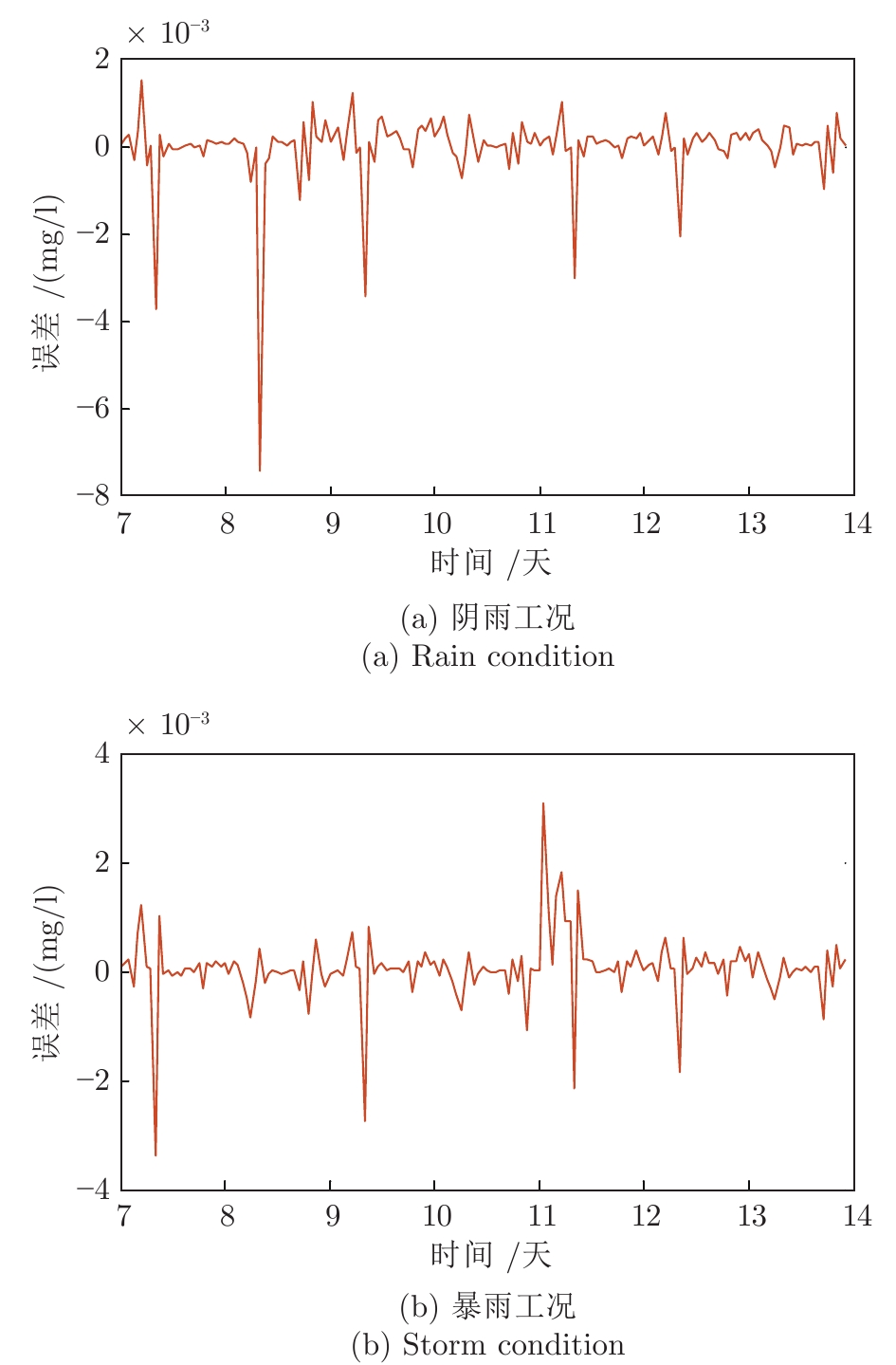
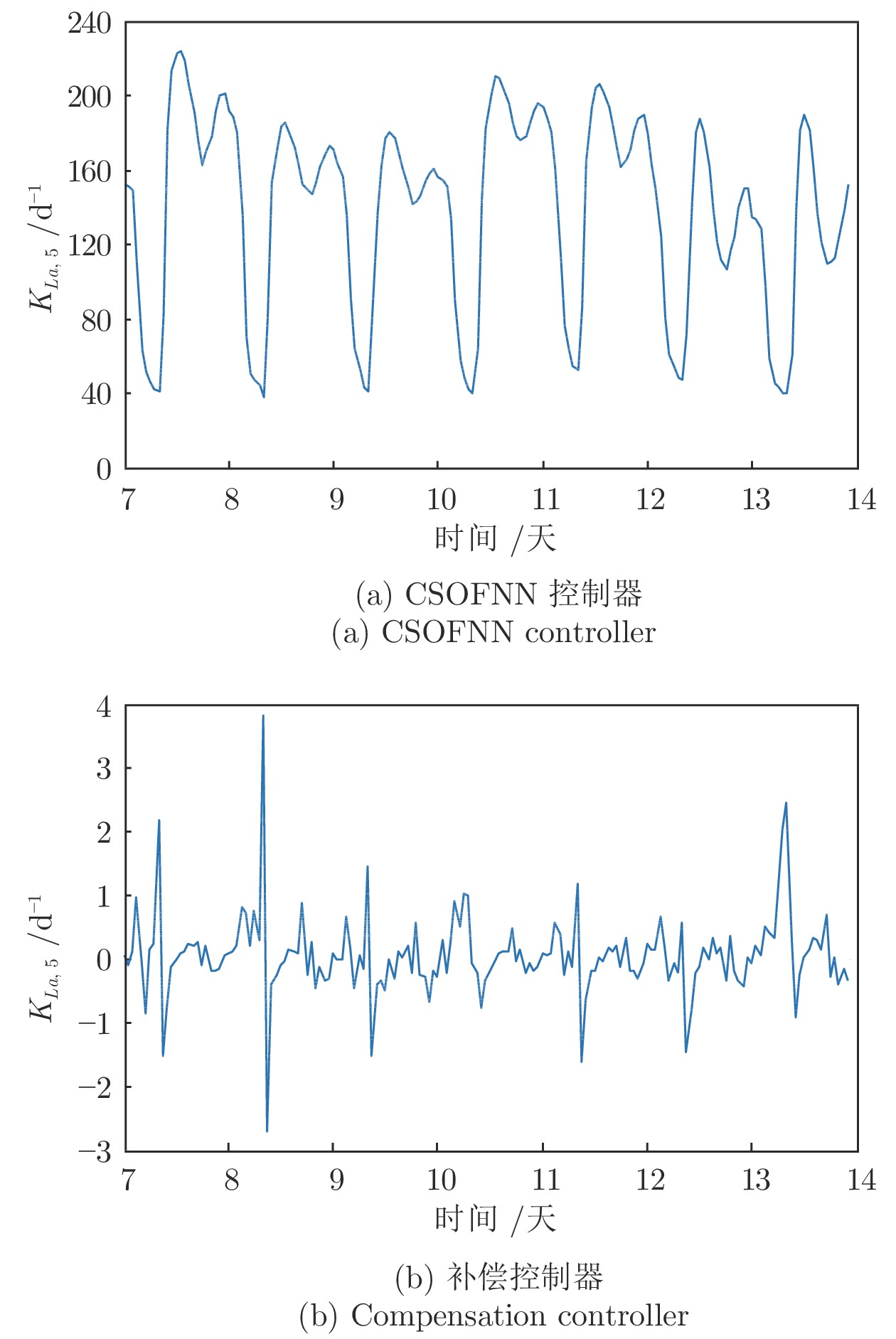
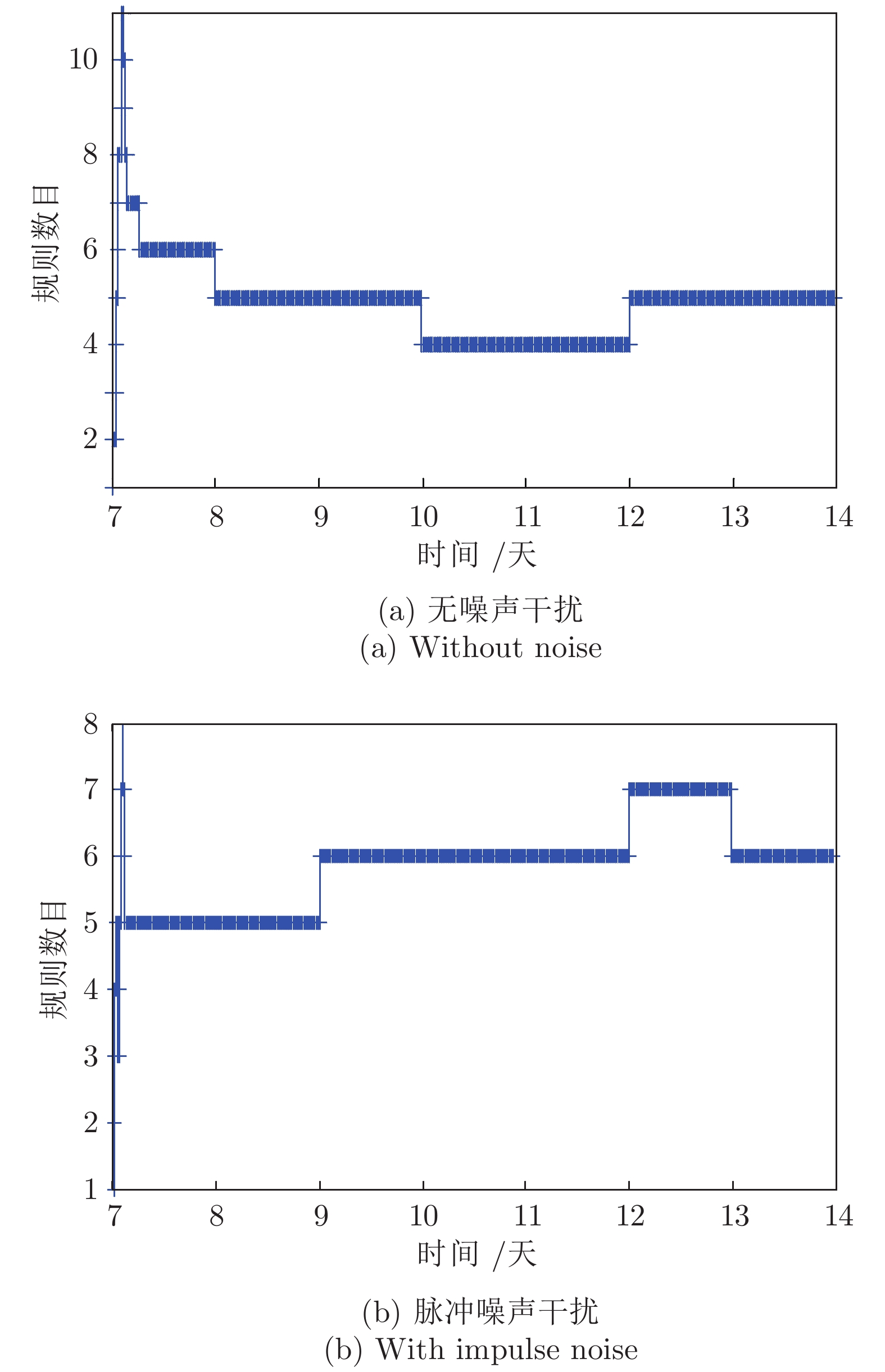
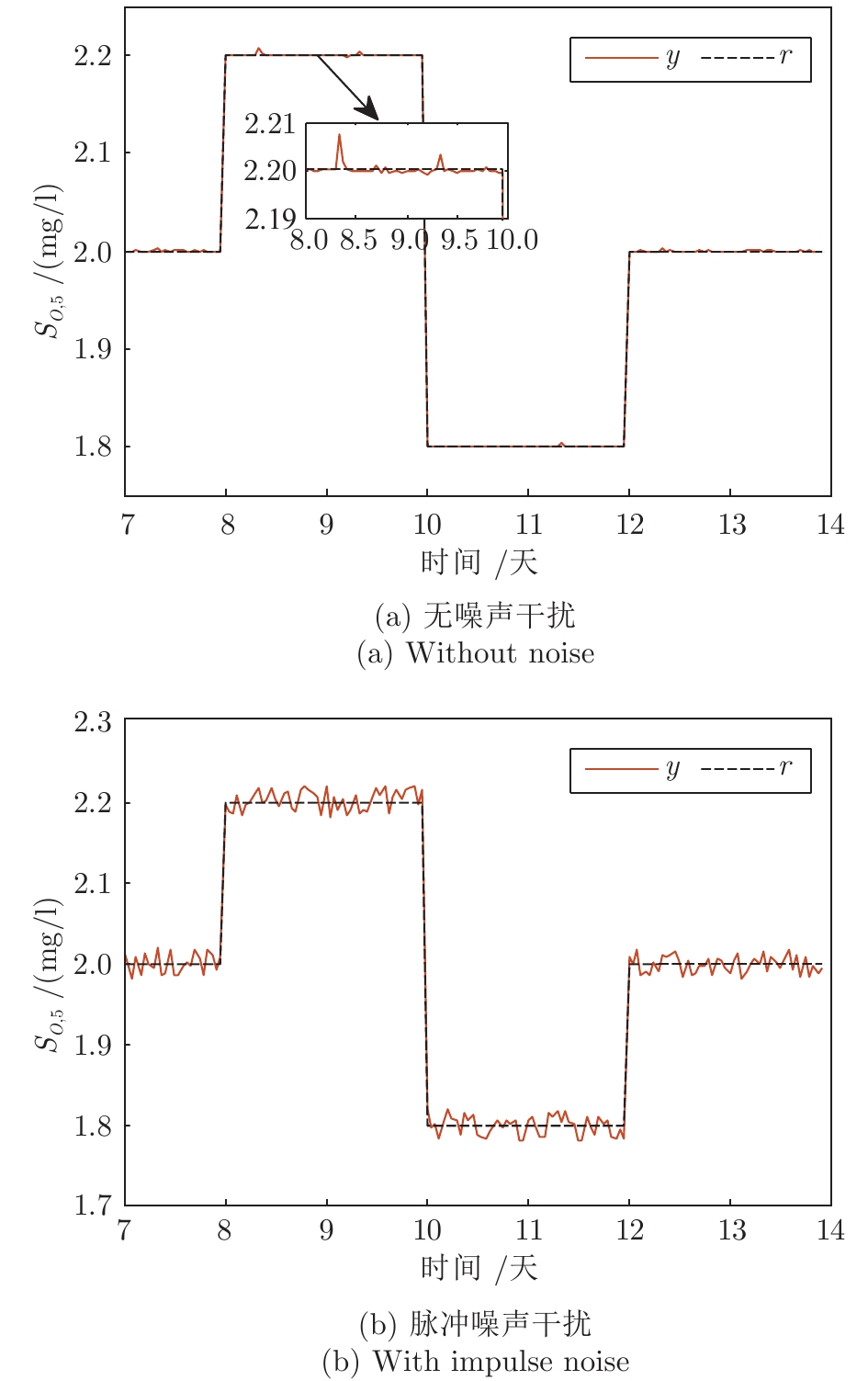
-
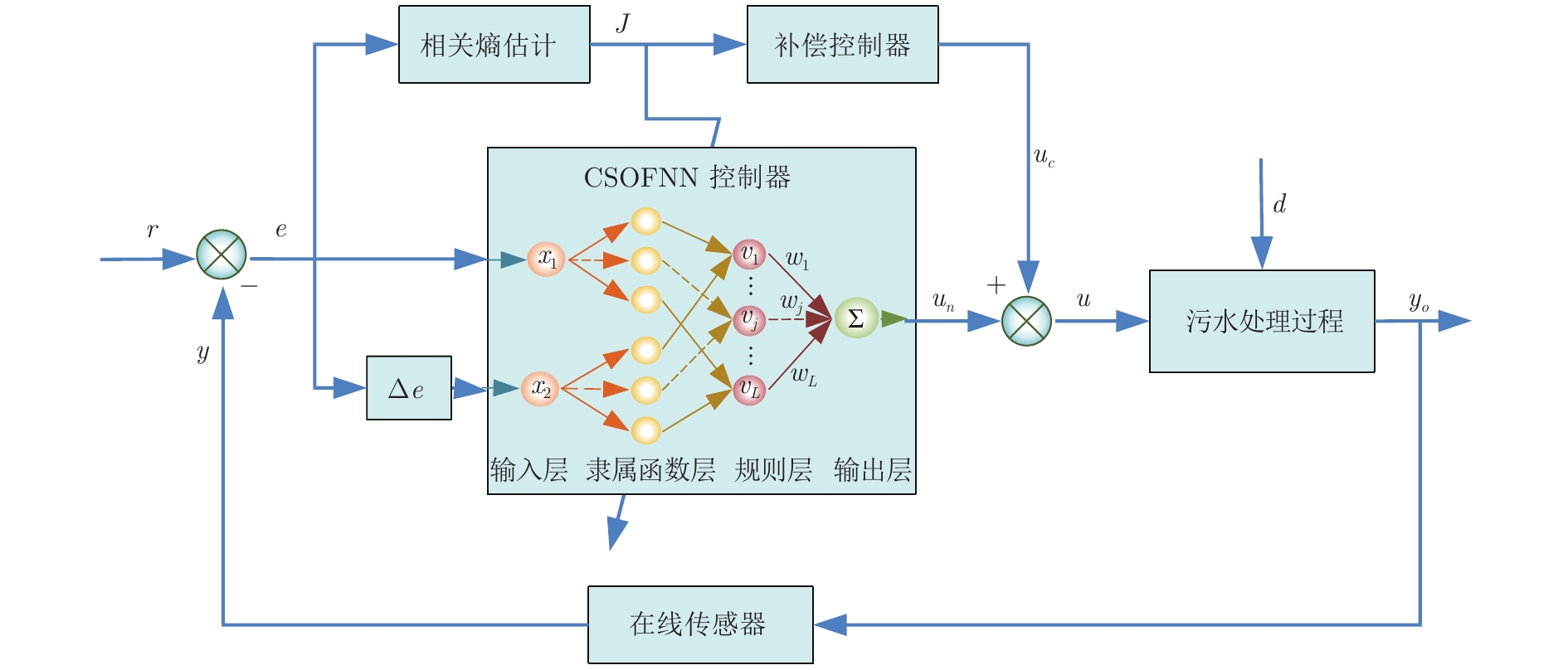
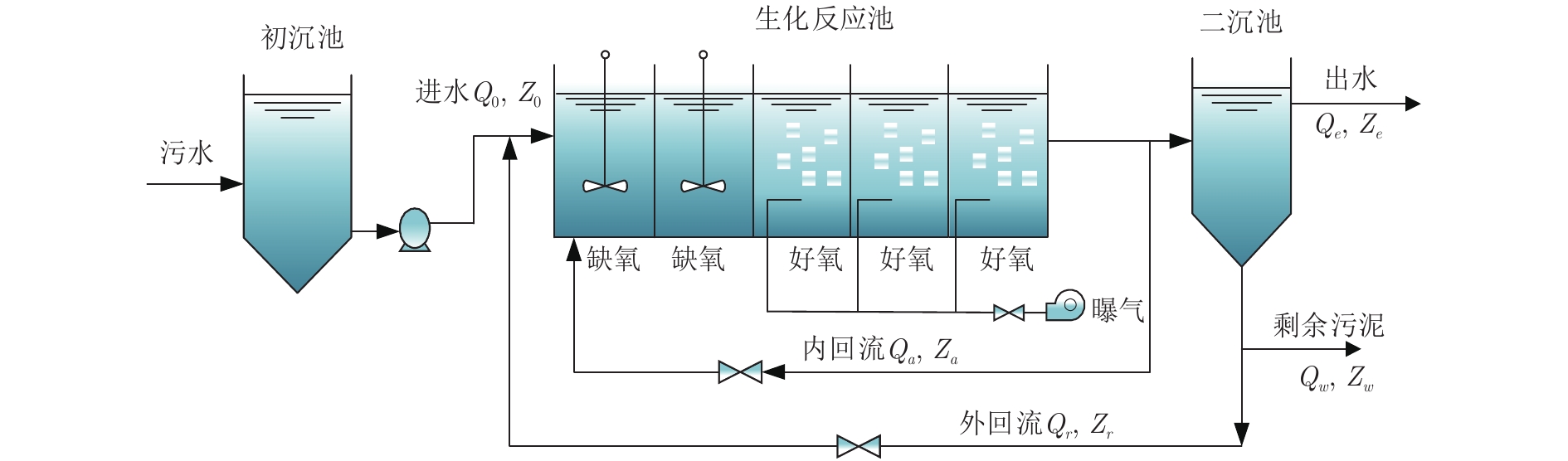
摘要: 针对城市污水处理过程的非线性、不确定性以及非高斯等特点, 提出一种数据驱动的溶解氧(Dissolved oxygen, DO)浓度在线自组织控制方法. 首先, 设计一种基于相关熵的自组织模糊神经网络控制器(Correntropy-based self-organizing fuzzy neural network, CSOFNN), 采用相关熵与规则贡献度指标实现控制器结构与参数的自动构建或修剪. 其次, 设计基于相关熵诱导准则的补偿控制器及参数自适应律, 充分利用相关熵抑制非高斯噪声的能力, 能够有效地降低系统中的不确定性. 然后, 分析所提出的控制方法的稳定性, 从而保证其在实际应用中的可靠性. 最后, 基于基准仿真1号模型(Benchmark simulation model No. 1, BSM1)的实验验证了所提方法的有效性.Abstract: To deal with the nonlinearity, uncertainty and non-Gaussianity of urban wastewater treatment processes, this paper proposes a data-driven online self-organizing control method for dissolved oxygen (DO). First, a correntropy-based self-organizing fuzzy neural network (CSOFNN) controller is designed. For CSOFNN, its structure and parameters can be automatically generated or pruned based on the correntropy and rules-contribution indexes. Second, the compensation controller and parameter adaptive laws are developed using the correntropy-induced criterion, thus can tackle non-Gaussian noise and reduce the system uncertainty. Third, the stability of the proposed control method is analyzed theoretically, thus ensuring its feasibility in practice. Finally, the proposed control method is tested in the benchmark simulation model No. 1 (BSM1). The experimental results show its effectiveness.
-
表 1 恒定So时不同控制器的性能比较
Table 1 Performance comparisons of different controllers under constant So
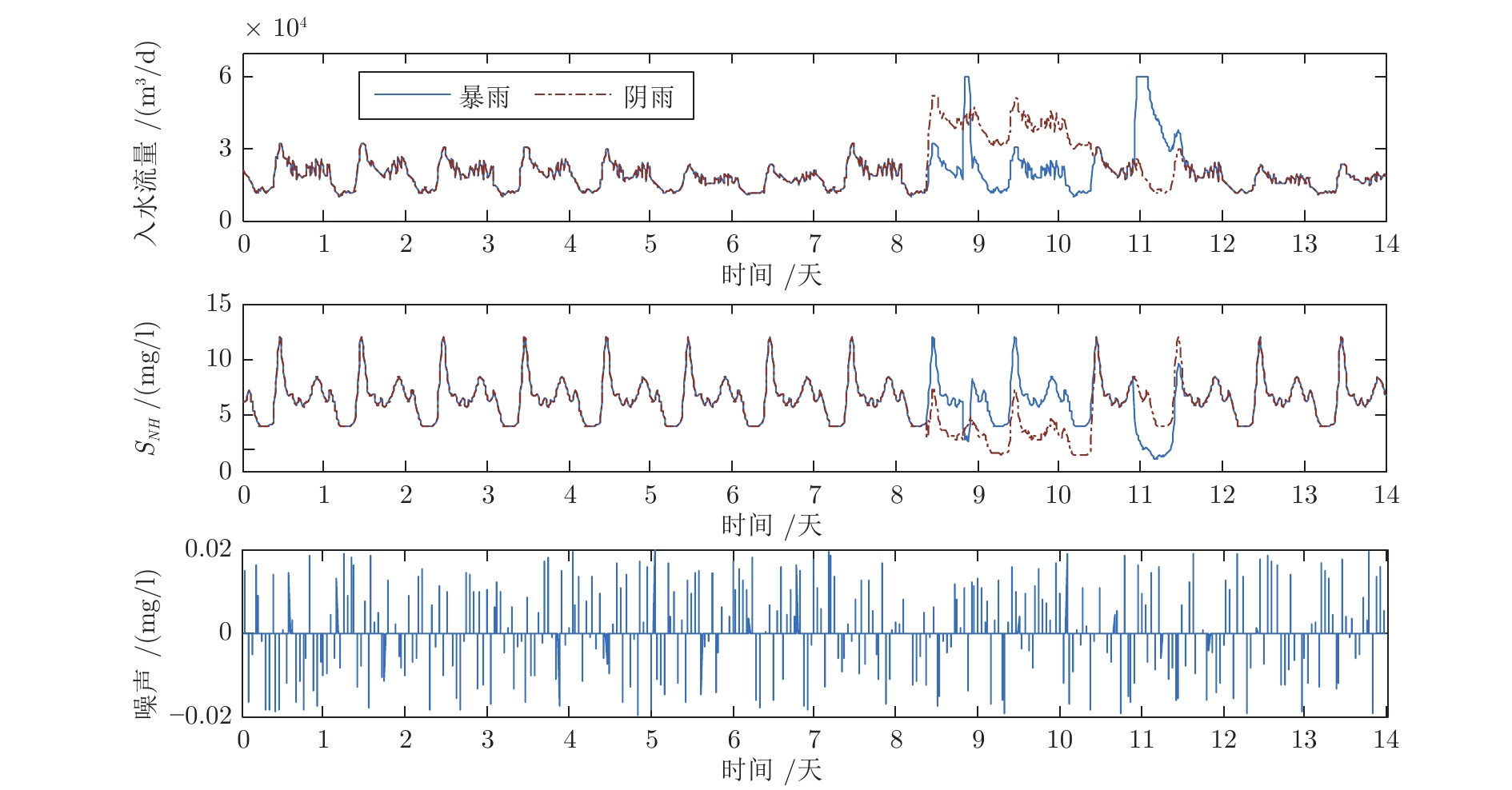
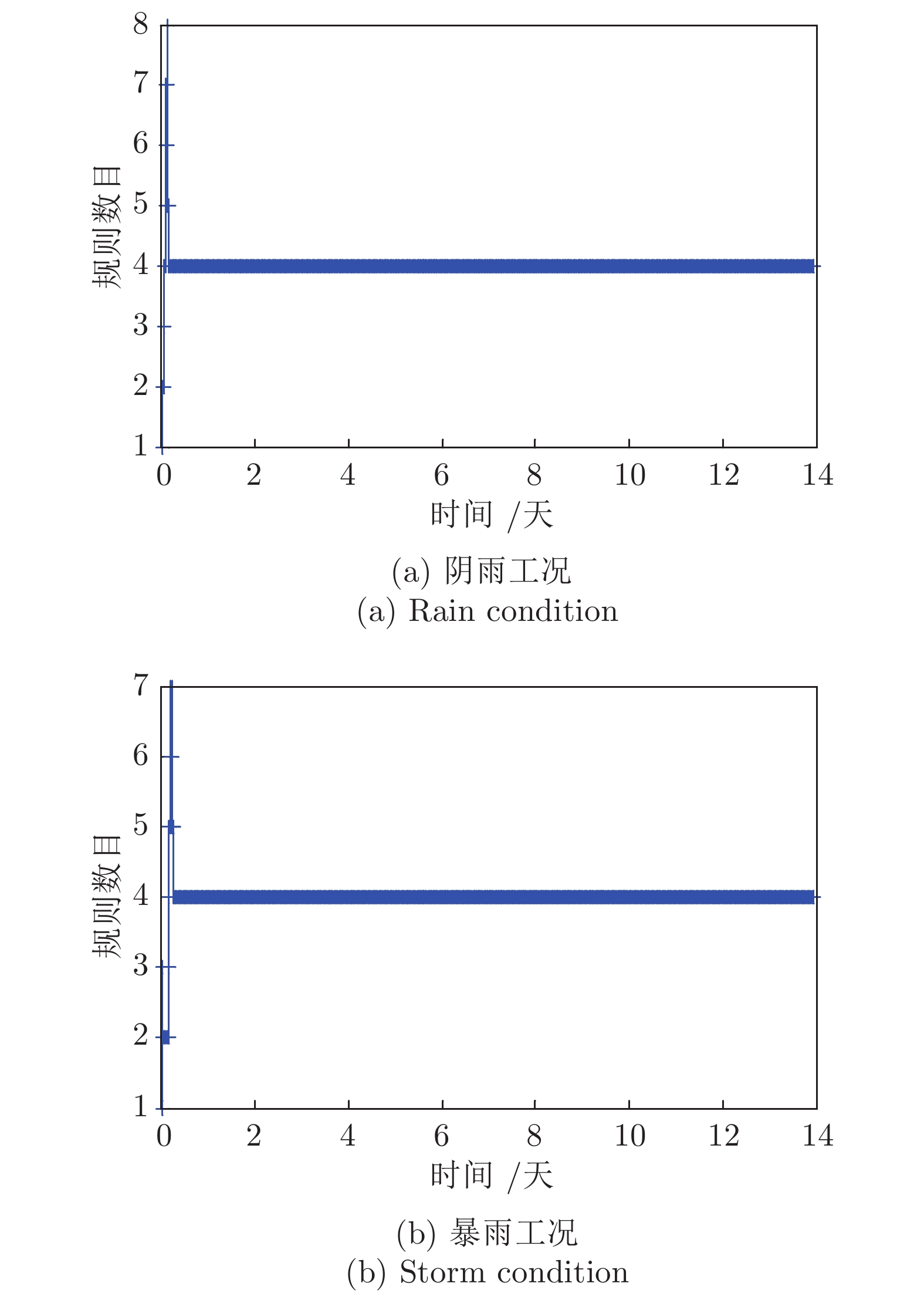
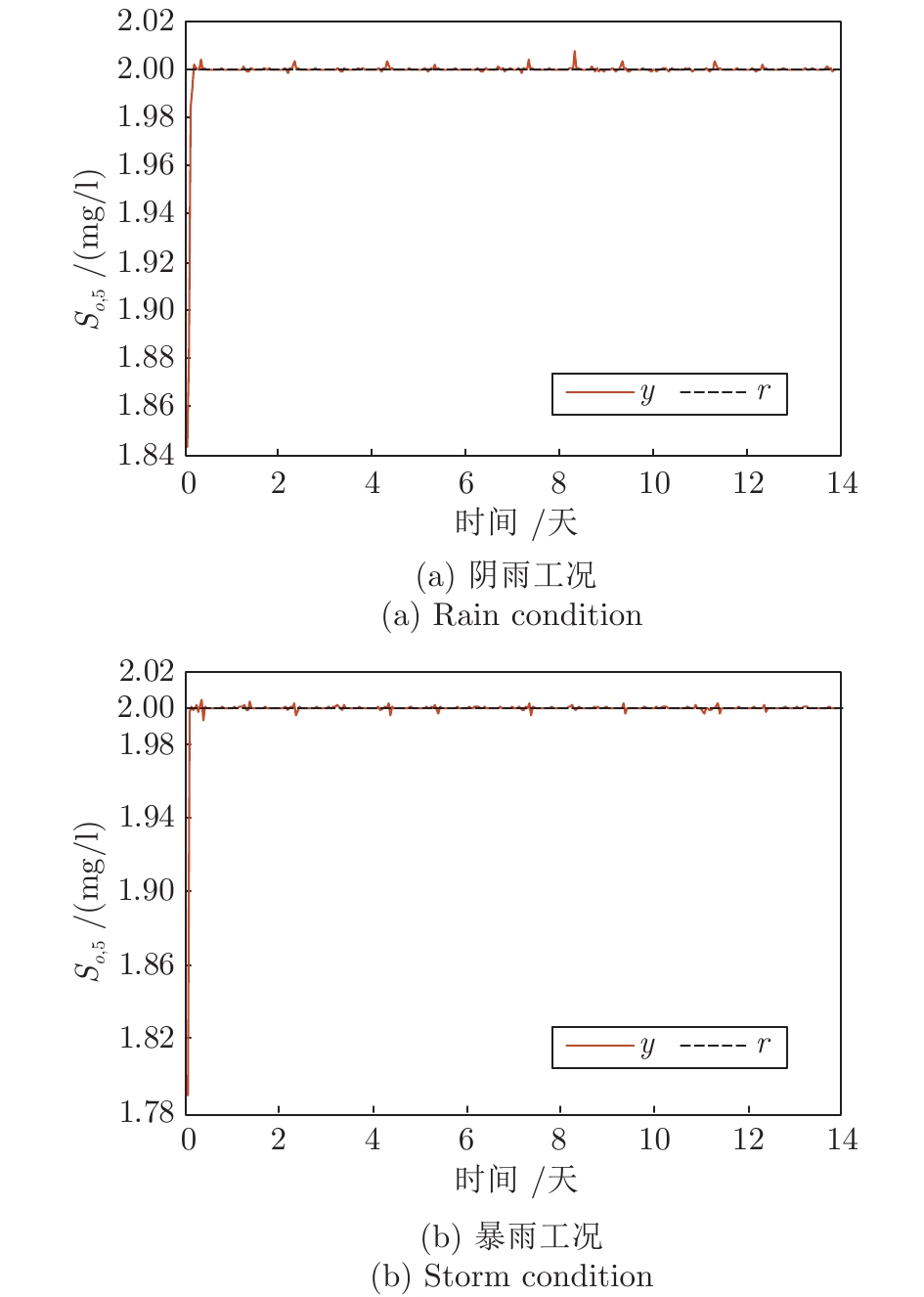
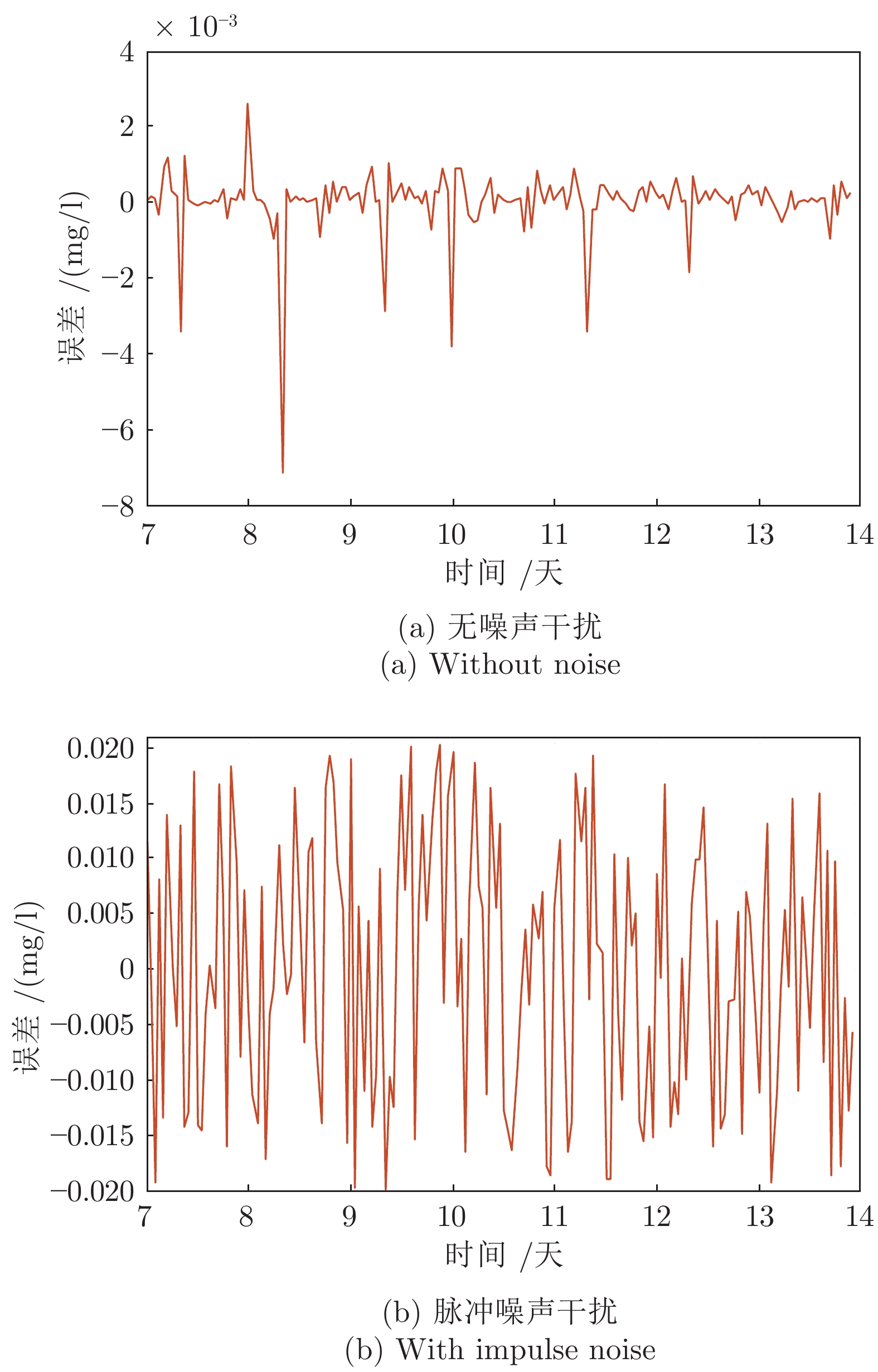
干扰类型 控制器 规则数 $IAE $ $ISE $ $Dev^{\max}$ 连续降雨 CSOFNN 4 2.1×10−3 3.00×10−6 7.44×10−3 CFNN[19] 6* 3.2×10−3* 8.76×10−6* 7.56×10−3* SOFC[15] 10* 3.1×10−2* 7.26×10−4* 3.6×10−2* SOFNN[20] 12* 4.2×10−2* 1.81×10−4* 1.12×10−2* 突发暴雨 CSOFNN 4 1.9×10−3 1.44×10−6 3.42×10−3 CFNN[19] 6* 2.1×10−3* 1.75×10−6* 3.46×10−3* SOFC[15] 9* 2.5×10−2* 8.63×10−4* 9.7×10−2* SOFNN[20] 12* 6.0×10−2* 1.19×10−3* 8.22×10−2* 注: * 表示原文中的结果, 粗体表示最好的结果. 表 2 变So下不同控制器的性能比较
Table 2 Performance comparisons of different controllers under variable So
干扰类型 控制器 规则数 $IAE $ $ISE $ $Dev^{\max}$ 降雨 CSOFNN 5 2.4×10−3 1.67×10−4 7.14×10−3 CFNN[19] 6* 2.1×10−3* 2.34×10−4* 7.60×10−3* SOFC[15] 14* 2.2×10−2* 2.86×10−4* 3.5×10−2* SOTSFNN[20] 9* 0.48* 9.7×10−4* 1.0×10−2* 降雨 + 脉冲噪声 CSOFNN 6 4.8×10−3 3.41×10−4 2.02×10−2 CFNN[19] 6 3.63×10−2 1.11×10−3 3.22×10−2 SOFC[15] 10 4.49×10−2 9.97×10−4 3.62×10−2 SOTSFNN[20] 20 1.33 2.47×10−2 4.29×10−2 注: * 表示原文中的结果, 粗体表示最好的结果. -
[1] Deletic A, Wang H. Water pollution control for sustainable development. Engineering, 2019, 5(05): 62-65. [2] 杨翠丽, 武战红, 韩红桂, 乔俊飞. 城市污水处理过程优化设定方法研究进展. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(10): 2092−2108.Yang Cui-Li, Wu Zhan-Hong, Han Hong-Gui, Qiao Jun-Fei. Perspectives on optimal setting methods for municipal wastewater treatment processes. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(10): 2092−2108. [3] 乔俊飞, 韩改堂, 周红标. 基于知识的污水生化处理过程智能优化方法. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(6): 1038−1046.Qiao Jun-Fei, Han Gai-Tang, Zhou Hong-Biao. Knowledge-based intelligent optimal control for wastewater biochemical treatment process. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(6): 1038−1046. [4] 魏伟, 陈楠, 左敏, 刘载文. 基于复合抗扰的溶解氧浓度控制. 控制理论与应用, 2020, 37(09): 1895-1903.Wei Wei, Chen Nan, Zuo Min, Liu Zai-Wen. Compound disturbance rejection control of dissolved oxygen concentration. Control Theory & Applications, 2020, 37(09): 1895-1903. [5] 蒙西, 乔俊飞, 韩红桂. 基于类脑模块化神经网络的污水处理过程关键出水参数软测量. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(5): 906-919.Meng Xi, Qiao Jun-Fei, Han Hong-Gui. Soft measurement of key effluent parameters in wastewater treatment process using brain-like modular neural networks. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(5): 906-919. [6] Santín I, Barbu M, Pedret C, Vilanova R. Dissolved oxygen control in biological wastewater treatments with non-ideal sensors and actuators. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2019, 58(45): 20639–20654. [7] van Waarde H J, Eising J, Trentelman H L, Camlibel M K. Data informativity: a new perspective on data-driven analysis and control. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2020, 65(11): 4753–4768. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2020.2966717 [8] Ding Y S, Xu N, Ren L H, and Hao K R, Data-driven neuroendocrine ultrashort feedback-based cooperative control system, IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2015, 23: 1205–1212. doi: 10.1109/TCST.2014.2359386 [9] Belchior, C A C, Araújo R A M, Landeck J A C. Dissolved oxygen control of the activated sludge wastewater treatment process using stable adaptive fuzzy control. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2012, 37: 152−162. [10] 张伟, 乔俊飞, 李凡军. 溶解氧浓度的直接自适应动态神经网络控制方法. 控制理论与应用, 2015, 32(1): 115-121. doi: 10.7641/CTA.2014.40311Zhang Wei, Qiao Jun-Fei, Li Fun-Jun. Direct adaptive dynamic neural network control for dissolved oxygen concentration. Control Theory & Applications, 2015, 32(1): 115-121. doi: 10.7641/CTA.2014.40311 [11] Wang D, Ha M M, Qiao J F. Data-driven iterative adaptive critic control towards an urban wastewater treatment plant. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2021, 68(8): 7362-7369. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2020.3001840 [12] Ruan J, Zhang C, Li Y, Yang Z, Chen X, Huang M, Zhang T. Improving the efficiency of dissolved oxygen control using an on-line control system based on a genetic algorithm evolving FWNN software sensor. Journal of Environmental Management, 2017, 187: 550–559. [13] Eltag K, Aslamx M S, Ullah R. Dynamic stability enhancement using fuzzy PID control technology for power system. International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems, 2019, 17: 234–242. doi: 10.1007/s12555-018-0109-7 [14] 张帅, 周平. 污水处理过程递推双线性子空间建模及无模型自适应控制. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(7): 1747−1759Zhang Shuai, Zhou Ping. Recursive bilinear subspace modeling and model-free adaptive control of wastewater treatment. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(7): 1747−1759 [15] Qiao J F, Zhang W, Han H G. Self-organizing fuzzy control for dissolved oxygen concentration using fuzzy neural network. Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems, 2016, 30(6): 3411–3422. [16] 韩广, 乔俊飞, 薄迎春. 溶解氧浓度的前馈神经网络建模控制方法. 控制理论与应用, 2013, 30(05): 585-591.Han Huang, Qiao Jun-Fei, Bo Ying-Chun. Feedforward neural network modeling and control for dissolved oxygen concentration, Control Theory & Applications, 2013, 30(05): 585-591. [17] Lin M J, Luo F. An adaptive control method for the dissolved oxygen concentration in wastewater treatment plants. Neural Computing and Applications, 2015, 26(8): 2027-2037. doi: 10.1007/s00521-015-1858-3 [18] Han H G, Zhang L, Liu H X, et al. Multiobjective design of fuzzy neural network controller for wastewater treatment process. Applied Soft Computing, 2018, 67: 467–478. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2018.03.020 [19] 权利敏, 杨翠丽, 乔俊飞. 基于CFNN的污水处理过程溶解氧浓度在线控制. 智能科学与技术学报, 2020, 2(03): 261-267.Quan Li-Min, Yang Cui-Li, Qiao Jun-Fei. CFNN-based online control for dissolved oxygen concentration of wastewater treatment processes. Chinese Journal of Intelligent Science and Technologie, 2020, 2(3): 261-267. [20] 乔俊飞, 付文韬, 韩红桂. 基于SOTSFNN的溶解氧浓度控制方法. 化工学报, 2016, 67(03): 960-966.Qiao Jun-Fei, Fu Wen-Tao, Han Hong-Gui. Dissolved oxygen control method based on self-organizing T-S fuzzy neural network. CIESC Journal, 2016, 67(3): 960-966. [21] 周红标, 基于自组织模糊神经网络的污水处理过程溶解氧控制. 化工学报, 2017, 68(04): 1516-1524.Zhou Hong-Biao. Dissolved oxygen control of wastewater treatment process using self-organizing fuzzy neural network. CIESC Journal, 2017, 68(04): 1516-1524. [22] Chen B, Liu X, Zhao H, Principe J C. Maximum correntropy Kalman filter. Automatica, 2017, 76: 70–77. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2016.10.004 [23] Yu, J. A nonlinear kernel Gaussian mixture model based inferential monitoring approach for fault detection and diagnosis of chemical processes. Chemical Engineering Science, 2012, 68: 506–519. doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2011.10.011 [24] Liu W, Pokharel P P, Principe J C. Correntropy: Properties and applications in non-Gaussian signal processing. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2007, 55(11): 5286-5298. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2007.896065 [25] Bao R-J, Rong H-J, Angelov P P, et al. Correntropy-based evolving fuzzy neural system. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2018, 26: 1324–1338. doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2017.2719619 [26] Cao J, Dai H, Lei B, Yin C, Zeng H, Kummert A. Maximum correntropy criterion-based hierarchical one-class classification. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2020, Doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2020.3015356. [27] Nayyeri M, Yazdi HS, Maskooki A, Rouhani M. Universal approximation by using the correntropy objective function. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2018, 29(9): 4515–4521. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2017.2753725 [28] Ren M, Gong M, Lin M, Zhang J. Generalized correntropy predictive control for waste heat recovery systems based on organic rankine cycle. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 151587–151594. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2948284 [29] Jeppsson U, Pons M N. The COST benchmark simulation model current state and future perspective. Control Engineering Practice, 2004, 12(3): 299–304. doi: 10.1016/j.conengprac.2003.07.001 [30] Chen C S. Robust self-organizing neural-fuzzy control with uncertainty observer for MIMO nonlinear systems. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2011, 19(4): 694–706. doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2011.2136349 [31] Sun M A. Barbalat-like lemma with its application to learning control. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2009, 54: 2222–2225. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2009.2026849 -




 下载:
下载: