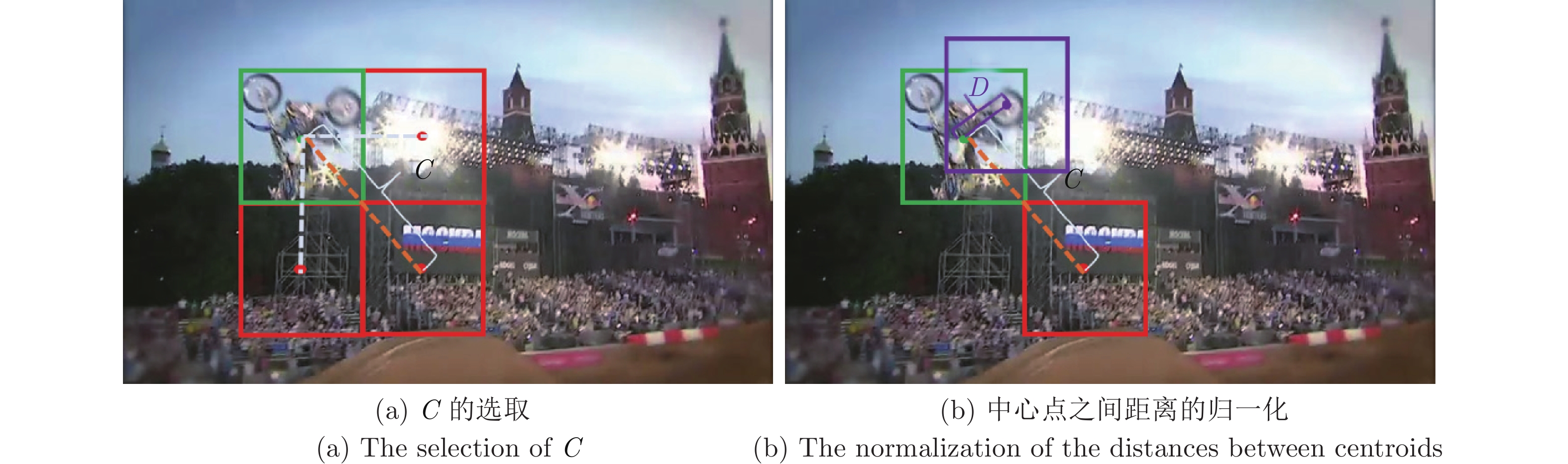
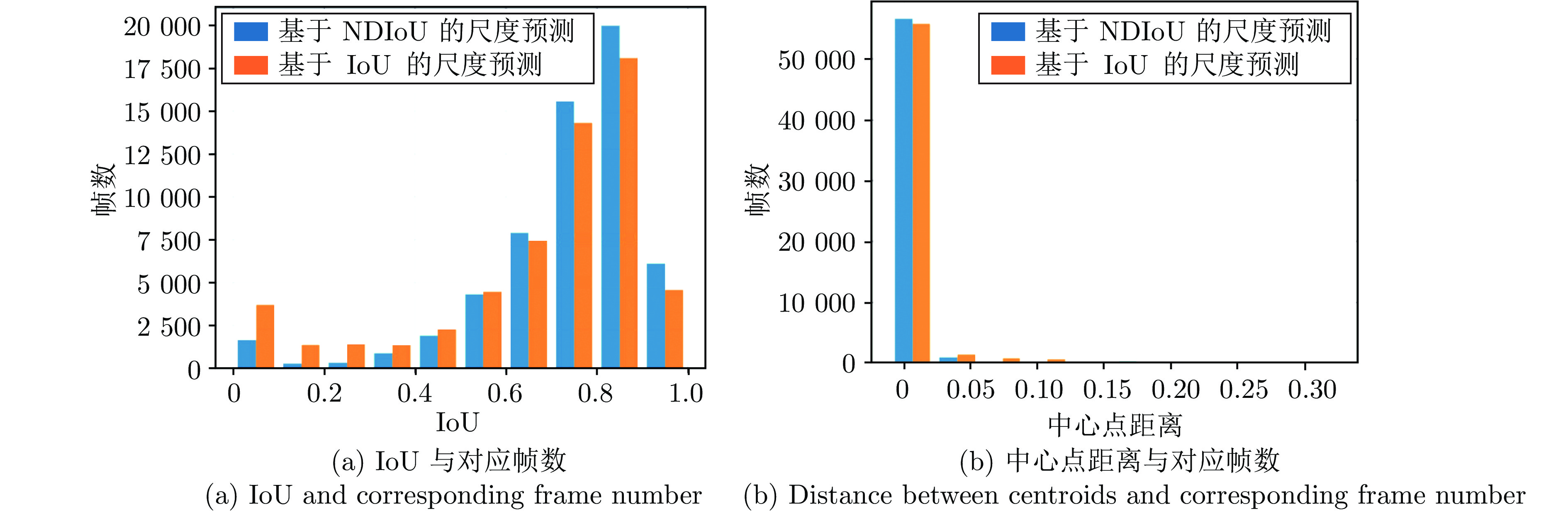
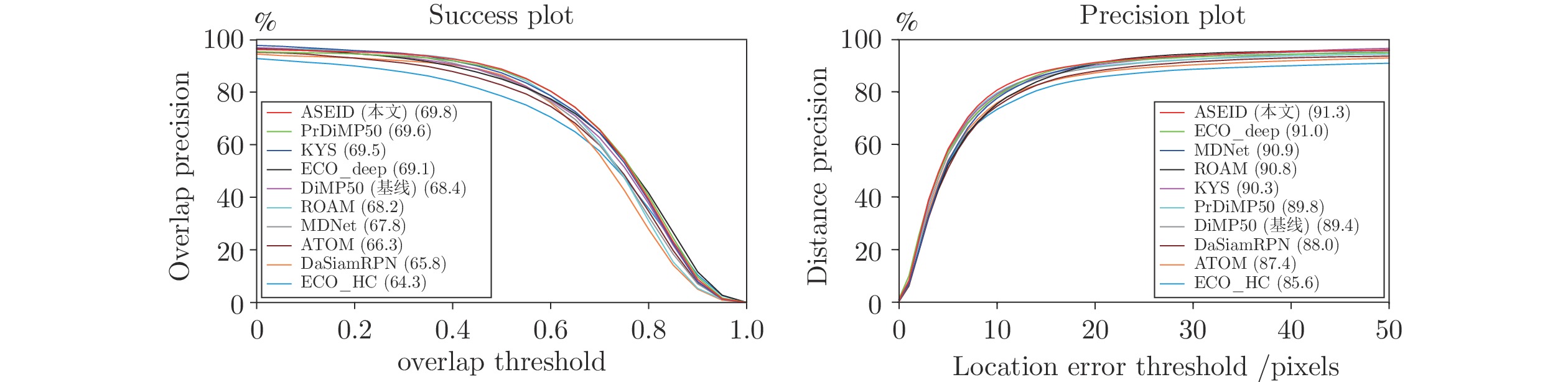
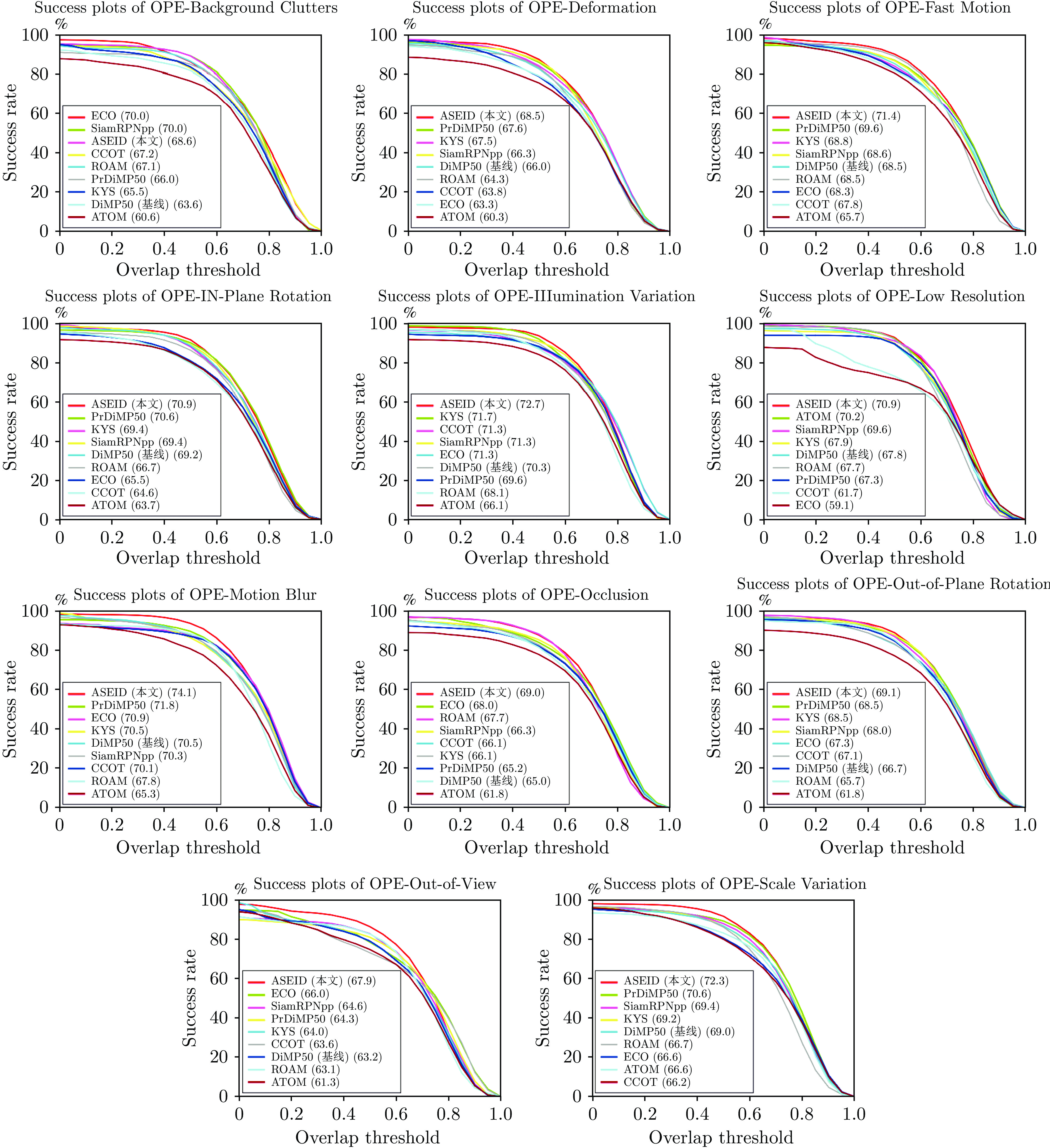
Accurate Scale Estimation With IoU and Distance Between Centroids for Object Tracking
-
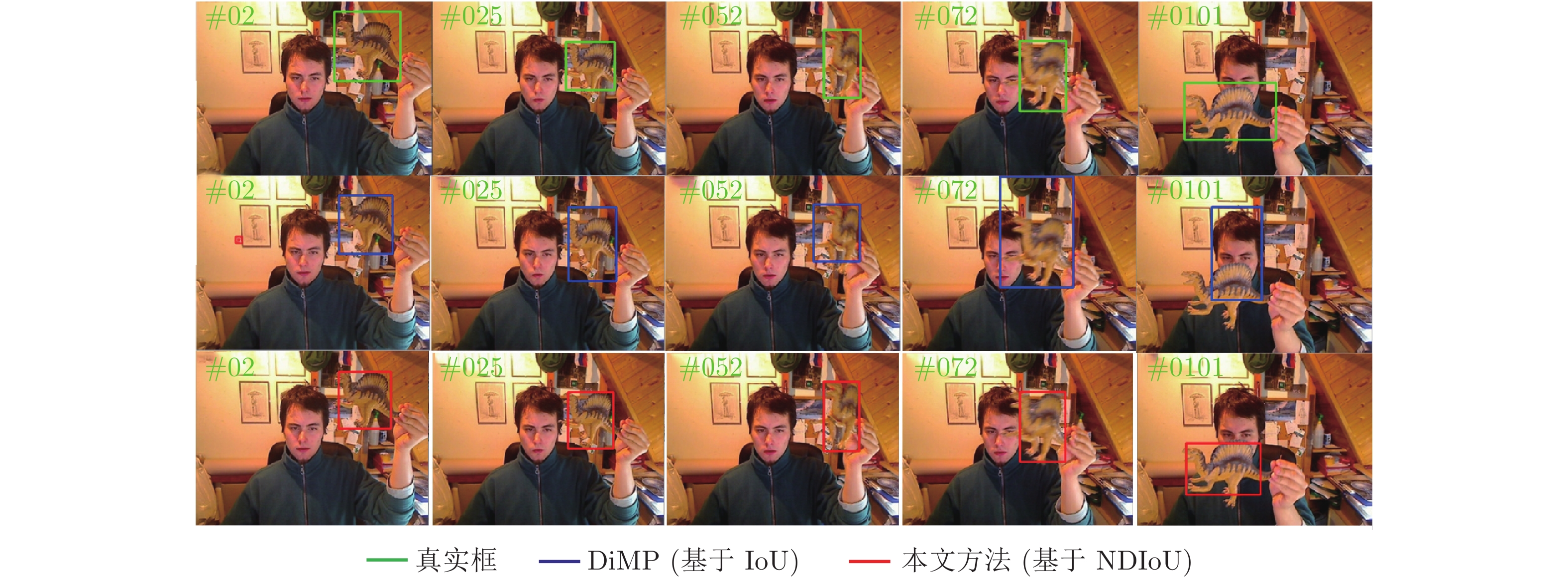
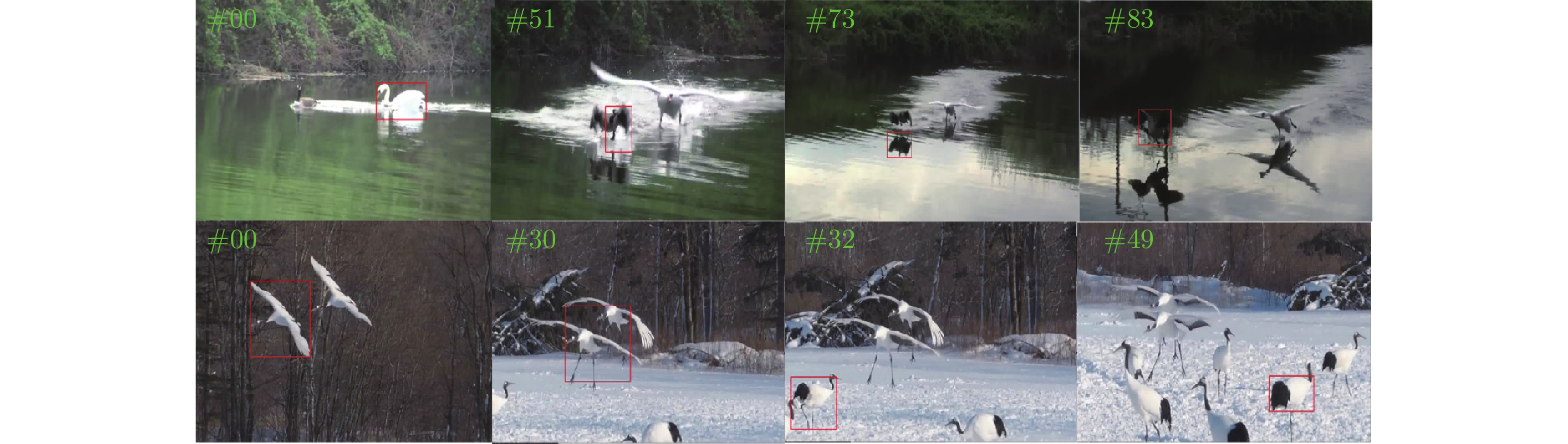
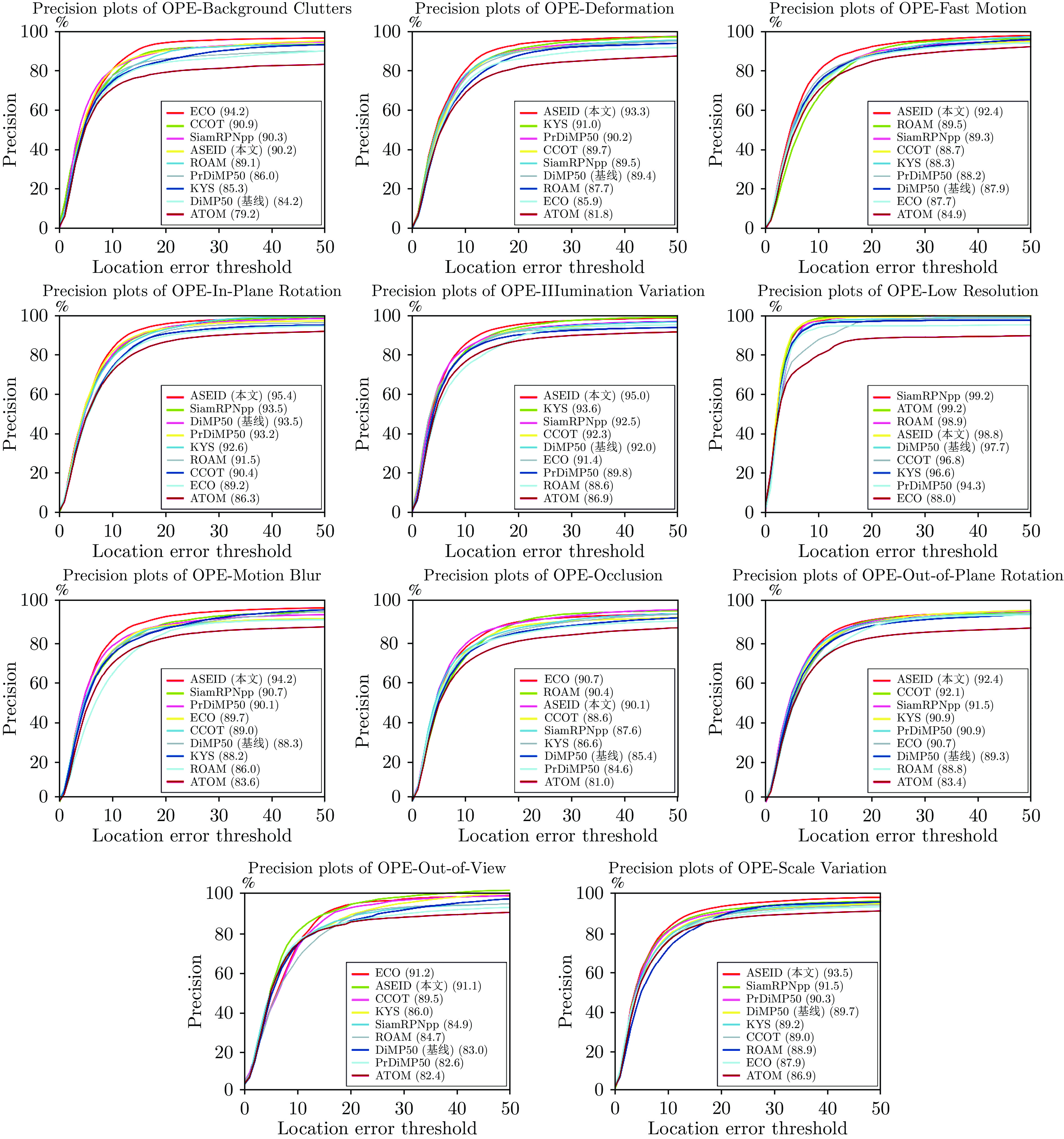
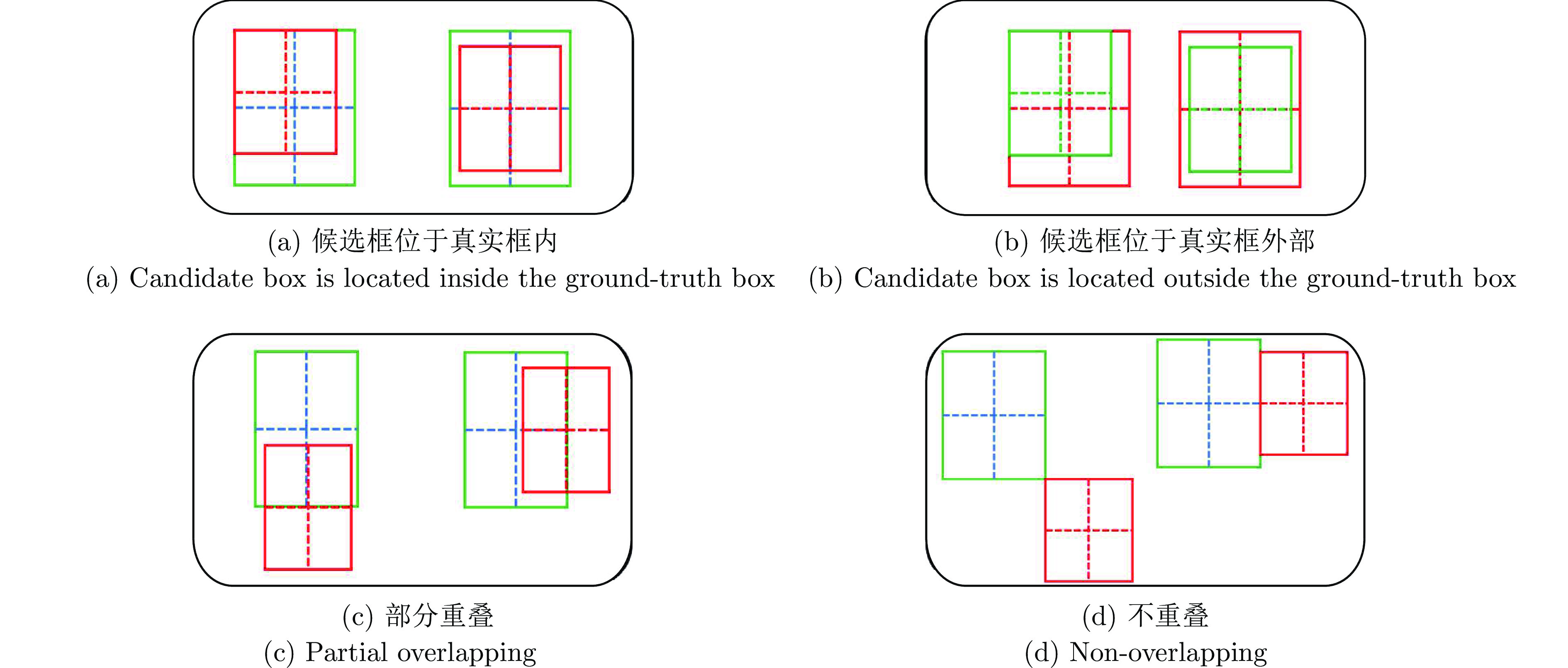
摘要: 通过分析基于交并比(Intersection over union, IoU)预测的尺度估计模型的梯度更新过程, 发现其在训练和推理过程仅将IoU作为度量, 缺乏对预测框和真实目标框中心点距离的约束, 导致外观模型更新过程中模板受到污染, 前景和背景分类时定位出现偏差. 基于此发现, 构建了一种结合IoU和中心点距离的新度量NDIoU (Normalization distance IoU), 在此基础上提出一种新的尺度估计方法, 并将其嵌入判别式跟踪框架. 即在训练阶段以NDIoU为标签, 设计了具有中心点距离约束的损失函数监督网络的学习, 在线推理期间通过最大化NDIoU微调目标尺度, 以帮助外观模型更新时获得更加准确的样本. 在七个数据集上与相关主流方法进行对比, 所提方法的综合性能优于所有对比算法. 特别是在GOT-10k数据集上, 所提方法的AO、$S{R}_{0.50}$和$ S{R}_{0.75} $三个指标达到了65.4%、78.7%和53.4%, 分别超过基线模型4.3%、7.0%和4.2%.Abstract: This paper first analyzes the gradient update process of the scale estimation model of intersection over union (IoU) prediction in detail, and finds that when the IoU is used as a metric in the training and inference process, the target scale estimation in the tracking process is inaccurate due to the absence of the constraint on the distance between the two centroids. As a result, the template is polluted in the updating process of the object appearance model, which cannot discriminate the target and environment. With this insight, we propose a new metric NDIoU (normalization distance IoU) that combines the IoU and distance between two centroids to estimate the target scale and proposes a new scale estimation method, which is embedded into the discriminative tracking framework. Using NDIoU as the label to supervise the distance between centroids, it is incorporated into the loss function to facilitate the learning of the network. During online inference, NDIoU is maximized to fine-tune the target scale. Finally, the proposed method is embedded into the discriminative tracking framework and compared with related state-of-the-art methods on seven data sets. The extensive experiments demonstrate that our method outperforms all the state-of-the-art algorithms. Especially, on the GOT-10k dataset, our method achieves 65.4%, 78.7% and 53.4% on the three metrics of AO, $S{R}_{0.50}$ and $ S{R}_{0.75} $, which are better than the baseline by 4.3%, 7.0% and 4.2%, respectively.
-
表 1 OTB-100数据集上的消融实验
Table 1 Ablation study on OTB-100 dataset
方法 AUC (%) Precision (%) Norm.Pre (%) 帧速率(帧/s) 多尺度搜索 68.4 88.8 83.8 21 IoU 68.4 89.4 84.2 35 NDIoU 69.8 91.3 87.3 35 表 2 在UAV123数据集上和SOTA算法的比较(%)
Table 2 Compare with SOTA trackers on UAV123 dataset (%)
表 3 在VOT2018数据集上与SOTA方法的比较
Table 3 Compare with SOTA trackers on VOT2018 dataset
表 4 在GOT-10k数据集上与SOTA方法的比较(%)
Table 4 Compare with SOTA trackers on GOT-10k dataset (%)
DCFST[32] PrDiMP50[15] KYS[17] SiamFC++[13] D3S[43] Ocean[12] ROAM[44] ATOM[9] DiMP50 (基线)[14] ASEID (本文) $ \mathit{S}{\mathit{R}}_{0.50}$ 68.3 73.8 75.1 69.5 67.6 72.1 46.6 63.4 71.7 78.7 $ \mathit{S}{\mathit{R}}_{0.75} $ 44.8 54.3 51.5 47.9 46.2 — 16.4 40.2 49.2 53.4 $ \mathit{A}\mathit{O}$ 59.2 63.4 63.6 59.5 59.7 61.1 43.6 55.6 61.1 65.4 表 5 在LaSOT数据集上与SOTA方法的比较(%)
Table 5 Compare with SOTA trackers on LaSOT dataset (%)
表 6 在TrackingNet上与SOTA方法的比较(%)
Table 6 Compare with SOTA trackers on TrackingNet (%)
-
[1] Wu Y, Lim J, Yang M H. Object tracking benchmark. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(9): 1834−1848 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2388226 [2] 孟琭, 杨旭. 目标跟踪算法综述. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(7): 1244−1260Meng Lu, Yang Xu. A survey of object tracking algorithms. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(7): 1244−1260 [3] 尹宏鹏, 陈波, 柴毅, 刘兆栋. 基于视觉的目标检测与跟踪综述. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(10): 1466−1489Yin Hong-Peng, Chen Bo, Chai Yi, Liu Zhao-Dong. Vision-based object detection and tracking: A review. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(10): 1466−1489 [4] 谭建豪, 郑英帅, 王耀南, 马小萍. 基于中心点搜索的无锚框全卷积孪生跟踪器. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(4): 801−812Tan Jian-Hao, Zheng Ying-Shuai, Wang Yao-Nan, Ma Xiao-Ping. AFST: Anchor-free fully convolutional siamese tracker with searching center point. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(4): 801−812 [5] Danelljan M, Häger G, Khan F S, Felsberg M. Learning spatially regularized correlation filters for visual tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Santiago, Chile: IEEE, 2015. 4310−4318 [6] Dai K, Wang D, Lu H C, Sun C, Li J. Visual tracking via adaptive spatially-regularized correlation filters. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 4665−4674 [7] Danelljan M, Häger G, Khan F S, Felsberg M. Discriminative scale space tracking. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(8): 1561−1575 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2609928 [8] Li Y, Zhu J. A scale adaptive kernel correlation filter tracker with feature integration. In: Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Computer Vision. Zurich, Switzerland: Springer, 2014. 254−265 [9] Danelljan M, Bhat G, Khan F S, Felsberg M. ATOM: Accurate tracking by overlap maximization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 4655−4664 [10] Li B, Yan J J, Wu W, Zhu Z, Hu X L. High performance visual tracking with Siamese region proposal network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 8971−8980 [11] Wang Q, Bertinetto L, Hu W M, Torr P H S. Fast online object tracking and segmentation: A unifying approach. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 1328−1338 [12] Zhang Z P, Peng H W, Fu J L, Li B, Hu W M. Ocean: Object-aware anchor-free tracking. In: Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision. Glasgow, UK: Springer, 2020. 771−787 [13] Xu Y D, Wang Z Y, Li Z X, Yuan Y, Yu G. SiamFC++: Towards robust and accurate visual tracking with target estimation guidelines. In: Proceedings of the 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. New York, USA: AAAI, 2020. 12549−12556 [14] Bhat G, Danelljan M, Van Gool L, Timofte R. Learning discriminative model prediction for tracking. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision. Seoul, South Korea: IEEE, 2019. 6181−6190 [15] Danelljan M, Van Gool L, Timofte R. Probabilistic regression for visual tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 7181−7190 [16] Li B, Wu W, Wang Q, Zhang F Y, Xing J L, Yan J J. SiamRPN++: Evolution of Siamese visual tracking with very deep networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 4277−4286 [17] Bhat G, Danelljan M, Van Gool L, Timofte R. Know your surroundings: Exploiting scene information for object tracking. In: Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision. Glasgow, UK: Springer, 2020. 205−221 [18] Girshick R. Fast R-CNN. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Santiago, Chile: IEEE, 2015. 1440−1448 [19] Ren S, He K M, Girshick R, Sun J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137−1149 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031 [20] Jiang B R, Luo R X, Mao J Y, Xiao T T, Jiang Y N. Acquisition of localization confidence for accurate object detection. In: Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 816−832 [21] Mueller M, Smith N, Ghanem B. A benchmark and simulator for UAV tracking. In: Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Springer, 2016. 445−461 [22] Kristan M, Leonardis A, Matas J, Felsberg M, Pflugfelder R, Zajc L Č, et al. The sixth visual object tracking VOT2018 challenge results. In: Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision workshop. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 3−53 [23] Huang L H, Zhao X, Huang K Q. Got-10k: A large high-diversity benchmark for generic object tracking in the wild. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2021, 43(5): 1562−1577 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2957464 [24] Fan H, Lin L T, Yang F, Chu P, Deng G, Yu S J, et al. LaSOT: A high-quality benchmark for large-scale single object tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 5369−5378 [25] Müller M, Bibi A, Giancola S, Subaihi S, Ghanem B. TrackingNet: A large-scale dataset and benchmark for object tracking in the wild. In: Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 310−327 [26] Liang P P, Blasch E, Ling H B. Encoding color information for visual tracking: Algorithms and benchmark. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(12): 5630−5644 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2015.2482905 [27] Zheng Z H, Wang P, Liu W, Li J Z, Ye R G, Ren D W. Distance-IoU loss: Faster and better learning for bounding box regression. In: Proceedings of the 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. New York, USA: AAAI, 2020. 12993−13000 [28] Lin T Y, Maire M, Belongie S, Hays J, Perona P, Ramanan D, et al. Microsoft COCO: Common objects in context. In: Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Computer Vision. Zurich, Switzerland: Springer, 2014. 740−755 [29] Li X, Ma C, Wu B Y, He Z Y, Yang M H. Target-aware deep tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 1369−1378 [30] Paszke A, Gross S, Massa F, Lerer A, Bradbury J, Chanan G, et al. PyTorch: An imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. In: Proceedings of the 2019 Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: MIT Press, 2019. Article No. 721 [31] Danelljan M, Bhat G. PyTracking: Visual tracking library based on PyTorch [Online], available: https://gitee.com/zengzheming/pytracking, November 2, 2021 [32] Zheng L Y, Tang M, Chen Y Y, Wang J Q, Lu H Q. Learning feature embeddings for discriminant model based tracking. In: Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision. Glasgow, UK: Springer, 2020. 759−775 [33] Chen Z D, Zhong B N, Li G R, Zhang S P, Ji R R. Siamese box adaptive network for visual tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 6667−6676 [34] Du F, Liu P, Zhao W, Tang X L. Correlation-guided attention for corner detection based visual tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 6835−6844 [35] Wang N, Zhou W G, Qi G J, Li H Q. POST: Policy-based switch tracking. In: Proceedings of the 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. New York, USA: AAAI, 2020. 12184−12191 [36] Jung I, You K, Noh H, Cho M, Han B. Real-time object tracking via meta-learning: Efficient model adaptation and one-shot channel pruning. In: Proceedings of the 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. New York, USA: AAAI, 2020. 11205−11212 [37] Danelljan M, Bhat G, Khan F S, Felsberg M. ECO: Efficient convolution operators for tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 6931−6939 [38] Bhat G, Johnander J, Danelljan M, Khan F S, Felsberg M. Unveiling the power of deep tracking. In: Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 493−509 [39] Zhu Z, Wang Q, Li B, Wei W, Yan J J, Hu W M. Distractor-aware Siamese networks for visual object tracking. In: Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 103−119 [40] Sun C, Wang D, Lu H C, Yang M H. Correlation tracking via joint discrimination and reliability learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 489−497 [41] Bai S, He Z Q, Dong Y, Bai H L. Multi-hierarchical independent correlation filters for visual tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME). London, UK: IEEE, 2020. 1−6 [42] Xu T Y, Feng Z H, Wu X J, Kittler J. Learning adaptive discriminative correlation filters via temporal consistency preserving spatial feature selection for robust visual object tracking. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28(11): 5596−5609 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2919201 [43] Lukezic A, Matas J, Kristan M. D3S——A discriminative single shot segmentation tracker. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 7131−7140 [44] Yang T Y, Xu P F, Hu R B, Chai H, Chan A B. ROAM: Recurrently optimizing tracking model. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 6717−6726 [45] Huang L H, Zhao X, Huang K Q. GlobalTrack: A simple and strong baseline for long-term tracking. In: Proceedings of the 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. New York, USA: AAAI, 2020. 11037−11044 [46] Nam H, Han B. Learning multi-domain convolutional neural networks for visual tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 4293−4302 [47] Wang N, Song Y B, Ma C, Zhou W G, Liu W. Unsupervised deep tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 1308−1317 [48] Huang J L, Zhou W G. Re.2EMA: Regularized and reinitialized exponential moving average for target model update in object tracking. In: Proceedings of the 33th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence and the 31st Innovative Applications of Artificial Intelligence Conference and the 9th AAAI Symposium on Educational Advances in Artificial Intelligence. Honolulu, USA: AIAA, 2019. Article No. 1037 [49] Jung I, Son J, Baek M, Han B. Real-time MDNet. In: Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 89−104 [50] Choi J, Kwon J, Lee K M. Deep meta learning for real-time target-aware visual tracking. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision. Seoul, South Korea: IEEE, 2019. 911−920 -




 下载:
下载: