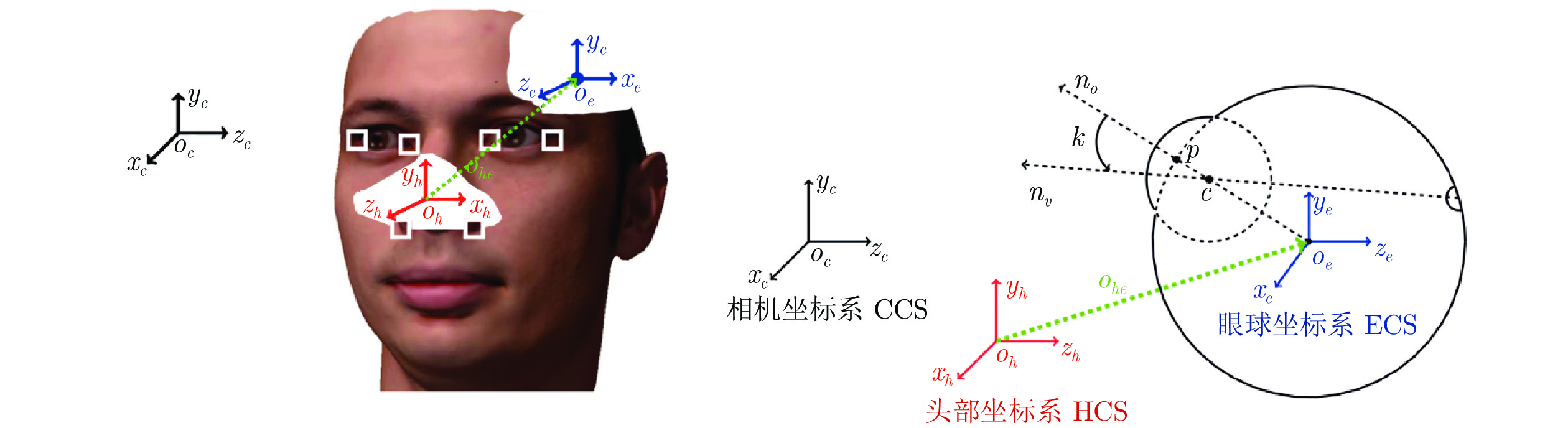
-
摘要: 眼动跟踪是指自动检测瞳孔中心位置或者识别三维视线方向及注视点的过程, 被广泛应用于人机交互、智能驾驶、人因工程等. 由于不同场景下的光照变化、个体眼球生理构造差异、遮挡、头部姿态多样等原因, 眼动跟踪的研究目前仍然是一个具有挑战性的热点问题. 针对眼动跟踪领域,首先概述眼动跟踪研究内容, 然后分别论述近年来瞳孔中心检测及视线估计领域的国内外研究进展, 综述目前眼动跟踪主要数据集、评价指标及研究成果, 接着介绍眼动跟踪在人机交互、智能驾驶等领域的应用, 最后对眼动跟踪领域的未来发展趋势进行展望.Abstract: Eye tracking is a process of automatically detecting the location of pupil or recognizing the gaze direction and gaze point, and is widely used in human-computer interaction, intelligent driving, ergonomics, and so on. Eye tracking is still a challenging and hot topic due to the changes of illumination, the differences of individual eyeball physiological structure, occlusion, and the diversity of head pose. In this paper, we focus on the study of eye tracking. Firstly, we give an introduction of eye tracking, followed by discussing the research progress of pupil detection and gaze estimation in recent years. Then, we review the datasets and evaluation metrics with results, followed by introducing the application of eye tracking in human-computer interaction, intelligent driving and other fields. Finally, the future trends of eye tracking are discussed.
-
Key words:
- Eye tracking /
- eye detection /
- gaze estimation /
- attention analysis
-
表 1 常用瞳孔中心检测数据集
Table 1 Datasets for pupil detection
数据集 发布年份 被试人数 图片/视频数量 图像区域 图像分辨率 (像素) BioID[105] 2001 23 图片 1521 张 上半身 384 × 280 CASIA-Iris[107] 2010 ≥ 1800 图片 54601 张 人眼、人脸 320 × 280, 640 × 480, 2352 × 1728 GI4E[106] 2013 103 图片 1236 张 上半身 800 × 600 ExCuSe[108] 2015 未知 图片 39001 张 人眼 384 × 288, 620 × 460 Else[14] 2016 未知 图片 55712 张 人眼 384 × 288 LPW[109] 2016 22 视频 66 段 人眼 640 × 480 OpenEDS[110] 2019 152 图片 356649 张 人眼 400 × 640 TEyeD[111] 2021 132 图片 20867073 张 人眼 384 × 288, 320 × 240, 640 × 480, 640 × 360 表 2 不同方法在BioID 数据集上的瞳孔中心检测结果对比
Table 2 Comparison of pupil center detection results by different methods on the BioID dataset
表 3 不同方法在GI4E 数据集上的瞳孔中心检测结果对比
Table 3 Comparison of pupil center detection results by different methods on the GI4E dataset
表 4 常用视线估计估计数据集
Table 4 Datasets for gaze estimation
数据集 人数 图片/视频数量 图像区域 图像分辨率 (像素) 视线角度范围 (偏航角, 俯仰角) 头部姿态范围 (偏航角, 俯仰角) ColumbiaGaze[106] 56 图片 5880 张 全脸 5184 × 3456 ±15°, ±10° ±30°, 0° EYEDIAP[117] 16 视频 94 段 全脸 640 × 480 ±40°, ±30° ±40°, ±40° UT-multiview[93] 50 图片 64000 张 全脸 1280 × 1024 ±50°, ±36° ±36°, ±36° GazeCapture[104] 1474 图片 2445504 张 全脸 640 × 480 ±18°, −1.5 ~ +20° ±30°, ±40° MPIIGaze[118] 15 图片 213659 张 全脸 未知 ±20°, ±20° ±25°, −10° ~ +30° RT-GENE[119] 15 图片 122531 张 全脸 1920 × 1080 ±40°, ±40° ±40°, ±40° Gaze360[120] 238 图片 172000 张 全脸 3382 × 4096 ±140°, −40° ~ +10° ±90°, 未知 U2Eyes[121] 1000 图片 5875000 张 双眼 3840 × 2160 未知 未知 ETH-Xgaze[122] 110 图片 1083492 张 全脸 6000 × 4000 ±120°, ±70° ±80°, ±80° 表 5 不同方法在 MPIIGaze及 EYEDIAP数据集上的视线估计绝对误差结果对比
Table 5 Comparison of gaze estimation results by different methods on the MPIIGaze and EYEDIAP datasets
表 6 主要眼动仪介绍
Table 6 Introduction to some main eye trackers
眼动仪型号 厂商 类型 特点 Tobii Pro Glasses 3 Tobii 眼镜式 搭载16个红外光源, 配备超广角摄像机, 内置陀螺仪, 具有完整的数据采集、分析、应用程序编程接口功能支持. EyeLink 1000 Plus SR Research 遥测式 具有高采样率、低噪声等特点, 允许头部自由运动, 兼容多种第三方数据处理平台, 适用于多种研究人群和场景. Dikablis Glasses 3 Ergoneers 眼镜式 轻便小巧, 误差范围约0.1° ~ 0.3°, 配备高清摄像机, 配备D-Lab数据分析软件, 可自动分析感兴趣区域. Smart Eye Pro Smart Eye 遥测式 可以配置多个摄像头, 自动捕捉面部关键点, 支持视线3D重建, 配备应用程序编程接口与多种第三方数据分析软件. GP3 Gazepoint 遥测式 误差范围能达到0.5° ~ 1°, 提供开放的标准应用程序编程接口和软件开发工具包, 兼容iMotions的眼动追踪模组. LooxidVR Looxid Labs 虚拟现实 可同步采集眼动和瞳孔数据. 支持脑电数据的采集, 配备数据可视化平台, 基于Unity引擎的应用程序编程接口支持定制用户交互界面和特效. VIVE Pro Eye HTC和Valve 虚拟现实 可采集眼动数据, 支持可视化. 整套系统融合了顶级的图像、音频、人体工程学硬件设计, 能营造更为真实的虚拟现实体验. -
[1] Hansen D W, Ji Q. In the eye of the beholder: A survey of models for eyes and gaze. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2010, 32(3): 478-500 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2009.30 [2] Klaib A F, Alsrehin N O, Melhem W Y, Bashtawi H O, Magableh A A. Eye tracking algorithms, techniques, tools, and applications with an emphasis on machine learning and Internet of Things technologies. Expert Systems With Applications, 2021, 166: 114037 [3] Kar A, Corcoran P. A review and analysis of eye-gaze estimation systems, algorithms and performance evaluation methods in consumer platforms. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 16495-16519 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2735633 [4] Modi N, Singh J. A review of various state of art eye gaze estimation techniques. Advances in Computational Intelligence and Communication Technology. Singapore: Springer, 2021. 501−510 [5] 刘佳惠, 迟健男, 尹怡欣. 基于特征的视线跟踪方法研究综述. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(2): 252-277Liu Jia-Hui, Chi Jian-Nan, Yin Yi-Xin. A review of feature-based gaze tracking methods. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(2): 252-277 [6] Yu Y, Odobez J M. Unsupervised representation learning for gaze estimation. In: Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 7312−7322 [7] Zhang R H, Walshe C, Liu Z D, Guan L, Muller K, Whritner J, et al. Atari-head: Atari human eye-tracking and demonstration dataset. In: Proceedings of the 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. New York, USA: AAAI, 2020, 34(4): 6811−6820 [8] Robinson D A. A method of measuring eye movement using a scleral search coil in a magnetic field. IEEE Transactions on Bio-Medical Electronics, 1963, 10(4): 137-145 doi: 10.1109/TBMEL.1963.4322822 [9] Eibenberger K, Eibenberger B, Rucci M. Design, simulation and evaluation of uniform magnetic field systems for head-free eye movement recordings with scleral search coils. In: Proceedings of the 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC). Orlando, USA: IEEE, 2016. 247−250 [10] Eibenberger K, Eibenberger B, Roberts D C, Haslwanter T, Carey J P. A novel and inexpensive digital system for eye movement recordings using magnetic scleral search coils. Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing, 2016, 54(2-3): 421-430 [11] Martinikorena I, Cabeza R, Villanueva A, Urtasun I, Larumbe A. Fast and robust ellipse detection algorithm for head-mounted eye tracking systems. Machine Vision and Applications, 2018, 29(5): 845-860 doi: 10.1007/s00138-018-0940-0 [12] Mestre C, Gautier J, Pujol J. Robust eye tracking based on multiple corneal reflections for clinical applications. Journal of Biomedical Optics, 2018, 23(3): 035001 [13] Santini T, Fuhl W, Geisler D, Kasneci E. EyeRecToo: Open-source software for real-time pervasive head-mounted eye tracking. In: Proceedings of the 12th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2017). Porto, Portugal: SciTePress, 2017. 96−101 [14] Fuhl W, Santini T C, Kübler T, Kasneci E. Else: Ellipse selection for robust pupil detection in real-world environments. In: Proceedings of the 9th Biennial ACM Symposium on Eye Tracking Research & Applications. South Carolina, Charleston: ACM, 2016. 123−130 [15] Păsărică A, Bozomitu R G, Cehan V, Lupu R G, Rotariu C. Pupil detection algorithms for eye tracking applications. In: Proceedings of the 21st International Symposium for Design and Technology in Electronic Packaging (SⅡTME). Brasov, Romania: IEEE, 2015. 161−164 [16] Chennamma H R, Yuan X H. A survey on eye-gaze tracking techniques. Indian Journal of Computer Science and Engineering (IJCSE), 2013, 4(5): 388-393 [17] Bulling A, Gellersen H. Toward mobile eye-based human-computer interaction. IEEE Pervasive Computing, 2010, 9(4): 8-12 doi: 10.1109/MPRV.2010.86 [18] Khamis M, Hoesl A, Klimczak A, Reiss M, Alt F, Bulling A. EyeScout: Active eye tracking for position and movement independent gaze interaction with large public displays. In: Proceedings of the 30th Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology. Québec City, Canada: ACM, 2017. 155−166 [19] Kong Y S, Lee S, Lee J, Nam Y. A head-mounted goggle-type video-oculography system for vestibular function testing. EURASIP Journal on Image and Video Processing, 2018, 2018(1): 28 [20] Brousseau B, Rose J, Eizenman M. Hybrid eye-tracking on a smartphone with CNN feature extraction and an infrared 3D model. Sensors, 2020, 20(2): 543 [21] Yuille A L, Hallinan P W, Cohen D S. Feature extraction from faces using deformable templates. International Journal of Computer Vision, 1992, 8(2): 99-111 doi: 10.1007/BF00127169 [22] Hansen D W, Pece A E C. Eye tracking in the wild. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2005, 98(1): 155-181 doi: 10.1016/j.cviu.2004.07.013 [23] Valenti R, Gevers T. Accurate eye center location and tracking using isophote curvature. In: Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Anchorage, USA: IEEE, 2008. 1−8 [24] Valenti R, Gevers T. Accurate eye center location through invariant isocentric patterns. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2012, 34(9): 1785-1798 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2011.251 [25] Tan X Y, Song F Y, Zhou Z H, Chen S C. Enhanced pictorial structures for precise eye localization under incontrolled conditions. In: Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Miami, USA: IEEE, 2009. 1621−1628 [26] Felzenszwalb P F, Huttenlocher D P. Pictorial structures for object recognition. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2005, 61(1): 55-79 doi: 10.1023/B:VISI.0000042934.15159.49 [27] Wang C Y, Zhu Y H, Liu Y F, He R, Sun Z N. Joint iris segmentation and localization using deep multi-task learning framework. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1901.11195, 2019 [28] Gowroju S, Aarti, Kumar S. Robust deep learning technique: U-net architecture for pupil segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 11th IEEE Annual Information Technology, Electronics and Mobile Communication Conference (IEMCON). Vancouver, Canada: IEEE, 2020. 609−613 [29] Araujo G M, Ribeiro F M L, Silva E A B, Goldenstein S K. Fast eye localization without a face model using inner product detectors. In: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP). Paris, France: IEEE, 2014. 1366−1370 [30] Wu Y, Ji Q. Learning the deep features for eye detection in uncontrolled conditions. In: Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Pattern Recognition. Stockholm, Sweden: IEEE, 2014. 455−459 [31] Fuhl W, Santini T, Kasneci G, Rosenstiel W, Kasneci E. PupilNet v2.0: Convolutional neural networks for CPU based real time robust pupil detection. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1711.00112, 2017 [32] Chen S, Liu C J. Clustering-based discriminant analysis for eye detection. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2014, 23(4): 1629-1638 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2013.2294548 [33] Lucio D R, Laroca R, Zanlorensi L A, Moreira G, Menotti D. Simultaneous iris and periocular region detection using coarse annotations. In: Proceedings of the 32nd SIBGRAPI Conference on Graphics, Patterns and Images (SIBGRAPI). Rio de Janeiro, Brazil: IEEE, 2019. 178−185 [34] Xia Y F, Yu H, Wang F Y. Accurate and robust eye center localization via fully convolutional networks. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2019, 6(5): 1127-1138 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2019.1911684 [35] Hsu W Y, Chung C J. A novel eye center localization method for head poses with large rotations. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 30: 1369-1381 [36] Zhou M C, Wang X Y, Wang H T, Heo J, Nam D. Precise eye localization with improved SDM. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP). Quebec City, Canada: IEEE, 2015. 4466−4470 [37] Xiong X H, De la Torre F. Supervised descent method and its applications to face alignment. In: Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Portland, USA: IEEE, 2013. 532−539 [38] Gou C, Wu Y, Wang K, Wang F Y, Ji Q. Learning-by-synthesis for accurate eye detection. In: Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR). Cancun, Mexico: IEEE, 2016. 3362−3367 [39] Gou C, Wu Y, Wang K, Wang K F, Wang F Y, Ji Q. A joint cascaded framework for simultaneous eye detection and eye state estimation. Pattern Recognition, 2017, 67: 23-31 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2017.01.023 [40] Xiao F, Huang K J, Qiu Y, Shen H B. Accurate iris center localization method using facial landmark, snakuscule, circle fitting and binary connected component. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2018, 77(19): 25333-25353 doi: 10.1007/s11042-018-5787-x [41] Gou C, Zhang H, Wang K F, Wang F Y, Ji Q. Cascade learning from adversarial synthetic images for accurate pupil detection. Pattern Recognition, 2019, 88: 584-594 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2018.12.014 [42] 王坤峰, 苟超, 王飞跃. 平行视觉: 基于ACP的智能视觉计算方法. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(10): 1490-1500Wang Kun-Feng, Gou Chao, Wang Fei-Yue. Parallel vision: An ACP-based approach to intelligent vision computing. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(10): 1490-1500 [43] Wang K F, Gou C, Zheng N N, Rehg J M, Wang F Y. Parallel vision for perception and understanding of complex scenes: Methods, framework, and perspectives. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2017, 48(3): 299-329 doi: 10.1007/s10462-017-9569-z [44] 李力, 林懿伦, 曹东璞, 郑南宁, 王飞跃. 平行学习—机器学习的一个新型理论框架. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(1): 1-8Li Li, Lin Yi-Lun, Cao Dong-Pu, Zheng Nan-Ning, Wang Fei-Yue. Parallel learning-a new framework for machine learning. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(1): 1-8 [45] Li L, Lin Y L, Zheng N N, Wang F Y. Parallel learning: A perspective and a framework. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2017, 4(3): 389-395 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2017.7510493 [46] Shrivastava A, Pfister T, Tuzel O, Susskind J, Wang W D, Webb R. Learning from simulated and unsupervised images through adversarial training. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 2242−2251 [47] 王坤峰, 苟超, 段艳杰, 林懿伦, 郑心湖, 王飞跃. 生成式对抗网络GAN的研究进展与展望. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(3): 321-332Wang Kun-Feng, Gou Chao, Duan Yan-Jie, Lin Yi-Lun, Zheng Xin-Hu, Wang Fei-Yue. Generative adversarial networks: The state of the art and beyond. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(3): 321-332 [48] Choi J H, Lee K I, Kim Y C, Song B C. Accurate eye pupil localization using heterogeneous CNN models. In: Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP). Taipei, China: IEEE, 2019. 2179−2183 [49] Lee K I, Jeon J H, Song B C. Deep Learning-Based Pupil Center Detection for Fast and Accurate Eye Tracking System In: Proceeding of European Conference on Computer Vision. Cham, Switzerland: Springer, 2020. 36−52 [50] Wang K, Ji Q. 3D gaze estimation without explicit personal calibration. Pattern Recognition, 2018, 79: 216-227 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2018.01.031 [51] Guestrin E D, Eizenman M. General theory of remote gaze estimation using the pupil center and corneal reflections. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2006, 53(6): 1124-1133 doi: 10.1109/TBME.2005.863952 [52] Villanueva A, Cabeza R. A novel gaze estimation system with one calibration point. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B (Cybernetics), 2008, 38(4): 1123-1138 doi: 10.1109/TSMCB.2008.926606 [53] Hennessey C, Noureddin B, Lawrence P. A single camera eye-gaze tracking system with free head motion. In: Proceedings of the 2006 Symposium on Eye Tracking Research & Applications. San Diego, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, 2006. 87−94 [54] Goss D A, West R W. Introduction to the Optics of the Eye. Boston: Butterworth-Heinemann Medical, 2001. [55] Liu J H, Chi J N, Hu W X, Wang Z L. 3D model-based gaze tracking via iris features with a single camera and a single light source. IEEE Transactions on Human-Machine Systems, 2021, 51(2): 75-86 doi: 10.1109/THMS.2020.3035176 [56] Zhou X L, Cai H B, Li Y F, Liu H H. Two-eye model-based gaze estimation from a Kinect sensor. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Singapore: IEEE, 2017. 1646−1653 [57] Yoo D H, Chung M J. A novel non-intrusive eye gaze estimation using cross-ratio under large head motion. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2005, 98(1): 25-51 doi: 10.1016/j.cviu.2004.07.011 [58] Yoo D H, Kim J H, Lee B R, Chung M J. Non-contact eye gaze tracking system by mapping of corneal reflections. In: Proceedings of the 5th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face Gesture Recognition. Washington, USA: IEEE, 2002. 101−106 [59] Cheng H, Liu Y Q, Fu W H, Ji Y L, Yang L, Zhao Y, et al. Gazing point dependent eye gaze estimation. Pattern Recognition, 2017, 71: 36-44 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2017.04.026 [60] Coutinho F L, Morimoto C H. Free head motion eye gaze tracking using a single camera and multiple light sources. In: Proceedings of the 19th Brazilian Symposium on Computer Graphics and Image Processing. Amazonas, Brazil: IEEE, 2006. 171−178 [61] Coutinho F L, Morimoto C H. A depth compensation method for cross-ratio based eye tracking. In: Proceedings of the 2010 Symposium on Eye-Tracking Research & Applications. Austin, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, 2010. 137−140 [62] Hansen D W, Agustin J S, Villanueva A. Homography normalization for robust gaze estimation in uncalibrated setups. In: Proceedings of the 2010 Symposium on Eye-Tracking Research & Applications. Austin, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, 2010. 13−20 [63] Cerrolaza J J, Villanueva A, Villanueva M, Cabeza R. Error characterization and compensation in eye tracking systems. In: Proceedings of the 2012 Symposium on Eye Tracking Research and Applications. Santa Barbara, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, 2012. 205−208 [64] Arar N M, Gao H, Thiran J P. Towards convenient calibration for cross-ratio based gaze estimation. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision. Waikoloa, USA: IEEE, 2015. 642−648 [65] Coutinho F L, Morimoto C H. Improving head movement tolerance of cross-ratio based eye trackers. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2013, 101(3): 459-481 doi: 10.1007/s11263-012-0541-8 [66] Arar N M, Gao H, Thiran J P. Robust gaze estimation based on adaptive fusion of multiple cameras. In: Proceedings of the 11th IEEE International Conference and Workshops on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FG). Ljubljana, Slovenia: IEEE, 2015. 1−7 [67] Sasaki M, Nagamatsu T, Takemura K. Screen corner detection using polarization camera for cross-ratio based gaze estimation. In: Proceedings of the 11th ACM Symposium on Eye Tracking Research & Applications. Denver, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, 2019. 24 [68] Kanai S, Date H. Homography-based low-cost gaze estimation and its application to the usability assessment of digital prototypes of information appliances. In: Proceedings of the 2013 International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference. Portland, USA: ASME, 2013. 12931 [69] Ma C F, Baek S J, Choi K A, Ko S J. Improved remote gaze estimation using corneal reflection-adaptive geometric transforms. Optical Engineering, 2014, 53(5): 053112 [70] Shin Y G, Choi K A, Kim S T, Ko S J. A novel single IR light based gaze estimation method using virtual glints. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 2015, 61(2): 254-260 doi: 10.1109/TCE.2015.7150601 [71] Luo K Q, Jia X, Xiao H, Liu D M, Peng L, Qiu J, et al. A new gaze estimation method based on homography transformation derived from geometric relationship. Applied Sciences, 2020, 10(24): Article No. 9079 [72] Huang J B, Cai Q, Liu Z C, Ahuja N, Zhang Z Y. Towards accurate and robust cross-ratio based gaze trackers through learning from simulation. In: Proceedings of the 2014 Symposium on Eye Tracking Research and Applications. Safety Harbor, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, 2014. 75−82 [73] Yamazoe H, Utsumi A, Yonezawa T, Abe S. Remote gaze estimation with a single camera based on facial-feature tracking without special calibration actions. In: Proceedings of the 2008 Symposium on Eye Tracking Research & Applications. Savannah, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, 2008. 245−250 [74] Chen J X, Ji Q. 3D gaze estimation with a single camera without IR illumination. In: Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Pattern Recognition. Tampa, USA: IEEE, 2008. 1−4 [75] Vicente F, Huang Z H, Xiong X H, De la Torre F, Zhang W D, Levi D. Driver gaze tracking and eyes off the road detection system. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2015, 16(4): 2014-2027 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2015.2396031 [76] Sesma L, Villanueva A, Cabeza R. Evaluation of pupil center-eye corner vector for gaze estimation using a web cam. In: Proceedings of the 2012 Symposium on Eye Tracking Research and Applications. Santa Barbara, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, 2012. 217−220 [77] Sun L, Liu Z C, Sun M T. Real time gaze estimation with a consumer depth camera. Information Sciences, 2015, 320: 346-360 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2015.02.004 [78] Wood E, Baltrušaitis T, Morency L P, Robinson P, Bulling A. A 3D morphable eye region model for gaze estimation. In: Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Springer, 2016. 297−313 [79] Wang K, Ji Q. Real time eye gaze tracking with 3D deformable eye-face model. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 1003−1011 [80] Park S, Zhang X C, Bulling A, Hilliges O. Learning to find eye region landmarks for remote gaze estimation in unconstrained settings. In: Proceedings of the 2018 ACM Symposium on Eye Tracking Research & Applications. Warsaw, Poland: Association for Computing Machinery, 2018. 21 [81] Wood E, Baltruaitis T, Zhang X C, Sugano Y, Robinson P, Bulling A. Rendering of eyes for eye-shape registration and gaze estimation. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Santiago, Chile: IEEE, 2015. 3756−3764 [82] Yiu Y H, Aboulatta M, Raiser T, Ophey L, Flanagin V L, zu Eulenburg P, et al. DeepVOG: Open-source pupil segmentation and gaze estimation in neuroscience using deep learning. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 2019, 324: 108307 [83] Świrski L, Dodgson N. A fully-automatic, temporal approach to single camera, glint-free 3D eye model fitting. Proc. ECEM. 2013. 1−10 [84] Huang M X, Kwok T C K, Ngai G, Leong H V, Chan S C F. Building a self-learning eye gaze model from user interaction data. In: Proceedings of the 22nd ACM international conference on Multimedia. Orlando, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, 2014. 1017−1020 [85] Zhang Y X, Bulling A, Gellersen H. Pupil-canthi-ratio: A calibration-free method for tracking horizontal gaze direction. In: Proceedings of the 2014 International Working Conference on Advanced Visual Interfaces. Como, Italy: Association for Computing Machinery, 2014. 129−132 [86] Wu Y L, Yeh C T, Hung W C, Tang C Y. Gaze direction estimation using support vector machine with active appearance model. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2014, 70(3): 2037-2062 doi: 10.1007/s11042-012-1220-z [87] Chuang M C, Bala R, Bernal E A, Paul P, Burry A. Estimating gaze direction of vehicle drivers using a smartphone camera. In: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. Columbus, USA: IEEE, 2014. 165−170 [88] Wang K, Ji Q. Real time eye gaze tracking with Kinect. In: Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR). Cancun, Mexico: IEEE, 2016. 2752−2757 [89] Cao L, Gou C, Wang K F, Xiong G, Wang F Y. Gaze-aided eye detection via appearance learning. In: Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR). Beijing, China: IEEE, 2018. 1965−1970 [90] Park S, Spurr A, Hilliges O. Deep pictorial gaze estimation. In: Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 741−757 [91] Zhang Y X, Bulling A, Gellersen H. Discrimination of gaze directions using low-level eye image features. In: Proceedings of the 1st International Workshop on Pervasive Eye Tracking & Mobile Eye-Based Interaction. Beijing, China: Association for Computing Machinery, 2011. 9−14 [92] Wood E, Baltrušaitis T, Morency L P, Robinson P, Bulling A. Learning an appearance-based gaze estimator from one million synthesised images. In: Proceedings of the 9th Biennial ACM Symposium on Eye Tracking Research & Applications. Charleston, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, 2016. 131−138 [93] Sugano Y, Matsushita Y, Sato Y. Learning-by-synthesis for appearance-based 3D gaze estimation. In: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Columbus, USA: IEEE, 2014. 1821−1828 [94] Wang Y F, Shen T Y, Yuan G L, Bian J M, Fu X P. Appearance-based gaze estimation using deep features and random forest regression. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2016, 110: 293-301 doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2016.07.038 [95] Kacete A, Séguier R, Collobert M, Royan J. Unconstrained gaze estimation using random forest regression voting. In: Proceedings of the 13th Asian Conference on Computer Vision. Taipei, China: Springer, 2017. 419−432 [96] Huang Q, Veeraraghavan A, Sabharwal A. TabletGaze: Dataset and analysis for unconstrained appearance-based gaze estimation in mobile tablets. Machine Vision and Applications, 2017, 28(5-6): 445-461 doi: 10.1007/s00138-017-0852-4 [97] Funes-Mora K A, Odobez J M. Gaze estimation in the 3D space using RGB-D sensors. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2016, 118(2): 194-216 doi: 10.1007/s11263-015-0863-4 [98] Yu Y, Liu G, Odobez J M. Deep multitask gaze estimation with a constrained landmark-gaze model. In: Proceedings of the 2018 European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Munich, Germany: Springer, 2019. 456−474 [99] Wang K, Zhao R, Su H, Ji Q. Generalizing eye tracking with Bayesian adversarial learning. In: Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 11899−11908 [100] Ali A, Kim Y G. Deep fusion for 3D gaze estimation from natural face images using multi-stream CNNs. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 69212-69221 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2986815 [101] Zhou X L, Jiang J Q, Liu Q Q, Fang J W, Chen S Y, Cai H B. Learning a 3D gaze estimator with adaptive weighted strategy. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 82142-82152 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2990685 [102] Wang Z C, Zhao J, Lu C, Huang H, Yang F, Li L J, et al. Learning to detect head movement in unconstrained remote gaze estimation in the wild. In: Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). Snowmass, USA: IEEE, 2020. 3432−3441 [103] Chen Z K, Shi B E. Towards high performance low complexity calibration in appearance based gaze estimation. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2001.09284, 2020 [104] Krafka K, Khosla A, Kellnhofer P, Kannan H, Bhandarkar S, Matusik W, et al. Eye tracking for everyone. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 2176−2184 [105] Jesorsky O, Kirchberg K J, Frischholz R W. Robust face detection using the hausdorff distance. In: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Audio-and Video-Based Biometric Person Authentication. Halmstad, Sweden: Springer, 2001. 90−95 [106] Smith B A, Yin Q, Feiner S K, Nayar S K. Gaze locking: passive eye contact detection for human-object interaction In: Proceeding of the 26th annual ACM symposium on User interface software and technology. New York, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, 2013. 271−280 [107] Alaslani M G, Elrefaei L A. Convolutional neural network based feature extraction for iris recognition. International Journal of Computer Science & Information Technology (IJCSIT), 2018, 10(2): 65-78 [108] Fuhl W, Kübler T, Sippel K, Rosenstiel W, Kasneci E. ExCuSe: Robust pupil detection in real-world scenarios. In: Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Computer Analysis of Images and Patterns. Valletta, Malta: Springer, 2015. 39−51 [109] Tonsen M, Zhang X C, Sugano Y, Bulling A. Labelled pupils in the wild: A dataset for studying pupil detection in unconstrained environments. In: Proceedings of the 9th Biennial ACM Symposium on Eye Tracking Research & Applications. Seattle, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, 2016. 139−142 [110] Garbin S J, Shen Y R, Schuetz I, Cavin R, Hughes G, Talathi S S. OpenEDS: Open eye dataset. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1905.03702, 2019 [111] Fuhl W, Kasneci G, Kasneci E. TEyeD: Over 20 million real-world eye images with pupil, eyelid, and iris 2D and 3D segmentations, 2D and 3D landmarks, 3D eyeball, gaze vector, and eye movement types. In: Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality (ISMAR). Bari, Italy: IEEE, 2021. 367−375 [112] Ahuja K, Banerjee R, Nagar S, Dey K, Barbhuiya F. Eye center localization and detection using radial mapping. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP). Phoenix, USA: IEEE, 2016. 3121−3125 [113] Choi I, Kim D. A variety of local structure patterns and their hybridization for accurate eye detection. Pattern Recognition, 2017, 61: 417−432 [114] Cai H B, Liu B L, Ju Z J, Thill S, Belpaeme T, Vanderborght B, et al. Accurate eye center localization via hierarchical adaptive convolution. In: Proceedings of the 29th British Machine Vision Conference. Newcastle, UK: British Machine Vision Association Press, 2018. 284 [115] Levinshtein A, Phung E, Aarabi P. Hybrid eye center localization using cascaded regression and hand-crafted model fitting. Image and Vision Computing, 2018, 71: 17-24 doi: 10.1016/j.imavis.2018.01.003 [116] Villanueva A, Ponz V, Sesma-Sanchez L, Ariz M, Porta S, Cabeza R. Hybrid method based on topography for robust detection of iris center and eye corners. ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing, Communications, and Applications (TOMM), 2013, 9(4): 1−20 [117] Funes Mora K A, Monay F, Odobez J M. EYEDIAP: A database for the development and evaluation of gaze estimation algorithms from RGB and RGB-D cameras. In: Proceedings of the 2014 Symposium on Eye Tracking Research and Applications. Safety Harbor, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, 2014. 255−258 [118] Zhang X C, Sugano Y, Fritz M, Bulling A. MPⅡGaze: Real-world dataset and deep appearance-based gaze estimation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2019, 41(1): 162-175 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2778103 [119] Fischer T, Chang H J, Demiris Y. RT-GENE: Real-time eye gaze estimation in natural environments. In: Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 339−357 [120] Kellnhofer P, Recasens A, Stent S, Matusik W, Torralba A. Gaze360: Physically unconstrained gaze estimation in the wild. In: Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Seoul, Korea: IEEE, 2019. 6911−6920 [121] Porta S, Bossavit B, Cabeza R, Larumbe-Bergera A, Garde G, Villanueva A. U2Eyes: A binocular dataset for eye tracking and gaze estimation. In: Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW). Seoul, Korea: IEEE, 2019. 3660−3664 [122] Zhang X C, Park S, Beeler T, Bradley D, Tang S, Hilliges O. ETH-XGaze: A large scale dataset for gaze estimation under extreme head pose and gaze variation. In: Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision. Glasgow, UK: Springer, 2020. 365−381 [123] Park S, De Mello S, Molchanov P, Iqbal U, Hilliges O, Kautz J. Few-shot adaptive gaze estimation. In: Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Seoul, Korea: IEEE, 2019. 9367−9376 [124] Cheng Y H, Zhang X C, Lu F, Sato Y. Gaze estimation by exploring two-eye asymmetry. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 5259-5272 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.2982828 [125] Cheng Y H, Huang S Y, Wang F, Qian C, Lu F. A coarse-to-fine adaptive network for appearance-based gaze estimation. In: Proceedings of the 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. New York, USA: AAAI, 2020. 10623−10630 [126] Wang K, Zhao R, Ji Q. A hierarchical generative model for eye image synthesis and eye gaze estimation. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 440−448 [127] Chen Z K, Shi B E. Appearance-based gaze estimation using dilated-convolutions. In: Proceedings of the 14th Asian Conference on Computer Vision. Perth, Australia: Springer, 2019. 309−324 [128] Zhang X C, Sugano Y, Fritz M, Bulling A. Appearance-based gaze estimation in the wild. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Boston, USA: IEEE, 2015. 4511−4520 [129] Santini T, Fuhl W, Kasneci E. CalibMe: Fast and unsupervised eye tracker calibration for gaze-based pervasive human-computer interaction. In: Proceedings of the 2017 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. Denver, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, 2017. 2594−2605 [130] Wood E, Bulling A. EyeTab: Model-based gaze estimation on unmodified tablet computers. In: Proceedings of the 2014 Symposium on Eye Tracking Research and Applications. Safety Harbor, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, 2014. 207−210 [131] Klaib A F, Alsrehin N O, Melhem W Y, Bashtawi H O. IoT smart home using eye tracking and voice interfaces for elderly and special needs people. Journal of Communications, 2019, 14(7): 614-621 [132] Lim Y, Ramasamy S, Gardi A, Kistan T, Sabatini R. Cognitive human-machine interfaces and interactions for unmanned aircraft. Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems, 2018, 91(3-4): 755-774 [133] Pongsakornsathien N, Lim Y X, Gardi A, Hilton S, Planke L, Sabatini R, et al. Sensor networks for aerospace human-machine systems. Sensors, 2019, 19(16): 3465 [134] Lee J, Ahn J H. Attention to banner ads and their effectiveness: An eye-tracking approach. International Journal of Electronic Commerce, 2012, 17(1): 119-137 doi: 10.2753/JEC1086-4415170105 [135] Higgins E, Leinenger M, Rayner K. Eye movements when viewing advertisements. Frontiers in Psychology, 2014, 5: 210 [136] Chen Y Y, Lv Y S, Li Z J, Wang F Y. Long short-term memory model for traffic congestion prediction with online open data. In: Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC). Rio de Janeiro, Brazil: IEEE, 2016. 132−137 [137] Rezaei M, Klette R. Novel adaptive eye detection and tracking for challenging lighting conditions. In: Proceedings of the 2013 Asian Conference on Computer Vision. Daejeon, Korea: Springer, 2013. 427−440 [138] Mandal B, Li L Y, Wang G S, Lin J. Towards detection of bus driver fatigue based on robust visual analysis of eye state. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2017, 18(3): 545-557 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2016.2582900 [139] Zeeb K, Buchner A, Schrauf M. What determines the take-over time? An integrated model approach of driver take-over after automated driving. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2015, 78: 212-221 [140] Deng T, Yan H M, Qin L, Ngo T, Manjunath B S. How do drivers allocate their potential attention? Driving fixation prediction via convolutional neural networks. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2020, 21(5): 2146-2154 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2019.2915540 [141] Li S P, Zhang X L, Kim F J, da Silva R D, Gustafson D, Molina W R. Attention-aware robotic laparoscope based on fuzzy interpretation of eye-gaze patterns. Journal of Medical Devices, 2015, 9(4): 041007 [142] Chen Y, Gale A. Using eye gaze in intelligent interactive imaging training. In: Proceedings of the 2010 Workshop on Eye Gaze in Intelligent Human Machine Interaction. Hong Kong, China: Association for Computing Machinery, 2010. 41−44 [143] Khosravan N, Celik H, Turkbey B, Jones E C, Wood B, Bagci U. A collaborative computer aided diagnosis (C-CAD) system with eye-tracking, sparse attentional model, and deep learning. Medical Image Analysis, 2019, 51: 101-115 doi: 10.1016/j.media.2018.10.010 [144] Jarodzka H, van Gog T, Dorr M, Scheiter K, Gerjets P. Learning to see: Guiding students'attention via a Model's eye movements fosters learning. Learning and Instruction, 2013, 25: 62-70 doi: 10.1016/j.learninstruc.2012.11.004 [145] Dalmaijer E S, Mathôt S, Van der Stigchel S. PyGaze: An open-source, cross-platform toolbox for minimal-effort programming of eyetracking experiments. Behavior Research Methods, 2014, 46(4): 913-921 doi: 10.3758/s13428-013-0422-2 [146] Krassanakis V, Filippakopoulou V, Nakos B. EyeMMV toolbox: An eye movement post-analysis tool based on a two-step spatial dispersion threshold for fixation identification. Journal of Eye Movement Research, 2014, 7(1): 1-10 [147] Halszka J, Holmqvist K, Gruber H. Eye tracking in Educational Science: Theoretical frameworks and research agendas. Journal of Eye Movement Research, 2017, 10(1), doi: 10.1.3. doi: 10.16910/jemr.10.1.3 [148] Zheng X L, Zeng D, Li H Q, Wang F Y. Analyzing open-source software systems as complex networks. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2008, 387(24): 6190-6200 doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2008.06.050 [149] 王飞跃. 平行系统方法与复杂系统的管理和控制. 控制与决策, 2004, 19(5): 485-489, 514 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-0920.2004.05.002Wang F Y. Parallel system methods for management and control of complex systems. Control and Decision, 2004, 19(5): 485-489, 514 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-0920.2004.05.002 [150] Wang F Y, Wang X, Li L X, Li L. Steps toward parallel intelligence. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2016, 3(4): 345-348 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2016.7510067 [151] Zheng N N, Liu Z Y, Ren P J, Ma Y Q, Chen S T, Yu S Y, et al. Hybrid-augmented intelligence: Collaboration and cognition. Frontiers of Information Technology & Electronic Engineering, 2017, 18(2): 153-179 -





 下载:
下载: