An Operation Optimization Method for Long Distance Belt Conveyors Driven by Digital Twin
-
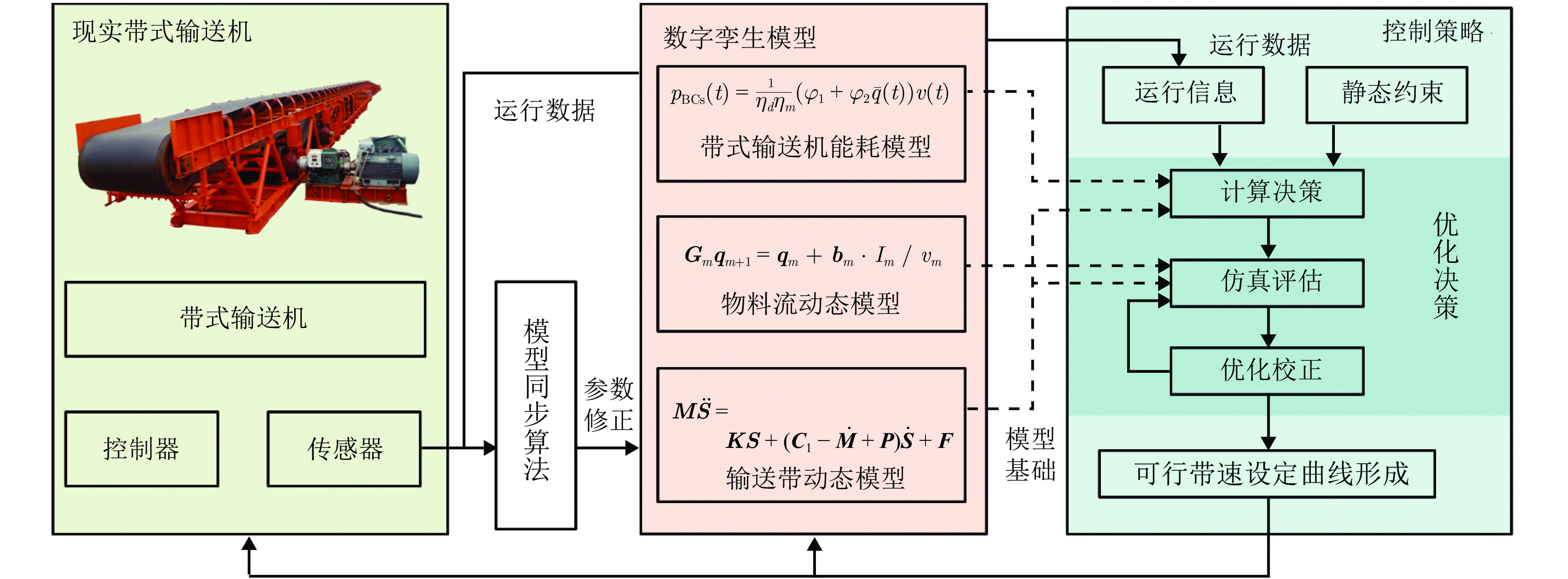
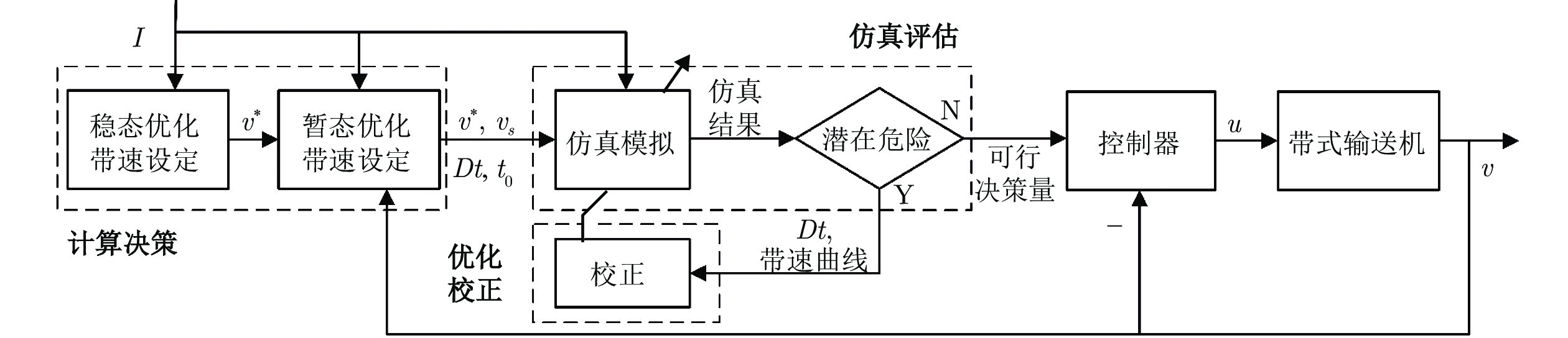
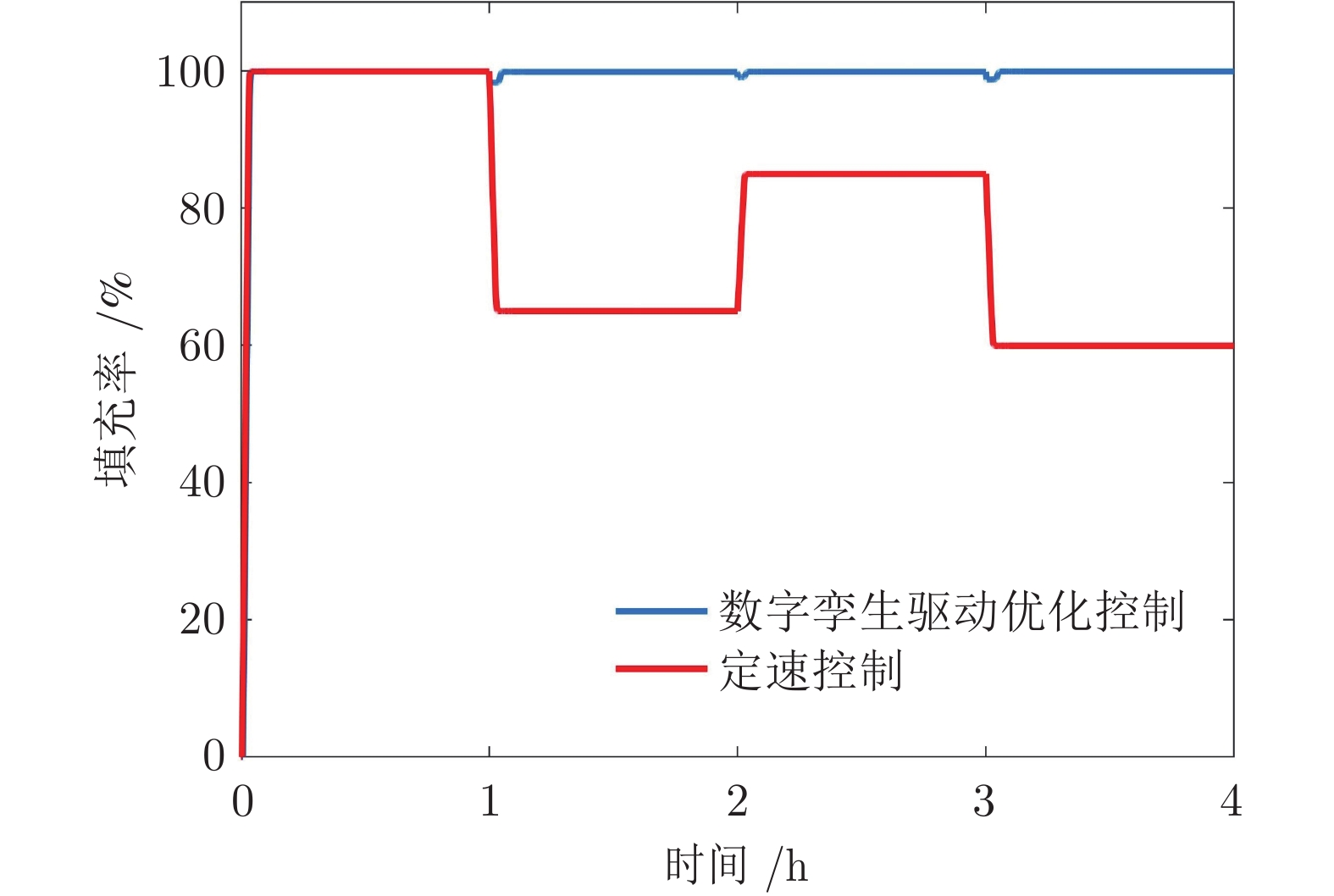
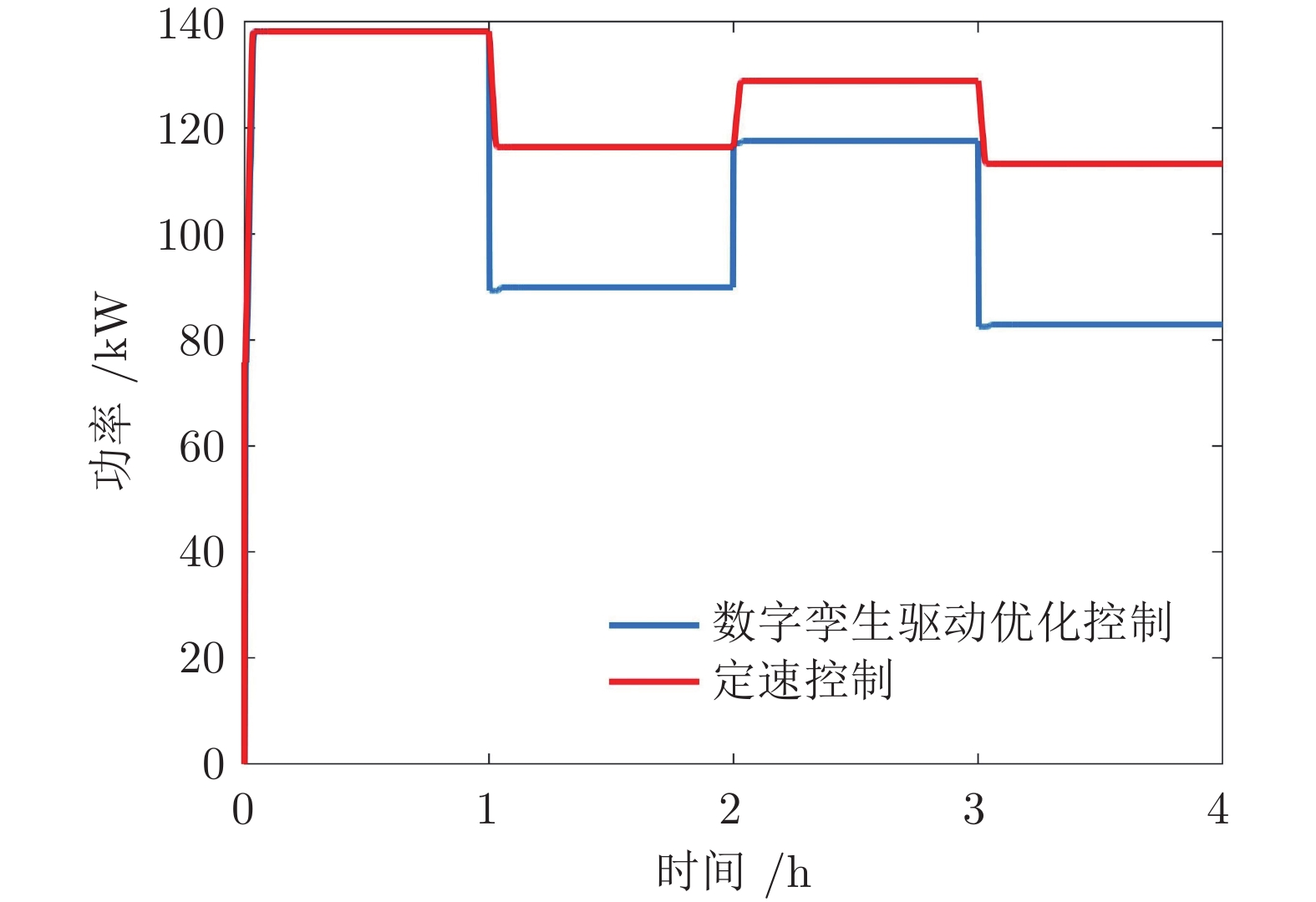
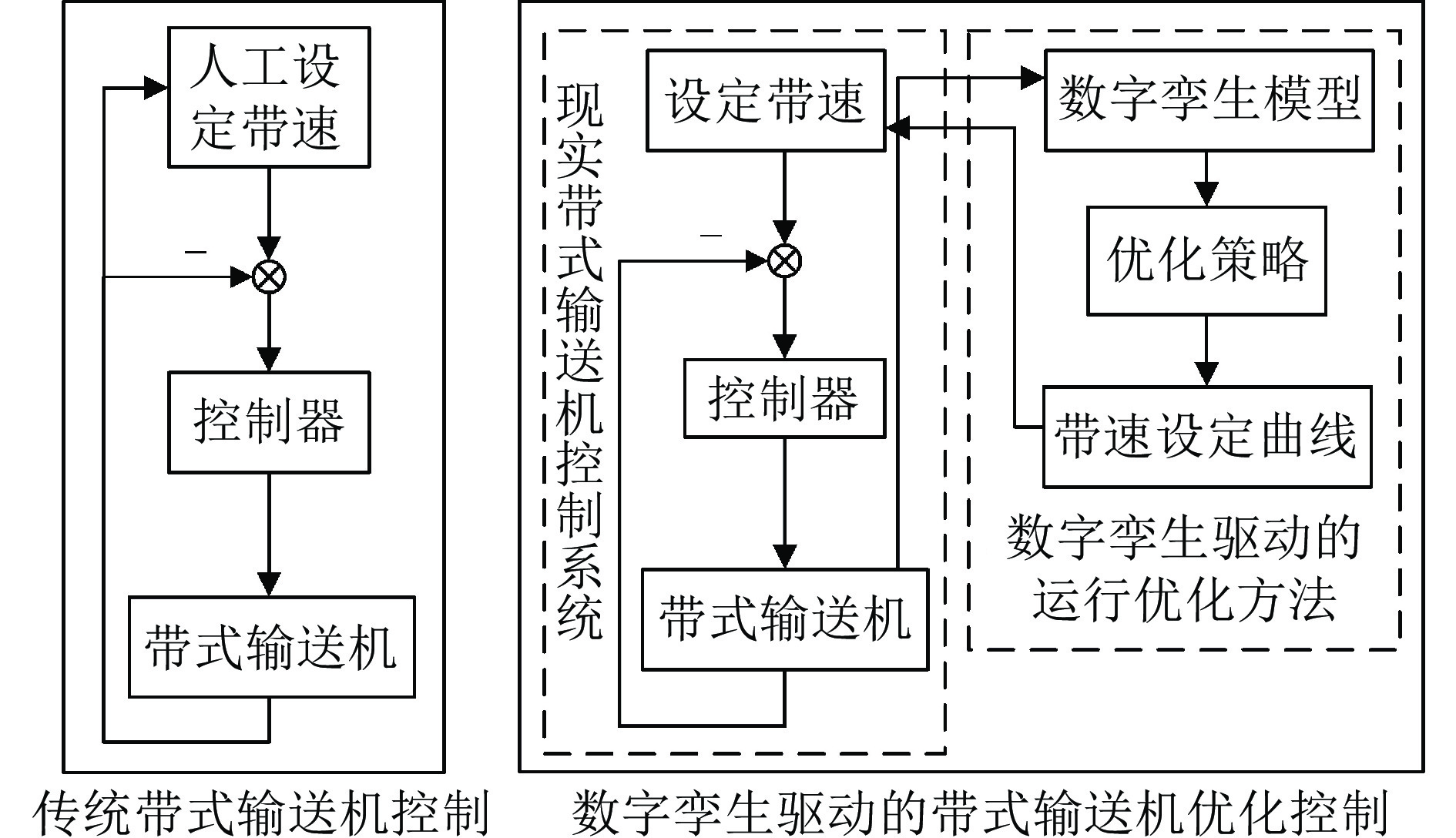
摘要: 长距离带式输送机是矿山、港口等领域运输散装物料的主要工具. 针对长距离带式输送机的安全节能运行问题, 研究数字孪生驱动的运行优化方法. 首先, 构建由数字孪生模型、模型同步算法、控制策略和现实带式输送机组成的数字孪生驱动运行优化框架; 然后, 建立数字孪生模型, 包括基于变质量牛顿第二定律和有限元分析法的输送带动力学模型、物料流动态模型和动态能耗模型; 最后, 提出数字孪生驱动的计算决策−仿真评估−优化校正(Decision-simulation-correction, DSC)优化决策方法, 优化带式输送机的稳态和暂态运行带速, 形成可行带速设定曲线. 实验结果表明, 数字孪生驱动的带式输送机运行优化方法可以实现带式输送机安全节能运行. 与传统控制方法相比, 能够根据运行工况实时调速, 提高输送带填充率, 节能13.87%.Abstract: Long distance belt conveyors are used as a main tool for transporting bulk materials in the fields of mines, ports and so on. For the safe and energy saving operation of long distance belt conveyors, the operation optimization method driven by digital twin is studied. Firstly, the framework of the operation optimization driven by digital twin is constructed, which includes digital twin models, model synchronization algorithms, control strategy, and realistic belt conveyors. Then, digital twin models are established, including the dynamic model of conveyor belt based on the variable quality Newton's second law and finite element analysis method, material flow dynamic model and dynamic energy model. Finally, the decision-simulation-correction (DSC) optimization method driven by digital twin is proposed, which can optimize the steady and transient belt speed of the belt conveyor to build a feasible speed setting curve. Experiments show that the operation optimization method driven by digital twin can result in a belt conveyor that is both safe and energy efficient. Compared with the traditional method, the proposed method can adjust the belt speed setpoint in real-time based on operating conditions, increasing the conveyor belt fill rate, which results in energy savings of 13.87%.
-
Key words:
- Long distance belt conveyor /
- digital twin /
- operation optimization /
- dynamic model
-
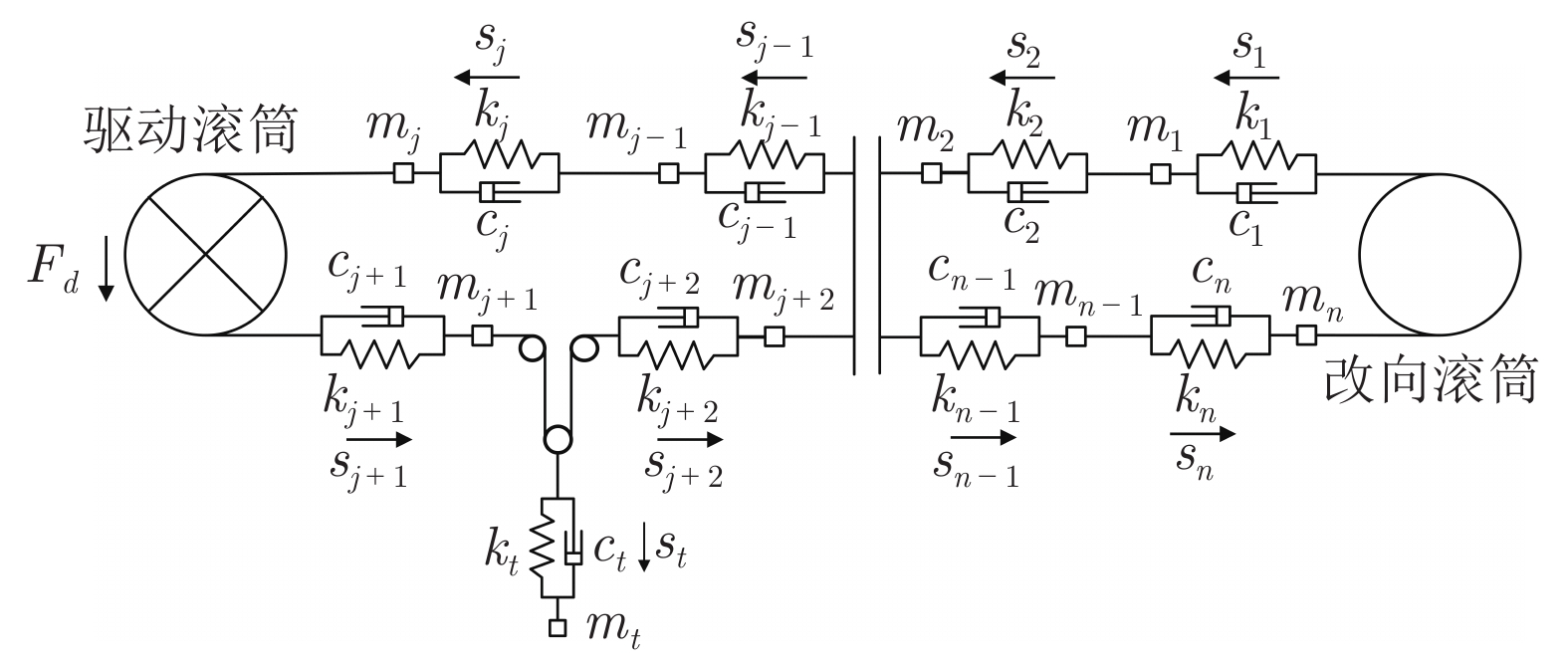
表 1 输送带动力学模型符号意义
Table 1 The significance of the symbols of the conveyor belt dynamic model
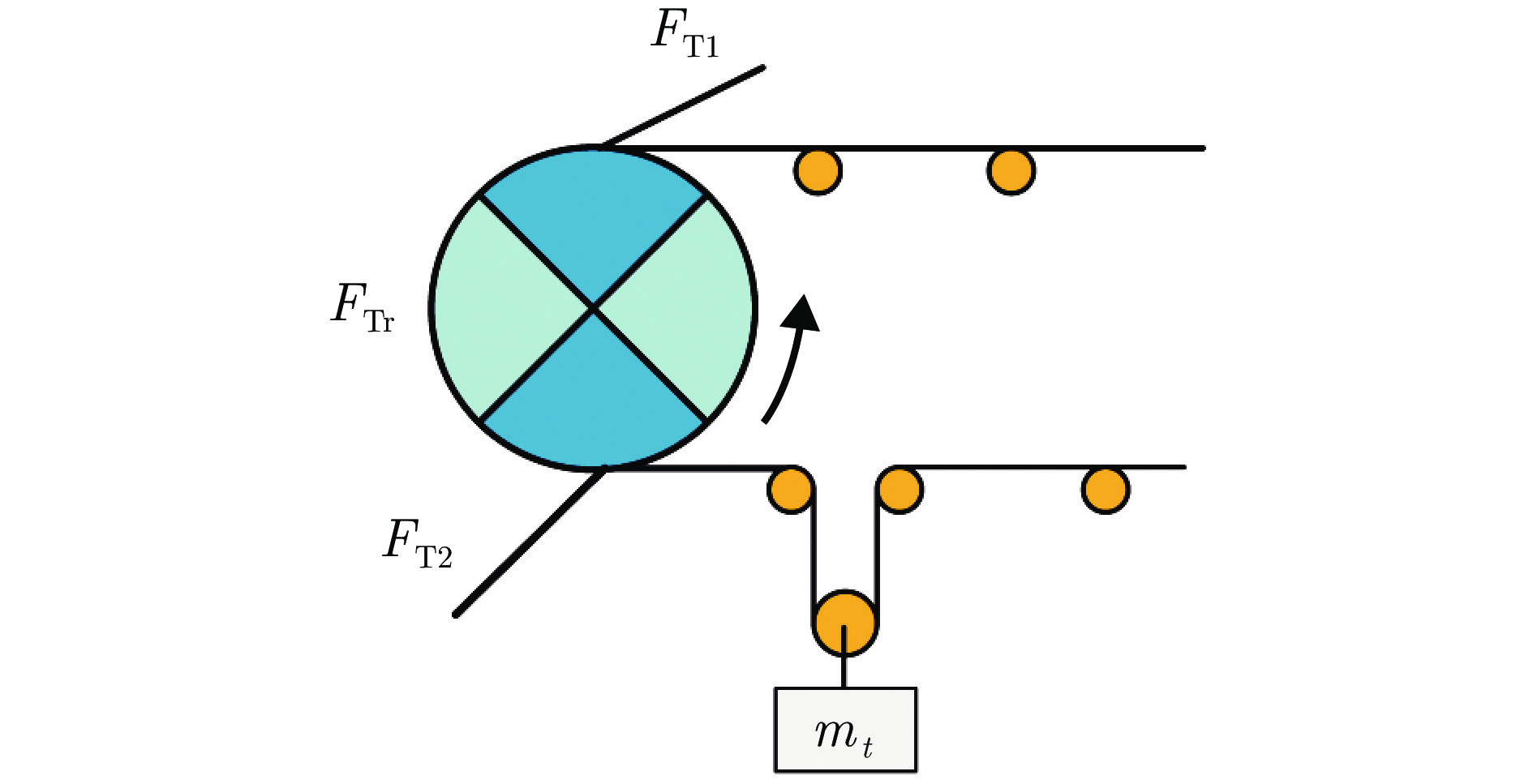
符号 含义(单位) 符号 含义(单位) ci 第 i 个微元段的等效黏性系数(N·s/m) q(i, m) m时刻输送带上 i 位置平均物质量(kg/m) ct 张紧装置微元段的等效黏性系数(N·s/m) qB 每米输送带的质量(kg/m) Fd 驱动电机作用在驱动滚筒上的驱动力(N) qRO 每米承载侧托辊平均质量(kg/m) Fi 第 i 个微元段承受的外力和(N) qRU 每米返回侧托辊平均质量(kg/m) fi 第 i 个微元段所受摩擦力(N) si 第 i 个微元段的位置(m) ft 张紧装置微元段所受摩擦力(N) $ {{\dot s}_i}$ 第 i 个微元段的速度(m/s) g 重力加速度(m/s2) $ {{\ddot s}_i}$ 第 i 个微元段的加速度(m/s2) ki 第 i 个微元段的等效弹性系数(N/m) $\Delta L_{{\rm{RO}}} $ 承载侧微元段的长度(m) kt 张紧装置微元段的等效弹性系数(N/m) $\Delta L_{{\rm{RU}}} $ 返回侧微元段的长度(m) mi 第 i 个微元段的等效质量(kg) μ 运载物料与输送带之间的摩擦系数 mt 张紧装置微元段的等效质量(kg) 表 2 带式输送机参数值
Table 2 The parameters value of belt conveyor
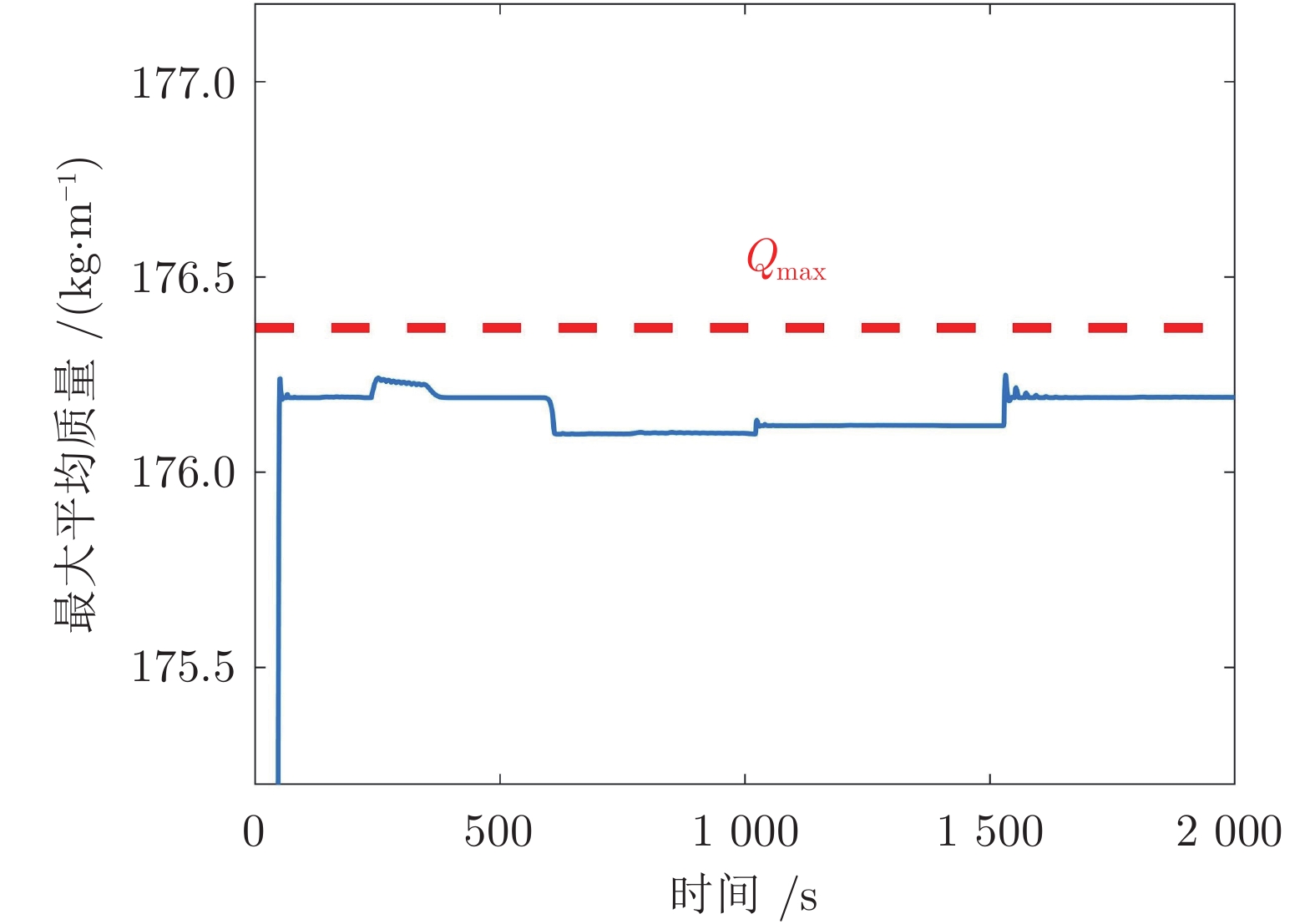
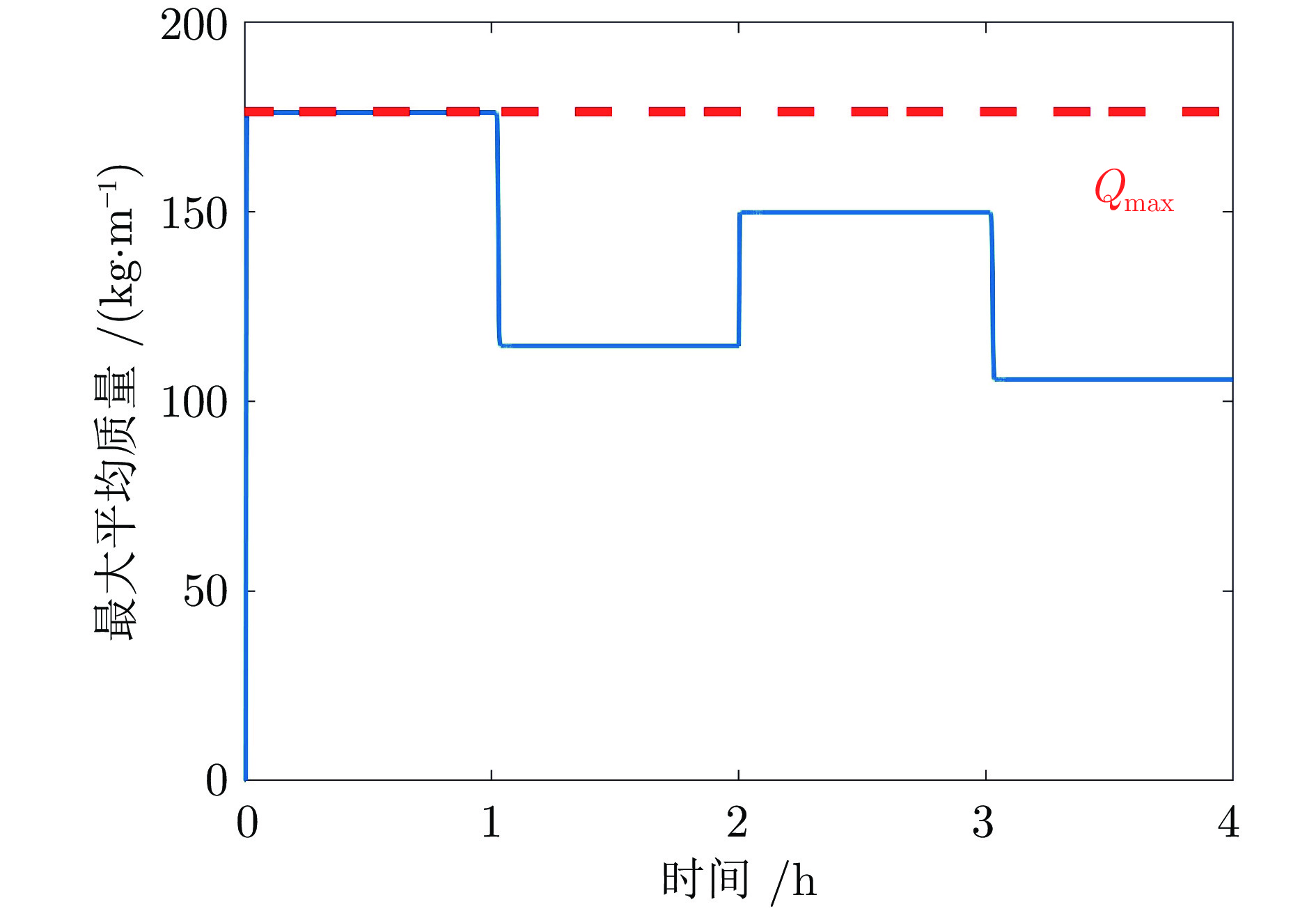
符号 数值 符号 数值 C 1.336 qRU 7.76 kg/m f 0.024 Qmax 176.37 kg/m g 9.8 m/s2 SA, min 5.4 L 313.25 m SB, min 8 mt 4000 kg$\alpha $ 180° qB 18.73 kg/m μ1 0.35 qRO 15.75 kg/m 表 3 迭代优化过程
Table 3 The process of iterative optimization
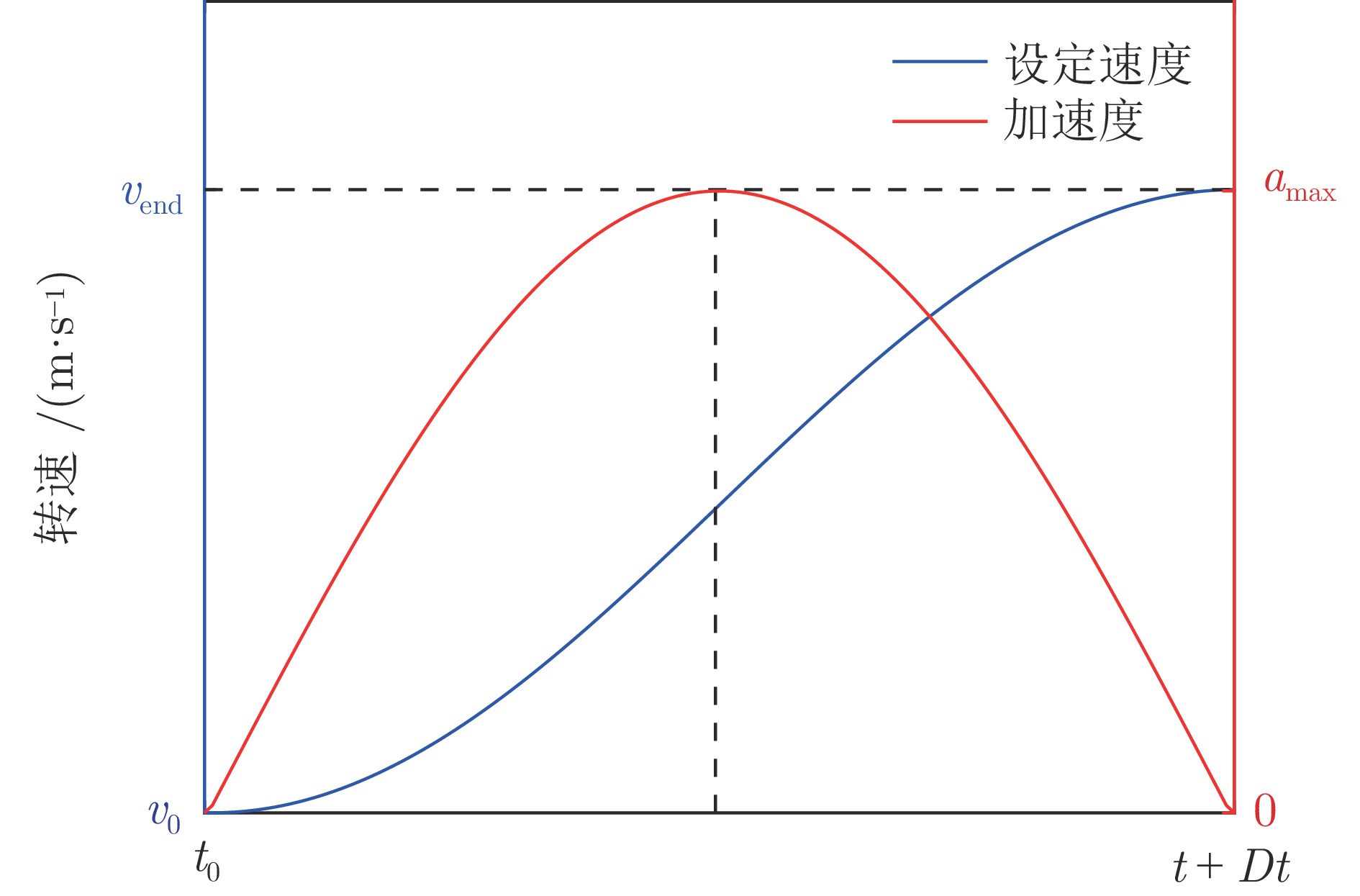
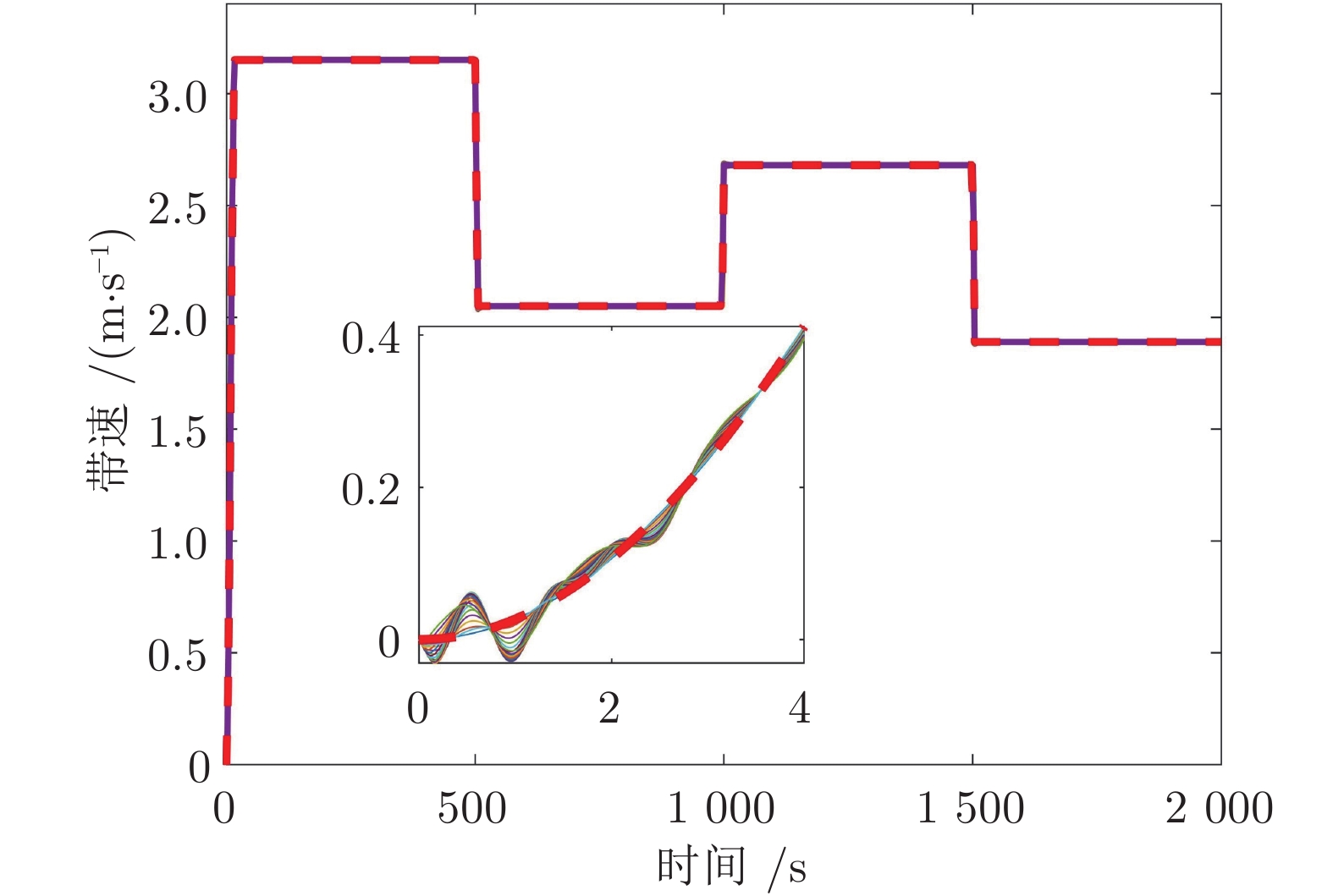
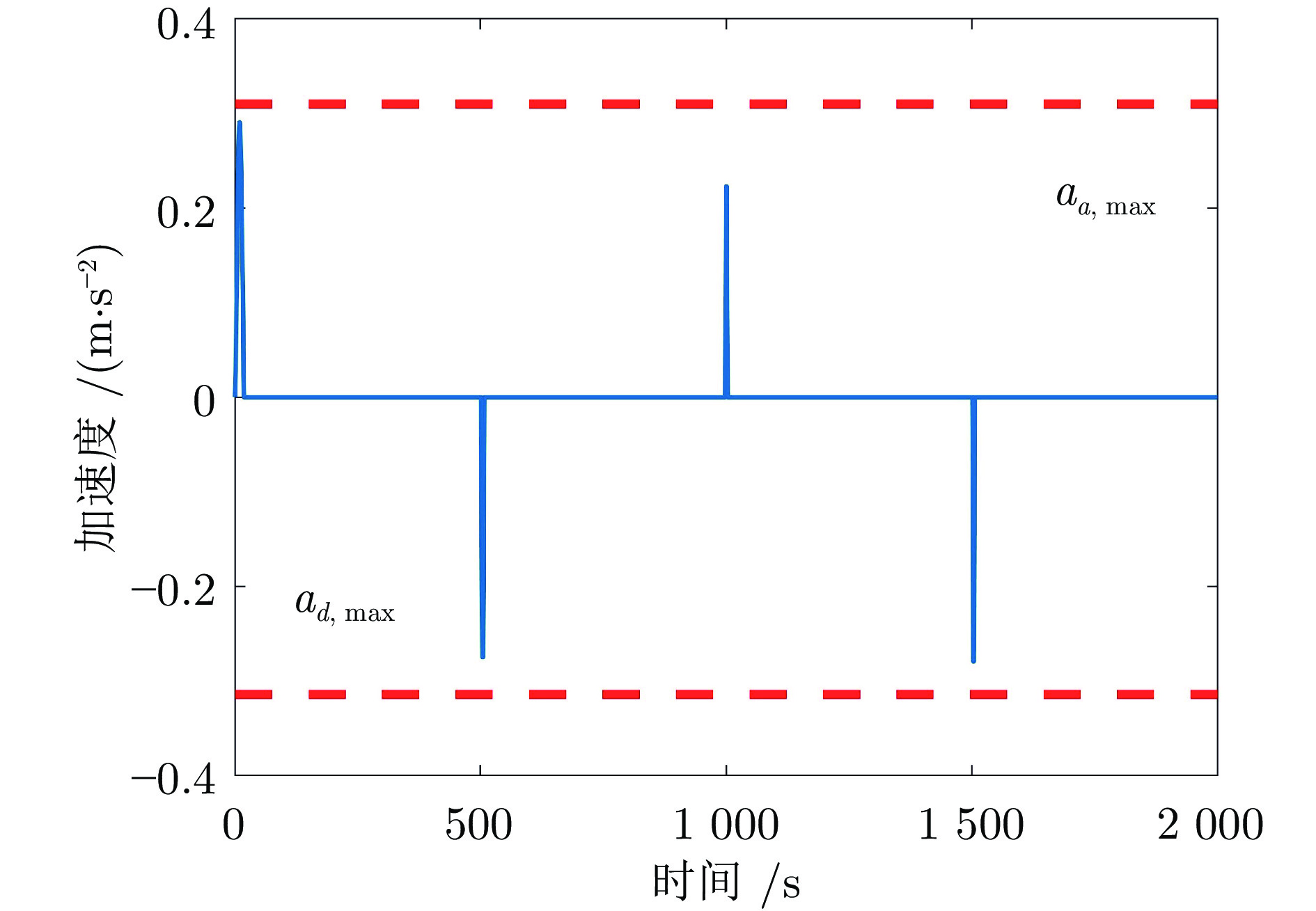
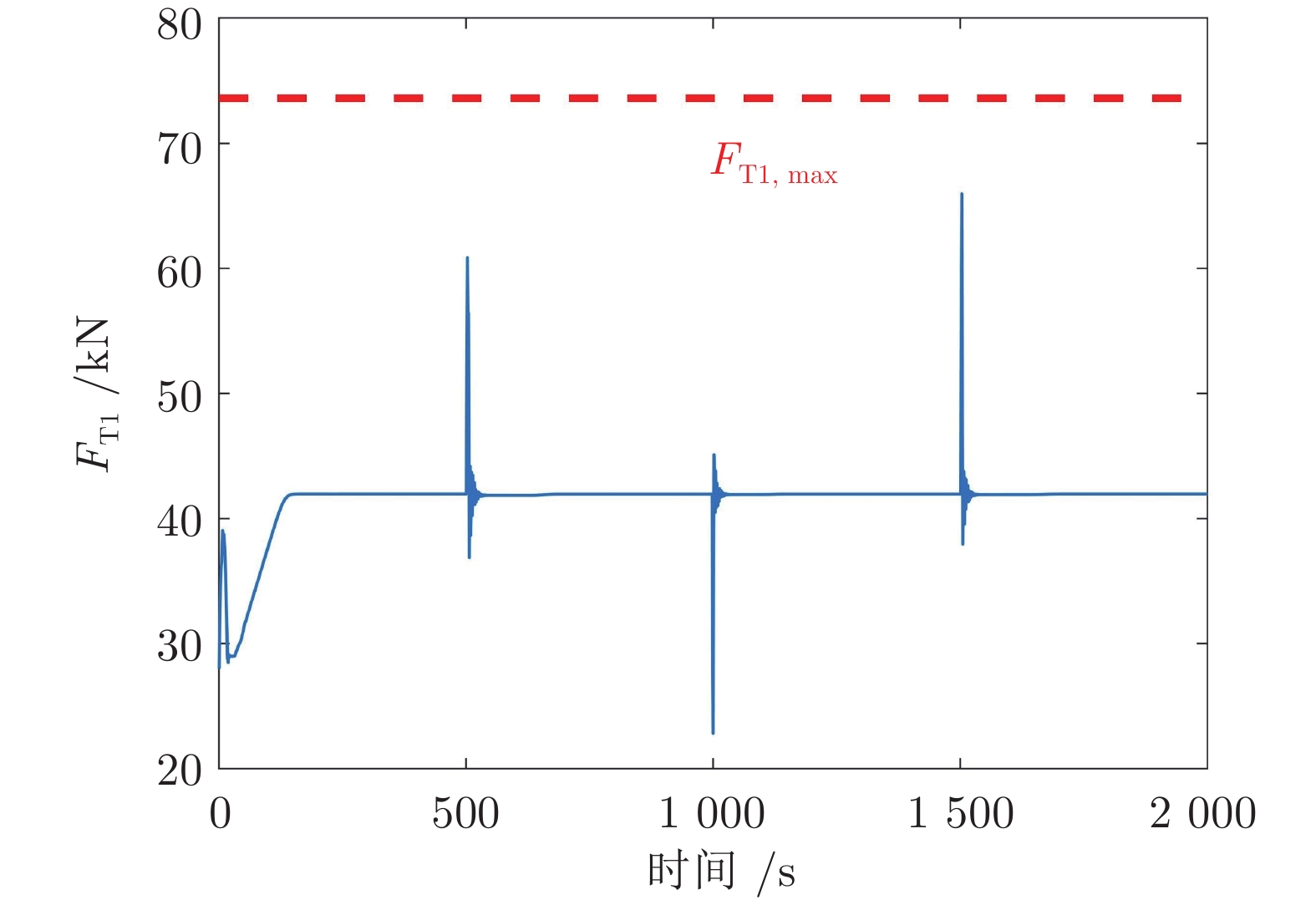
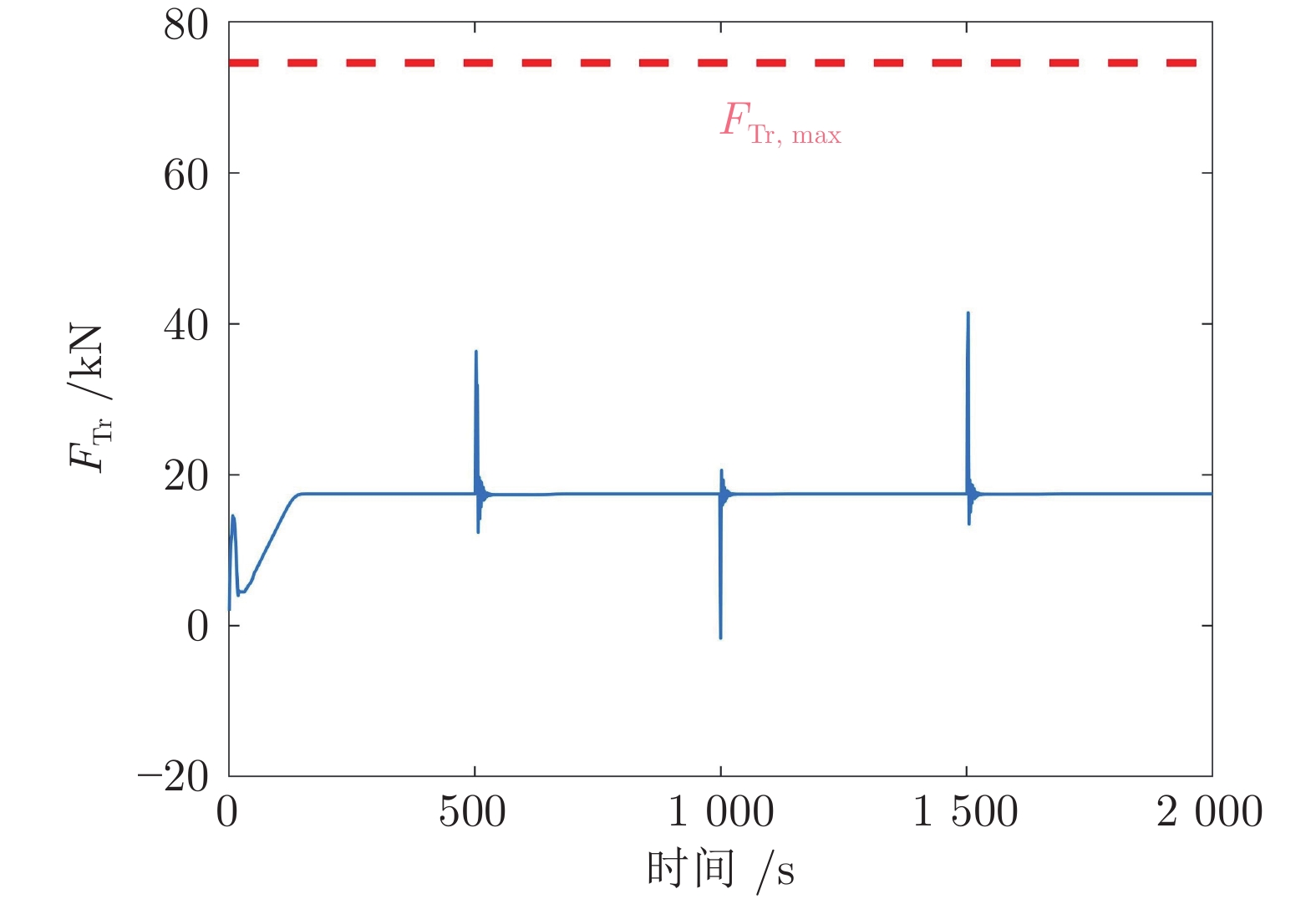
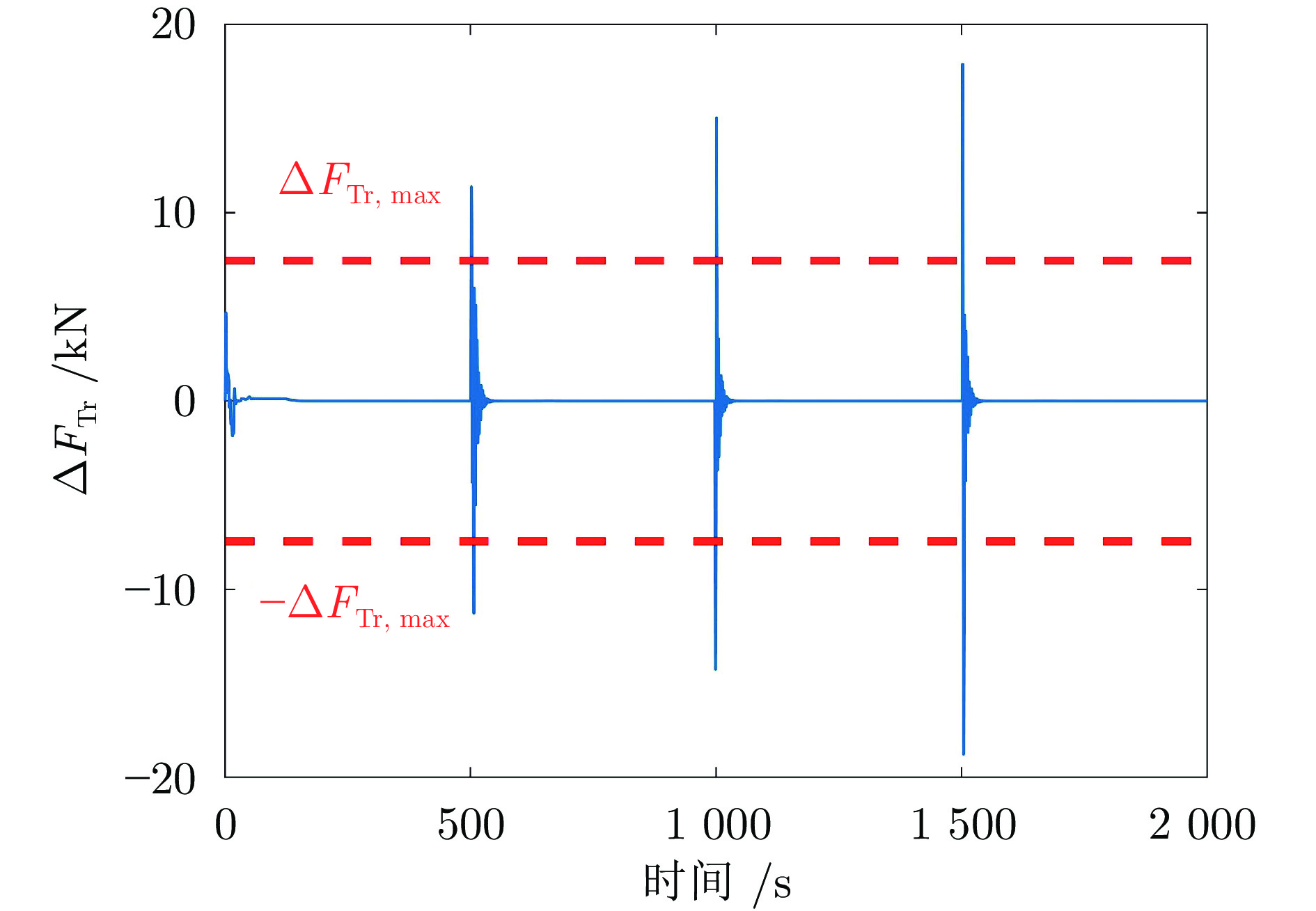
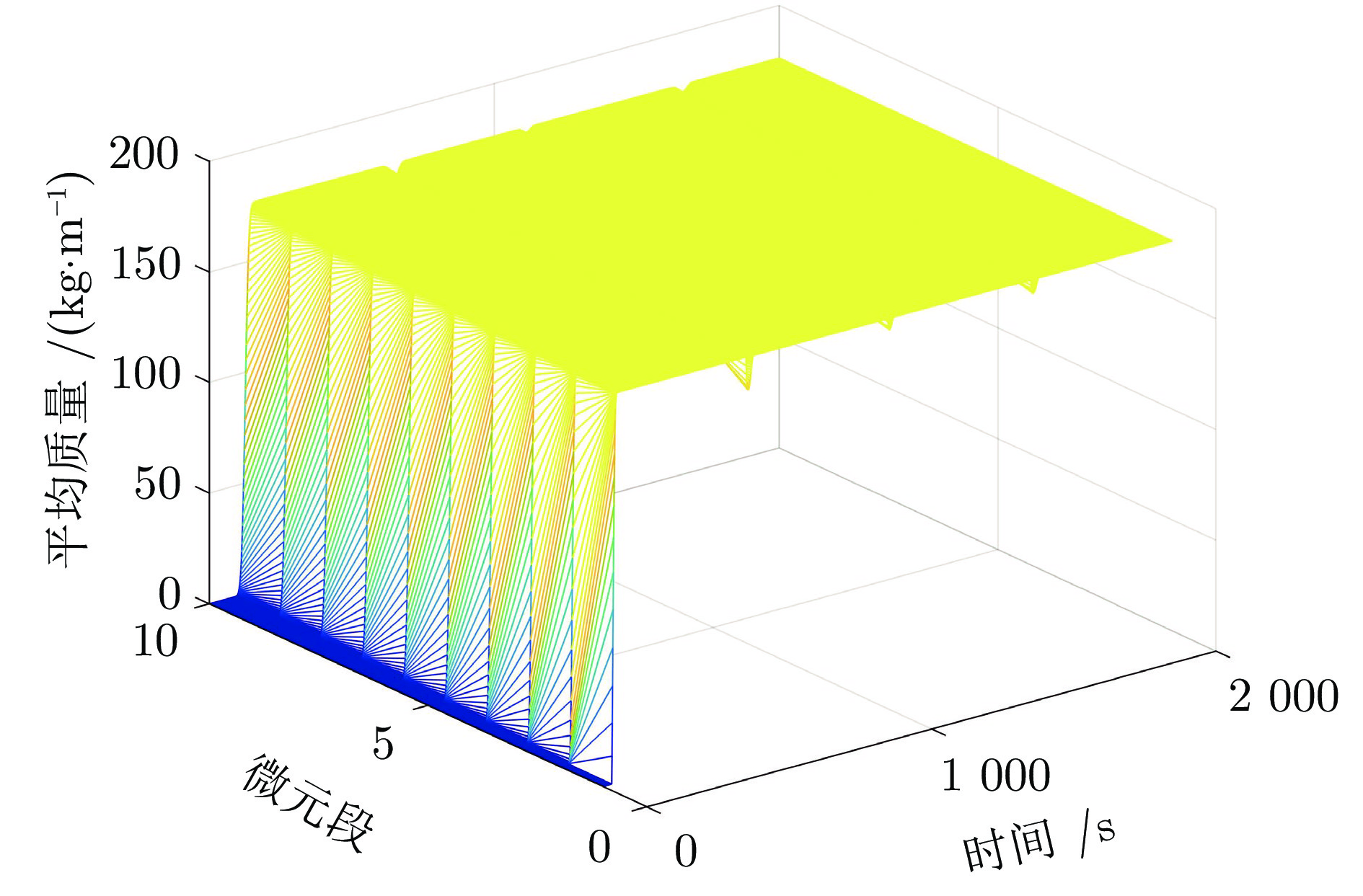
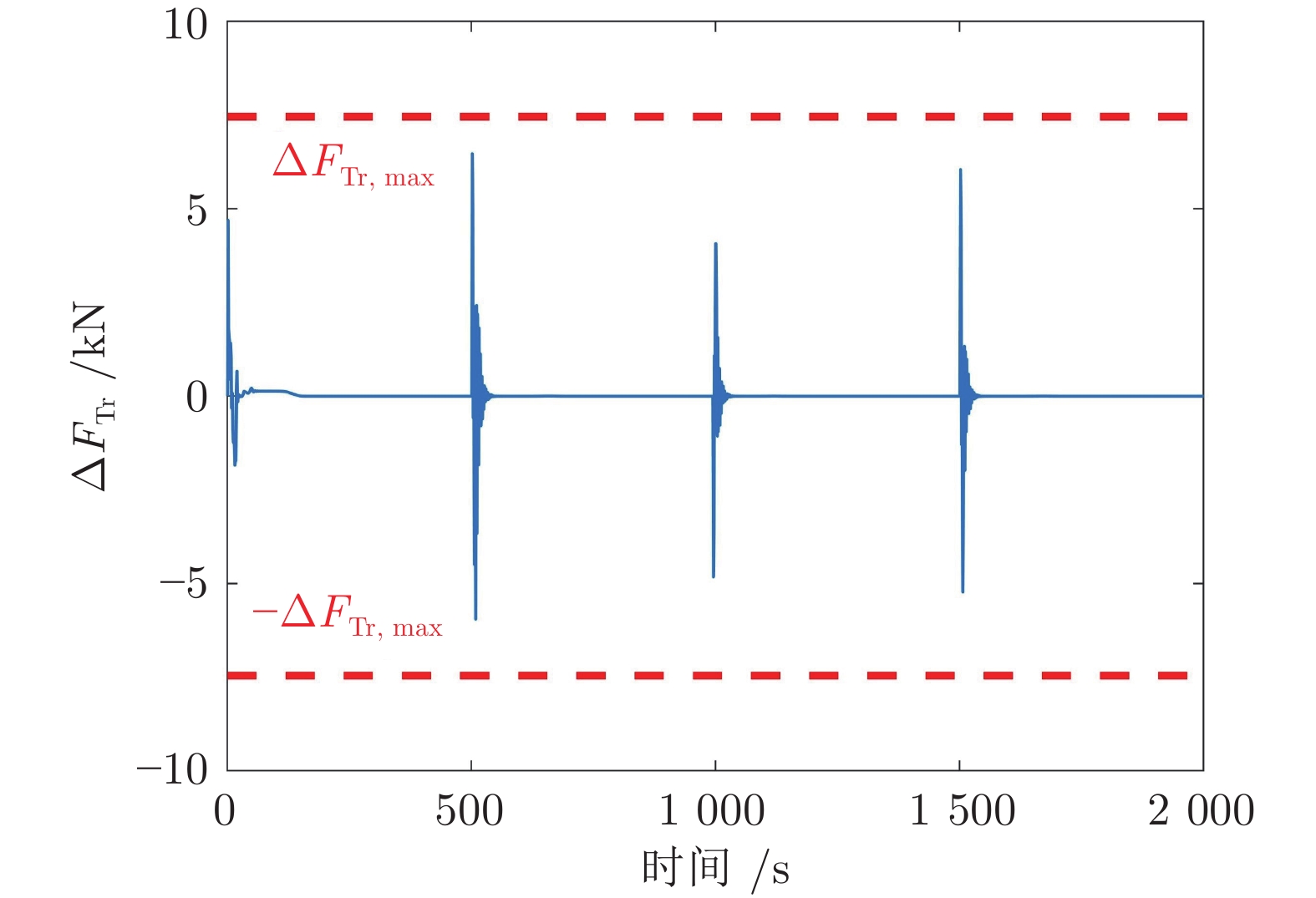
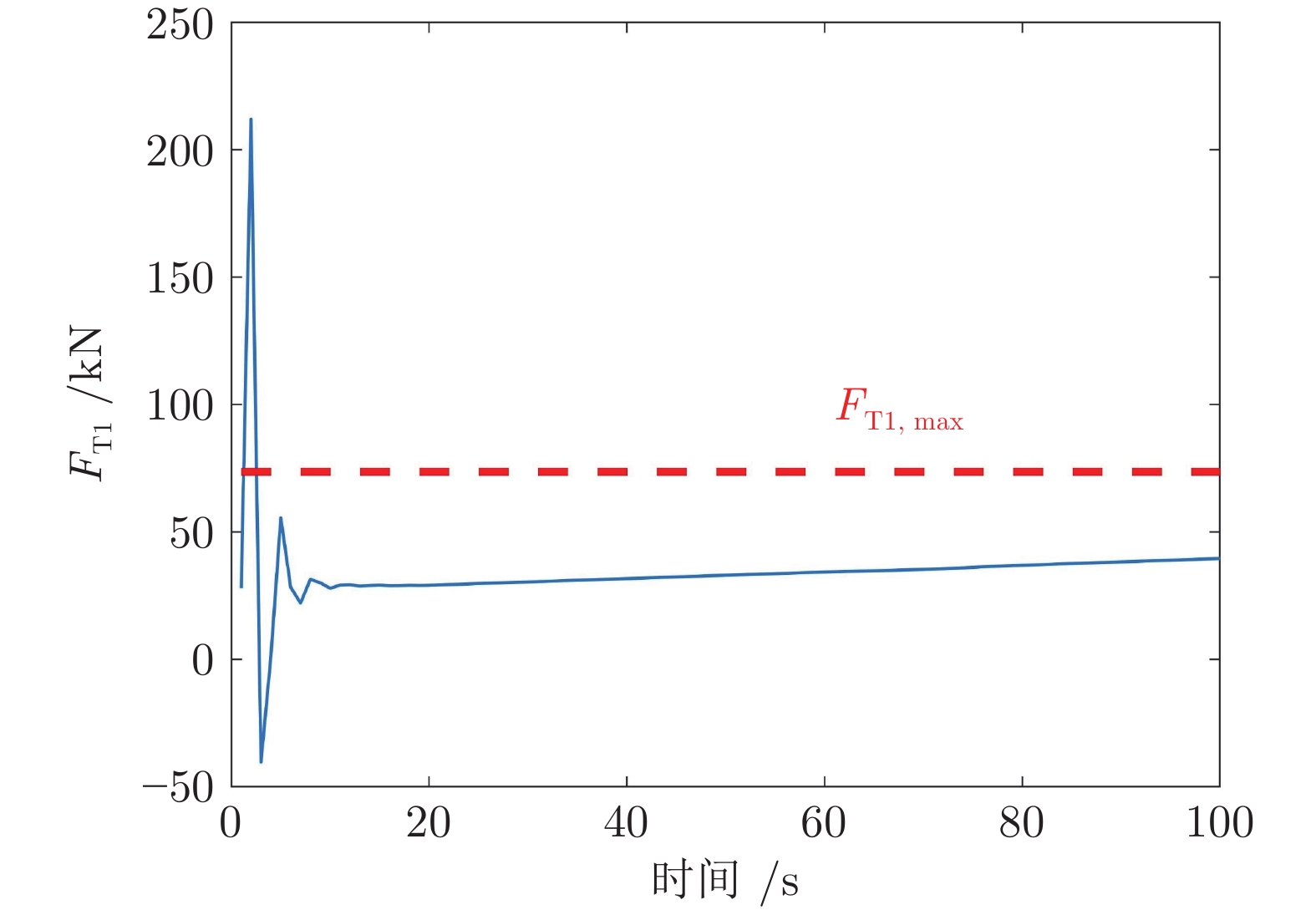
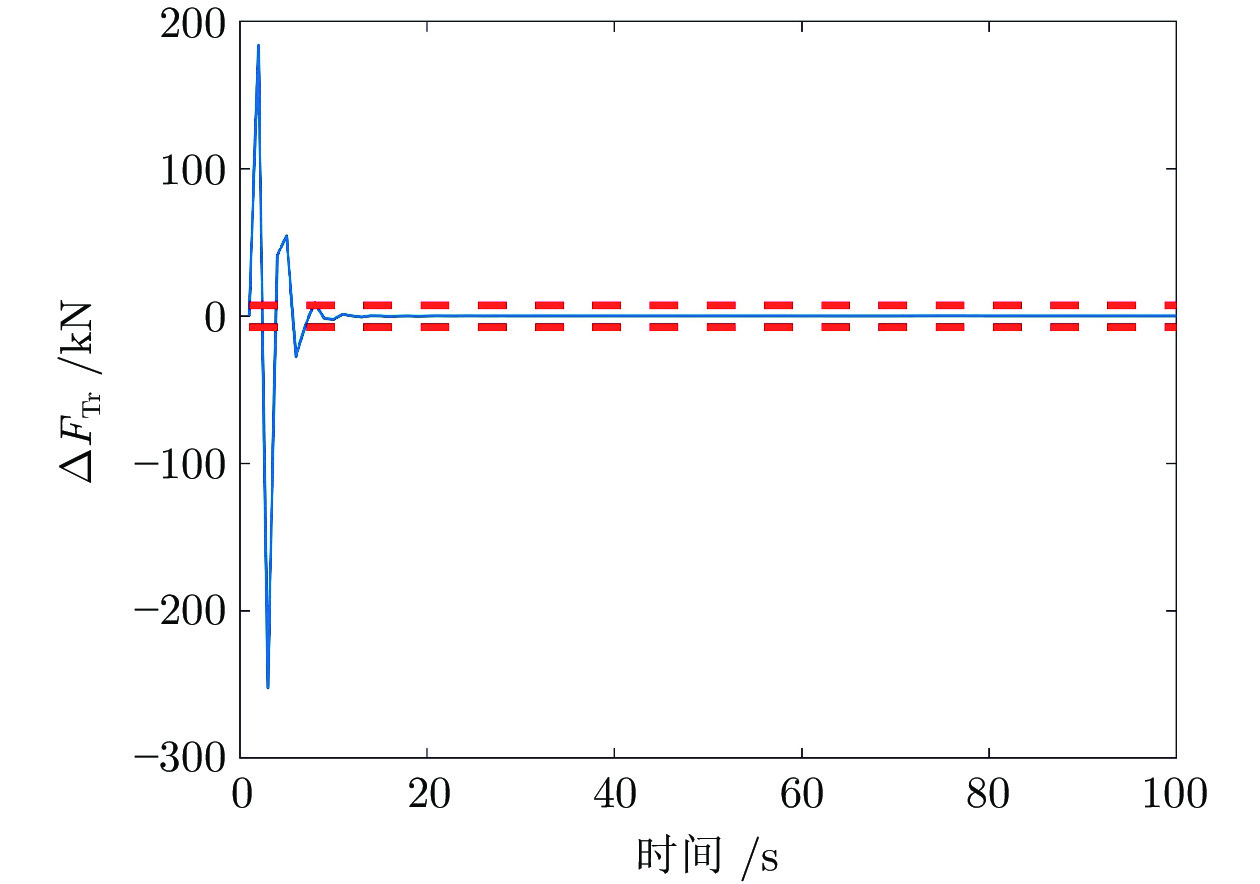
迭代次数 变速次数 Dt (s) amax (m·s−2) ${F_{ { { {\rm{T} }1} } } }\;({\rm{kN} })$ ${F_{ { { {\rm{Tr} } } } } }\;({\rm{kN} })$ $\Delta {F_{ { { {\rm{Tr} } } } } }\;({\rm{kN} })$ ${\bar q}\; ({\rm{kg} } \cdot{\rm{m}}^{-1})$ 0 1 17 0.291 41.97 17.47 4.69 0 2 6 −0.275 60.86 36.36 11.39 176.19 3 4 0.223 45.10 20.60 15.04 176.10 4 4 −0.279 65.96 41.46 17.88 176.12 1 1 17 0.291 41.97 17.47 4.69 0 2 8 −0.212 55.27 30.77 6.47 176.19 3 7 0.140 42.84 18.34 4.07 176.10 4 7 −0.176 52.42 27.92 6.05 176.12 -
[1] Yang C, Bu L, Chen B. Energy modeling and online parameter identification for permanent magnet synchronous motor driven belt conveyors. Measurement, 2021, 178: Article No. 109342 doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2021.109342 [2] Zhang S, Xia X. Optimal control of operation efficiency of belt conveyor systems. Applied Energy, 2010, 87(6): 1929−1937 doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2010.01.006 [3] Mu Y, Yao T, Jia H, Yu X, Zhao B, Zhang X, et al. Optimal scheduling method for belt conveyor system in coal mine considering silo virtual energy storage. Applied Energy, 2020, 275: Article No. 115368 doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.115368 [4] Ristic L B, Bebic M Z, Jevtic D S, Mihailovic I D, Statkic S Z, Rasic N T, et al. Fuzzy speed control of belt conveyor system to improve energy efficiency. In: Proceedings of the 15th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference. Novi Sad, Serbia: IEEE, 2012. 9−17 [5] Zhang S, Xia X. Modeling and energy efficiency optimization of belt conveyors. Applied Energy, 2011, 88(9): 3061−3071 doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2011.03.015 [6] 杨春雨, 李恒, 车志远. 煤矿双电机驱动带式输送机的能耗建模与参数辨识. 控制理论与应用, 2018, 35(3): 335−341 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2017.70335Yang Chun-Yu, Li Heng, Che Zhi-Yuan. Energy consumption modeling and parameter identification for double-motor driven coal mine belt conveyors. Control Theory & Applications, 2018, 35(3): 335−341 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2017.70335 [7] Zeng F, Wu Q, Chu X, Yue Z. Measurement of bulk material flow based on laser scanning technology for the energy efficiency improvement of belt conveyors. Measurement, 2015, 75: 230−243 doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2015.05.041 [8] Yang C, Liu J, Li H, Zhou L. Energy modeling and parameter identification of dual-motor-driven belt conveyors without speed sensors. Energies, 2018, 11(12): 1−17 doi: 10.3390/en11123313 [9] Zhang S, Mao W. Optimal operation of coal conveying systems assembled with crushers using model predictive control methodology. Applied Energy, 2017, 198: 65−76 doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.04.037 [10] He D, Liu X, Zhong B. Sustainable belt conveyor operation by active speed control. Measurement, 2020, 154: Article No. 107458 doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2019.107458 [11] Continuous Conveyors-belt Conveyors for Loose Bulk Materials-basis for Calculation and Dimensioning, IEEE Criteria for Class IE Electric Systems (Standards Style), IEEE Standard 308, 1969. [12] Mathaba T, Xia X. A parametric energy model for energy management of long belt conveyors. Energies, 2015, 8(12): 13590− 13608 doi: 10.3390/en81212375 [13] Mathaba T, Xia X. Optimal and energy efficient operation of conveyor belt systems with down-hill conveyors. Energy Efficiency, 2017, 10(2): 405−417 [14] Li J, Zhang J, Wang N. The study and application of examples of starting impact limitation for the belt conveyor. In: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Manufacturing Engineering and Technology for Manufacturing Growth. Vancou-ver, Canada: Information Engineering Research Institute, 2015. 77−81 [15] He D, Pang Y, Lodewijks G. Determination of acceleration for belt conveyor speed control in transient operation. International Journal of Engineering and Technology, 2016, 8(3): 206−211 doi: 10.7763/IJET.2016.V8.886 [16] He D, Pang Y, Lodewijks G. Speed control of belt conveyors during transient operation. Powder Technology, 2016, 301: 622− 631 doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2016.07.004 [17] He D, Pang Y, Lodewijks G. Green operations of belt conveyors by means of speed control. Applied Energy, 2017, 188: 330−341 doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.12.017 [18] 孙滔, 周铖, 段晓东, 陆璐, 陈丹阳, 杨红伟, 等. 数字孪生网络(DTN): 概念、架构及关键技术. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(3): 569−582Sun Tao, Zhou Cheng, Duan Xiao-Dong, Lu Lu, Chen Dan-Yang, Yang Hong-Wei, et al. Digital twin network (DTN): Concepts, architecture, and key technologies. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(3): 569−582 [19] 侯正航, 何卫平. 基于数字孪生的飞机装配状态巡检机器人的建模与控制. 计算机集成制造系统, 2021, 27(4): 981−989Hou Zheng-Hang, He Wei-Ping. Modeling and control of digital twin-based aircraft assembly state inspection robot. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 2021, 27(4): 981−989 [20] 江献良, 陈凌宇, 郑杰基, 谭若愚, 李宝宇, 范大鹏. 基于数字孪生模型的直驱部件高精度控制方法. 机械工程学报, 2021, 57(17): 98−109Jiang Xian-Liang, Chen Ling-Yu, Zheng Jie-Ji, Tan Ruo-Yu, Li Bao-Yu, Fan Da-Peng. High-precision control method of direct drive components based on digital twin model. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2021, 57(17): 98−109 [21] 杨林瑶, 陈思远, 王晓, 张俊, 王成红. 数字孪生与平行系统: 发展现状、对比及展望. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(11): 2001−2031Yang Lin-Yao, Chen Si-Yuan, Wang Xiao, Zhang Jun, Wang Cheng-Hong. Digital twins and parallel systems: State of the art, comparisons and prospect. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(11): 2001−2031 [22] Tao F, Zhang H, Liu A, Nee A Y C. Digital twin in industry: State-of-the-art. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2019, 15(4): 2405−2415 doi: 10.1109/TII.2018.2873186 [23] 葛世荣, 张帆, 王世博, 王忠宾. 数字孪生智采工作面技术架构研究. 煤炭学报, 2020, 45(6): 1925−1936Ge Shi-Rong, Zhang Fan, Wang Shi-Bo, Wang Zhong-Bin. Digital twin for smart coal mining work-face: Technological frame and construction. Journal of China Coal Society, 2020, 45(6): 1925−1936 [24] 金杰, 夏超, 肖士利, 郭逸婧, 王晓菲. 基于数字孪生的火箭起飞安全系统设计. 计算机集成制造系统, 2019, 25(6): 1337−1347Jin Jie, Xia Chao, Xiao Shi-Li, Guo Yi-Jing, Wang Xiao-Fei. Rocket launch safety system design scheme based on digital twins. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 2019, 25(6): 1337−1347 [25] Tao F, Qi Q. Make more digital twins. Nature, 2019, 573(7775): 490−491 doi: 10.1038/d41586-019-02849-1 [26] Yang G. Dynamics analysis and modeling of rubber belt in large mine belt conveyors. Sensors & Transducers, 2014, 181(10): 210− 218 [27] Lodewijks G, Kruse D J. The power of field measurements: Part I. Bulk Solids Handling, 1998, 18(3): 415−427 [28] 周广林, 韩忠惠, 张继通. 基于分形维数的大型带式输送机动态特性研究. 煤炭科学技术, 2019, 47(2): 125−130Zhou Guang-Lin, Han Zhong-Hui, Zhang Ji-Tong. Research on dynamic characteristics of large belt conveyor based on fractal dimension. Coal Science and Technology, 2019, 47(2): 125−130 [29] 李军霞, 寇子明. 下运带式输送机复合制动系统仿真及试验研究. 煤炭学报, 2015, 40(S2): 553−559Li Jun-Xia, Kou Zi-Ming. Simulation and experimental study of a composite brake system for downward belt conveyor. Journal of China Coal Society, 2015, 40(S2): 553−559 [30] 王成山, 董博, 于浩, 吴建中, 严晋跃, 李鹏. 智慧城市综合能源系统数字孪生技术及应用. 中国电机工程学报, 2021, 41(5): 1597−1608Wang Cheng-Shan, Dong Bo, Yu Hao, Wu Jian-Zhong, Yan Jin-Yue, Li Peng. Digital twin technology and its application in the integrated energy system of smart city. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2021, 41(5): 1597−1608 [31] Zhang K, Qu T, Zhou D, Zhang K, Qu T, Zhou D, et al. Digital twin-based opti-state control method for a synchronized production operation system. Robotics and Computer-integrated Manufacturing, 2020, 63: Article No. 101892 doi: 10.1016/j.rcim.2019.101892 [32] Luo J, Huang W, Zhang S. Energy cost optimal operation of belt conveyors using model predictive control methodology. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2015, 105: 196−205 doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.09.074 [33] Continuous Mechanical Handling Equipment-belt Conveyors With Carrying Idlers-calculation of Operating Power and Tensile Forces, ISO5048, 1989. [34] 杨小林, 葛世荣, 祖洪斌, 鲍久圣, 常国强, 张磊, 等. 带式输送机永磁智能驱动系统及其控制策略. 煤炭学报, 2020, 45(6): 2116−2126Yang Xiao-Lin, Ge Shi-Rong, Zu Hong-Bin, Bao Jiu-Sheng, Chang Guo-Qiang, Zhang Lei, et al. Permanent magnet intelligent drive system and control strategy of belt conveyor. Journal of China Coal Society, 2020, 45(6): 2116−2126 [35] 陈龙, 王晓, 杨健健, 艾云峰, 田滨, 李宇宸, 等. 平行矿山: 从数字孪生到矿山智能. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(7): 1633−1645Chen Long, Wang Xiao, Yang Jian-Jian, Ai Yun-Feng, Tian Bin, Li Yu-Chen, et al. Parallel mining operating systems: From digital twins to mining intelligence. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(7): 1633−1645 [36] 李铬, 李春广, 梁睦, 武福军. 煤矿带式输送机事故分析及防护措施. 中国安全科学学报, 2006, 16(3): 140−144 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3033.2006.03.027Li Ge, Li Chun-Guang, Liang Mu, Wu Fu-Jun. Accident analysis of belt conveyor used in coal mine and its protective measures. China Safety Science Joumal, 2006, 16(3): 140−144 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3033.2006.03.027 [37] 孙汪萍. 长距离带式输送机节能优化策略的研究 [硕士论文], 合肥工业大学, 中国, 2015.Sun Wang-Ping. Studies of Long Distance Belt Conveyor and Energy Saving Optimization Strategy [Master thesis], Hefei University of Technology, China, 2015. [38] Pang Y, Lodewijks G. Improving energy efficiency in material transport systems by fuzzy speed control. In: Proceedings of the 3rd IEEE International Symposium on Logistics and Industrial Informatics. Budapest, Hungary: IEEE, 2011. 159−164 [39] 李玉瑾. 带式输送机的动态特性分析与软起动设计. 煤炭学报, 2002, (3): 294−299Li Yu-Jin. Dynamic analysis and soft starting design of belt conveyor. Journal of China Coal Society, 2002, (3): 294−299 [40] He D, Pang Y, Lodewijks G, He D, Pang Y, Lodewijks G, et al. Healthy speed control of belt conveyors on conveying bulk materials. Powder Technology, 2018, 327: 408−419 doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2018.01.002 [41] Zhang S, Xia X. A new energy calculation model of belt conveyor. In: Proceedings of the Africon. Nairobi, Kenya: IEEE, 2009. 1−6 -




 下载:
下载: