-
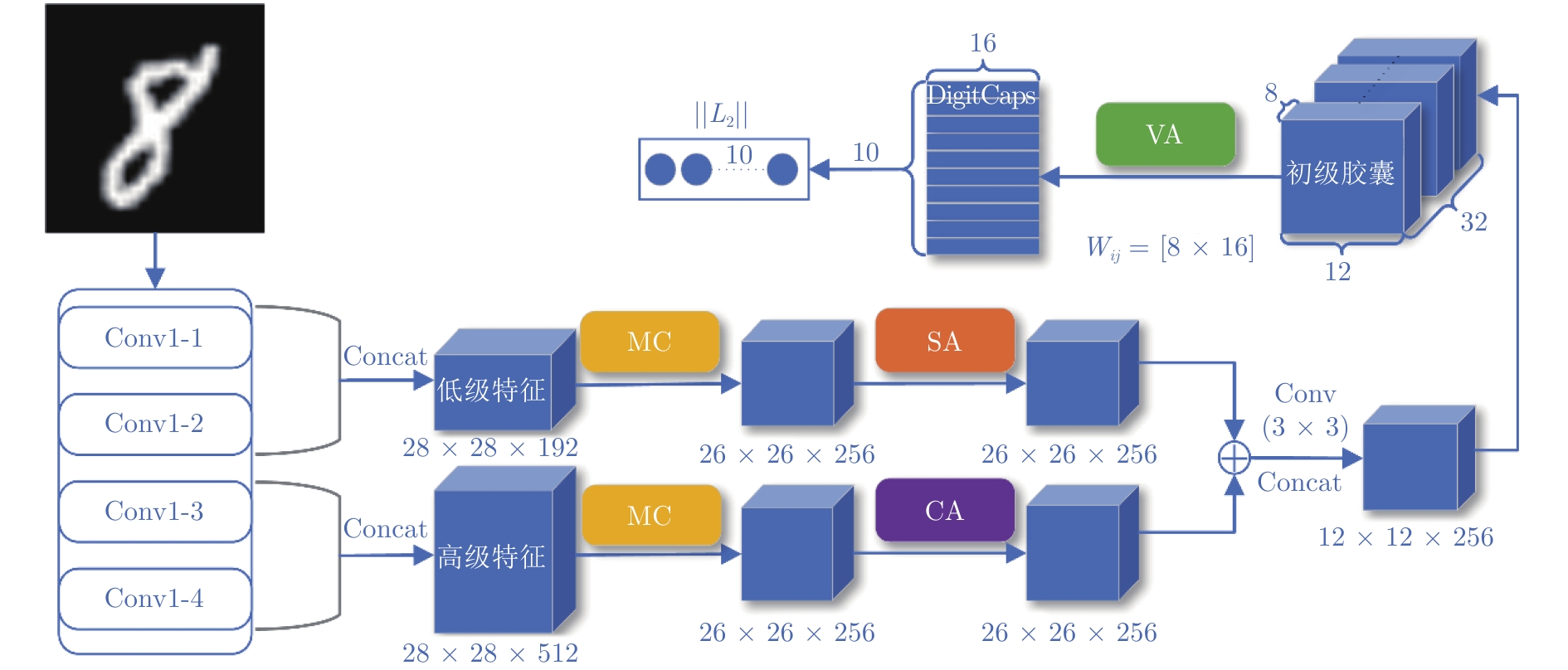
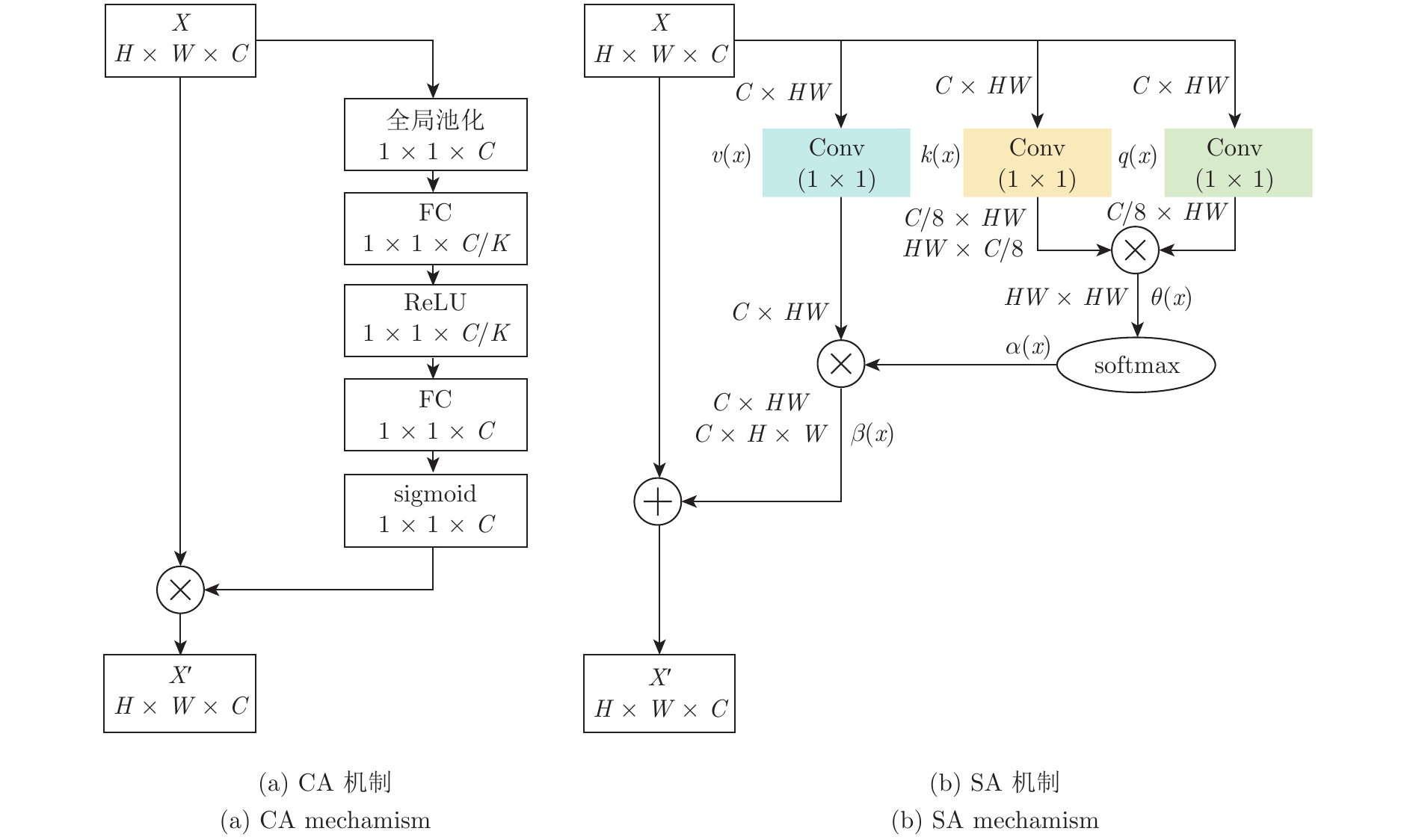
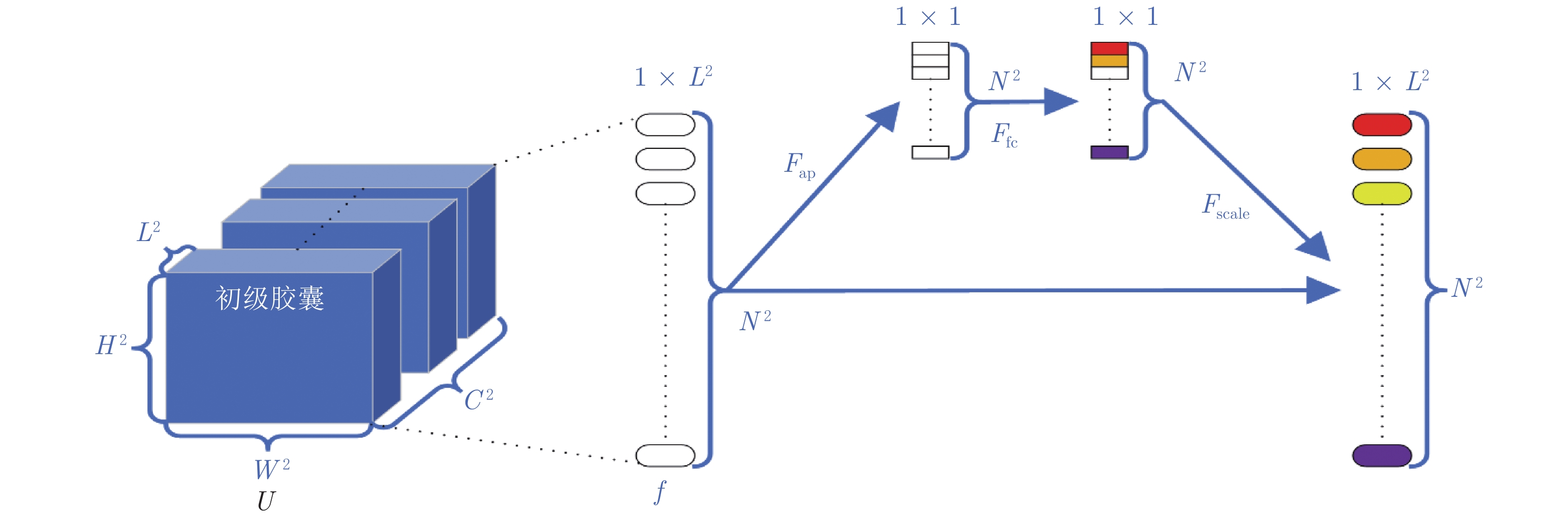
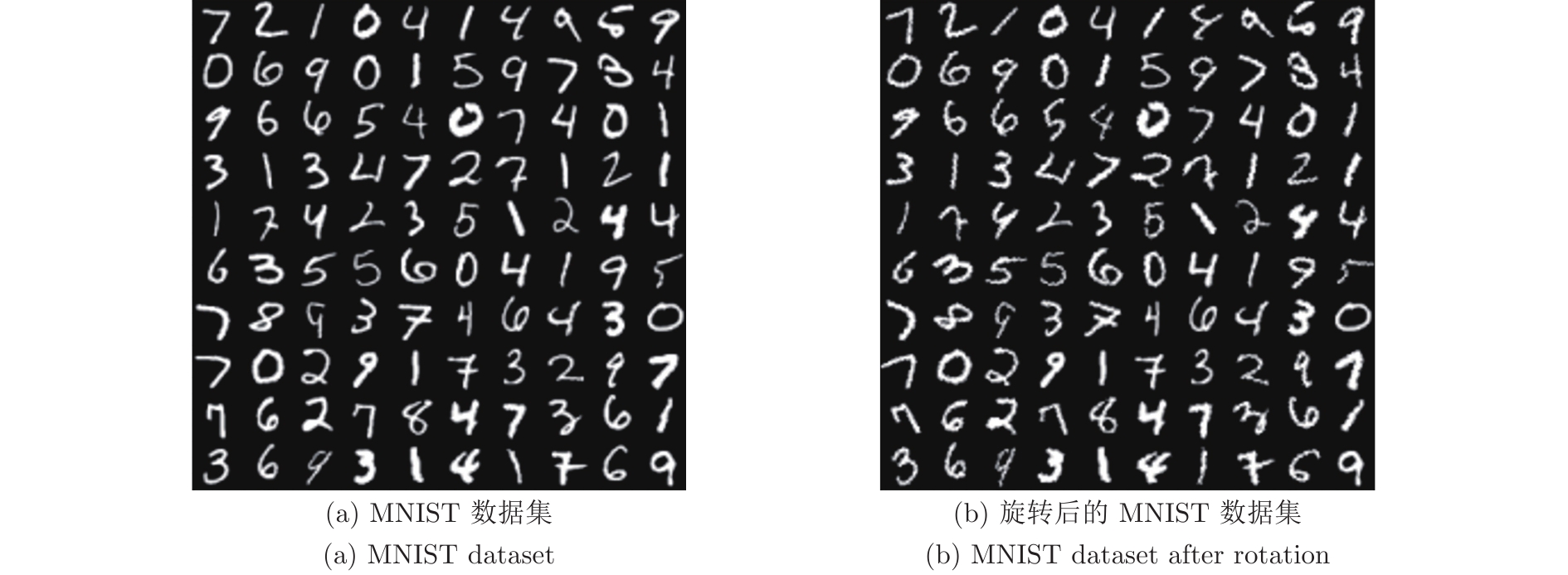
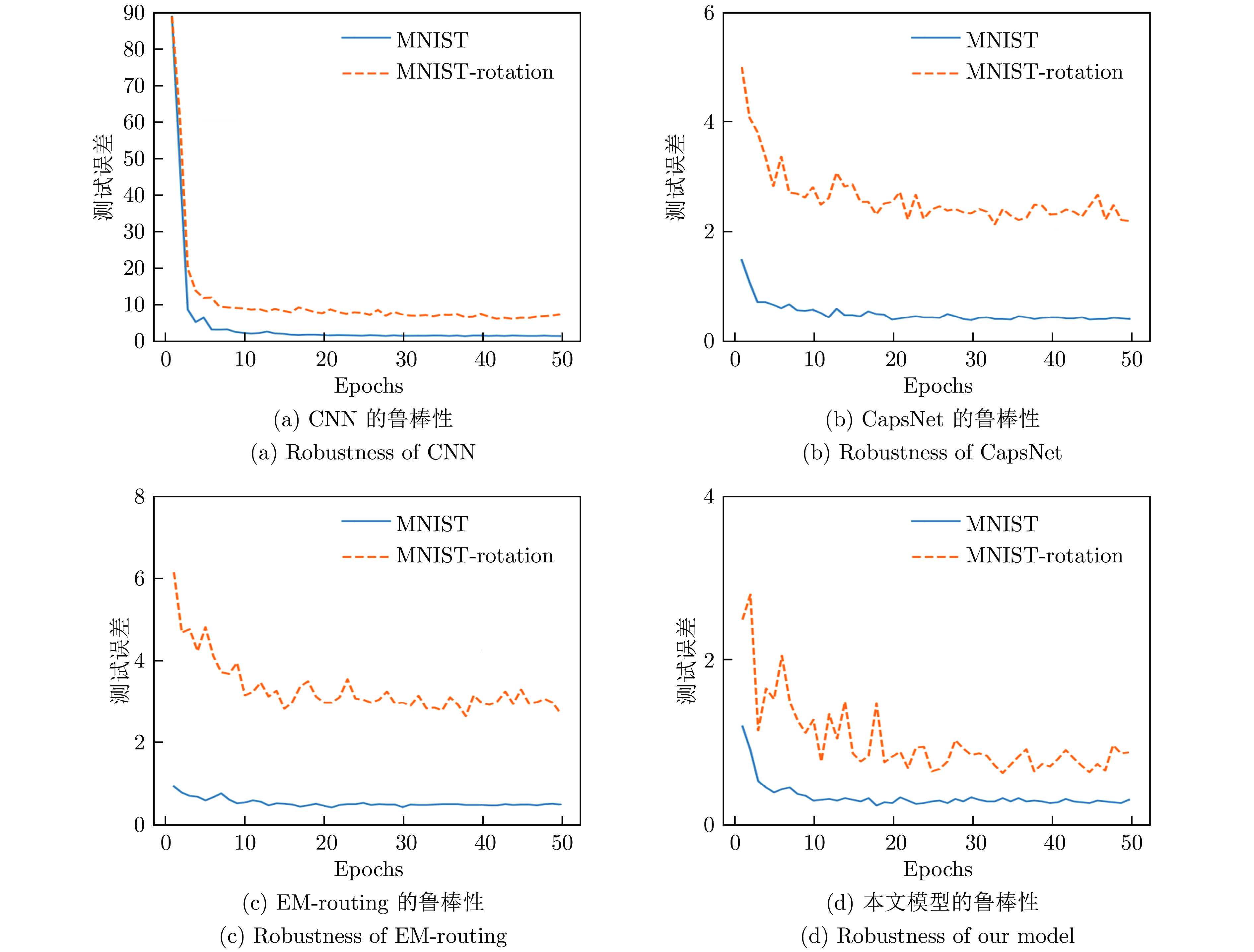
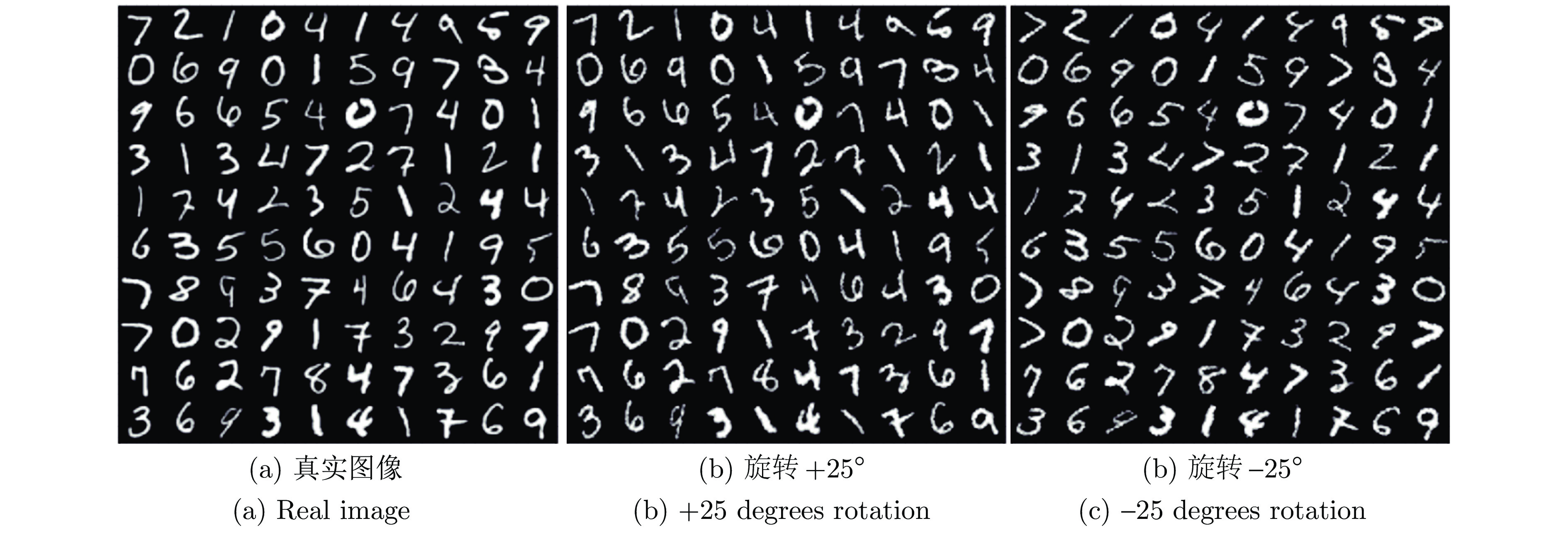
摘要: 针对传统的胶囊网络(Capsule network, CapsNet)特征提取不充分的问题, 提出一种图像分类的多阶段注意力胶囊网络模型. 首先, 在卷积层对低层特征和高层特征分别采用注意力(Spatial attention, SA)和通道注意力(Channel attention, CA)来提取有效特征; 然后, 提出基于向量的注意力(Vector attention, VA)机制作用于动态路由层, 增加对重要胶囊的关注, 进而提高低层胶囊对高层胶囊预测的准确性; 最后, 在五个公共数据集上进行图像分类的对比实验. 结果表明, 所提出的CapsNet模型在分类精度和鲁棒性上优于其他胶囊网络模型, 在仿射变换图像重构方面也表现良好.Abstract: Aiming to address the inadequate feature extraction problems in the traditional capsule networks (CapsNets), a multi-stage attention-based CapsNet model is proposed in this paper for image classification. Firstly, spatial attention (SA) and channel attention (CA) are used to extract effective features in the convolutional layer from low-level features and high-level features, respectively. Then, attention mechanism based on vector direction is introduced into the dynamic routing layer to enhance the focus on the important capsules, thereby improving the prediction accuracy of the low-layer capsules to the high-layer capsules. Finally, the comparison experiments on image classification are carried out on five public datasets. The experimental results show that the proposed CapsNet outperforms other CapsNets at the classification accuracy and the robustness, and its shows a good performance on the image reconstruction for affine images.
-
Key words:
- Image classification /
- capsule network (CapsNet) /
- attention mechanism /
- multi-stage /
- robustness
-
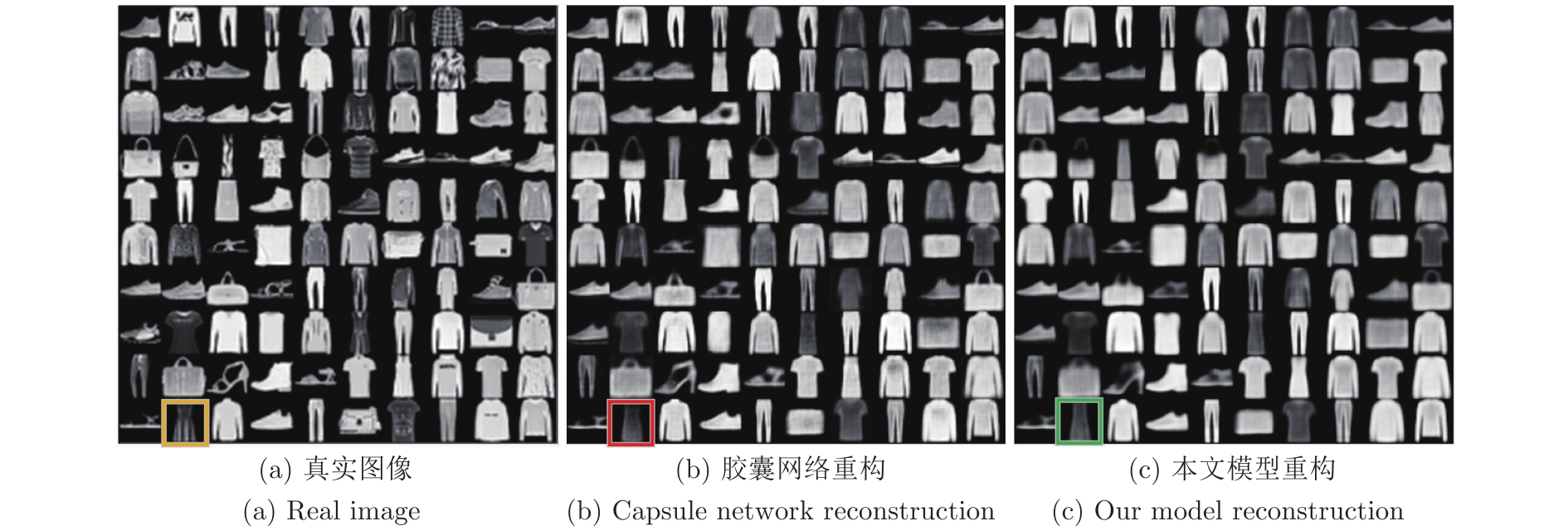
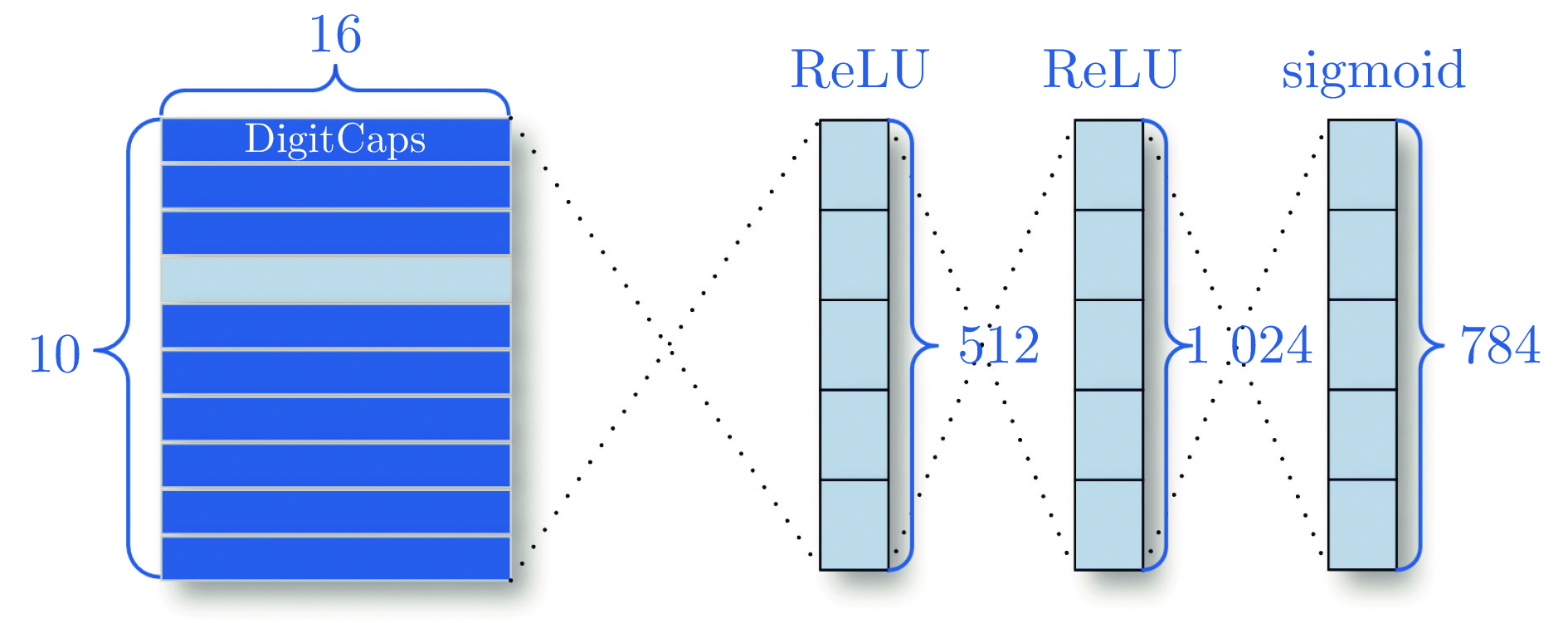
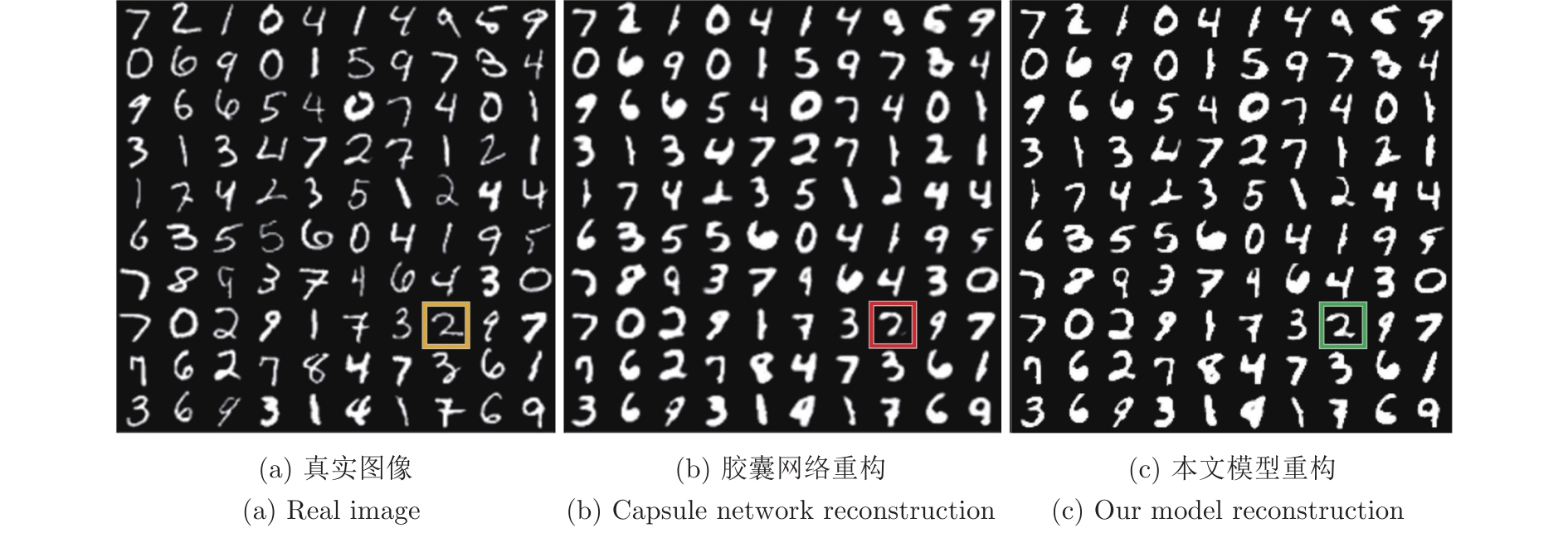
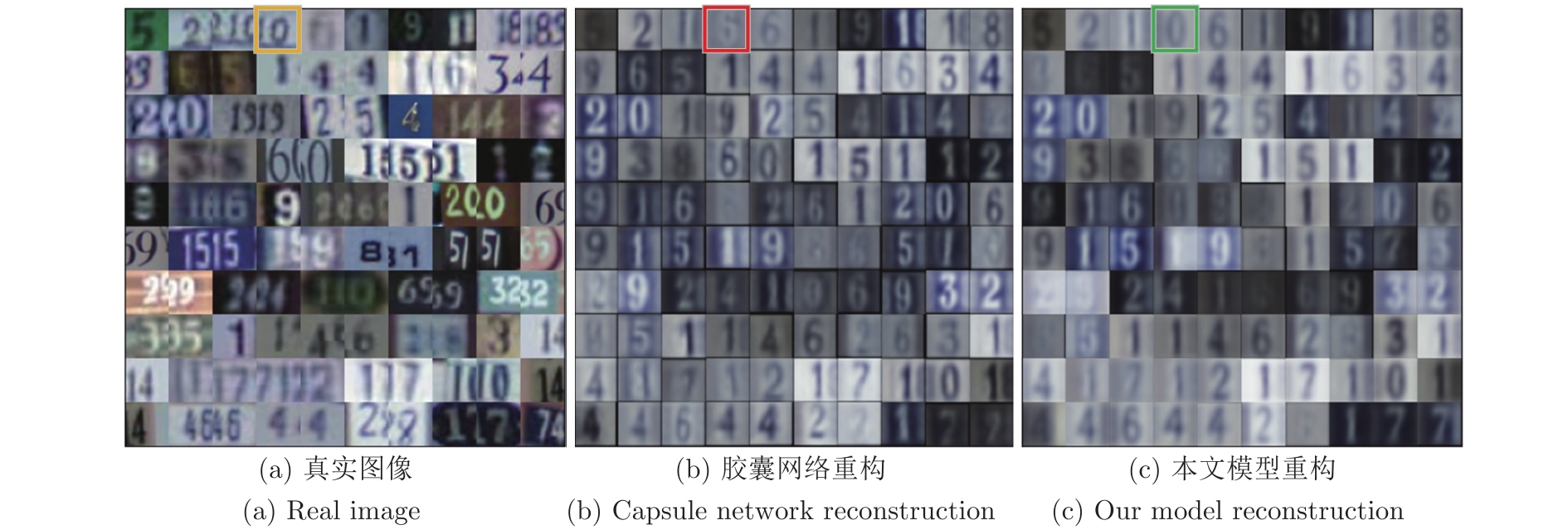
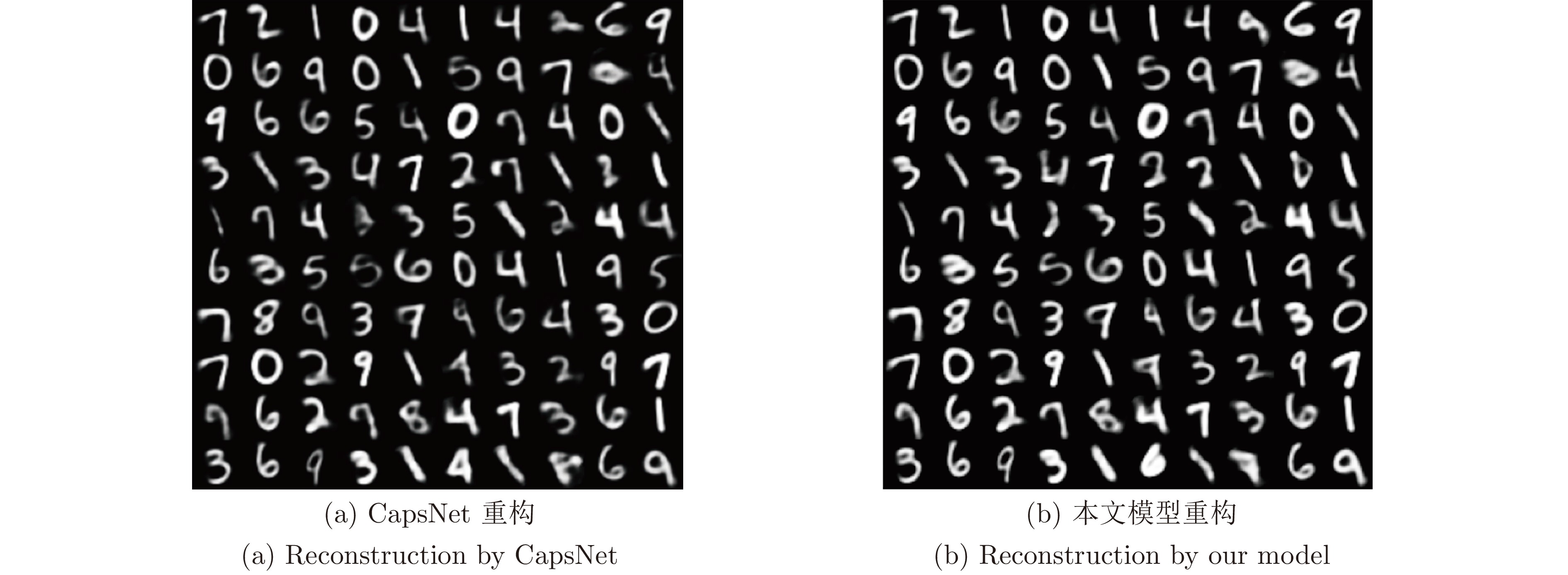
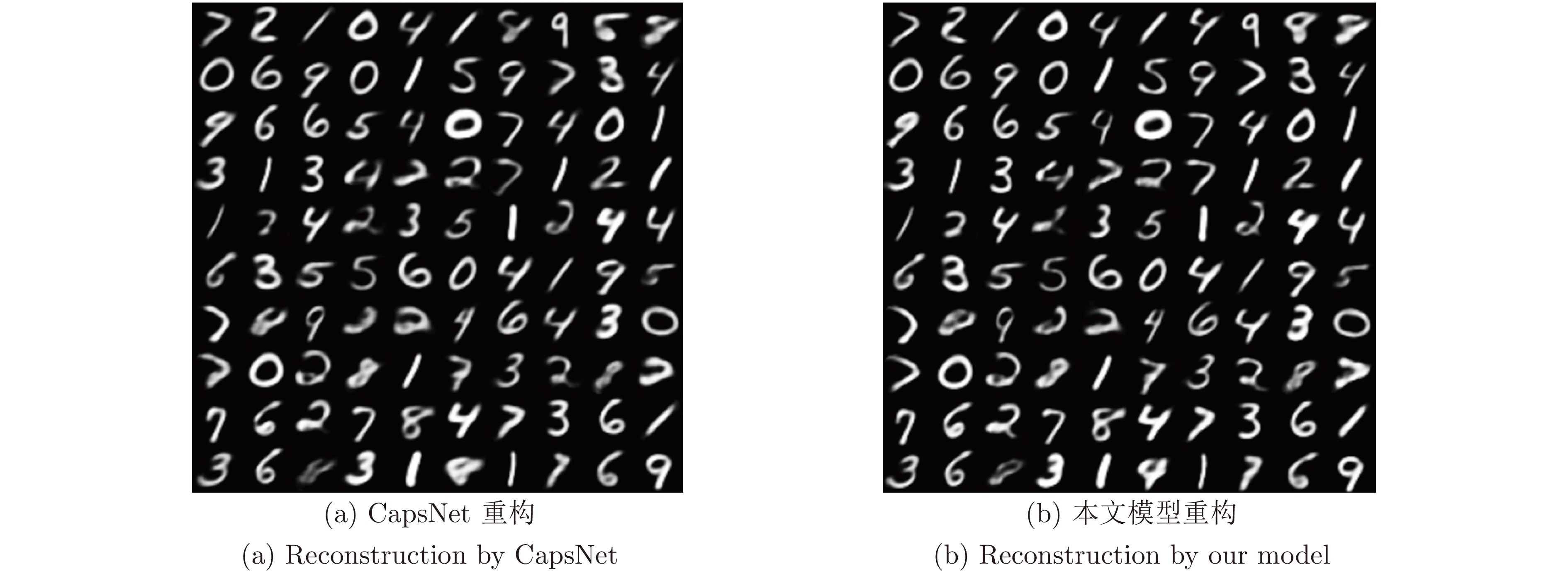
图 15 图14(b)的重构实验对比图
Fig. 15 Comparison of reconstructions to Fig. 14(b)
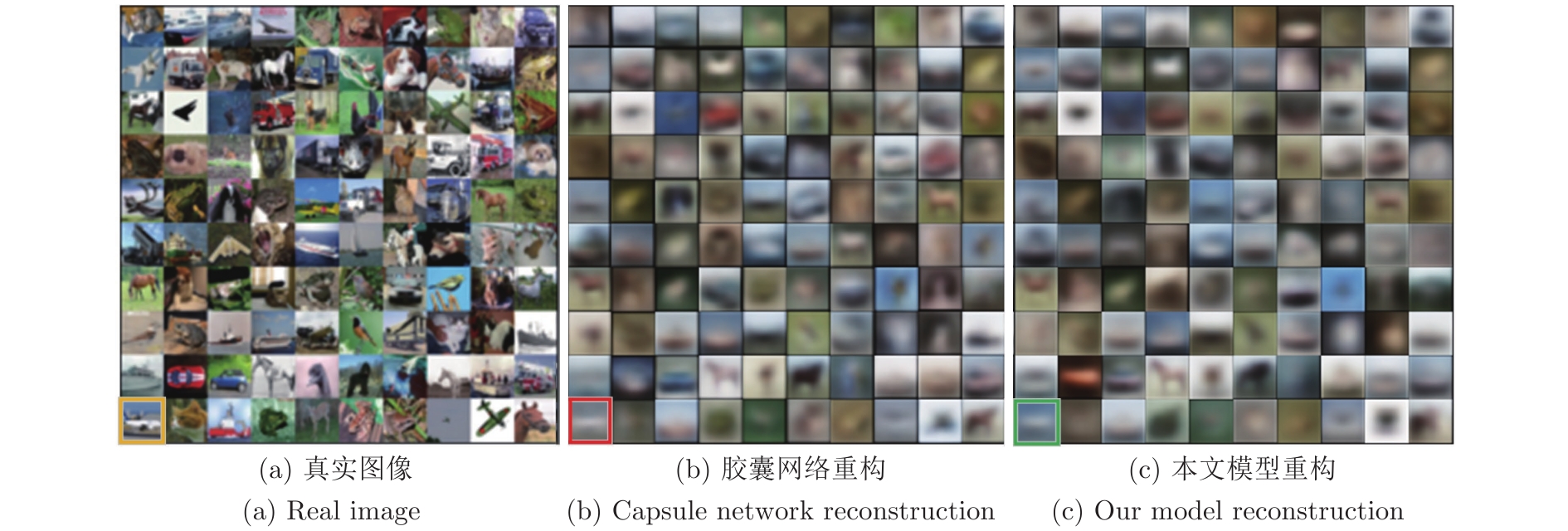
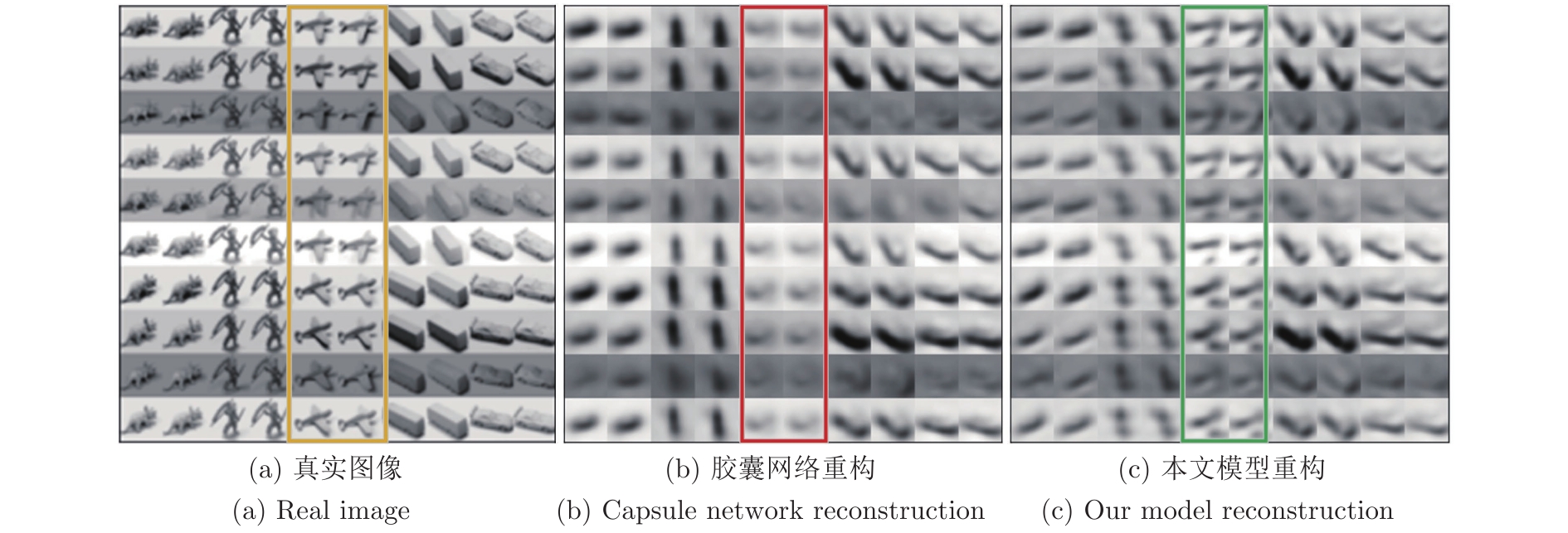
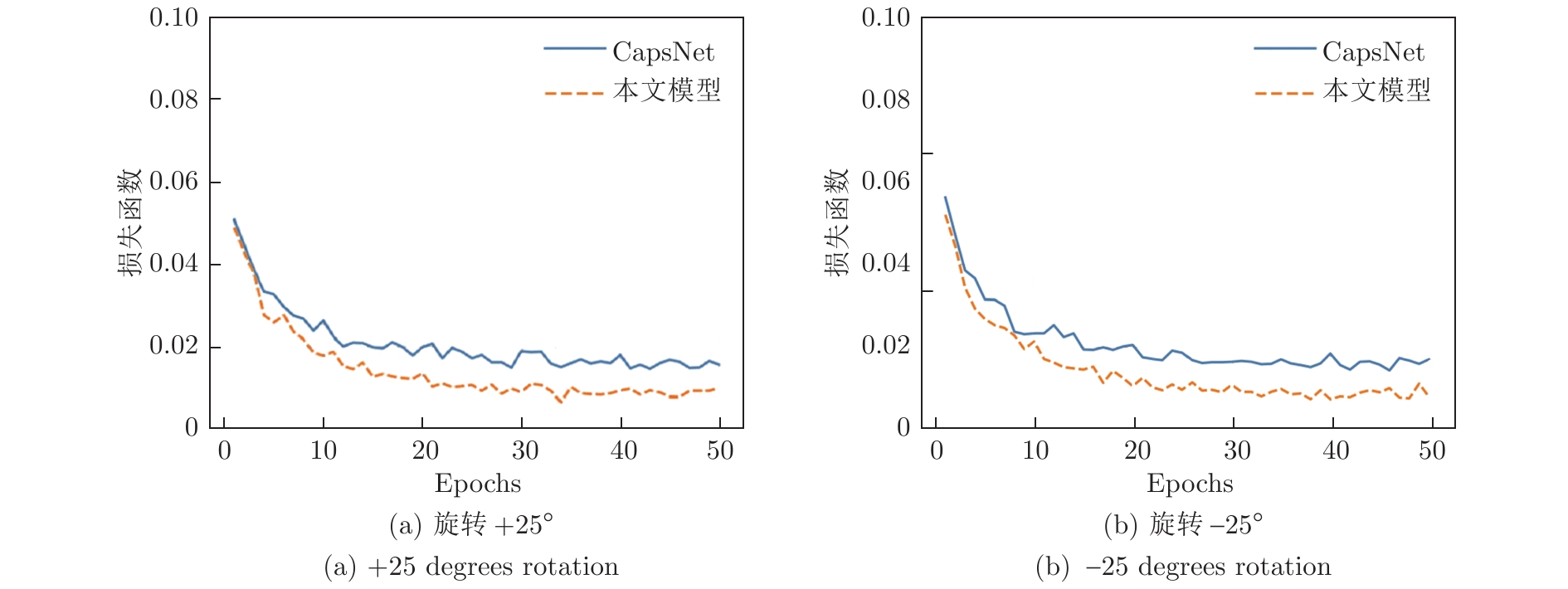
图 16 图14(c)的重构实验对比图
Fig. 16 Comparison of reconstructions to Fig. 14(c)
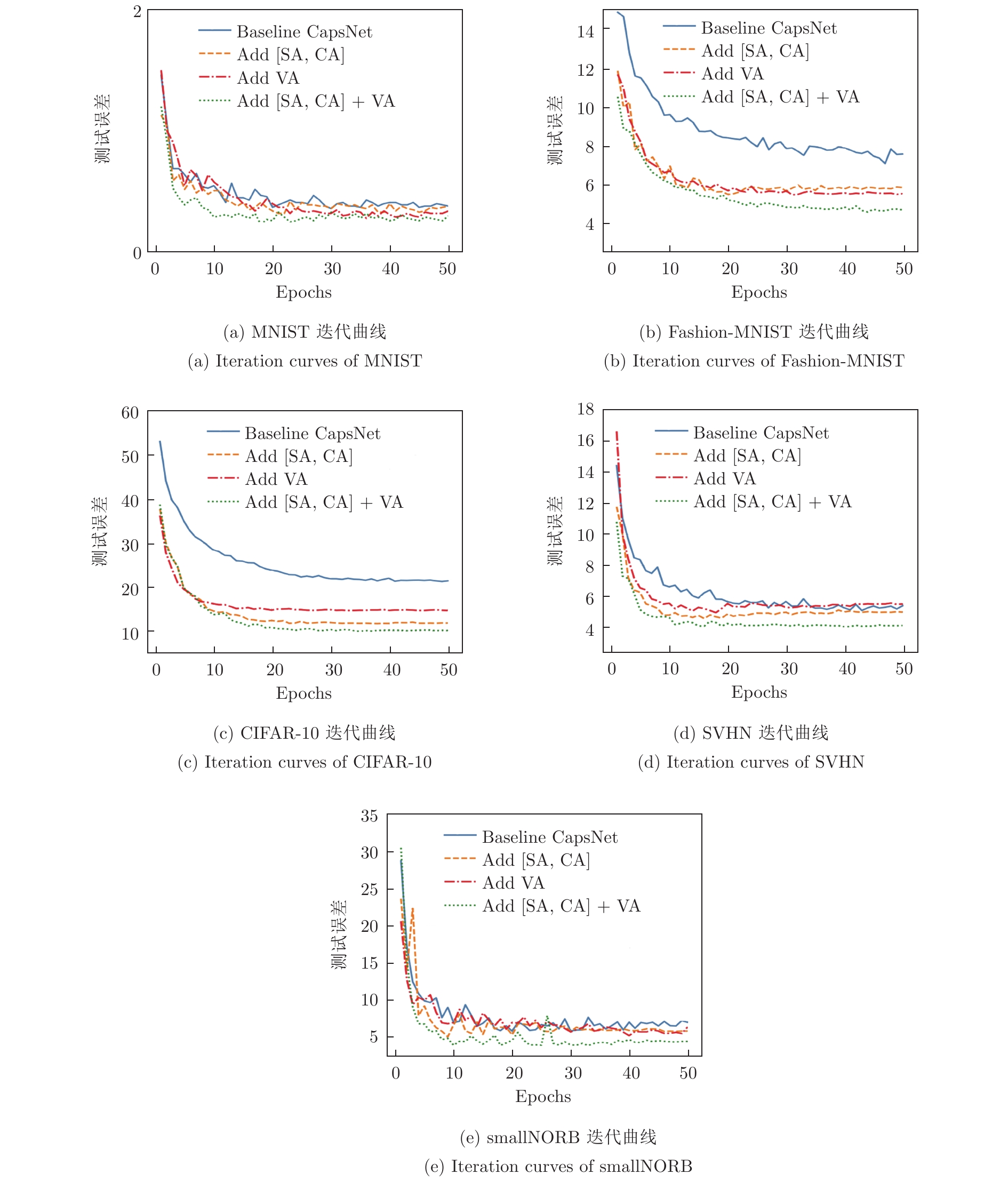
表 1 不同改进模块在五个数据集上的分类错误率(%)
Table 1 Classification error rates of different improvement modules on five datasets (%)
模型 MNIST Fashion-MNIST CIFAR-10 SVHN smallNORB Baseline 0.38 7.11 21.21 5.12 5.62 Baseline + (SA + CA) 0.32 5.54 11.69 4.61 5.07 Baseline + VA 0.28 5.53 14.65 4.99 5.21 Baseline + (SA + CA + VA) 0.22 4.63 9.99 4.08 4.89 表 2 不同模型在五个数据集上的分类错误率(%)
Table 2 Classification error rates of different models on five datasets (%)
模型 MNIST Fashion-MNIST CIFAR-10 SVHN smallNORB Prem Nair et al.'s CapsNet[5] 0.50 10.20 31.47 8.94 — HitNet[7] 0.32 7.70 26.70 5.50 — Matrix Capsule EM-routing[9] 0.70 5.97 16.79 9.64 5.20 SACN[10] 0.50 5.98 16.65 5.01 7.79 AR-CapsNet[11] 0.54 — 12.71 — — DCNet[30] 0.25 5.36 17.37 4.42 5.57 MS-CapsNet[31] — 6.01 18.81 — — VB-routing[32] — 5.20 11.20 4.75 1.60 Aff-CapsNets[33] 0.46 7.47 23.72 7.85 — 本文模型 0.22 4.63 9.99 4.08 4.89 -
[1] Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Lake Tahoe, USA: NIPS, 2012. 1097−1105 [2] Simonyan K, Zissweman A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations. San Diego, USA: ICLR, 2015. 1−14 [3] Howard A G, Zhu M, Chen B, Kalenichenko D, Wang W, Weyand T, et al. Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1704.04861, 2017. [4] Huang G, Liu Z, Van Der Maaten L, Weinberger K Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 2261−2269 [5] Nair P, Doshi R, Keselj S. Pushing the limits of capsule networks. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2103.08074, 2021. [6] Sabour S, Frosst N, Hinton G E. Dynamic routing between capsules. In: Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach, USA: NIPS, 2017. 3856−3866 [7] Deliege A, Cioppa A, Van Droogenbroeck M. HitNet: A neural network with capsules embedded in a hit-or-miss layer, extended with hybrid data augmentation and ghost capsules. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1806.06519, 2018. [8] Xi E, Bing S, Jin Y. Capsule network performance on complex data. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1712.03480, 2017. [9] Hinton G E, Sabour S, Frosst N. Matrix capsules with EM routing. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations. Vancouver, Canada: ICLR, 2018. 1−15 [10] Hoogi A, Wilcox B, Gupta Y, Rubin D L. Self-attention capsule networks for object classification. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1904.12483, 2019. [11] Choi J, Seo H, Im S, Kang M. Attention routing between capsules. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Seoul, South Korea: IEEE, 2019. 1981−1989 [12] Wang X, Tu Z, Zhang M. Incorporating statistical machine translation word knowledge into neural machine translation. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Proceeding, 2018, 26(12): 2255−2266 doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2018.2860287 [13] Zhang B, Xiong D, Su J. Neural machine translation with deep attention. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 42(1): 154−163 [14] Zhang B, Xiong D, Xie J, Su J. Neural machine translation with gru-gated attention model. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2020, 31(11): 4688−4698 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2019.2957276 [15] 王金甲, 纪绍男, 崔琳, 夏静, 杨倩. 基于注意力胶囊网络的家庭活动识别. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(11): 2199−2204Wang Jin-Jia, Ji Shao-Nan, Cui Lin, Xia Jing, Yang Qian. Identification of family activities based on attention capsule network. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(11): 2199−2204 [16] Xu K, Ba J, Kiros R, Cho K, Courville A, Salakhutdinov R, et al. Show, attend and tell: Neural image caption generation with visual attention. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning. Lugano, Switzerland: ICML, 2015. 2048−2057 [17] Gao L, Li X, Song J, Shen H T. Hierarchical lstms with adaptive attention for visual captioning. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2019, 42(5): 1112−1131 [18] Lu X, Wang B, Zheng X. Sound active attention framework for remote sensing image captioning. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 58(3): 1985−2000 [19] Wang X, Duan H. Hierarchical visual attention model for saliency detection inspired by avian pathways. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2017, 6(2): 540−552 [20] Xu H, Saenko K. Ask, attend and answer: Exploring question-guided spatial attention for visual question answering. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: ECCV, 2016. 451−466 [21] Liang J, Jiang L, Cao L, Kalantidis Y, Li L J, Hauptmann A G. Focal visual-text attention for memex question answering. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2019, 41(8): 1893−1908 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2890628 [22] 肖进胜, 申梦瑶, 江明俊, 雷俊峰, 包振宇. 融合包注意力机制的监控视频异常行为检测. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(12): 2951−2959Xiao Jin-Sheng, Shen Meng-Yao, Jiang Ming-Jun, Lei Jun-Feng, Bao Zhen-Yu. Abnormal behavior detection algorithm with video-bag attention mechanism in surveillance video. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(12): 2951−2959 [23] Zhao X, Chen Y, Guo J, Zhao D. A spatial-temporal attention model for human trajectory prediction. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2020, 7(4): 965−974 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2020.1003228 [24] 王亚珅, 黄河燕, 冯冲, 周强. 基于注意力机制的概念化句嵌入研究. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(7): 1390−1400Wang Ya-Kun, Huang He-Yan, Feng Chong, Zhou Qiang. A study of conceptual sentence embedding based on attentional mechanism. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(7): 1390−1400 [25] 冯建周, 马祥聪. 基于迁移学习的细粒度实体分类方法的研究. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(8): 1759−1766Feng Jian-Zhou, Ma Xiang-Cong. Research on fine-grained entity classification method based on transfer learning. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(8): 1759−1766 [26] 王县县, 禹龙, 田生伟, 王瑞锦. 独立RNN和胶囊网络的维吾尔语事件缺失元素填充. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(4): 903−912Wang Xian-Xian, Yu Long, Tian Sheng-Wei, Wang Rui-Jin. Independent RNN and CAPE networks were populated with missing elements of Uyghur events. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(4): 903−912 [27] Wang X, Girshick R, Gupta A, He K. Non-local neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake, USA: IEEE, 2018. 7794−7803 [28] Woo S, Park J, Lee J Y, Kweon I S. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: ECCV, 2018. 3−19 [29] Hu J, Shen L, Sun G, Wu E. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(8): 2011−2023 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2913372 [30] Phaye S S R, Sikka A, Dhall A, Bathula D. Dense and diverse capsule networks: Making the capsules learn better. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1805.04001, 2018. [31] Xiang C, Zhang L, Tang Y, Zou W, Xu C. MS-CapsNet: A novel multi-scale capsule network. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2018, 25(12): 1850−1854 doi: 10.1109/LSP.2018.2873892 [32] Ribeiro F D S, Leontidis G, Kollias S. Capsule routing via variational bayes. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. New York, USA: AAAI, 2020. 3749−3756 [33] Gu J, Tresp V. Improving the robustness of capsule networks to image affine transformation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 7283−7291 -




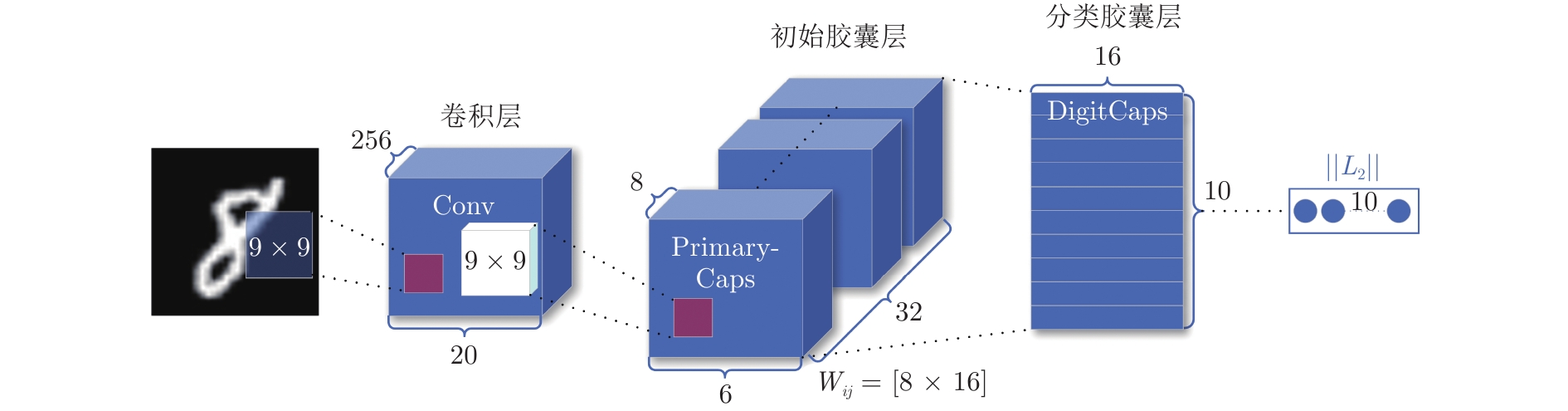
 下载:
下载: