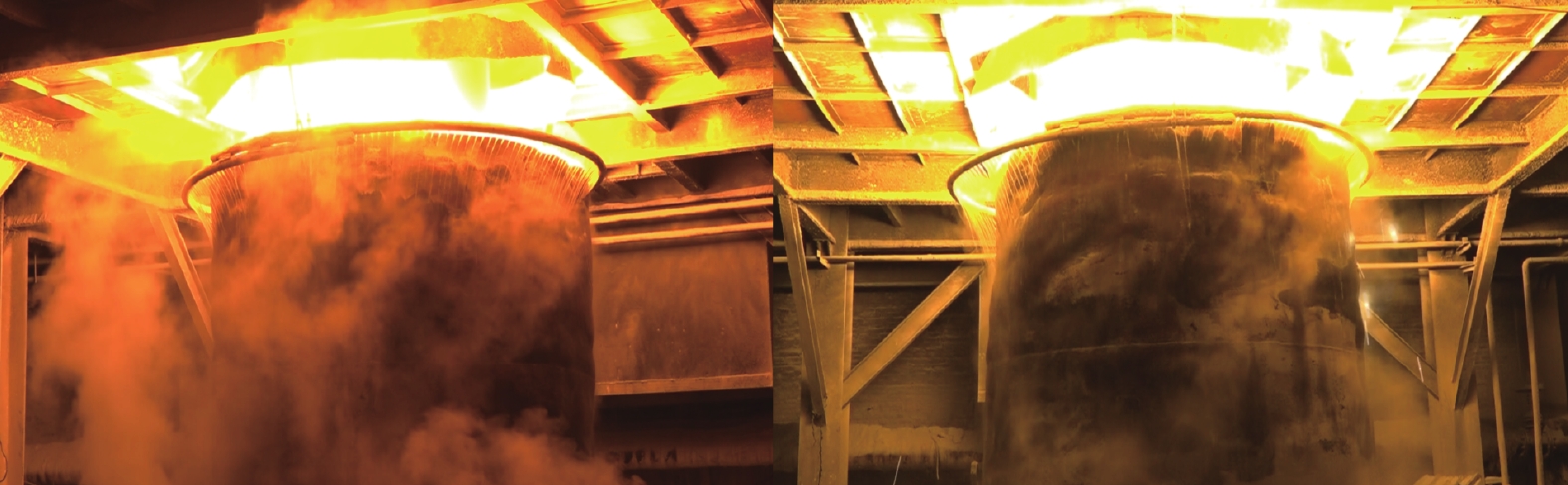
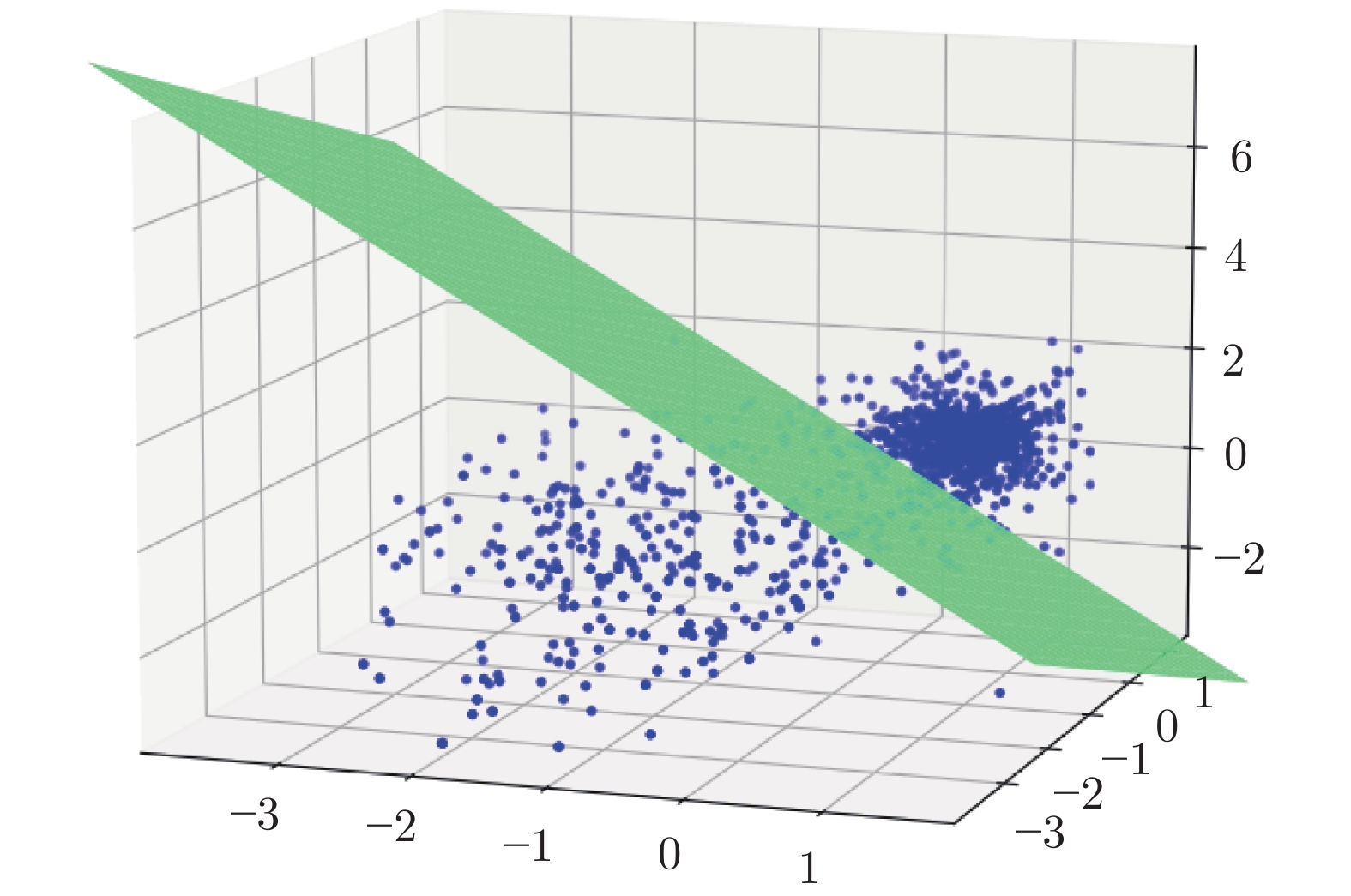
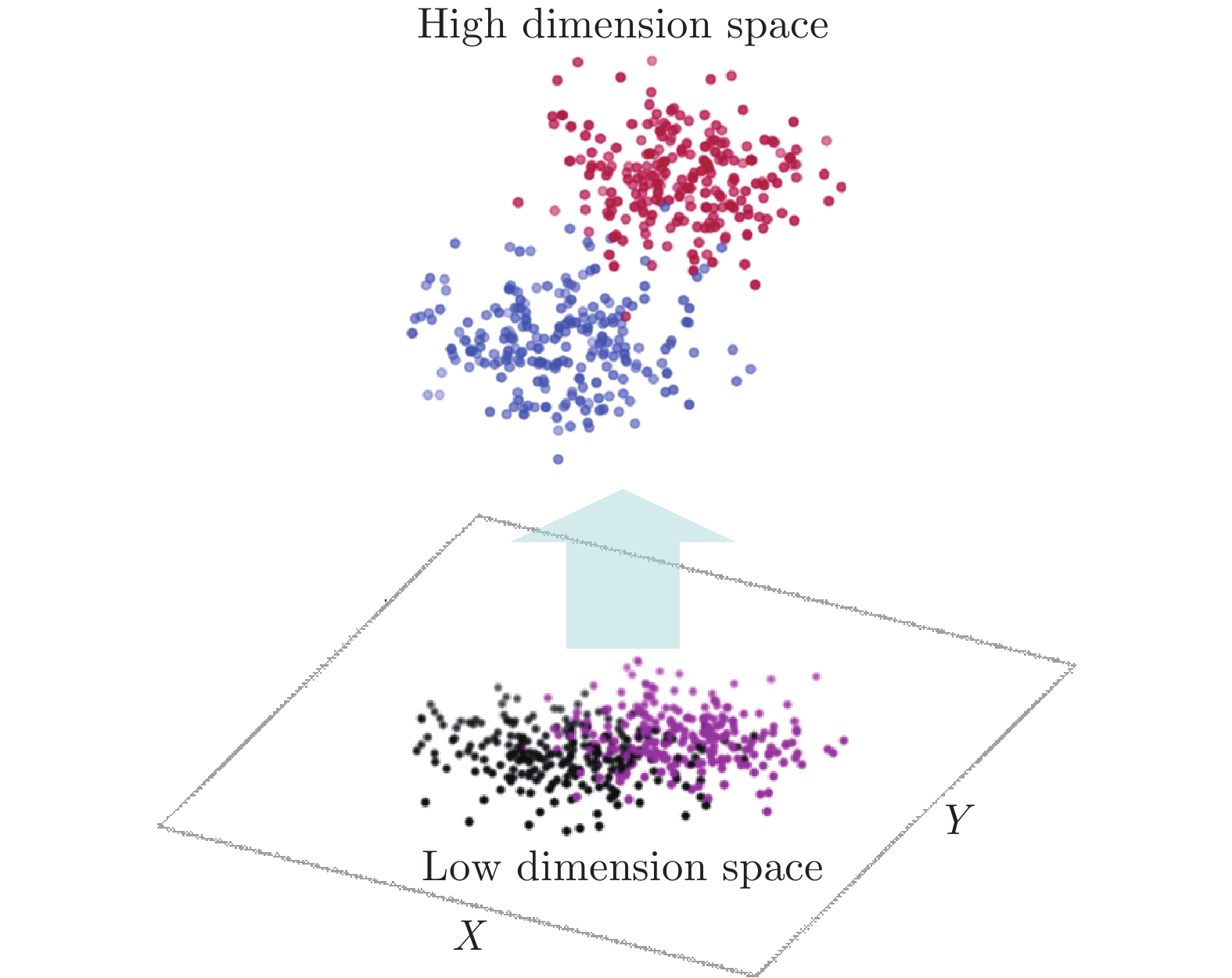
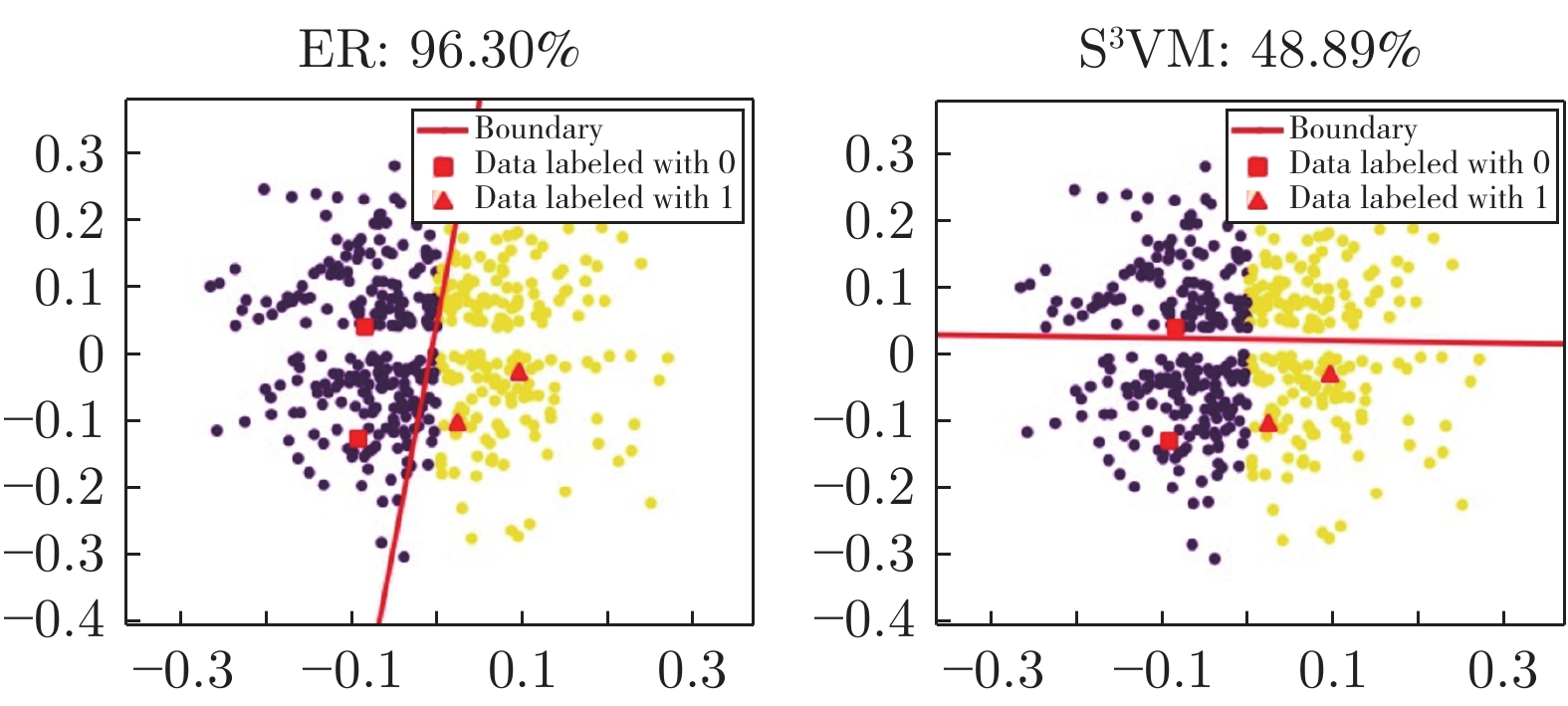
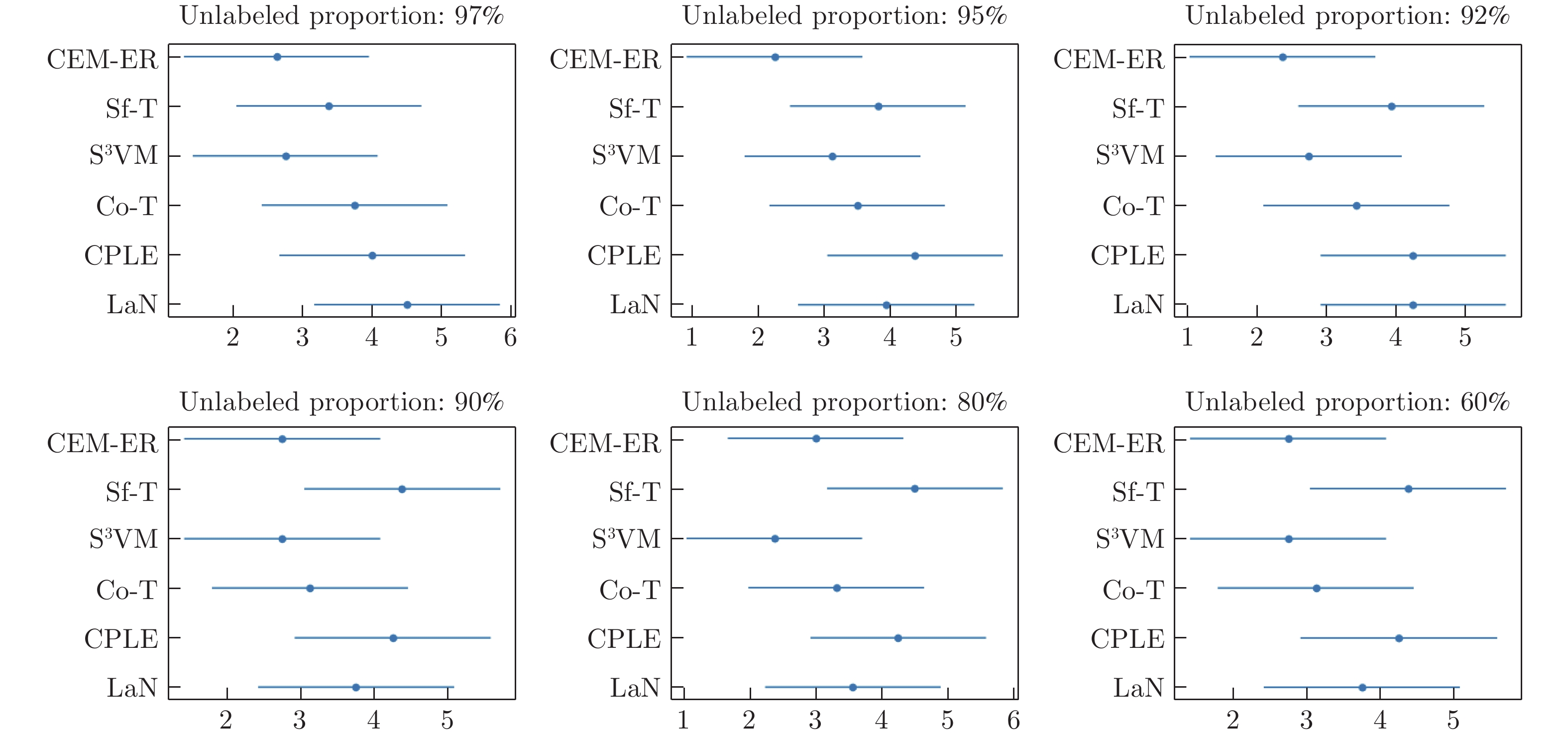
Semi-supervised Classification of Semi-molten Working Condition of Fused Magnesium Furnace Based on Image and Current Features
-
摘要: 针对电熔镁炉异常工况识别任务, 在半监督学习框架下提出一种将电流与图像两类特征融合的解决方案. 主要贡献为: 使用多元图像分析(Multivariate image analysis, MIA)技术代替人眼, 更为准确客观地对镁炉火焰进行特征提取; 利用基于熵正则化(Entropy regularization, ER)的半监督学习框架, 同时使用具有强互补性的生产图像与电流数据进行工况分类, 从而弥补了基于单一特征分类的某些缺点; 采用交叉熵方法(Cross-entropy method, CEM)优化分类器目标函数, 较传统优化方法显著地提升了训练速度. 通过仿真数据与公开数据集测试并讨论了本文算法的优势, 并通过工业数据验证了所提方法的有效性、应用价值与良好的鲁棒性.Abstract: Aiming at the task of identifying abnormal working conditions of fused magnesium furnace, this paper proposes a solution that combines the two types of features of current and image under the framework of semi-supervised learning. The main contributions of this paper are: Using multivariate image analysis (MIA) technology to replace the human eyes, and extracting features of magnesium furnace flames more accurately and objectively; using a semi-supervised learning framework based on entropy regularization (ER), and at the same time using strong complementary production images and current data to classify working conditions, thereby making up for some shortcomings in classification based on single feature; the cross-entropy method (CEM) is used to optimize the objective function of the classifier, which significantly improves the training speed compared with the traditional optimization method. The advantages of the algorithm in this paper are tested and discussed through simulation data and public data sets; and the effectiveness, application value and good robustness of the method proposed in this paper are verified through industrial data.
-
表 1 分类准确率结果比较(97%与95%无标记占比)
Table 1 Comparison of classification accuracy (97% and 95% unlabeled)
数据 无标记占比: 97% 无标记占比: 95% CEM-ER Sf-T S3VM Co-T CPLE LaN CEM-ER Sf-T S3VM Co-T CPLE LaN 1 $56.8{\pm4.2}$ $53.8{\pm6.8}$ $52.2{\pm5.7}$ $49.7{\pm6.3}$ $56.0{\pm3.0}$ $52.3{\pm4.7}$ $59.9{\pm5.7}$ $48.0{\pm7.8}$ $50.5{\pm5.8}$ $50.8{\pm8.0}$ $53.7{\pm3.6}$ $53.9{\pm5.8}$ 2 $63.2{\pm15.0}$ $65.5{\pm20.0}$ $50.2{\pm16.0}$ $64.8{\pm21.0}$ $75.7{\pm3.6}$ $57.5{\pm16.0}$ $64.0{\pm8.1}$ $50.6{\pm22.0}$ $49.9{\pm13.0}$ $60.9{\pm13.0}$ $76.1{\pm2.3}$ $60.5{\pm11.0}$ 3 $51.9{\pm9.0}$ $51.7{\pm12.0}$ $52.7{\pm13.0}$ $41.2{\pm13.0}$ $28.5{\pm3.3}$ $53.0{\pm10.1}$ $62.3{\pm7.7}$ $60.1{\pm17.0}$ $53.6{\pm11.0}$ $56.2{\pm9.8}$ $30.9{\pm3.5}$ $58.8{\pm8.8}$ 4 $72.9{\pm6.4}$ $61.3{\pm16.0}$ $69.7{\pm6.7}$ $59.1{\pm12.0}$ $60.9{\pm3.8}$ $45.0{\pm7.5}$ $73.2{\pm11.0}$ $57.6{\pm13.0}$ $75.7{\pm9.2}$ $65.7{\pm11.0}$ $35.8{\pm11.0}$ $47.5{\pm10.0}$ 5 $57.9{\pm5.9}$ $51.8{\pm8.3}$ $56.7{\pm8.3}$ $57.3{\pm8.0}$ $45.7{\pm8.8}$ $52.7{\pm6.6}$ $58.9{\pm4.8}$ $52.5{\pm11.0}$ $57.8{\pm9.0}$ $56.4{\pm10.0}$ $47.6{\pm4.2}$ $52.5{\pm6.5}$ 6 $67.2{\pm9.7}$ $67.8{\pm12.0}$ $70.1{\pm8.7}$ $69.8{\pm16.0}$ $42.7{\pm5.3}$ $54.7{\pm9.8}$ $62.1{\pm5.0}$ $60.9{\pm8.9}$ $71.4{\pm5.1}$ $75.7{\pm6.3}$ $46.4{\pm4.4}$ $57.7{\pm7.5}$ 7 $53.5{\pm5.8}$ $51.0{\pm7.0}$ $56.9{\pm3.0}$ $52.4{\pm4.6}$ $61.1{\pm1.3}$ $47.8{\pm6.0}$ $50.0{\pm4.2}$ $51.7{\pm4.6}$ $57.6{\pm6.0}$ $49.7{\pm2.2}$ $62.2{\pm1.2}$ $52.0{\pm5.2}$ 8 $93.1{\pm1.5}$ $96.2{\pm1.6}$ $96.6{\pm1.4}$ $94.1{\pm1.7}$ $68.8{\pm 5.3}$ $89.5{\pm1.8}$ $94.0{\pm1.0}$ $96.5{\pm1.3}$ $96.3{\pm1.2}$ $93.7{\pm1.5}$ $70.7{\pm4.8}$ $89.7{\pm1.5}$ 平均 64.56 62.38 63.14 61.01 54.93 56.56 65.54 59.73 64.08 63.61 52.91 59.07 表 3 分类准确率结果比较(80%与60%无标记占比)
Table 3 Comparison of classification accuracy (80% and 60% unlabeled)
数据 无标记占比: 80% 无标记占比: 60% CEM-ER Sf-T S3VM Co-T CPLE LaN CEM-ER Sf-T S3VM Co-T CPLE LaN 1 $65.1{\pm5.5}$ $47.8{\pm8.8}$ $50.9{\pm5.5}$ $45.5{\pm6.3}$ $59.0{\pm2.8}$ $56.7{\pm6.1}$ $63.7{\pm3.6}$ $55.7{\pm5.9}$ $49.8{\pm6.6}$ $52.9{\pm4.3}$ $56.6{\pm3.3}$ $58.7{\pm4.6}$ 2 $64.9{\pm3.9}$ $50.2{\pm13.0}$ $64.9{\pm8.0}$ $71.7{\pm6.8}$ $72.2{\pm1.9}$ $68.0{\pm7.0}$ $68.8{\pm4.3}$ $53.2{\pm5.4}$ $65.9{\pm3.5}$ $72.1{\pm5.4}$ $67.6{\pm2.6}$ $71.6{\pm4.8}$ 3 $66.4{\pm8.0}$ $50.8{\pm19.0}$ $59.8{\pm9.7}$ $58.4{\pm10.0}$ $34.7{\pm2.7}$ $67.4{\pm8.5}$ $64.4{\pm7.2}$ $44.1{\pm23.0}$ $62.6{\pm11.0}$ $58.6{\pm7.5}$ $39.2{\pm19.0}$ $69.6{\pm8.9}$ 4 $80.8{\pm3.0}$ $68.5{\pm3.9}$ $83.8{\pm4.4}$ $74.9{\pm8.1}$ $39.5{\pm13.0}$ $67.9{\pm4.7}$ $81.6{\pm2.8}$ $73.7{\pm3.0}$ $85.9{\pm3.0}$ $83.9{\pm4.9}$ $67.5{\pm20.0}$ $77.4{\pm3.1}$ 5 $60.0{\pm7.4}$ $61.6{\pm8.0}$ $70.5{\pm7.2}$ $66.8{\pm5.7}$ $54.6{\pm6.8}$ $57.1{\pm7.2}$ $66.5{\pm5.8}$ $61.9{\pm7.6}$ $73.0{\pm6.7}$ $72.4{\pm6.8}$ $58.1{\pm7.7}$ $58.7{\pm6.4}$ 6 $76.3{\pm2.7}$ $71.0{\pm3.6}$ $78.2{\pm5.4}$ $80.0{\pm2.9}$ $52.4{\pm8.8}$ $71.6{\pm6.1}$ $81.0{\pm2.9}$ $76.1{\pm4.2}$ $82.8{\pm4.8}$ $83.0{\pm3.9}$ $64.6{\pm6.8}$ $80.3{\pm4.8}$ 7 $59.7{\pm2.2}$ $34.7{\pm3.5}$ $60.4{\pm3.1}$ $51.4{\pm4.2}$ $65.3{\pm2.7}$ $55.6{\pm3.2}$ $61.1{\pm2.1}$ $36.8{\pm3.9}$ $61.5{\pm2.8}$ $58.3{\pm2.5}$ $64.2{\pm3.0}$ $56.9{\pm2.9}$ 8 $96.0{\pm1.0}$ $96.7{\pm1.2}$ $96.8{\pm1.3}$ $96.2{\pm1.4}$ $80.4{\pm9.3}$ $96.2{\pm1.9}$ $95.9{\pm1.0}$ $96.7{\pm1.0}$ $96.9{\pm0.8}$ $96.8{\pm1.0}$ $90.6{\pm3.1}$ $97.1{\pm1.0}$ 平均 71.15 60.15 70.64 68.11 57.26 67.57 72.86 62.28 72.29 72.24 63.56 71.27 表 2 分类准确率结果比较(92%与90%无标记占比)
Table 2 Comparison of classification accuracy (92% and 90% unlabeled)
数据 无标记占比: 92% 无标记占比: 90% CEM-ER Sf-T S3VM Co-T CPLE LaN CEM-ER Sf-T S3VM Co-T CPLE LaN 1 $59.1{\pm5.5}$ $51.3{\pm8.9}$ $48.2{\pm7.1}$ $49.0{\pm6.5}$ $56.7{\pm2.8}$ $53.4{\pm6.6}$ $61.1{\pm5.6}$ $48.4{\pm9.0}$ $47.4{\pm7.1}$ $47.3{\pm5.7}$ $58.4{\pm4.6}$ $53.8{\pm5.8}$ 2 $65.6{\pm7.7}$ $50.1{\pm21.0}$ $58.1{\pm15.0}$ $72.6{\pm11.0}$ $73.7{\pm1.6}$ $63.1{\pm9.5}$ $64.7{\pm5.5}$ $49.4{\pm15.0}$ $58.2{\pm11.0}$ $72.2{\pm4.2}$ $77.9{\pm2.3}$ $65.8{\pm6.5}$ 3 $60.3{\pm8.4}$ $53.8{\pm23.0}$ $61.7{\pm11.0}$ $51.7{\pm11.0}$ $28.2{\pm3.0}$ $52.4{\pm8.8}$ $62.0{\pm10.0}$ $44.4{\pm13.0}$ $56.3{\pm6.7}$ $56.9{\pm10.4}$ $27.5{\pm3.5}$ $57.6{\pm7.8}$ 4 $73.3{\pm11.0}$ $61.8{\pm13.0}$ $82.7{\pm9.5}$ $68.4{\pm10.0}$ $38.5{\pm11.0}$ $57.8{\pm11.0}$ $78.4{\pm10.0}$ $57.5{\pm19.0}$ $80.7{\pm6.9}$ $72.2{\pm4.4}$ $37.6{\pm6.6}$ $64.2{\pm9.5}$ 5 $57.1{\pm6.5}$ $56.7{\pm8.6}$ $65.7{\pm8.0}$ $56.7{\pm8.4}$ $47.3{\pm9.7}$ $51.1{\pm8.5}$ $59.5{\pm6.8}$ $54.3{\pm7.0}$ $66.7{\pm9.9}$ $58.7{\pm9.2}$ $48.4{\pm4.8}$ $55.6{\pm8.7}$ 6 $70.4{\pm5.0}$ $66.9{\pm8.5}$ $77.4{\pm3.5}$ $79.8{\pm5.2}$ $44.7{\pm7.8}$ $58.5{\pm6.5}$ $71.0{\pm4.2}$ $71.1{\pm4.7}$ $78.6{\pm4.6}$ $80.5{\pm6.2}$ $50.2{\pm8.5}$ $65.4{\pm5.5}$ 7 $54.2{\pm4.3}$ $49.3{\pm4.5}$ $51.7{\pm6.0}$ $51.4{\pm2.5}$ $65.6{\pm2.1}$ $54.2{\pm5.8}$ $58.2{\pm3.3}$ $49.9{\pm4.5}$ $59.0{\pm3.5}$ $57.6{\pm4.7}$ $61.4{\pm3.3}$ $54.9{\pm4.7}$ 8 $94.1{\pm1.3}$ $96.4{\pm1.5}$ $96.2{\pm2.0}$ $94.9{\pm1.9}$ $70.2{\pm4.6}$ $91.9{\pm1.9}$ $95.7{\pm1.3}$ $97.2{\pm1.4}$ $96.8{\pm1.1}$ $96.0{\pm1.5}$ $69.1{\pm3.0}$ $95.7{\pm2.2}$ 平均 66.76 60.77 67.74 65.56 53.11 60.30 68.82 59.00 67.96 67.68 53.79 64.12 表 4 分类器训练速度比较(UCI数据集)
Table 4 Comparison of classifiers′ training speed (UCI dataset)
数据集 无标记 97% 无标记 95% 无标记 92% 无标记 90% 无标记 80% 无标记 60% ER CEM-ER ER CEM-ER ER CEM-ER ER CEM-ER ER CEM-ER ER CEM-ER Bupa 6.94 1.77 6.95 1.77 6.73 1.71 6.94 1.73 7.17 1.75 7.12 1.79 Blood 20.06 2.34 20.31 2.36 20.22 2.41 20.16 2.45 20.14 2.36 19.44 2.47 Haberman 8.31 2.55 7.58 2.25 7.28 1.92 7.66 2.27 6.31 2.27 6.97 1.91 Ionosphere 9.16 1.92 8.98 1.80 7.59 2.22 8.98 2.55 8.63 1.80 7.95 1.80 Sonar 6.19 2.25 5.05 1.83 5.16 1.80 5.67 1.92 5.23 1.86 5.55 1.70 Statlog (Heart) 6.19 2.16 6.05 1.89 5.81 2.05 5.97 1.86 6.31 1.77 5.64 1.81 Tic-tac-toe 31.00 2.97 28.75 2.88 20.03 2.89 30.14 3.11 32.36 3.08 32.58 3.20 WBC 28.66 5.16 21.76 3.02 21.58 2.78 19.69 2.56 20.91 2.56 16.45 2.64 平均值 14.56 2.64 13.18 2.22 11.80 2.22 13.15 2.31 13.38 2.18 12.71 2.17 表 5 电熔镁炉生产数据实验结果
Table 5 Experimental results of fused magnesium furnace production data
无标记占比 $\phi_v^{{\rm{SSL}}}$准确率 $\phi_{vc}^{{\rm{SSL}}}$准确率 准确率提升 97% 66.72% 86.77% 30.05% 95% 67.79% 91.84% 35.49% 92% 70.72% 93.01% 31.51% 90% 71.67% 93.98% 31.14% 80% 72.86% 94.30% 29.43% 60% 74.00% 94.68% 27.93% 表 6 过渡态样本准确率测试
Table 6 Accuracy of the test on transition state samples
无标记占比 CEM-ER Sf-T ${\rm{S}}^3$VM Co-T CPLE LaN 97% 52.22% 48.89% 48.89% 46.67% 50.00% 49.53% 95% 50.00% 49.17% 47.78% 48.61% 50.00% 49.07% 92% 48.33% 47.50% 47.78% 46.94% 50.00% 50.00% 90% 49.72% 48.61% 50.83% 49.17% 50.00% 54.17% 80% 50.83% 45.00% 48.33% 47.50% 50.00% 50.27% 60% 52.22% 50.56% 50.83% 46.39% 50.00% 50.92% 表 7 分类器鲁棒性测试结果
Table 7 Classifier robustness test results
无标记占比 原准确率 新测试集准确率 97% 86.77% 84.06% 95% 91.84% 86.63% 92% 93.01% 88.32% 90% 93.98% 89.75% 80% 94.30% 91.02% 60% 94.68% 91.14% 表 8 分类器训练速度测试(生产数据)
Table 8 Comparison of classifiers′ training speed (production data)
无标记占比 ER CEM-ER 速度提升 97% 94.57 4.12 95.64% 95% 86.63 4.06 95.31% 92% 83.92 4.15 95.05% 90% 73.48 4.18 94.31% 80% 59.47 4.24 92.87% 60% 15.21 4.39 71.14% 表 9 优化算法准确率对比测试结果
Table 9 Comparison of accuracy in different optimization algorithms
无标记占比 ER CEM-ER 97% 88.33% 92.04% 95% 89.62% 90.80% 92% 91.00% 93.11% 90% 92.16% 93.16% 80% 93.76% 93.58% 60% 94.50% 94.15% -
[1] 卢绍文, 王克栋, 吴志伟, 李鹏琦, 郭章. 基于深度卷积网络的电熔镁炉欠烧工况在线识别. 控制与决策, 2017, 23(9): 1−8Lu Shao-Wen, Wang Ke-Dong, Wu Zhi-Wei, Li Peng-Qi, Guo Zhang. Online detection of semi-molten of fused magnesium furnace based on deep convolutional neural network. Control and Decision, 2017, 23(9): 1−8 [2] 赵磊, 卢绍文, 郑秀萍. 基于火焰动态纹理的电熔镁炉工况识别. 控制理论与应用, 2019, 36(9): 1565−1572 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2018.80556Zhao Lei, Lu Shao-Wen, Zheng Xiu-Ping. Conditions recognition of fused magnesia furnace based on flame dynamic texture. Control Theory and Applications, 2019, 36(9): 1565−1572 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2018.80556 [3] 吴高昌, 刘强, 柴天佑, 秦泗钊. 基于时序图像深度学习的电熔镁炉异常工况诊断. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(8): 1475−1485Wu Gao-Chang, Liu Qiang, Chai Tian-You, Qin S. Joe. Abnormal condition diagnosis through deep learning of image sequences for fused magnesium furnaces. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(8): 1475−1485 [4] 吴志伟. 嵌入式电熔镁炉智能控制系统研究 [博士学位论文], 东北大学, 中国, 2014Wu Zhi-Wei. Embedded Intelligent Control System for Fused Magnesium Furnace [Ph. D. dissertation], Northeastern University, China, 2014 [5] 吴志伟, 方正, 柴天佑, 张新海, 王超. 电熔镁炉嵌入式专用控制器及其控制方法研究. 仪器仪表学报, 2012, 33(6): 1261−1267 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-3087.2012.06.009Wu Zhi-Wei, Fang Zheng, Chai Tian-You, Zhang Xin-Hai, Wang Chao. Research on special embedded controller and its control method for fused magnesium furnace. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2012, 33(6): 1261−1267 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-3087.2012.06.009 [6] 吴永健. 电熔镁炉智能控制系统研究 [博士学位论文], 东北大学, 中国, 2012Wu Yong-Jian. Intelligent Control System of Electro-Fused Magnesia Furnace [Ph. D. dissertation], Northeastern University, China, 2012 [7] 卢绍文, 李鹏琦, 郑秀萍, 郭章. 动态火焰图像分割及在电熔镁炉视频监控中的应用. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 40(2): 153−157 doi: 10.12068/j.issn.1005-3026.2019.02.001Lu Shao-Wen, Li Peng-Qi, Zheng Xiu-Ping, Guo Zhang. A dynamic flame image segmentation method and its application in video monitoring of fused magnesium furnace process. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science), 2019, 40(2): 153−157 doi: 10.12068/j.issn.1005-3026.2019.02.001 [8] 刘强, 孔德志, 郎自强. 基于多级动态主元分析的电熔镁炉异常工况诊断. 自动化学报, DOI: 10.16383/j.aas.c190313Liu Qiang, Kong De-Zhi, Lang Zi-Qiang. Multi-level dynamic principal component analysis for abnormality diagnosis of fused magnesia furnaces. Acta Automatica Sinica, DOI: 10.16383/j.aas.c190313 [9] Kittler J, Hatef M, Duin R P W, Matas J. On combining classifiers. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1998, 20(3): 226−239 doi: 10.1109/34.667881 [10] Li S T, Yin H T, Fang L Y. Remote sensing image fusion via sparse representations over learned dictionaries. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(9): 4779−4789 doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2230332 [11] Qiao L S, Chen S C, Tan X Y. Sparsity preserving projections with applications to face recognition. Pattern Recognition, 2010, 43(1): 331−341 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2009.05.005 [12] Singh M, Singh S, Gupta S. An information fusion based method for liver classification using texture analysis of ultrasound images. Information Fusion, 2014, 19: 91−96 doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2013.05.007 [13] 薛丽霞, 钟欣, 汪荣贵, 杨娟, 胡敏. 基于深度特征融合的中低分辨率车型识别. 计算机工程, 2019, 45(1): 233−238Xue Li-Xia, Zhong Xin, Wang Rong-Gui, Yang Juan, Hu Min. Mid-low resolution vehicle type recognition based on deep feature fusion. Computer Engineering, 2019, 45(1): 233−238 [14] Chapelle O, Schölkopf B, Zien A. Semi-Supervised Learning. Cambridge: The MIT Press, 2006. [15] Zhu X J, Goldberg A B. Introduction to Semi-Supervised Learning. San Rafael: Morgan & Claypool Publishers, 2009. [16] 周志华. 基于分歧的半监督学习. 自动化学报, 2013, 39(11): 1871−1878 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2013.01871Zhou Zhi-Hua. Disagreement-based semi-supervised learning. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(11): 1871−1878 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2013.01871 [17] Chapelle O, Schölkopf B, Zien A. Semi-supervised learning (Chapelle, O. et al., Eds.; 2006) [Book reviews]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2009, 20(3): 542 [18] Blum A, Mitchell T. Combining labeled and unlabeled data with co-training. In: Proceedings of the 11th Annual Conference on Computational Learning Theory. Madison, Wisconsin, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, 1998. 92−100 [19] Zhu X J, Ghahramani Z, Lafferty J D. Semi-supervised learning using gaussian fields and harmonic functions. In: Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Machine learning. Washington D.C., USA: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 2003. 912−919 [20] Zhou D Y, Bousquet O, Lal T N, Weston J, Schölkopf B. Learning with local and global consistency. In: Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Cambridge, MA, United States: MIT Press, 2003. 321−328 [21] Vapnik V N. Statistical Learning Theory. New York: Wiley, 1998. [22] Yves G, Yoshua B. Entropy regularization. Semi-Supervised Learning. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, 2006. 151−168 [23] Adrian C, Tommi J. Data-dependent regularization. Semi-Supervised Learning. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, 2006. 169−190 [24] Wang C Y, Xu Z F, Wang S T, Zhang H B, Chen Z C. Research on semi-supervised learning for hyperspectral remote sensing imaging classification base on confidence entropy. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Parallel and Distributed Systems (ICPADS). Wuhan, China: IEEE, 2016. 1225−1228 [25] Hu T C, Yu J H. Generalized entropy based semi-supervised learning. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/ACIS International Conference on Computer and Information Science (ICIS). Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2015. 259−263 [26] Kim H I, Kim J B, Lee J E, Lee T Y, Park R H. Gaze estimation using a webcam for region of interest detection. Signal, Image and Video Processing, 2016, 10(5): 895−902 doi: 10.1007/s11760-015-0837-6 [27] Esbensen K, Geladi P. Strategy of multivariate image analysis (MIA). Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 1989, 7(1−2): 67−86 [28] Geladi P, Grahn H. Multivariate Image Analysis. Britain: Wiley, 1996. [29] 徐德刚, 赵盼磊, 陈晓, 谢永芳, 阳春华. 基于多变量图像分析的铜矿泡沫浮选分类与识别. 北京工业大学学报, 2014, 40(7): 967−973Xu De-Gang, Zhao Pan-Lei, Chen Xiao, Xie Yong-Fang, Yang Chun-Hua. Classification and recognition for copper froth flotation process based on multivariate image analysis. Journal of Beijing University of Technology, 2014, 40(7): 967−973 [30] 李帷韬. 水泥回转窑烧成状态识别与熟料质量指标软测量的研究 [博士学位论文], 东北大学, 中国, 2012Li Wei-Tao. A Study on Burning State Recognition and Estimations of Clinker Quality Index in Cement Rotary Kiln Process [Ph. D. dissertation], Northeastern University, China, 2012 [31] 郭章, 王克栋, 卢绍文, 吴志伟. 基于图像的电熔镁炉欠烧工况的判别系统. 第28届中国过程控制会议. 重庆, 中国: 中国自动化学会过程控制专业委员会, 2017. 210Guo Zhang, Wang Ke-Dong, Lu Shao-Wen, Wu Zhi-Wei. Image based semimolten condition diagnosis system of fused magnesium furnace. In: Proceedings of the 28th Chinese Process Control Conference (CPCC). Chongqing, China: CAA, 2017. 210 [32] Castiñeira D, Rawlings B C, Edgar T F. Multivariate image analysis (MIA) for industrial flare combustion control. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2012, 51(39): 12642−12652 [33] Grandvalet Y, Bengio Y. Semi-supervised learning by entropy minimization. In: Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Cambridge, MA, United States: MIT Press, 2004. 529−536 [34] Ueda N, Nakano R. Deterministic annealing EM algorithm. Neural Networks, 1998, 11(2): 271−282 doi: 10.1016/S0893-6080(97)00133-0 [35] Friedman J, Hastie T, Tibshirani R. Additive logistic regression: A statistical view of boosting. The Annals of Statistics, 2000, 28(2): 337−407 [36] Rubinstein R Y, Kroese D P. The Cross-Entropy Method: A Unified Approach to Combinatorial Optimization, Monte-Carlo Simulation and Machine Learning. New York: Springer, 2004. [37] Rubinstein R Y. Optimization of computer simulation models with rare events. European Journal of Operational Research, 1997, 99(1): 89−112 doi: 10.1016/S0377-2217(96)00385-2 [38] Rubinstein R Y, Kroese D P. The Cross-Entropy Method. New York: Springer, 2004. [39] Rubinstein R Y, Shapiro A. Discrete Event Systems: Sensitivity Analysis and Stochastic Optimization by the Score Function Method. New York: John Wiley & Sons Inc., 1993. [40] Loog M. Contrastive pessimistic likelihood estimation for semi-supervised classification. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 38(3): 462−475 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2452921 [41] Rasmus A, Valpola H, Honkala M, Berglund M, Raiko T. Semi-supervised learning with ladder networks. In: Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Cambridge, MA, United States: MIT Press, 2015. 3546−3554 -
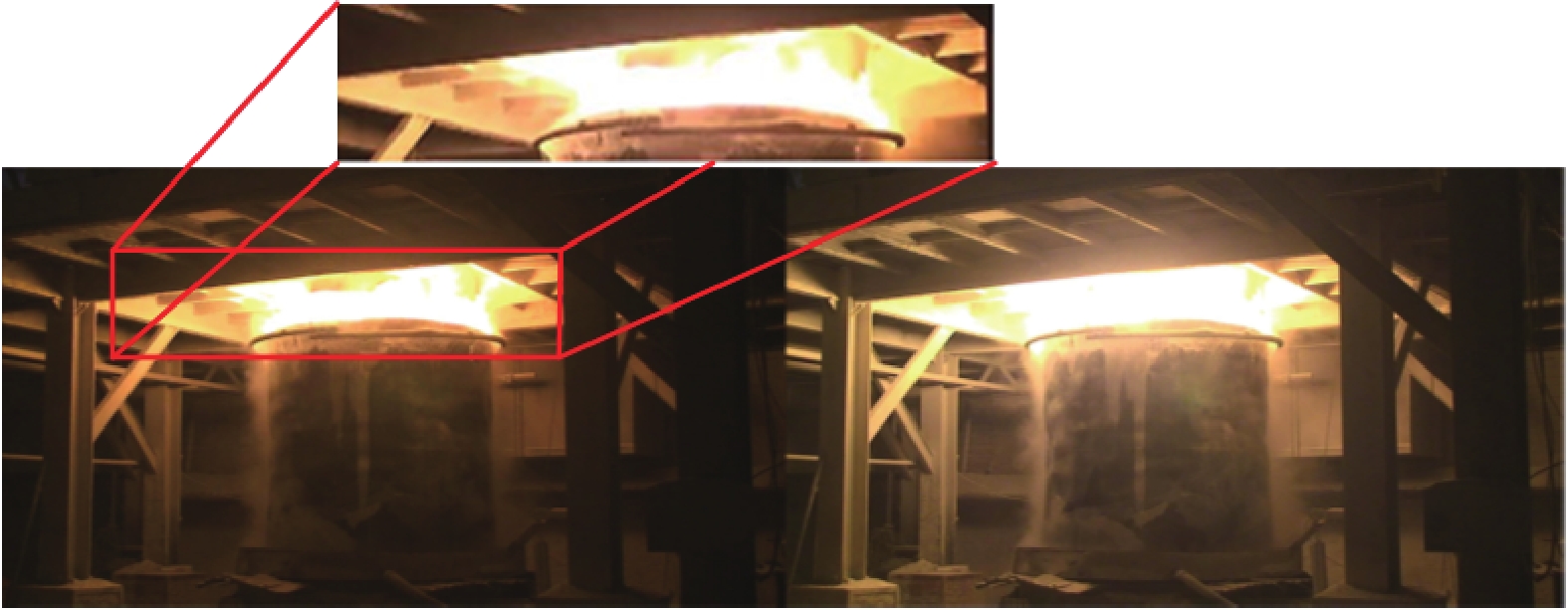





 下载:
下载: