Neural Network Embedded Learning Control for Nonlinear System With Unknown Dynamics and Disturbance
-
摘要:
针对带有不确定性与扰动的非线性系统的性能优化问题, 提出一种基于神经网络嵌入的学习控制方法. 对一类常见的 Lyapunov 函数导数形式, 将神经网络控制器集成到某种对系统稳定的基准控制器中, 其意义在于将原控制器改进为满足Lyapunov稳定的神经网络参数可调控制器, 从而能够利用先进的神经网络学习技术实现控制器的在线优化. 建立了跟踪误差的等效目标函数, 避免了对系统输入–输出的辨识问题. 建立了一种未知非线性与扰动等效值自适应方法, 并依此方法设计基准控制器. 以RBF (Radial basis function) 反步自适应控制、基于卷积神经网络的滑模控制和深度强化学习控制为对比方法, 对带有死区、饱和、三角函数等数值与物理非线性模型进行仿真分析以测试方法有效性, 并针对上肢康复机器人控制问题进行虚拟实验以验证该方法的实用性. 仿真与实验结果表明, 该方法能在Lyapunov 稳定条件下有效优化基础控制器性能, 对比结果证实了该方法的实用性与先进性.
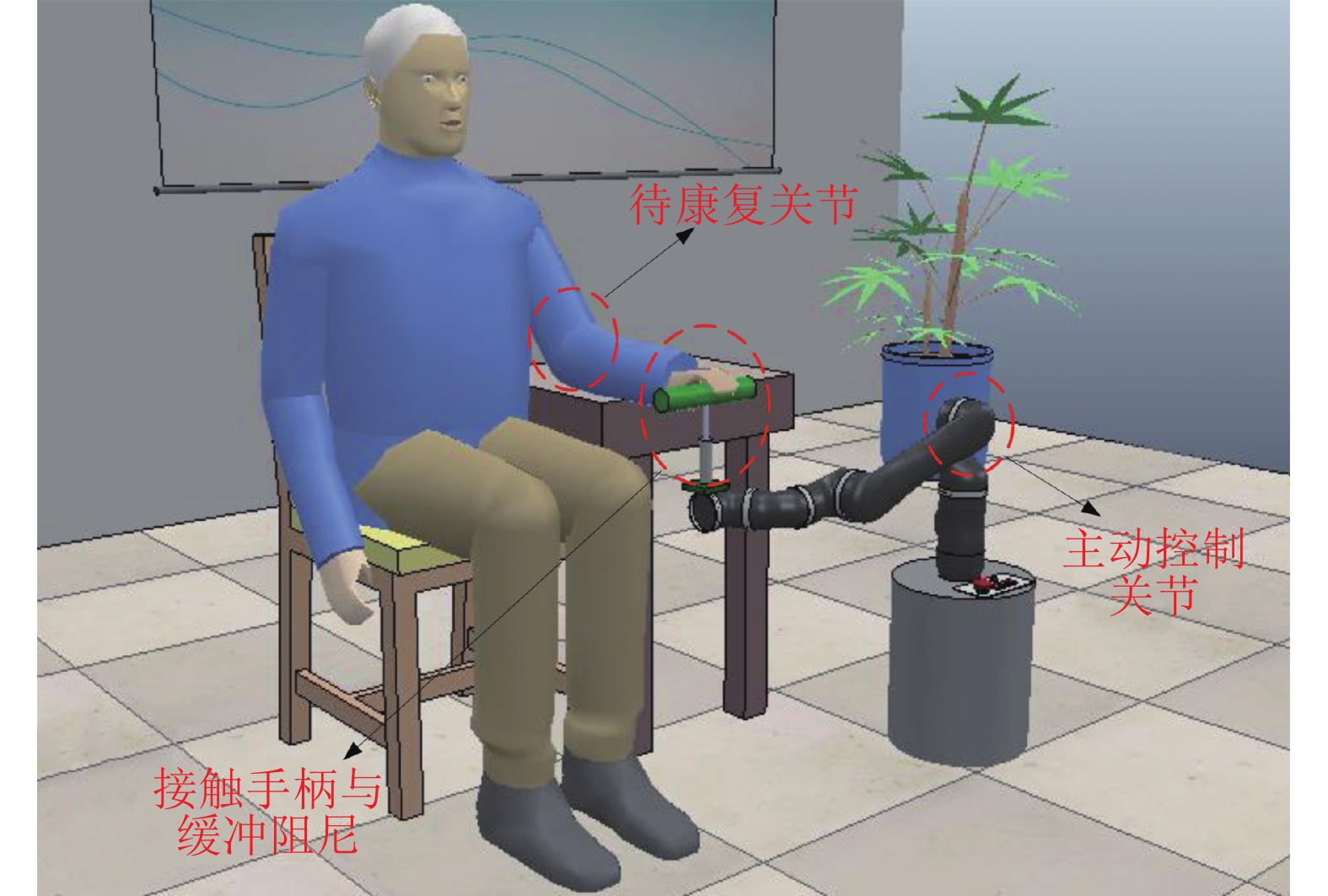
Abstract:To address the problem of controlling performance optimization for the nonlinear uncertain system with disturbance, a neural network embedded learning control scheme is proposed in this paper. This method works on a common formal derivative of Lyapunov function, in which a neural network controller is integrated with a benchmark controller that is stable for the system. The main contribution of our work lies in that the benchmark controller is improved to a new one with tunable parameters under Lyapunov stability condition, and the new controller can be online optimized by using frontier technology of neural network. Hence an equivalent objective function based on tracking errors is characterized in this paper, avoiding identification to the relations between inputs and outputs of system. We use a value adaptive method for estimating equivalent term composed of unknown nonlinear function and disturbance, and the benchmark controller is designed based on this method. Some baseline methods are employed for comparison with the proposed method, which contain adaptive control based on RBF (Radial basis function)-backstepping, sliding mode control based on convolutional neural network and deep reinforcement learning control. And for verifying the effectiveness of our method we test some numerical and physical nonlinear model simulations, which contain trigonometric function saturation and dead zone nonlinearities. And virtual experiments of robot arm controlling of upper limb rehabilitation to be tested to verify the practicability of our method. These results show that the method proposed is able to optimize control performance of benchmark controller with Lyapunov stability. And the results of comparisons of tests show our method is efficient and advanced.
1) 收稿日期 2020-04-06 录用日期 2020-07-21 Manuscript received April 6, 2020; accepted July 21, 2020 国家自然科学基金 (61673101), 吉林重点行业与产业科技创新计划人工智能专项 (2019001090) 资助 Supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (61673101), Special Foundation for Artificial Intelligence in Innovative Project of Science and Technology Key Industries of Jilin (2019001090) 本文责任编委 王占山2) Recommended by Associate Editor WANG Zhan-Shan 1. 东北电力大学自动化工程学院 吉林 132012 2. 吉林省精密驱动智能控制国际联合研究中心 吉林 132012 1. School of Automation and Engineering, Northeast Electric Power University, Jilin 132012 2. Jilin Province International Research Center of Precision Drive and Intelligent Control, Jilin 132012 -
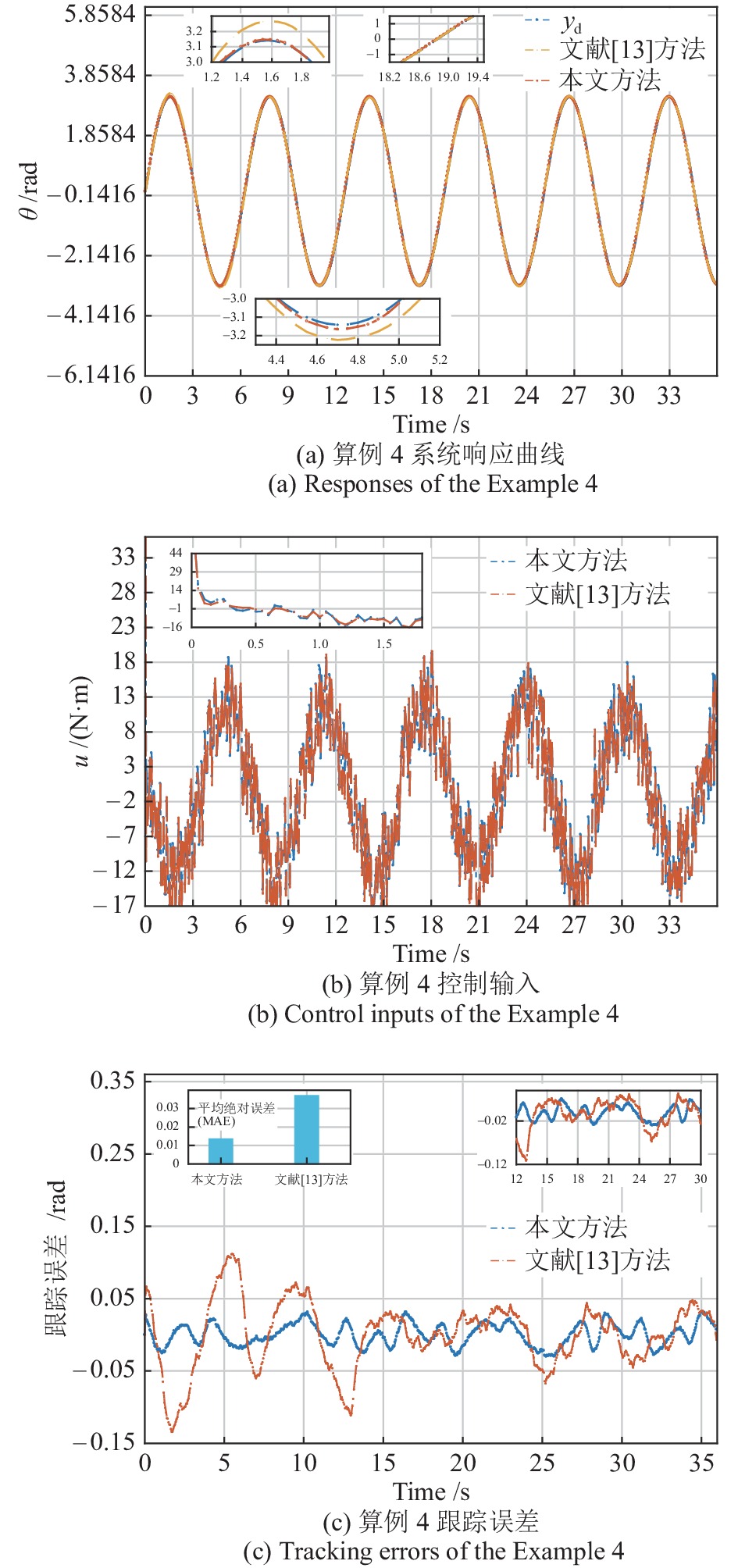
表 1 算例4两种方法控制性能统计数据对比
Table 1 The comparison for control statistical indicators of two methods in the Example 4
B1
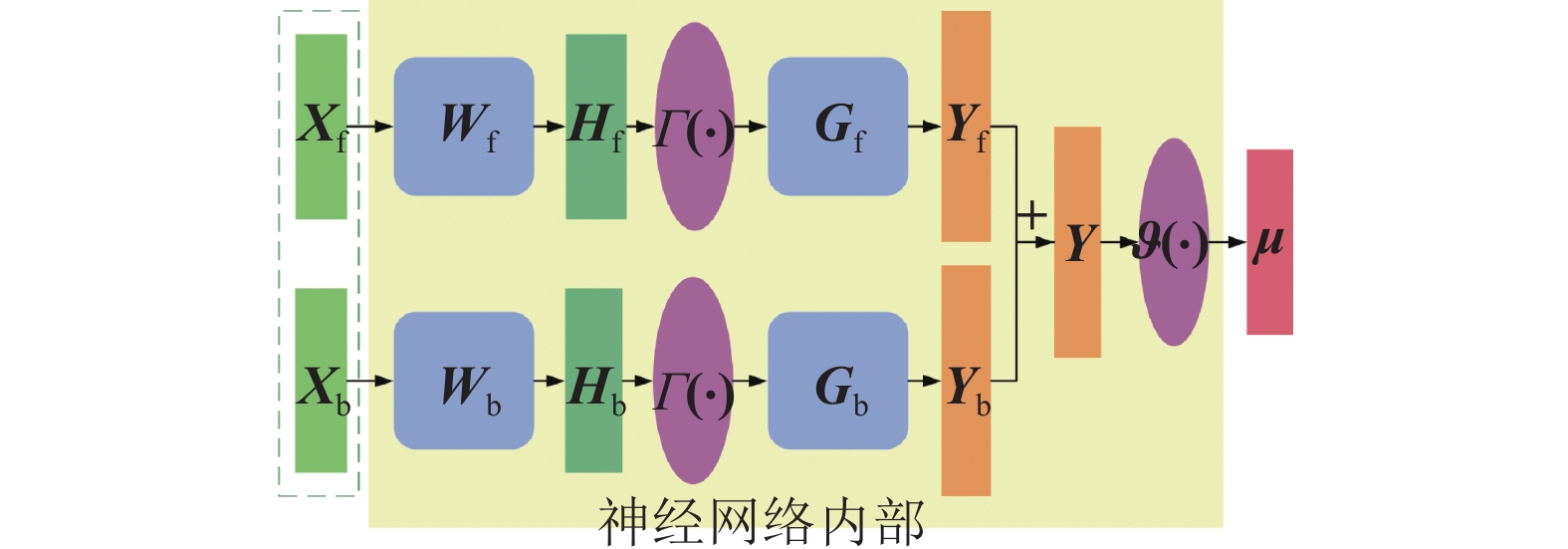
第 1 节变量与符号 说明 $ {\cal{S}} $ $ n $阶$ m $维状态反馈系统 $ {\boldsymbol{F}} $ 未知非线性函数向量 $ {\boldsymbol{d}} $ 有界未知扰动向量 $ {\boldsymbol{b}} $ $ m $阶未知可逆对角常数矩阵 $ V $, $ \dot{V} $ Lyapunov 函数及其导数 $ {\cal{B}} $, $ {\cal{M}} $ $ \dot{V} $中已知函数向量 ${{\varphi} }$ $ \dot{V} $中不含$ {\boldsymbol{u}} $的其余项之和 $ {\boldsymbol{u}}_{{\rm{b}}} $ 基础控制器 $ {\boldsymbol{\mu}}( \cdot | {\boldsymbol{\theta}}) $ 神经网络嵌入控制器 $ {\boldsymbol{u}}_{{\rm{b}}}^{{\boldsymbol{\mu}}} $ 基于$ {\boldsymbol{u}}_{{\rm{b}}} $与$ {\boldsymbol{\mu}}( \cdot | {\boldsymbol{\theta}}) $的学习控制器 $ \circ $ Hadamard 积运算符 $ {\boldsymbol{\vartheta}}(\cdot) $ 嵌入控制器约束函数向量 $ {\cal{L}} $ 系统控制性能的量度 B2
第 2 ~ 3 节变量与符号 说明 $ {\cal{L}}_{{\cal{S}}} $ 系统$ {\cal{S}} $的性能优化目标函数 $ \psi $ $ {\cal{L}}_{{\cal{S}}} $中其他控制指标正则项 $ {\boldsymbol{b}}_{0} $ $ m $阶已知对角常值矩阵 $ {\cal{F}} $, $ \dot{{\cal{F}}} $ 不确定与扰动值项的等效值与导数 $ \hat{{\cal{F}}} $, $ \dot{\hat{{\cal{F}}}} $ $ {\cal{F}} $的估计值及其导数 $ \tilde{{\cal{F}}} $, $ \dot{\tilde{{\cal{F}}}} $ $ {\cal{F}} $与$ \hat{{\cal{F}}} $的误差及其导数 $ {\boldsymbol{u}}_{{\rm{b}}}^{{\cal{F}}} $ 基于值自适应的基础控制器 ${\boldsymbol{\varpi}}(\cdot)$ 构造$ {\boldsymbol{u}}_{{\rm{b}}}^{{\cal{F}}} $所需函数 B3
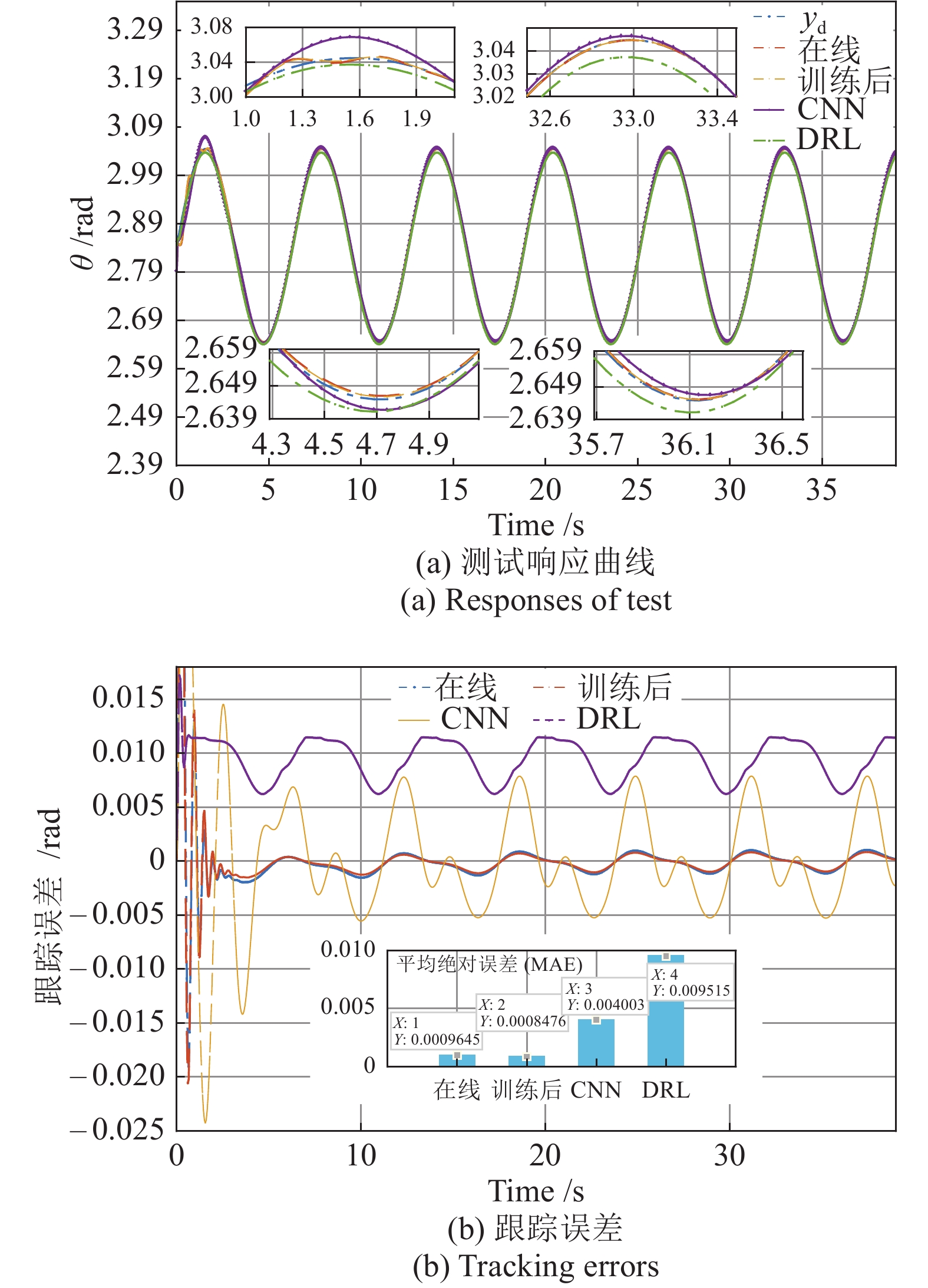
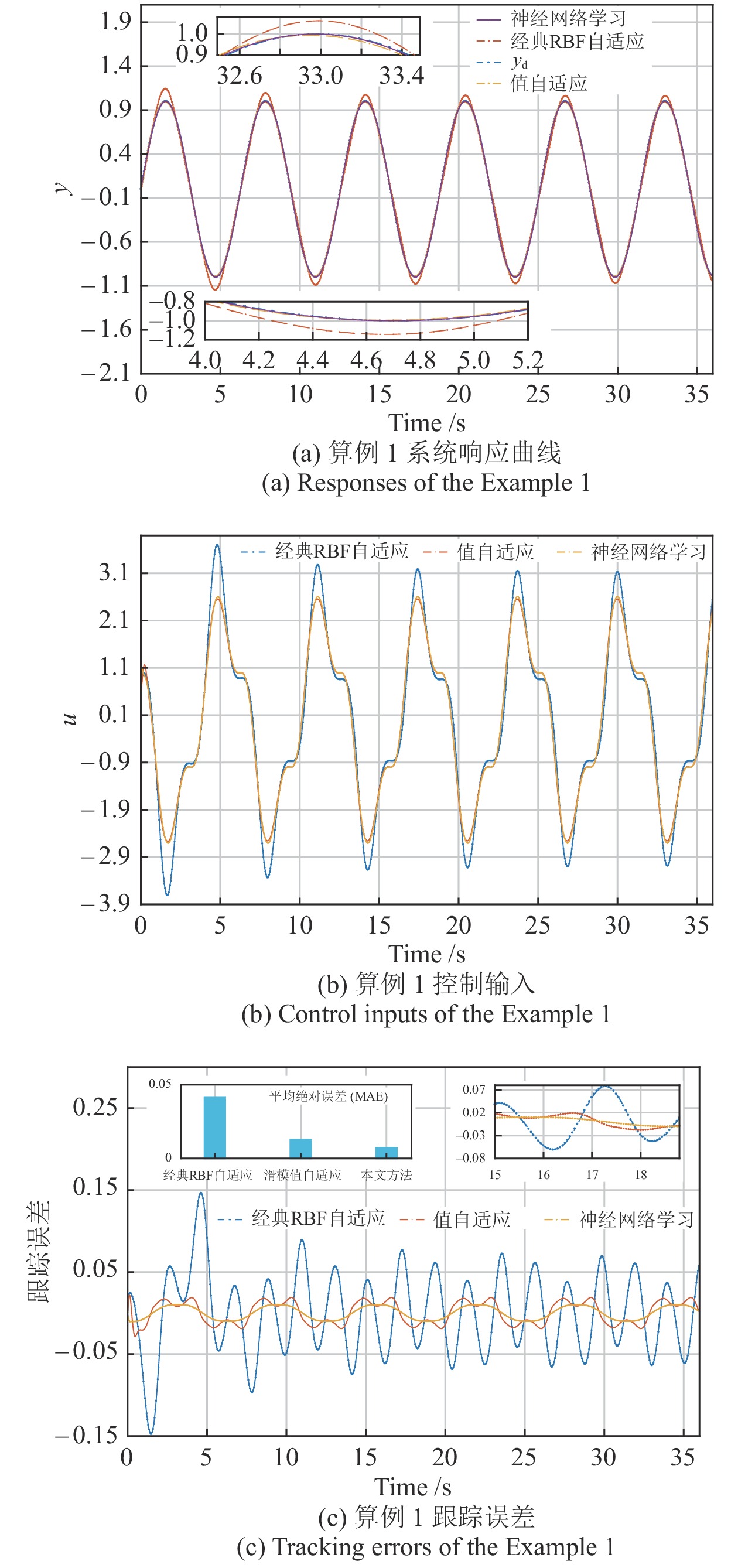
第 4 ~ 5 节变量与符号 说明 $ y_{{\rm{d}}} $ 系统期望输出 $ b_{0} $ 已知系统增益 ($ {\boldsymbol{b}}_{0} $的一维形式) $ \hat{f} $ 待估计不确定项 $ k $ 控制器增益 $ \xi(t) $ 随机变量 $ \theta $, $ \omega $ 电机角度与角速度 $ f_{{\rm{M}}} $ 电机模型未知非线性项 $ \theta_{{\rm{J}}} $, $ \omega_{{\rm{J}}} $ 机械臂关节角度与角速度 $ \gamma $ DRL 方法的奖励函数 -
[1] Wang H Q, Liu P X, Li S, Wang D. Adaptive neural output-feedback control for a class of nonlower triangular nonlinear systems with unmodeled dynamics. IEEE Transactions On Neural Networks and Learning System, 2018, 29(8): 3658-3668 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2017.2716947 [2] Cheng G Y, Yu W T, Hu J G.Improving the performance of motor drive servo systems via composite nonlinear control. CES Transactions on Electrical Machines and Systems, 2018, 2(4): 399-408 doi: 10.30941/CESTEMS.2018.00051 [3] Jamwal P K, Hussain S, Ghayesh M H, Rogozina S V. Impedance control of an intrinsically compliant parallel ankle rehabilitation robot.IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2016, 63(6): 3638-3647 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2016.2521600 [4] Chen C, Modares H, Xie K, et al. Reinforcement learning-based adaptive optimal exponential tracking control of linear systems with unknown dynamics. IEEE Transactions On Automatic Control, 2019, 64(11): 4423-4438 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2019.2905215 [5] Haddad W M, Chellaboina V. Nonlinear Dynamical Systems and Control: A Lyapunov-based Approach. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 2007. 135−198 [6] 田福庆, 姜尚, 梁伟阁. 含齿隙弹载舵机的全局反步模糊自适应控制, 自动化学报, 2019, 45(6): 1177-1185Tian Fuqing, Jiang Shang, Liang Weige. Global backstepping fuzzy adaptive control for ammunition actuator with backlash Acta Automatica Sinica, 45(06): 1177-1185 [7] Guerrerocastellanos J F, Rifai H, Arnezpaniagua V, et al. Robust active disturbance rejection control via control lyapunov functions: Application to actuated-ankle foot-orthosis. Control Engineering Practice, 2019, 80(18): 49-60 [8] 马乐, 刘跃峰, 李志伟, 徐东甫, 张玉龙. 一种基于Lyapunov约束的学习控制方法及应用. 仪器仪表学报, 40(9): 189-198, 2019Ma Le, Liu Yue-feng, Li Zhi-wei, Xu Dong-fu, Zhang Yu-long, A framework of learning controller with Lyapunov-based constraint and application, Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2019, 40(9): 189-198 [9] Chen B, Zhang H G, Liu X P, Lin C. Neural observer and adaptive neural control design for a class of nonlinear systems. IEEE Transactions On Neural Networks and Learning System, 2018, 29(9): 4261-4271 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2017.2760903 [10] Li Y M, Tong S C. Adaptive neural networks prescribed performance control design for switched interconnected uncertain nonlinear systems. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2018, 29(7): 3059-3068 [11] Fei J T, Lu C. Adaptive sliding mode control of dynamic systems using double loop recurrent neural network structure. IEEE Transactions On Neural Networks and Learning System, 2018, 29(4): 1275-1286 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2017.2672998 [12] Zhang X Y, Chen X K, Zhu G Q, Su C Y. Output feedback adaptive motion control and its experimental verification for time-delay nonlinear systems with asymmetric hysteresis. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2019, 67(8): 6824-6834 [13] 李洋, 刘明雍, 张小件. 基于自适应RBF神经网络的超空泡航行体反演控, 自动化学报, 2020, 46(4): 734-743Li Yang, Liu Ming-yong, Zhang Xian-jian.Adaptive RBF neural network based backstepping control for supercavitating vehicles Acta Automatica Sinica, 46(4): 734-743 [14] Park M, Chwa D, Eom M. Adaptive sliding-mode antisway control of uncertain overhead cranes with high-speed hoisting motion. IEEE Transactions On Fuzzy Systems, 2014, 22(5): 1262-1271 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2013.2290139 [15] 欧阳慧珉, 王健, 张广明, 梅磊, 邓歆. 基于新型滑模算法的双摆旋转起重机消摆跟踪控制, 自动化学报, 2019, 45(7): 1344-1353Ouyang Hui-Min, Wang Jian, Zhang Guang-Ming, Mei Lei, Deng Xin.Tracking and anti-sway control for double-pendulum rotary cranes using novel sliding mode algorithm.Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(7): 1344-1353 [16] Chen W H, Yang J, Guo L, Li S H. Disturbance-observer-based control and related methods-an overview. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2016, 63(2): 1083-1095 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2015.2478397 [17] Zhong Q C, Kuperman A, Stobart R. Design of ude-based controllers from their two-degree-of-freedom nature.International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2001 21(17): 1994-2008 [18] Lv M, Baldi S, Liu Z C. The non-smoothness problem in disturbance observer design: A set-invariance based adaptive fuzzy control method. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2019, 27(3): 598-604 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2019.2892353 [19] Han J Q. From pid to active disturbance rejection control. IEEE Transactions On Industrial Electronics, 2009, 56(3): 900-906 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2008.2011621 [20] 李杰, 齐晓慧, 万慧, 夏元清. 自抗扰控制: 研究成果总结与展望, 控制理论与应用, 2017, 34(3): 281-295 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2017.60363Li Jie, Qi Xiao-hui, Wan Hui, Xia Yuan-qing. Active disturbance rejection control: theoretical results summary and future researches Control Theory and Applications, 34(3): 281-295 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2017.60363 [21] Wen G X, Ge S S, Tu F W. Optimized backstepping for tracking control of strict-feedback systems. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2018, 29(8): 3850-3862 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2803726 [22] Bu X H, Hou Z S. Adaptive iterative learning control for linear systems with binary-valued observations. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2018, 29(1): 232-237 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2016.2616885 [23] Meng T T, He W. Iterative learning control of a robotic arm experiment platform with input constraint. IEEE Transactions On Industrial Electronics, 2018, 65(1): 664-672 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2017.2719598 [24] Xu D Z, Liu J X, Yan X G, Yan W X. A novel adaptive neural network constrained control for a multi-area interconnected power system with hybrid energy storage. IEEE Transactions On Industrial Electronics, 2018, 65(8): 6625-6634 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2017.2767544 [25] Mnih V, Kavukcuoglu K, Silver D, et al. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning.Nature, 2015, 518(7540): 529-541 doi: 10.1038/nature14236 [26] Kang Y, Chen S F, Wang X F, Cao Y. Deep convolutional identifier for dynamic modeling and adaptive control of unmanned helicopter.IEEE Transactions On Neural Networks and Learning System, 2019, 30(2): 524-538 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2844173 [27] Zhou M, Feng Y, Xue C, Han F. Deep convolutional neural network based fractional-order terminal sliding-mode control for robotic manipulators. Neurocomputing, DOI: 10.1016/j.neucom.2019.04.087 [28] Carlucho I, De Paula M, Wang S, Petillot Y, Acosta G G. Adaptive low-level control of autonomous underwater vehicles using deep reinforcement learning. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2018, 107(2018): 71-86. [29] Xiong H, Ma T Q, Zhang L, Diao X M. Comparison of end-to-end and hybrid deep reinforcement learning strategies for controlling cable-driven parallel robots. Neurocomputing, 2020, 377(2020): 73-84 [30] Yang Z Y, Merrick K E, Jin L W, Abbass H A. Hierarchical deep reinforcement learning for continuous action control. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2018, 29(11): 5174-5184 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2805379 [31] Zhang Y Y, Li S, Liu X P. Neural network-based model-free adaptive near-optimal tracking control for a class of nonlinear systems. IEEE Transactions On Neural Networks and Learning System, 2018, 29(12): 6227-6241 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2828114 [32] Liu L, Jiang H, He P, Chen W, Liu X, Gao J, et al. On the variance of the adaptive learning rate and beyond [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.03265, April 17, 2020 [33] Vu V, Wang W. State/disturbance observer and controller synthesis for the t-s fuzzy system with an enlarged class of disturbances. IEEE Transactions On Fuzzy Systems, 2018, 26(6): 3645-3659 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2018.2841858 [34] Li S, Wang H, Aitouche A, Tian Y, Christov N. Actuator fault and disturbance estimation using the T-S fuzzy model.IFAC Papers OnLine, 2017, 50(1): 15722-15727 doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2017.08.2414 [35] Guo B Z, Zhao Z L. On convergence of tracking differentiator. International Journal of Control, 2011, 84(4): 693-701. doi: 10.1080/00207179.2011.569954 -




 下载:
下载: