A Stochastic Incremental Learning Model With Maximizing Spatial Geometry Angle and Its Application
-
摘要: 针对随机权神经网络(Random weight neural networks, RWNNs)隐含层节点随机生成过程可解释性不足和节点随机生成而导致的网络结构不紧致等问题, 提出了一种空间几何角度最大化随机增量学习模型(Stochastic incremental learning model with maximizing spatial geometry angle, SGA-SIM). 首先, 以空间几何视角深入分析随机增量学习过程, 建立了具有可解释性的空间几何角度最大化约束, 以改善隐含层节点质量, 并证明该学习模型具有无限逼近特性; 同时, 引入格雷维尔迭代法优化学习模型输出权值计算方法, 提高模型学习效率. 在真实的分类和回归数据集以及数值模拟实例上的实验结果表明, 所提增量学习模型在建模速度、模型精度和模型网络结构等多个方面具有明显优势.
-
关键词:
- 随机权神经网络 /
- 增量学习 /
- 空间几何角度最大化约束 /
- 无限逼近性
Abstract: Aiming at the problems of insufficient interpretability and incompact network structure caused by random generation of hidden nodes in random weight neural networks (RWNNs), this paper proposes a stochastic incremental learning model with maximizing spatial geometry angle (SGA-SIM). Firstly, the random incremental learning process is deeply analyzed from the perspective of spatial geometry, then an interpretable spatial geometric angle maximization constraint is established to improve the quality of the hidden nodes, and the universal approximation property of this model is proved. Besides, the Grenville iteration method is introduced to optimize the output weight calculation, which improves the learning efficiency of the learning model. Experimental results on the real datasets and numerical simulation examples show that the proposed model has obvious advantages in modeling speed, model accuracy and model network structure. -
表 1 数据集信息
Table 1 Information of datasets
数据集 训练样本数 测试样本数 特征 类别 nonlinear function 600 400 1 — 回归问题 Abalone 2000 2177 7 — Compactiv 6144 2048 21 — Iris 120 30 4 3 分类问题 HAR 7352 2947 561 6 Gesture recognition 3595 1241 54 24 表 2 各模型在不同数据集上的初始参数
Table 2 Initial parameters of each model on different datasets
数据集(期望残差$\ell $) IRWNNs (${L_{\max }}$, $\lambda $, ${T_{\max }}$) SGA-SIM (${L_{\max }}$, $\Upsilon $, ${T_{\max }}$) SCNs (${L_{\max }}$, $\Upsilon $, ${T_{\max }}$) nonlinear function (0.05) 100, 150, 1 100, 150:10:200, 20 100, 150:10:200, 20 Abalone (0.16) 100, 0.5, 1 100, 0.5:0.1:10, 20 100, 0.5:0.1:10, 20 Compactiv (0.15) 200, 0.5, 1 200, 0.5:0.1:10, 20 200, 0.5:0.1:10, 20 Iris (0.01) 50, 1, 1 50, 1:1:10, 20 50, 1:1:10, 20 HAR (0.01) 500, 50, 1 500, 1:1:10, 20 500, 1:1:10, 20 Gesture recognition (0.05) 500, 0.5, 1 500, 0.5:0.5:10, 20 500, 0.5:0.5:10, 20 表 3 数值模拟例子的实验结果
Table 3 Experimental results of numerical simulation examples
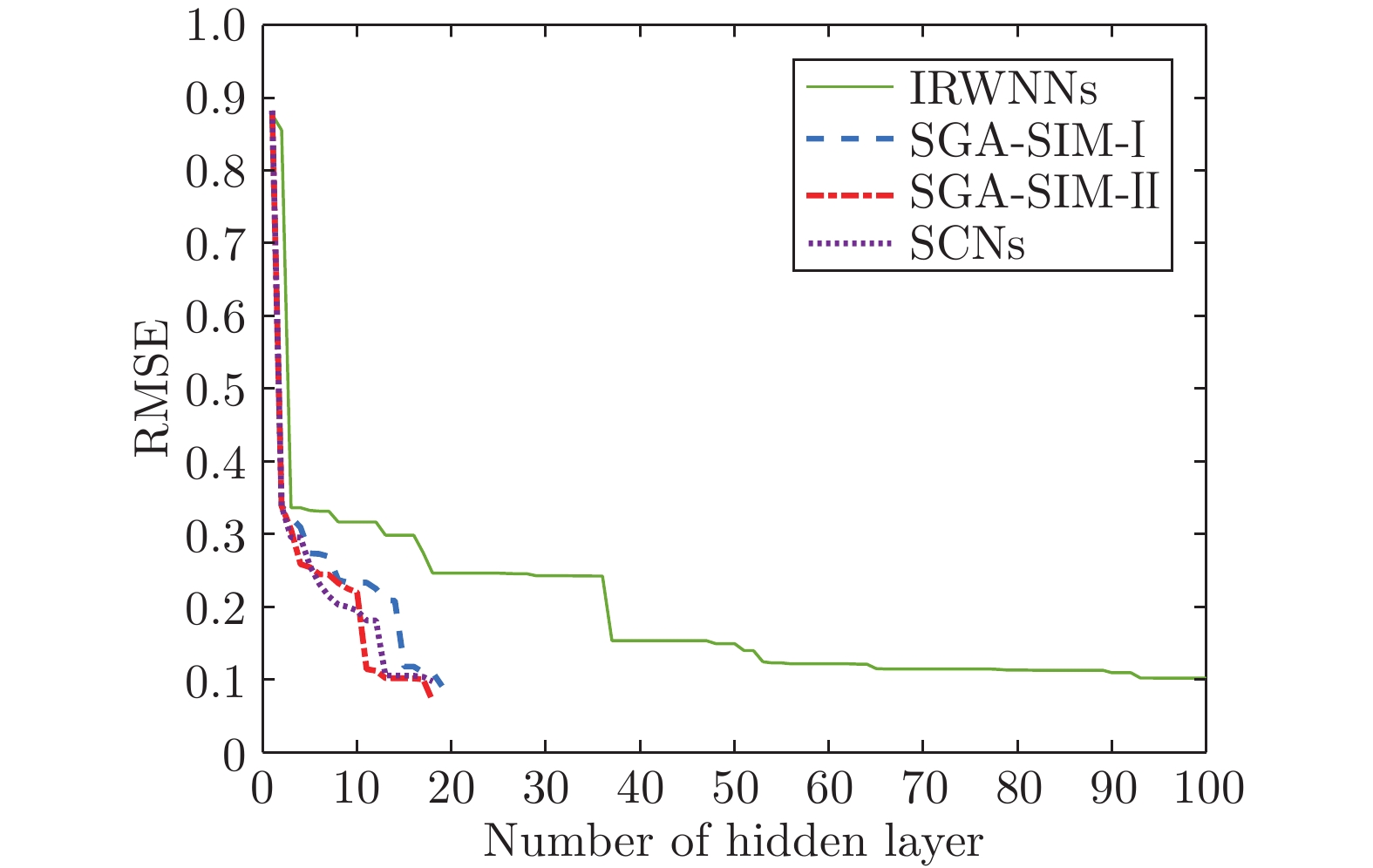
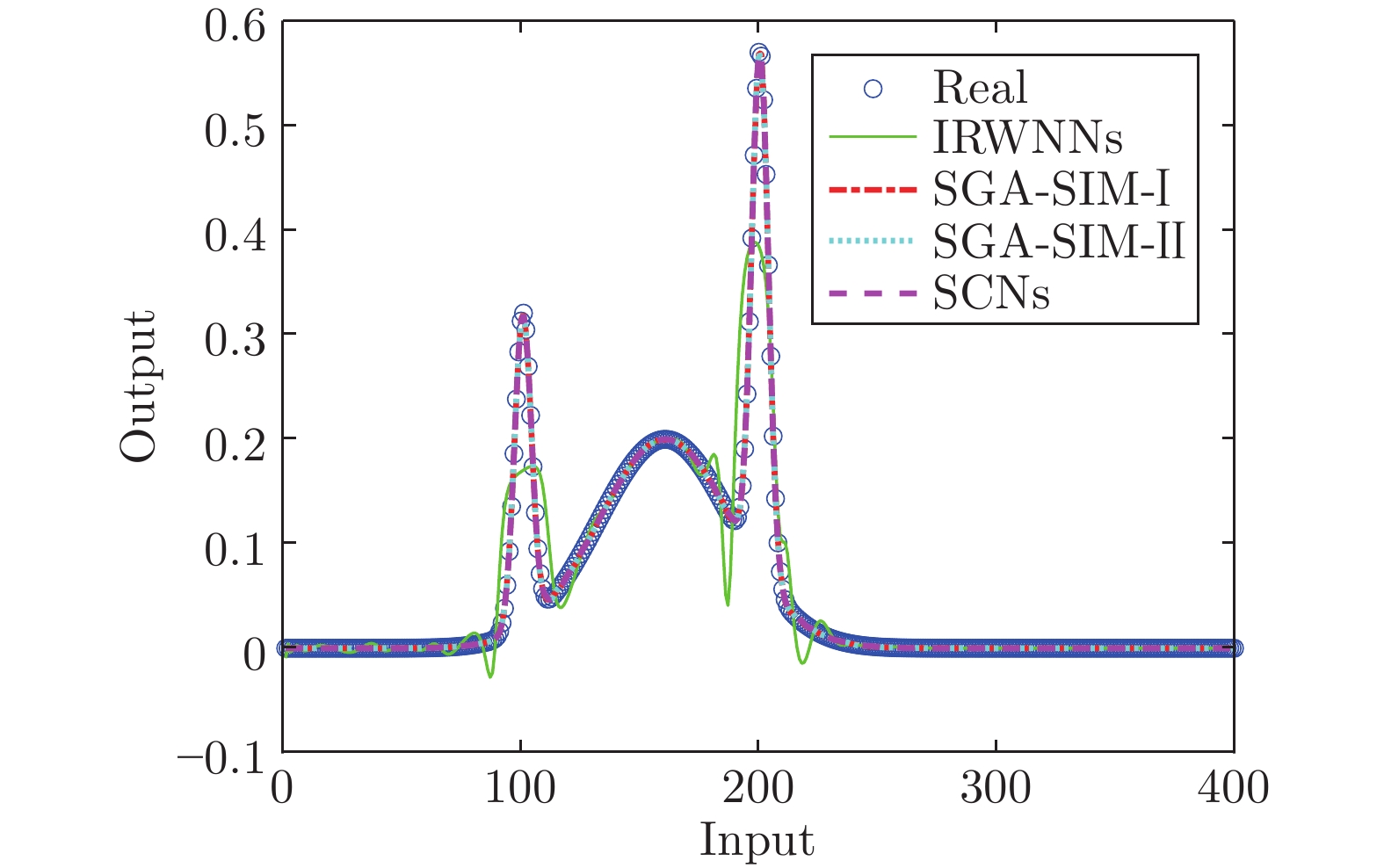
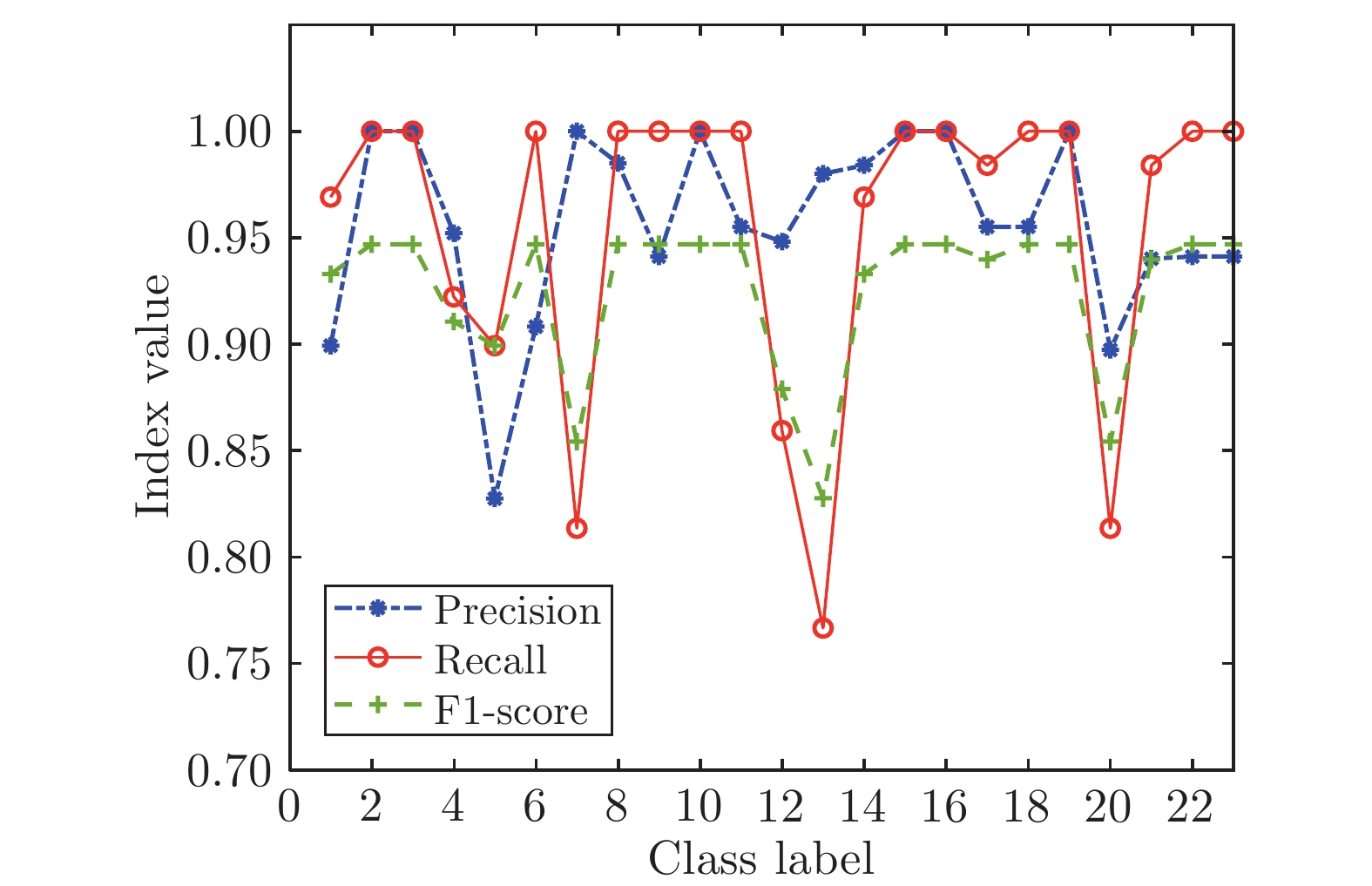
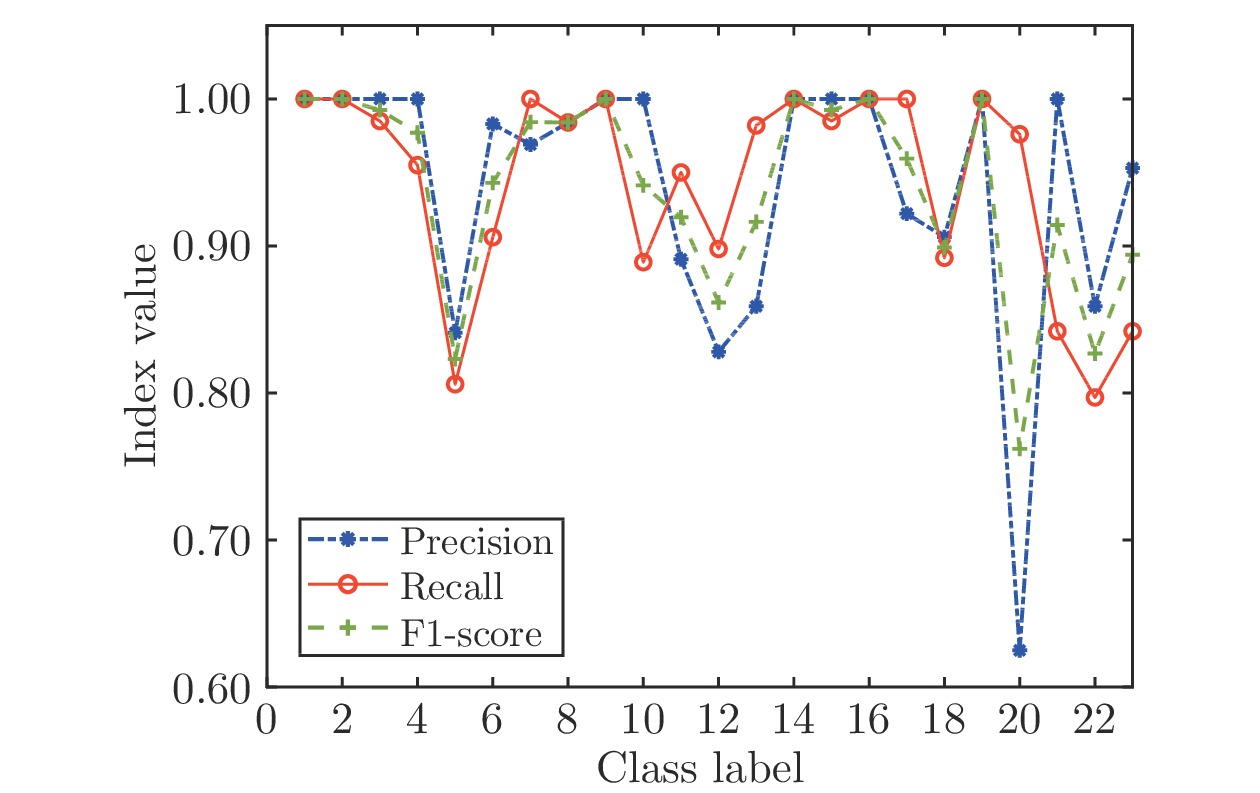
模型 节点数$(L)$ 建模时间(s) AVE DEV IRWNNs 100.0 3.25 0.1060 0.0301 SGA-SIM-I 79.8 2.70 0.0014 0.0003 SGA-SIM-II 79.2 0.15 0.0010 0.0002 SCNs 79.3 2.93 0.0014 0.0003 表 4 公共数据集的实验结果
Table 4 Experimental results of public datasets
数据集 模型 节点数$(L)$ 建模时
间(s)训练
误差测试
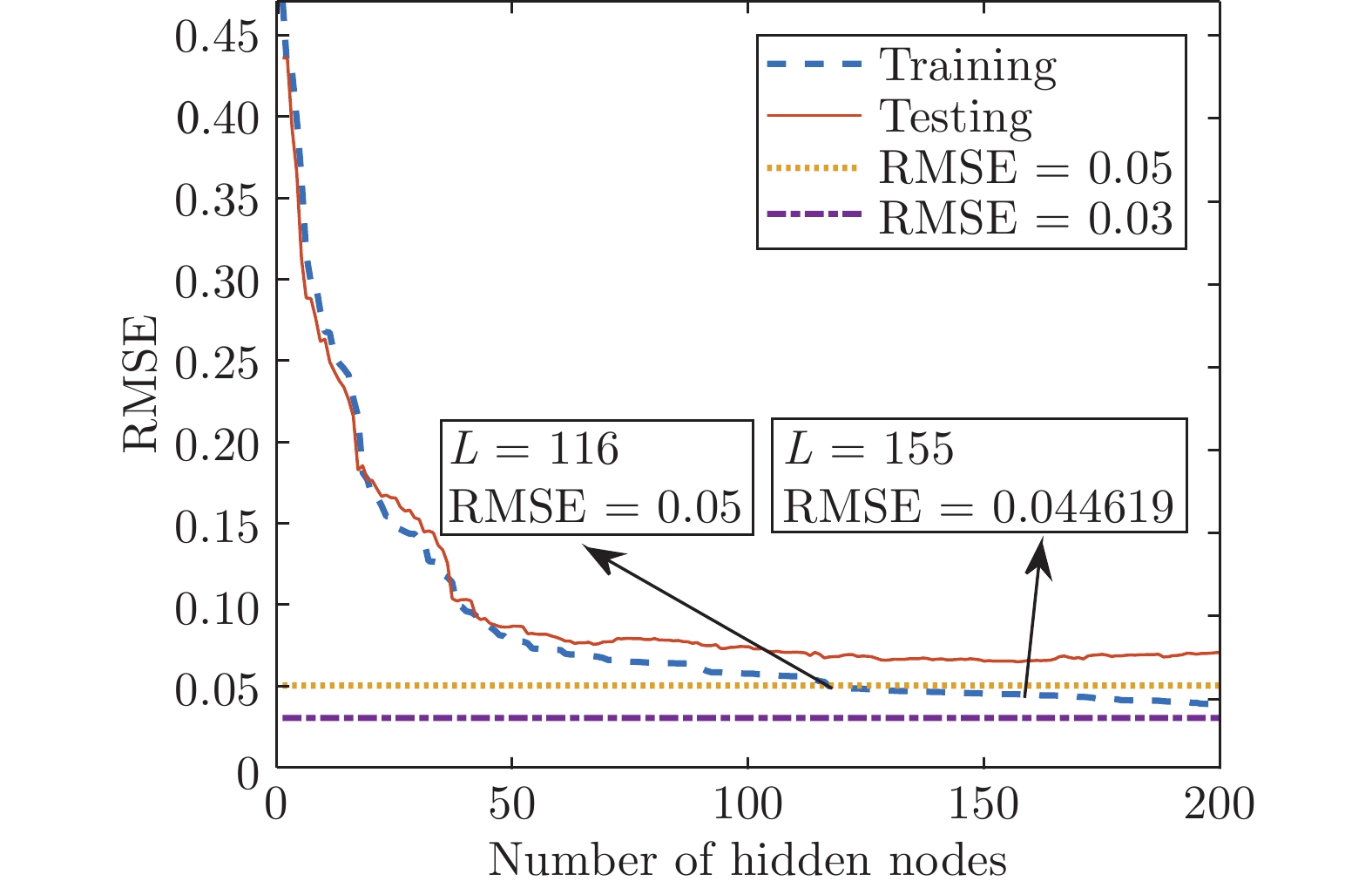
误差Abalone IRWNNs 100 0.2543 0.2209 0.2178 SGA-SIM-I 0.8190 0.1479 0.1763 SGA-SIM-II 0.2024 0.1446 0.1727 SCNs 0.8876 0.1477 0.1723 Compactiv IRWNNs 200 1.3461 0.2720 0.2715 SGA-SIM-I 5.3443 0.0573 0.0695 SGA-SIM-II 1.8827 0.0571 0.0670 SCNs 5.7920 0.0573 0.0695 Iris IRWNNs 50 0.0169 0.0222 0.0556 SGA-SIM-I 0.0794 0.0167 0.0333 SGA-SIM-II 0.0616 0.0167 0.0333 SCNs 0.0918 0.0173 0.0333 HAR IRWNNs 500 50.0381 0.0739 0.1233 SGA-SIM-I 110.7238 0.0147 0.0450 SGA-SIM-II 27.4965 0.0140 0.0441 SCNs 111.3737 0.0160 0.0550 表 5 智能手套传感器描述
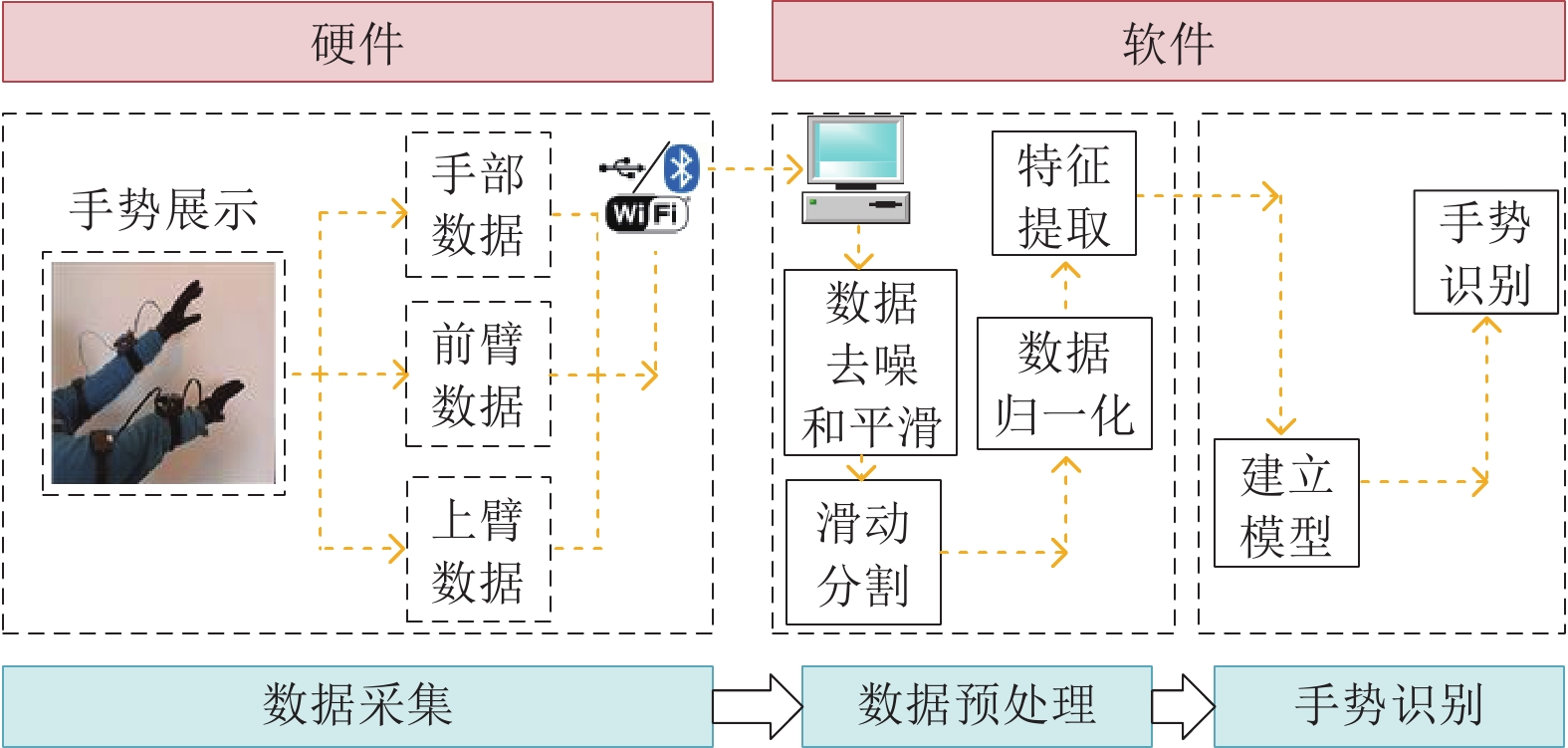
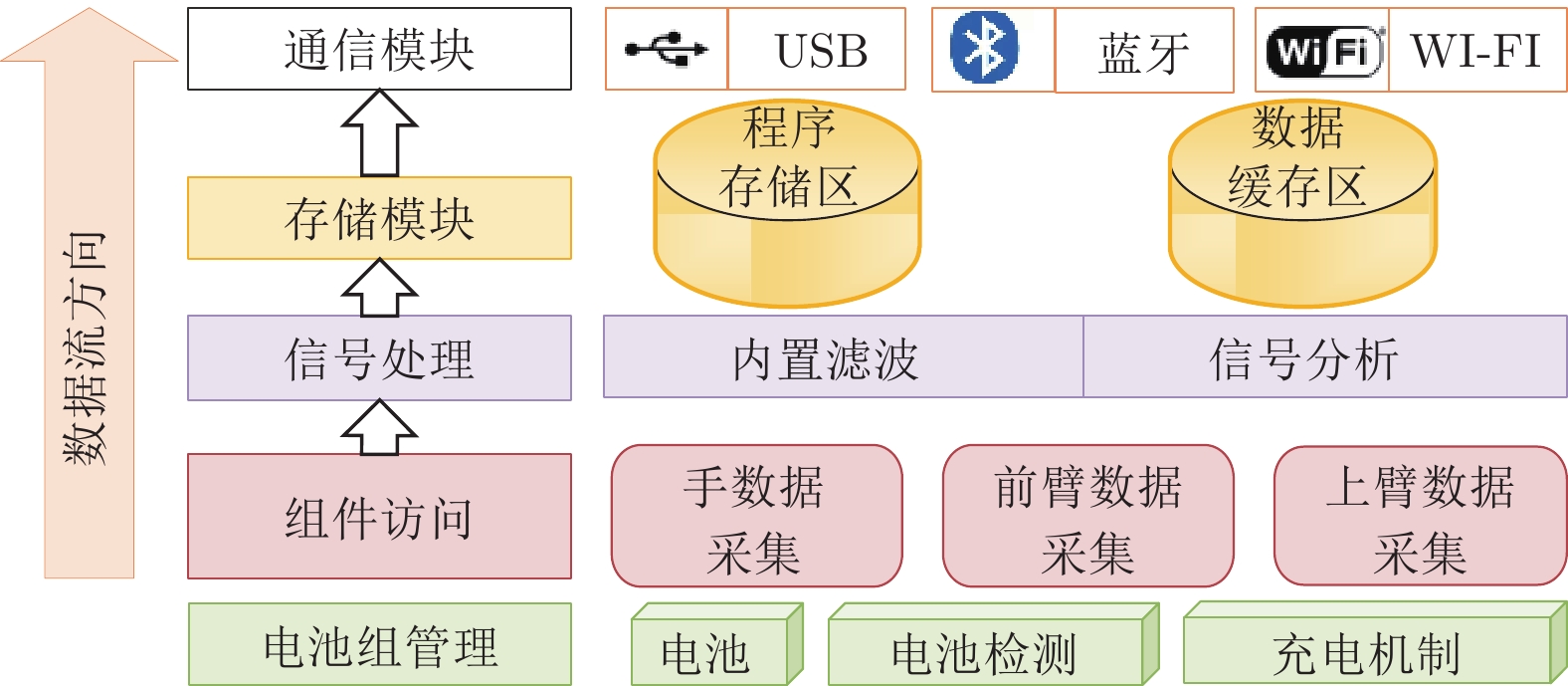
Table 5 Smart gloves sensor description
传感器 描述 加速度传感器 1)加速度传感器是一种能够测量加速度的传感器, 其能感受加速度并转换成可用输出信号; 2)数据主要来自 $x$, $y$, $z$ 三个轴. 陀螺仪传感器 1)陀螺仪通过测量物体运动时的角速度来计算物体旋转的角度和方向; 2)数据主要来自 $x$, $y$, $z$ 三个轴. 弯曲传感器 1)弯曲传感器通过阻值将弯曲程度数字化; 2)弯曲传感器能够测量的弯曲范围为$\left[{{{1}^ \circ },{{180}^ \circ }} \right]$. 表 6 手势识别结果
Table 6 Gesture recognition result
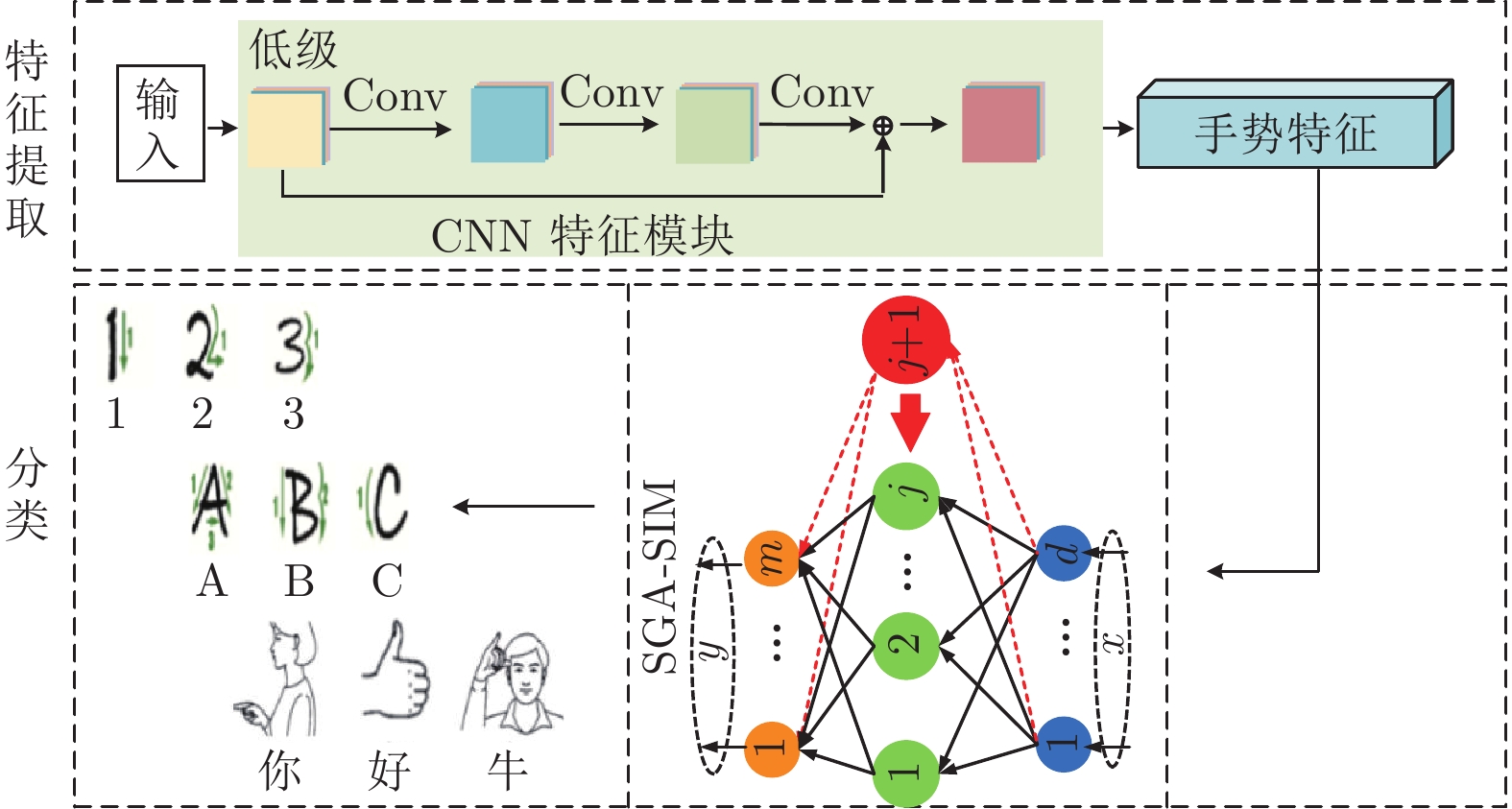
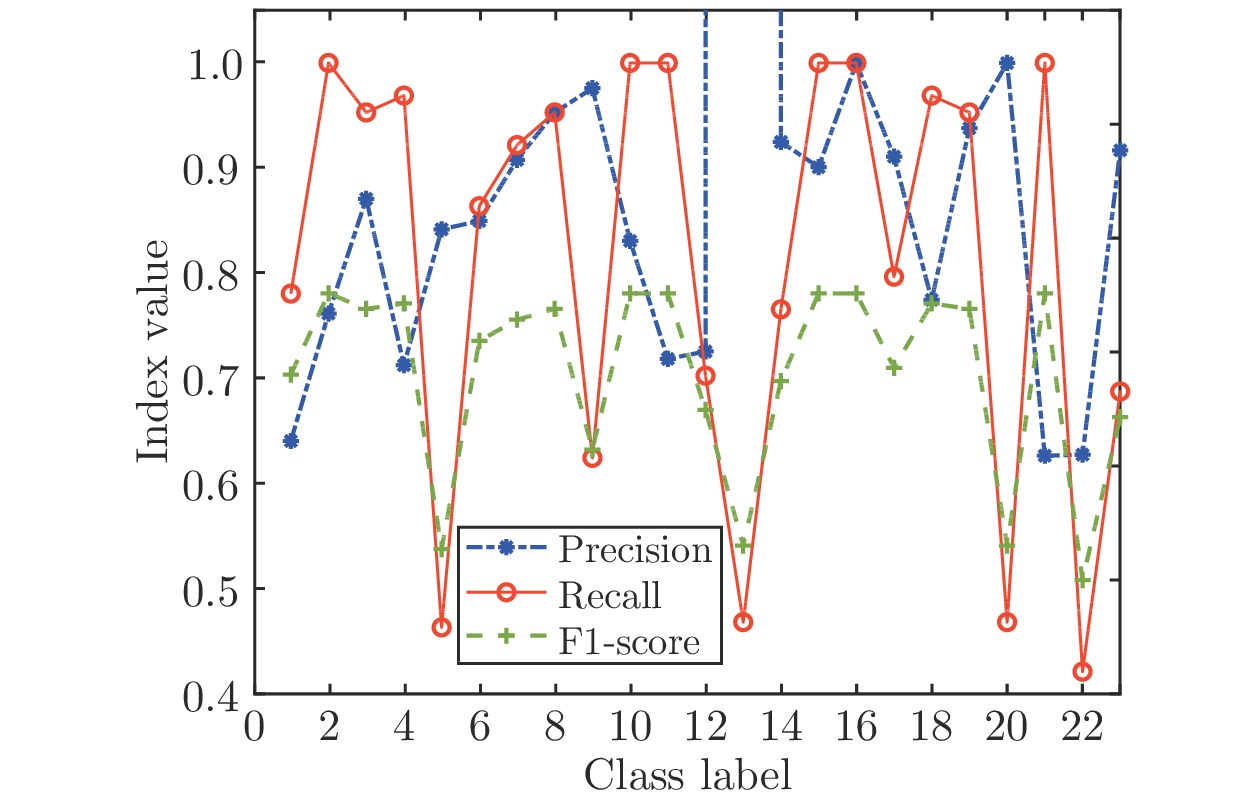
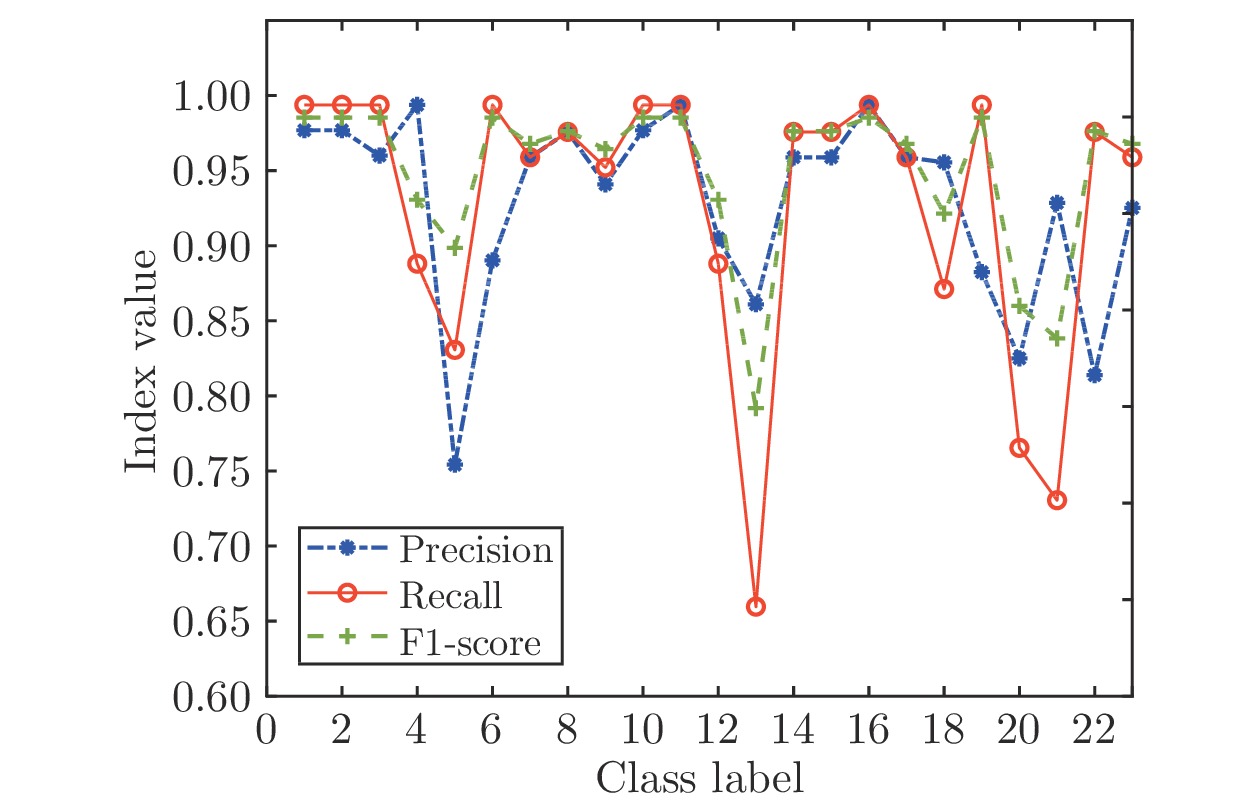
算法 建模时间(s) 测试精度 节点数 IRWNNs 67.84 81.92% 500 SGA-SIM-I 110.80 94.49% 500 SGA-SIM-II 15.26 95.19% 500 SCNs 113.08 94.49% 500 -
[1] Wang X, Chen H, Gan C X, Lin H G, Dou Q, Tsougenis E, et al. Weakly supervised deep learning for whole slide lung cancer image analysis. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2020, 50(9): 3950-3962 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2019.2935141 [2] Chai L, Du J, liu Q F, Lee C H. A cross-entropy-guided measure (CEGM) for assessing speech recognition performance and optimizing DNN-based speech enhancement. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2021, 29: 106-117 doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2020.3036783 [3] Wang N, Er M J, Han M. Generalized single-hidden layer feedforward networks for regression problems. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2015, 26(6): 1161-1176 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2014.2334366 [4] Ginanjar R R, Kim D S. Real-time SLFN-based node localization using UAV. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Industrial Cyber Physical Systems (ICPS). Taiwan, China: IEEE, 2019. 101−106 [5] Cao, W P, Wang X Z, Zhong M, Gao J Z. A review on neural networks with random weights. Neurocomputing, 2018, 275: 278-287 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2017.08.040 [6] Broomhead D S, Lowe D. Multivariable functional interpolation and adaptive networks. Complex System, 1988, 2: 321-355 [7] Igelnik B, Pao Y H. Stochastic choice of basis functions in adaptive function approximation and the functional-link net. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 1955, 6(6): 1320-1329 [8] Pao Y H, Takefuji Y. Functional-link net computing: Theory, system architecture, and functionalities. Computer, 1992, 25(5): 76-79 doi: 10.1109/2.144401 [9] Schmidt W F, Kraaijveld M A, Duin R P W. Feedforward neural networks with random weights. In: Proceedings of the 1st IAPR International Conference on Pattern Recognition. Hague, Netherlands: IEEE, 1992. 1−4 [10] Husmeier D. Neural Networks for Conditional Probability Estimation: Forecasting Beyond Point Predictions. New York: Springer, 2012. [11] Kwok T Y, Yeung D Y. Objective functions for training new hidden units in constructive neural networks. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks. 1997, 8(5): 1131-1148 doi: 10.1109/72.623214 [12] Lauret P, Fock E, Mara T A. A node pruning algorithm based on a fourier amplitude sensitivity test method. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2006, 17(2): 273-293 [13] Ainsworth T L, Wang Y T, Lee J S. Model-based polarimetric SAR decomposition: an L1 regularization approach. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 1-13 [14] Lin M B, Ji R R, Li S J. Network pruning using adaptive exemplar filters. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2006, 17(2): 273-293 [15] Amari S, Murata N. Asymptotic statistical theory of overtraining and cross-validation. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 1997, 8(5): 985-996 doi: 10.1109/72.623200 [16] Hanson S J, Pratt L Y. Comparing biases for minimal network construction with back-propagation. In: Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Colorado, USA: MIT Press, 1988. 177−185 [17] Liu D, Chang T, Zhang Y. A constructive algorithm for feedforward neural networks with incremental training. IEEE Transactions on Circuits & Systems Part I Fundamental Theory & Applications, 2002, 49: 1876-1879 [18] Zhou P, Jiang Y, Wen C. Data modeling for quality prediction using improved orthogonal incremental random vector functional-link networks. Neurocomputing, 2019, 365: 1-9 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2019.06.062 [19] Qiu X H, Suganthan P N, Amaratunga A J G. Ensemble incremental random vector functional link network for short-term crude oil price forecasting. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence (SSCI). Bengaluru, India: IEEE, 2018. 1758−1763 [20] Li M, Wang D H. Insights into randomized algorithms for neural networks: Practical issues and common pitfalls. Information Sciences, 2017, 382: 170-178 [21] Dudek G. A method of generating random weights and biases in feedforward neural networks with random hidden nodes. Information Sciences, 2019, 481: 33-56 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2018.12.063 [22] Tyukin I Y, Prokhorov D V. Feasibility of random basis function approximators for modeling and control. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Control Applications, (CCA) & Intelligent Control, (ISIC). St. Petersburg, Russia: IEEE, 2009. 1391−1396 [23] Wang D H, Li M. Stochastic configuration networks: Fundamentals and algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2017, 47(10): 3466-3479 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2017.2734043 [24] Li M, Huang C, Wang D H. Robust stochastic configuration networks with maximum correntropy criterion for uncertain data regression. Information Sciences, 2018, 473: 73-86 [25] 代伟, 李德鹏, 杨春雨, 马小平. 一种随机配置网络的模型与数据混合并行学习方法. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(10): 2427-2437 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190411Dai Wei, Li De-Peng, Yang Chun-Yu, Ma Xiao-Ping. A model and data hybrid parallel learning method for stochastic configuration networks. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(10): 2427-2437 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190411 [26] Dai W, Li D P, Zhou P. Stochastic configuration networks with block increments for data modeling in process industries. Information Sciences, 2019, 484: 367-386 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2019.01.062 [27] Chen C L P, Liu Z L. Broad learning system: An effective and efficient incremental learning system without the need for deep architecture. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2018, 29(1): 10-24 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2017.2716952 [28] Chu F, Liang T, Chen C L P, Wang X, Ma X. Weighted broad learning system and its application in nonlinear industrial process modeling. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2020, 31(8): 3017-3031 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2019.2935033 [29] Feng S, Chen C L P. Fuzzy broad learning system: A novel neuro-fuzzy model for regression and classification. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2020, 50(2): 414-424 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2018.2857815 [30] Wang X H, Zhang T, Xu X M, Chen L, Xing X F, Chen C L P. EEG emotion recognition using dynamical graph convolutional neural networks and broad learning system. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM). Madrid, Spain: IEEE, 2018. 1240−1244 [31] Albert A. Regression and the Moore-Penrose Pseudoinverse. New York: Academic Press, 1972. [32] Howland P, Park H. Generalizing discriminant analysis using the generalized singular value decomposition. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2004, 26(8): 995-1006 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2004.46 [33] Ben-Israel A, Greville T. Generalized Inverses: Theory and Applications. New York: John Wiley and Sons, 1974. [34] Anguita D, Ghio A, Oneto L, Parra X, Reyes-Ortiz J L. Human activity recognition on smartphones using a multiclass hardware-friendly support vector machine. In: Proceedings of the International Workshop on Ambient Assisted Living. Vitoria-Gasteiz, Spain: Springer, 2012. 216−223 [35] Fdez J A, Fernandez A, Luengo J. KEEL data-mining software tool: Data set repository. Integration of Algorithms and Experimental Analysis Framework, Journal of Multiple-Valued Logic & Soft Computing, 2011, 17(2-3): 255-287 [36] Cheng L, Liu Y, Hou Z G. A rapid spiking neural network approach with an application on hand gesture recognition. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive and Developmental Systems, 2019, 99: 151-161 [37] Hong C, Lu Y, Liu Z. Survey on 3D hand gesture recognition. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2016, 26(9): 1659-1673 doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2015.2469551 -




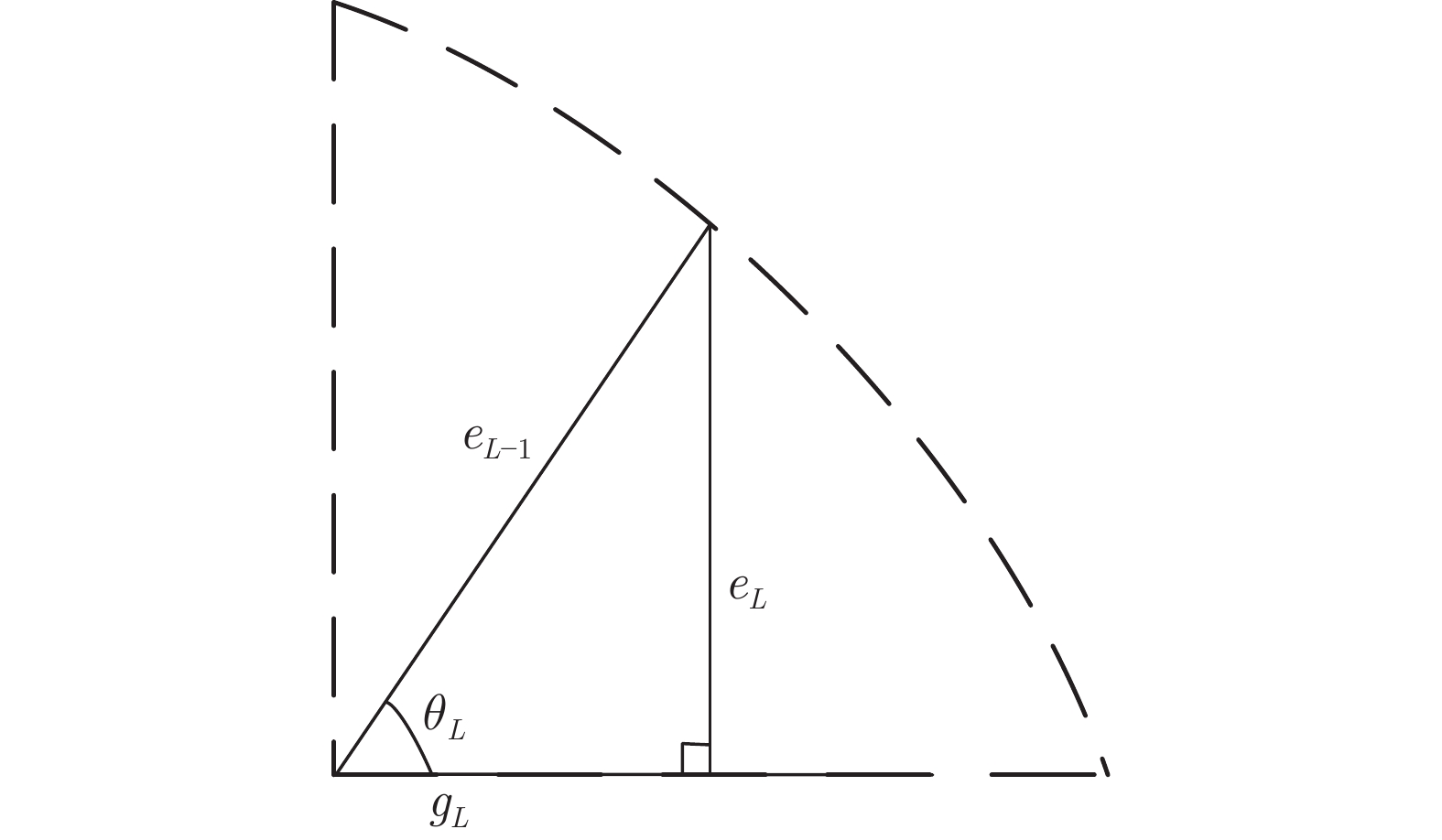
 下载:
下载: