Research on Gesture Recognition Based on Pressure-based Mechanomyogram and Improved Neural Fuzzy Inference System
-
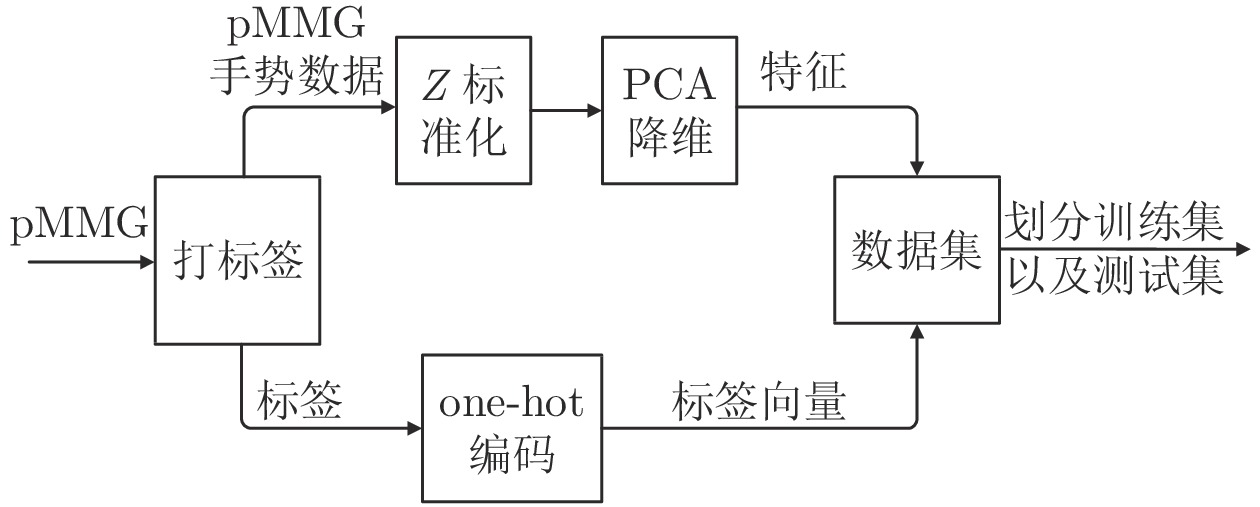
摘要: 手势识别是人机交互领域的重要研究内容, 为截肢患者控制智能假肢手提供基础. 当前主流方法之一是利用表面肌电图(Electromyogram, EMG)识别手部运动意图, 但肌电信号存在信号弱和易受噪声、汗液、疲劳影响等缺点. 同时肌电图在识别准确率方面, 尤其是截肢患者手势识别方面仍然具有较大的提升空间. 针对这些问题, 设计了基于气压肌动图(Pressure-based mechanomyogram, pMMG)的穿戴式信号采集装置, 为手势识别提供了优质的信号源. 结合深度神经网络中全连接层结构、典型抽样和标准正则化技术, 提出了一种改进多类神经模糊推理系统(Improved multicalss neural fuzzy inference system, IMNFIS), 与传统自适应神经模糊推理系统(Adaptive neural fuzzy inference system, ANFIS)相比, 泛化能力得到显著提升. 招募了7名健康受试者和1名截肢受试者, 并用8种算法开展离线实验. 所提方法在残疾人手势识别实验中取得了97.25%的最高平均准确率, 在健康人手势识别实验中取得了98.18%的最高平均准确率. 与近年公开报道的多种手势识别研究相比, 所提方法的综合性能更优.Abstract: Gesture recognition, which provides a foundation for amputees to control smart prosthetic hands, is an important research content in the field of human-robot interaction. One of the current mainstream methods is using surface electromyogram (EMG) to identify the intention of hand motion, while EMG signals are weak and show some shortages of being interfered easily by noise, sweat, fatigue, etc. At the same time, there is still large room for the improvement in the recognition accuracy, especially in the gesture recognition of amputees by using EMG. To solve these problems, a wearable signal acquisition device based on pressure-based mechanomyogram (pMMG) is designed in this paper, which provides a signal source of high quality for gesture recognition. We proposed an improved multicalss neural fuzzy inference system (IMNFIS) by combining the full connection layer structure, typical sampling and uniformed regularization techniques in deep neural network, which significantly improved the generalization ability compared with the traditional adaptive neural fuzzy inference system (ANFIS). We recruited seven healthy subjects and an amputee subject, and then conducted an offline experiment in which eight algorithms are used. The proposed method got the highest average accuracy of 97.25% in the experiment of the disabled, and 98.18% in the experiment of the healthy. Compared with many reported gesture recognition researches in recent years, the method proposed in this paper achieves the better comprehensive performance.1) 收稿日期 2020-10-27 录用日期 2021-03-02 Manuscript received October 27, 2020; accepted March 2, 2021 国家自然科学基金联合基金重点支持项目 (U1913207), 湖北省技术创新专项 (2019AEA171), 科技部政府间国际科技创新合作重点专项 (2017YFE0128300) 资助 Supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (U1913207), Technology Innovation Project of Hubei Province(2019AEA171), and International Science and Technology Cooperation Program of China (2017YFE0128300) 本文责任编委 郑伟诗 Recommended by Associate Editor ZHENG Wei-Shi 1. 华中科技大学人工智能与自动化学院图像信息处理与智能控制教育部重点实验室 武汉 430074 2. 华中科技大学机械科学与2) 工程学院数字制造装备与技术国家重点实验室 武汉 430074 1. Ministry of Education Key Laboratory on Image Information Processing and Intelligent Control, School of Artificial Intelligence and Automation, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074 2. State Key Laboratory of Manufacturing Equipment and Technology, School of Mechanical Science and Engineering, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074
-
表 1 参与手势识别实验的受试者信息
Table 1 Information of the subjects participating in the gesture recognition experiment
受试者 性别 年龄 身高 (cm) 体重 (kg) 腕围 (cm) 健康状况 Subject-1 男 25 180.4 72.4 18.8 健康 Subject-2 男 24 169.5 58.5 16.5 健康 Subject-3 男 56 164.6 61.2 15.8 手部截肢 Subject-4 男 25 172.3 62.8 17.9 健康 Subject-5 男 22 177.5 57.0 16.8 健康 Subject-6 男 26 166.6 65.7 18.4 健康 Subject-7 男 23 170.1 73.3 19.1 健康 Subject-8 男 25 175.5 66.9 17.1 健康 表 2 6种手腕手势对应的肌肉信息
Table 2 Muscles information of the corresponding six gestures
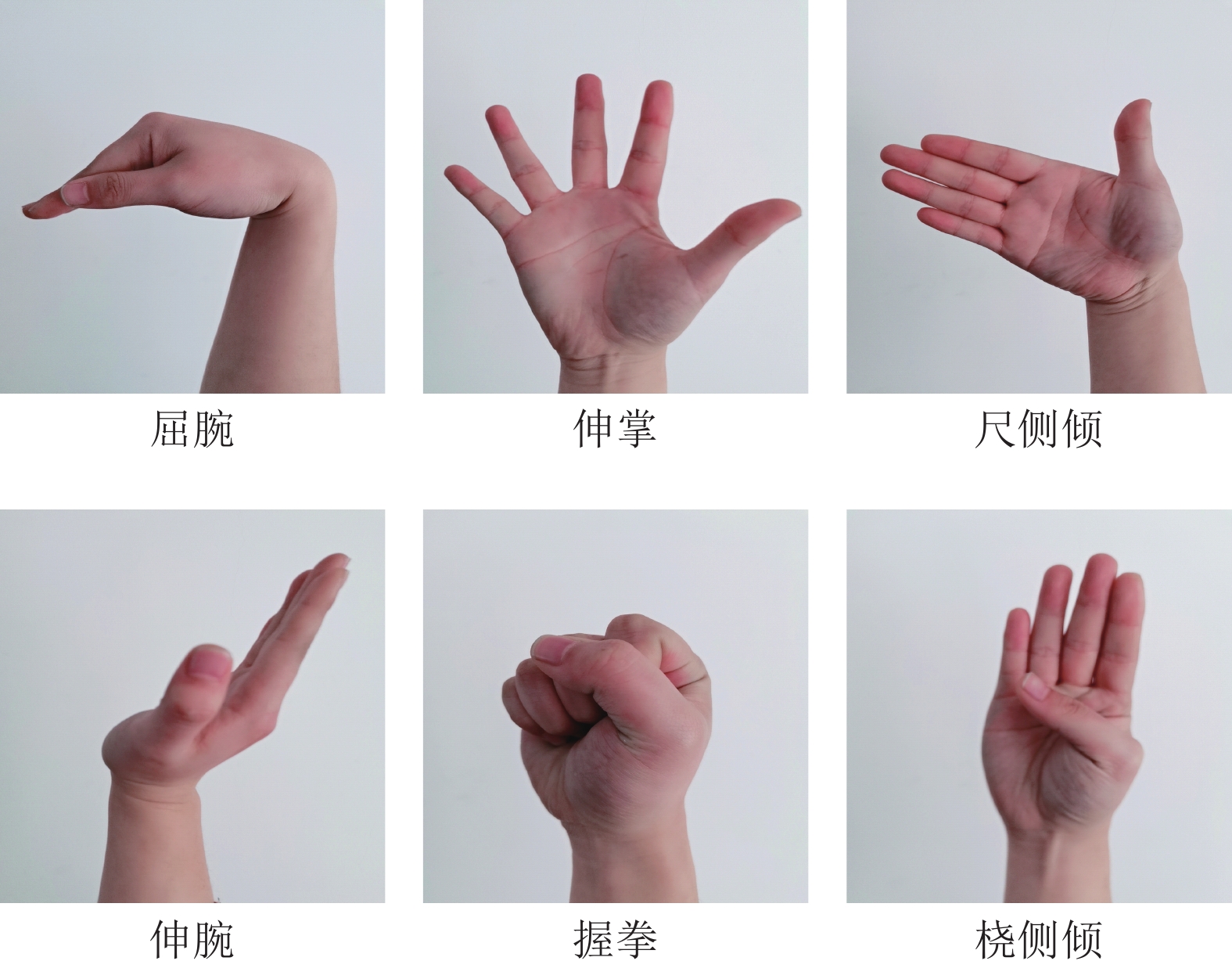
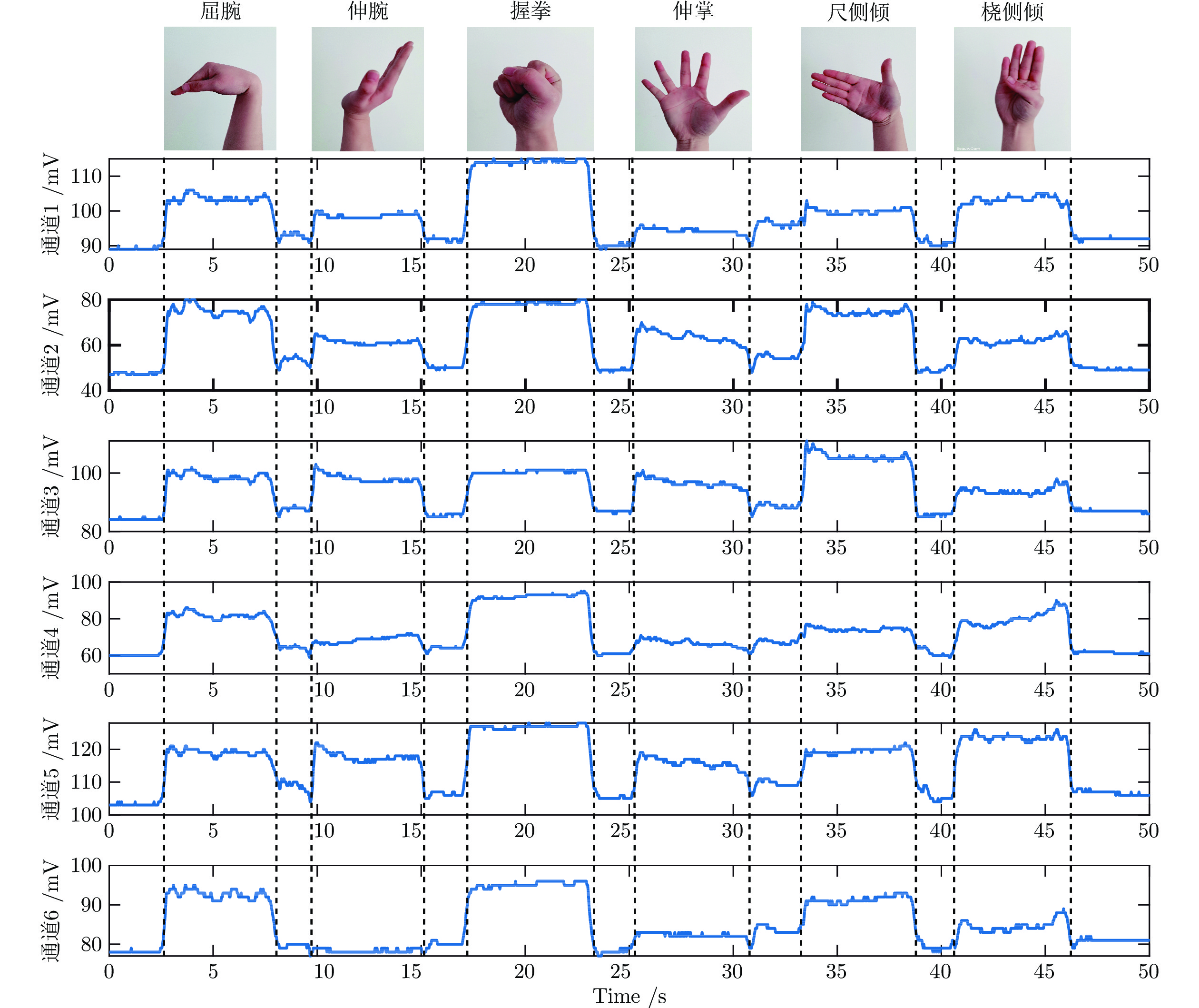
手势 肌肉 作用 屈腕 尺侧腕屈肌 手腕屈曲和尺侧偏移 握拳 指浅屈肌 手指弯曲 尺侧倾 桡侧腕屈肌 手腕弯曲和径向偏移 伸腕 尺侧腕伸肌 手腕伸展和尺侧偏移 伸掌 指伸肌 手指伸展 桡侧倾 桡侧腕伸肌 手腕伸展和径向偏移 表 3 8种算法在健康人数据集上的离线实验结果
Table 3 The offline experiment results of eight algorithms on datasets of the normal
指标 SVM GBDT LDA TSK_GD_LSE MC MC_TS MC_UR MC_TS_UR ${\rm{RER}}$ 6.07% 7.82% 5.15% 5.26% 3.16% 2.52% 2.30% 1.82% ${\rm{BER}}$ 6.18% 8.74% 5.21% 5.35% 2.83% 2.41% 2.33% 1.77% $\kappa$ 0.9258 0.9018 0.9375 0.9358 0.9660 0.9711 0.9720 0.9787 $T_t$ 224.6 4.4 0.6 1121.9 796.1 886.5 734.7 310.2 表 4 8种算法在残疾人数据集上的离线实验结果
Table 4 The offline experiment results of eight algorithms on datasets of the disabled
指标 SVM GBDT LDA TSK_GD_LSE MC MC_TS MC_UR MC_TS_UR ${\rm{RER}}$ 5.94% 8.13% 4.46% 5.77% 4.64% 3.83% 3.77% 2.75% ${\rm{BER}}$ 6.10% 8.27% 4.48% 6.11% 4.72% 3.98% 3.65% 2.73% $\kappa$ 0.9268 0.9008 0.9462 0.9267 0.9434 0.9522 0.9562 0.9672 $T_t$ 173.0 5.3 0.7 1006.5 766.8 942.9 768.6 313.1 表 5 与近期同类研究工作文献的比较
Table 5 Comparison with similar research work literature
文献 传感器 实验对象 是否为公共数据集 分类算法 手势类别数 识别准确率 [25] 6 通道 pMMG 6 名健康人 否 Fuzzy logic 6 95.30% [26] 8 通道 FMG 10 名健康人 否 SVM 6 93.00% [27] 2 通道 sEMG 7 名健康人 否 SVM 4 95.00% [28] 4 通道 sEMG + 1 通道 IMU 10 名健康人 否 LDA 8 92.60% [29] 8 通道 sEMG 21 名健康人 否 LDA 6 94.70% [30] 8 通道 sEMG 8 名健康人 否 Hidden Markov model 6 94.20% Proposed 6 通道 pMMG + 1 通道 IMU 7 名健康人 否 MC_TS_UR 6 98.18% [31] 8 通道 sEMG 4 名残疾人 否 LDA 7 92.00% [32] 7 通道 sEMG 3 名残疾人 否 SVM 5 94.02% Proposed 6 通道 pMMG + 1 通道 IMU 1 名残疾人 否 MC_TS_UR 6 97.25% -
[1] Liu H Y, Wang L H. Gesture recognition for human-robot collaboration: A review. International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics, 2018, 68(1): 355-367 [2] Ding J, Lin R Z, Lin Z Y. Service robot system with integration of wearable Myo armband for specialized hand gesture human–computer interfaces for people with disabilities with mobility problems. Computers Electrical Engineering, 2018, 69(1): 815-827 [3] 丁其川, 赵新刚, 李自由, 韩建达. 基于自更新混合分类模型的肌电运动识别方法. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(8): 1464-1474Ding Q C, Zhao X G, Li Z Y, Han J D. An EMG-motion recognition method with self-update hybrid classification model. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(8): 1464-1474 [4] Zhang X, Chen X, Li Y, Lantz V, Wang K, Yang J. A framework for hand gesture recognition based on accelerometer and EMG sensors. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics-Part A: Systems and Humans, 2011, 41(6): 1064-1076 doi: 10.1109/TSMCA.2011.2116004 [5] Duan T, Huang J, Xie Z, Wang L, Xiong C H. Continuous control of wrist-hand prosthesis by extracting independent sEMG signals from cross-talk muscle groups. In: Proceedings of the 2019 Chinese Control Conference. Guangzhou, China: IEEE, 2019. 4537−4542 [6] 李自由, 王丰焱, 赵新刚, 丁其川, 张道辉, 韩建达. 基于 Myo 旋转偏移估计与自适应校正的手势识别方法. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(9): 1896-1907Li Z Y, Wang F Y, Zhao X G, Ding Q C, Zhang D H, Han J D. The method for gestures recognition based on Myo rotation shifts estimation and adaptive correction. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(9): 1896-1907 [7] Orizio C, Liberati D, Locatelli C, et al. Surface mechanomyogram reflects muscle fibres twitches summation. Journal of Biomechanics, 1996, 29(4): 475-481 doi: 10.1016/0021-9290(95)00063-1 [8] Akataki K, Mita K, Watakabe M, Itoh K. Mechanomyogram and force relationship during voluntary isometric ramp contractions of the biceps brachii muscle. European Journal of Applied Physiology, 2001, 84(1-2): 19-25 doi: 10.1007/s004210000321 [9] McIntosh J, Marzo A, Fraser M, Phillips C. Echoflex: Hand gesture recognition using ultrasound imaging. In: Proceedings of the 2017 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. Denver, USA: ACM, 2017. 1923−1934 [10] Liu M K, Lin Y T, Qiu Z W, Kuo C K, Wu C K. Hand Gesture Recognition by a MMG-Based Wearable Device. Journal of The Neurological Sciences, 2020, 20(24): 14703-14712 [11] Feng W, Xia C, Zhang Y, Yu J, Jiang W. Research on Chinese sign language recognition methods based on mechanomyogram signals analysis. In: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Signal and Image Processing. Wuxi, China: IEEE, 2019. 46−50 [12] Stokes M J, Dalton P A. Acoustic myographic activity increases linearly up to maximal voluntary isometric force in the human quadriceps muscle. Journal of The Neurological Sciences, 1991, 101(2): 163-167 doi: 10.1016/0022-510X(91)90041-5 [13] Ahsan M R, Ibrahimy M I, Khalifa O O. Electromygraphy (EMG) signal based hand gesture recognition using artificial neural network (ANN). In: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Mechatronics. Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia: IEEE, 2011. 1−6 [14] Zhang Z, Yang K, Qian J, Zhang L. Real-time surface emg pattern recognition for hand gestures based on an artificial neural network. Sensors, 2019, 19(14): 3170-3184 doi: 10.3390/s19143170 [15] Yao B, Hagras H, Alhaddad M J, Alghazzawi D. A fuzzy logic-based system for the automation of human behavior recognition using machine vision in intelligent environments. Soft Computing, 2015, 19(2): 499-506 doi: 10.1007/s00500-014-1270-4 [16] Hachaj T, Ogiela M R. Rule-based approach to recognizing human body poses and gestures in real time. Multimedia Systems, 2014, 20(1): 81-99 doi: 10.1007/s00530-013-0332-2 [17] Mufarroha F A, Utaminingrum F. Hand gesture recognition using adaptive network based fuzzy inference system and k-nearest neighbor. International Journal of Technology, 2017, 8(3): 559-567 doi: 10.14716/ijtech.v8i3.3146 [18] Khezri M, Jahed M. A neuro–fuzzy inference system for sEMG-based identification of hand motion commands. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2010, 58(5): 1952-60 [19] Hill A V. The Heat of Shortening and the Dynamic Constants of Muscle. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, 1938, 126(843): 136-195 [20] Belyea A, Englehart K, Scheme E. FMG Versus EMG: A comparison of usability for real-time pattern recognition based control. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2019, 66(11): 3098-3104 doi: 10.1109/TBME.2019.2900415 [21] Peng X Y, Li L, Wang F Y. Accelerating minibatch stochastic gradient descent using typicality sampling. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2019, 31(11): 4649-4659 [22] Cui Y Q, Wu D R, Huang J. Optimize TSK fuzzy systems for classification problems: Mini-batch gradient descent with uniform regularization and batch normalization. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2020, 28(12): 3065-3075 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2020.2967282 [23] You H, Ma Z, Tang Y, Wang Y, Yan J, Ni M, Cen K, Huang Q. Comparison of ANN (MLP), ANFIS, SVM, and RF models for the online classification of heating value of burning municipal solid waste in circulating fluidized bed incinerators. Waste Management, 2017, 68(10): 186-197 [24] Shariati S, Haghighi M M. Comparison of anfis neural network with several other ANNs and support vector the machine for diagnosing hepatitis and thyroid diseases. In: Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Computer Information Systems and Industrial Management Applications. Krackow, Poland: IEEE, 2010. 596−599 [25] Jung P G, Lim G, Kim S, Kong K. A wearable gesture recognition device for detecting muscular activities based on air-pressure sensors. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2015, 11(2): 485-494 [26] Anvaripour M, Saif M. Hand gesture recognition using force myography of the forearm activities and optimized features. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology. Lyon, France: IEEE, 2018. 187−192 [27] Tavakoli M, Benussi C, Lopes P A, et al. Robust hand gesture recognition with a double channel surface EMG wearable armband and SVM classifier. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2018, 46(1): 121-130 [28] Jiang S, Lv B, Guo W, Zhang C, Wang H, Sheng X, Shull P B. Feasibility of wrist-worn, real-time hand, and surface gesture recognition via sEMG and IMU Sensing. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2017, 14(8): 3376-3385 [29] Botros F, Phinyomark A, Scheme E. EMG-based gesture recognition: Is it time to change focus from the forearm to the wrist?. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2022, 18(1), 174−184 [30] Shaabana A, Legere J, Li J, Zheng R, Mohrenschildt MV, Shedden JM. Portable electromyography: A case study on ballistic finger movement recognition. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2019, 19(16): 7043-55 doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2019.2908312 [31] Powell M A, Kaliki R R, Thakor N V. User training for pattern recognition-based myoelectric prostheses: Improving phantom limb movement consistency and distinguishability. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2014, 22(3): 522-532 doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2013.2279737 [32] Kartsch V, Benatti S, Mancini M, Magno M, Benini L. Smart wearable wristband for EMG based gesture recognition powered by solar energy harvester. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems. Florence, Italy: IEEE, 2018. 1−5 -
 AAS-CN-2020-0901手势数据.zip
AAS-CN-2020-0901手势数据.zip

-





 下载:
下载: