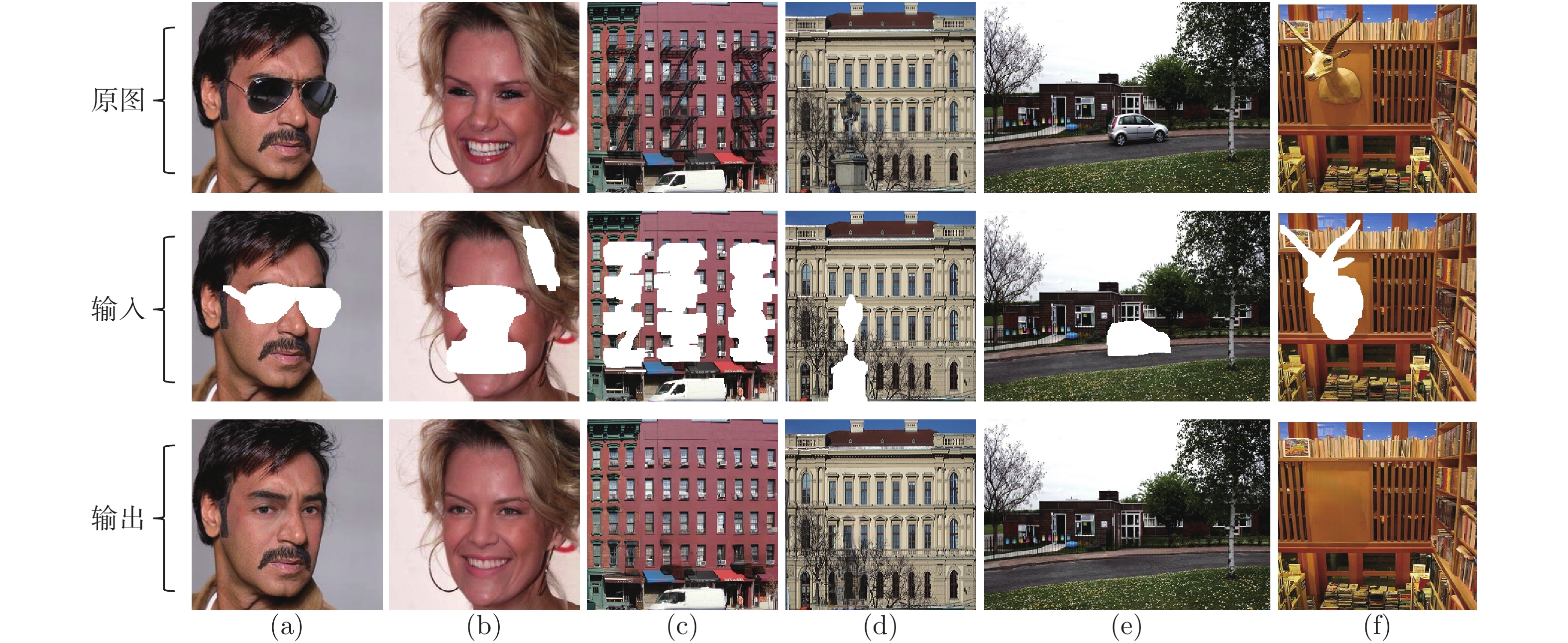
-
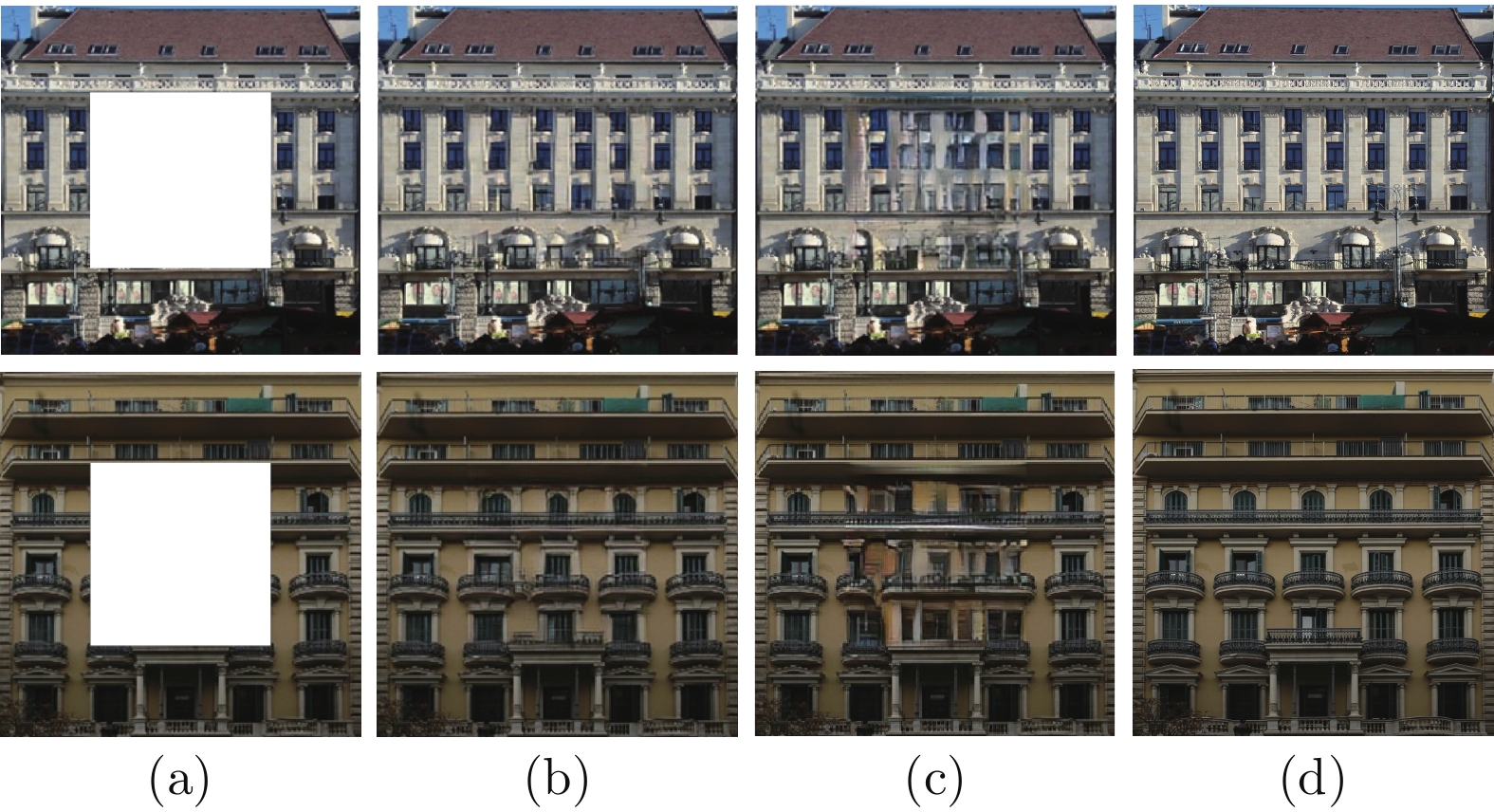
摘要: 现有图像修复方案普遍存在着结构错乱和细节纹理模糊的问题, 这主要是因为在图像破损区域的重建过程中, 修复网络难以充分利用非破损区域内的信息来准确地推断破损区域内容. 为此, 本文提出了一种由多级注意力传播驱动的图像修复网络. 该网络通过将全分辨率图像中提取的高级特征压缩为多尺度紧凑特征, 进而依据尺度大小顺序驱动紧凑特征进行多级注意力特征传播, 以期达到包括结构和细节在内的高级特征在网络中充分传播的目标. 为进一步实现细粒度图像修复重建, 本文还同时提出了一种复合粒度判别器, 以期实现对图像修复过程进行全局语义约束与非特定局部密集约束. 大量实验表明, 本文提出的方法可以产生更高质量的修复结果.Abstract: There are disordered structures and blurred detail textures in most existing image inpainting methods, because the inpainting network cannot make full use of the information in the non-damaged regions to infer the contents of the damaged regions during reconstructing process. To address the issues, an image inpainting network driven by multi-scale attention propagation is proposed in this paper. Firstly, the high-level features extracted from the full-resolution images are compressed into multi-scale compact features, and then the compact features are driven to perform multi-scale attention feature propagation in order of scale size. As a result, the high-level features including structures and details are fully propagated in the network. In order to realize fine-grained image inpainting, a compound granularity discriminator is proposed to constrain image inpainting process with global semantic constraints and non-specific local dense constraints. A large number of experimental results show that the proposed method can restore higher quality inpainting results.
-
表 1 3个数据集的训练和测试分割
Table 1 Training and test splits on three datasets
数据集 训练 测试 总数 Facade 506 100 606 CelebA-HQ 28000 2000 30000 Places2 8026628 328500 8355128 表 2 CelebA-HQ、Facade和Places2数据集上的定量对比
Table 2 Quantitative comparisons on CelebA-HQ, Facade and Places2
数据集 掩码率 PSNR SSIM Mean L1 loss CA MC Ours CA MC Ours CA MC Ours CelebA-HQ 10% ~ 20% 26.16 29.62 31.35 0.901 0.933 0.945 0.038 0.022 0.018 20% ~ 30% 23.03 26.53 28.38 0.835 0.888 0.908 0.066 0.038 0.031 30% ~ 40% 21.62 24.94 26.93 0.787 0.855 0.882 0.087 0.051 0.040 40% ~ 50% 20.18 23.07 25.46 0.727 0.809 0.849 0.115 0.069 0.052 Facade 10% ~ 20% 25.93 27.05 28.28 0.897 0.912 0.926 0.039 0.032 0.028 20% ~ 30% 25.30 24.49 25.36 0.870 0.857 0.871 0.064 0.052 0.047 30% ~ 40% 22.00 23.21 24.53 0.780 0.815 0.841 0.084 0.068 0.059 40% ~ 50% 20.84 21.92 23.32 0.729 0.770 0.803 0.106 0.086 0.074 Places2 10% ~ 20% 22.49 27.34 27.68 0.867 0.910 0.912 0.059 0.031 0.029 20% ~ 30% 19.95 24.58 25.05 0.786 0.854 0.857 0.097 0.051 0.048 30% ~ 40% 18.49 22.72 23.41 0.714 0.800 0.805 0.131 0.071 0.066 40% ~ 50% 17.54 21.42 22.29 0.658 0.755 0.765 0.159 0.089 0.081 表 3 组件有效性研究
Table 3 Effectiveness study on each component
Att8 无 有 有 有 有 有 Att4 无 无 有 有 有 有 Att2 无 无 无 有 有 有 Att0 无 无 无 无 有 有 Single-D 有 有 有 有 有 无 Cg-D 无 无 无 无 无 有 Mean L1 loss 0.091 0.089 0.086 0.081 0.078 0.074 -
[1] Wang Y, Tao X, Qi X, Shen X, Jia J. Image inpainting via generative multi-column convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 32nd Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Montreal, Canada: Curran Associates, Inc., 2018. 331−340 [2] Yu J, Lin Z, Yang J, Shen X, Lu X, Huang T S. Generative image inpainting with contextual attention. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision And Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 5505−5514 [3] Barnes C, Shechtman E, Finkelstein A, Goldman D B. PatchMatch: A randomized correspondence algorithm for structural image editing. In: Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH Conference. New Orleans, LA, USA: ACM, 2009. 1−11 [4] Levin A, Zomet A, Peleg S, Weiss Y. Seamless image stitching in the gradient domain. In: Proceedings of the 8th European Conference on Computer Vision. Prague, Czech Republic: Springer, 2004. 377−389 [5] Voronin V V, Sizyakin R A, Marchuk V I, Cen, Y, Galustov G G, Egiazarian K O. Video inpainting of complex scenes based on local statistical model. Electronic Imaging, 2016, 111(2): 681-690 [6] Park E, Yang J, Yumer E, Berg A C. Transformation-grounded image generation network for novel 3D view synthesis, In: Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, HI, USA: IEEE, 2017. 702−711 [7] Simakov D, Caspi Y, Shechtman E, Irani M. Summarizing visual data using bidirectional similarity. In: Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Anchorage, AK, USA: IEEE, 2008. 1−8 [8] Yeh R, Chen C, Lim T Y, Hasegawa J M, Do N M. Semantic image inpainting with perceptual and contextual losses. arXiv: 1607.07539v2, 2016. [9] Goodfellow I, Pouget-Abadie J, Mirza M, Xu B, Warde F D, Ozair S, et al. Generative adversarial nets. In: Proceedings of the 2014 Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, arXiv: 1406.2661v1, 2014. [10] Mirza M, Osindero S. Conditional generative adversarial nets. arXiv: 14111784, 2014. [11] Iizuka Satoshi, Edgar. S-S, Hiroshi I. Globally and locally consistent image completion. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2017, 36(4): 107:1-107:14 [12] Song Y, Yang C, Lin Z, Liu X, Huang Q, Li H, et al. Contextual-based image inpainting: Infer, match, and translate. In: Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 3−18 [13] Ballester C, Bertalmio M, Caselles V, Sapiro G, Verdera J, et al. Filling-in by joint interpolation of vector fields and gray levels. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2001, 10(8): 1200-1211 doi: 10.1109/83.935036 [14] Bertalmio M, Sapiro G, Caselles V, Ballester C, et al. Image inpainting. In: Proceedings of the 27th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, New Orleans, LA, USA: SIGGRAPH, 2000. 417−424 [15] Efros A A, Freeman W T. Image quilting for texture synthesis and transfer. In: Proceedings of the 28th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, New York, NY, USA: SIGGRAPH, 2001. 341−346 [16] 朱为, 李国辉. 基于自动结构延伸的图像修补方法. 自动化学报, 2009, 35(8): 1041-1047 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2009.01041ZHU Wei, LI Guo-Hui. Image Completion Based on Automatic Structure Propagation. ACTA AUTOMATICA SINICA, 2009, 35(8): 1041-1047 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2009.01041 [17] 王志明, 张丽. 局部结构自适应的图像扩散. 自动化学报, 2009, 35(3): 244-250 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2009.00244WANG Zhi-Ming, ZHANG Li. Local-structure-adapted Image Diffusion. ACTA AUTOMATICA SINICA, 2009, 35(3): 244-250 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2009.00244 [18] 孟祥林, 王正志. 基于视觉掩蔽效应的图像扩散. 自动化学报, 2011, 37(1): 21-27 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2011.00021MENG Xiang-Lin, WANG Zheng-Zhi. Image Diffusion Based on Visual Masking Effect. ACTA AUTOMATICA SINICA, 2011, 37(1): 21-27 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2011.00021 [19] Pathak D, Krahenbuhl P, Donahue J, Darrell T, Efros A A. Context encoders: Feature learning by inpainting. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle, WA, USA: IEEE, 2016. 2536−2544 [20] Liu G, Reda F A, Shih K J, Wang T, Tao A, Catanzaro b. Image inpainting for irregular holes using partial convolutions. In: Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 89−105 [21] Zeng Y, Fu J, Chao H, Guo B. Learning pyramid-context encoder network for high-quality image inpainting. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA: IEEE, 2019. 1486−1494 [22] Hao D, Neekhara P, Chao W, Guo Y. Unsupervised image-to-image translation with generative adversarial networks. arXiv: 1701.02676, 2017. [23] Gulrajani I, Ahmed F, Arjovsky M, Vincent D, Aaron C. Improved training of wasserstein gans. In: Proceedings of the 2017 Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA: Curran Associates, Inc., 2017. 5767−5777 [24] Johnson J, Alahi A, Fei-Fei L. Perceptual losses for real-time style transfer and super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the 2016 European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, the Netherlands: Springer, 2016. 694−711 [25] Gatys L A, Ecker A S, Bethge M. Image style transfer using convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle, WA, USA: IEEE, 2016. 2414−2423 [26] Gatys L, Ecker A S, Bethge M. Texture synthesis using convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 2015 Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Quebec, Canada: Curran Associates, Inc., 2015. 262−270 [27] Zhou B, Lapedriza A, Khosla A, Khosla A, Oliva A, Torralba A. Places: A 10 million Image Database for Scene Recognition. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(6): 1452-1464 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2723009 [28] Karras T, Aila T, Laine S, Lehtinen J. Progressive growing of GANs for improved quality, stability, and variation. arXiv: 1710.10196, 2017. [29] Tyleček R, Šára R. Spatial pattern templates for recognition of objects with regular structure. In: Proceedings of the 2013 German Conference on Pattern Recognition, Münster, Germany: Springer, 2013. 364−374 -





 下载:
下载: