Enhanced Restricted Boltzmann Machine-driven Interactive Estimation of Distribution Algorithms With Attention Mechanism
-
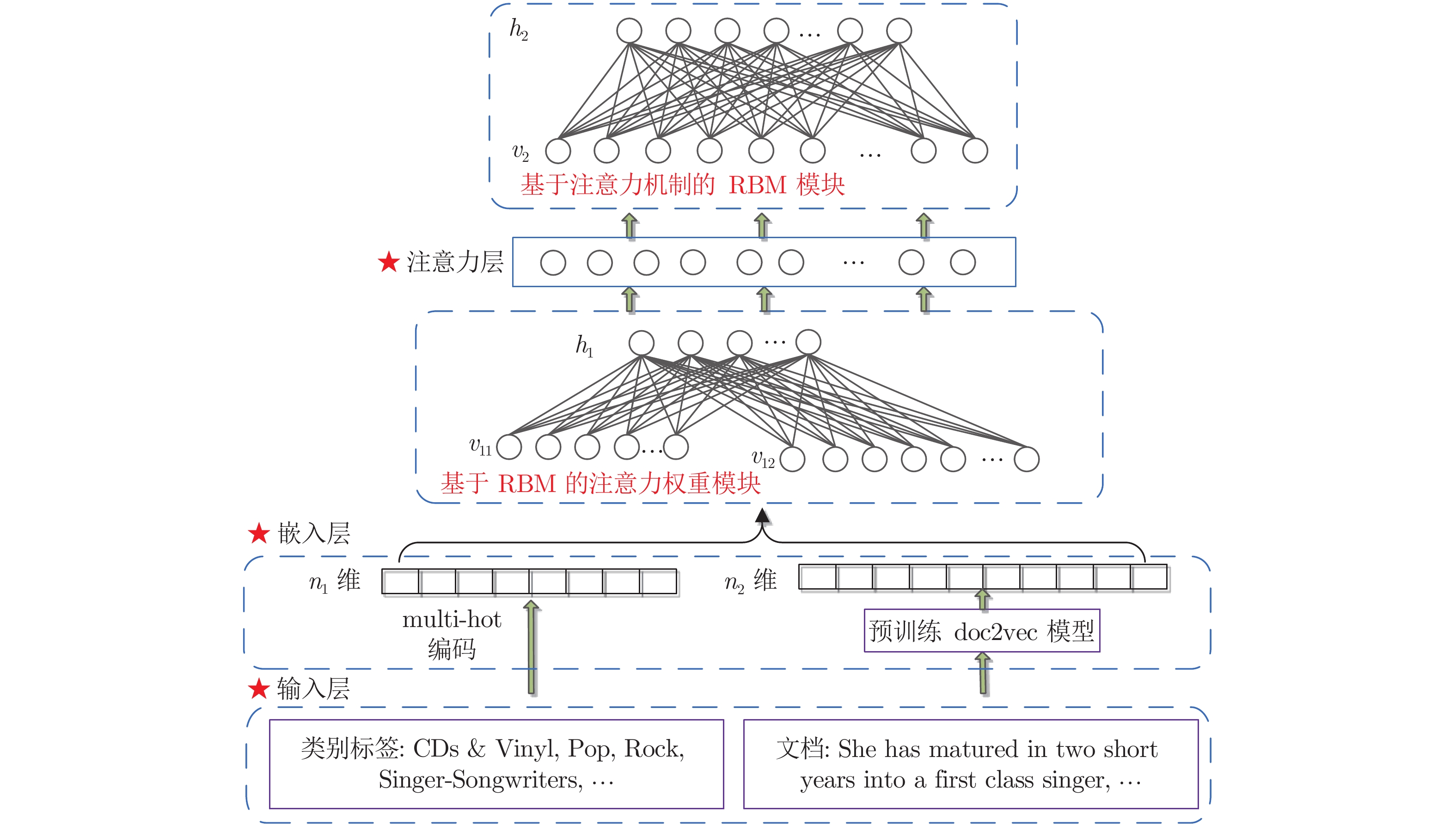
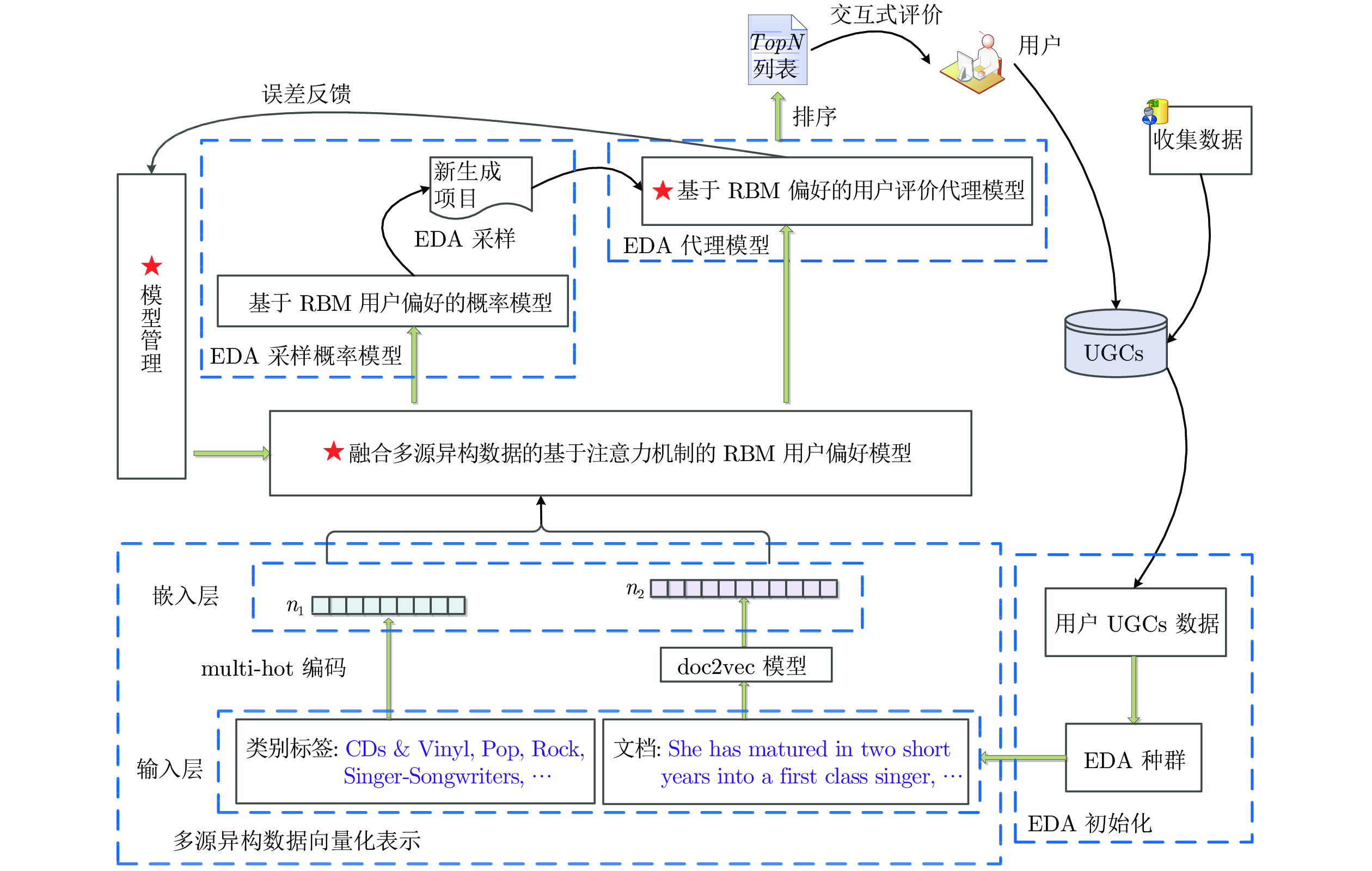
摘要: 面向用户生成内容(User generated content, UGC)的进化搜索在大数据及个性化服务领域已引起广泛关注, 其关键在于基于多源异构用户生成内容构建用户认知偏好模型, 进而设计高效的进化搜索机制. 针对此, 提出融合注意力机制(Attention mechanism, AM)的受限玻尔兹曼机(Restricted Boltzmann machine, RBM)偏好认知代理模型构建机制, 并应用于交互式分布估计算法(Interactive estimation of distribution algorithm, IEDA), 设计含用户生成内容的个性化进化搜索策略. 基于用户群体提供的文本评论, 以及搜索物品的类别文本, 构建无监督受限玻尔兹曼机模型提取广义特征; 设计注意力机制, 融合广义特征, 获取对用户认知偏好高度相关特征的集成; 利用该特征再次训练受限玻尔兹曼机, 实现对用户偏好认知代理模型的构建; 根据用户偏好认知代理模型, 给出交互式分布估计算法概率更新模型以及物品适应度评价函数, 实现物品个性化进化搜索. 算法在亚马逊个性化搜索实例的应用验证了用户认知偏好模型的可靠性, 以及个性化进化搜索的有效性.Abstract: User generated content (UGC)-oriented evolutionary search has attracted widespread attention in the field of big data and personalized services. The key is to construct a user cognitive preference model based on multi-source heterogeneous user generated content, and then design efficient evolutionary search mechanism. To solve this problem, this paper proposed a preference cognitive surrogate model based on restricted Boltzmann machine (RBM) with the attention mechanism (AM) in an interactive estimation of distribution algorithm (IEDA) to design personalized evolutionary search strategies with user generated content. Based on the text comments provided by user groups and the category text of searched items, an unsupervised restricted Boltzmann machine model is built to extract generalized features. The attention mechanism is designed to integrate generalized features to obtain the integration of highly relevant features of user cognitive preferences. These features are used to train a restricted Boltzmann machine to construct the surrogate model of user cognitive preferences. According to this surrogate model, a probability updating model of interactive estimation of distribution algorithm and a fitness evaluation function of searched items are given to realize personalized evolutionary search. The application of the algorithm in Amazon personalized search examples verifies the reliability of the user cognitive preference model and the effectiveness of personalized evolutionary search.
-
表 1 数据集统计信息
Table 1 Statistical information of datasets
数据集 # 用户 # 项目 # 评分 Digital_Music (Music) 478235 266414 836006 Video_Games (Games) 826767 50210 1324753 Apps_for_Android (Apps) 1323884 61275 2638173 Kindle_Store (Kindle) 1406890 430530 3205467 CDs_and_Vinyl (CDs) 1578597 486360 3749004 Movies_and_TV (Movies) 2088620 200941 4607047 Yelp 1912494 180347 7778794 表 2 算法的实验参数
Table 2 Experimental parameters of our algorithm
参数 数值 ${n_1}$ 类别标签数量 ${n_2}$ 200 $m$ 0.8 ~ 1.2倍类别标签数量 学习率 0.1 动量 0.5 ~ 0.9 训练次数 20 $Pop$ 0.3倍测试数据集规模 $k$ 10 $\alpha $ 0.3 $\beta $ 0.2 $N$ 10 表 3 对比实验结果
Table 3 Experiments compared with popular recommendation algorithms
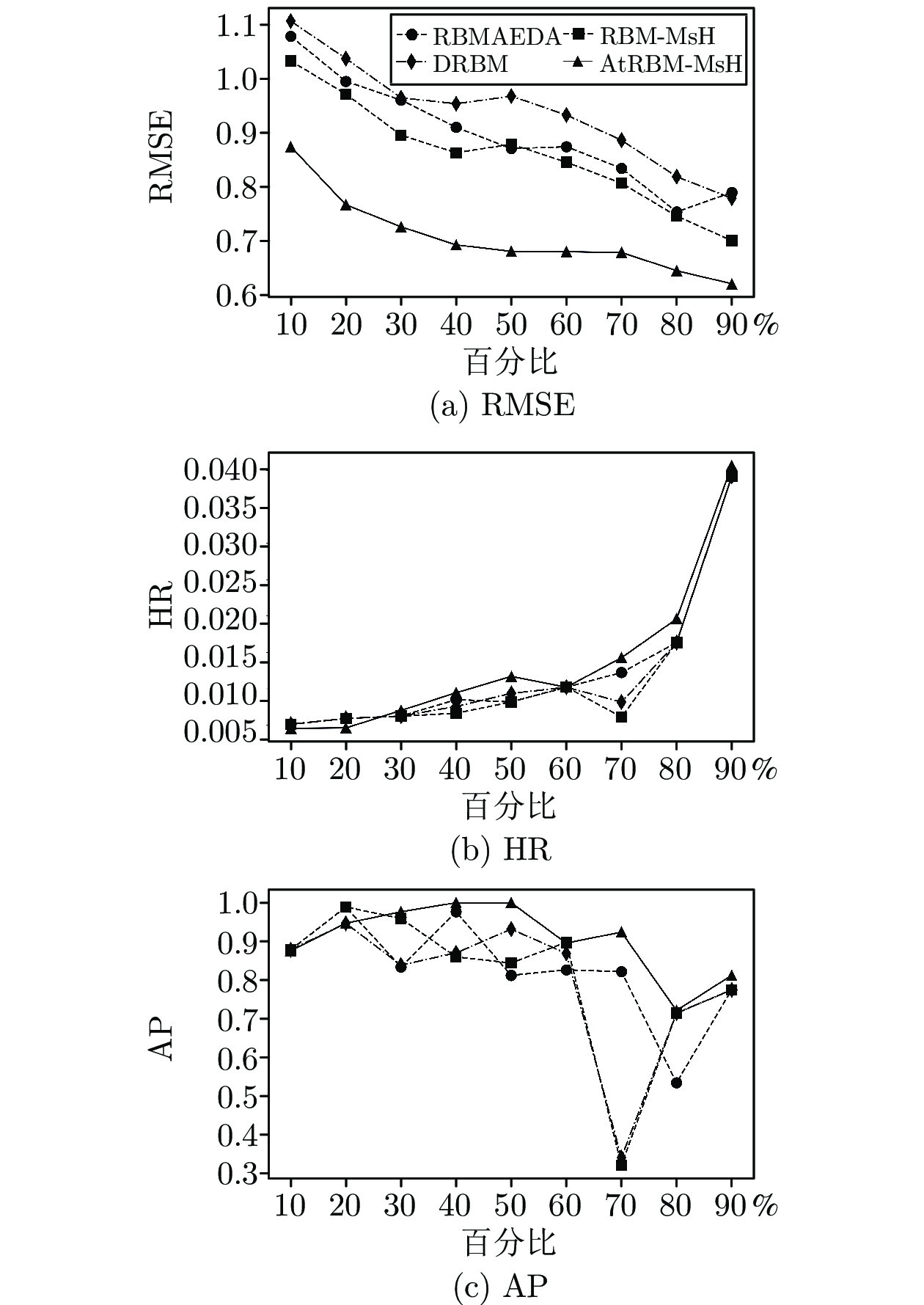
算法 评价指标 Random Popularity BPRMF ConvMF ATRank RBMAEDA DRBM RBM-MsH AtRBM-MsH Music RMSE — 3.144 1.898 3.130 2.198 1.298 1.264 1.297 1.221* HR 0.0765 0.0793 0.0764 0.0742 0.0778 0.0784 0.0924 0.0906 0.0951* mAP 0.761 0.723 0.811 0.728 0.778 0.811 0.887 0.880 0.879* 运行时间(s) 0.020 0.182 0.494 276.716 2.900 0.221 1.599 0.672 1.766* Games RMSE — 3.516 1.973 3.497 2.482 1.285 1.332 1.271 1.242* HR 0.0810 0.0930 0.0753 0.0945 0.0869 0.0804 0.0815 0.0809 0.0985* mAP 0.747 0.873 0.707 0.915 0.785 0.736 0.760 0.777 0.827* 运行时间(s) 0.014 0.196 0.402 131.716 3.095 0.151 2.346 0.719 2.785* Apps RMSE — 3.164 2.146 3.119 2.699 1.523 1.543 1.507 1.486* HR 0.0799 0.0795 0.0852 0.0701 0.0887 0.0759 0.0746 0.0760 0.0818* mAP 0.736 0.714 0.736 0.688 0.759 0.718 0.712 0.748 0.771* 运行时间(s) 0.014 0.170 0.344 90.489 2.573 0.103 0.646 0.388 1.476* Kindle RMSE — 4.319 2.284 4.317 2.213 1.437 1.549 1.445 1.168* HR 0.0298 0.0222 0.0278 0.0221 0.0301 0.0286 0.0295 0.0297 0.0308* mAP 0.914 0.920 0.857 0.833 0.900 0.894 0.867 0.875 0.926* 运行时间(s) 0.014 0.761 1.205 416.532 8.745 10.060 26.223 7.224 23.478* CDs RMSE — 4.218 2.182 4.217 2.694 1.482 1.534 1.432 1.241* HR 0.0119 0.0136 0.0101 0.0107 0.0108 0.0110 0.0110 0.0105 0.0147* mAP 0.847 0.825 0.826 0.817 0.844 0.845 0.852 0.838 0.921* 运行时间(s) 0.016 3.833 5.406 884.519 32.307 5.345 31.382 28.111 35.836* Movies RMSE — 3.068 1.960 3.029 2.271 1.191 1.185 1.167 1.176* HR 0.0134 0.0153 0.0144 0.0183 0.0166 0.0138 0.0154 0.0171 0.0173* mAP 0.668 0.769 0.702 0.838 0.682 0.672 0.766 0.800 0.770* 运行时间(s) 0.014 2.186 3.261 506.125 18.341 0.465 9.468 1.815 10.978* Yelp RMSE — 3.132 1.709 3.194 2.195 0.998 1.025 0.989 0.967* HR 0.0185 0.0228 0.0196 0.0259 0.0210 0.0208 0.0232 0.0233 0.0268* mAP 0.671 0.775 0.735 0.871 0.783 0.735 0.812 0.886 0.912* 运行时间(s) 0.017 65.504 27.729 4824.915 159.446 23.325 26.669 11.326 20.551 表 4 测试用户个性化搜索实验结果
Table 4 Experimental results of a test user
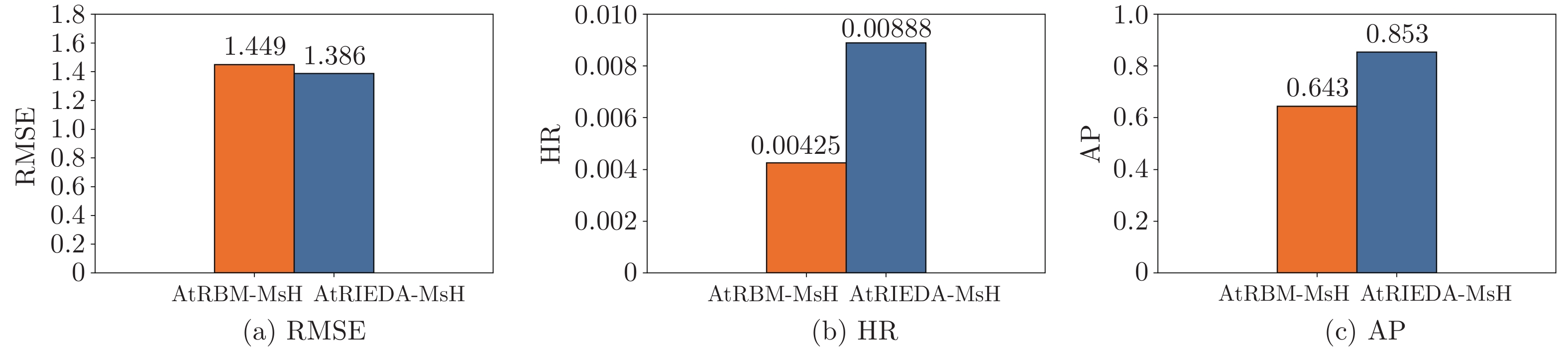
百分比 (%) 测试用户 RMSE HR AP 10 0.874 0.00455 0.876 20 0.766 0.00459 0.947 30 0.725 0.00700 0.977 40 0.692 0.00944 1.000 50 0.680 0.01168 1.000 60 0.679 0.01020 0.895 70 0.678 0.01426 0.924 80 0.644 0.01961 0.721 90 0.620 0.04068 0.812 表 5 对比实验结果
Table 5 Comparison of experimental results
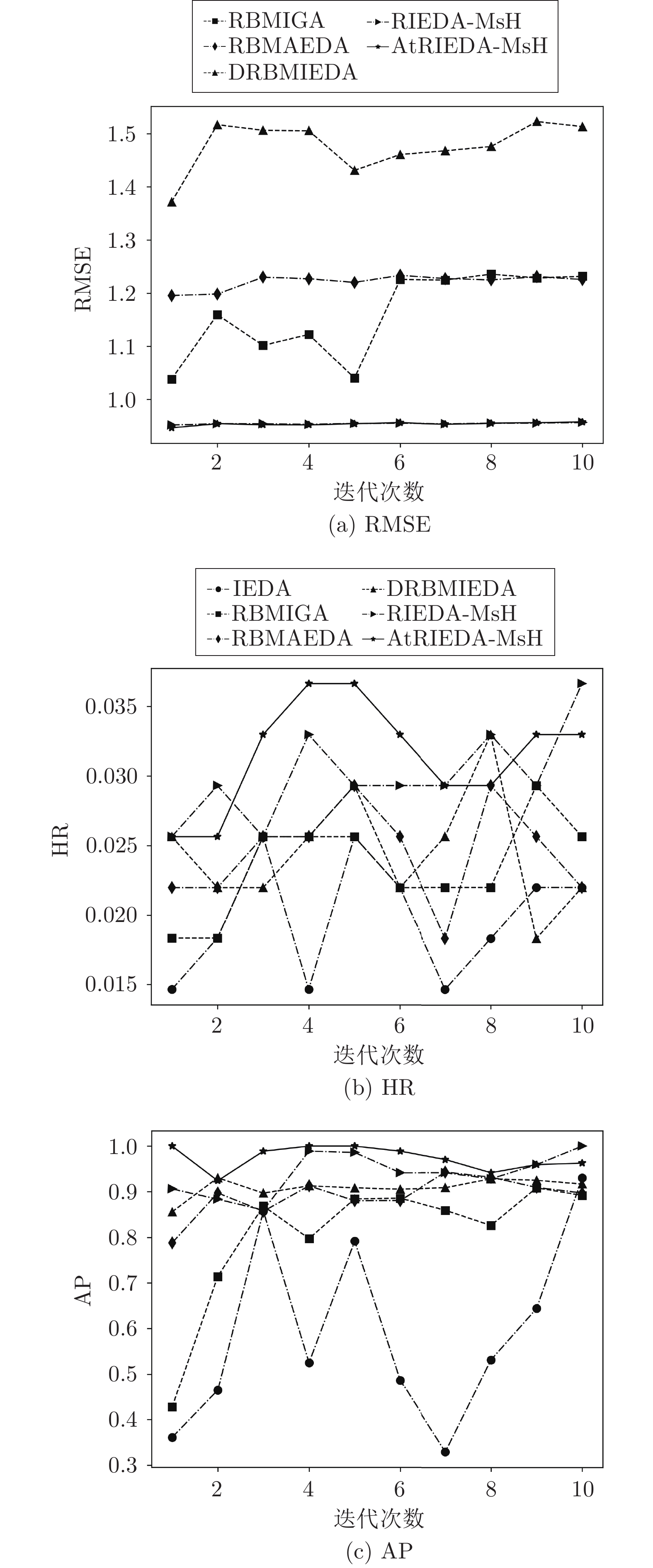
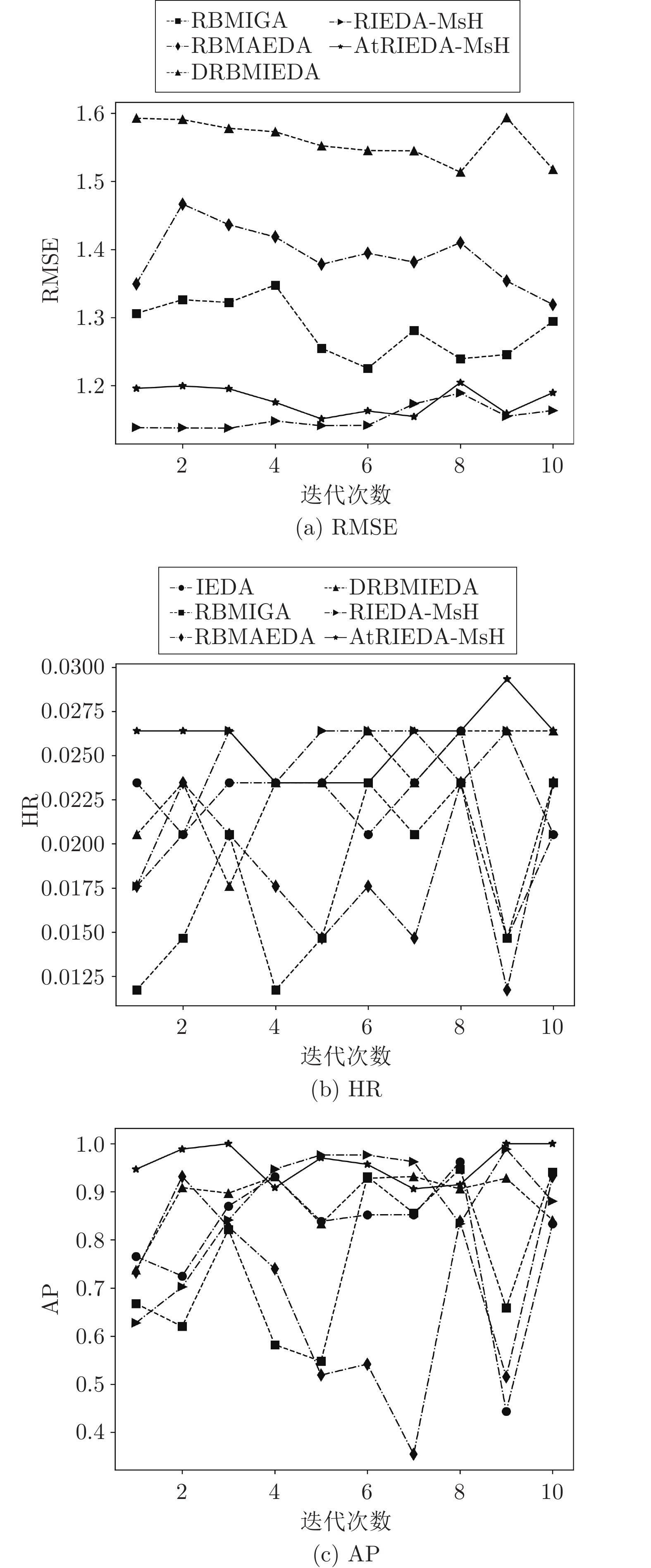
算法 评价指标 IEDA RBMIGA RBMAEDA DRBMIEDA RIEDA-MsH AtRIEDA-MsH Music RMSE — 1.160 1.204 1.480 0.955 0.955 HR 0.0184 0.0222 0.0236 0.0230 0.0286 0.0305* AP 0.601 0.815 0.897 0.914 0.931 0.956* Games RMSE — 1.331 1.351 1.560 1.187 1.176* HR 0.0231 0.0205 0.0201 0.0238 0.0245 0.0246 AP 0.710 0.764 0.787 0.870 0.879 0.928* Apps RMSE — 1.537 1.534 1.630 1.574 1.572* HR 0.0330 0.0325 0.0324 0.0350 0.0351 0.0354* AP 0.639 0.657 0.638 0.751 0.736 0.779* Kindle RMSE — 0.908 0.900 1.064 0.700 0.711* HR 0.00756 0.00758 0.00770 0.00760 0.00874 0.00888* AP 0.752 0.783 0.740 0.733 0.834 0.853* CDs RMSE — 1.406 1.405 1.589 1.388 1.386 HR 0.00396 0.00426 0.00452 0.00480 0.00480 0.00486* AP 0.818 0.849 0.890 0.931 0.929 0.923* Movies RMSE — 1.275 1.276 1.210 1.188 1.132* HR 0.00690 0.00738 0.00696 0.00742 0.00840 0.00851* AP 0.485 0.539 0.499 0.526 0.630 0.642* Yelp RMSE — 0.752 0.749 0.896 0.723 0.746* HR 0.00469 0.00469 0.00590 0.00646 0.00698 0.00970* AP 0.516 0.582 0.637 0.702 0.754 0.924* -
[1] 李金忠, 刘关俊, 闫春钢, 蒋昌俊. 排序学习研究进展与展望. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(8): 1345-1369Li Jin-Zhong, Liu Guan-Jun, Yan Chun-Gang, Jiang Chang-Jun. Research advances and prospects of learning to rank. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(8): 1345-1369 [2] Batmaz Z, Yurekli A, Bilge A, Kaleli C. A review on deep learning for recommender systems: Challenges and remedies. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2019, 52(1): 1-37 doi: 10.1007/s10462-018-9654-y [3] Wang Z K, Liu H Z, Du Y P, Wu Z H, Zhang X. Unified embedding model over heterogeneous information network for personalized recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 28th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Macao, China: AAAI Press, 2019. 3813−3819 [4] 饶子昀, 张毅, 刘俊涛, 曹万华. 应用知识图谱的推荐方法与系统[J]. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(9): 2061-2077Rao Zi-Yun, Zhang Yi, Liu Jun-Tao, Cao Wan-Hua. Recommendation methods and systems using knowledge graph. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(9): 2061-2077 [5] Rendle S, Freudenthaler C, Gantner Z, Schmidt-Thieme L. BPR: Bayesian personalized ranking from implicit feedback. In: Proceedings of the 25th Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence. Montreal, Canada: AUAI Press, 2009. 452−461 [6] He X N, Liao L Z, Zhang H W, Nie L Q, Hu X, Chua T S. Neural collaborative filtering. In: Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on World Wide Web. Perth, Australia: ACM, 2017. 173−182 [7] Truong Q T, Salah A, Lauw H W. Bilateral variational autoencoder for collaborative filtering. In: Proceedings of the 14th ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining. New York, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, 2021. 292–300 [8] Bao L, Sun X Y, Chen Y, Gong D W, Zhang Y W. Restricted Boltzmann machine-driven interactive estimation of distribution algorithm for personalized search. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2020, 43: Article No. 106030 [9] Kim D, Park C, Oh J, Lee S, Yu H. Convolutional matrix factorization for document context-aware recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 10th ACM Conference on Recommender Systems. Boston, USA: ACM, 2016. 233−240 [10] Jin J R, Qin J R, Fang Y C, Du K, Zhang W N, Yu Y, et al. An efficient neighborhood-based interaction model for recommendation on heterogeneous graph. In: Proceedings of the 26th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. Virtual Event, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, 2020. 75−84 [11] Mnih V, Heess N, Graves A, Kavukcuoglu K. Recurrent models of visual attention. In: Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Montreal, Canada: ACM, 2014. 2204−2212 [12] Zhou C, Bai J Z, Song J S, Liu X F, Zhao Z C, Chen X S, et al. ATRank: An attention-based user behavior modeling framework for recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 32nd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence and 30th Innovative Applications of Artificial Intelligence Conference and 8th AAAI Symposium on Educational Advances in Artificial Intelligence. New Orleans, USA: AAAI, 2018. Article No. 559 [13] 汤文兵, 任正云, 韩芳. 基于注意力机制的协同卷积动态推荐网络. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(10): 2438-2448 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190820Tang Wen-Bing, Ren Zheng-Yun, Han Fang. Attention-based collaborative convolutional dynamic network for recommendation. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(10): 2438-2448 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190820 [14] Li J C, Wang Y J, McAuley J. Time interval aware self-attention for sequential recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining. Houston, USA: ACM, 2020. 322−330 [15] Sun X Y, Gong D W, Jin Y C, Chen S S. A new surrogate-assisted interactive genetic algorithm with weighted semisupervised learning. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2013, 43(2): 685-698 doi: 10.1109/TSMCB.2012.2214382 [16] Zhou G R, Mou N, Fan Y, Pi Q, Bian W J, Zhou C, et al. Deep interest evolution network for click-through rate prediction. In: Proceedings of the 33rd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence and 31st Innovative Applications of Artificial Intelligence Conference and 9th AAAI Symposium on Educational Advances in Artificial Intelligence. Honolulu, USA: AAAI, 2019. Article No. 729 [17] Chen Y, Jin Y C, Sun X Y. Language model based interactive estimation of distribution algorithm. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2020, 200: Article No. 105980 doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2020.105980 [18] Salameh M, Singh S, Li S W, Krishnamurthy M. Surrogate vibration modeling approach for design optimization of electric machines. IEEE Transactions on Transportation Electrification, 2020, 6(3): 1126-1133 doi: 10.1109/TTE.2020.3017232 [19] Gao Y, Yang T, Bozhko S, Wheeler P, Dragičević T. Filter design and optimization of electromechanical actuation systems using search and surrogate algorithms for more-electric aircraft applications. IEEE Transactions on Transportation Electrification, 2020, 6(4): 1434-1447 doi: 10.1109/TTE.2020.3019729 [20] Bao L, Sun X Y, Chen Y, Man G Y, Shao H. Restricted Boltzmann machine-assisted estimation of distribution algorithm for complex problems. Complexity, 2018, 2018: 2609014 [21] Zhao F, Zeng Z, Liu H Q, Lan R, Fan J L. Semisupervised approach to surrogate-assisted multiobjective kernel intuitionistic fuzzy clustering algorithm for color image segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2020, 28(6): 1023-1034 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2020.2973121 [22] Min A T W, Ong Y S, Gupta A, Goh C K. Multiproblem surrogates: Transfer evolutionary multiobjective optimization of computationally expensive problems. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2019, 23(1): 15-28 doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2017.2783441 [23] Wang S, Liu J, Jin Y C. Surrogate-assisted robust optimization of large-scale networks based on graph embedding. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2020, 24(4): 735-749 doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2019.2950935 [24] Cai X W, Gao L, Li X Y. Efficient generalized surrogate-assisted evolutionary algorithm for high-dimensional expensive problems. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2020, 24(2): 365-379 doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2019.2919762 [25] Le Q, Mikolov T. Distributed representations of sentences and documents. In: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Machine Learning. Beijing, China: ACM, 2014. 1188−1196 [26] Hinton G E. Training products of experts by minimizing contrastive divergence. Neural Computation, 2002, 14(8): 1771-1800 doi: 10.1162/089976602760128018 [27] Feng S, Chen C L P. A fuzzy restricted Boltzmann machine: Novel learning algorithms based on the crisp possibilistic mean value of fuzzy numbers. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2018, 26(1): 117-130 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2016.2639064 -




 下载:
下载: