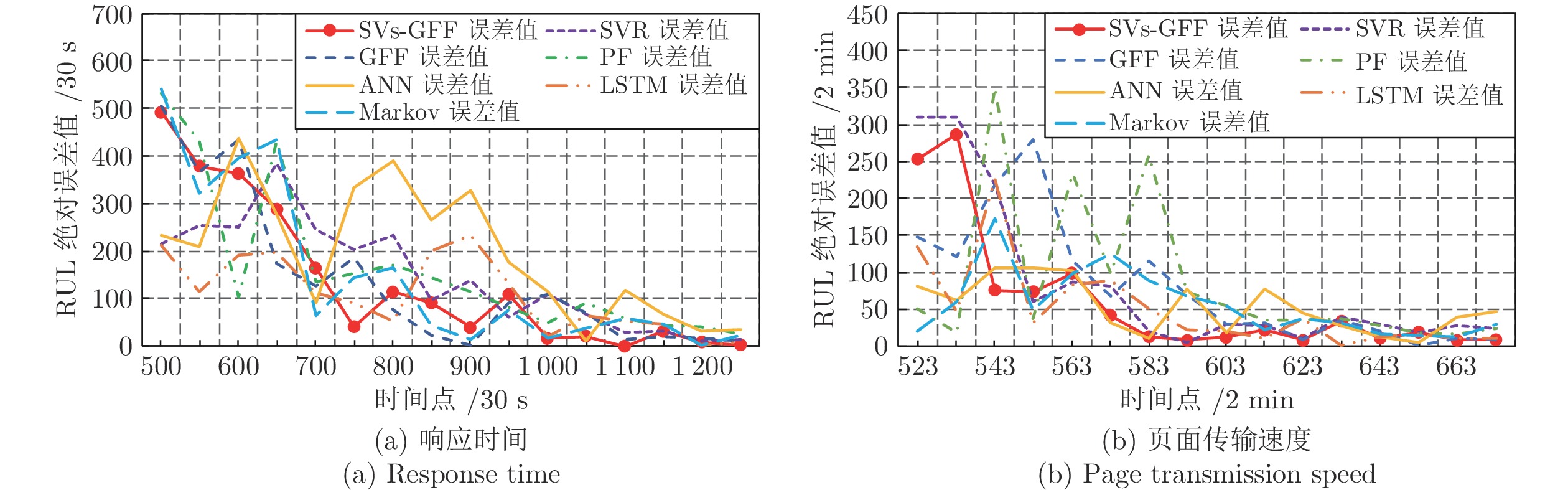
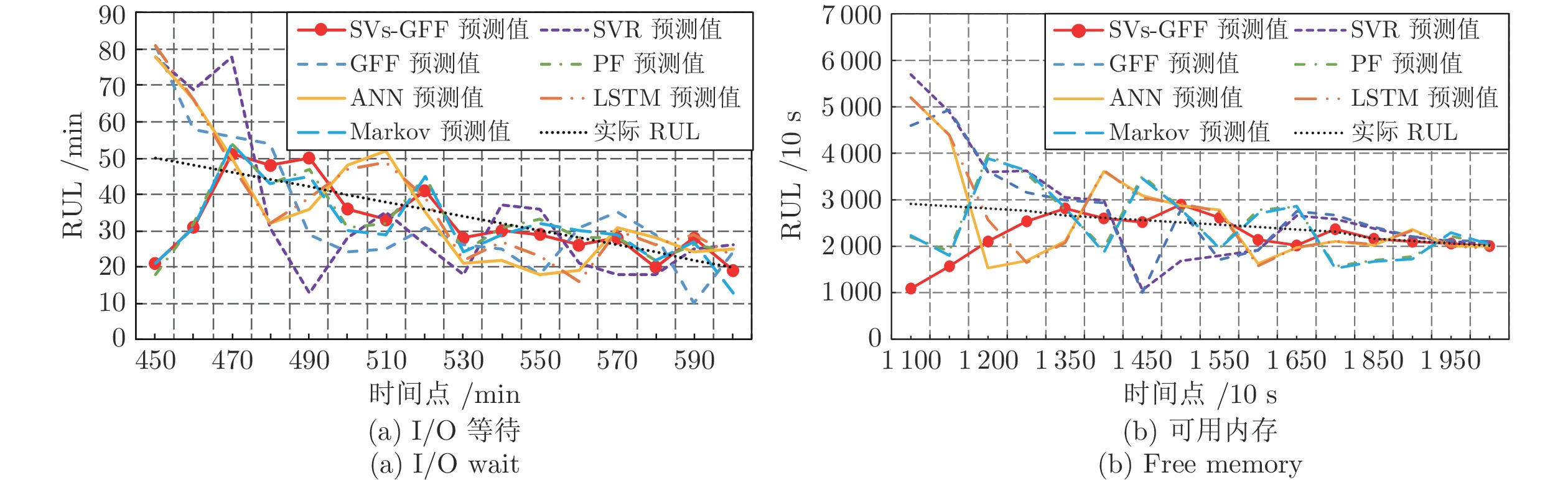
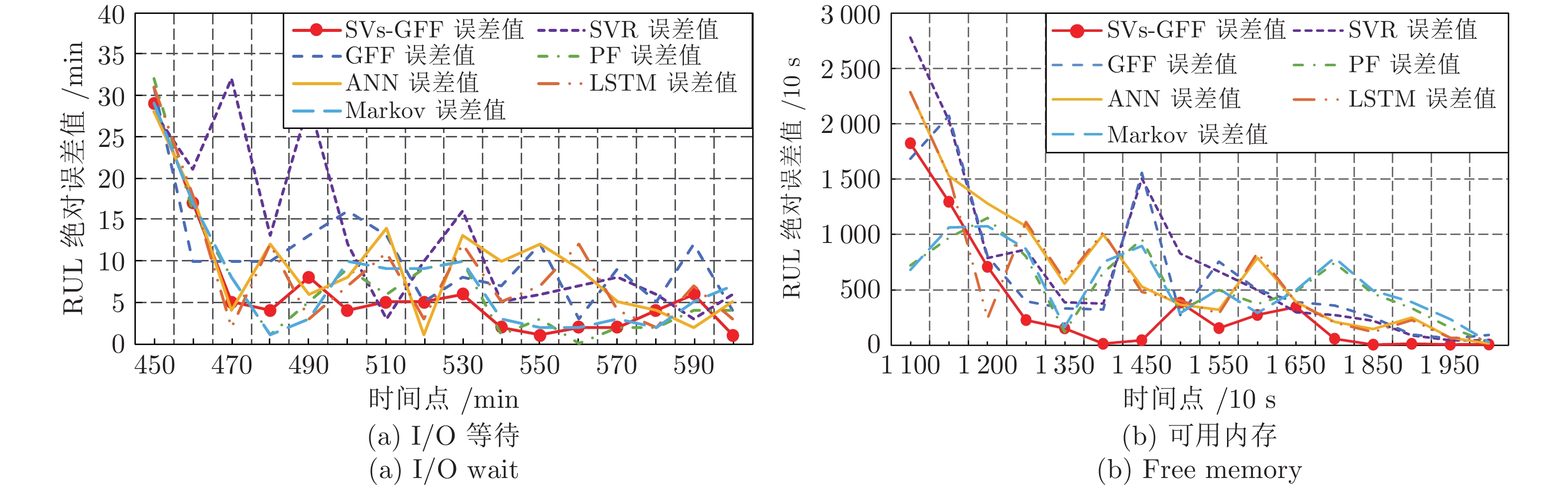
数据集名称 评价指标 SVs-GFF GFF SVR PF ANN LSTM Markov 响应时间数据集 ${\rm{CRA}}$ 0.904 0.769 0.891 0.841 0.737 0.901 0.858 $C_{PE}$ 15.117 15.896 16.035 15.369 18.353 19.360 15.371 页面传输速度数据集 ${\rm{CRA}}$ 0.879 0.698 0.861 0.801 0.721 0.792 0.813 $C_{PE}$ 16.487 16.945 16.987 17.897 19.547 20.487 17.881 -
[1] Grottke M, Matias R, Trivedi K S. The fundament of software aging. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Software Reliability Engineering Workshops. Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2008. 1−6 [2] Vizarreta P, Sieber C, Blenk A, Bemten A V, Trivedi K. Ares: A framework for management of aging and rejuvenation in softwarized networks. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 2021, 18(2): 1389−1400 doi: 10.1109/TNSM.2020.3030589 [3] Tai A T, Chau S N, Alkalaj L. On-board preventive maintenance: Analysis of effectiveness and optimal duty period. In: Proceedings of the 3rd International Workshop on Object Oriented Real-time Dependable Systems. Newport Beach, USA: IEEE, 1997. 40−47 [4] Xiang J, Weng C, Zhao D, Andrzejak A. Software aging and rejuvenation in android: New models and metrics. Software Quality Journal, 2020, 28(3): 85−106 [5] Grottke M, Li L, Vaidyanathan K, Trivedi K S. Analysis of software aging in a web server. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2006, 55(3): 411−420 doi: 10.1109/TR.2006.879609 [6] Pietrantuono R, Russo S. A survey on software aging and rejuvenation in the cloud. Software Quality Control, 2020, 28(1): 7−38 doi: 10.1007/s11219-019-09448-3 [7] 施权, 胡昌华, 司小胜, 扈晓翔, 张正新. 考虑执行器性能退化的控制系统剩余寿命预测方法. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(5): 941−952Shi Quan, Hu Chang-Hua, Si Xiao-Sheng, Hu Xiao-Xiang, Zhang Zheng-Xin. Remaining useful lifetime prediction method of controlled systems considering performance degradation of actuator. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(5): 941−952 [8] Huang Y, Kintala C, Kolettis N, Fulton N D. Software rejuvenation: Analysis, module and applications. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Symposium on Fault-tolerant Computing. Pasadena, USA: IEEE, 1995. 381−390 [9] Andrade E, Machida F. Analysis of software aging impacts on plant anomaly detection with edge computing. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Software Reliability Engineering Workshops. Berlin, Germany: IEEE, 2019. 204−210 [10] Machida F, Maciel P R M. Markov chains and Petri nets for software rejuvenation systems. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Software Reliability Engineering Workshops. Coimbra, Portugal: IEEE, 2020. 325−326 [11] Dohi T, Goseva-Popstojanova K, Trivedi K S. Estimating software rejuvenation schedule in high assurance systems. The Computer Journal, 2001, 47: 473−485 [12] Machida F, Xiang J, Tadano K, Maeno Y. Lifetime extension of software execution subject to aging. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2017, 66(1): 123−134 doi: 10.1109/TR.2016.2615880 [13] Ning G, Zhao J, Lou Y. Optimization of two-granularity software rejuvenation policy based on the Markov regenerative process. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2016, 65(4): 1630−1646 doi: 10.1109/TR.2016.2570539 [14] Okamura H, Dohi T. Performance-aware software rejuvenation strategies in a queuing system. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Second International Workshop on Software Aging and Rejuvenation. San Jose, USA: IEEE, 2010. 1−6 [15] Levitin G, Xing L, Xiang Y. Cost minimization of real-time mission for software systems with rejuvenation. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2020, 193: Article No. 106593 [16] Zheng Z, Trivedi K S. Guest editorial: Special issue on modeling and mitigation techniques for software aging. Software Quality Journal, 2020, 28(1): 3−5 doi: 10.1007/s11219-020-09496-0 [17] Vaidyanathan K, Trivedi K S. A comprehensive model for software rejuvenation. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2005, 2(2): 124−137 doi: 10.1109/TDSC.2005.15 [18] Yan Y, Guo P. A practice guide of software aging prediction in a web server based on machine learning. China Communications, 2016, 13(6): 225−235 doi: 10.1109/CC.2016.7513217 [19] Pereira P, Araujo J, Matos R. Software rejuvenation in computer systems: An automatic forecasting approach based on time series. In: Proceedings of the 37th IEEE International Performance Computing and Communications Conference. Orlando, USA: IEEE, 2018. 1−8 [20] Cotroneo D, Natella R, Pietrantuono R. Software aging analysis of the Linux operating system. In: Proceedings of the IEEE 21st International Symposium on Software Reliability Engineering. San Jose, USA: IEEE, 2010. 71−80 [21] Matos R, Araujo J, Maciel P. Software rejuvenation in eucalyptus cloud computing infrastructure: A method based on time series forecasting and multiple thresholds. In: Proceedings of the IEEE 3rd International Workshop on Software Aging and Rejuvenation. Hiroshima, Japan: IEEE, 2011. 38−43 [22] 郑鹏飞, 齐勇, 陈鹏飞. 软件老化的多元时间序列分析方法. 计算机科学与探索, 2012, 6(2): 33−41Zheng Peng-Fei, Qi Yong, Chen Peng-Fei. Multivariate time series analysis of software aging. Journal of Frontiers of Computer Science & Technology, 2012, 6(2): 33−41 [23] Islam S, Keung J, Lee K. Empirical prediction models for adaptive resource provisioning in the cloud. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2012, 28(1): 155−162 doi: 10.1016/j.future.2011.05.027 [24] Yan Y, Guo P, Liu L. A practice of forecasting software aging in an IIS web server using SVM. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Software Reliability Engineering Workshops. Naples, Italy: IEEE, 2014. 443−448 [25] Qiao Y, Zheng Z, Fang Y. An empirical study on software aging indicators prediction in android mobile. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Software Reliability Engineering Workshops. Memphis, USA: IEEE, 2018. 271−277 [26] Padhy N, Panigrahi R, Neeraja K. Threshold estimation from software metrics by using evolutionary techniques and its proposed algorithms, models. Evolutionary Intelligence, 2021, 14(2): 315−329 doi: 10.1007/s12065-019-00201-0 [27] Yan Y. Software aging prediction using neural network with ridge. IET Software, 2020, 14(6): 517−524 [28] Liu J, Tan X, Wang Y. CSSAP: Software aging prediction for cloud services based on ARIMA-LSTM hybrid model. In: Proce-edings of the IEEE International Conference on Web Services. Beijing, China: IEEE, 2019. 283−290 [29] 孟海宁, 童新宇, 石月开, 朱磊, 冯锴, 黑新宏. 基于ARIMA-RNN组合模型的云服务器老化预测方法. 通信学报, 2021, 42(1): 163−171Meng Hai-Ning, Tong Xin-Yu, Shi Yue-Kai, Zhu Lei, Feng Kai, Hei Xin-Hong. Cloud server aging prediction method based on hybrid model of auto-regressive integrated moving average and recurrent neural network. Journal on Communications, 2021, 42(1): 163−171 [30] Nguyen H, Choi Y, Bui X N. Predicting blast-induced ground vibration in open-pit mines using vibration sensors and support vector regression-based optimization algorithms. Sensors, 2020, 20(1): 1−21 [31] Kwak M, Lkhagvasuren B, Sun X. An efficient method for fitting Gaussian functions. Iranian Journal of Science and Technology, Transactions A: Science, 2021, 45(3): 1043−1056 [32] Guo L, Li N, Jia F. A recurrent neural network-based health indicator for remaining useful life prediction of bearings. Neurocomputing, 2017, 240(3): 98−109 [33] Cotroneo D, Natella R, Pietrantuono R, Russo S. A survey of software aging and rejuvenation studies. ACM Journal on Emerging Technologies in Computing Systems, 2014, 10(1): 1−34 [34] Ahmed F. K and starting means for K-means algorithm. Journal of Computational Science, 2021, 55(1): Article No. 101445 [35] Gudmundsson J, Van Renssen A, Saeidi Z. Translation invariant Fréchet distance queries. Algorithmica, 2021, 83: 1−19 doi: 10.1007/s00453-020-00746-y [36] Si X S, Wang W, Hu C H. A wiener-process-based degradation model with a recursive filter algorithm for remaining useful life estimation. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2013, 35(1): 219−237 [37] Matias R, Barbetta P A, Trivedi K S. Accelerated degradation tests applied to software aging experiments. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2010, 59(1): 102−114 doi: 10.1109/TR.2009.2034292 [38] Engel Y, Mannor S, Meir R. The kernel recursive least-squares algorithm. IEEE Transaction on Signal Process, 2004, 52(8): 2275−2285 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2004.830985 [39] Qiu G, Gu Y, Chen J. Selective health indicator for bearings ensemble remaining useful life prediction with genetic algorithm and Weibull proportional hazards model. Measurement, 2020, 150: Article No. 107097 doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2019.107097 [40] Aye S A, Heyns P S. An integrated Gaussian process regression for prediction of remaining useful life of slow speed bearings based on acoustic emission. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2017, 84: 485−498 doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2016.07.039 [41] Guo R, Sui J. Remaining useful life prognostics for the electrohydraulic servo actuator using Hellinger distance-based particle filter. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2020, 69(4): 1148−1158 doi: 10.1109/TIM.2019.2910919 [42] Fauzi M F A M, Aziz I A, Amiruddin A. The prediction of remaining useful life (RUL) in oil and gas industry using artificial neural network (ANN) algorithm. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Big Data and Analytics. Milan, Italy: IEEE, 2019. 7−11 [43] Xia J, Feng Y W, Lu C. LSTM-based multi-layer self-attention method for remaining useful life estimation of mechanical systems. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2021, 125(12): Article No. 105385 [44] Wang T, Liu Z, Mrad N A. Probabilistic framework for remaining useful life prediction of bearings. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2021, 70: 1−12 [45] Saxena A, Celaya J, Saha B A. Metrics for offline evaluation of prognostic performance. International Journal of Prognostics & Health Management, 2010, 1(1): 2153−2648 [46] Wang B, Lei Y, Li N. A hybrid prognostics approach for estimating remaining useful life of rolling element bearings. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2018, 86: 1452−1463 [47] 张正新, 胡昌华, 司小胜, 张伟. 双时间尺度下的设备随机退化建模与剩余寿命预测方法. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(10): 1789−1798Zhang Zheng-Xin, Hu Chang-Hua, Si Xiao-Sheng, Zhang Wei. Degradation modeling and remaining useful life prediction with bivariate time scale. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(10): 1789−1798 [48] 裴洪, 胡昌华, 司小胜, 张正新, 杜党波. 不完美维护下基于剩余寿命预测信息的设备维护决策模型. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(4): 719−729Pei Hong, Hu Chang-Hua, Si Xiao-Sheng, Zhang Zheng-Xin, Du Dang-Bo. Remaining life prediction information-based maintenance decision model for equipment under imperfect maintenance. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(4): 719−729 -




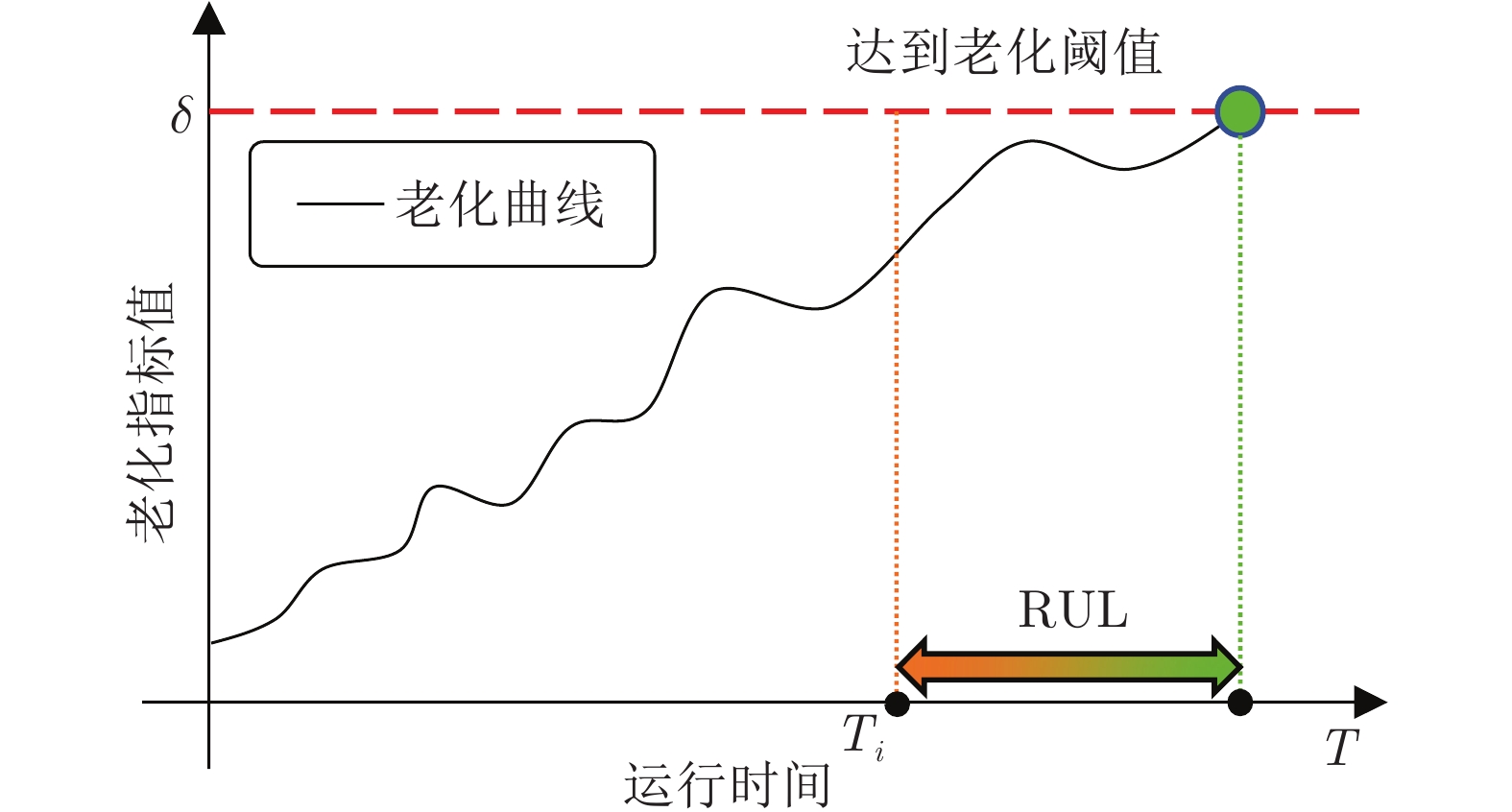
 下载:
下载: