Interval Type-2 Fuzzy Sets and Systems: Overview and Outlook
-
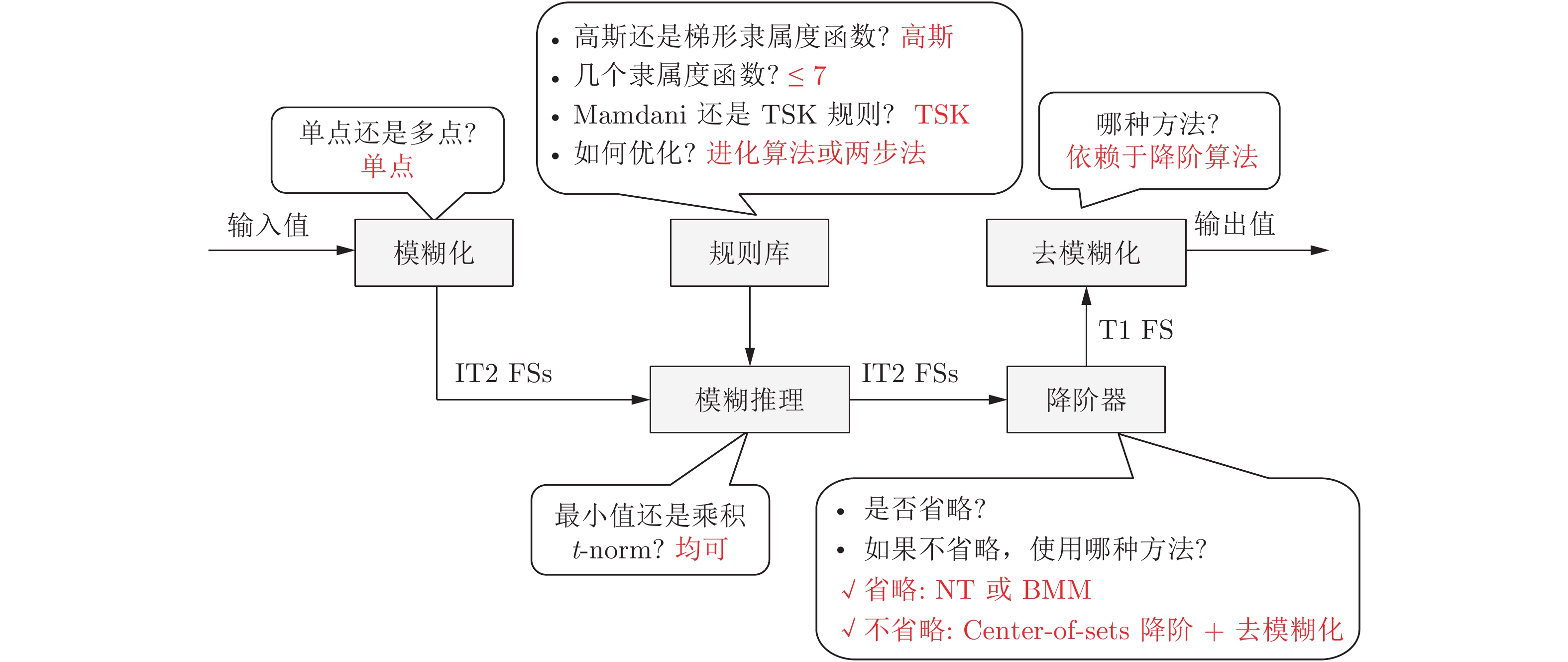
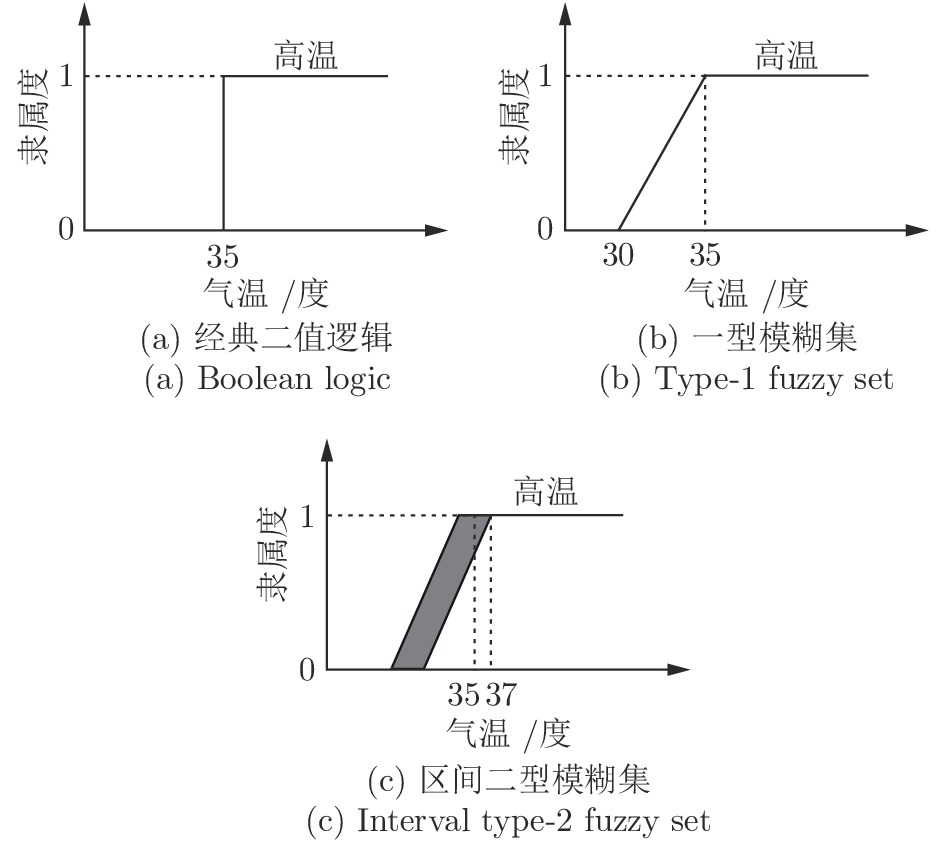
摘要: 一型模糊集可以建模单个用户的语义概念中的不确定性, 即个体内不确定性. 一型模糊系统在控制和机器学习中得到了大量成功应用. 区间二型模糊集能同时建模个体内不确定性和个体间不确定性, 因而在很多应用中显示了比一型模糊系统更好的性能, 是近年来的研究热点. 本文首先介绍了区间二型模糊集的重要概念和理论研究进展, 总结了其在决策和机器学习中的成功应用, 然后介绍了区间二型模糊系统的基本操作和理论研究进展, 并回顾了其在控制和机器学习中的典型应用. 最后, 对区间二型模糊集和模糊系统未来的研究方向进行了展望.Abstract: Type-1 fuzzy sets can model the linguistic uncertainty from a single user, i.e., intra-personal uncertainty. Type-1 fuzzy systems have been widely used in controls and machine learning applications. Interval type-2 fuzzy sets can simultaneously model both intra-personal uncertainty and inter-personal uncertainty, and hence have demonstrated better performance than type-1 fuzzy systems in many applications, becoming a hot research topic recently. This paper first introduces main concepts and theoretical research progresses of interval type-2 fuzzy sets, summarizes their successful applications in decision-making and machine learning, then introduces basic operations and theoretical research progresses of interval type-2 fuzzy systems, and reviews their typical applications in controls and machine learning. Finally, it points out several future research directions on interval type-2 fuzzy sets and systems.
-
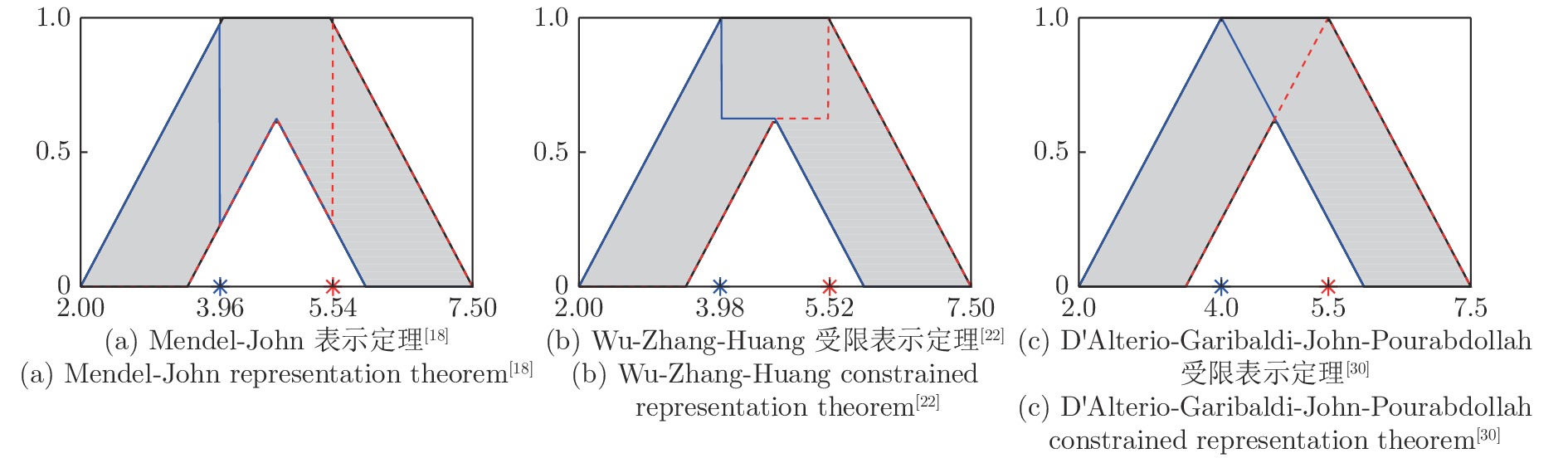
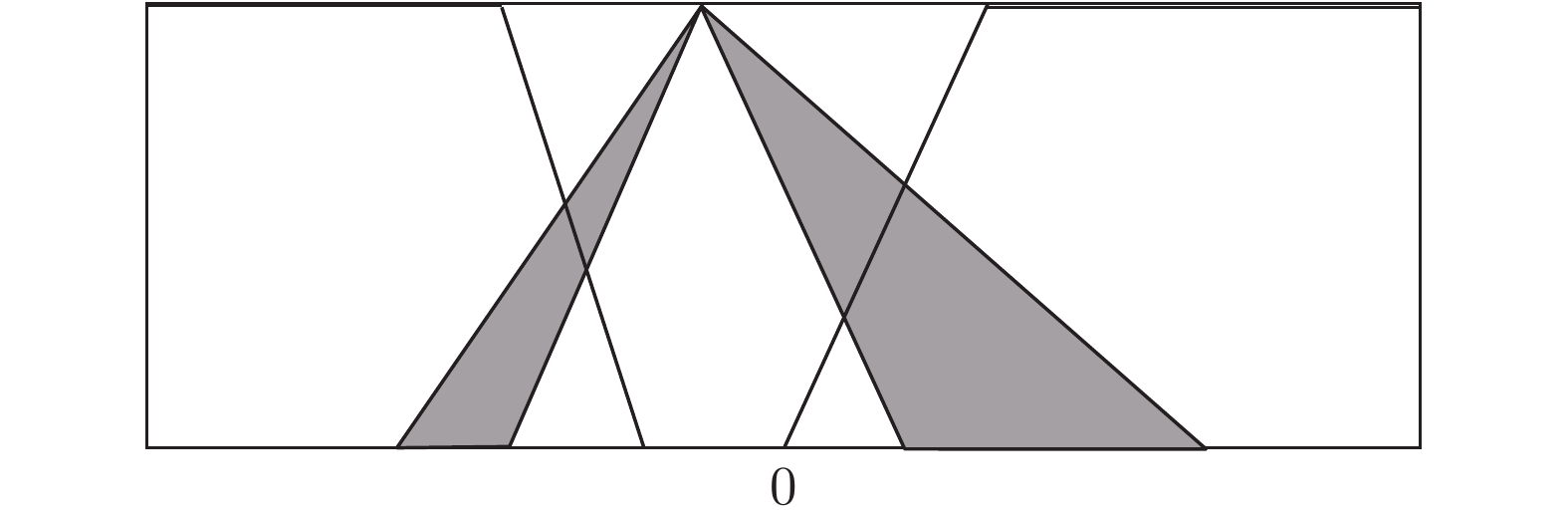
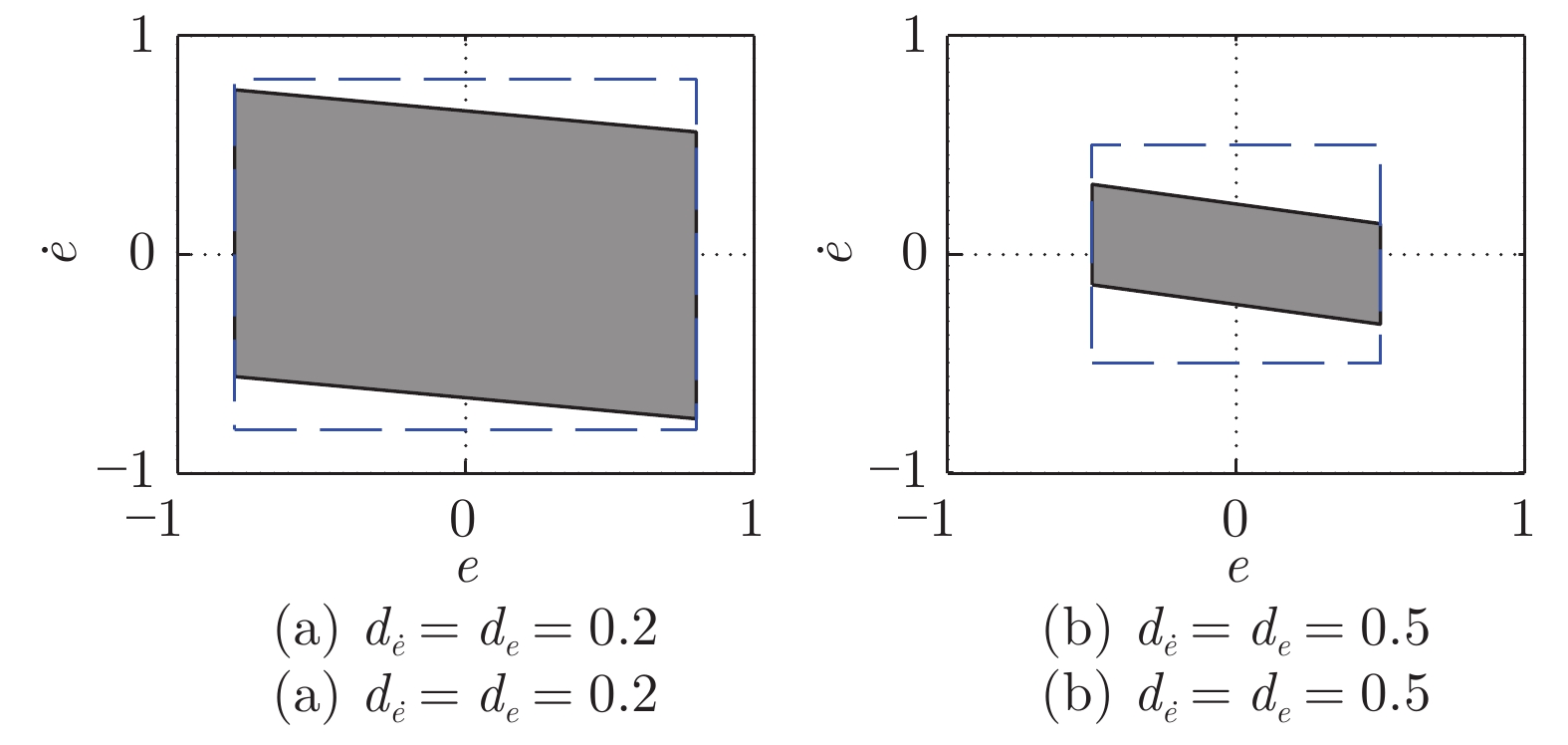
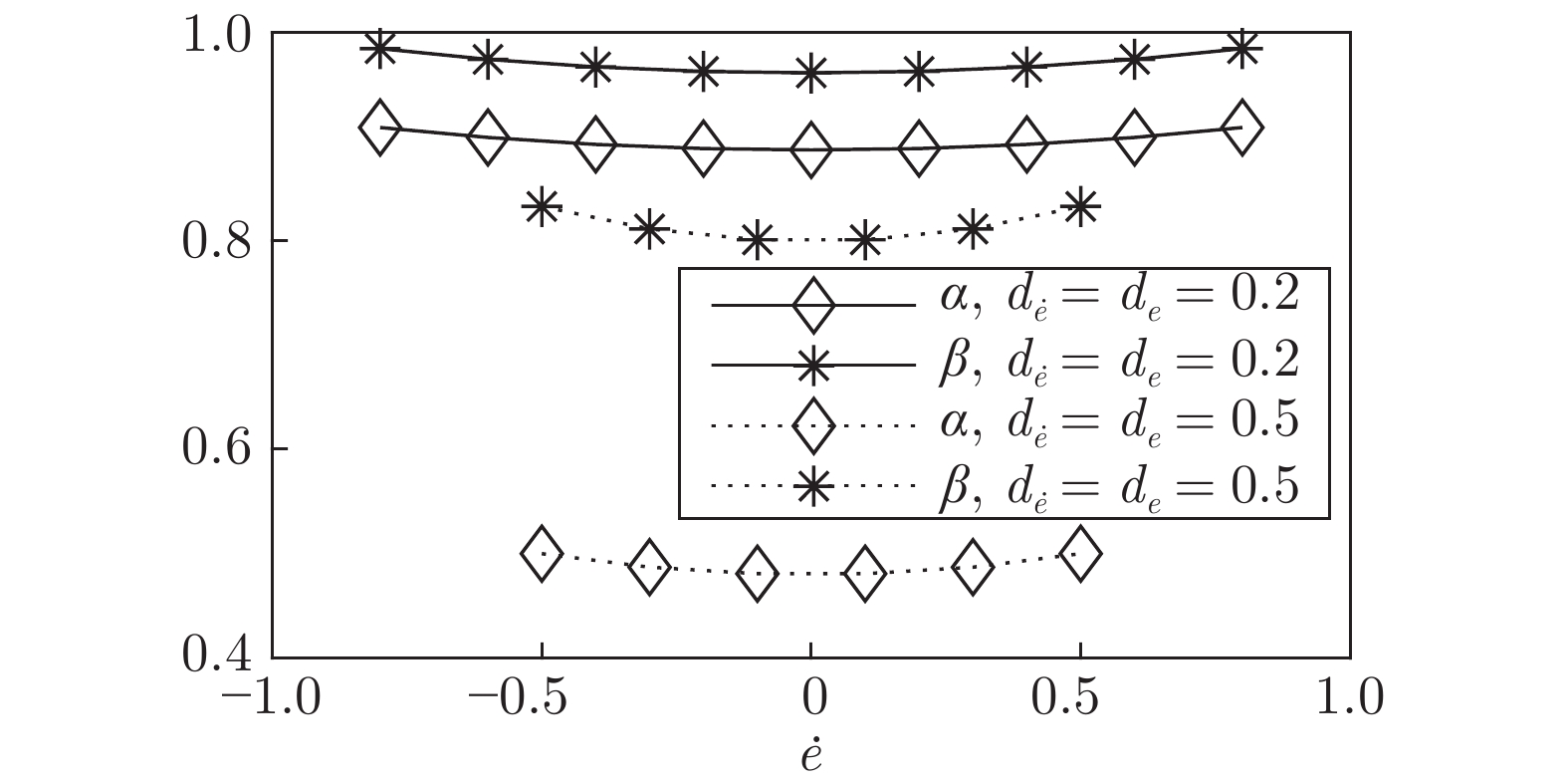
图 4 根据不同的表示定理, 计算区间二型模糊集质心所用到的嵌入一型模糊集(左边的点是由实线嵌入一型模糊集决定的质心的下界, 右边的点是由虚线嵌入一型模糊集决定的质心的上界.)
Fig. 4 Embedded type-1 fuzzy sets in computing the centroid of the interval type-2 fuzzy set, according to different representation theorems (The left dot is the lower bound of the centroid determined by the solid embedded type-1 fuzzy set, and the right dot is the upper bound determined by the dashed embedded type-1 fuzzy set.)
-
[1] Zadeh L A. Fuzzy sets. Information and Control, 1965, 8(3): 338−353 doi: 10.1016/S0019-9958(65)90241-X [2] Zadeh L A. The concept of a linguistic variable and its application to approximate reasoning-I. Information Sciences, 1975, 8(3): 199−249 doi: 10.1016/0020-0255(75)90036-5 [3] Turksen I B. Interval valued fuzzy sets based on normal forms. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 1986, 20(2): 191−210 doi: 10.1016/0165-0114(86)90077-1 [4] Gorzałczany M B. A method of inference in approximate reasoning based on interval-valued fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 1987, 21(1): 1−17 doi: 10.1016/0165-0114(87)90148-5 [5] Bustince H. Indicator of inclusion grade for interval-valued fuzzy sets. International Journal of Approximate Reasoning, 2000, 23(3): 137−209 doi: 10.1016/S0888-613X(99)00045-6 [6] Atanassov K T. Intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 1986, 20(1): 87−96 doi: 10.1016/S0165-0114(86)80034-3 [7] Deschrijver G, Kerre E E. On the relationship between some extensions of fuzzy set theory. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 2003, 133(2): 227−235 doi: 10.1016/S0165-0114(02)00127-6 [8] Sola H B, Fernandez J, Hagras H, Herrera F, Pagola M, Barrenechea E. Interval type-2 fuzzy sets are generalization of interval-valued fuzzy sets: Toward a wider view on their relationship. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2015, 23(5): 1876−1882 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2014.2362149 [9] Mendel J M, Hagras H, Bustince H, Herrera F. Comments on “Interval type-2 fuzzy sets are generalization of interval-valued fuzzy sets: Towards a wide view on their relationship”. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2016, 24(1): 249−250 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2015.2446508 [10] Mendel J M. Uncertain Rule-Based Fuzzy Systems: Introduction and New Directions (Second Edition). Berlin: Springer, 2017. [11] Zadeh L A. Outline of a new approach to the analysis of complex systems and decision processes. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 1973, SMC-3(1): 28−44 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.1973.5408575 [12] Mamdani E H. Application of fuzzy algorithms for control of simple dynamic plant. Proceedings of the Institution of Electrical Engineers, 1974, 121(12): 1585−1588 doi: 10.1049/piee.1974.0328 [13] Holmblad L P, Ostergaard J J. Control of a cement kiln by fuzzy logic techniques. IFAC Proceedings, 1981, 14(2): 809−814 doi: 10.1016/S1474-6670(17)63582-1 [14] 潘永平, 黄道平, 孙宗海. II型模糊控制综述. 控制理论与应用, 2011, 28(1): 13−23Pan Yong-Ping, Huang Dao-Ping, Sun Zong-Hai. Overview of type-2 fuzzy logic control. Control Theory & Applications, 2011, 28(1): 13−23 [15] Mendel J M. Fuzzy logic systems for engineering: A tutorial. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1995, 83(3): 345−377 doi: 10.1109/5.364485 [16] Wang L X. A Course in Fuzzy Systems and Control. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall, 1997. [17] 王飞跃, 莫红. 关于二型模糊集合的一些基本问题. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(7): 1114−1141Wang Fei-Yue, Mo Hong. Some fundamental issues on type-2 fuzzy sets. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(7): 1114−1141 [18] Mendel J M, John R I B. Type-2 fuzzy sets made simple. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2002, 10(2): 117−127 doi: 10.1109/91.995115 [19] Wu D R, Mendel J M. Uncertainty measures for interval type-2 fuzzy sets. Information Sciences, 2007, 177(23): 5378−5393 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2007.07.012 [20] Wu D R, Mendel J M. A comparative study of ranking methods, similarity measures and uncertainty measures for interval type-2 fuzzy sets. Information Sciences, 2009, 179(8): 1169−1192 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2008.12.010 [21] Mendel J M, Wu D R. Perceptual Computing: Aiding People in Making Subjective Judgments. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley-IEEE Press, 2010. [22] Wu D R, Zhang H T, Huang J. A constrained representation theorem for well-shaped interval type-2 fuzzy sets, and the corresponding constrained uncertainty measures. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2019, 27(6): 1237−1251 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2018.2874018 [23] Liu F L, Mendel J M. Encoding words into interval type-2 fuzzy sets using an interval approach. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2008, 16(6): 1503−1521 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2008.2005002 [24] Wu D R, Mendel J M, Coupland S. Enhanced interval approach for encoding words into interval type-2 fuzzy sets and its convergence analysis. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2012, 20(3): 499−513 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2011.2177272 [25] Hao M S, Mendel J M. Encoding words into normal interval type-2 fuzzy sets: HM approach. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2016, 24(4): 865−879 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2015.2486814 [26] Wu D R, Mendel J M. Aggregation using the linguistic weighted average and interval type-2 fuzzy sets. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2007, 15(6): 1145−1161 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2007.896325 [27] Wu D R, Mendel J M. Ordered fuzzy weighted averages and ordered linguistic weighted averages. In: Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems. Barcelona, Spain: IEEE, 2010. [28] Wu D R, Mendel J M. Perceptual reasoning for perceptual computing: A similarity-based approach. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2009, 17(6): 1397−1411 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2009.2032652 [29] Mendel J M, Wu D R. Perceptual reasoning for perceptual computing. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2008, 16(6): 1550−1564 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2008.2005691 [30] D'Alterio P, Garibaldi J M, John R, Pourabdollah A. Constrained interval type-2 fuzzy sets. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2020, DOI: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2020.2970911 [31] Huang J, Ri M, Wu D R, Ri S. Interval type-2 fuzzy logic modeling and control of a mobile two-wheeled inverted pendulum. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2018, 26(4): 2030−2038 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2017.2760283 [32] Wu D, Tan W W. A type-2 fuzzy logic controller for the liquid-level process. In: Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems. Budapest, Hungary: IEEE, 2004. 953−958 [33] Tahayori H, Livi L, Sadeghian A, Rizzi A. Interval type-2 fuzzy set reconstruction based on fuzzy information-theoretic kernels. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2015, 23(4): 1014−1029 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2014.2336673 [34] Wu D R, Tan W W. A simplified type-2 fuzzy logic controller for real-time control. ISA Transactions, 2006, 45(4): 503−516 doi: 10.1016/S0019-0578(07)60228-6 [35] Zadeh L A. Toward a generalized theory of uncertainty (GTU) — An outline. Information Sciences, 2005, 172(1-2): 1−40 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2005.01.017 [36] Klir G J. Principles of uncertainty: What are they? Why do we need them? Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 1995, 74(1): 15−31 [37] Christensen R. Entropy minimax multivariate statistical modeling-I: Theory. International Journal of General Systems, 1985, 11(3): 231−277 doi: 10.1080/03081078508934916 [38] Christensen R. Entropy minimax multivariate statistical modeling-II: Applications. International Journal of General Systems, 1986, 12(3): 227−305 doi: 10.1080/03081078608934938 [39] Paris J B. The Uncertain Reasoner's Companion-A Mathematical Perspective. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1994. [40] Geer J F, Klir G J. A mathematical analysis of information-preserving transformations between probabilistic and possibilistic formulations of uncertainty. International Journal of General Systems, 1992, 20(2): 143−176 doi: 10.1080/03081079208945024 [41] Klir G J. A principle of uncertainty and information invariance. International Journal of General Systems, 1990, 17(2-3): 249−275 doi: 10.1080/03081079008935110 [42] Klir G J, Parviz B. Probability-possibility transformations: A comparison. International Journal of General Systems, 1992, 21(3): 291−310 doi: 10.1080/03081079208945083 [43] Wonneberge S. Generalization of an invertible mapping between probability and possibility. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 1994, 64(2): 229−240 doi: 10.1016/0165-0114(94)90336-0 [44] Liu F L, Mendel J M. Aggregation using the fuzzy weighted average as computed by the Karnik-Mendel algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2008, 16(1): 1−12 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2007.896229 [45] Wu D R, Mendel J M. Corrections to “Aggregation using the linguistic weighted average and interval type-2 fuzzy sets”. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2008, 16(6): 1664−1666 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2008.2005941 [46] Klir G J, Yuan B. Fuzzy Sets and Fuzzy Logic: Theory and Applications. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice-Hall, 1995 [47] Karnik N N, Mendel J M, Liang Q L. Type-2 fuzzy logic systems. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 1999, 7(6): 643−658 doi: 10.1109/91.811231 [48] Wu D R, Huang J. Ordered novel weighted averages. Type-2 Fuzzy Logic and Systems. Berlin: Springer, 2018. 25-47 [49] Yager R R. On ordered weighted averaging aggregation operators in multicriteria decisionmaking. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 1988, 18(1): 183−190 doi: 10.1109/21.87068 [50] Mendel J M. Computing with words: Zadeh, Turing, Popper and Occam. IEEE Computational Intelligence Magazine, 2007, 2(4): 10−17 doi: 10.1109/MCI.2007.9066897 [51] Mendel J M. Type-2 fuzzy sets as well as computing with words. IEEE Computational Intelligence Magazine, 2019, 14(1): 82−95 doi: 10.1109/MCI.2018.2881646 [52] Mendel J M. The perceptual computer: An architecture for computing with words. In: Proceedings of the 10th IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems. Melbourne, Australia: IEEE, 2001. 35−38 [53] Acosta H, Wu D R, Forrest B M. Fuzzy experts on recreational vessels, a risk modelling approach for marine invasions. Ecological Modelling, 2010, 221(5): 850−863 doi: 10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2009.11.025 [54] Wu D R, Mendel J M. Computing with words for hierarchical decision making applied to evaluating a weapon system. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2010, 18(3): 441−460 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2010.2043439 [55] Chen S M, Hong J A. Fuzzy multiple attributes group decision-making based on ranking interval type-2 fuzzy sets and the TOPSIS method. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2014, 44(12): 1665−1673 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2014.2314724 [56] Qin J D, Liu X W, Pedrycz W. An extended VIKOR method based on prospect theory for multiple attribute decision making under interval type-2 fuzzy environment. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2015, 86: 116−130 doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2015.05.025 [57] Qin J D, Liu X W, Pedrycz W. An extended TODIM multi-criteria group decision making method for green supplier selection in interval type-2 fuzzy environment. European Journal of Operational Research, 2017, 258(2): 626−638 doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2016.09.059 [58] 李润梅, 梁秋鸿. 基于区间二型模糊集合的人工交通系统可信度评估. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(10): 1915−1922Li Run-Mei, Liang Qiu-Hong. Artificial traffic system credibility evaluation with interval type-2 fuzzy sets. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(10): 1915−1922 [59] Yager R R. A new approach to the summarization of data. Information Sciences, 1982, 28(1): 69−86 doi: 10.1016/0020-0255(82)90033-0 [60] Wu D R, Mendel J M. Linguistic summarization using IF-THEN rules and interval type-2 fuzzy sets. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2011, 19(1): 136−151 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2010.2088128 [61] Boran F E, Akay D. A generic method for the evaluation of interval type-2 fuzzy linguistic summaries. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2014, 44(9): 1632−1645 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2013.2291272 [62] Karnik N N, Mendel J M. Centroid of a type-2 fuzzy set. Information Sciences, 2001, 132(1-4): 195−220 doi: 10.1016/S0020-0255(01)00069-X [63] Sumati V, Patvardhan C. Interval type-2 mutual subsethood fuzzy neural inference system (IT2MSFuNIS). IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2018, 26(1): 203−215 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2016.2646750 [64] Wu D R. Approaches for reducing the computational cost of interval type-2 fuzzy logic systems: Overview and comparisons. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2013, 21(1): 80−99 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2012.2201728 [65] Wu D R, Mendel J M. Enhanced Karnik-Mendel algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2009, 17(4): 923−934 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2008.924329 [66] Wu D R, Nie M W. Comparison and practical implementation of type-reduction algorithms for type-2 fuzzy sets and systems. In: Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems (FUZZ-IEEE 2011). Taipei, China: IEEE, 2011. 2131−2138 [67] Wu D R, Tan W W. Computationally efficient type-reduction strategies for a type-2 fuzzy logic controller. In: Proceedings of the 14th IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems. Reno, USA: IEEE, 2005. 353−358 [68] Begian M B, Melek W W, Mendel J M. Stability analysis of type-2 fuzzy systems. In: Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems. Hong Kong, China: IEEE, 2008. 947−953 [69] Nie M W, Tan W W. Towards an efficient type-reduction method for interval type-2 fuzzy logic systems. In: Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems. Hong Kong, China: IEEE, 2008. 1425−1432 [70] Wu D R, Tan W W. Genetic learning and performance evaluation of interval type-2 fuzzy logic controllers. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2006, 19(8): 829−841 doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2005.12.011 [71] Wu D, Tan X. Multitasking genetic algorithm (MTGA) for fuzzy system optimization. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy System, 2020, 28(6): 1050−1061 [72] Das A K, Subramanian K, Sundaram S. An evolving interval type-2 neurofuzzy inference system and its metacognitive sequential learning algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2015, 23(6): 2080−2093 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2015.2403793 [73] Lin Y Y, Liao S H, Chang J Y, Lin C T. Simplified interval type-2 fuzzy neural networks. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2014, 25(5): 959−969 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2013.2284603 [74] Juang C F, Tsao Y W. A self-evolving interval type-2 fuzzy neural network with online structure and parameter learning. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2008, 16(6): 1411−1424 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2008.925907 [75] Juang C F, Huang R B, Lin Y Y. A recurrent self-evolving interval type-2 fuzzy neural network for dynamic system processing. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2009, 17(5): 1092−1105 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2009.2021953 [76] Deng Z H, Choi K S, Cao L B, Wang S T. T2FELA: Type-2 fuzzy extreme learning algorithm for fast training of interval type-2 TSK fuzzy logic system. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2014, 25(4): 664−676 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2013.2280171 [77] Wu D R, Mendel J M. On the continuity of type-1 and interval type-2 fuzzy logic systems. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2011, 19(1): 179−192 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2010.2091962 [78] Lam H K, Seneviratne L D. Stability analysis of interval type-2 fuzzy-model-based control systems. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B (Cybernetics), 2008, 38(3): 617−628 doi: 10.1109/TSMCB.2008.915530 [79] Biglarbegian M, Melek W W, Mendel J M. On the stability of interval type-2 TSK fuzzy logic control systems. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B (Cybernetics), 2010, 40(3): 798−818 doi: 10.1109/TSMCB.2009.2029986 [80] Jafarzadeh S, Fadali M S, Sonbol A H. Stability analysis and control of discrete type-1 and type-2 TSK fuzzy systems: Part I. Stability analysis. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2011, 19(6): 989−1000 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2011.2158218 [81] Kumbasar T. Robust stability analysis and systematic design of single-input interval type-2 fuzzy logic controllers. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2016, 24(3): 675−694 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2015.2471805 [82] Xiao B, Lam H K, Li H Y. Stabilization of interval type-2 polynomial-fuzzy-model-based control systems. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2017, 25(1): 205−217 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2016.2554153 [83] Rong N N, Wang Z S, Zhang H G. Finite-time stabilization for discontinuous interconnected delayed systems via interval type-2 T-S fuzzy model approach. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2019, 27(2): 249−261 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2018.2856181 [84] Li C D, Yi J Q, Wang M, Zhang G Q. Monotonic type-2 fuzzy neural network and its application to thermal comfort prediction. Neural Computing and Applications, 2013, 23(7-8): 1987−1998 doi: 10.1007/s00521-012-1140-x [85] Li C D, Yi J Q, Zhang G Q. On the monotonicity of interval type-2 fuzzy logic systems. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2014, 22(5): 1197−1212 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2013.2286416 [86] Wang T C, Tong S C, Yi J Q, Li H Y. Adaptive inverse control of cable-driven parallel system based on type-2 fuzzy logic systems. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2015, 23(5): 1803−1816 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2014.2379284 [87] Wu D R. Design and Analysis of Type-2 Fuzzy Logic Systems [Master thesis], National University of Singapore, Singapore, 2006 [88] Wu D R, Tan W W. Interval type-2 fuzzy PI controllers: Why they are more robust. In: Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Granular Computing. San Jose, USA: IEEE, 2010. 802−807 [89] Wu D R. On the fundamental differences between interval type-2 and type-1 fuzzy logic controllers. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2012, 20(5): 832−848 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2012.2186818 [90] Du X Y, Ying H. Derivation and analysis of the analytical structures of the interval type-2 fuzzy-PI and PD controllers. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2010, 18(4): 802−814 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2010.2049022 [91] Nie M W, Tan W W. Analytical structure and characteristics of symmetric Karnik-Mendel type-reduced interval type-2 fuzzy PI and PD controllers. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2012, 20(3): 416−430 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2011.2174061 [92] Zhou H B, Ying H. A method for deriving the analytical structure of a broad class of typical interval type-2 Mamdani fuzzy controllers. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2013, 21(3): 447−458 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2012.2226891 [93] Zhou H B, Ying H. Deriving and analyzing analytical structures of a class of typical interval type-2 TS fuzzy controllers. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2017, 47(9): 2492−2503 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2016.2570239 [94] Zhou H B, Ying H, Zhang C L. Effects of increasing the footprints of uncertainty on analytical structure of the classes of interval type-2 mamdani and TS fuzzy controllers. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2019, 27(9): 1881−1890 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2019.2892354 [95] Wu D R, Tan W W. Type-2 FLS modeling capability analysis. In: Proceedings of the 14th IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems. Reno, USA: IEEE, 2005. 242−247 [96] Wu D R, Mendel J M. Recommendations on designing practical interval type-2 fuzzy systems. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2019, 85: 182−193 doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2019.06.012 [97] Hagras H. Type-2 FLCs: A new generation of fuzzy controllers. IEEE Computational Intelligence Magazine, 2007, 2(1): 30−43 doi: 10.1109/MCI.2007.357192 [98] Hagras H A. A hierarchical type-2 fuzzy logic control architecture for autonomous mobile robots. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2004, 12(4): 524−539 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2004.832538 [99] Liu Z, Zhang Y, Wang Y N. A type-2 fuzzy switching control system for biped robots. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part C (Applications and Reviews), 2007, 37(6): 1202−1213 doi: 10.1109/TSMCC.2007.900649 [100] Chaoui H, Gueaieb W. Type-2 fuzzy logic control of a flexible-joint manipulator. Journal of Intelligent and Robotic Systems, 2008, 51(2): 159−186 doi: 10.1007/s10846-007-9185-2 [101] Lin F J, Chou P H. Adaptive control of two-axis motion control system using interval type-2 fuzzy neural network. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2009, 56(1): 178−193 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2008.927225 [102] Martínez R, Castillo O, Aguilar L T. Optimization of interval type-2 fuzzy logic controllers for a perturbed autonomous wheeled mobile robot using genetic algorithms. Information Sciences, 2009, 179(13): 2158−2174 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2008.12.028 [103] Lin T C, Liu H L, Kuo M J. Direct adaptive interval type-2 fuzzy control of multivariable nonlinear systems. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2009, 22(3): 420−430 doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2008.10.024 [104] 李成栋, 易建强, 余意, 赵冬斌. 柔索驱动并联机构的二型模糊神经逆控制. 自动化学报, 2010, 36(3): 459−464Li Cheng-Dong, Yi Jian-Qiang, Yu Yi, Zhao Dong-Bin. Inverse control of cable-driven parallel mechanism using type-2 fuzzy neural network. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2010, 36(3): 459−464 [105] Abiyev R H, Kaynak O. Type 2 fuzzy neural structure for identification and control of time-varying plants. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2010, 57(12): 4147−4159 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2010.2043036 [106] Biglarbegian M, Melek W W, Mendel J M. Design of novel interval type-2 fuzzy controllers for modular and reconfigurable robots: Theory and experiments. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2011, 58(4): 1371−1384 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2010.2049718 [107] Lam H K, Li H Y, Deters C, Secco E L, Wurdemann H, Althoefer K. Control design for interval type-2 fuzzy systems under imperfect premise matching. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2014, 61(2): 956−968 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2013.2253064 [108] Taghavifar H, Xu B, Hu C, Qin Y , Wei C. Commercial vehicle-based robust control of seated whole-body vibration using adaptive indirect type-2 fuzzy neural network. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 124949−124960 [109] Li Y M, Sun Y Y, Hua J, Li L. Indirect adaptive type-2 fuzzy impulsive control of nonlinear systems. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2015, 23(4): 1084−1099 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2014.2346235 [110] Raju S K, Pillai G N. Design and implementation of type-2 fuzzy logic controller for DFIG-based wind energy systems in distribution networks. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 2016, 7(1): 345−353 doi: 10.1109/TSTE.2015.2496170 [111] Navarro G, Umberger D K, Manic M. VD-IT2, virtual disk cloning on disk arrays using a type-2 fuzzy controller. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2017, 25(6): 1752−1764 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2016.2633371 [112] Ren G P, Chen Z Y, Zhang H T, Wu Y, Meng H F, Wu D R, et al. Design of interval type-2 fuzzy controllers for active magnetic bearing systems. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2020, DOI: 10.1109/TMECH.2020.2978018 [113] Wei Z X, Doctor F, Liu Y X, Fan S Z, Shieh J S. An optimized type-2 self-organizing fuzzy logic controller applied in anesthesia for propofol dosing to regulate BIS. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2020, 28(6): 1062−1072 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2020.2969384 [114] Liang Q, Karnik N N, Mendel J M. Connection admission control in ATM networks using survey-based type-2 fuzzy logic systems. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part C (Applications and Reviews), 2000, 30(3): 329−339 doi: 10.1109/5326.885114 [115] Li H Y, Wu C W, Shi P, Gao Y B. Control of nonlinear networked systems with packet dropouts: Interval type-2 fuzzy model-based approach. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2015, 45(11): 2378−2389 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2014.2371814 [116] Zhao T, Dian S Y. State feedback control for interval type-2 fuzzy systems with time-varying delay and unreliable communication links. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2018, 26(2): 951−966 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2017.2699947 [117] Tang X M, Deng L, Yu J M, Qu H C. Output feedback predictive control of interval type-2 T-S fuzzy systems with Markovian packet loss. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2018, 26(4): 2450−2459 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2017.2771502 [118] Khooban M H, Gheisarnejad M. A novel deep reinforcement learning controller based type-II fuzzy system: frequency regulation in microgrids. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computational Intelligence, 2020, DOI: 10.1109/TETCI.2020.2964886 [119] Hu Z J, Liu S C, Yang L, Wu L G. Distributed fuzzy filtering for load frequency control of non-linear interconnected power systems under cyber-physical attacks. IET Control Theory & Applications, 2020, 14(4): 527−538 [120] Li X H, Ye D. Asynchronous event-triggered control for networked interval type-2 fuzzy systems against dos attacks. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2020, DOI: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2020.2975495 [121] Zhang Z N, Niu Y G, Cao Z R, Song J. Security sliding mode control of interval type-2 fuzzy systems subject to cyber attacks: the stochastic communication protocol case. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2020, DOI: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2020.2972785 [122] Das A K, Sundaram S, Sundararajan N. A self-regulated interval type-2 neuro-fuzzy inference system for handling nonstationarities in EEG signals for BCI. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2016, 24(6): 1565−1577 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2016.2540072 [123] Herman P A, Prasad G, McGinnity T M. Designing an interval type-2 fuzzy logic system for handling uncertainty effects in brain-computer interface classification of motor imagery induced EEG patterns. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2017, 25(1): 29−42 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2016.2637934 [124] Singh V, Dev R, Dhar N K, Agrawal P, Verma N K. Adaptive type-2 fuzzy approach for filtering salt and pepper noise in grayscale images. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2018, 26(5): 3170−3176 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2018.2805289 [125] Wu H Y, Wu Y Y, Luo J P. An interval type-2 fuzzy rough set model for attribute reduction. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2009, 17(2): 301−315 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2009.2013458 [126] Maji P, Garai P. IT2 fuzzy-rough sets and max relevance-max significance criterion for attribute selection. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2015, 45(8): 1657−1668 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2014.2357892 [127] Lin C T, Pal N R, Wu S L, Liu Y T, Lin Y Y. An interval type-2 neural fuzzy system for online system identification and feature elimination. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2015, 26(7): 1442−1455 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2014.2346537 [128] Chakraborty B, Ghosh L, Konar A. Optimal selection of EEG electrodes using interval type-2 fuzzy-logic-based semiseparating signaling game. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2020, DOI: 10.1109/TCYB.2020.2968625 [129] Hwang C, Rhee F C H. Uncertain fuzzy clustering: Interval type-2 fuzzy approach to C-means. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2007, 15(1): 107−120 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2006.889763 [130] Zhao F, Chen Y L, Liu H Q, Fan J L. Alternate PSO-based adaptive interval type-2 intuitionistic fuzzy C-means clustering algorithm for color image segmentation. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 64028−64039 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2916894 [131] Zeng J, Liu Z Q. Type-2 fuzzy hidden Markov models and their application to speech recognition. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2006, 14(3): 454−467 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2006.876366 [132] Subramanian K, Savitha R, Suresh S. A metacognitive complex-valued interval type-2 fuzzy inference system. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2014, 25(9): 1659−1672 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2014.2321420 [133] Cao X Q, Liu Z Q. Type-2 fuzzy topic models for human action recognition. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2015, 23(5): 1581−1593 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2014.2370678 [134] Juang C F, Wang P H. An interval type-2 neural fuzzy classifier learned through soft margin minimization and its human posture classification application. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2015, 23(5): 1474−1487 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2014.2362547 [135] Rubio-Solis A, Panoutsos G. Interval type-2 radial basis function neural network: a modeling framework. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2015, 23(2): 457−473 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2014.2315656 [136] Mo H, Wang J, Li X, Wu Z L. Linguistic dynamic modeling and analysis of psychological health state using interval type-2 fuzzy sets. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2015, 2(4): 366−373 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2015.7296531 [137] Kim E H, Oh S K, Pedrycz W. Design of reinforced interval type-2 fuzzy C-means-based fuzzy classifier. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2018, 26(5): 3054−3068 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2017.2785244 [138] Eyoh I, John R, De Maere G, Kayacan E. Hybrid learning for interval type-2 intuitionistic fuzzy logic systems as applied to identification and prediction problems. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2018, 26(5): 2672−2685 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2018.2803751 [139] Cao B, Zhao J W, Lv Z H, Gu Y, Yang P, Halgamuge S. Multiobjective evolution of fuzzy rough neural network via distributed parallelism for stock prediction. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2020, 28(5): 939−952 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2020.2972207 [140] Han M, Zhong K, Qiu T, Han B. Interval type-2 fuzzy neural networks for chaotic time series prediction: A concise overview. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2019, 49(7): 2720−2731 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2018.2834356 [141] Pratama M, Lu J, Zhang G Q. Evolving type-2 fuzzy classifier. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2016, 24(3): 574−589 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2015.2463732 [142] Aisbett J, Rickard J T, Morgenthaler D G. Type-2 fuzzy sets as functions on spaces. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2010, 18(4): 841−844 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2010.2046176 [143] Mendel J M, Rajati M R, Sussner P. On clarifying some definitions and notations used for type-2 fuzzy sets as well as some recommended changes. Information Sciences, 2016, 340-341: 337−345 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2016.01.015 [144] Wu D R, Lin C T, Huang J, Zeng Z G. On the functional equivalence of TSK fuzzy systems to neural networks, mixture of experts, CART, and stacking ensemble regression. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2020, DOI: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2019.2941697 [145] Wu D R, Yuan Y, Huang J, Tan Y H. Optimize TSK fuzzy systems for regression problems: Minibatch gradient descent with regularization, DropRule, and AdaBound (MBGD-RDA). IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2020, 28(5): 1003−1015 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2019.2958559 [146] Cui Y Q, Wu D R, Huang J. Optimize TSK fuzzy systems for classification problems: mini-batch gradient descent with uniform regularization and batch normalization. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2020, DOI: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2020.2967282 [147] Zhou Z H, Feng J. Deep forest. National Science Review, 2019, 6(1): 74−86 doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwy108 [148] Ying H. General interval type-2 Mamdani fuzzy systems are universal approximators. In: Proceedings of the 2008 Annual Meeting of the North American Fuzzy Information Processing Society. New York City, USA: IEEE, 2008. [149] Ying H. Interval type-2 Takagi-Sugeno fuzzy systems with linear rule consequent are universal approximators. In: Proceedings of the 2009 Annual Meeting of the North American Fuzzy Information Processing Society. Cincinnati, USA: IEEE, 2009. [150] Liu Z, Chen C P L, Zhang Y, Li H X. Type-2 hierarchical fuzzy system for high-dimensional data-based modeling with uncertainties. Soft Computing, 2012, 16(11): 1945−1957 doi: 10.1007/s00500-012-0867-8 [151] Deng Y, Ren Z Q, Kong Y Y, Bao F, Dai Q H. A hierarchical fused fuzzy deep neural network for data classification. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2017, 25(4): 1006−1012 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2016.2574915 -




 下载:
下载: