-
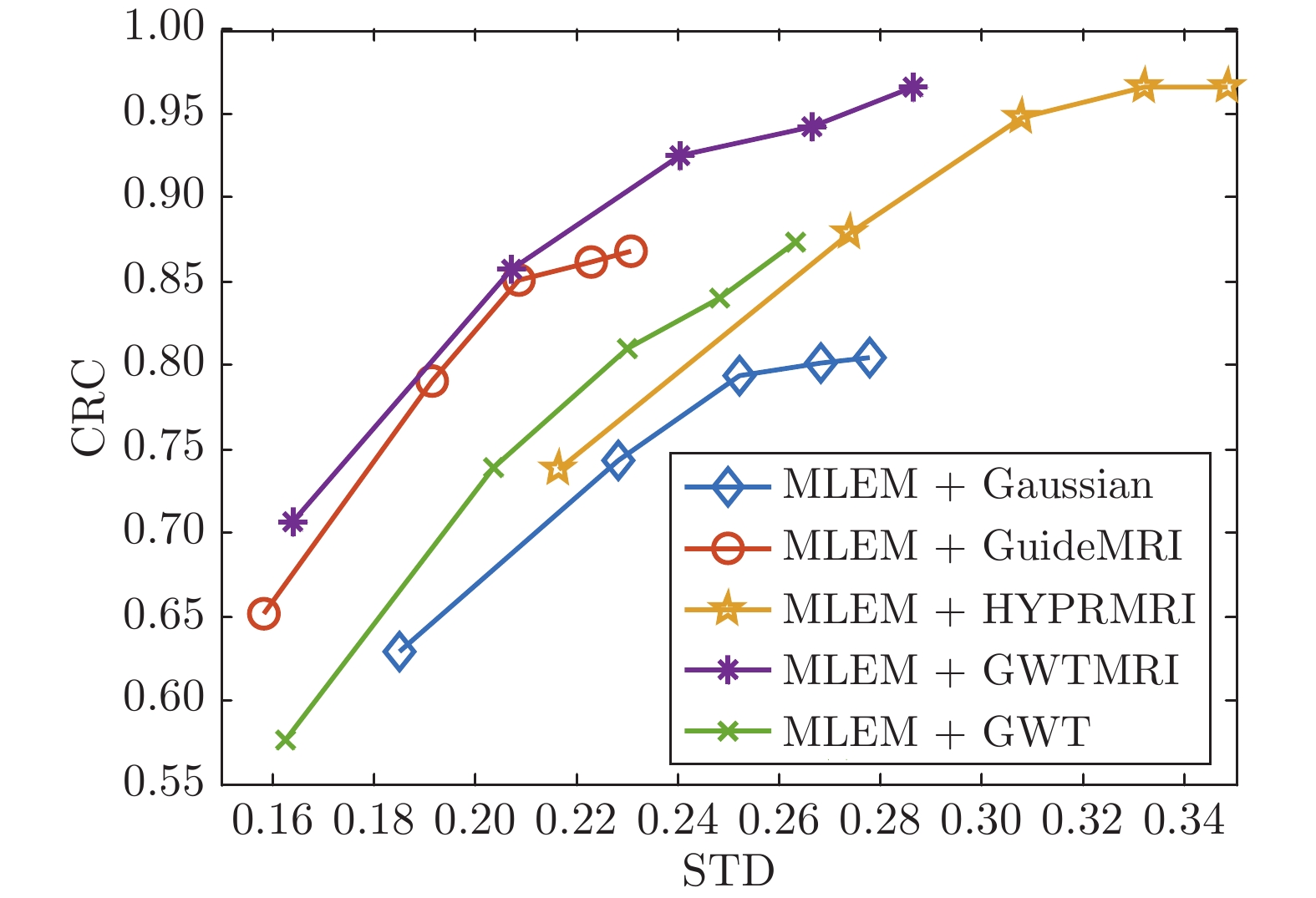
摘要: 正电子发射断层成像(Positron emission tomography, PET)是一种强大的核医学功能成像模式, 广泛应用于临床诊断, 但PET图像的空间分辨率低且含有噪声, 有必要对PET图像进行去噪以提升PET图像的质量. 随着PET/MR (Magnetic resonance)等一体化成像设备的出现, 磁共振成像(Magnetic resonance imaging, MRI)的先验信息可用于PET图像去噪, 提高PET图像质量. 针对动态PET图像, 提出了一种融合MRI先验信息的PET图像图小波去噪新方法. 首先构建PET合成图像; 再将PET合成图像与MRI信息通过硬阈值方法进行融合; 接着在融合图像上构造图拉普拉斯矩阵; 最后通过图小波变换(Graph wavelet transfrom, GWT)对动态PET图像去噪. 仿真实验结果表明, 与单独的图滤波、图小波去噪方法以及其他结合MRI的PET图像去噪方法相比, 本文方法有更高的信噪比(Signal-to-noise ratio, SNR), 更好地保留了病灶信息; 本文方法的去噪性能与VGG (Visual Geometry Group)深度神经网络等基于学习的方法相当, 但不需要大量数据的训练, 计算复杂度低.Abstract: Positron emission tomography (PET) is a powerful nuclear medicine functional imaging modality, which is widely used in clinical diagnosis. However, the PET images have low spatial resolution and contain noise. It is necessary to improve the quality of PET images by denoising. As hybrid imaging devices such as PET/MR (magnetic resonance) have become available, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) prior information could be used to improve the denoising quality of PET images. For dynamic PET images, this paper presents a novel denoising method based on graph wavelet transform (GWT) with MRI information. Firstly, the composite image is generated by the dynamic PET frames. Then, we fuse the MRI image and the composite image through the hard threshold method to obtain a new fusion image. Next, the graph Laplacian matrix is constructed based on the fusion image. Finally, we perform GWT on the dynamic PET images to denoise. The simulation experiments show that, compared with graph filtering and GWT, and other MRI incorporated methods, the proposed approach has higher SNR (signal-to-noise ratio) while preserving the image lesions details. Compared with VGG (Visual Geometry Group) deep neural network based method, the proposed method has the similar denoising performance, but it does not need a lot of data training and has low computational complexity.
-
表 1 本文方法参数设置
Table 1 Parameter setting in this paper
参数符号 参数设置 n 5 k 11 $\theta $ 20 $\eta $ 0.0008 J 4 Threshold 0.75 表 2 无病灶情况下结合MRI的PET图像去噪方法比较
Table 2 Comparison of PET image denoising methods incorporated with MRI on the normal dataset
表 3 无病灶情况下由PET合成图像构图的方法与本文方法比较
Table 3 Comparison of the methods of constructing graph by PET composite image with the proposed method on the normal dataset
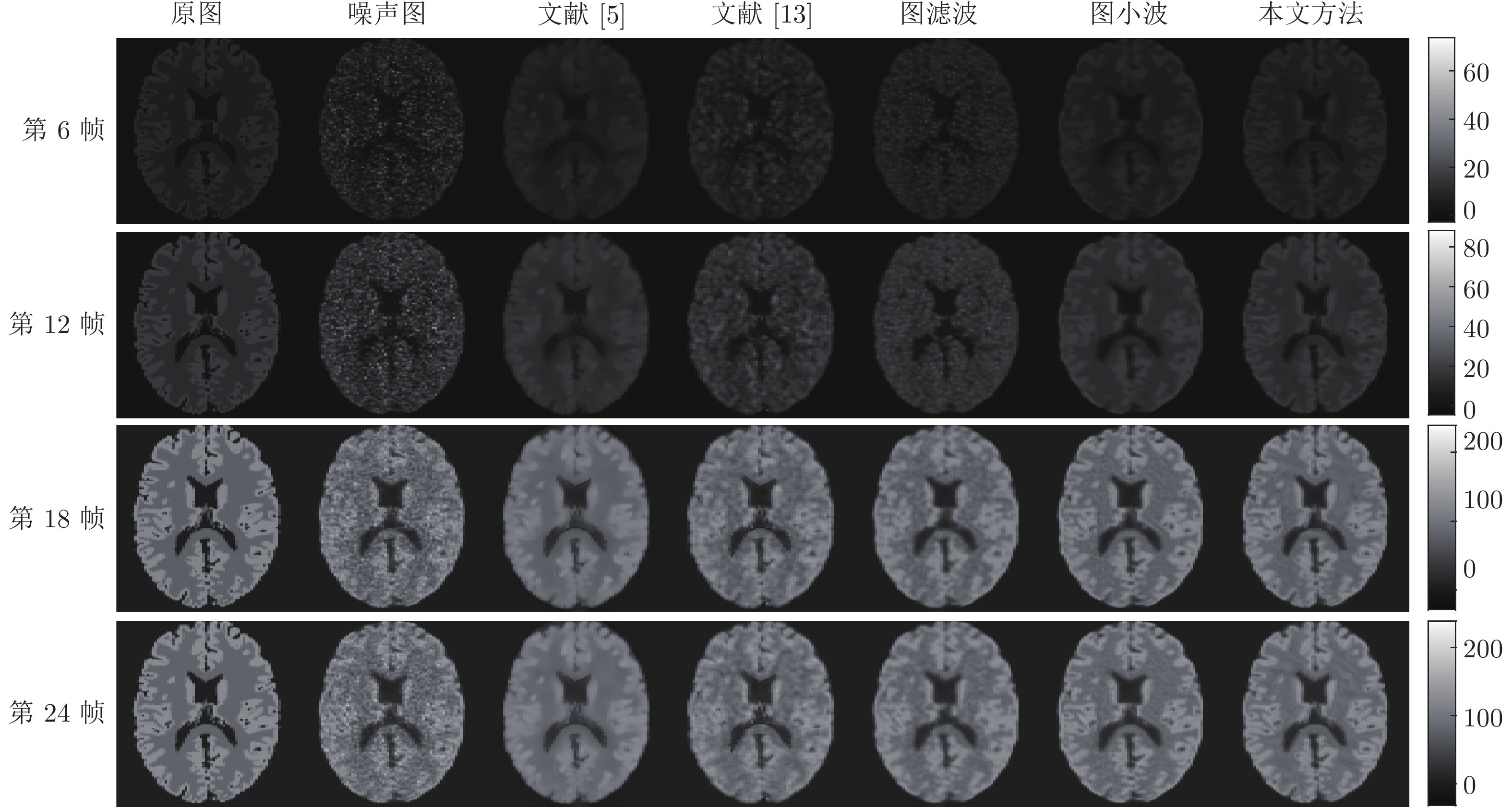
方法 第6帧 第12帧 第18帧 第24帧 SNR RMSE SNR RMSE SNR RMSE SNR RMSE 图滤波 7.7670 2.2577 9.7258 3.5488 11.5317 18.7104 11.4831 19.5350 图小波 11.4064 1.4849 11.7967 2.7960 12.5395 16.6608 12.4637 17.4495 本文方法 11.7851 1.4215 12.2803 2.6445 12.6945 16.3661 12.6693 17.0413 表 4 单病灶情况下结合MRI的PET图像去噪方法比较
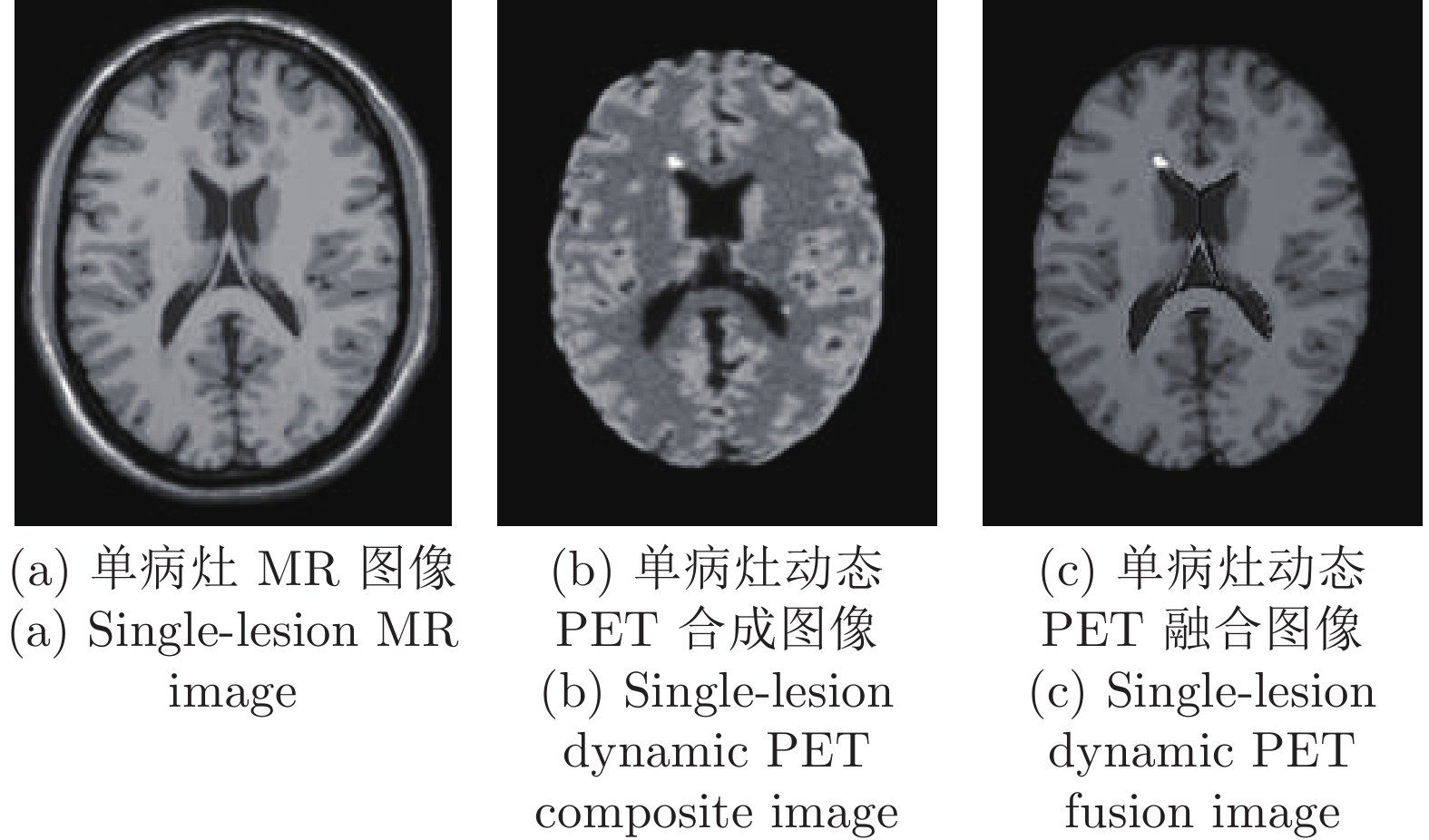
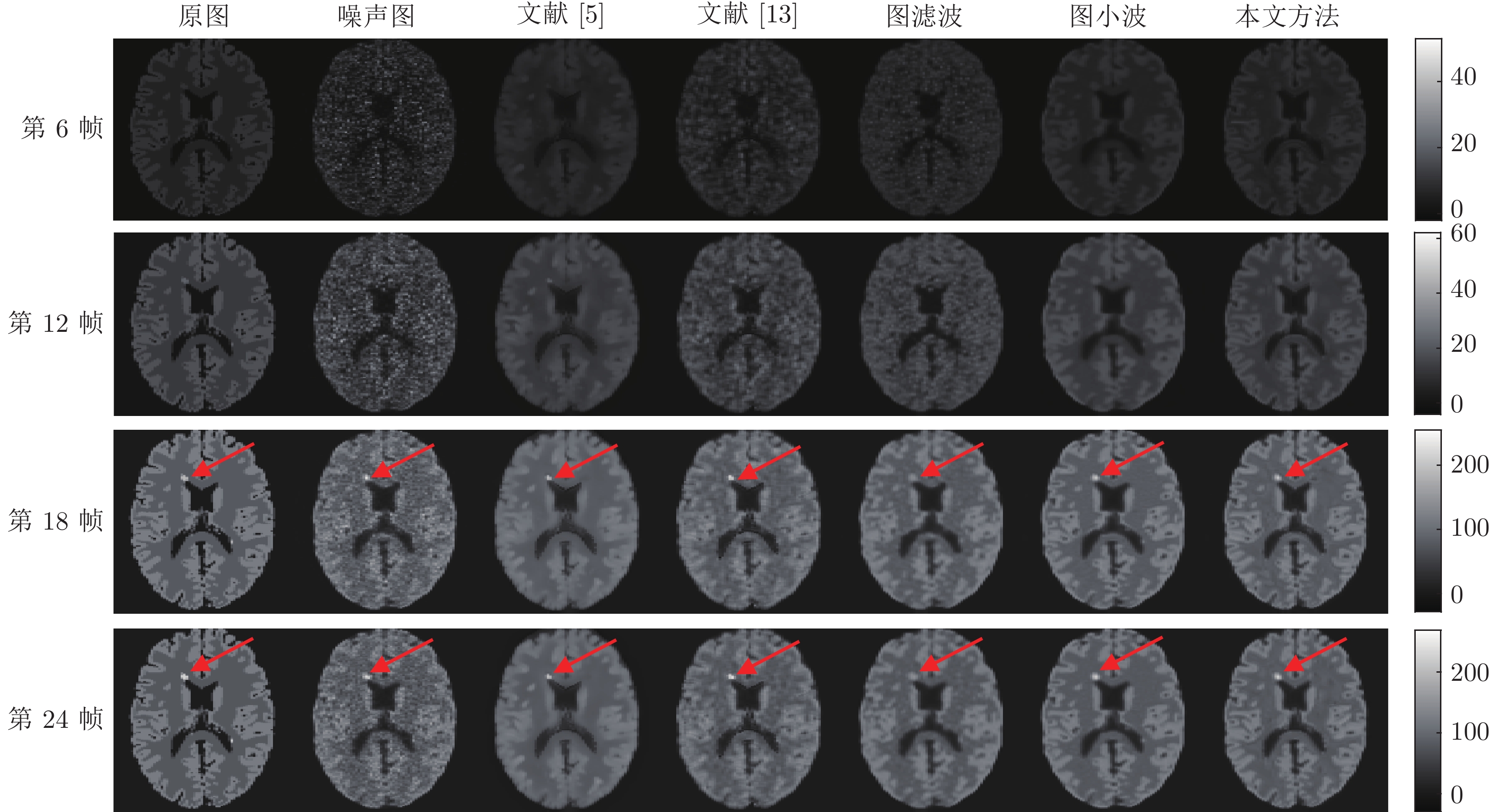
Table 4 Comparison of PET image denoising methods incorporated with MRI on the single-lesion dataset
表 5 单病灶情况下由PET合成图像构图的方法与本文方法比较
Table 5 Comparison of the methods of constructing graph by PET composite image with the proposed method on the single-lesion dataset
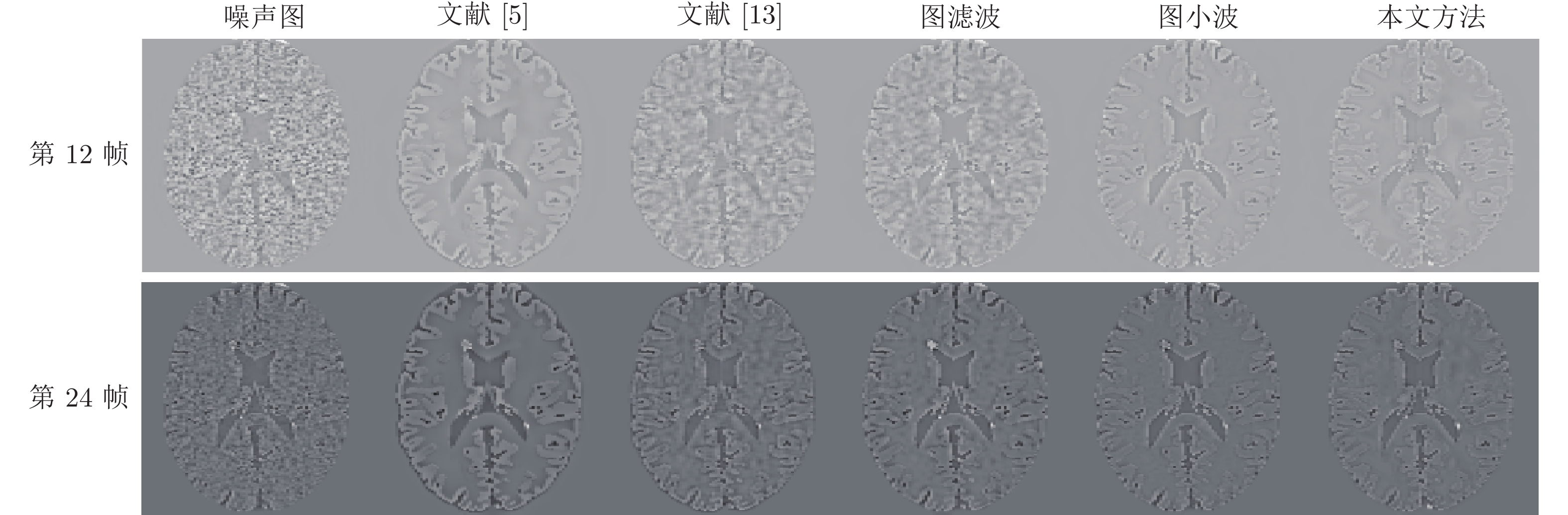
方法 第6帧 第12帧 第18帧 第24帧 SNR RMSE SNR RMSE SNR RMSE SNR RMSE 图滤波 8.7456 2.0190 10.2172 3.3621 11.5850 18.6797 11.4849 19.6554 图小波 11.3632 1.4998 11.7036 2.8333 12.5196 16.7742 12.4090 17.6698 本文方法 11.6739 1.4419 12.2405 2.6635 12.7017 16.4262 12.5982 17.2910 表 6 单病灶PET图像在不同光子数时各种去噪方法比较
Table 6 Comparison of different denoising methods for single-lesion PET images with different photon numbers
方法 光子数$7\times10^8 $/第12帧 光子数$7\times10^8 $/第24帧 光子数$7\times10^9$/第12帧 光子数$7\times10^9$/第24帧 SNR RMSE SNR RMSE SNR RMSE SNR RMSE 文献[5] 11.4403 2.9205 11.2873 20.1078 11.4398 2.9207 11.2884 20.1053 文献[13] 11.4789 2.9076 11.4751 19.6777 11.4690 2.9109 11.2807 20.1229 图滤波 11.2474 2.9861 11.2387 20.2206 11.6630 2.8466 11.4971 19.6278 图小波 11.3028 2.9671 11.5849 19.4305 11.3609 2.9473 11.8315 18.8866 本文方法 11.9611 2.7506 11.9411 18.6497 11.9734 2.7467 12.0638 18.3881 -
[1] Dutta J, Leahy R M, Li Q. Non-local means denoising of dynamic PET images. PloS ONE, 2013, 8(12): e81390. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0081390 [2] Mansoor A, Bagci U, Mollura D J. Optimally stabilized PET image denoising using trilateral filtering. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Boston, USA: 2014. 130–137 [3] Buades A, Coll B, Morel J M. A non-local algorithm for image denoising. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. San Diego, USA: IEEE, 2005. 60–65 [4] Jommaa H, Mabrouk R, Khlifa N, Morain-Nicolier, F. Denoising of dynamic PET images using a multi-scale transform and non-local means filter. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2018, 41: 69–80. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2017.11.002 [5] Yan J, Lim J C S, Townsend D W. MRI-guided brain PET image filtering and partial volume correction. Physics in Medicine and Biology, 2015, 60(3): 961–976. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/60/3/961 [6] Song T A, Yang F, Chowdhury S R, Kim K, Johnson K A, Fakhri, G A et al. PET image deblurring and super-resolution with an MR-based joint entropy prior. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2019, 5(4): 530–539. doi: 10.1109/TCI.2019.2913287 [7] Song T A, Chowdhury S R, Yang F, Dutta J. PET image super-resolution using generative adversarial networks. Neural Networks, 2020, 125: 83-91. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2020.01.029 [8] Li T, Jiang C H, Gao J, Yang Y F, Liang D, Liu X, et al. Low-count PET image restoration using sparse representation. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A Accelerators Spectrometers Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2018, 888: 222-227. doi: 10.1016/j.nima.2018.01.083 [9] Wang Y, Ma G, An L, Shi F, Zhang P, Lalush D S, et al. Semisupervised tripled dictionary learning for standard-dose PET image prediction using low-dose PET and multimodal MRI. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2017, 64(3): 569-579. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2016.2564440 [10] An L, Zhang P, Adeli E, Wang Y, Ma G K, Shi F, et al. Multi-level canonical correlation analysis for standard-dose PET image estimation. IEEE Transactions Image Process, 2016, 25(7): 3303-3315. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2016.2567072 [11] Zhang Y, Zhang X. PET-MRI joint reconstruction with common edge weighted total variation regularization. Inverse Problems, 2018, 34(6): 065006. doi: 10.1088/1361-6420/aabce9 [12] Bergounioux M, Papoutsellis E, Stute S, Tauber C. Infimal convolution spatiotemporal PET reconstruction using total variation based priors [Online], available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/322918637_Infimal_convolution_spatiotemporal_PET_reconstruction_using_total_variation_based_priors, 26 January, 2018 [13] Cheng J C K, Matthews J, Boellaard R, Sossi V. A MR guided denoising for PET using IHYPR-LR. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference. Atlanta, USA: IEEE, 2017. 1–3 [14] Tahaei M S, Reader A J, Collins D L. Two novel PET image restoration methods guided by PET-MR kernels: Application to brain imaging. Medical Physics, 2019, 46(5): 2085-2102. doi: 10.1002/mp.13418 [15] Gong K, Berg E, Cherry S R, Qi J. Machine learning in PET: From photon detection to quantitative image reconstruction. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2020, 108(1): 51-68. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2019.2936809 [16] 田娟秀, 刘国才, 谷珊珊, 鞠忠建, 刘劲光, 顾冬冬. 医学图像分析深度学习方法研究与挑战. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(3): 401-424.Tian Juan-Xiu, Liu Guo-Cai, Gu Shan-Shan, Ju Zhong-Jian, Liu Jin-Guang, Gu Dong-Dong. Deep learning in medical image analysis and its challenges. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(3): 401-424. [17] 施俊, 汪琳琳, 王珊珊, 陈艳霞, 王乾, 魏冬铭, 等. 深度学习在医学影像中的应用综述. 中国图象图形学报, 2020, 25(10): 1953-1981. doi: 10.11834/jig.200255Shi Jun, Wang Lin-Lin, Wang Shan-Shan, Chen Yan-Ming, Wang Qian, Wei Dong-Ming et al. Applications of deep learning in medical imaging: A survey. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2020, 25(10): 1953-1981. doi: 10.11834/jig.200255 [18] 范家伟, 张如如, 陆萌, 何佳雯, 康霄阳, 柴文俊, 等. 深度学习方法在糖尿病视网膜病变诊断中的应用. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(3): 985−1004.Fan Jia-Wei, Zhang Ru-Ru, Lu Meng, He Jia-Wen, Kang Xiao-Yang, Chai Wen-Jun, et al. Applications of deep learning techniques for diabetic retinal diagnosis. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(3): 985−1004. [19] Reader A J, Corda G, Mehranian A, Costa-Luis C D, Ellis S, Schnabel J A. Deep learning for PET image reconstruction. IEEE Transactions on Radiation and Plasma Medical Sciences, 2020, 5(1): 1-25. [20] Gong K, Guan J H, Liu C, Liu C C, Qi J Y. PET image denoising using a deep neural network through fine tuning. IEEE Transactions on Radiation and Plasma Medical Sciences, 2019, 3(2): 153-161. doi: 10.1109/TRPMS.2018.2877644 [21] Gong Y, Shan H M, Teng Y Y, Zheng H R, Wang G, Wang S S. Deeply-supervised multi-dose prior learning for low-dose PET imaging. In: Proceedings of the 17th IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging Workshops. Iowa, USA: IEEE, 2020. 1–4 [22] Gong Y, Shan H M, Teng Y Y, Zheng H R, Wang G, Wang S S. Low-dose PET image restoration with 2D and 3D network prior learning. In: Proceedings of the 17th IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging Workshops. Iowa, USA: IEEE, 2020. 1–4 [23] Gong Y, Shan H G, Teng Y Y, Tu N, Li M, Liang G D, et al. Parameter-Transferred Wasserstein Generative Adversarial Network (PT-WGAN) for low-dose PET image denoising. IEEE Transactions on Radiation and Plasma Medical Sciences, 2021, 5(2): 213-223. doi: 10.1109/TRPMS.2020.3025071 [24] Wang Y, Zhou L P, Yu B T, Wang L, Zu C, Lalush D S, et al. 3D auto-context-based locality adaptive multi-modality GANs for PET synthesis. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2019, 38(6): 1328-1339. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2018.2884053 [25] Shuman D I, Narang S K, Frossard P, Ortega A, Vandergheynst P. The emerging field of signal processing on graphs: Extending high-dimensional data analysis to networks and other irregular domains. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2013, 30(3): 83–98. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2012.2235192 [26] Sandryhaila A F, Moura J M. Big data analysis with signal processing on graphs: Representation and processing of massive data sets with irregular structure. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2014, 31(5): 80–90. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2014.2329213 [27] 杨杰, 赵磊, 郭文彬. 基于图谱域移位的带限图信号重构算法. 自动化学报, 2021, x(x): 1−11.Yang Jie, Zhao Lei, Guo Wen-Bin. Graph band-limited signals reconstruction method based graph spectral domain shifting. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, x(x): 1−11. [28] Cheung G, Magli E, Tanaka Y, Ng M K. Graph spectral image processing. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2018, 106(5): 907-930. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2018.2799702 [29] Guo S Y, Sheng Y X, Chai L, Zhang J X. Graph filtering approach to PET image denoising. In: Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Industrial Artificial Intelligence. Shenyang, China: IEEE, 2019. 1–6 [30] Hammond D K, VandergheynstT P, Gribonval R. Wavelets on graphs via spectral graph theory. Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis, 2011, 30(2): 129–150. doi: 10.1016/j.acha.2010.04.005 [31] Hammond D K, Vandergheynst P, Gribonval R. The spectral graph wavelet transform: Fundamental theory and fast computation. Vertex-Frequency Analysis of Graph Signals. Springer, 2019. 141–175 [32] Deutsch S, Ortega A, Medioni G. Manifold denoising based on spectral graph wavelets. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing. Shanghai, China: IEEE, 2016. 4673–4677 [33] Wang G, Qi J. PET image reconstruction using kernel method. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2014, 34(1): 61–71. [34] Shepp L A, Vardi Y. Maximum likelihood reconstruction for positron emission tomography. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 1982, 1(2): 113-122. doi: 10.1109/TMI.1982.4307558 [35] Aubert-Broche B, Griffin M, Pike G B, Evans A C, Collins D L. Twenty new digital brain phantoms for creation of validation image databases. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2006, 25(11): 1410–1416. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2006.883453 [36] Feng D, Wong K P, Wu C M, Siu W C. A technique for extracting physiological parameters and the equired input function simultaneously from PET image measurements: Theory and simulation study. IEEE Transactions on Information Technology in Biomedicine, 1997, 1(4): 243–254. doi: 10.1109/4233.681168 -




 下载:
下载: