-
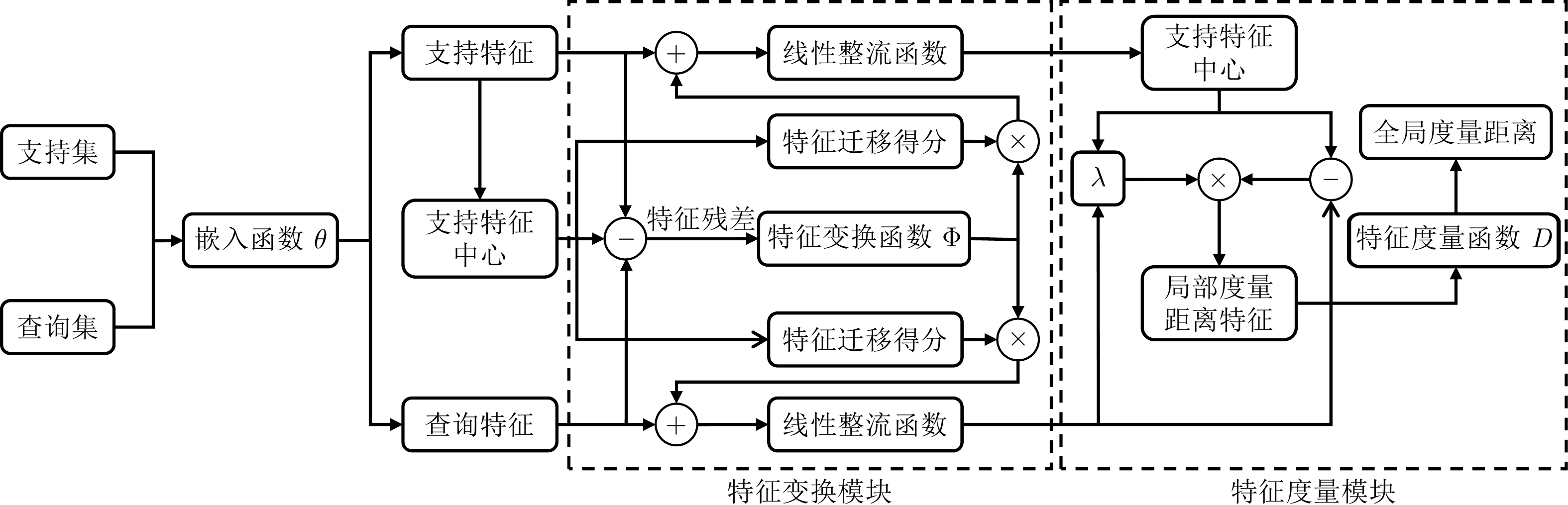
摘要: 在小样本分类任务中, 每个类别可供训练的样本数量非常有限. 因此在特征空间中同类样本分布稀疏, 异类样本间边界模糊. 提出一种新的基于特征变换和度量网络(Feature transformation and metric networks, FTMN)的小样本学习算法用于小样本分类任务. 算法通过嵌入函数将样本映射到特征空间, 并计算输入该样本与所属类别中心的特征残差. 构造一个特征变换函数对该残差进行学习, 使特征空间内的样本特征经过该函数后向同类样本中心靠拢. 利用变换后的样本特征更新类别中心, 使各类别中心间的距离增大. 算法进一步构造了一种新的度量函数, 对样本特征中每个局部特征点的度量距离进行联合表达, 该函数能够同时对样本特征间的夹角和欧氏距离进行优化. 算法在小样本分类任务常用数据集上的优秀表现证明了算法的有效性和泛化性.Abstract: For few-shot classification, training samples for each class are highly limited. Consequently, samples from the same class tend to distribute sparsely while boundaries between different classes are indistinct in the feature space. Therefore, a novel few-shot learning algorithm based on feature transformation and metric networks (FTMN) is proposed for few-shot learning. The algorithm maps samples to the feature space through an embedding function and calculates the residual between the input features and their class center. A feature transformation function is then constructed to learn from the residual, enabling input features to move closer to their class center after transformation. The transformed features are used to update the class centers, increasing the distance between centers of different classes. Furthermore, the algorithm introduces a novel metric function that jointly expresses the metric distances of each point within the features. The metric function simultaneously optimizes both cosine similarity and Euclidean distance. The performance of the algorithm on commonly used datasets for few-shot classification validates its effectiveness and generalization ability.
-
Key words:
- Feature transformation /
- metric learning /
- few-shot learning /
- residual learning
-
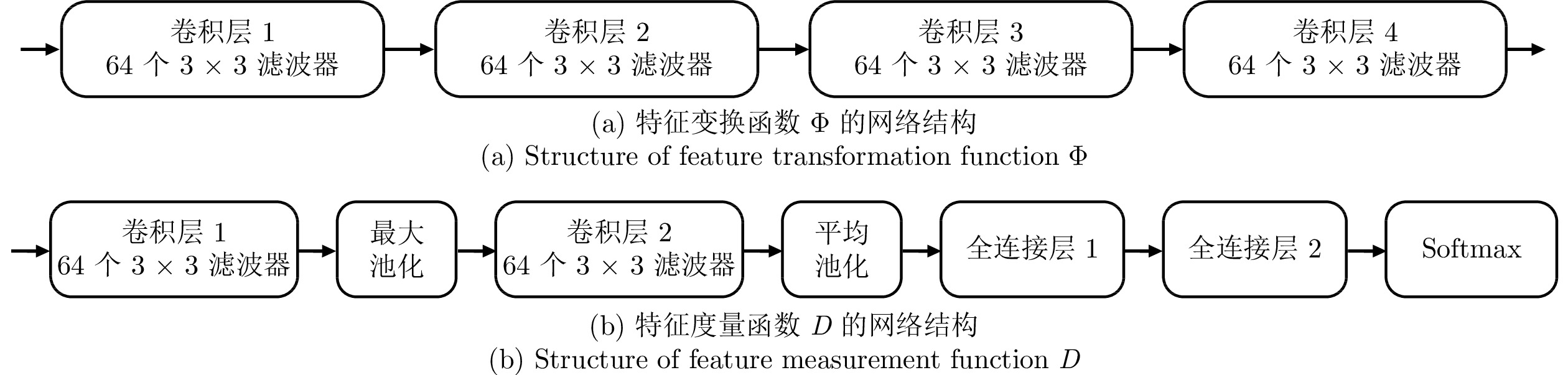
表 1 网络模型的嵌入函数与重要结构
Table 1 Embedding function and important structures of networks
表 2 在Omniglot数据集上的小样本分类性能(%)
Table 2 Few-shot classification performance on Omniglot dataset (%)
模型 5-类 20-类 1-样本 5-样本 1-样本 5-样本 MN 98.1 98.9 93.8 98.5 ProtoNet[12] 98.8 99.7 96.0 98.9 SN 97.3 98.4 88.2 97.0 RN 99.6 ± 0.2 99.8 ± 0.1 97.6 ± 0.2 99.1 ± 0.1 SM[15] 98.4 99.6 95.0 98.6 MetaNet[16] 98.95 — 97.00 — MANN[17] 82.8 94.9 — — MAML[18] 98.7 ± 0.4 99.9 ± 0.1 95.8 ± 0.3 98.9 ± 0.2 MMNet[26] 99.28 ± 0.08 99.77 ± 0.04 97.16 ± 0.10 98.93 ± 0.05 FTMN 99.7 ± 0.1 99.9 ± 0.1 98.3 ± 0.1 99.5 ± 0.1 表 3 在miniImageNet数据集上的小样本分类性能 (%)
Table 3 Few-shot classification performance on miniImageNet dataset (%)
模型 5-类 1-样本 5-样本 MN 43.40 ± 0.78 51.09 ± 0.71 ML-LSTM[11] 43.56 ± 0.84 55.31 ± 0.73 ProtoNet[12] 49.42 ± 0.78 68.20 ± 0.66 RN 50.44 ± 0.82 65.32 ± 0.70 MetaNet[16] 49.21 ± 0.96 — MAML[18] 48.70 ± 1.84 63.11 ± 0.92 EGNN — 66.85 EGNN + Transduction[22] — 76.37 DN4[24] 51.24 ± 0.74 71.02 ± 0.64 DC[25] 62.53 ± 0.19 78.95 ± 0.13 DC + IMP[25] — 79.77 ± 0.19 MMNet[26] 53.37 ± 0.08 66.97 ± 0.09 PredictNet[27] 54.53 ± 0.40 67.87 ± 0.20 DynamicNet[28] 56.20 ± 0.86 72.81 ± 0.62 MN-FCE[29] 43.44 ± 0.77 60.60 ± 0.71 MetaOptNet[30] 60.64 ± 0.61 78.63 ± 0.46 FTMN 59.86 ± 0.91 75.96 ± 0.82 FTMN-R12 61.33 ± 0.21 79.59 ± 0.47 表 4 在CUB-200、CIFAR-FS和tieredImageNet数据集上的小样本分类性能(%)
Table 4 Few-shot classification performance on CUB-200, CIFAR-FS and tieredImageNet datasets (%)
模型 CUB-200 5-类 CIFAR-FS 5-类 tieredImageNet 5-类 1-样本 5-样本 1-样本 5-样本 1-样本 5-样本 MN 61.16 ± 0.89 72.86 ± 0.70 — — — — ProtoNet[12] 51.31 ± 0.91 70.77 ± 0.69 55.5 ± 0.7 72.0 ± 0.6 53.31 ± 0.89 72.69 ± 0.74 RN 62.45 ± 0.98 76.11 ± 0.69 55.0 ± 1.0 69.3 ± 0.8 54.48 ± 0.93 71.32 ± 0.78 MAML[18] 55.92 ± 0.95 72.09 ± 0.76 58.9 ± 1.9 71.5 ± 1.0 51.67 ± 1.81 70.30 ± 1.75 EGNN — — — — 63.52 ± 0.52 80.24 ± 0.49 DN4[24] 53.15 ± 0.84 81.90 ± 0.60 — — — — MetaOptNet[30] — — 72.0 ± 0.7 84.2 ± 0.5 65.99 ± 0.72 81.56 ± 0.53 FTMN-R12 69.58 ± 0.36 85.46 ± 0.79 70.3 ± 0.5 82.6 ± 0.3 62.14 ± 0.63 81.74 ± 0.33 表 5 消融实验结果 (%)
Table 5 Results of ablation study (%)
模型 5-类 1-样本 5-样本 ProtoNet-4C 49.42 ± 0.78 68.20 ± 0.66 ProtoNet-8C 51.18 ± 0.73 70.23 ± 0.46 ProtoNet-Trans-4C 53.47 ± 0.46 71.33 ± 0.23 ProtoNet-M-4C 56.54 ± 0.57 73.46 ± 0.53 ProtoNet-VLAD-4C 52.46 ± 0.67 70.83 ± 0.62 Trans*-M-4C 59.86 ± 0.91 67.86 ± 0.56 仅使用余弦相似度 54.62 ± 0.57 72.58 ± 0.38 仅使用欧氏距离 55.66 ± 0.67 73.34 ± 0.74 FTMN 59.86 ± 0.91 75.96 ± 0.82 -
[1] Szegedy C, Liu W, Jia Y Q, Sermanet P, Reed S, Anguelov D, et al. Going deeper with convolutions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Boston, USA: IEEE, 2015. 1−9 [2] He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, Sun J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 770−778 [3] Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Lake Tahoe, USA: NIPS, 2012. 1106−1114 [4] Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations. San Diego, USA: ICLR, 2015. [5] 刘颖, 雷研博, 范九伦, 王富平, 公衍超, 田奇. 基于小样本学习的图像分类技术综述. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(2): 297−315 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190720Liu Ying, Lei Yan-Bo, Fan Jiu-Lun, Wang Fu-Ping, Gong Yan-Chao, Tian Qi. Survey on image classification technology based on small sample learning. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(2): 297−315 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190720 [6] Miller E G, Matsakis N E, Viola P A. Learning from one example through shared densities on transforms. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Hilton Head Island, USA: IEEE, 2000. 464−471 [7] Li F F, Fergus R, Perona P. One-shot learning of object categories. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2006, 28(4): 594−611 [8] Lake B M, Salakhutdinov R, Gross J, Tenenbaum J B. One shot learning of simple visual concepts. In: Proceedings of the 33rd Annual Meeting of the Cognitive Science Society. Boston, USA: CogSci, 2011. 2568−2573 [9] Lake B M, Salakhutdinov R, Tenenbaum J B. Human-level concept learning through probabilistic program induction. Science, 2015, 350(11): 1332−1338 [10] Edwards H, Storkey A J. Towards a neural statistician. In: Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Learning Representations. Toulon, France: ICLR, 2017. [11] Vinyals O, Blundell C, Lillicrap T, Kavukcuoglu K, Wierstra D. Matching networks for one shot learning. In: Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Barcelona, Spain: 2016. 3637−3645 [12] Snell J, Swersky K, Zemel R. Prototypical networks for few-shot learning. In: Proceedings of the 31th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach, USA: 2017. 4080−4090 [13] Koch G, Zemel R, Salakhutdinov R. Siamese neural networks for one-shot image recognition. In: Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning. Lille, France: JMLR, 2015. [14] Sung F, Yang Y X, Zhang L, Xiang T, Torr P H S, Hospedales T M. Learning to compare: Relation network for few-shot learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 1199−1208 [15] Kaiser L, Nachum O, Roy A, Bengio S. Learning to remember rare events. In: Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Learning Representations. Toulon, France: ICLR, 2017. [16] Munkhdalai T, Yu H. Meta networks. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning. Sydney, Australia: JMLR.org, 2017. 2554−2563 [17] Santoro A, Bartunov S, Botvinick M, Wierstra D, Lillicrap T. Meta-learning with memory-augmented neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Machine Learning. New York, USA: PMLR, 2016. 1842−1850 [18] Finn C, Abbeel P, Levine S. Model-agnostic meta-learning for fast adaptation of deep networks. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning. Sydney, Australia: JMLR.org, 2017. 1126−1135 [19] Arandjelovic R, Gronat P, Torii A, Pajdla T, Sivic J. Net-VLAD: CNN architecture for weakly supervised place recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 5297−5307 [20] Jégou H, Douze M, Schmid C, Pérez P. Aggregating local descriptors into a compact image representation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. San Francisco, USA: IEEE, 2010. 3304−3311 [21] Bertinetto L, Henriques J F, Torr P H, Vedaldi A. Meta-learning with differentiable closed-form solvers. In: Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Learning Representations. New Orleans, USA: ICLR, 2019. [22] Kim J, Kim T, Kim S, Yoo C D. Edge-labeling graph neural network for few-shot learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 11−20 [23] Yue Z Q, Zhang H W, Sun Q R, Hua X S. Interventional few-shot learning. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: Curran Associates Incorporated, 2020. Article No. 230 [24] Li W B, Wang L, Xu J L, Huo J, Gao Y, Luo J B. Revisiting local descriptor based image-to-class measure for few-shot learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 7253−7260 [25] Lifchitz Y, Avrithis Y, Picard S, Bursuc A. Dense classification and implanting for few-shot learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 9250−9259 [26] Cai Q, Pan Y W, Yao T, Yan C G, Mei T. Memory matching networks for one-shot image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 4080−4088 [27] Qiao S Y, Liu C X, Shen W, Yuille A L. Few-shot image recognition by predicting parameters from activations. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 7229−7238 [28] Gidaris S, Komodakis N. Dynamic few-shot visual learning without forgetting. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 4367−4375 [29] Ravi S, Larochelle H. Optimization as a model for few-shot learning. In: Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Learning Representations. Toulon, France: ICLR, 2017. [30] Lee K, Maji S, Ravichandran A, Soatto S. Meta-learning with differentiable convex optimization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/ CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 10649−10657 -




 下载:
下载: