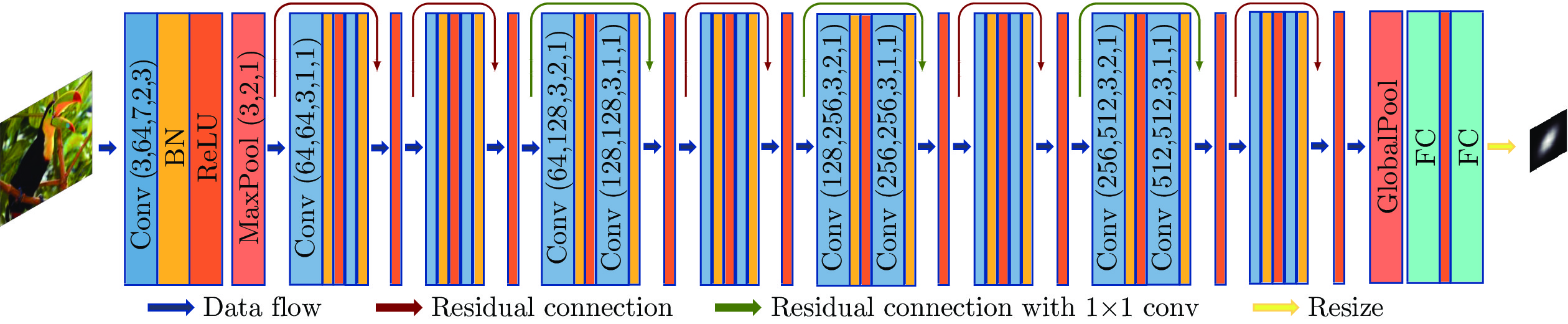
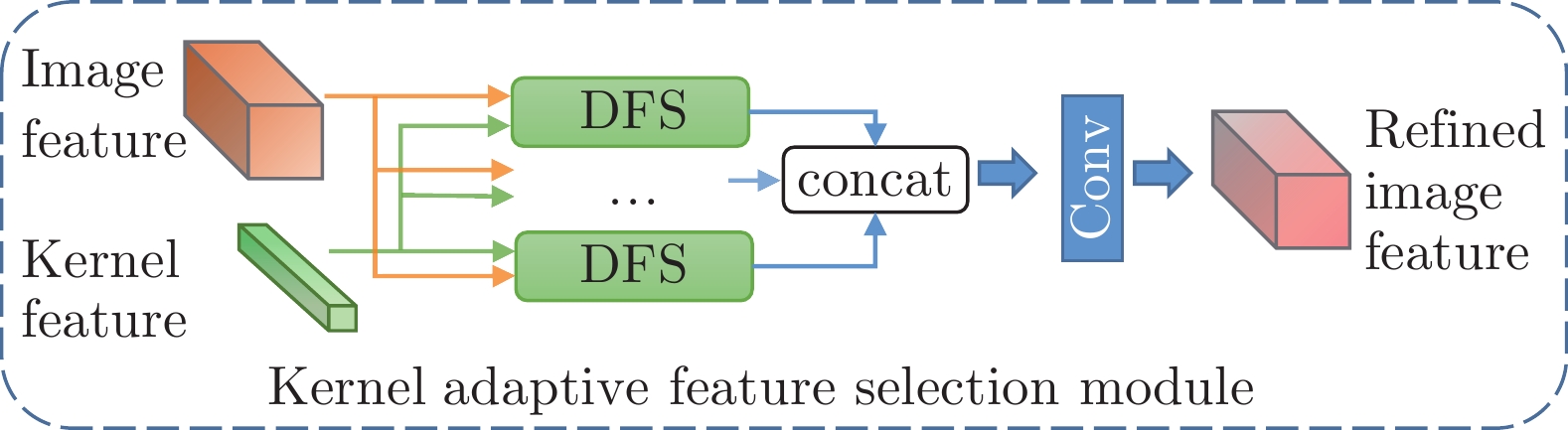
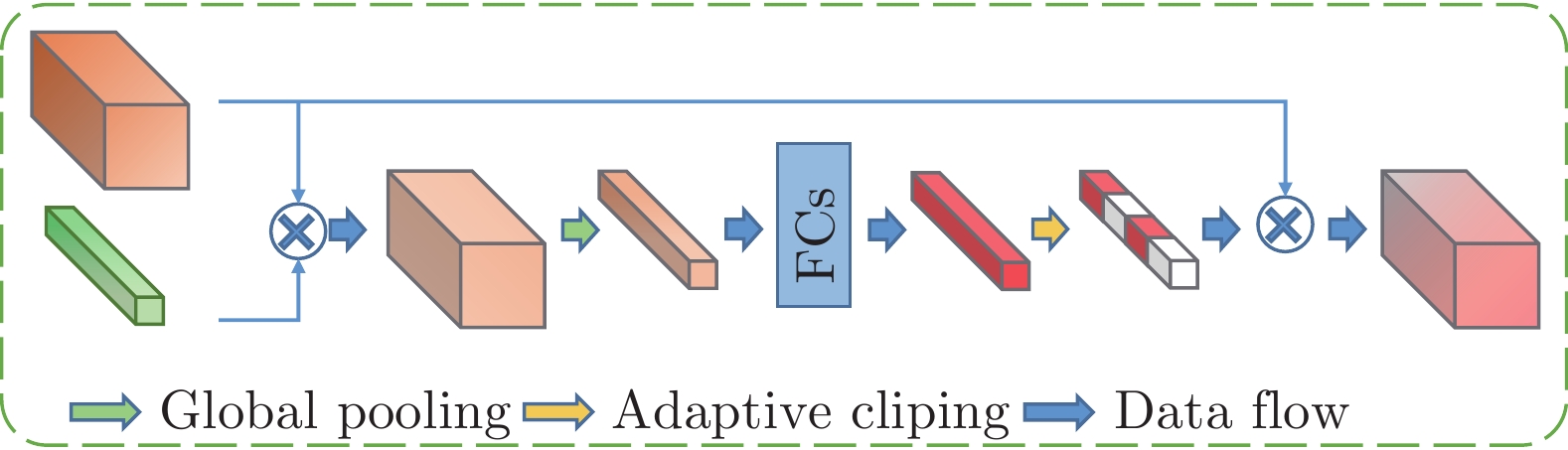
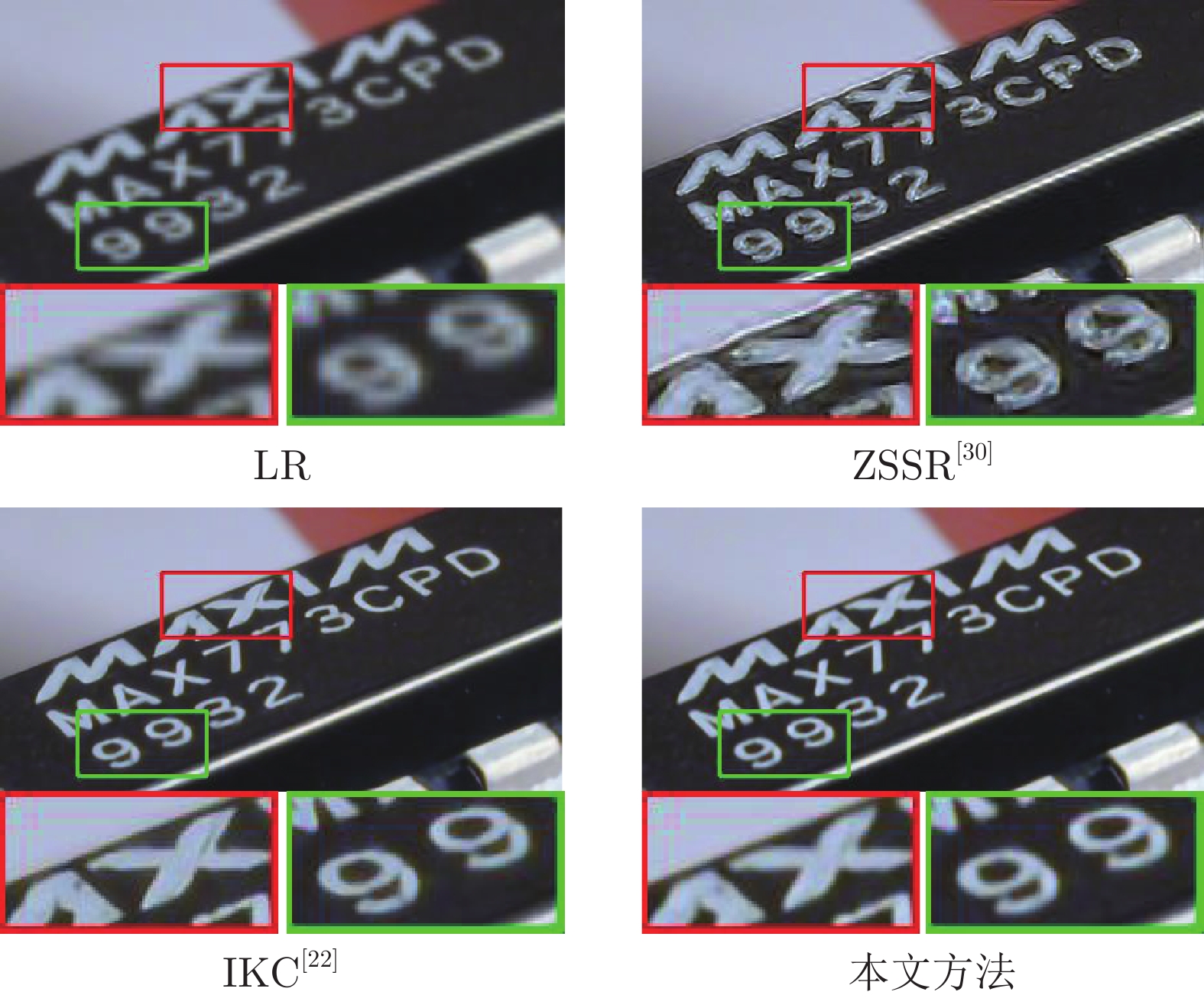
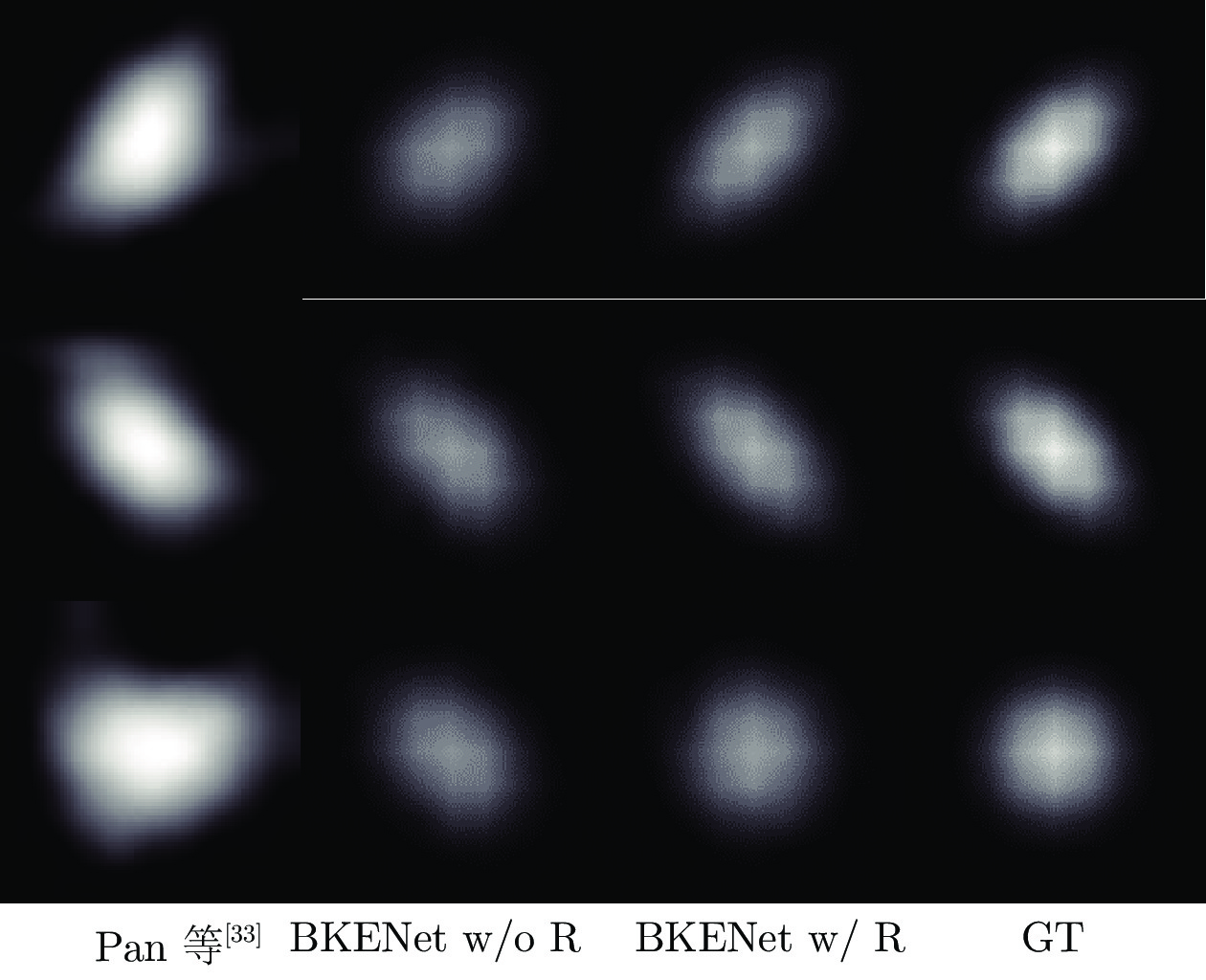
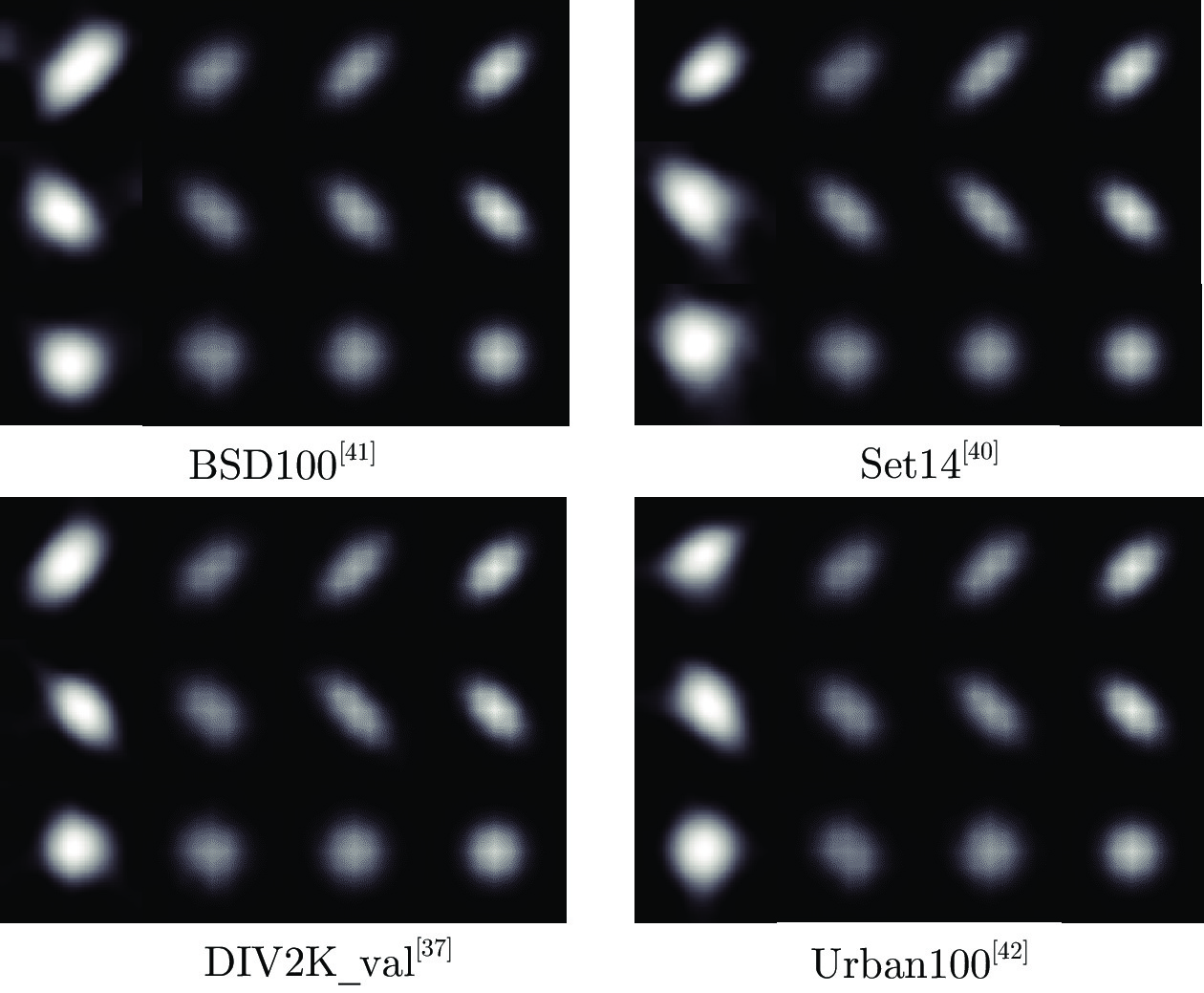
-
摘要: 模糊图像的超分辨率重建具有挑战性并且有重要的实用价值. 为此, 提出一种基于模糊核估计的图像盲超分辨率神经网络(Blurred image blind super-resolution network via kernel estimation, BESRNet). 该网络主要包括两个部分: 模糊核估计网络 (Blur kernel estimation network, BKENet)和模糊核自适应的图像重建网络(Kernel adaptive super-resolution network, SRNet). 给定任意低分辨率图像(Low-resolution image, LR), 首先利用模糊核估计子网络从输入图像估计出实际的模糊核, 然后根据估计到的模糊核, 利用模糊核自适应的图像重建子网络完成输入图像的超分辨率重建. 与其他图像盲超分辨率方法不同, 所提出的模糊核估计网络能够显式地从输入低分辨率图像中估计出完整的模糊核, 然后模糊核自适应的图像重建网络根据估计到的模糊核, 动态地调整网络各层的图像特征, 从而适应不同输入图像的模糊. 在多个基准数据集上进行了有效性实验, 定性和定量的结果都表明该网络优于同类的图像盲超分辨率神经网络.Abstract: Blind blurred image super-resolution is challenging and has important application values. This paper proposes a blurred image blind super-resolution network via kernel estimation (BESRNet), which mainly includes two parts: Blur kernel estimation network (BKENet) and kernel adaptive super-resolution network (SRNet). Given a low-resolution image (LR), the network uses the blur kernel estimation subnetwork to estimate the blur kernel from the input image, and then it uses the kernel adaptive super-resolution subnetwork to super-resolve the input low-resolution image. Different from other blind super-resolution methods, the proposed blur kernel estimation subnetwork gives the whole blur kernel, then the kernel adaptive super-resolution subnetwork dynamically adjusts the image features of different network layers according to the estimated blur kernel to adapt to different image degradations. In this paper, extensive experiments are carried out on multiple benchmark datasets. The qualitative and quantitative results show that proposed method is superior to other blind super-resolution methods.
-
表 1 各个超分方法在基准数据集上的性能对比(PSNR (dB)/SSIM)
Table 1 Performance comparison of different super-resolution methods on benchmark datasets (PSNR (dB)/SSIM)
方法 放大倍数 数据集 Set5[39] Set14[40] BSD100[41] Urban100[42] DIV2K_val[37] Bicubic × 2 25.76/0.800 23.73/0.699 24.15/0.681 21.51/0.670 25.73/0.776 RDN[14] × 2 28.03/0.840 25.20/0.713 25.44/0.697 23.04/0.699 27.93/0.807 RCAN[17] × 2 24.53/0.751 23.05/0.668 23.49/0.653 21.04/0.633 24.70/0.733 DRN[8] × 2 — — — — — HAN[19] × 2 24.45/0.714 22.90/0.650 23.29/0.634 20.91/0.615 24.54/0.708 RDNMD × 2 29.00/0.879 25.89/0.803 25.97/0.798 24.16/0.818 28.23/0.863 ZSSR[30] × 2 26.06/0.804 24.02/0.707 24.43/0.688 21.90/0.685 25.99/0.785 IKC[22] × 2 — — — — — BESRNet (本文) × 2 30.96/0.903 27.73/0.834 27.20/0.827 25.38/0.845 29.96 /0.886 Bicubic × 4 24.72/0.755 22.83/0.647 23.34/0.628 20.65/0.613 24.79/0.733 RDN[14] × 4 27.46/0.808 24.72/0.694 25.03/0.671 22.53/0.690 27.24/0.775 RCAN[17] × 4 22.83/0.619 21.62/0.548 22.16/0.541 19.77/0.521 23.25/0.619 DRN[8] × 4 23.07/0.679 21.92/0.596 22.50/0.580 20.07/0.562 23.96/0.683 HAN[19] × 4 22.65/0.603 20.81/0.524 22.09/0.536 19.33/0.497 22.83/0.605 RDNMD × 4 28.63/0.834 25.33/0.716 25.51/0.690 23.29/0.718 27.68/0.793 ZSSR[30] × 4 25.09/0.710 23.75/0.640 24.15/0.620 21.52/0.622 26.72/0.752 IKC[22] × 4 28.93/0.844 25.94/0.719 25.73/0.696 23.49/0.729 28.15/0.800 BESRNet (本文) × 4 29.18/0.860 26.10/0.742 25.74/0.714 23.81/0.751 28.23/0.813 Bicubic × 8 21.90/0.622 20.68/0.535 21.58/0.530 18.73/0.493 22.66/0.640 RDN[14] × 8 — — — — — RCAN[17] × 8 20.91/0.518 20.15/0.468 21.10/0.463 18.51/0.434 22.26/0.567 DRN[8] × 8 21.09/0.536 20.76/0.499 21.31/0.493 18.81/0.471 22.67/0.594 HAN[19] × 8 20.30/0.492 19.88/0.486 19.53/0.467 18.17/0.401 21.47/0.529 RDNMD × 8 23.86/0.710 21.79/0.560 22.70/0.569 20.29/0.586 24.18/0.686 ZSSR[30] × 8 — — — — — IKC[22] × 8 — — — — — BESRNet (本文) × 8 24.15/0.722 22.64/0.600 22.87/0.571 20.54/0.599 24.75/0.691 表 2 各个模糊核预测方法在基准数据集上的定量结果对比 (MSE × 10−5/MAE × 10−3)
Table 2 Quantitative comparison of kernel estimation methods on the benchmark datasets (MSE × 10−5/MAE × 10−3)
表 3 (×4) 使用真值模糊核作为先验的不同方法的量化指标对比(PSNR (dB)/SSIM)
Table 3 (×4) Quantitative comparison of different methods with real blur kernels as prior (PSNR (dB)/SSIM)
表 4 (×4) 不同DFS分支数的KAFS 模块在Set5[39]数据集上的定量结果对比
Table 4 (×4) Quantitative comparison of KAFS module with different numbers of DFS on Set5[39]
DFS PSNR (dB)/SSIM Params (M) Multi-adds (G) 1 29.50/0.861 12.92 151.04 2 29.61/0.863 12.98 151.05 4 29.54/0.862 13.12 151.06 -
[1] Luo Y M, Zhou L G, Wang S, Wang Z Y. Video satellite imagery super resolution via convolutional neural networks. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(12): 2398-2402 doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2766204 [2] Shi W Z, Caballero J, Ledig C, Zhuang X H, Bai W J, Bhatia K, et al. Cardiac image super-resolution with global correspondence using multi-atlas PatchMatch. In: Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Nagoya, Japan: Springer, 2013. 9−16 [3] Zou W W W, Yuen P C. Very low resolution face recognition problem. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2011, 21(1): 327-340 [4] Dong C, Loy C C, He K M, Tang X O. Image super-resolution using deep convolutional networks. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 38(2): 295-307 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2439281 [5] Kim J, Lee J K, Lee K M. Accurate image super-resolution using very deep convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 1646−1654 [6] Ledig C, Theis L, Huszár F, Caballreo J, Cunningham A, Acosta A, et al. Photo-realistic single image super-resolution using a generative adversarial network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Hawaii, USA: IEEE, 2017. 4681−4690 [7] Lim B, Son S, Kim H, Nah S, Lee K M. Enhanced deep residual networks for single image super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW). Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 136−144 [8] Guo Y, Chen J, Wang J D, Chen Q, Cao J Z, Deng Z S, et al. Closed-loop matters: Dual regression networks for single image super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 5407−5416 [9] Kim J, Lee J K, Lee K M. Deeply-recursive convolutional network for image super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 1637−1645 [10] Tai Y, Yang J, Liu X M. Image super-resolution via deep recursive residual network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 3147−3155 [11] 周登文, 赵丽娟, 段然, 柴晓亮. 基于递归残差网络的图像超分辨率重建. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(6): 1157-1165 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c180334Zhou Deng-Wen, Zhao Li-Juan, Duan Ran, Chai Xiao-Liang. Image super-resolution based on recursive residual networks. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(6): 1157-1165 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c180334 [12] Han W, Chang S Y, Liu D, Yu M, Witbrock M, Huang T S. Image super-resolution via dual-state recurrent networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 1654−1663 [13] Tong T, Li G, Liu X J, Gao Q Q. Image super-resolution using dense skip connections. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 4799−4807 [14] Zhang Y L, Tian Y P, Kong Y, Zhong B N, Fu Y. Residual dense network for image super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 2472−2481 [15] Liu J, Zhang W J, Tang Y T, Tang J, Wu G S. Residual feature aggregation network for image super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 2359−2368 [16] 李金新, 黄志勇, 李文斌, 周登文. 基于多层次特征融合的图像超分辨率重建. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(1): 161-171 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c200585Li Jin-Xin, Huang Zhi-Yong, Li Wen-Bin, Zhou Deng-Wen. Image super-resolution based on multi-hierarchical features fusion network. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(1): 161-171 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c200585 [17] Zhang Y L, Li K P, Li K, Wang L C, Zhong B N, Fu Y. Image super-resolution using very deep residual channel attention networks. In: Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 286−301 [18] Dai T, Cai J R, Zhang Y B, Xia S T, Zhang L. Second-order attention network for single image super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 11065−11074 [19] Niu B, Wen W L, Ren W Q, Zhang X D, Yang L P, Wang S Z, et al. Single image super-resolution via a holistic attention network. In: Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision. Glasgow, UK: Springer, 2020. 191−207 [20] Bulat A, Yang J, Tzimiropoulos G. To learn image super-resolution, use a GAN to learn how to do image degradation first. In: Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 185−200 [21] Zhang K, Zuo W M, Zhang L. Learning a single convolutional super-resolution network for multiple degradations. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 3262−3271 [22] Gu J J, Lu H N, Zuo W M, Dong C. Blind super-resolution with iterative kernel correction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 1604−1613 [23] Wang X T, Yu K, Dong C, Loy C C. Recovering realistic texture in image super-resolution by deep spatial feature transform. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 606−615 [24] Luo Z X, Huang Y, Li S, Wang L, Tan T N. Unfolding the alternating optimization for blind super resolution. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: Curran Associates Inc., 2020. Article No. 473 [25] 常振春, 禹晶, 肖创柏, 孙卫东. 基于稀疏表示和结构自相似性的单幅图像盲解卷积算法. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(11): 1908-1919 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c160357Chang Zhen-Chun, Yu Jing, Xiao Chuang-Bai, Sun Wei-Dong. Single image blind deconvolution using sparse representation and structural self-similarity. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(11): 1908-1919 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c160357 [26] Pan J S, Lin Z C, Su Z X, Yang M H. Robust kernel estimation with outliers handling for image deblurring. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 2800−2808 [27] Yan R M, Shao L. Blind image blur estimation via deep learning. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(4): 1910-1921 [28] Yuan Y, Liu S Y, Zhang J W, Zhang Y B, Dong C, Lin L. Unsupervised image super-resolution using cycle-in-cycle generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW). Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 701−710 [29] Zhang Y B, Liu S Y, Dong C, Zhang X F, Yuan Y. Multiple cycle-in-cycle generative adversarial networks for unsupervised image super-resolution. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 1101-1112 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2938347 [30] Shocher A, Cohen N, Irani M. Zero-shot super-resolution using deep internal learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 3118−3126 [31] Soh J W, Cho S, Cho N I. Meta-transfer learning for zero-shot super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 3516−3525 [32] Efrat N, Glasner D, Apartsin A, Nadler B, Levin A. Accurate blur models vs. image priors in single image super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Sydney, Australia: IEEE, 2013. 2832−2839 [33] Pan J S, Sun D Q, Pfister H, Yang M H. Blind image deblurring using dark channel prior. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 1628−1636 [34] He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, Sun J. Identity mappings in deep residual networks. In: Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Springer, 2016. 630−645 [35] Su Z, Fang L P, Kang W X, Hu D W, Pietikäinen M, Liu L. Dynamic group convolution for accelerating convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision. Glasgow, UK: Springer, 2020. 138−155 [36] Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2015. 234−241 [37] Agustsson E, Timofte R. NTIRE 2017 challenge on single image super-resolution: Dataset and study. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW). Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 126−135 [38] Timofte R, Agustsson E, Van Gool L, Yang M H, Zhang L, Lim B, et al. NTIRE 2017 challenge on single image super-resolution: Methods and results. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW). Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 114−125 [39] Bevilacqua M, Roumy A, Guillemot C, Alberi-Morel M L. Low-complexity single-image super-resolution based on nonnegative neighbor embedding. In: Proceedings of the 23rd British Machine Vision Conference BMVC 2012. Surrey, UK: BMVA Press, 2012. 135.1−135.10 [40] Zeyde R, Elad M, Protter M. On single image scale-up using sparse-representations. In: Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Curves and Surfaces. Avignon, France: Springer, 2010. 711−730 [41] Martin D, Fowlkes C, Tal D, Malik J. A database of human segmented natural images and its application to evaluating segmentation algorithms and measuring ecological statistics. In: Proceedings of the 8th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. ICCV 2001. Vancouver, Canada: IEEE, 2001. 416−423 [42] Huang J B, Singh A, Ahuja N. Single image super-resolution from transformed self-exemplars. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Boston, USA: IEEE, 2015. 5197−5206 [43] Kingma D P, Ba J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1412.6980v8, 2015. -




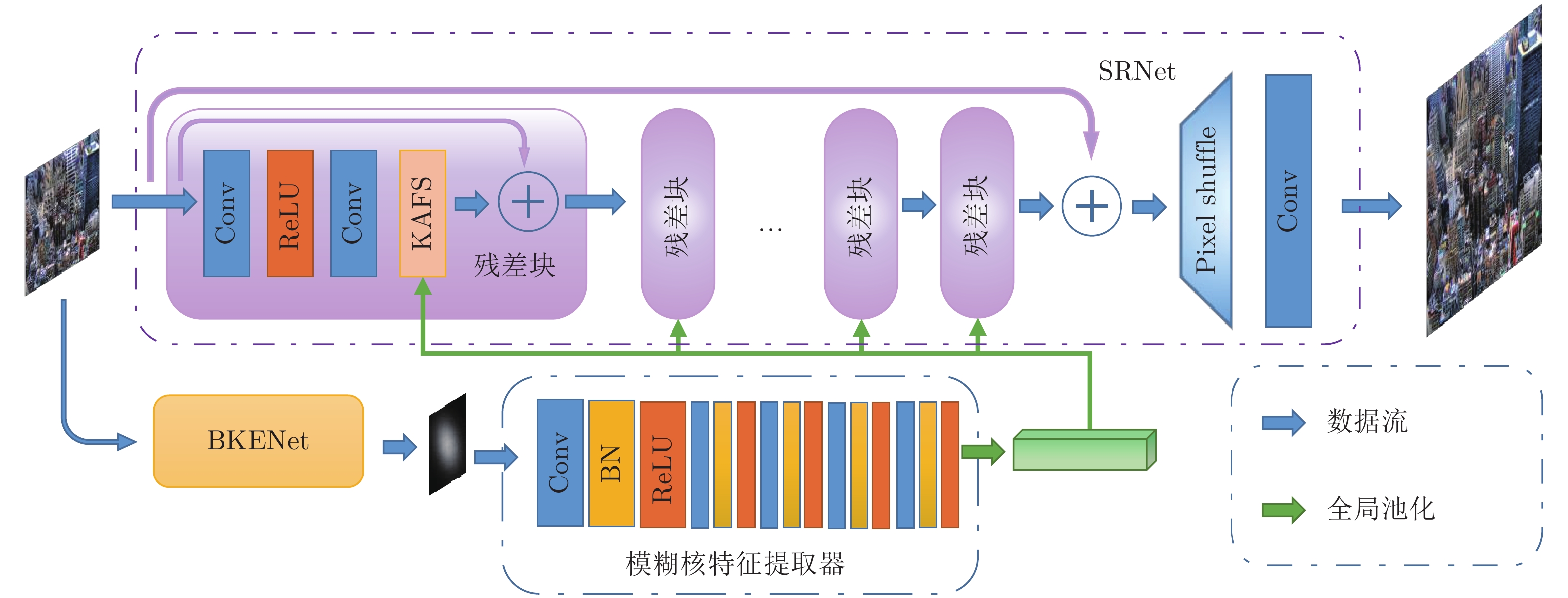
 下载:
下载: