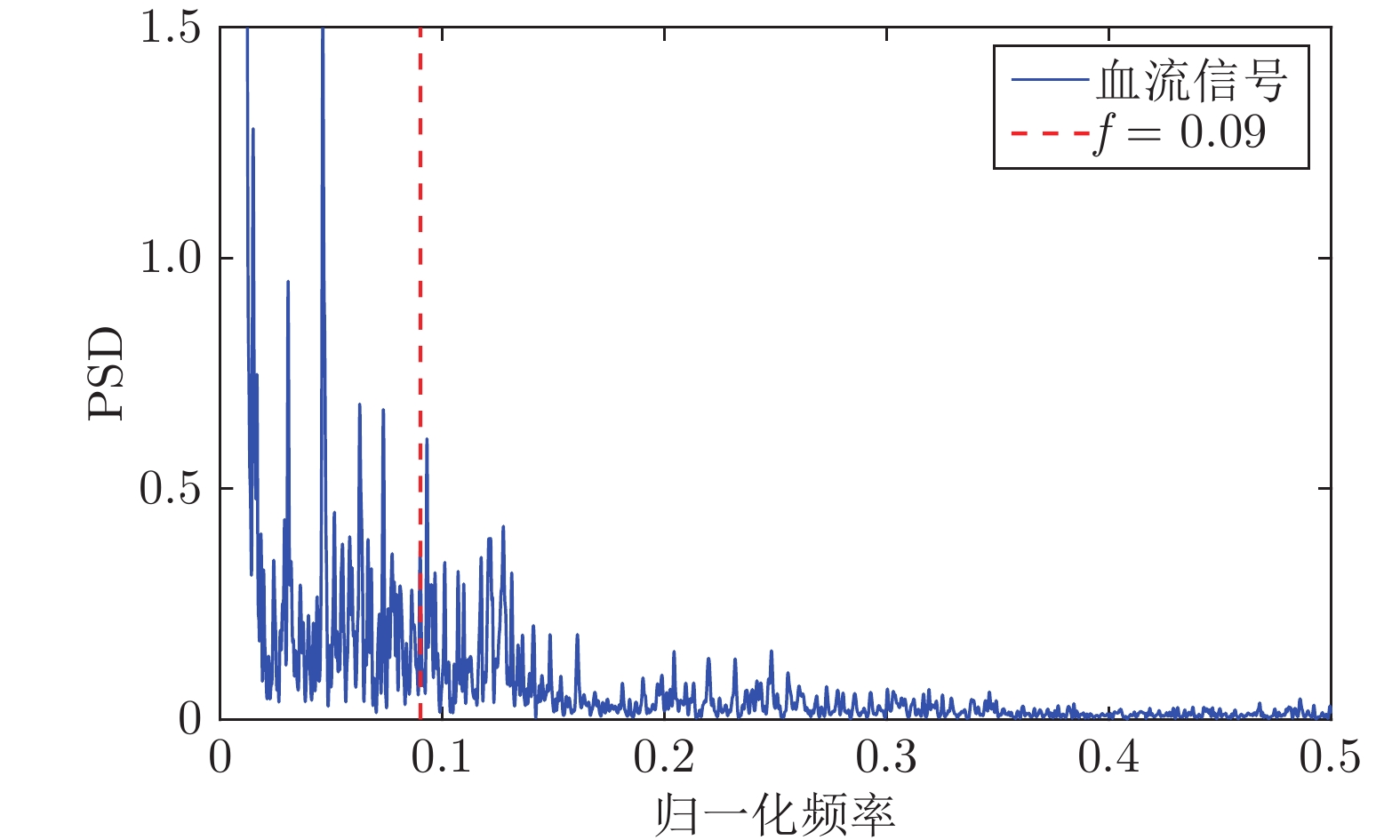
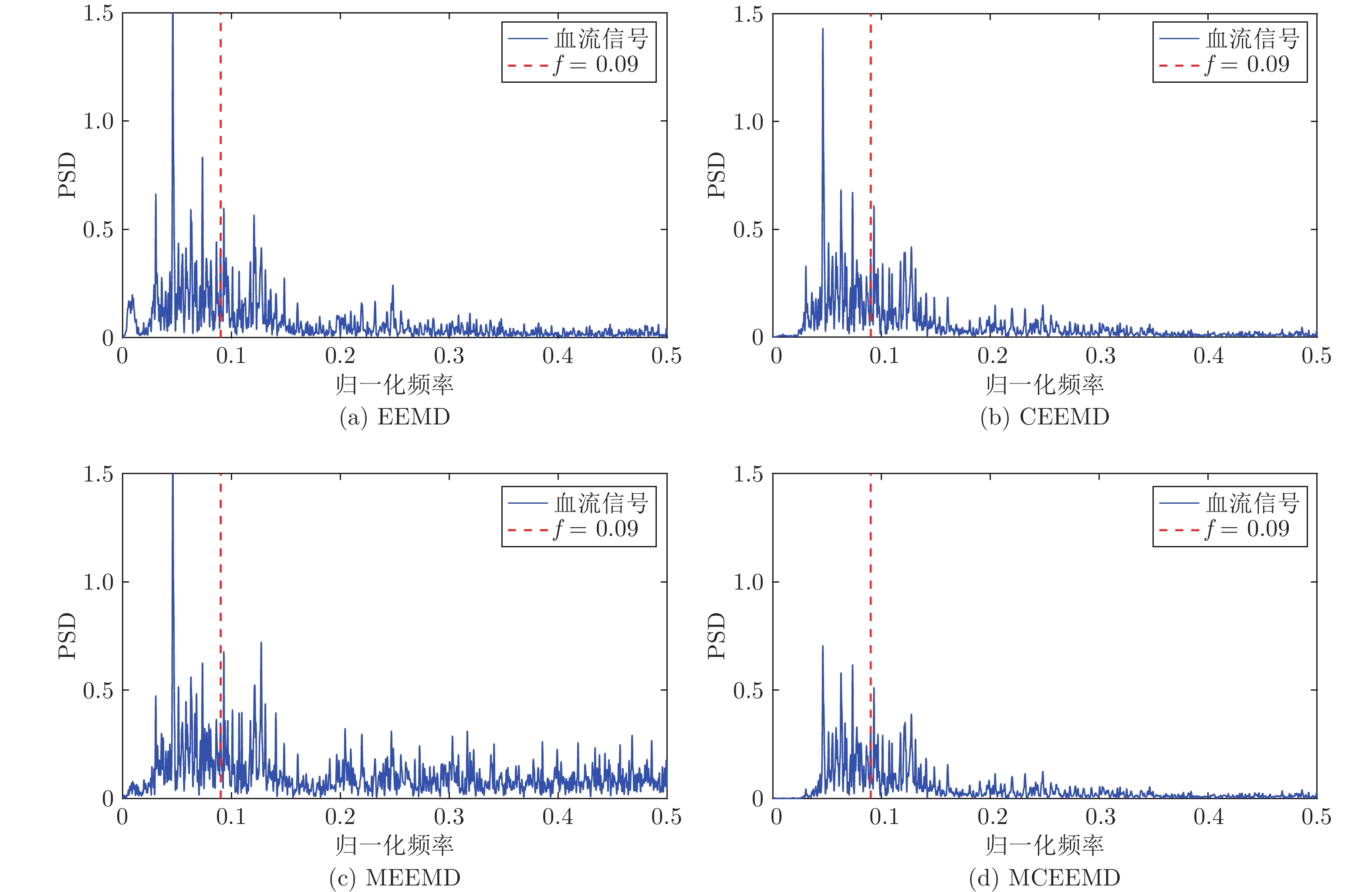
-
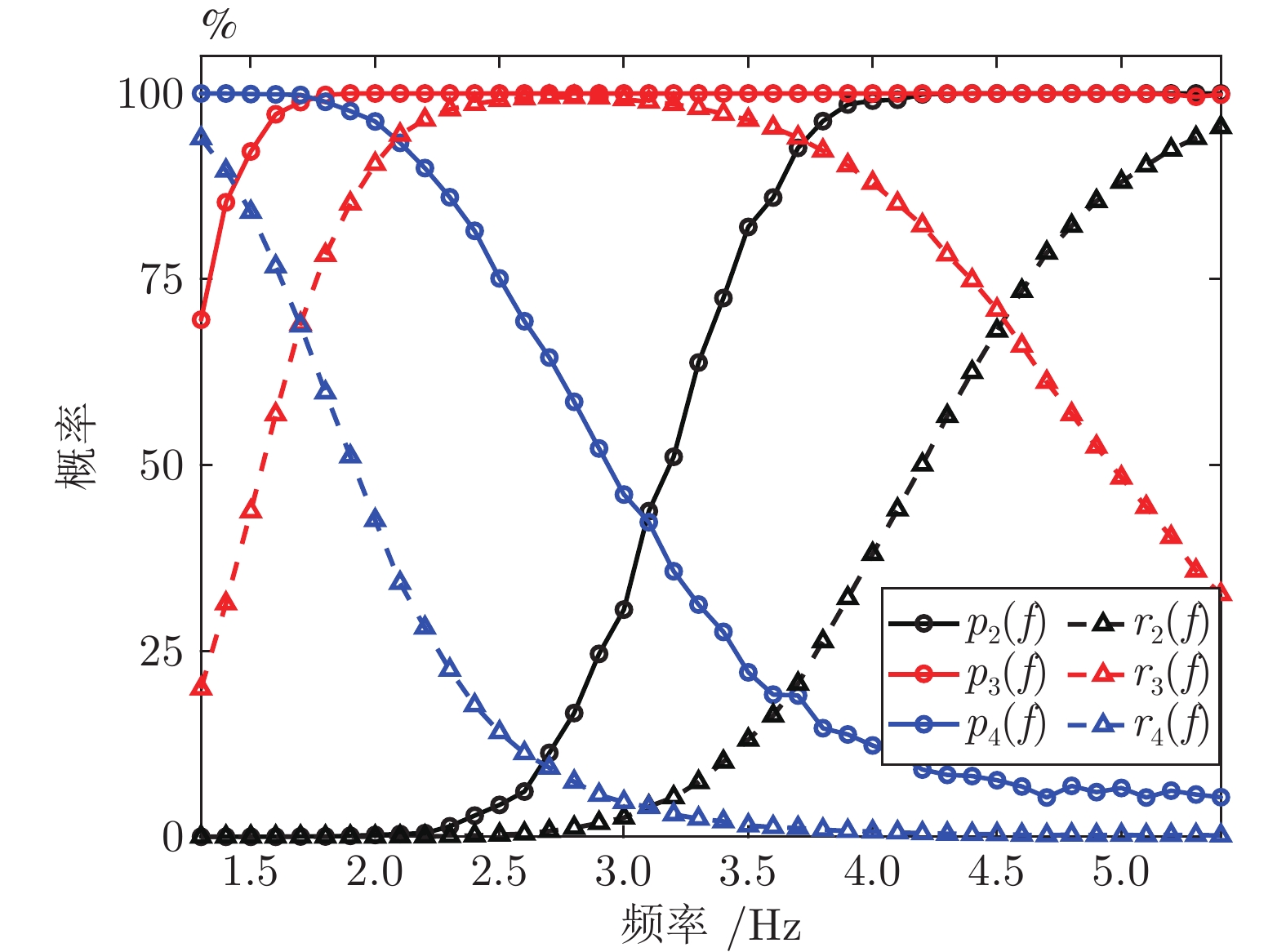
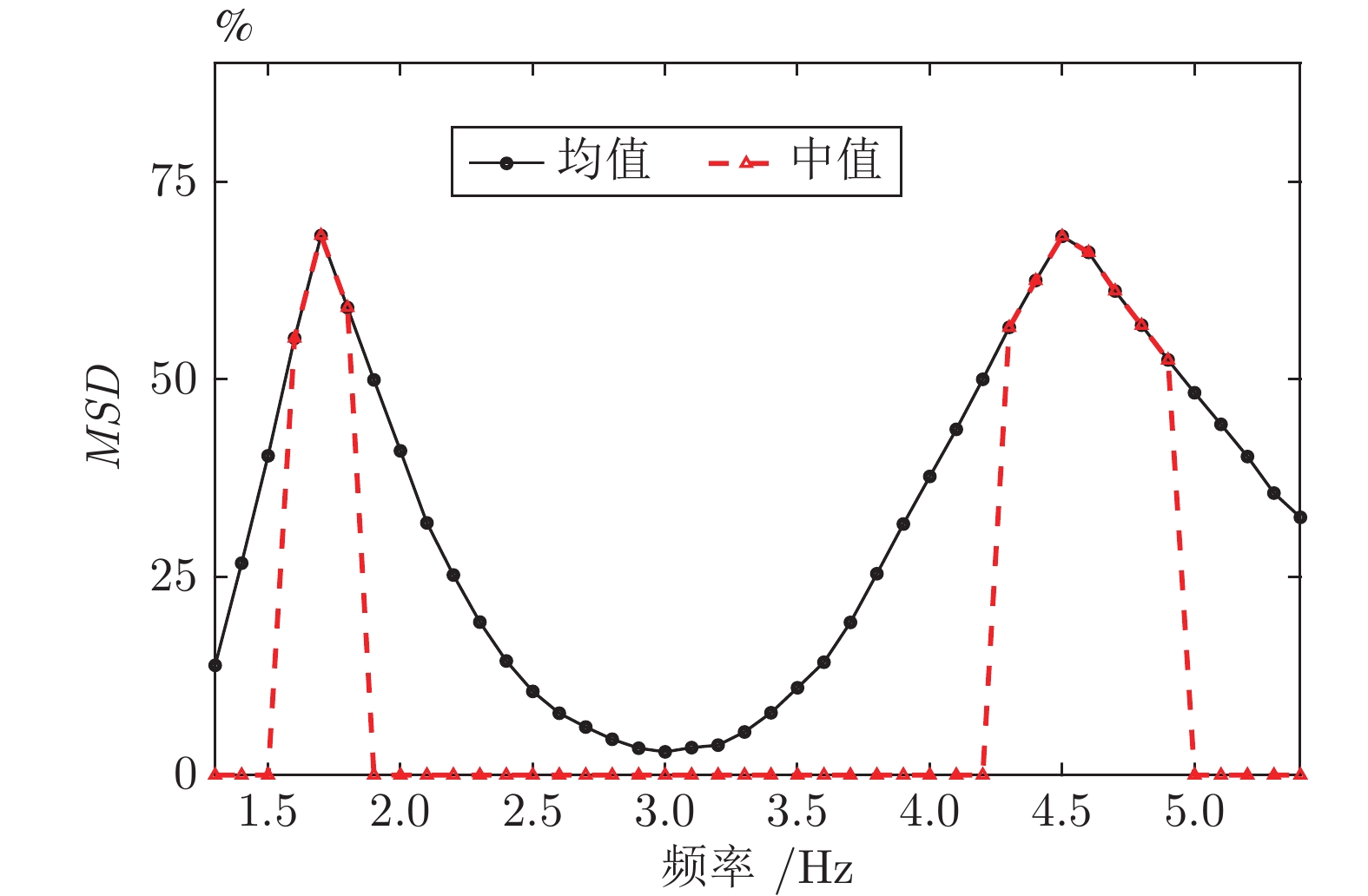
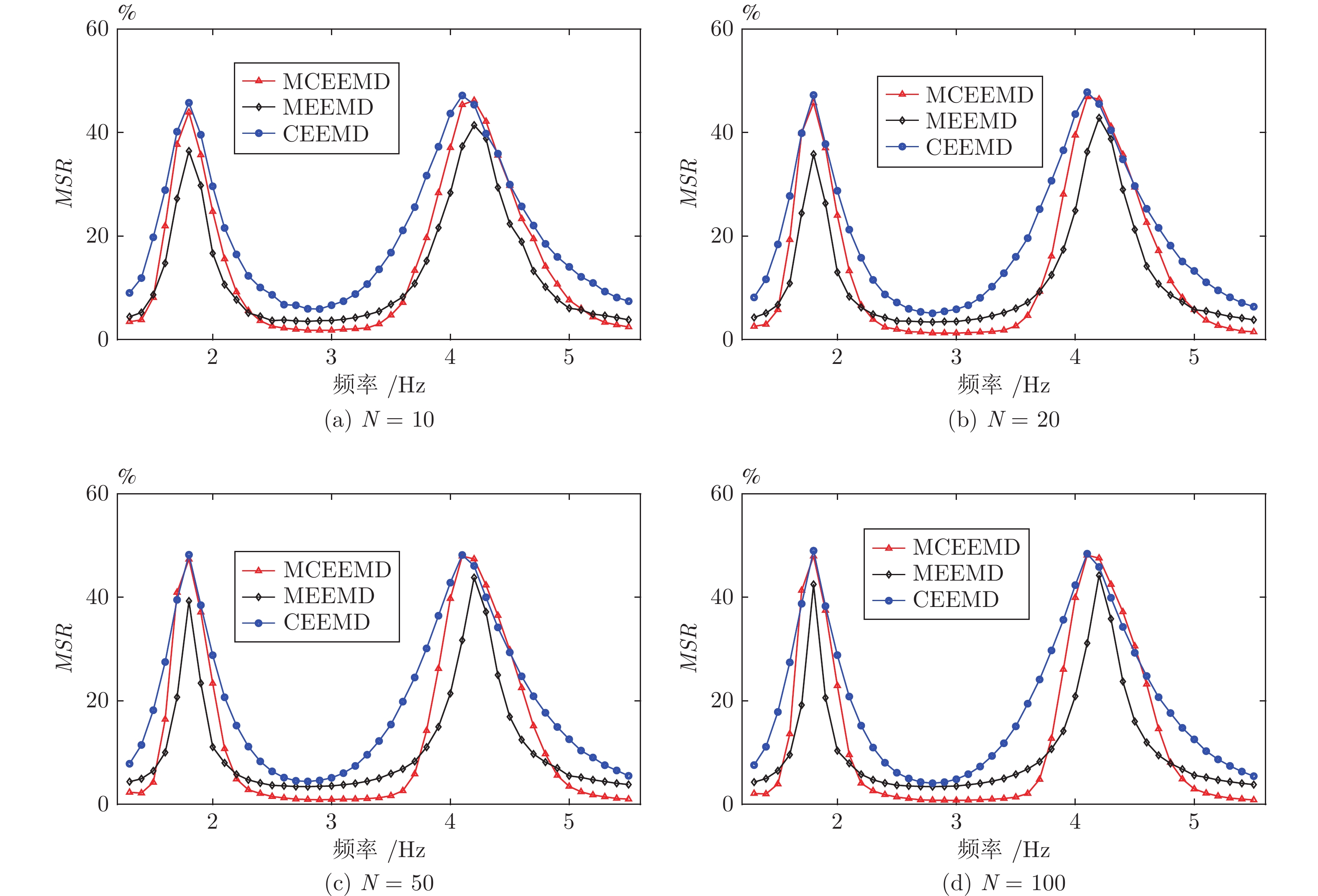
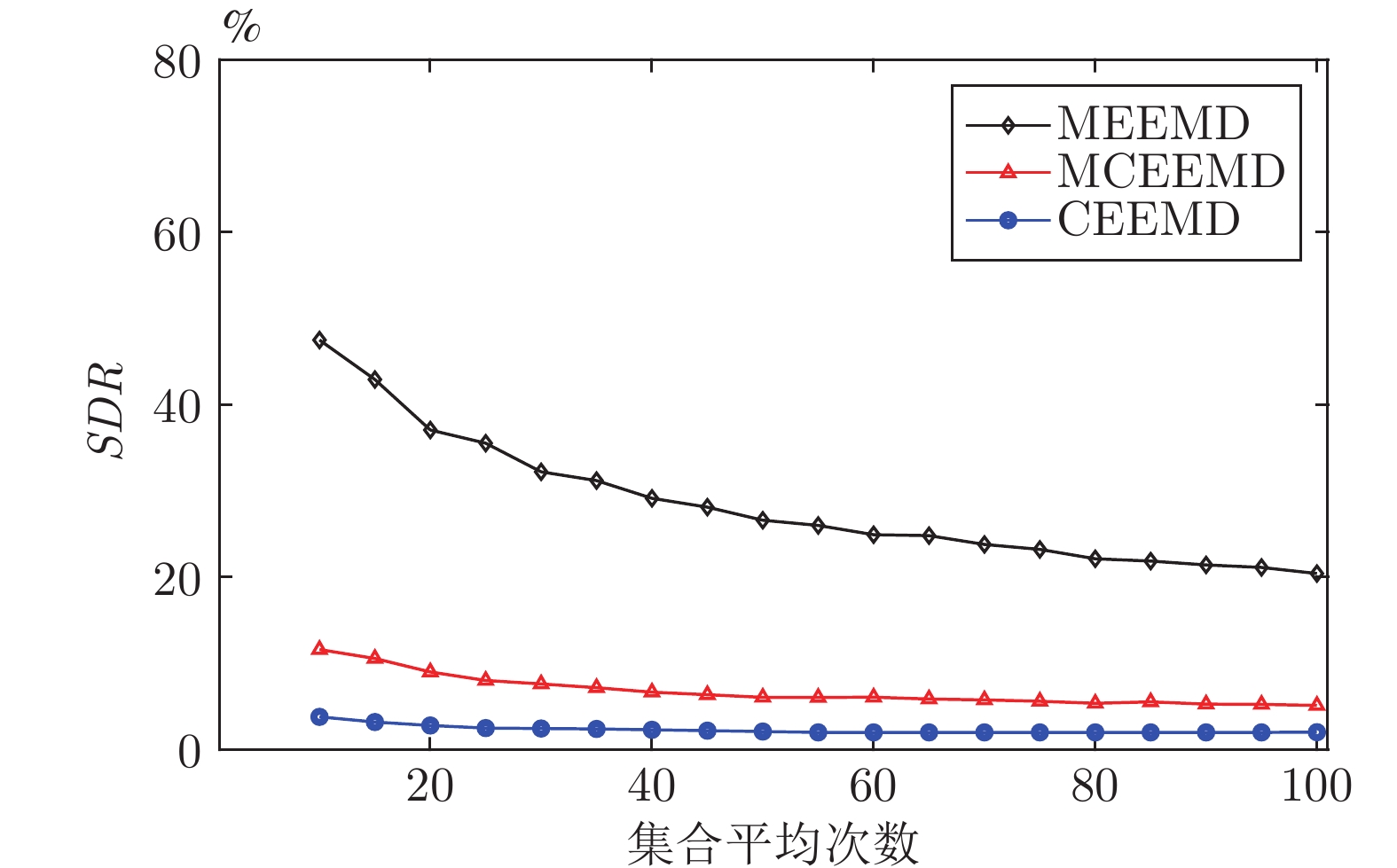
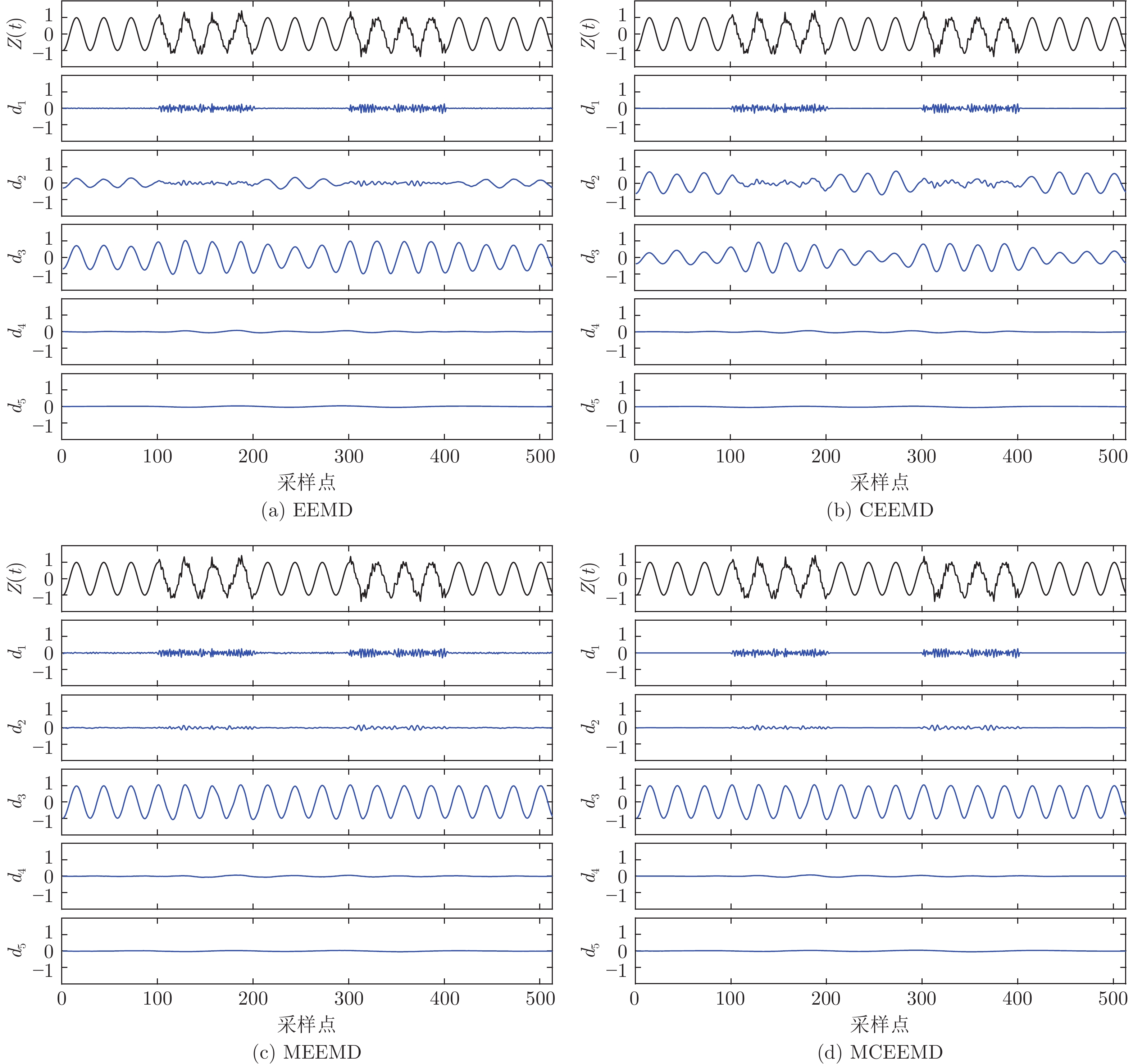
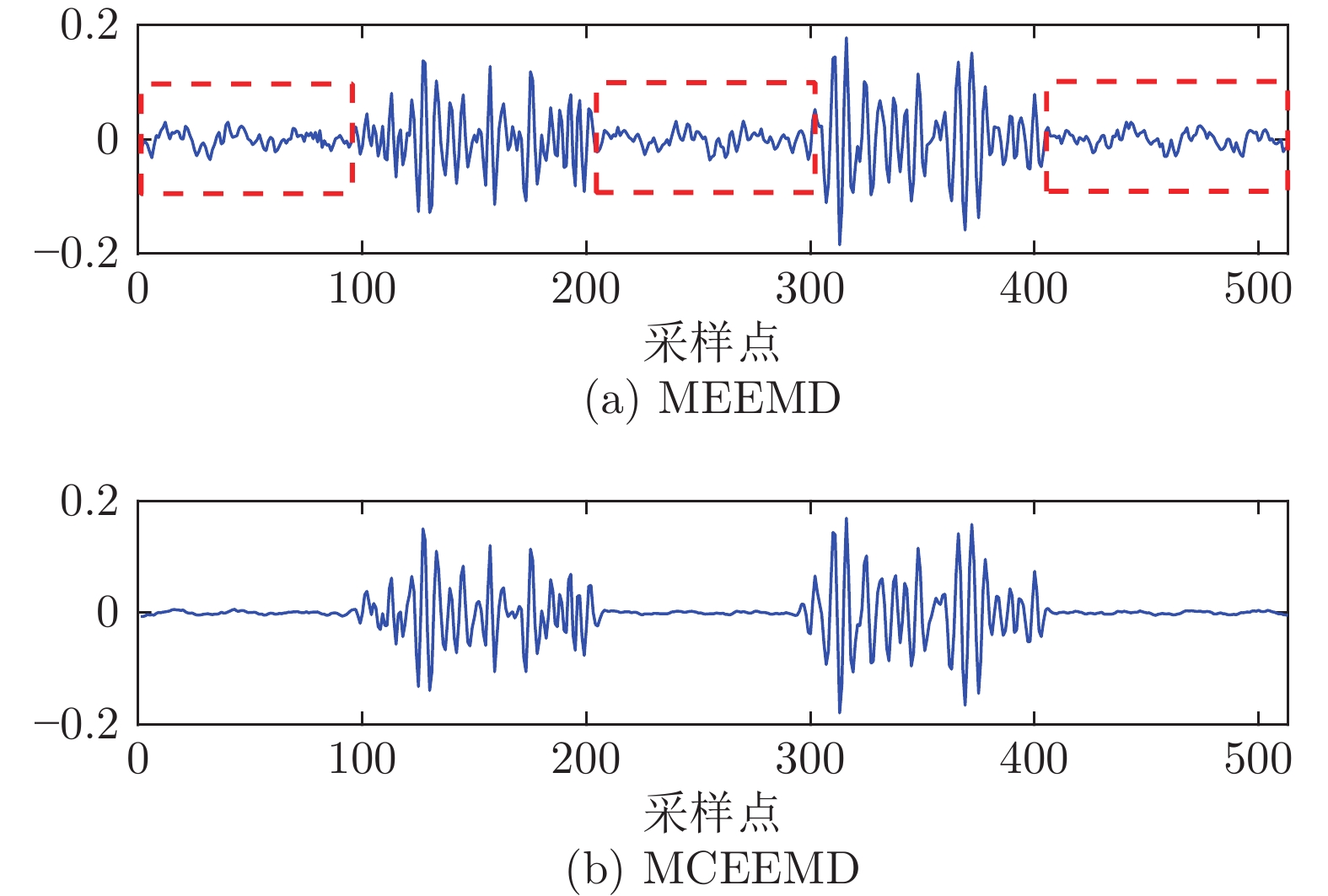
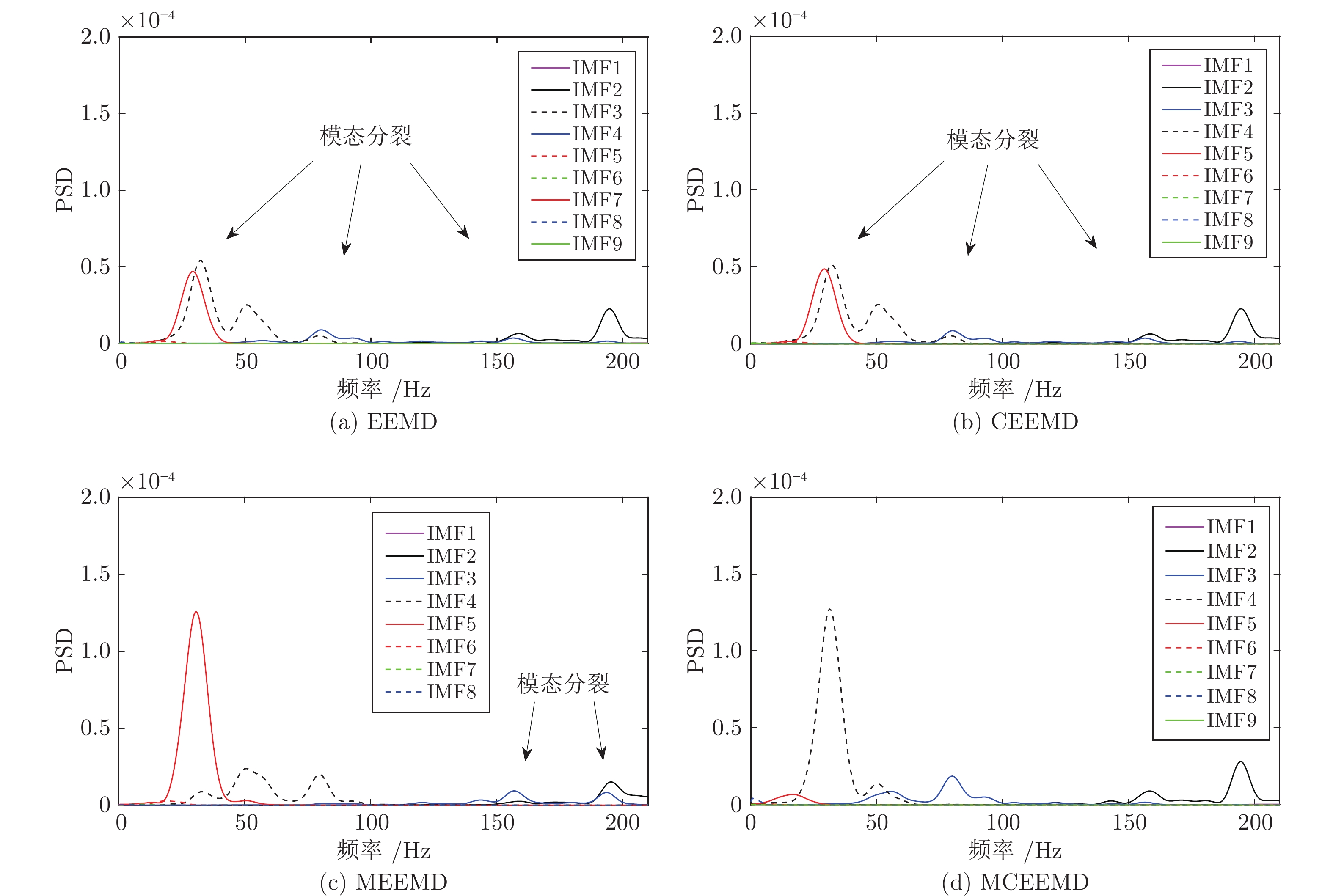
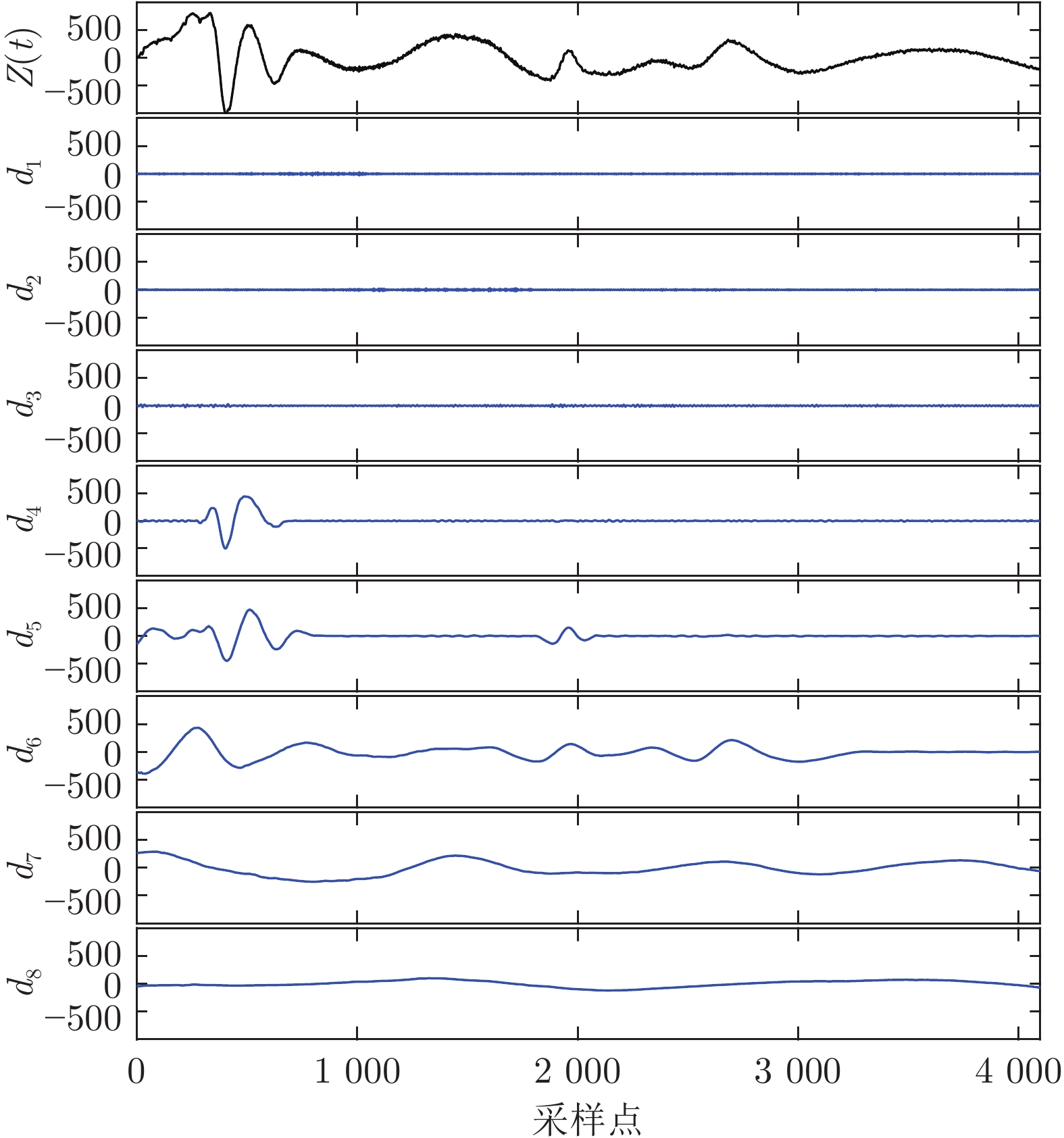
摘要: 针对经验模态分解(Empirical mode decomposition, EMD)系列方法存在的模态分裂(Mode splitting, MS)问题, 提出中值互补集合经验模态分解(Median complementary ensemble EMD, MCEEMD)算法. 通过概率模型量化互补集合经验模态分解(Complementary ensemble EMD, CEEMD)的MS问题, 证明了使用中值算子替代算术平均算子对抑制MS的有效性. 为了兼具抑制MS和残留噪声的性能, MCEEMD算法首次在集合过程中结合了中值和平均算子. 具体地, 所提方法首先添加N对互补的白噪声至原信号中, 并经过EMD分解得到2N组固有模态函数(Intrinsic mode functions, IMFs), 然后分别对其中互补相关的IMFs两两取平均得到N组IMFs, 最后使用中值算子处理上述N组IMFs得到输出结果. 对仿真信号与两个真实案例的分析结果表明, 本文提出的MCEEMD方法不仅有效抑制了CEEMD的MS问题, 而且避免了单一使用中值算子的两个缺点: 分解完备性差和IMFs中存在的毛刺现象.
-
关键词:
- 模态分裂 /
- 中值算子 /
- 互补白噪声 /
- 互补集合经验模式分解
Abstract: In order to restrain the mode splitting (MS) problem of the empirical mode decomposition (EMD) series methods, a median complementary ensemble EMD (MCEEMD) algorithm is proposed in this paper. We first present novel probabilistic tools to quantify the MS phenomenon of complementary ensemble EMD (CEEMD), which aims at demonstrating the effectiveness of using the median operator to replace the mean operator during the ensemble process. To combine the advantages of suppressing MS and residual noise, the MCEEMD algorithm integrates both median and mean operators within the ensemble process for the first time. Specifically, the MCEEMD algorithm is enlightened and featured by following procedures: 1) Add N pairs of complementary white noise to the original signal to obtain 2N groups of intrinsic mode functions (IMFs) by EMD decomposition; 2) By averaging each pair of the complementary IMFs, the 2N groups of IMFs are computed into N IMF groups; 3) Assemble same-index components across the N groups of IMFs using the median operator to obtain the final IMFs within MCEEMD. Through typical simulations as well as two real-world cases, we show that the present work not only effectively alleviates the MS problem, but also avoids two shortcomings of using a single median operator, i.e., the poor decomposition completeness and the presence of burr in IMFs. -
表 1 4种方法的性能指标
Table 1 Performance indicators of the four methods
方法 PCC RMSE PSD面积比 (%) EEMD 0.9568 0.3087 0.28 CEEMD 0.9986 0.0031 0.21 MEEMD 0.7293 1.2938 0.24 MCEEMD 0.9980 0.1614 0.14 表 2 4种方法的计算时间
Table 2 Calculation time of the four methods
方法 计算时间 (s) EEMD 14.32 CEEMD 28.95 MEEMD 14.58 MCEEMD 29.01 -
[1] Huang N E, Shen Z, Long S R, Wu M C, Shih H H, Zheng Q, et al. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proceedings Mathematical Physical & Engineering ences, 1998, 454(1971): 903-995. doi: 10.1098/rspa.1998.0193 [2] Mandic D P, Rehman N U, Wu Z, Huang N E. Empirical mode decomposition-based time-frequency analysis of multivariate signals: the power of adaptive data analysis. Signal Processing Magazine IEEE, 2013, 30(6): 74-86. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2013.2267931 [3] 杨默涵, 陈万忠, 李明阳. 基于总体经验模态分解的多类特征的运动想象脑电识别方法研究. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(5): 743−752.Yang Mo-Han, Chen Wan-Zhong, Li Ming-Yang. Multiple feature extraction based on ensemble empirical mode decomposition for motor imagery EEG recognition tasks. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(5): 743-752. [4] Lang X, Lu S, Xie L, Zakharov A, Zhong D, Sirkka-Liisa Jämsä-Jounela. Bihocerence based industrial control loop nonlinearity detection and diagnosis in short nonstationary time series. Journal of Process Control, 2018, 63: 15-28. doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2018.01.001 [5] Lang X, Zhang Y F, Xie L, Jin X, Horch A, Su H Y. Use of fast multivariate empirical mode decomposition for oscillation monitoring in noisy process plant. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2020, 59(25): 11537-51. doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.9b06351 [6] Devi A S, Maragatham G, Boopathi K, Rangaraj A G. Hourly day-ahead wind power forecasting with the EEMD-CSO-LSTM-EFG deep learning technique. Soft Computing, 2020, 24(16): 12391-12411. doi: 10.1007/s00500-020-04680-7 [7] 李霞, 卢官明, 闫静杰, 张正言. 多模态维度情感预测综述. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(12): 2142-2159.Li Xia, Lu Guan-Ming, Yan Jing-Jie, Zhang Zheng-Yan. A survey of dimensional emotion prediction by multimodal cues. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(12): 2142-2159. [8] Wu Z, Huang N E. Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: a noise-assisted data analysis method. Advances in Adaptive Data Analysis, 2009, 1(1): 1-41. doi: 10.1142/S1793536909000047 [9] Flandrin P, Rilling G, Goncalves P. Empirical mode decomposition as a filter bank. IEEE signal processing letters, 2004, 11(2): 112-114. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2003.821662 [10] Yeh J R, Shieh J S, Huang N E. Complementary ensemble empirical mode decomposition: A novel noise enhanced data analysis method. Advances in Adaptive Data Analysis, 2010, 02(02): 135-156. doi: 10.1142/S1793536910000422 [11] Torres M E, Colominas M A, Schlotthauer G, Flandrin P. A complete ensemble empirical mode decomposition with adaptive noise. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). Prague, Czech Republic: IEEE, 2011. 4144−4147 [12] Rehman N, Mandic D P. Multivariate empirical mode decomposition. Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 2010, 466(2117): 1291-1302. doi: 10.1098/rspa.2009.0502 [13] Lang X, Zheng Q, Zhang Z M, Lu S, Xie L. Fast multivariate empirical mode decomposition. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 65521-65538. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2877150 [14] Lang X, ur Rehman N, Zhang Y F, Xie L, Su H Y. Median Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition. Signal Processing, 2020, 176: 107686. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2020.107686 [15] Cheng J S, Yu D J, Tang J S, Yang Y. Application of SVM and SVD technique based on EMD to the fault diagnosis of the rotating machinery. Shock and Vibration, 2009, 16(1): 89-98. doi: 10.1155/2009/519502 [16] 赵春晖, 余万科, 高福荣. 非平稳间歇过程数据解析与状态监控 —回顾与展望. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(10): 2072−2091. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190586Zhao Chun-Hui, Yu Wan-Ke, Gao Fu-Rong. Data analytics and condition monitoring methods for nonstationary batch processes — current status and future. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(10): 2072−2091. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190586 [17] 周成江, 吴建德, 杨静宗. 基于CEEMD-SVD-LSSVM的矿浆管线核心设备故障诊断. 云南大学学报自然科学版, 2018, 40(05): 886-896.Zhou Cheng-Jiang, Wu Jian-De, Yang Jing-Zong. Fault diagnosis of core equipment of slurry pipeline based on CEEMD-SVD-LSSVM. Journal of Yunnan University Natural Sciences Edition, 2018, 40(05): 886-896. [18] 罗继辉, 黄国勇. 基于广义S变换和深度置信网络的单向阀故障诊断. 电子测量与仪器学报, 2019, 33 (09): 197-203.Luo Ji-Zhong, Huang Guo-Yong. Check valve fault diagnosis based on generalized S-transform and deep belief network. Journal of Electronic Measurement and Instrumentation, 2019, 33 (09): 197-203. [19] He B B, Zhang Y F, Zhang K X, Chen J H, Zhang J H, Liang H. Optimum speckle tracking based on ultrafast ultrasound for improving blood flow velocimetry. IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control, 2020, 68(3): 494-509. [20] 夏平, 施宇, 雷帮军, 龚国强, 胡蓉, 师冬霞. 复小波域混合概率图模型的超声医学图像分割. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(1): 185-196.Xia Ping, Shi Yu, Lei Bang-Jun, Gong Guo-Qiang, Hu Rong, Shi Dong-Xia. Ultrasound medical image segmentation based on hybrid probabilistic graphical model in complex-wavelet domain. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(1): 185-196. [21] 林文晶, 张榆锋, 章克信, 李支尧, 李海燕, 高莲, 等. 总体经验模态细分法提取血流超声多普勒信号的研究. 电子学报, 2014, 42(007): 1424-1428.Lin Wen-Jing, Zhang Yu-Feng, Zhang Ke-Xin, Li Zhi-Yao, Li Hai-Yan, Gao Lian, et al. Extraction of doppler ultrasound blood signals using the delicate separation method based on the EEMD algorithm. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2014, 42(007): 1424-1428. [22] Zhang Y F, Gao Y L, Wang L, Chen J H, Shi X L. The removal of wall components in Doppler ultrasound signals by using the empirical mode decomposition algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2007, 54(9): 1631-1642. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2007.891936 [23] Majd S M M T, Asl B M. Adaptive spectral doppler estimation based on the modified amplitude spectrum capon. IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control, 2021, 68(5): 1664-1675. doi: 10.1109/TUFFC.2020.3044774 [24] Lang X, Zheng Q, Xie L, Horch A, Su H Y. Direct Multivariate Intrinsic Time-Scale Decomposition for Oscillation Monitoring. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2020, 28(6): 2608-2615. doi: 10.1109/TCST.2019.2940374 [25] Xie X Y, Liu H, Shu M L, Zhu Q, Huang A P, Kong X Q, et al. A multi-stage denoising framework for ambulatory ECG signal based on domain knowledge and motion artifact detection. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2021, 116: 103-116. doi: 10.1016/j.future.2020.10.024 -




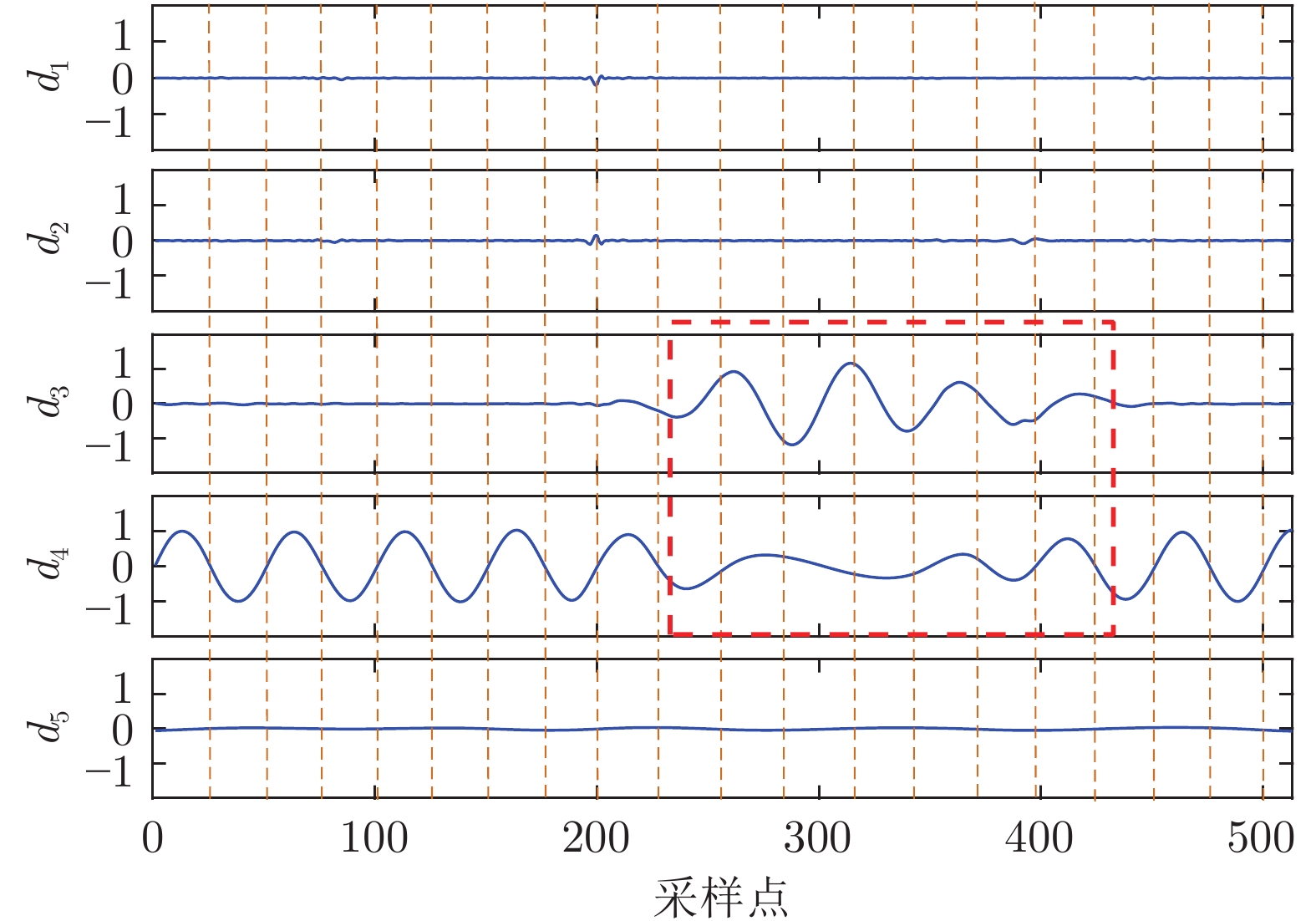
 下载:
下载: