-
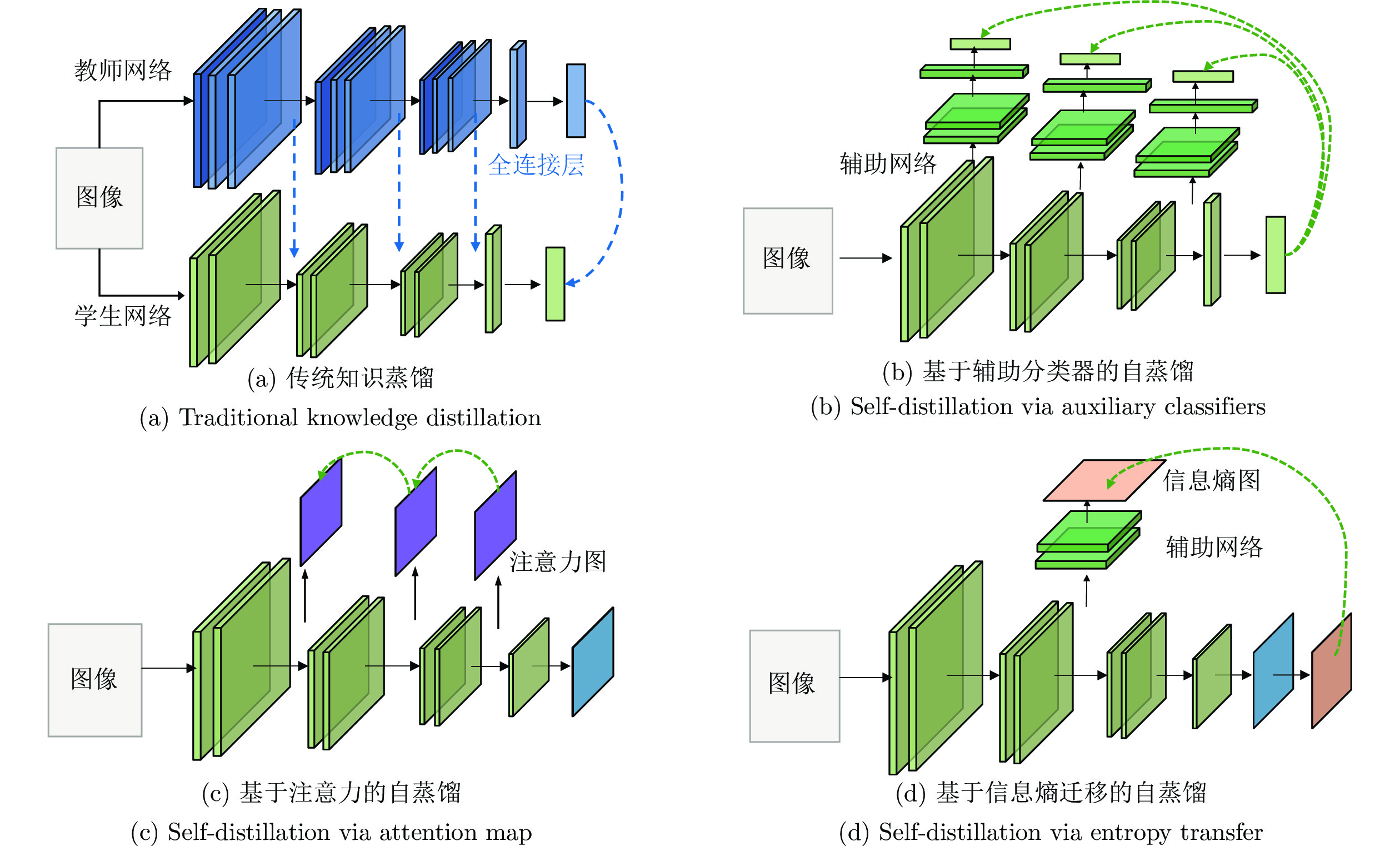
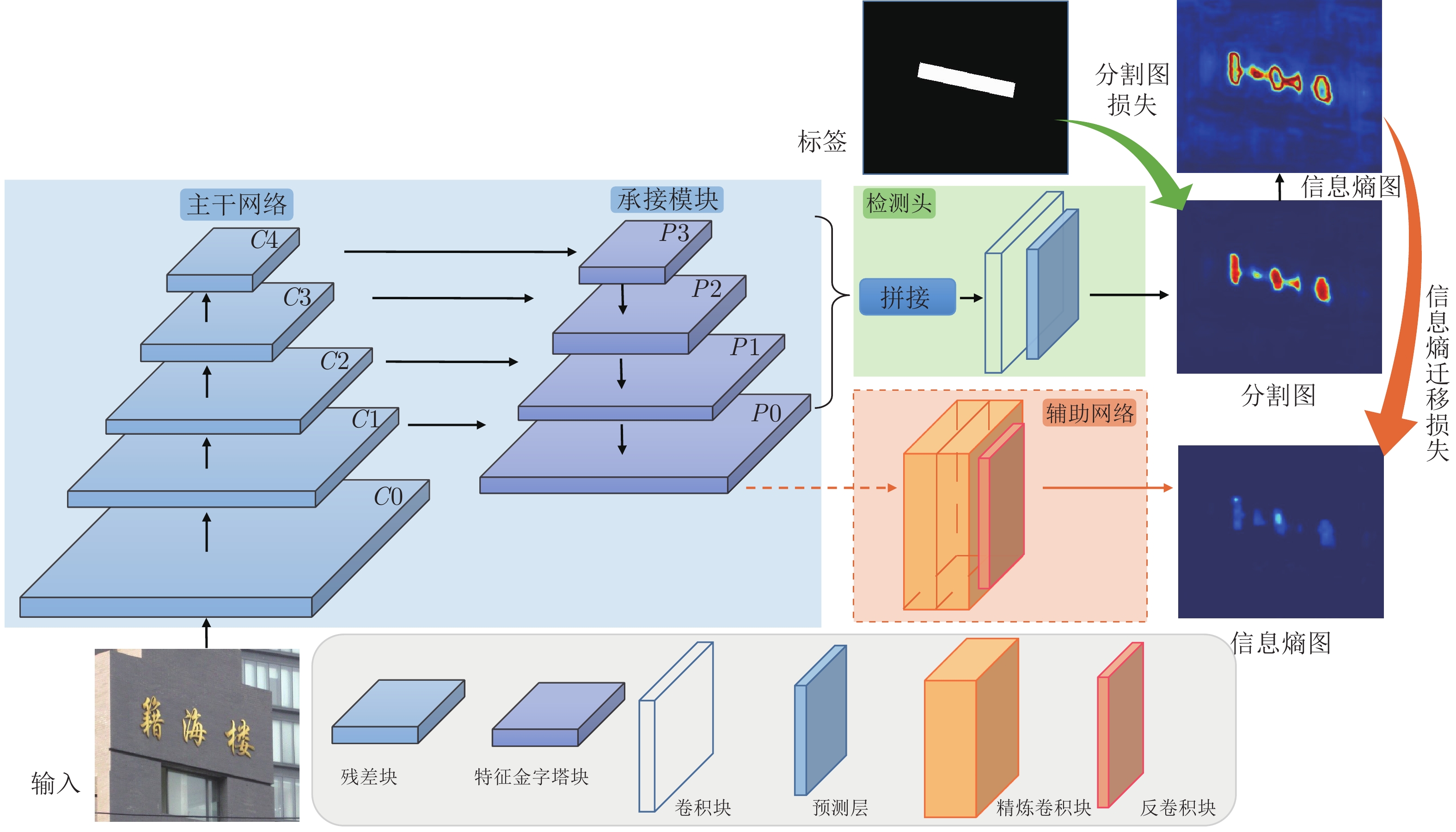
摘要: 前沿的自然场景文本检测方法大多基于全卷积语义分割网络, 利用像素级分类结果有效检测任意形状的文本, 其主要缺点是模型大、推理时间长、内存占用高, 这在实际应用中限制了其部署. 提出一种基于信息熵迁移的自蒸馏训练方法(Self-distillation via entropy transfer, SDET), 利用文本检测网络深层网络输出的分割图(Segmentation map, SM)信息熵作为待迁移知识, 通过辅助网络将信息熵反馈给浅层网络. 与依赖教师网络的知识蒸馏 (Knowledge distillation, KD)不同, SDET仅在训练阶段增加一个辅助网络, 以微小的额外训练代价实现无需教师网络的自蒸馏(Self-distillation, SD). 在多个自然场景文本检测的标准数据集上的实验结果表明, SDET在基线文本检测网络的召回率和F1得分上, 能显著优于其他蒸馏方法.Abstract: Most of the state-of-the-art text detection methods in natural scenes are based on full convolutional network, which can effectively detect arbitrary shape text by using the pixel level classification results from the segmentation network. The main defects of these methods, i.e. large size of the networks, time-consuming forward reasoning and large memory occupation, hinder their deployment in practical applications. In this paper, we propose self-distillation via entropy transfer (SDET), which takes the information entropy of the segmentation map (SM) output by the deep layers of the text detection network as the knowledge to be transferred, and feeds it directly back into the shallow layers through an auxiliary network. Different from traditional knowledge distillation (KD) which relies on teacher network, SDET utilizes an auxiliary network in the training stage and realizes self-distillation (SD) at a small extra training cost. Experiments conducted on multiple standard datasets for natural scene text detection demonstrate that SDET significantly improves the recall rate and F1 score of the baseline text detection networks, and outperforms other distillation methods.
-
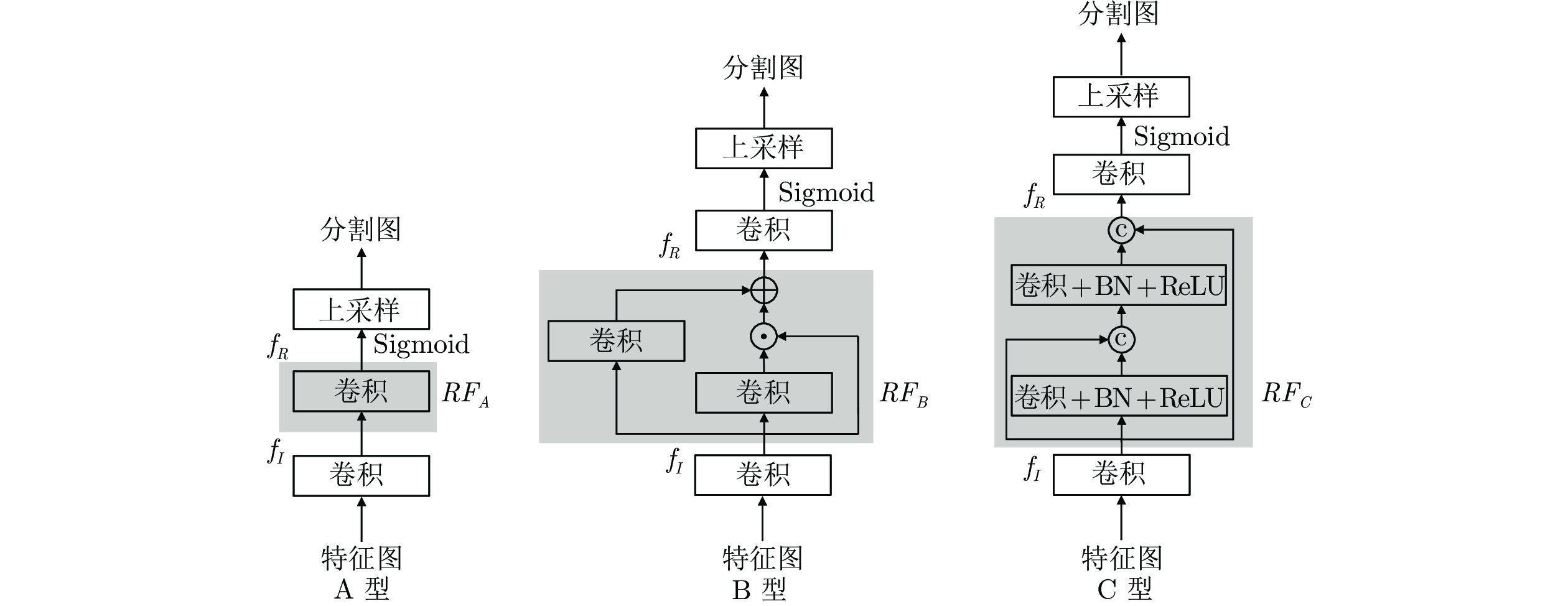
表 1 不同辅助分类器对SDET的影响 (%)
Table 1 The impact of different auxiliary classifiers on SDET (%)
模型 方法 ICDAR2013 ICDAR2015 P R F P R F MV3-EAST 基线 81.7 64.4 72.0 80.9 75.4 78.0 A型 78.8 65.9 71.8 78.8 76.3 77.5 B型 84.4 66.5 74.4 81.3 77.0 79.1 C型 81.4 67.4 73.7 78.9 77.7 78.3 MV3-DB 基线 83.7 66.0 73.8 87.1 71.8 78.7 A型 84.1 68.8 75.7 86.5 73.9 79.7 B型 81.1 67.3 73.6 87.8 71.7 78.9 C型 84.9 67.9 75.4 87.8 73.0 79.7 表 2 不同特征金字塔位置对B型的影响 (%)
Table 2 The impact of different feature pyramid positions on type B (%)
方法 特征图尺寸(像素) P R F 基线 — 80.9 75.4 78.0 P0 ${\text{16}} \times {\text{16}}$ 79.1 75.8 77.4 P1 ${\text{32}} \times {\text{32}}$ 79.5 76.5 78.0 P2 ${\text{64}} \times {\text{64}}$ 80.7 77.4 79.0 P3 ${\text{128}} \times {\text{128}}$ 81.3 77.0 79.1 表 3 MV3-DB在不同数据集上的知识蒸馏实验结果(%)
Table 3 Experimental results of knowledge distillation of MV3-DB on different datasets (%)
方法 ICDAR2013 TD500 TD-TR ICDAR2015 Total-text CASIA-10K P R F P R F P R F P R F P R F P R F 基线 83.7 66.0 73.8 78.7 71.4 74.9 83.6 74.4 78.7 87.1 71.8 78.7 87.2 66.9 75.7 88.1 51.9 65.3 ST 82.5 65.8 73.2 77.0 73.0 74.9 84.6 73.5 78.7 85.4 72.2 78.2 87.4 65.3 74.8 88.8 49.4 63.5 KA 82.5 66.8 73.8 79.5 71.3 75.2 86.3 72.5 78.8 85.0 73.3 78.7 85.9 66.8 75.2 87.8 51.4 64.8 FitNets 84.7 65.4 73.8 78.6 73.3 75.8 85.3 74.0 79.2 85.3 73.3 78.8 87.4 67.5 76.2 88.0 52.3 65.6 SKD 82.4 68.8 75.0 81.2 70.6 75.5 84.8 74.5 79.3 87.4 71.6 78.7 87.4 67.0 75.9 88.6 51.6 65.2 SD 83.5 67.8 74.8 79.4 72.2 75.6 85.0 74.0 79.1 85.1 73.0 78.6 87.0 67.6 76.1 87.1 52.0 65.1 SAD 82.8 66.7 73.9 78.7 72.3 75.4 87.3 72.0 78.9 86.7 72.7 79.1 86.5 67.1 75.6 88.4 50.7 64.4 本文方法 84.1 68.8 75.7 80.6 72.2 76.2 85.6 74.6 79.7 86.5 73.9 79.7 87.5 68.4 76.8 87.4 53.4 66.3 表 4 MV3-EAST在不同数据集上的知识蒸馏实验结果(%)
Table 4 Experimental results of knowledge distillation of MV3-EAST on different datasets (%)
方法 ICDAR2013 ICDAR2015 CASIA-10K P R F P R F P R F 基线 81.7 64.4 72.0 80.9 75.4 78.0 66.1 64.9 65.5 ST 77.8 64.9 70.8 80.9 75.1 77.9 64.7 65.1 64.9 KA 78.6 64.0 70.5 78.2 76.4 77.3 67.7 63.0 65.3 FitNets 82.4 65.8 73.2 78.0 77.8 77.9 65.4 64.2 64.8 SKD 79.5 66.3 72.3 81.9 75.6 78.6 66.6 64.7 65.6 SD 80.2 63.8 71.1 79.6 74.7 77.1 66.2 63.5 64.8 SAD 81.4 65.6 72.6 80.2 76.5 78.3 65.7 64.1 64.9 本文方法 84.4 66.5 74.4 81.3 77.0 79.1 70.8 63.0 66.7 表 5 SDET与DSN在不同数据集上的对比(%)
Table 5 Comparison of SDET and DSN on different datasets (%)
方法 ICDAR2013 TD500 TD-TR ICDAR2015 Total-text CASIA-10K P R F P R F P R F P R F P R F P R F 基线 83.7 66.0 73.8 78.7 71.4 74.9 83.6 74.4 78.7 87.1 71.8 78.7 87.2 66.9 75.7 88.1 51.9 65.3 DSN 84.4 68.0 75.3 79.7 71.5 75.4 86.4 72.2 78.7 85.8 73.4 79.1 86.1 67.9 75.9 87.9 52.3 65.6 本文方法 84.1 68.8 75.7 80.6 72.2 76.2 85.6 74.6 79.7 86.5 73.9 79.7 87.5 68.4 76.8 87.4 53.4 66.3 表 6 SDET在不同数据集上提升ResNet50-DB的效果(%)
Table 6 The effect of SDET on improving ResNet50-DB on different datasets (%)
方法 ICDAR2013 TD500 TD-TR ICDAR2015 Total-text CASIA-10K P R F P R F P R F P R F P R F P R F 基线 86.3 72.9 79.0 84.1 75.9 79.8 87.3 80.4 83.7 90.3 80.1 84.9 87.7 79.4 83.3 90.1 64.7 75.3 本文方法 82.7 77.2 79.9 79.9 81.5 80.7 87.2 83.0 85.0 90.3 82.1 86.0 87.4 81.8 84.5 86.0 68.7 76.4 -
[1] Long J, Shelhamer E, Darrell T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Boston, USA: IEEE, 2015. 3431−3440 [2] Yuan Y H, Chen X L, Wang J D. Object-contextual representations for semantic segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1909.11065, 2019. [3] Lv P Y, Liao M H, Yao C, Wu W H, Bai X. Mask textspotter: An end-to-end trainable neural network for spotting text with arbitrary shapes. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 67−83 [4] He K M, Gkioxari G, Dollár P, Girshick R. Mask R-CNN. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 2961−2969 [5] Ye J, Chen Z, Liu J H, Du B. TextFuseNet: Scene text detection with richer fused features. In: Proceedings of the 29th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Yokohama, Japan: 2020. 516−522 [6] He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, Sun J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 770−778 [7] Hinton G E, Vinyals O, Dean J. Distilling the knowledge in a neural network. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1503.02531, 2015. [8] 赖轩, 曲延云, 谢源, 裴玉龙. 基于拓扑一致性对抗互学习的知识蒸馏. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(1): 102−110 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.200665Lai Xuan, Qu Yan-Yun, Xie Yuan, Pei Yu-Long. Topology-guided adversarial deep mutual learning for knowledge distillation. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(1): 102−110 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.200665 [9] Romero A, Ballas N, Kahou S E, Chassang A, Gatta C, Bengio Y. FitNets: Hints for thin deep nets. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1412.6550, 2014. [10] Zagoruyko S, Komodakis N. Paying more attention to attention: Improving the performance of convolutional neural networks via attention transfer. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1612.03928, 2016. [11] Karatzas D, Gomez-Bigorda L, Nicolaou A, Ghosh S, Bagdanov A, Iwamura M, et al. ICDAR2015 competition on robust reading. In: Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition. Nancy, France: IEEE, 2015. 1156−1160 [12] Chng C K, Chan C S. Total-text: A comprehensive data-set for scene text detection and recognition. In: Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition. Kyoto, Japan: IEEE, 2017. 935−942 [13] Cho J H, Hariharan B. On the efficacy of knowledge distillation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Seoul, South Korea: IEEE, 2019. 4794−4802 [14] Yang P, Yang G W, Gong X, Wu P P, Han X, Wu J S, et al. Instance segmentation network with self-distillation for scene text detection. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 45825−45836 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2978225 [15] Vu T H, Jain H, Bucher M, Cord M, Pérez P. Advent: Adversarial entropy minimization for domain adaptation in semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 2517−2526 [16] Lee C Y, Xie S N, Gallagher P, Zhang Z Y, Tu Z W. Deeply-supervised nets. In: Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics. San Diego, USA: PMLR, 2015. 562−570 [17] Hou Y N, Ma Z, Liu C X, Loy C C. Learning lightweight lane detection CNNs by self attention distillation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Seoul, South Korea: IEEE, 2019. 1013−1021 [18] 王润民, 桑农, 丁丁, 陈杰, 叶齐祥, 高常鑫, 等. 自然场景图像中的文本检测综述. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(12): 2113−2141Wang Run-Min, Sang Nong, Ding Ding, Chen Jie, Ye Qi-Xiang, Gao Chang-Xin, et al. Text detection in natural scene image: A survey. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(12): 2113−2141 [19] Ren S Q, He K M, Girshick R, Sun J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1506.01497, 2015. [20] Liu W, Anguelov D, Erhan D, Szegedy C, Reed S, Fu C Y, et al. SSD: Single shot multi-box detector. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Amsterdam, Netherlands: 2016. 21−37 [21] Liao M H, Shi B G, Bai X, Wang X G, Liu W Y. Textboxes: A fast text detector with a single deep neural network. In: Proceedings of the 31st AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. San Francisco, USA: AAAI, 2017. 4161−4167 [22] Tian Z, Huang W L, He T, He P, Qiao Y. Detecting text in natural image with connectionist text proposal network. In: Proce-edings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Springer, 2016. 56−72 [23] Zhou X Y, Yao C, Wen H, Wang Y Z, Zhou S C, He W R, et al. East: An efficient and accurate scene text detector. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 5551−5560 [24] Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2015. 234−241 [25] Liao M H, Wan Z Y, Yao C, Chen K, Bai X. Real-time scene text detection with differentiable binarization. In: Proceedings of the 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. New York, USA: AAAI, 2020. 11474−11481 [26] Wang W H, Xie E Z, Li X, Hou W B, Lu T, Yu G, et al. Shape robust text detection with progressive scale expansion network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 9336−9345 [27] Wang W H, Xie E Z, Song X G, Zang Y H, Wang W J, Lu T, et al. Efficient and accurate arbitrary-shaped text detection with pixel aggregation network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Seoul, South Korea: IEEE, 2019. 8440−8449 [28] Xu Y C, Wang Y K, Zhou W, Wang Y P, Yang Z B, Bai X. Textfield: Learning a deep direction field for irregular scene text detection. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28(11): 5566−5579 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2900589 [29] He T, Shen C H, Tian Z, Gong D, Sun C M, Yan Y L. Knowledge adaptation for efficient semantic segmentation. In: Proce-edings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 578−587 [30] Liu Y F, Chen K, Liu C, Qin Z C, Luo Z B, Wang J D. Structured knowledge distillation for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 2604−2613 [31] Wang Y K, Zhou W, Jiang T, Bai X, Xu Y C. Intra-class feature variation distillation for semantic segmentation. In: Proce-edings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Glasg-ow, UK: Springer, 2020. 346−362 [32] Zhang L F, Song J B, Gao A, Chen J W, Bao C L, Ma K S. Be your own teacher: Improve the performance of convolutional neural networks via self distillation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Seo-ul, South Korea: IEEE, 2019. 3713−3722 [33] Howard A, Sandler M, Chu G, Chen L C, Chen B, Tan M X, et al. Searching for MobileNetV3. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/ CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Seoul, South Korea: IEEE, 2019. 1314−1324 [34] Lin T Y, Dollár P, Girshick R, He K M, Hariharan B, Belongie S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 2117−2125 [35] Chen Z Y, Xu Q Q, Cong R M, Huang Q M. Global context-aware progressive aggregation network for salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. New York, USA: AAAI, 2020. 10599−10606 [36] Karatzas D, Shafait F, Uchida S, Iwamura M I, Bigorda L G, Mestre S R, et al. ICDAR2013 robust reading competition. In: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition. Washington DC, USA: IEEE, 2013. 1484−1493 [37] Yao C, Bai X, Liu W Y, Ma Y, Tu Z W. Detecting texts of arbitrary orientations in natural images. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Providence, USA: IEEE, 2012. 1083−1090 [38] Xue C H, Lu S J, Zhan F N. Accurate scene text detection through border semantics awareness and bootstrapping. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: IEEE, 2018. 355−372 [39] He W H, Zhang X Y, Yin F, Liu C L. Multi-oriented and multi-lingual scene text detection with direct regression. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(11): 5406−5419 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2855399 -




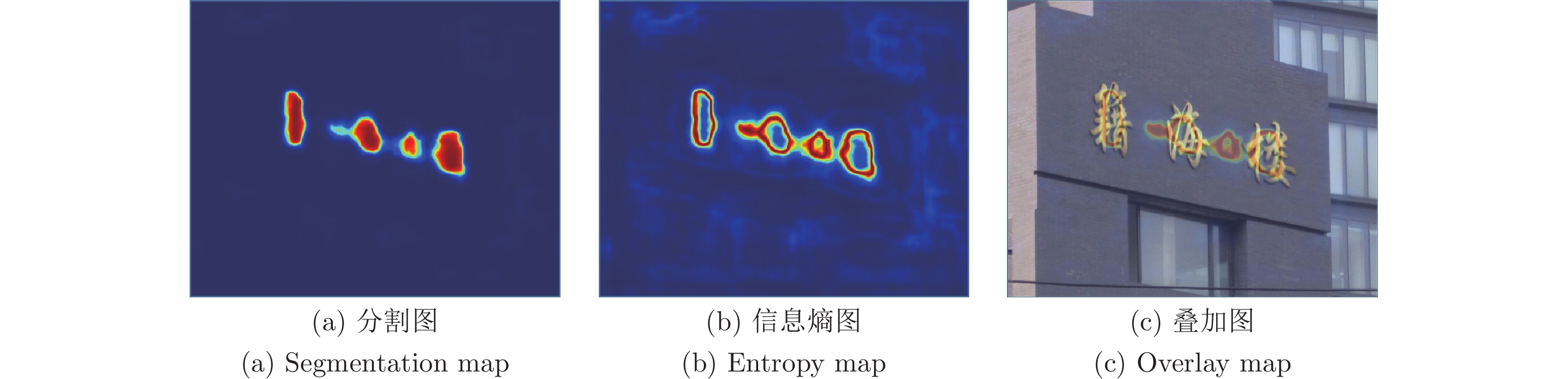
 下载:
下载: