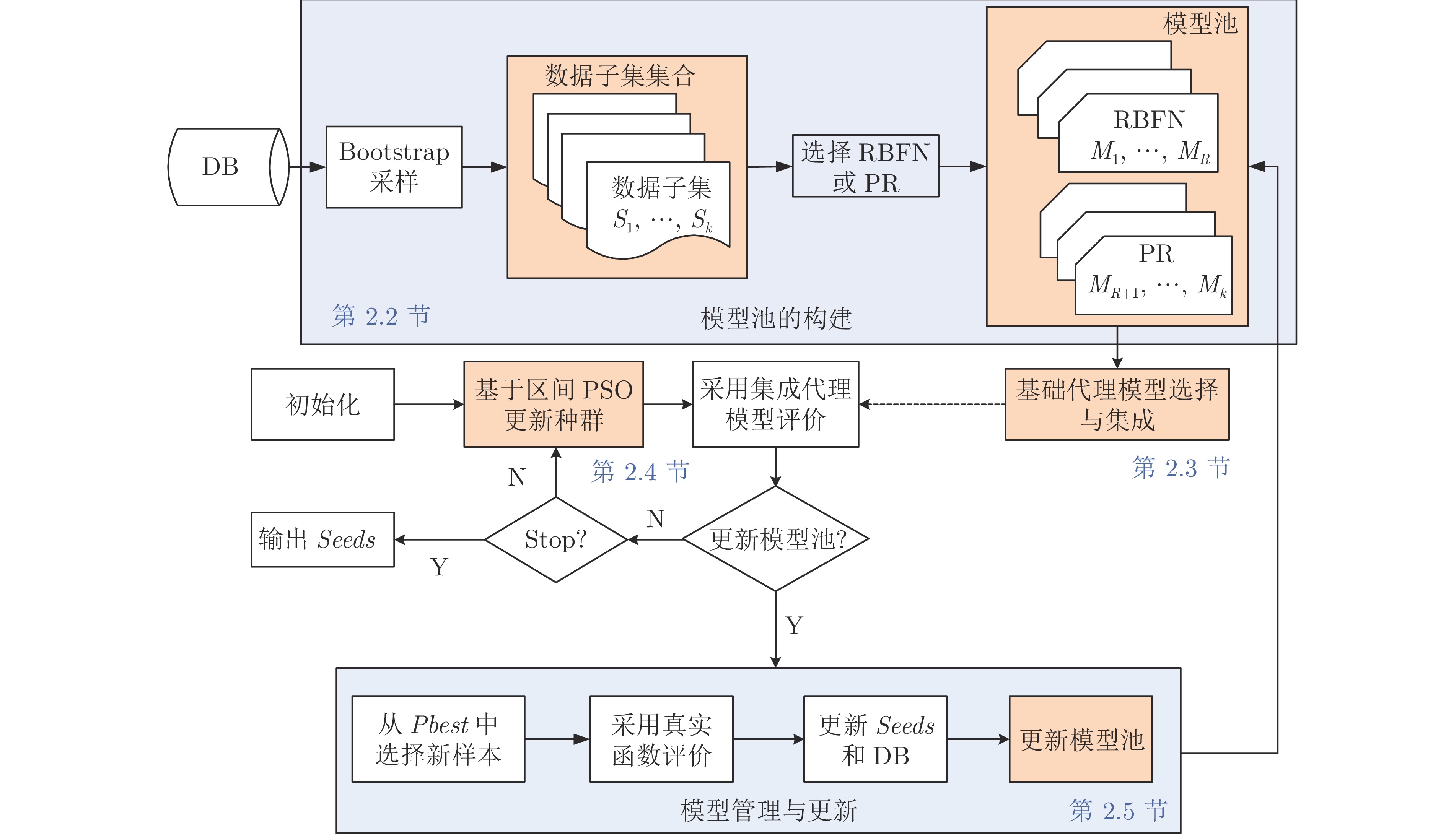
Interval Multimodal Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm Assisted by Heterogeneous Ensemble Surrogate
-
摘要: 现实生活中的很多黑盒优化问题可归为高计算代价的多模态优化问题(Multimodal optimization problem, MMOP), 即昂贵多模态优化问题(Expensive MMOP, EMMOP). 在处理该类问题时, 决策者希望以尽量少的计算代价(即尽量少的真实函数评价次数)找到多个高质量的最优解. 然而, 已有代理辅助的进化优化算法(Surrogate-assisted evolutionary algorithm, SAEA)很少考虑问题的多模态属性, 运行一次仅可获得问题的一个最优解. 鉴于此, 研究一种异构集成代理辅助的区间多模态粒子群优化(Interval multimodal particle swarm optimization algorithm assisted by heterogeneous ensemble surrogate, IMPSO-HES)算法. 首先, 借助异构集成的思想构建一个由多个基础代理模型组成的模型池; 随后, 依据待评价粒子与已发现模态之间的匹配关系, 从模型池中自主选择部分基础代理模型进行集成, 并使用集成后的代理模型预测该粒子的适应值. 进一步, 为节约代理模型管理的代价, 设计一种增量式的代理模型管理策略; 为减少代理模型预测误差对算法性能的影响, 首次将区间排序关系引入到进化过程中. 将所提算法与当前流行的5种代理辅助进化优化算法和7 种最先进的多模态优化算法进行对比, 在20个测试函数和1个建筑节能实际问题上的实验结果表明, 所提算法可以在较少计算代价下获得问题的多个高竞争最优解.Abstract: Many real-world black-box optimization problems can be classified as multimodal optimization problems (MMOPs) with high computational cost, that is, expensive multimodal optimization problems (EMMOPs). When dealing with such problems, decision-makers hope to find multiple high-quality solutions with less computational cost (i.e., the least number of real function evaluations). However, existing surrogate-assisted evolutionary algorithms (SAEAs) seldom consider the multimodal properties of problem, and they can only obtain one optimal solution of the problem at a time. In view of this, this paper studies an interval multimodal particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm assisted by heterogeneous ensemble surrogate (IMPSO-HES). Firstly, a model pool composed of multiple basic surrogate models is constructed with the idea of heterogeneous ensemble. Then, according to the matching relationship between the particle to be evaluated and the discovered modalities, some basic surrogate models will be selected from the model pool for integration, and the integrated surrogate model is utilized to predict the fitness value of the particle. Furthermore, in order to save the cost of model management, an incremental surrogate model management strategy is designed. In order to reduce the influence of prediction error of surrogate model on the algorithm's performance, the interval ordering relation is introduced into the evolutionary process for the first time. The proposed algorithm is compared with five SAEAs and seven state-of-the-art multimodal algorithms, experimental results on 20 benchmark functions and the building energy conservation problem show that the proposed algorithm can obtain multiple highly-competitive optimal solutions at a low computational cost.
-
表 1 基准问题
Table 1 Benchmark problems
问题 测试函数 维数 变量空间 全局/局部解个数 全局最优解的目标值 F1 Ellipsoid 10/20 $\boldsymbol{X} \in [-1,1]^{D}$ 1/0 0 F2 Ackley 10/20 $\boldsymbol{X} \in [-30,30]^{D}$ 1/many 0 F3 Rastrigin 10/20 $\boldsymbol{X }\in [-5.12,5.12]^{D}$ 1/many 0 F4 Rosenbrock 10/20 $\boldsymbol{X} \in [-2.048,2.048]^{D}$ 1/many 0 F5 Griewank 10/20 $\boldsymbol{X} \in [-600,600]^{D}$ 1/many 0 F6 Reverse five-uneven-peak trap 1 $\boldsymbol{X} \in [0,30] $ 2/3 −200 F7 Reverse equal maxima 1 $\boldsymbol{X} \in [0,1] $ 5/0 −1 F8 Reverse uneven decreasing maxima 1 $\boldsymbol{X} \in [0,1] $ 1/4 −1 F9 Reverse himmelblau 2 $\boldsymbol{X} \in [-6,6]^{D}$ 4/0 −200 F10 Six-hump camel 2 $x_1\in[-1.9,1.9], x_2\in[-1.1,1.1] $ 2/2 −1.031 6 F11 Reverse shubert 2 $\boldsymbol{X} \in [-10,10]^{D}$ 18/many −186.73 F12 Reverse vincent 2 $\boldsymbol{X} \in [0.25,10]^{D}$ 36/0 −1 F13 Reverse modified rastrigin 2 $\boldsymbol{X} \in [0,1]^{D}$ 12/0 2 F14 Reverse CF1 2 $\boldsymbol{X}\in [-5,5]^D$ 6/0 0 F15 Reverse CF2 2 $\boldsymbol{X}\in [-5,5]^D$ 8/0 0 F16 Reverse CF3 2 $\boldsymbol{X} \in[-5,5]^D $ 6/0 0 F17 Reverse CF4 3 $\boldsymbol{X}\in [-5,5]^D$ 8/0 0 F18 UrsemF4 back 2 $\boldsymbol{X }\in [-2,2]^{D}$ 2/0 −0.267 9 F19 Branin RCOS 2 $x_1\in[-5,10], x_2\in[0,15] $ 3/0 0.397 8 F20 Waves 2 $x_1\in[-0.9,1.2], x_2\in[-1.2,1.2]$ 1/9 −7.776 表 2 F6 ~ F20的幅值精度和距离精度
Table 2 Amplitude accuracy and distance accuracy for F6 ~ F20
F6 F7 F8 F9 F10 F11 F12 F13 F14 F15 F16 F17 F18 F19 F20 $R_{v}$ 1 0.05 0.1 0.5 0.05 10 0.1 0.5 1 1 1 1 0.1 0.1 0.5 $R_{d}$ 1 0.05 0.5 0.5 0.2 2 0.5 0.5 1 1 1 1 0.5 1 0.2 表 3 不同$g_{{\rm{max}}}$取值下IMPSO-HES所得的性能指标值
Table 3 Performance values obtained by IMPSO-HES under different $g_{{\rm{max}}}$ values
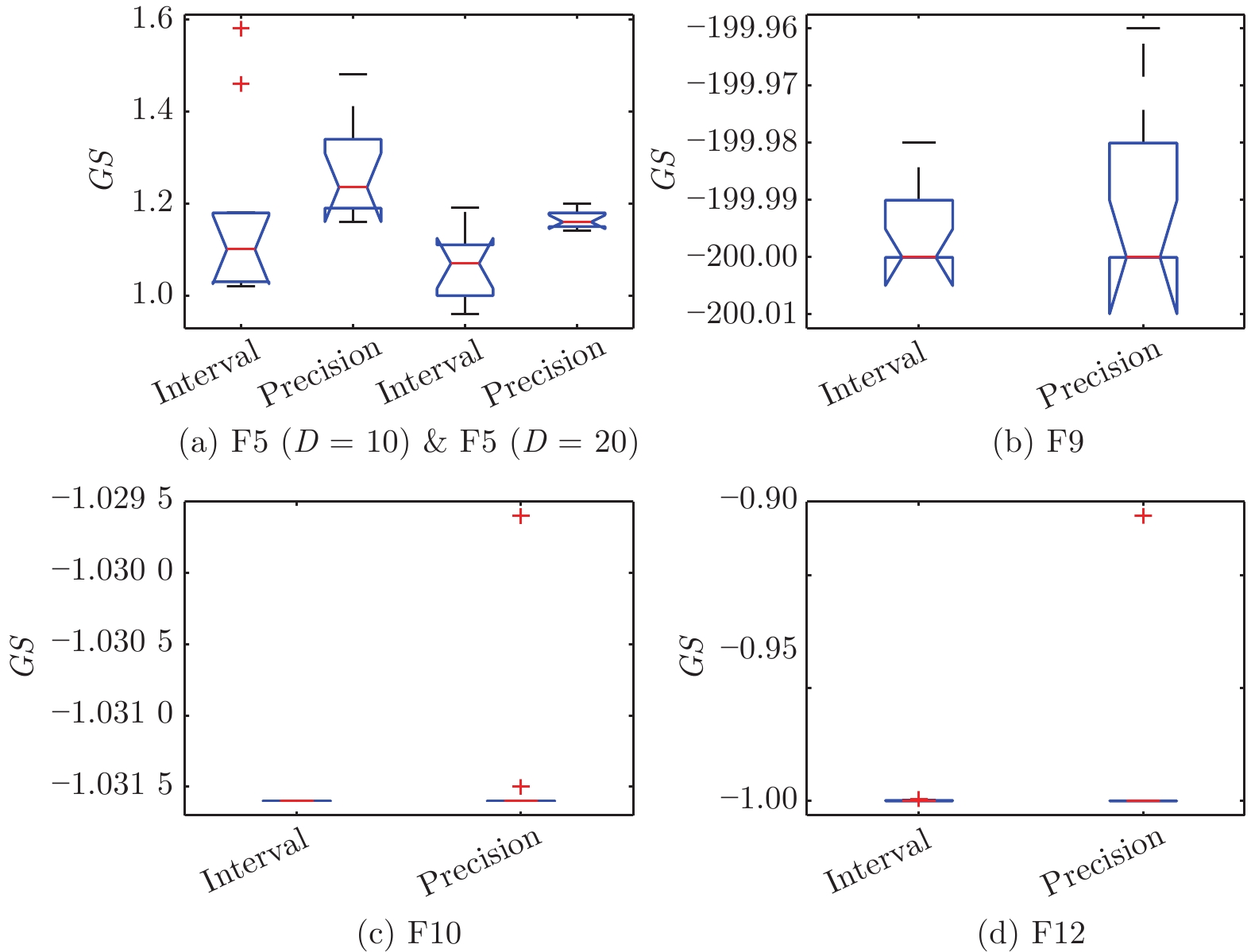
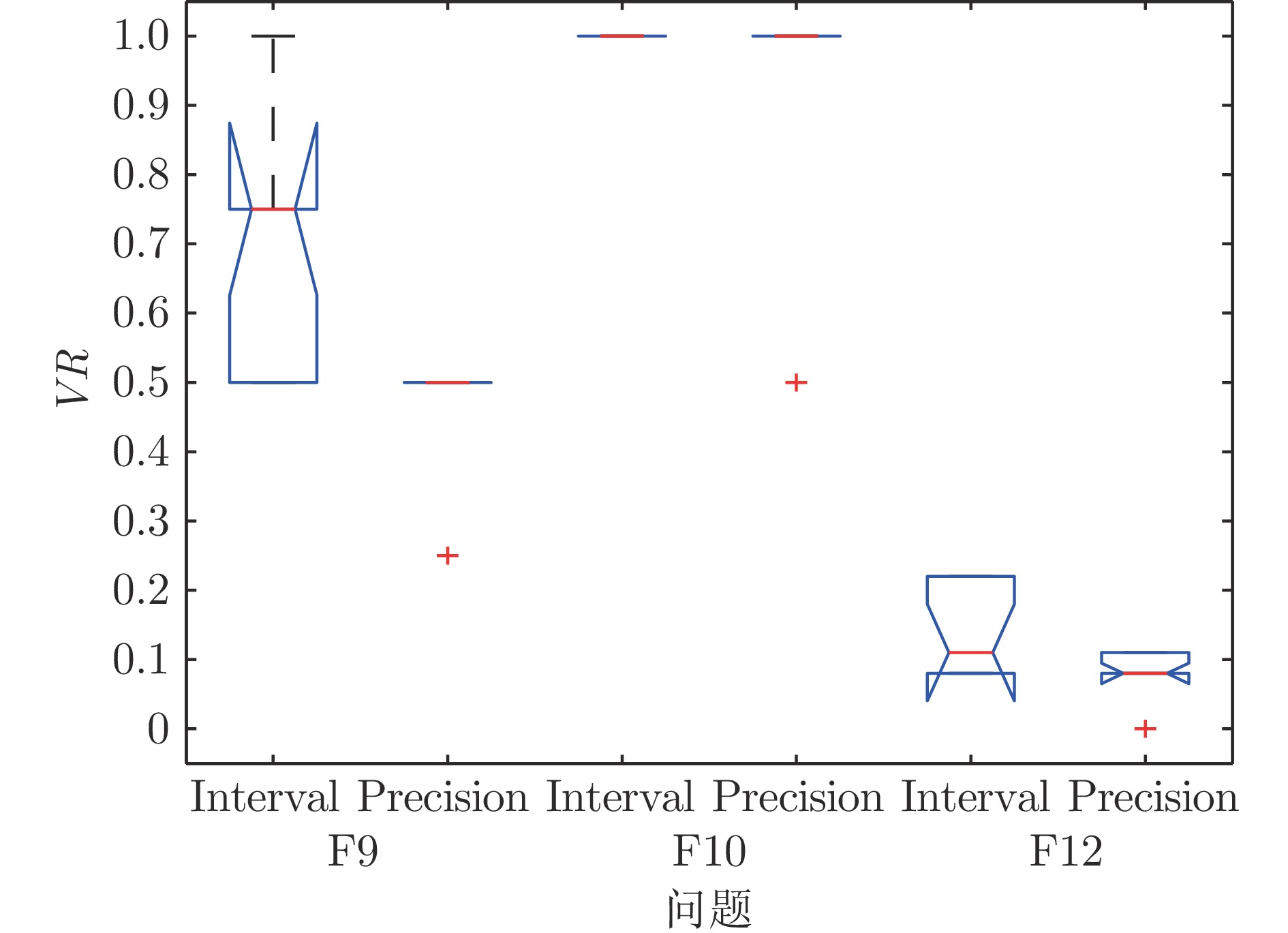
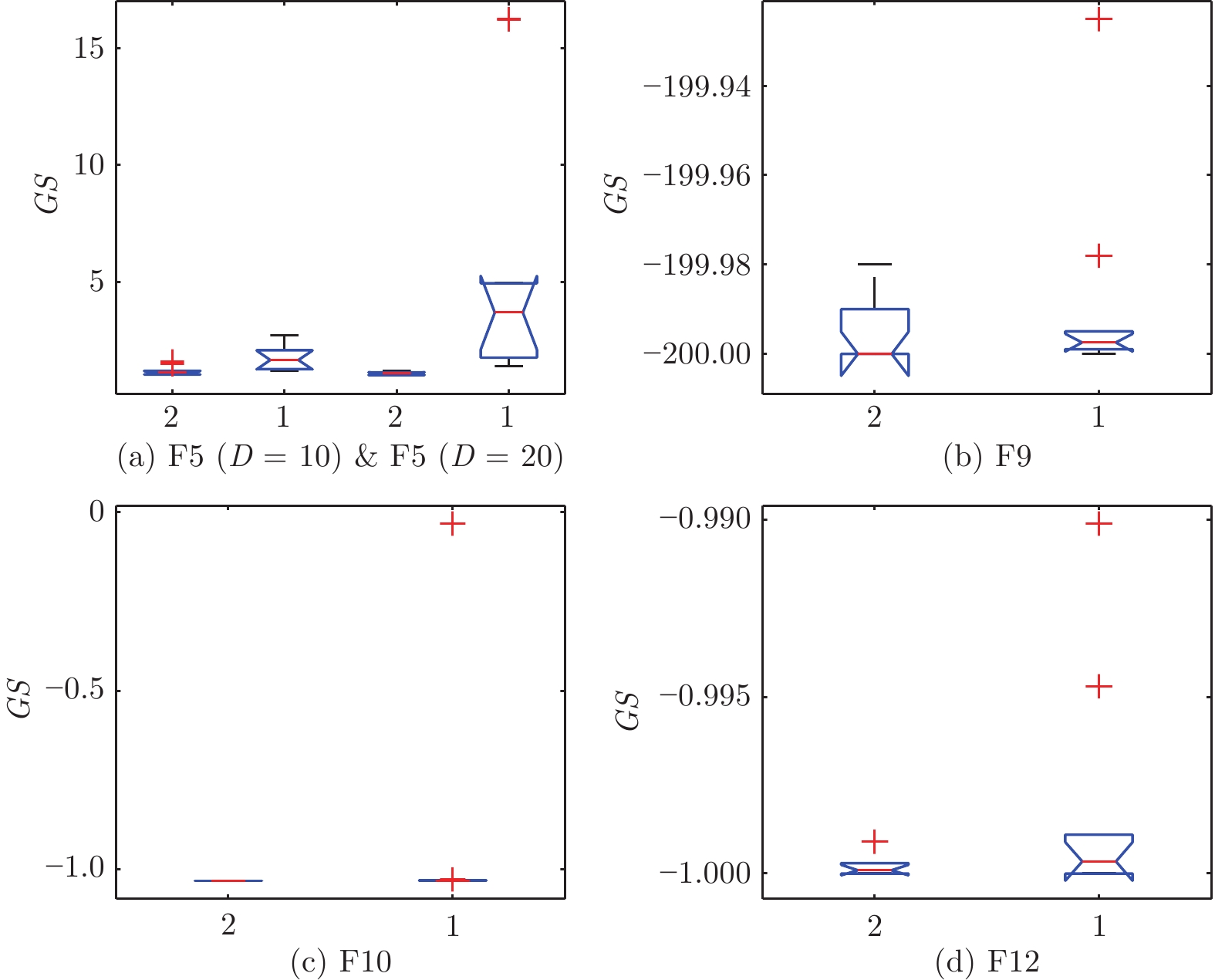
问题 $g_{{\rm{max}}}$ $GS $均值(标准差) $VR $均值 耗时(s) F5 (D = 10) 3 3.800 7 (3.5E+00)+ — 64 6 1.174 5 (3.7E−02) — 85 9 1.108 3 (2.5E−02) = — 116 F5 (D = 20) 3 8.198 0 (9.8E+00) + — 776 6 1.075 7 (1.6E−02) — 1 400 9 0.807 9 (2.8E−01) − — 2 045 F9 3 −199.93 (3.1E−03) = 0.68 11 6 −199.99 (1.0E−04) 0.70 19 9 −200.00 (1.4E−03) = 0.63 36 F10 3 −1.031 6 (1.7E−06) = 1.00 19 6 −1.031 6 (9.8E−07) 1.00 28 9 −1.031 6 (9.8E−07) = 1.00 38 F12 3 −0.999 0 (7.1E−06) = 0.13 10 6 −0.999 9 (1.0E−06) 0.13 14 9 −0.999 9 (2.2E−06) = 0.11 25 注: 加粗字体表示各组的最优结果值. 表 4 不同Q取值下IMPSO-HES所得的性能指标值
Table 4 Performance values obtained by IMPSO-HES under different Q values
问题 Q GS 均值(标准差) VR 均值 耗时(s) F5 (D = 10) K/5 1.658 1 (2.2E−01) + — 64 K/4 1.174 5 (3.7E−02) — 85 K/3 1.382 1 (1.5E−01) + — 108 K/2 1.269 6 (5.1E−02) + — 160 F5 (D = 20) K/5 1.980 0 (1.0E+00) + — 1137 K/4 1.075 7 (1.6E−02) — 1400 K/3 1.832 1 (1.1E+00) + — 1920 K/2 1.835 2 (1.7E+00) + — 2700 F9 K/5 −199.98 (7.2E−04) = 0.53 17 K/4 −199.99 (1.0E−04) 0.70 19 K/3 −199.98 (4.6E−04) = 0.55 24 K/2 −199.14 (6.8E+00) + 0.33 34 F10 K/5 −1.031 6 (1.1E−09) = 1.00 28 K/4 −1.031 6 (9.8E−07) 1.00 28 K/3 −1.031 6 (9.8E−07) = 1.00 30 K/2 −1.030 0 (1.4E−03) + 0.85 48 F12 K/5 −0.999 1 (2.3E−06) + 0.12 12 K/4 −0.999 9 (1.0E−06) 0.13 14 K/3 −0.999 6 (8.5E−07) + 0.10 18 K/2 −0.994 9 (9.2E−05) + 0.10 24 注: 加粗字体表示各组的最优结果值. 表 5 异构集成与同质集成下IMPSO-HES所得结果
Table 5 Performance values obtained by IMPSO-HES under heterogeneous and homogeneous ensemble
问题 算法 GS均值(标准差) VR均值 耗时(s) F5 (D = 10) IMPSO-PR 1.631 0 (7.1E−01) + — 86 IMPSO-RBFN 45.27 2 (8.9E+02) + — 39 IMPSO-HES 1.174 5 (3.7E−02) — 85 F5 (D = 20) IMPSO-PR 2.003 7 (2.9E+00) + — 1 478 IMPSO-RBFN 116.7 8 (9.5E+02) + — 180 IMPSO-HES 1.075 7 (1.6E−02) — 1 400 F9 IMPSO-PR −196.81 (9.5E+00) + 0.05 16 IMPSO-RBFN −199.99 (4.7E−07) = 0.65 22 IMPSO-HES −199.99 (1.0E−04) 0.70 19 F10 IMPSO-PR −0.962 0 (2.5E−03) + 0.2 17 IMPSO-RBFN −1.031 6 (9.8E−09) = 1.00 20 IMPSO-HES −1.031 6 (9.8E−07) 1.00 28 F12 IMPSO-PR −0.988 6 (1.5E−04) + 0.06 11 IMPSO-RBFN −0.999 5 (9.4E−07) + 0.09 19 IMPSO-HES −0.999 9 (1.0E−06) 0.13 14 注: 加粗字体表示各组的最优结果值. 表 6 不同更新概率$p_{m}$下IMPSO-HES所得结果
Table 6 Performance values obtained by IMPSO-HES under different $p_{m}$ values
问题 $p_{m}$ GS 均值 (标准差) VR 均值 耗时(s) F5 (D = 10) 固定 1.439 3 (3.8E−01) + — 84 自适应 1.174 5 (3.7E−02) — 85 F5 (D = 20) 固定 1.750 3 (1.7E+00) + — 1313 自适应 1.075 7 (1.6E−02) — 1400 F9 固定 −199.91 (2.6E−02) + 0.40 19 自适应 −199.99 (1.0E−04) 0.70 19 F10 固定 −1.031 6 (4.7E−08) = 1.00 26 自适应 −1.031 6 (9.8E−07) 1.00 28 F12 固定 −0.996 9 (4.8E−05) + 0.12 14 自适应 −0.999 9 (1.0E−06) 0.13 14 注: 加粗字体表示各组的最优结果值. 表 7 使用All-S和Mod-S时IMPSO-HES所得结果
Table 7 Performance values obtained by IMPSO-HES with All-S and Mod-S
问题 集成策略 GS 均值 (标准差) VR 均值 耗时(s) F5 (D = 10) All-S 3.878 5 (3.8E+00) + — 243 Mod-S 1.174 5 (3.7E−02) — 85 F5 (D = 20) All-S 8.838 7 (8.1E+00) + — 3 362 Mod-S 1.075 7 (1.6E−02) — 1 400 F9 All-S −187.33 (2.0E+2) + 0.05 80 Mod-S −199.99 (1.0E−04) 0.70 19 F10 All-S −0.9751 (1.4E−02) + 0.70 57 Mod-S −1.031 6 (9.8E−07) 1.00 28 F12 All-S −0.973 7 (1.9E−02) + 0.08 42 Mod-S −0.999 9 (1.0E−06) 0.13 14 注: 加粗字体表示各组的最优结果值. 表 8 不同模型更新策略下IMPSO-HES所得结果
Table 8 Performance values obtained by IMPSO-HES under different model update strategies
问题 更新策略 GS 均值 (标准差) VR 均值 耗时(s) F5 (D = 10) All-up 1.500 9 (3.9E−02) + — 97 Inc-up 1.174 5 (3.7E−02) — 85 F5 (D = 20) All-up 32.184 (2.4E+04) + — 1 509 Inc-up 1.075 7 (1.6E−02) — 1 400 F9 All-up −200.00 (3.6E-10) = 0.63 30 Inc-up −199.99 (1.0E−04) 0.70 19 F10 All-up −1.031 6 (1.2E−04) = 0.95 30 Inc-up −1.031 6 (9.8E−07) 1.00 28 F12 All-up −0.999 8 (2.7E−07) = 0.11 16 Inc-up −0.999 9 (1.0E−06) 0.13 14 注: 加粗字体表示各组的最优结果值. 表 9 IMPSO-HES与5种SAEA所得GS值(均值(方差))
Table 9 GS values obtained by IMPSO-HES and 5 SAEAs (mean (variance))
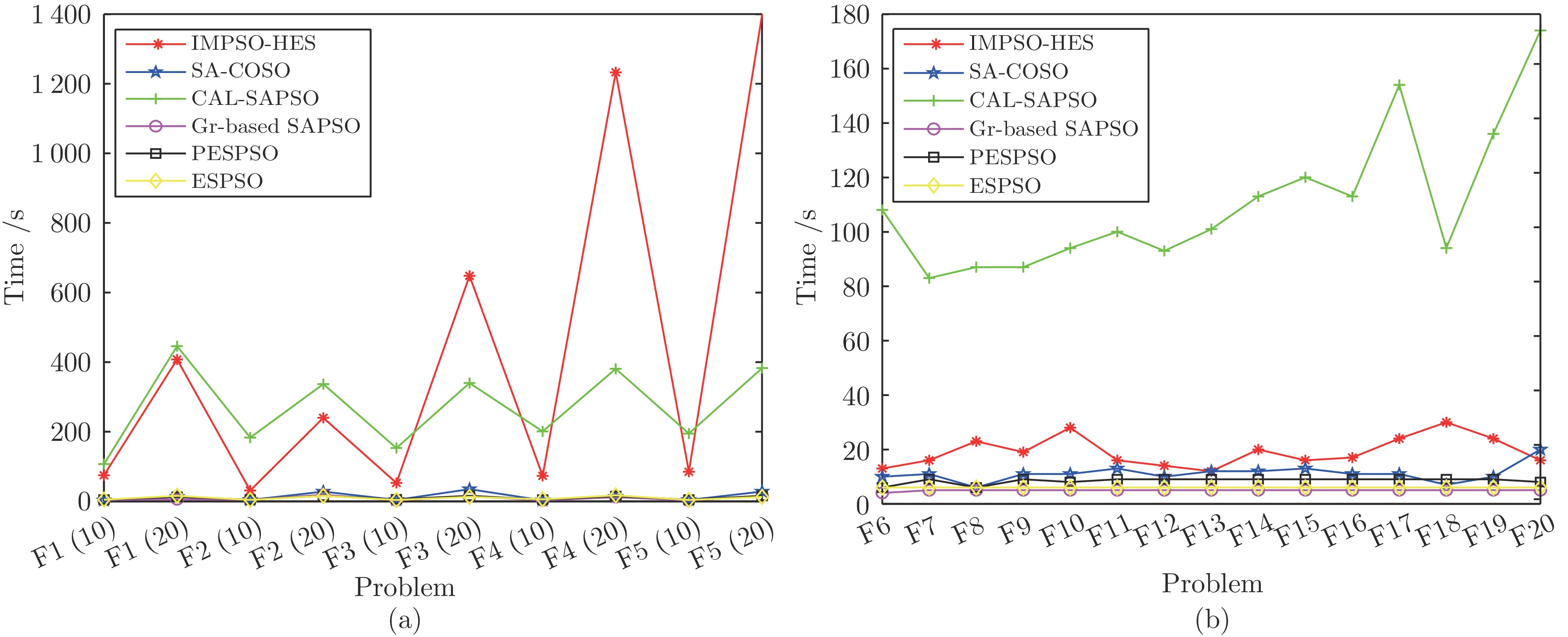
问题 D IMPSO-HES SA-COSO CAL-SAPSO Gr-based SAPSO PESPSO ESPSO F1 10 3.660 0 3.160 0− 0.115 3− 0.147 6− 0.296 2− 0.664 5− (4.2E+00) (6.5E−02) (4.9E−02) (1.1E−03) (1.3E−03) (5.0E−02) 20 21.398 11.017− 0.229 2− 0.027 9− 1.377 0− 1.866 4− (6.1E+01) (1.2E+01) (1.9E−02) (8.2E−06) (1.2E−01) (2.4E−01) F2 10 17.990 17.248= 18.606+ 15.910− 11.820− 13.786− (1.1E+00) (4.1E−02) (4.8E−01) (6.4E−01) (4.3E+00) (2.0E+00) 20 18.866 18.025− 18.421= 14.717− 12.584− 15.958− (9.0E−01) (4.4E−01) (2.4E+00) (1.1E+00) (2.3E+01) (1.6E+01) F3 10 78.266 97.683+ 79.727= 94.349+ 82.325= 89.952= (1.3E+02) (5.8E+02) (1.6E+03) (7.3E+01) (1.2E+02) (2.0E+02) 20 173.97 177.43= 128.71− 168.14= 173.99= 175.65= (2.4E+02) (6.6E+02) (4.0E+03) (1.6E+02) (1.7E+02) (1.1E+02) F4 10 37.310 537.31+ 39.003= 173.66+ 90.531+ 66.581+ (1.1E+02) (2.4E+04) (2.0E+02) (3.3E+02) (6.7E+02) (1.0E+02) 20 41.469 891.97+ 42.758= 330.37+ 97.508+ 195.90+ (5.7E+02) (1.7E+04) (2.0E+02) (3.9E+03) (6.8E+02) (1.9E+03) F5 10 1.174 5 66.556+ 1.736 4+ 1.310 6+ 2.798 7+ 2.317 2+ (3.7E−02) (1.8E+02) (1.4E−01) (1.7E−02) (2.4E+00) (3.9E−01) 20 1.075 7 43.897+ 2.255 3+ 1.057 2= 6.701 8+ 10.373+ (1.6E−02) (1.9E+02) (3.2E−01) (2.0E−05) (7.4E+00) (6.2E+00) F6 1 −199.15 −200.00− −200.00− −190.91+ −200.00− −200.00− (4.6E+00) (2.1E-10) (1.6E−09) (3.2E+01) (1.2E-13) (1.0E-11) F7 1 −0.999 9 −1.00= −0.505 2+ −0.999 1+ −0.999 9= −0.999 8= (3.1E−06) (0.0E+00) (1.2E−01) (1.1E−07) (2.7E−05) (3.8E−06) F8 1 −0.985 4 −0.980 8= −0.511 4+ −0.944 7+ −0.948 6+ −0.948 6+ (1.3E−05) (1.0E-10) (8.0E−02) (7.4E−04) (5.1E−04) (5.1E−04) F9 2 −199.99 −196.14+ −157.69+ −199.93+ −199.98= −199.74+ (1.0E−04) (3.8E+01) (8.6E+02) (5.1E−04) (2.7E−04) (6.4E−03) F10 2 −1.031 6 −0.995 6+ −0.464 6+ −1.030 6+ −1.030 3+ −1.029 2+ (9.8E−07) (1.6E−03) (1.3E−01) (1.9E−06) (1.7E−07) (5.3E−07) F11 2 −158.32 −89.368+ −52.464+ −113.85+ −130.53+ −94.463+ (1.9E+03) (2.4E+03) (2.6E+03) (3.5E+04) (2.5E+03) (1.5E+03) F12 2 −0.999 9 −0.979 8+ −0.719 4+ −0.984 5+ −0.995 4+ −0.980 0+ (1.0E−06) (5.6E−04) (9.0E−02) (1.9E−04) (2.0E−06) (5.5E−05) F13 2 2.232 9 2.890 3+ 7.846 7+ 2.298 5= 2.022 8− 2.060 9− (2.3E−01) (6.4E−02) (3.0E+01) (1.0E−01) (4.6E−03) (3.1E−03) F14 2 0.087 9 40.011+ 197.39+ 23.774+ 7.588 4+ 9.961 7+ (5.0E−01) (2.6E+02) (9.2E+03) (6.3E+03) (1.1E+02) (3.0E+02) F15 2 36.423 89.091+ 183.14+ 80.557+ 26.116= 57.889+ (3.7E+03) (2.7E+02) (3.6E+03) (1.1E+03) (7.6E+02) (2.8E+03) F16 2 0.242 3 90.430+ 350.88+ 60.296+ 1.162 1+ 18.280+ (1.3E−01) (1.2E+04) (4.8E+04) (3.2E+03) (2.5E+00) (1.2E+03) F17 3 32.566 88.270+ 173.56+ 57.380+ 26.079= 37.233= (2.0E+04) (5.3E+02) (2.6E+04) (2.1E+03) (6.2E+02) (6.0E+02) F18 2 −0.267 9 −0.245 7+ −0.130 4+ −0.267 1+ −0.267 8= −0.267 8= (1.6E−06) (3.6E−04) (5.6E−03) (6.8E−08) (1.6E−06) (5.4E−09) F19 2 0.399 9 1.148 8+ 2.260 3+ 0.425 9+ 0.424 9+ 0.513 6+ (2.4E−05) (8.6E−01) (6.2E+00) (1.3E−03) (1.2E−03) (5.3E−02) F20 2 −7.429 9 −7.776 0− −7.775 3− −6.340 8+ −7.294 3+ −7.451 1= (1.7E−02) (0.0E+00) (4.2E−06) (8.4E−01) (2.2E−01) (2.7E−01) 注: 加粗字体表示各行GS值的最优结果值. 问题 IMPSO-HES SA-COSO CAL-SAPSO Gr-based SAPSO PESPSO ESPSO F2 ~ F5 好/平/差 — 5/2/1 3/4/1 4/2/2 4/2/2 4/2/2 Rank 2.500 0 5.500 0 3.000 0 3.125 0 3.125 0 3.750 0 Adjusted p-value — 0.006 6 0.689 2 0.689 2 0.689 2 0.393 8 F6 ~ F20 好/平/差 — 11/2/2 13/0/2 14/1/0 8/5/2 9/4/2 Rank 1.833 3 4.166 6 5.433 3 4.000 0 2.266 6 3.300 0 Adjusted p-value — 0.001 6 0.000 0 0.002 5 0.525 8 0.039 5 注: 加粗字体表示各组的最优结果值. 表 11 处理F1 ~ F5时IMPSO-HES与7种多模态进化算法所得GS值(均值(方差))
Table 11 GS values obtained by IMPSO-HES and the 7 multimodal EAs on F1 ~ F5 (mean (variance))
问题 D IMPSO-HES LIPS EMO-MMO R3PSO FERPSO NCDE NSDE ANDE F1 10 3.6600 3.3110 −5.0580+ 5.9282 +4.3713 +5.7227 +5.8277 +5.2888 +(4.2E+00) (7.8E-01) (1.3E+00) (2.3E+00) (1.2E+00) (6.4E+00) (1.6E+00) (2.6E+00) 20 21.398 19.528= 26.709+ 31.059+ 18.792- 28.868+ 29.060+ 32.311+ (6.1E+01) (9.8E+00) (2.2E+01) (2.2E+01) (1.2E+01) (5.8E+01) (1.5E+01) (5.5E+01) F2 10 17.990 18.046= 18.022= 19.159+ 18.073= 19.411+ 19.432+ 19.523+ (1.1E+00) (8.1E−01) (7.0E−01) (3.9E−01) (1.06E+00) (1.3E+00) (3.0E−01) (1.5E−01) 20 18.866 18.924= 18.922= 19.663+ 19.313+ 19.895+ 20.108+ 19.950+ (9.0E-01) (3.6E+01) (1.7E−01) (6.5E−02) (2.5E−01) (9.9E−02) (4.9E−02) (8.2E−06) F3 10 78.266 95.069+ 89.325= 108.58+ 100.83+ 110.95+ 101.33+ 106.90+ (1.3E+02) (6.3E+01) (1.2E+02) (2.2E+02) (8.2E+01) (5.5E+02) (1.3E+02) (1.3E+02) 20 173.97 212.48+ 207.09+ 258.90+ 225.25+ 251.77+ 262.26+ 268.57+ (2.4E+02) (2.6E+02) (2.8E+02) (3.3E+02) (5.1E+02) (3.2E+02) (6.5E+02) (1.1E+02) F4 10 37.310 343.96+ 257.96+ 670.32+ 451.41+ 812.90+ 982.18+ 523.1+ (1.1E+02) (4.2E+05) (3.6E+05) (1.3E+05) (2.8E+04) (1.0E+05) (1.1E+05) (2.7E+05) 20 41.469 1431.9 +1399.6 +2853.3 +1722.6 +3031.2 +2737.0 +2416.1 +(5.7E+02) (1.1E+05) (1.5E+05) (3.6E+05) (5.1E+04) (6.9E+05) (7.1E+05) (1.6E+05) F5 10 1.1745 66.246+ 65.750+ 94.936+ 71.342+ 129.69+ 115.66+ 109.05+ (3.7E-02) (3.1E+02) (6.7E+02) (4.7E+02) (4.8E+02) (3.5E+02) (8.8E+02) (6.6E+01) 20 1.0757 160.00+ 156.27+ 305.74+ 194.22+ 298.18+ 300.28+ 300.13+ (1.6E-02) (4.8E+02) (1.1E+03) (7.0E+02) (1.5E+03) (3.7E+03) (2.1E+03) (2.2E+03) 注: 加粗字体表示各组的最优结果值. 表 12 处理F6 ~ F20时IMPSO-HES与7种多模态进化算法所得结果
Table 12 Results of IMPSO-HES and the 7 multimodal EAs on F6 ~ F20
问题 D IMPSO-HES LIPS EMO-MMO R3PSO FERPSO NCDE NSDE ANDE F6 GS 均值 −199.15 −185.64+ −196.52+ −190.93+ −186.31+ −191.25+ −197.86+ −195.52+ (标准差) (4.6E+00) (8.8E+01) (1.0E+02) (6.1E+01) (1.0E+02) (3.4E+02) (4.5E+01) (5.0E+02) VR 均值 0.80 0.20+ 0.40+ 0.10+ 0.00+ 0.65+ 0.75= 0.40+ F7 GS 均值 −0.999 9 −0.999 4+ −0.999 5+ −0.999 1+ −0.998 6+ −0.998 7+ −0.998 4+ −0.998 0+ (标准差) (3.1E−06) (7.3E−07) (2.5E−07) (7.2E−07) (1.0E−06) (8.5E−07) (5.6E−06) (4.6E−06) VR均值 0.78 0.78= 0.76= 0.70= 0.66+ 0.74= 0.78= 0.67+ F8 GS 均值 −0.985 4 −0.969 3+ −0.993 7− −0.993 1− −0.975 8+ −0.966 0+ −0.948 3+ −0.968 3+ (标准差) (1.3E−04) (6.8E−04) (2.5E−04) (6.7E−05) (4.1E−04) (8.9E−04) (5.1E−03) (3.1E−03) VR均值 1.00 0.80+ 0.90+ 1.00= 1.00= 0.90+ 0.60+ 0.80+ F9 GS 均值 −199.99 −197.58+ −197.79+ −196.99+ −196.92+ −197.04+ −196.10+ −197.22+ (标准差) (1.0E−04) (1.7E+00) (9.9E+00) (1.3E+01) (8.6E+00) (5.2E+00) (1.6E+01) (1.3E+01) VR均值 0.70 0.02+ 0.05+ 0.07+ 0.07+ 0.10+ 0.05+ 0.05+ F10 GS 均值 −1.031 6 −1.004 7+ −1.001 6+ −1.003 2+ −0.994 9+ −0.987 8+ −0.973 0+ −1.002 0+ (标准差) (9.8E−07) (3.6E−04) (2.8E−03) (2.8E−03) (8.8E−04) (8.7E−03) (5.0E−03) (3.4E−02) VR均值 1.00 0.55+ 0.10+ 0.45+ 0.30+ 0.40+ 0.35+ 0.5+ F11 GS 均值 −158.32 −105.20+ −134.50= −90.154+ −114.099+ −123.777+ −111.92+ −132.37= (标准差) (1.9E+03) (1.3E+03) (1.7E+03) (5.4E+02) (1.3E+03) (1.0E+03) (2.3E+03) (1.6E+03) VR均值 0.02 0.01= 0.01= 0.00+ 0.00+ 0.00+ 0.00+ 0.01= F12 GS 均值 −0.999 9 −0.973 3+ −0.975 3+ −0.972 7+ −0.976 4+ −0.976 4+ −0.989 0+ −0.988 7+ (标准差) (1.0E−06) (3.2E−04) (4.9E−04) (4.6E−04) (5.8E−04) (5.2E−04) (3.0E−04) (4.6E−03) VR均值 0.13 0.08+ 0.05+ 0.07+ 0.07+ 0.08+ 0.10+ 0.09+ F13 GS 均值 2.232 9 2.714 6+ 2.560 4+ 2.438 4+ 2.590 3+ 2.481 7+ 2.344 6= 2.579 2+ (标准差) (2.3E−01) (3.2E−01) (2.3E+00) (2.1E−01) (2.4E−01) (7.3E−01) (8.7E−01) (2.2E+00) VR均值 0.09 0.08= 0.08= 0.07= 0.08= 0.13+ 0.09= 0.08= F14 GS 均值 0.087 9 44.360+ 45.829+ 43.836+ 38.669+ 40.250+ 38.149+ 41.010+ (标准差) (5.0E−01) (4.0E+03) (4.8E+03) (4.5E+03) (4.5E+03) (4.3E+03) (1.6E+03) (1.2E+02) VR均值 0.24 0.01+ 0.01+ 0.00+ 0.01+ 0.01+ 0.00+ 0.00+ F15 GS 均值 36.423 103.12+ 85.620+ 108.46+ 82.451+ 67.647+ 75.308+ 89.100+ (标准差) (3.7E+03) (1.4E+03) (6.8E+03) (3.2E+03) (2.7E+03) (1.7E+03) (6.6E+03) (1.8E+03) VR均值 0.03 0.00+ 0.01= 0.00+ 0.01= 0.00+ 0.00+ 0.00+ F16 GS 均值 0.242 3 74.272+ 52.296+ 132.800+ 52.555+ 81.104+ 114.04+ 67.231+ (标准差) (1.3E−01) (8.2E+03) (8.1E+03) (6.6E+03) (3.2E+03) (9.0E+03) (1.6E+03) (1.6E+03) VR均值 0.15 0.00+ 0.02+ 0.00+ 0.00+ 0.00+ 0.00+ 0.00+ F17 GS 均值 32.566 127.50+ 141.05+ 165.93+ 148.05+ 192.72+ 162.20+ 100.12+ (标准差) (2.0E+04) (2.3E+03) (2.5E+04) (5.7E+03) (2.0E+03) (8.5E+03) (5.2E+03) (3.2E+03) VR均值 0.13 0.00+ 0.00+ 0.00+ 0.00+ 0.00+ 0.00+ 0.00+ F18 GS 均值 −0.267 9 −0.264 2+ −0.260 3+ −0.257 9+ −0.262 5+ −0.254 8+ −0.260 4+ −0.263 0+ (标准差) (1.6E−06) (6.0E−05) (6.8E−05) (9.1E−05) (4.9E−05) (1.6E−04) (1.8E−05) (1.5E−04) VR均值 1.00 1.00= 0.95= 0.95= 1.00= 0.80+ 0.80+ 0.85+ F19 GS 均值 0.399 9 0.529 2+ 0.882 5+ 0.797 9+ 0.776 3+ 0.789 5+ 1.337 5+ 0.885 8+ (标准差) (2.4E−05) (1.9E−01) (1.8E−01) (1.8E−01) (1.8E−01) (1.7E+00) (8.6E−02) (2.0E−01) VR均值 0.60 0.03+ 0.03+ 0.10+ 0.06+ 0.16+ 0.06+ 0.2+ F20 GS 均值 −7.429 9 −6.619 2+ −6.649 6+ −6.664 4+ −6.728 0+ −6.679 1+ −6.420 4+ −6.981 8+ (标准差) (1.7E−02) (2.9E−01) (8.6E−01) (4.0E−01) (3.3E−01) (4.5E−01) (3.8E−01) (4.6E−01) VR均值 0.40 0.26+ 0.26+ 0.26+ 0.20+ 0.29+ 0.27+ 0.28+ 注: 加粗字体表示各组的最优结果值. 表 13 IMPSO-HES与7种多模态进化算法的统计对比结果
Table 13 Statistical comparison results of IMPSO-HES and the 7 multimodal EAs
问题 IMPSO-HES LIPS EMO-MMO R3PSO FERPSO NCDE NSDE ANDE F1 ~ F5 好/平/差 GS — 6/3/1 7/3/0 10/0/0 8/1/1 10/0/0 10/0/0 10/0/0 Rank 1.300 0 2.800 0 3.000 0 6.100 0 3.300 0 6.300 0 6.800 0 6.700 0 Adjusted p-value — 0.315 3 0.116 0 0.000 2 0.0937 0.000 1 0.000 0 0.000 0 好/平/差 GS — 15/0/0 13/1/1 14/0/1 15/0/0 15/0/0 14/1/0 14/1/0 F6 ~ F20 VR — 11/4/0 10/5/0 11/4/0 11/4/0 14/1/0 12/3/0 13/2/0 Rank 1.258 6 4.827 5 4.268 9 5.551 7 4.603 4 6.103 4 4.862 0 4.224 1 Adjusted p-value — 0.000 0 0.000 0 0.000 0 0.000 0 0.000 0 0.000 0 0.000 0 表 14 问题的决策变量信息
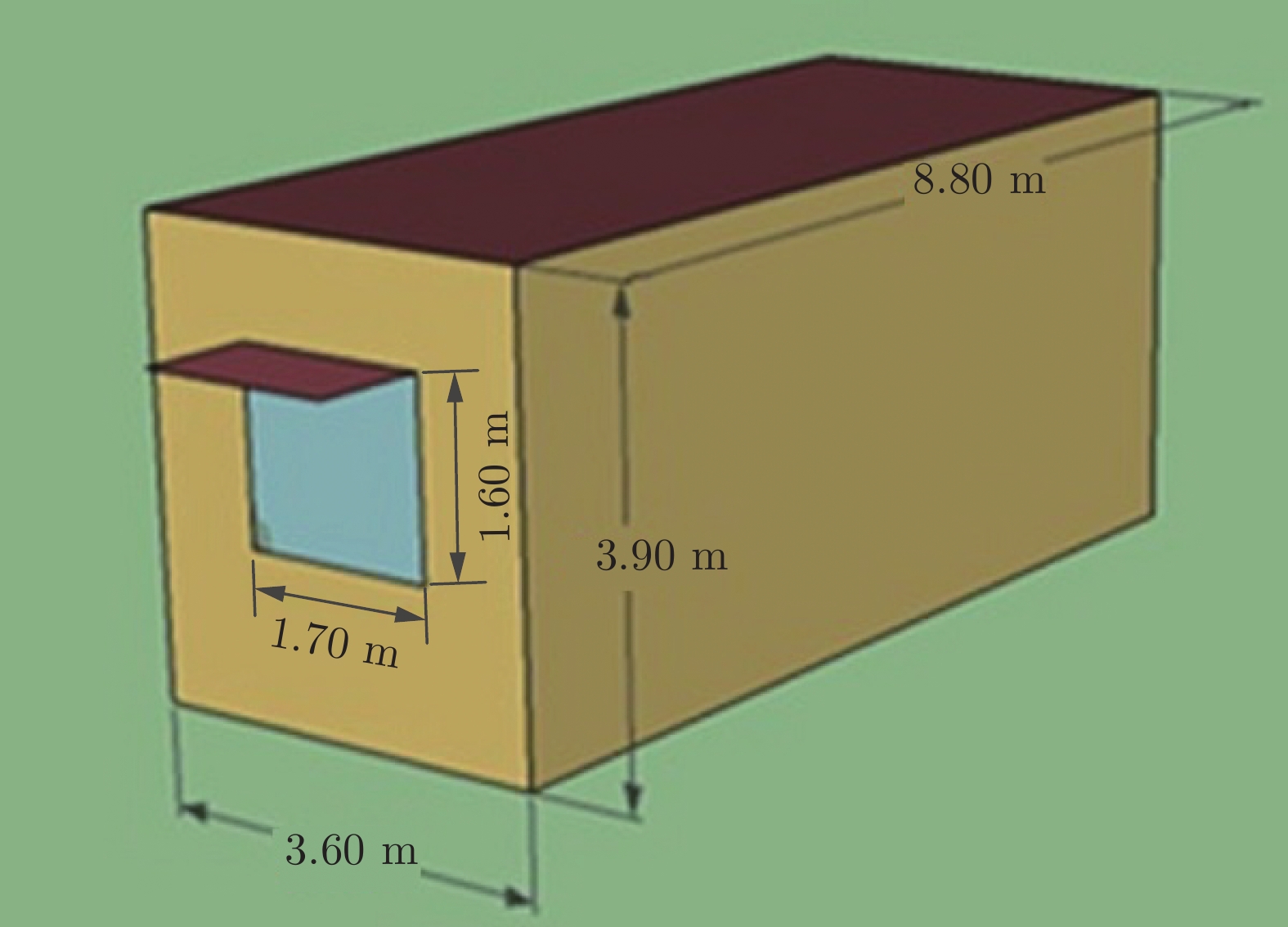
Table 14 Decision variable information of the problem
决策变量 单位 范围 房屋方向 $( ^{ {\circ} } )$ [0, 360) 窗户的长 m (0, 3.6) 窗户的高 m (0, 3.9) 窗户的传热系数 ${\rm{W} }/({\rm{m} }^{2}\cdot{\rm{K} })$ [2, 6] 窗户的日射热取得率 — (0, 0.7) 墙体外保温层厚度 m (0, 0.1] 墙体日射吸收率 — [0.1, 1] 人员密度 ${{\text{人}}/\rm{m} }^{2}$ [0.1, 1) 照明功率密度 ${\rm{W} }/{\rm{m} }^{2}$ [6, 12] 设备功率密度 $\rm{W}/{\rm{m} }^{2}$ [10, 18] 空调供热设置温度 ℃ [18, 23] 空调制冷设置问题 ℃ [24, 28] 表 15 处理建筑节能设计问题时两种算法所得的实验结果
Table 15 Results of the two algorithms on building energy conservation
GS Optimal solutions 时间(s) IMPSO-HES 5.02 X = 71.8, 1.06, 1.85, 3.64, 0.0382 ,0.0905 ,0.2212 ,0.1033 , 6.5, 14.0, 22.3, 26.4, f = 5.1450 X = 297.3, 2.53, 1.63, 4.0065 ,0.0556 ,0.0402 ,0.5983 ,0.1027 , 6.0, 17.2, 19.6, 24.0, f = 5.1X = 351.7, 3.50, 0.38, 2.266, 0.1604 ,0.0567 ,0.8882 ,0.1062 , 6.1, 17.3, 22.6, 24.6, f = 5.11EMO-MMO 4.96 X = 183.2, 1.19, 2.36, 2.32, 0.3439 ,0.0489 ,0.9743 ,0.1085 , 6.18, 12.3, 21.1, 26.3, f = 5.0142 357 X = 215.1, 2.41, 2.09, 5.38, 0.2847 ,0.0532 ,0.4720 ,0.1015 , 6.44, 11.8, 19.3, 27.1, f = 5.02X = 134.7, 1.07, 2.87, 3.73, 0.3129 ,0.0418 ,0.9553 ,0.1015 , 6.02, 12.8, 20.4, 25.3, f = 5.02 -
[1] Kruisselbrink J W, Aleman A, Emmerich M T M, Ijzerman A P, Bender A, Baeck T, et al. Enhancing search space diversity in multi-objective evolutionary drug molecule design using niching. In: Proceedings of the 11th Annual Conference on Genetic and Evolutionary Computation. Montreal, Canada: ACM, 2009. 217−224 [2] Pérez E, Herrera F, Hernández C. Finding multiple solutions in job shop scheduling by niching genetic algorithms. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 2003, 14(3−4): 323−339 [3] 李章维, 肖璐倩, 郝小虎, 周晓根, 张贵军. 蛋白质构象空间的多模态优化算法. 计算机科学, 2020, 47(7): 161−165Li Zhang-Wei, Xiao Lu-Qian, Hao Xiao-Hu, Zhou Xiao-Gen, Zhang Gui-Jun. Multimodal optimization algorithm for protein conformation space. Computer Science, 2020, 47(7): 161−165 [4] Wang Z J, Zhan Z H, Lin Y, Yu W J, Wang H, Kwong S, et al. Automatic niching differential evolution with contour prediction approach for multimodal optimization problems. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2020, 24(1): 114−128 doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2019.2910721 [5] 李航, 李敏强, 寇纪淞. 遗传算法求解多模态优化问题的动力性. 自动化学报, 2008, 34(2): 180−187Li Hang, Li Min-Qiang, Kou Ji-Song. Dynamical behavior of genetic algorithms on multi-modal optimization. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2008, 34(2): 180−187 [6] Zhang Y, Yuan L J, Zhang Q, Sun X Y. Multi-objective optimization of building energy performance using a particle swarm optimizer with less control parameters. Journal of Building Engineering, 2020, 32: Article No. 101505 doi: 10.1016/j.jobe.2020.101505 [7] Ji X F, Zhang Y, Gong D W, Sun X Y. Dual-surrogate-assisted cooperative particle swarm optimization for expensive multimodal problems. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2021, 25(4): 794−808 doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2021.3064835 [8] Li X D. Adaptively choosing neighbourhood bests using species in a particle swarm optimizer for multimodal function optimization. In: Proceedings of the Genetic and Evolutionary Computation Conference. Seattle, USA: Springer, 2004. 105−116 [9] Cheng R, Li M Q, Li K, Yao X. Evolutionary multiobjective optimization-based multimodal optimization: Fitness landscape approximation and peak detection. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2018, 22(5): 692−706 doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2017.2744328 [10] Li X D, Epitropakis M G, Deb K, Engelbrecht A. Seeking multiple solutions: An updated survey on niching methods and their applications. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2017, 21(4): 518−538 doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2016.2638437 [11] 张淑美, 王福利, 谭帅, 王姝. 多模态过程的全自动离线模态识别方法. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(1): 60−80Zhang Shu-Mei, Wang Fu-Li, Tan Shuai, Wang Shu. A fully automatic offline mode identification method for multi-mode processes. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(1): 60−80 [12] Mahfoud S W. Crowding and preselection revisited. In: Proceedings of the Parallel Problem Solving from Nature 2, PPSN-Ⅱ. Brussels, Belgium: Elsevier, 1992. 27−36 [13] 张贵军, 何洋军, 郭海锋, 冯远静, 徐建明. 基于广义凸下界估计的多模态差分进化算法. 软件学报, 2013, 24(6): 1177−1195Zhang Gui-Jun, He Yang-Jun, Guo Hai-Feng, Feng Yuan-Jing, Xu Jian-Ming. Differential evolution algorithm for multimodal optimization based on abstract convex underestimation. Journal of Software, 2013, 24(6): 1177−1195 [14] Petrowski A. A clearing procedure as a niching method for genetic algorithms. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Evolutionary Computation. Nagoya, Japan: IEEE, 1996. 798−803 [15] Li X D. Niching without niching parameters: Particle swarm optimization using a ring topology. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2010, 14(1): 150−169 doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2009.2026270 [16] 王湘中, 喻寿益. 多模态函数优化的多种群进化策略. 控制与决策, 2006, 21(3): 285−288Wang Xiang-Zhong, Yu Shou-Yi. Multi-population evolution strategies for multi-modal function optimization. Control and Decision, 2006, 21(3): 285−288 [17] 张贵军, 陈铭, 周晓根. 动态小生境半径两阶段多模态差分进化算法. 控制与决策, 2016, 31(7): 1185−1191Zhang Gui-Jun, Chen Ming, Zhou Xiao-Gen. Two-stage differential evolution algorithm using dynamic niche radius for multimodal optimization. Control and Decision, 2016, 31(7): 1185−1191 [18] Holland J H. Adaptation in Natural and Artificial Systems. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan, 1975. [19] 李敏强, 寇纪淞. 多模态函数优化的协同多群体遗传算法. 自动化学报, 2002, 28(4): 497−504Li Min-Qiang, Kou Ji-Song. Coordinate multi-population genetic algorithms for multi-modal function optimization. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2002, 28(4): 497−504 [20] Qu B Y, Suganthan P N, Das S. A distance-based locally informed particle swarm model for multimodal optimization. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2013, 17(3): 387−402 doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2012.2203138 [21] Biswas S, Kundu S, Das S. Inducing niching behavior in differential evolution through local information sharing. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2015, 19(2): 246−263 doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2014.2313659 [22] Deb K, Saha A. Multimodal optimization using a Bi-objective evolutionary algorithm. Evolutionary Computation, 2012, 20(1): 27−62 doi: 10.1162/EVCO_a_00042 [23] Bandaru S, Deb K. A parameterless-niching-assisted bi-objective approach to multimodal optimization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation. Cancún, Mexico: IEEE, 2013. 95−102 [24] Yue C T, Liang J J, Qu B Y, Yu K J, Song H. Multimodal multiobjective optimization in feature selection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC). Wellington, New Zealand: IEEE, 2019. 302−309 [25] Lim D, Jin Y C, Ong Y S, Sendhoff B. Generalizing surrogate-assisted evolutionary computation. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2010, 14(3): 329−355 doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2009.2027359 [26] Liu B, Zhang Q F, Gielen G G E. A Gaussian process surrogate model assisted evolutionary algorithm for medium scale expensive optimization problems. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2014, 18(2): 180−192 doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2013.2248012 [27] Clarke S M, Griebsch J H, Simpson T W. Analysis of support vector regression for approximation of complex engineering analyses. Journal of Mechanical Design, 2005, 127(6): 1077−1087 doi: 10.1115/1.1897403 [28] Regis R G. Evolutionary programming for high-dimensional constrained expensive black-box optimization using radial basis functions. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2014, 18(3): 326−347 doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2013.2262111 [29] Roux W J, Stander N, Haftka R T. Response surface approximations for structural optimization. Numerical Methods in Engineering, 1998, 42(3): 517−534 doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0207(19980615)42:3<517::AID-NME370>3.0.CO;2-L [30] Wang H D, Jin Y C, Doherty J. Committee-based active learning for surrogate-assisted particle swarm optimization of expensive problems. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2017, 47(9): 2664−2677 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2017.2710978 [31] Min A T W, Ong Y S, Gupta A, Goh C K. Multiproblem surrogates: Transfer evolutionary multiobjective optimization of computationally expensive problems. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2019, 23(1): 15−28 doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2017.2783441 [32] Wang H D, Jin Y C, Sun C L, Doherty J. Offline data-driven evolutionary optimization using selective surrogate ensembles. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2019, 23(2): 203−216 doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2018.2834881 [33] Loshchilov I, Schoenauer M, Sebag M. Comparison-based optimizers need comparison-based surrogates. In: Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Parallel Problem Solving From Nature. Krakow, Poland: Springer, 2010. 364−373 [34] 龙腾, 郭晓松, 彭磊, 刘莉. 基于信赖域的动态径向基函数代理模型优化策略. 机械工程学报, 2014, 50(7): 184−190 doi: 10.3901/JME.2014.07.184Long Teng, Guo Xiao-Song, Peng Lei, Liu Li. Optimization strategy using dynamic radial basis function metamodel based on trust region. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2014, 50(7): 184−190 doi: 10.3901/JME.2014.07.184 [35] Chugh T, Jin Y C, Miettinen K, Hakanen J, Sindhya K. A surrogate-assisted reference vector guided evolutionary algorithm for computationally expensive many-objective optimization. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2018, 22(1): 129−142 doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2016.2622301 [36] 孙超利, 李贞, 金耀初. 模型辅助的计算费时进化高维多目标优化. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(4): 1119−1128Sun Chao-Li, Li Zhen, Jin Yao-Chu. Surrogate-assisted expensive evolutionary many-objective optimization. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(4): 1119−1128 [37] 田杰, 孙超利, 谭瑛, 曾建潮. 基于多点加点准则的代理模型辅助社会学习微粒群算法. 控制与决策, 2020, 35(1): 131−138Tian Jie, Sun Chao-Li, Tan Ying, Zeng Jian-Chao. Similarity-based multipoint infill criterion for surrogate-assisted social learning particle swarm optimization. Control and Decision, 2020, 35(1): 131−138 [38] 田杰, 谭瑛, 孙超利, 曾建潮. 代理模型辅助进化算法在高维优化问题中的应用. 机械设计与制造, 2018, 12: 269−272Tian Jie, Tan Ying, Sun Chao-Li, Zeng Jian-Chao. Surrogate-assisted evolutionary optimization for high-dimensional expensive optimization. Machinery Design and Manufacture, 2018, 12: 269−272 [39] Sun C L, Jin Y C, Zeng J C, Yu Y. A two-layer surrogate-assisted particle swarm optimization algorithm. Soft Computing, 2015, 19(6): 1461−1475 doi: 10.1007/s00500-014-1283-z [40] Cai X W, Qiu H B, Gao L, Jiang C, Shao X Y. An efficient surrogate-assisted particle swarm optimization algorithm for high-dimensional expensive problems. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2019, 184: Article No. 104901 doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2019.104901 [41] Liao P, Sun C L, Zhang G C, Jin Y C. Multi-surrogate multi-tasking optimization of expensive problems. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2020, 205: Article No. 106262 doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2020.106262 [42] Tang Y F, Chen J Q, Wei J H. A surrogate-based particle swarm optimization algorithm for solving optimization problems with expensive black box functions. Engineering Optimization, 2013, 45(5): 557−576 doi: 10.1080/0305215X.2012.690759 [43] Li F, Cai X W, Gao L. Ensemble of surrogates assisted particle swarm optimization of medium scale expensive problems. Applied Soft Computing, 2019, 74: 291−305 doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2018.10.037 [44] Liu Q F, Wu X F, Lin Q Z, Ji J K, Wong K C. A novel surrogate-assisted evolutionary algorithm with an uncertainty grouping based infill criterion. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 2021, 60: Article No. 100787 doi: 10.1016/j.swevo.2020.100787 [45] Dong H C, Li C S, Song B W, Wang P. Multi-surrogate-based differential evolution with multi-start exploration (MDEME) for computationally expensive optimization. Advances in Engineering Software, 2018, 123: 62−76 doi: 10.1016/j.advengsoft.2018.06.001 [46] Gu J C, Li W Q, Cai Y Z. A hybrid meta-model based global optimization method for expensive problems. Computers and Industrial Engineering, 2019, 136: 421−428 [47] Guo D, Jin Y C, Ding J L, Chai T Y. Heterogeneous ensemble-based infill criterion for evolutionary multiobjective optimization of expensive problems. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2019, 49(3): 1012−1025 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2018.2794503 [48] Tenne Y. Online ensemble topology selection in expensive optimization problems. International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems, 2020, 18(4): 955−965 doi: 10.1007/s12555-018-0356-7 [49] 陈万芬, 王宇嘉, 林炜星. 异构集成代理辅助多目标粒子群优化算法. 计算机工程与应用, 2021, 57(23): 71−80Chen Wan-Fen, Wang Yu-Jia, Lin Wei-Xing. Heterogeneous ensemble surrogate assisted multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2021, 57(23): 71−80 [50] Branke J, Schmidt C. Faster convergence by means of fitness estimation. Soft Computing, 2005, 9(1): 13−20 doi: 10.1007/s00500-003-0329-4 [51] Wang H D, Jin Y C, Yang C E, Jiao L C. Transfer stacking from low-to high-fidelity: A surrogate-assisted bi-fidelity evolutionary algorithm. Applied Soft Computing, 2020, 92: Article No. 106276 doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106276 [52] Emmerich M, Giotis A, Özdemir M, Bäeck T, Giannakoglou K. Metamodel-assisted evolution strategies. In: Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Parallel Problem Solving From Nature. Granada, Spain: Springer, 2002. 361−370 [53] Yahyaie F, Filizadeh S. A surrogate-model based multi-modal optimization algorithm. Engineering Optimization, 2011, 43(7): 779−799 doi: 10.1080/0305215X.2010.517528 [54] Eberhart R, Kennedy J. A new optimizer using particle swarm theory. In: Proceedings of the 6th International Symposium on Micro Machine and Human Science. Nagoya, Japan: IEEE, 1995. 39−43 [55] Shi Y, Eberhart R. A modified particle swarm optimizer. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Evolutionary Computation, IEEE World Congress on Computational Intelligence (Cat. No.98TH8360). Anchorage, USA: IEEE, 1998. 69−73 [56] Sun C L, Jin Y C, Cheng R, Ding J L, Zeng J C. Surrogate-assisted cooperative swarm optimization of high-dimensional expensive problems. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2017, 21(4): 644−660 doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2017.2675628 [57] Tian J, Sun C L, Tan Y, Zeng J C. Granularity-based surrogate-assisted particle swarm optimization for high-dimensional expensive optimization. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2020, 187: Article No. 104815 doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2019.06.023 [58] Goel T, Haftka R T, Shyy W, Queipo N V. Ensemble of surrogates. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization, 2007, 33(3): 199−216 doi: 10.1007/s00158-006-0051-9 [59] Gutmann H M. A radial basis function method for global optimization. Journal of Global Optimization, 2001, 19(3): 201−227 doi: 10.1023/A:1011255519438 [60] Zhou L G, Chen H Y, Merigó J M, Gil-Lafuente A M. Uncertain generalized aggregation operators. Expert Systems With Applications, 2012, 39(1): 1105−1117 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2011.07.110 [61] 李德清, 韩国柱, 曾文艺, 余先川. 基于布尔矩阵的区间数排序方法. 控制与决策, 2016, 31(4): 629−634Li De-Qing, Han Guo-Zhu, Zeng Wen-Yi, Yu Xian-Chuan. Ranking method of interval numbers based on Boolean matrix. Control and Decision, 2016, 31(4): 629−634 [62] Fan C D, Hou B, Zheng J H, Xiao L Y, Yi L Z. A surrogate-assisted particle swarm optimization using ensemble learning for expensive problems with small sample datasets. Applied Soft Computing, 2020, 91: Article No. 106242 doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106242 [63] Efron B, Tibshirani R J. An Introduction to the Bootstrap. New York: Chapman & Hall, 1993. [64] Li X D, Engelbrecht A, Epitropakis M G. Benchmark Functions for CEC'2013 Special Session and Competition on Niching Methods for Multimodal Function Optimization, Technical Report, RMIT University, Melbourne, Australia, 2013. [65] Stoean C, Preuss M, Stoean R, Dumitrescu D. Multimodal optimization by means of a topological species conservation algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2010, 14(6): 842−864 doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2010.2041668 [66] Qu B Y, Suganthan P N, Liang J J. Differential evolution with neighborhood mutation for multimodal optimization. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2012, 16(5): 601−614 doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2011.2161873 [67] Friedman M. The use of ranks to avoid the assumption of normality implicit in the analysis of variance. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 1937, 32(200): 675−701 doi: 10.1080/01621459.1937.10503522 [68] Finner H. On a monotonicity problem in step-down multiple test procedures. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 1993, 88(423): 920−923 doi: 10.1080/01621459.1993.10476358 -




 下载:
下载: