A Survey on Machine Consciousness
-
摘要:
意识问题是尚未解决的重大哲学问题与科学问题. 机器意识是人工智能最前沿的研究领域之一. 研发意识机器人对于人工智能与机器人学的发展具有重要科学意义与应用价值. 本文首先介绍了意识与感受性的相关概念和理论; 然后, 详细讨论了机器意识的概念与研究分类、实现方法与计算模型, 重点论述了实现机器意识的量子方法; 最后, 总结了机器意识目前面临的困境与未来可能的发展, 并给出了一套机器意识总体实现框架.
Abstract:Consciousness is an unsolved significant philosophical and scientific issue. Machine consciousness is one of the forefront research areas of artificial intelligence, and developing conscious robots is of great scientific significance and application value for artificial intelligence and robotics. In this survey, the concepts and theories of consciousness and qualia are introduced first. Then, the concept and taxonomy, the implementation methods and computational models of machine consciousness are discussed in detail. Especially, the quantum method on implementing machine consciousness is emphasized. Finally, the current difficulties and future development of machine consciousness are summarized; and an overall implementation framework of machine consciousness is proposed.
-
Key words:
- Consciousness /
- machine consciousness /
- conscious robot /
- qualia /
- artificial intelligence
-
表 1 意识的哲学理论
Table 1 Philosophical theories of consciousness
理论名称 英文 主要观点 一元论 Monism 意识或物质是世界的本源 二元论 Dualism 意识和物质都是世界的本源 神秘论 Mysticism 意识是人类自身永远无法理解的 还原论 Reductionism 意识可还原为大脑神经细胞的物理过程 涌现论 Emergentism 意识是大脑神经元整体相互作用涌现出的 泛心论 Panpsychism 意识是物质固有的本质 副现象论 Epiphenomenalism 意识是行为产生的附带现象而不起任何作用 幻觉论 Illusionism 意识是一种幻觉 唯识论 Vijñāptimātratāsiddhi 五蕴八识理论 表 2 意识的科学理论
Table 2 Scientific theories of consciousness
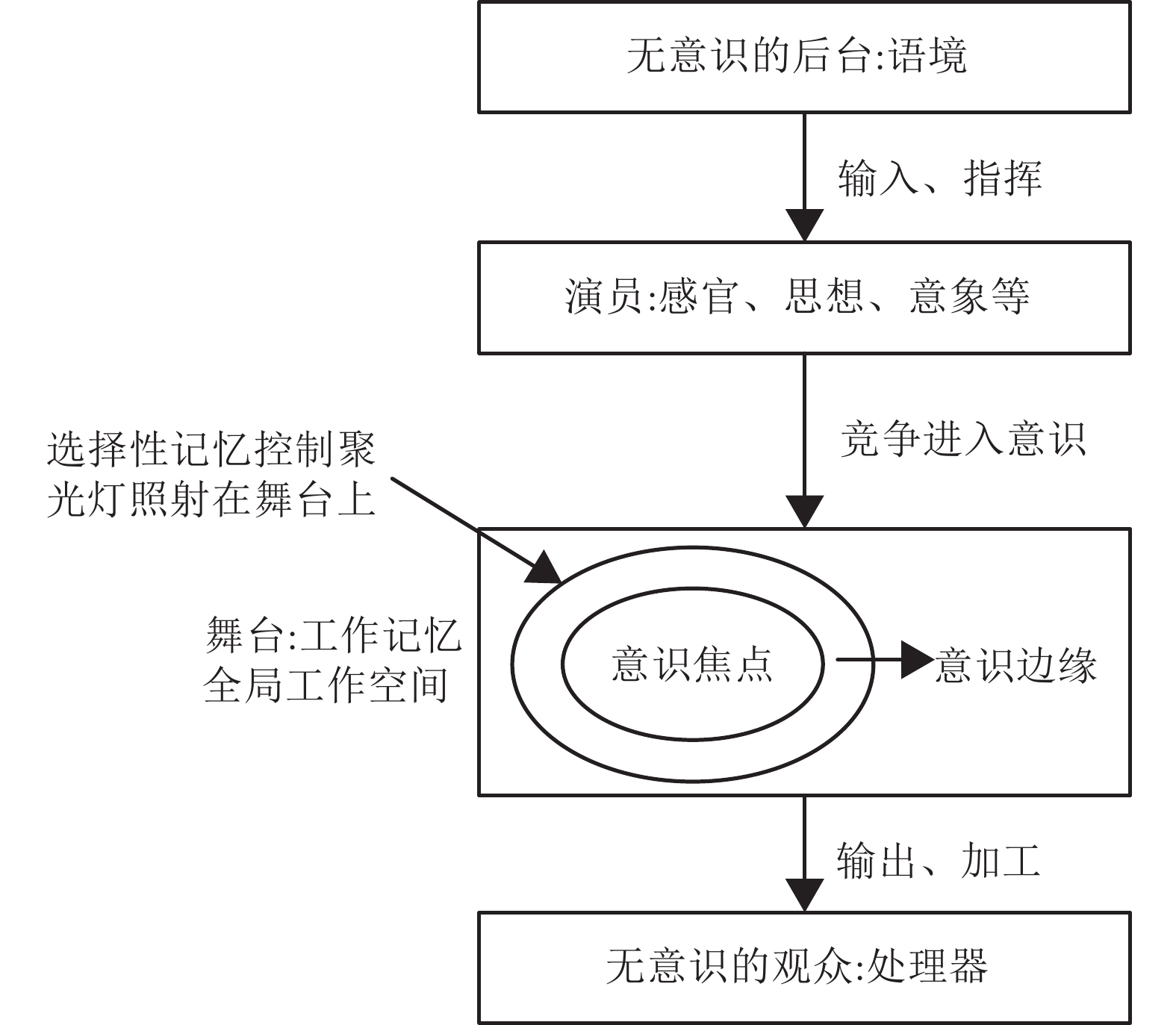
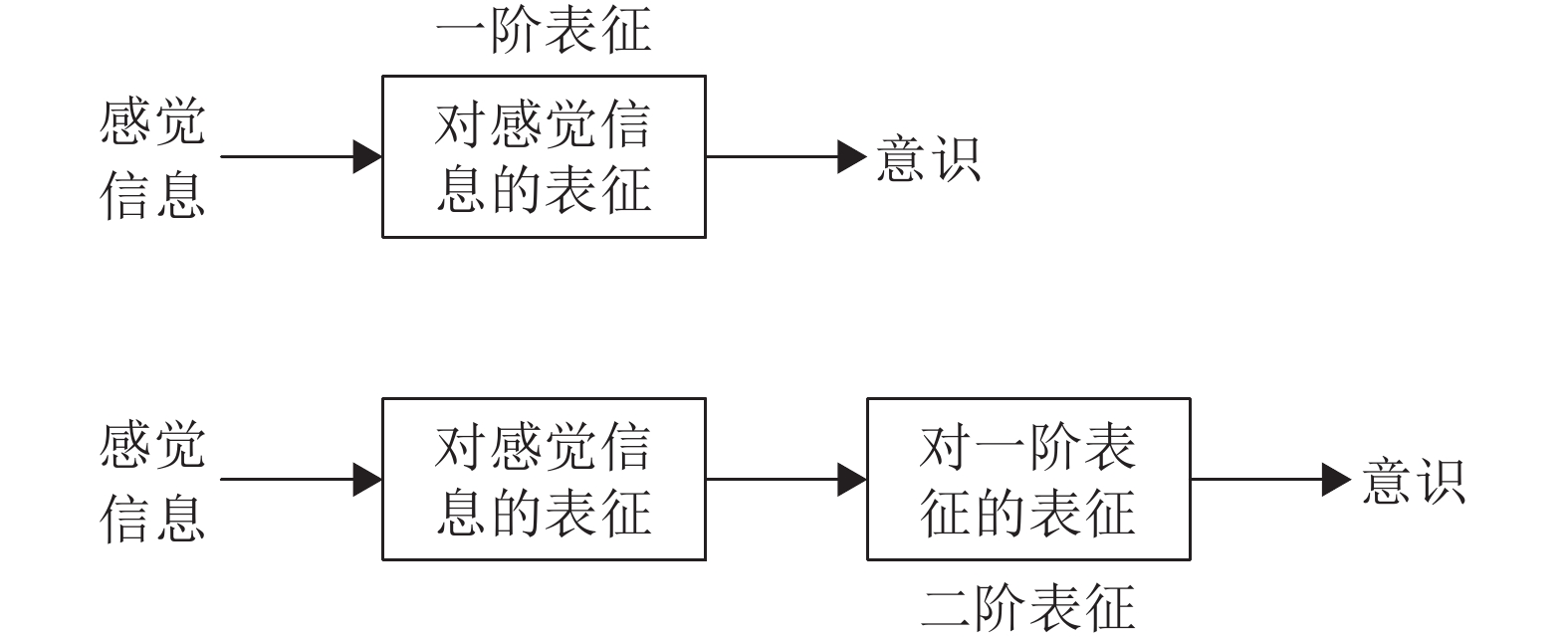
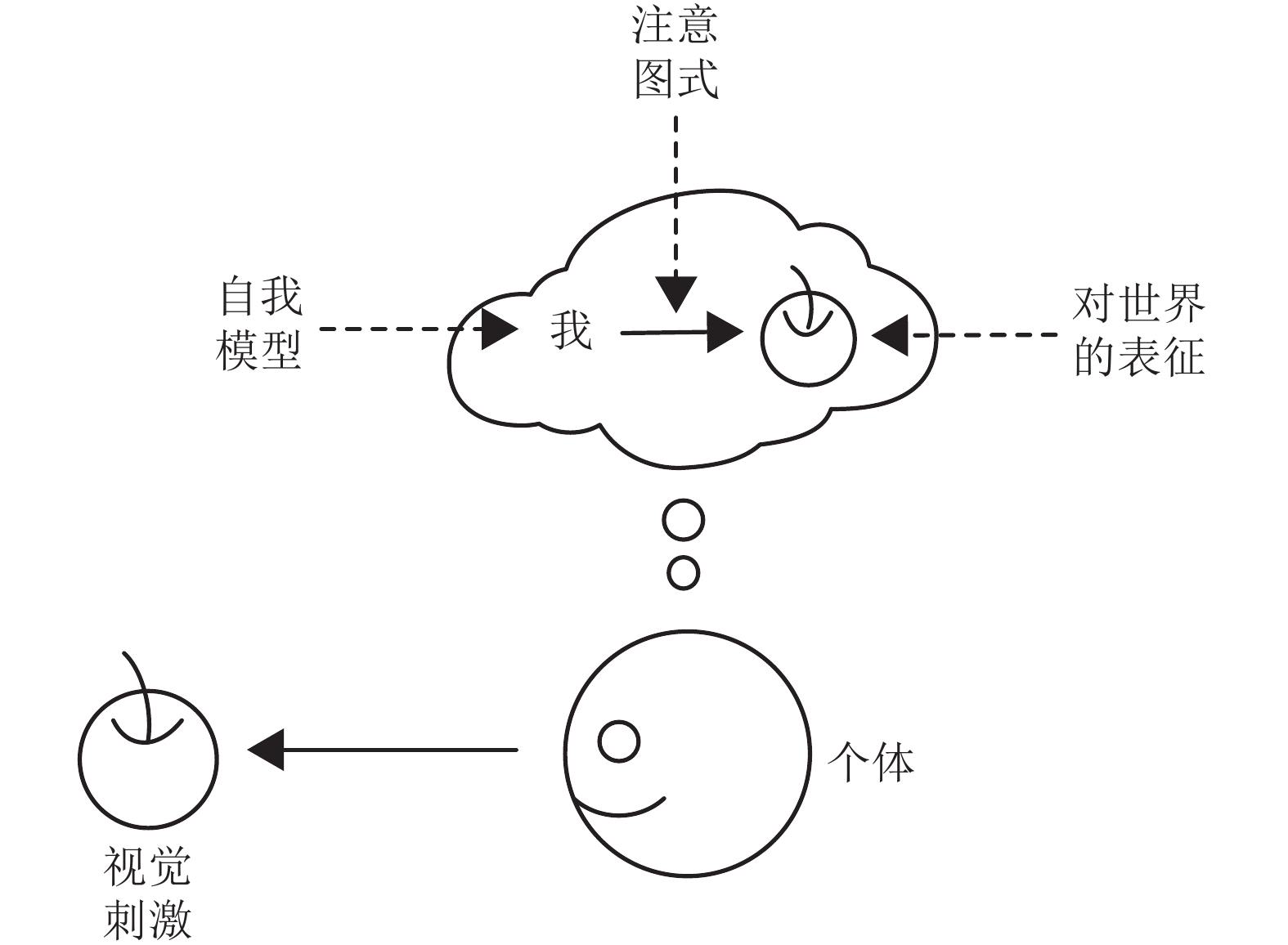
理论名称 英文 简称 提出时间 主要研究者 主要观点 高阶表征理论[31] Higher-order representation theory HOR 1968 Armstrong、Rosenthal 意识由对一阶心理状态的知觉或想法构成 全局工作空间理论[32] Global workspace theory GWT 1988 Baars、Dehaene 意识产生于全局工作空间 多重草稿理论[1] Multiple drafts theory MDT 1991 Dennett 意识产生于大脑中叙事脚本间的竞争 量子意识理论[7] Quantum consciousness QC 1994 Penrose、Hameroff 意识产生于大脑中的量子计算 Damasio意识理论[33] Damasio's theory 无 1999 Damasio 在原我的基础上产生核心意识和扩展意识 动态核心假说[34] Dynamic core hypothesis DCH 2000 Edelman、Tononi 意识产生于时空上高兴奋性的神经集团, 即动态核心 感觉运动理论[35] Sensorimotor theory SMT 2001 O'Regan 意识产生于身体的感觉运动 整合信息理论[36] Integrated information theory IIT 2004 Tononi、Koch 意识产生于大脑对信息的整合 注意图式理论[37] Attention schema theory AST 2013 Graziano 意识产生于注意图式 预测处理理论[38] Predictive processing theory PPT 2013 Clark、Seth 意识产生于大脑对信息的预测 表 3 机器意识研究分类
Table 3 The taxonomy of machine consciousness
类别 问题归属 研究内容 具体分类 研究举例 感知意识 容易 机器通过外部传感器和内部感知模型感知外界各种刺激并产生行为 视觉 图像感知[45] 听觉 声音感知[46] 触觉 皮肤触摸感知[47] 嗅觉 化学物质感知[48] 味觉 化学物质感知[49] 认知意识 容易 构建机器内部认知模型, 使机器具有意识的认知特性及其行为表现 语言 语音识别和表达[50] 想象 梦境与意识[51] 记忆 情景记忆[52] 情感 情感识别和表达[53] 机制意识 容易 研究人类意识的产生机制, 并在此基础上进行机器模拟实现 脑科学研究 意识的神经相关物[54-58] 意识科学理论 GWT[32]、IIT[36]、HOR[31]、AST[37]、QC[7] 机器模拟实现 心智建模[59]、银纳米线神经网络[60]、大脑模型[61] 自我意识 困难 如何使机器具有内省反思能力, 并能意识到“我”是区别于其他个体的存在 自我模拟 机械臂自我建模[15]、“粒子”机器人自我修复[16] 镜像认知 镜像测试[62] 高阶理论 CiceRobot[63]、内部言语[64]、GMU-BICA[65] 其他方面 自我意识模型ARTSELF[66]、本体感受传感器[67] 感受意识 困难 如何使机器具有感受性 能否实现 能实现[68-69]、不能实现[70-71] 实现方法 Aleksander公理系统[72]、感觉运动融合[73]、计算相关物[74]、大脑时空结构[43]、Meme[75]、内稳态[76]、合成现象学[77] 系统开发 交互式教学机器人[78] 意识测试 困难 检测机器是否具有意识, 意识能力程度如何 图灵测试 完全图灵测试[79] 量表 ConsScale量表[80] 表 4 机器意识的实现方法
Table 4 Implementation methods of machine consciousness
实现方法 具体内容 实现机器意识的可能性 符号计算 数理逻辑、计算推理 不可能 人工神经网络 模拟神经元活动机制建模 不可能 生物神经网络 用生物神经元搭建神经网络 有可能 量子计算 根据量子特有性质解释意识并建模 有可能 脑机融合 构造脑机混合的意识机器 有可能 表 5 机器意识的主要理论与计算模型
Table 5 Main theories and computational models of machine consciousness
理论 基本观点 研究内容 研究举例 面临问题 GWT[32] 意识产生于全局工作空间 理论研究 GNWT[89]、GNWT+PPT[90]、GWT+元认知[91]、GWT+SMT+PPT[92] 缺少神经层面的解释[93] 机器实现 LIDA[94-95]、CERA-CRANIUM[96] IIT[36] 意识产生于大脑对信息的整合 理论研究 IIT 3.0[97]、IIT+幻觉论[98]、IIT+QC[99] 计算复杂性、还原论、泛心论[100] 机器实现 工具箱PyPhi[101]、Aleksander公理系统实现[72]、XCR-1[73] HOR[31] 意识由对一阶心理状态的知觉或想法构成 理论研究 SOMA[102]、情感意识高阶理论[103] 意识统一性、无穷倒退[31] 机器实现 Cicerobot[63]、CLARION[104]、GMU-BICA[65]、eBICA[105] AST[37] 意识产生于注意图式 理论研究 理论验证[106]、AST+PPT[107] 理论本身和具体实现方法有待完善[108] 机器实现 注意系统[109]、CONAIM[110] QC[7] 意识产生于大脑中的量子计算 量子与意识的相关性 量子相干、量子叠加、量子纠缠、量子塌缩等[111-112] 缺乏实验证实、量子计算机成本高[7] 大脑中是否存在量子计算 存在[113-114]、不存在[115-116] 建模方法 量子力学的数学形式以及量子逻辑[117-118]、量子计算+经典计算[119-120]、量子计算+神经生物学[121-122] 表 6 量子和意识的可能关联
Table 6 The possible relationship between quantum and consciousness
量子
性质含义 与意识的可能关联 量子
相干粒子之间存在干涉效应 意识统一性的物理基础 量子
叠加粒子可以同时处于多种状态 前意识与潜意识加工、梦与意识改变状态 量子
纠缠粒子间可以存在非局域性关联 联想记忆、非局域性意识关联 量子
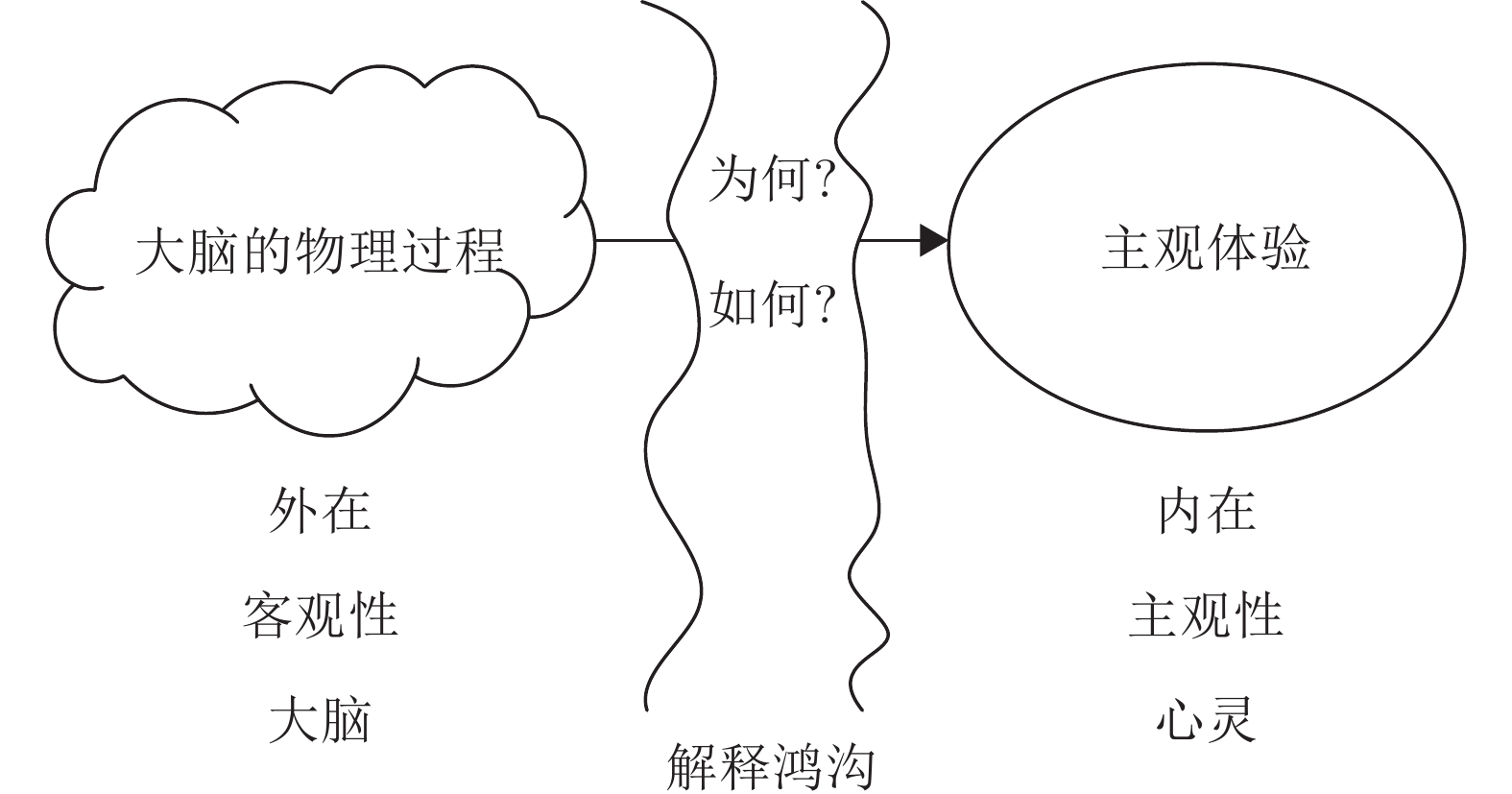
塌缩粒子可从叠加态塌缩到本征态 从前意识到意识的转变 表 7 关于大脑中是否存在量子计算的观点
Table 7 Views on the existence of quantum computing in the brain
表 8 意识量子计算模型的主要构建方法
Table 8 Main methods on constructing quantum computational model of consciousness
表 9 意识机器人实例对比分析
Table 9 Comparative analysis of conscious robot examples
实例 Santos的机器人[95] XCR-1[73] CiceRobot[63] 实验条件 仿真平台V-REP、Pioneer 3-AT虚拟机器人 自制三轮机器人 RWI B21机器人 感知意识 听觉 (声呐) 视觉、听觉、触觉 (压力) 视觉 认知意识 情感表达 (面部表情) 语音识别和表达、情感理解, 选择性注意, 情感记忆 选择性注意、长期记忆 机制意识 GWT IIT HOR 自我意识 无 自我对话、内部言语、内省反思 自我动作想象, 内省反思, 自我预期 感受意识 不考虑 类模态 (amodal) 感受 无 实现方法 机器人操作系统ROS 硬接线神经回路、联想神经网络、信息整合、感觉运动整合 概念层: 概念空间中的几何计算. 语言层: KL-ONE 系统实现的语义网络 认知架构 LIDA HCA 基于 HOR 提出 实现目标 室内虚拟环境移动导航与避障 目标搜寻与检测, 验证 HCA 博物馆导游机器人 主要问题 和意识脑机制的关联不明确 机器人缺少动作的长期记忆 数据量庞大, 动态场景的实时三维重建只能在简单环境下实现 未来改进 真实环境下移动导航与避障 具有更多神经元和突触的神经网络 机器人能够对所有过去经验进行总结 -
[1] Dennett D C. Consciousness Explained. New York, USA: Little, Brown and Company, 1991, 21−21 [2] Miller G. What is the biological basis of consciousness. Science, 2005, 309(5731): 79−79 doi: 10.1126/science.309.5731.79 [3] Koch C. What is consciousness? Nature, 2018, 557(7704): S8−S12 doi: 10.1038/d41586-018-05097-x [4] Koch C, Massimini M, Boly M, Tononi G. Neural correlates of consciousness: progress and problems. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 2016, 17(5): 307−321 doi: 10.1038/nrn.2016.22 [5] Sohn E. Decoding consciousness. Nature, 2019, 571(7766): S2−S5 doi: 10.1038/d41586-019-02207-1 [6] Mashour G A. The controversial correlates of consciousness. Science, 2018, 360(6388): 493−494 doi: 10.1126/science.aat5616 [7] Li T W, Tang H H, Zhu J H, Zhang J H. The finer scale of consciousness: quantum theory. Annals of Translational Medicine, 2019, 7(20): 585 doi: 10.21037/atm.2019.09.09 [8] Gornitz T. Quantum theory and the nature of consciousness. Foundations of Science, 2018, 23(3): 475−510 doi: 10.1007/s10699-017-9536-9 [9] Georgiev D D. Inner privacy of conscious experiences and quantum information. Bio Systems, 2020, 187: 104051 doi: 10.1016/j.biosystems.2019.104051 [10] Angel L. How to Build a Conscious Machine. Boulder, USA: Westview Press, 1989 [11] 周昌乐. 机器意识能走多远: 未来的人工智能哲学. 人民论坛·学术前沿, 2016, 5(13): 81−95Zhou Chang-Le. Prospect of machine consciousness: the future artificial intelligence philosophy. Frontiers, 2016, 5(13): 81−95 [12] Gamez D. Human and Machine Consciousness. Cambridge, United Kingdom: Open Book Publishers, 2018 [13] Dehaene S, Lau H, Kouider S. What is consciousness, and could machines have it? Science, 2017, 358(6362): 486−492 doi: 10.1126/science.aan8871 [14] Carter O, Hohwy J, Van Boxtel J, Lamme V, Block N, Koch C, et al. Conscious machines: defining questions. Science, 2018, 359(6374): 400−400 [15] Kwiatkowski R, Lipson H. Task-agnostic self-modeling machines. Science Robotics, 2019, 4(26): eaau9354 doi: 10.1126/scirobotics.aau9354 [16] Li S G, Batra R, Brown D, Chang H D, Ranganathan N, Hoberman C, et al. Particle robotics based on statistical mechanics of loosely coupled components. Nature, 2019, 567(7748): 361−366 doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1022-9 [17] Graziano M S A, Guterstam A, Bio B J, Wilterson A I. Toward a standard model of consciousness: reconciling the attention schema, global workspace, higher-order thought, and illusionist theories. Cognitive Neuropsychology, 2019 doi: 10.1080/02643294.2019.1670630 [18] Lake B M, Ullman T D, Tenenbaum J B, Gershman S J. Building machines that learn and think like people. Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 2017, 40: e253 doi: 10.1017/S0140525X16001837 [19] Koumpis A, Christoforaki M, Handschuh S. The robot who loved me: building consciousness models for use in human robot interaction following a collaborative systems approach. In: Proceedings of the 19th IFIP WG 5.5 Working Conference on Virtual Enterprises. Cham, Switzerland: Springer Publishing, 2018. 409−416 [20] Chella A, Cangelosi A, Metta G, Bringsjord S. Editorial: consciousness in humanoid robots. Frontiers in Robotics and AI, 2019, 6: 17 doi: 10.3389/frobt.2019.00017 [21] 乔少杰, 韩楠, 丁治明, 金澈清, 孙未未, 舒红平. 多模式移动对象不确定性轨迹预测模型. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(4): 608−618Qiao Shao-Jie, Han Nan, Ding Zhi-Ming, Jin Che-Qing, Sun Wei-Wei, Shu Hong-Ping. A multiple-motion-pattern trajectory prediction model for uncertain moving objects. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(4): 608−618 [22] 曹风魁, 庄严, 闫飞, 杨奇峰, 王伟. 移动机器人长期自主环境适应研究进展和展望. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(2): 205−221Cao Feng-Kui, Zhuang Yan, Yan Fei, Yang Qi-Feng, Wang Wei. Long-term autonomous environment adaptation of mobile robots: state-of-the-art methods and prospects. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(2): 205−221 [23] Qiao S J, Han N, Gao Y J, Li R H, Huang J B, Guo J, et al. A fast parallel community discovery model on complex networks through approximate optimization. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2018, 30(9): 1638−1651 doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2018.2803818 [24] Qiao S J, Han N, Wang J F, Li R H, Gutierrez L A, Wu X D. Predicting long-term trajectories of connected vehicles via the prefix-projection technique. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2018, 19(7): 2305−2315 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2017.2750075 [25] Qiao S J, Han N, Zhou J L, Li R H, Jin C Q, Gutierrez L A. SocialMix: a familiarity-based and preference-aware location suggestion approach. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2018, 68: 192−204 doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2017.11.006 [26] Kügler P. The ever-shifting problem of consciousness. Theory & Psychology, 2013, 23(1): 46−59 [27] De Sousa A. Towards an integrative theory of consciousness: Part 2 (an anthology of various other models). Mens Sana Monographs, 2013, 11(1): 151−209 doi: 10.4103/0973-1229.109341 [28] Chalmers D J. Facing up to the problem of consciousness. Journal of Consciousness Studies, 1995, 2(3): 200−219 [29] Block N. On a confusion about a function of consciousness. Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 1995, 18(2): 227−247 doi: 10.1017/S0140525X00038188 [30] Levine J. Materialism and qualia: the explanatory gap. Pacific Philosophical Quarterly, 1983, 64(4): 354−361 doi: 10.1111/j.1468-0114.1983.tb00207.x [31] Brown R, Lau H, Ledoux J E. Understanding the higher-order approach to consciousness. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 2019, 23(9): 754−768 doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2019.06.009 [32] Baars B. A Cognitive Theory of Consciousness. Cambridge, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press, 1988 [33] Damasio A R. The Feeling of What Happens: Body and Emotion in the Making of Consciousness. San Diego, USA: Harcourt, 1999 [34] Edelman G, Tononi G. A Universe of Consciousness: How Matter Becomes Imagination. New York, USA: Basic books, 2000 [35] O'regan J K. How the sensorimotor approach to consciousness bridges both comparative and absolute explanatory gaps and some refinements of the theory. Journal of Consciousness Studies, 2016, 23(5—6): 39−65 [36] Tononi G. An information integration theory of consciousness. BMC Neuroscience, 2004, 5(1): 42 doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-5-42 [37] Graziano M. Consciousness and the Social Brain. Oxford, United Kingdom: Oxford University Press, 2013 [38] Clark A. Whatever next? predictive brains, situated agents, and the future of cognitive science. Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 2013, 36(3): 181−204 doi: 10.1017/S0140525X12000477 [39] Dennett D C. Facing up to the hard question of consciousness. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 2018, 373(1755): 20170342 doi: 10.1098/rstb.2017.0342 [40] Chalmers D J. The meta-problem of consciousness. Journal of Consciousness Studies, 2018, 25(9-10): 6−61 [41] Holland O, Goodman R. Robots with internal models: a route to machine consciousness? Journal of Consciousness Studies, 2003, 10(4-5): 77−109 [42] 周昌乐, 刘江伟. 机器能否拥有意识-机器意识研究及其意向性分析. 厦门大学学报(哲学社会科学版), 2011, 86(1): 1−8Zhou Chang-Le, Liu Jiang-Wei. Can machines have consciousness? Journal of Xiamen University (Arts & Social Sciences), 2011, 86(1): 1−8 [43] Gamez D. Four preconditions for solving MC4 machine consciousness. In: Proceedings of the 2019 AAAI Spring Symposium: Towards Conscious AI Systems. Palo Alto, USA: Stanford University Press, 2019. 1−6 [44] Jung Y H, Park B, Kim J U, Kim T I. Bioinspired electronics for artificial sensory systems. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(34): 1803637 doi: 10.1002/adma.201803637 [45] Yousef A, Bakr M, Shirani S, Milliken B. An edge detection approach for conscious machines. In: Proceedings of the 9th Annual Information Technology, Electronics and Mobile Communication Conference. Vancouver, Canada: IEEE Press, 2018. 595−596 [46] Eliakim I, Cohen Z, Kosa G, Yovel Y. A fully autonomous terrestrial bat-like acoustic robot. PLOS Computational Biology, 2018, 14(9): e1006406 doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006406 [47] Klimaszewski J, Janczak D, Piorun P. Tactile robotic skin with pressure direction detection. Sensors, 2019, 19(21): 4697 doi: 10.3390/s19214697 [48] Saeed M S, Alim N. Design and implementation of a dual mode autonomous gas leakage detecting robot. In: Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Robotics, Electrical and Signal Processing Techniques. Dhaka, Bangladesh: IEEE Press, 2019. 79−84 [49] Ciui B, Martin A, Mishra R K, Nakagawa T, Dawkins T J, Lyu M, et al. Chemical sensing at the robot fingertips: toward automated taste discrimination in food samples. Acs Sensors, 2018, 3(11): 2375−2384 doi: 10.1021/acssensors.8b00778 [50] Davila-Chacon J, Liu J D, Wermter S. Enhanced robot speech recognition using biomimetic binaural sound source localization. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2019, 30(1): 138−150 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2830119 [51] Pagel J F, Kirshtein P. Machine Dreaming and Consciousness. Cambridge, USA: Academic Press, 2017 [52] Balkenius C, Tjøstheim T A, Johansson B, Gärdenfors P. From focused thought to reveries: a memory system for a conscious robot. Frontiers in Robotics and AI, 2018, 5: 29 doi: 10.3389/frobt.2018.00029 [53] Yang J, Wang R, Guan X, Hassan M M, Almogren A, Alsanad A. AI-enabled emotion-aware robot: the fusion of smart clothing, edge clouds and robotics. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2020, 102: 701−709 doi: 10.1016/j.future.2019.09.029 [54] Förster J, Koivisto M, Revonsuo A. ERP and MEG correlates of visual consciousness: the second decade. Consciousness and Cognition, 2020, 80: 102917 doi: 10.1016/j.concog.2020.102917 [55] Paul E S, Sher S, Tamietto M, Winkielman P, Mendl M T. Towards a comparative science of emotion: affect and consciousness in humans and animals. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 2020, 108: 749−770 [56] Keromnes G, Chokron S, Celume M-P, Berthoz A, Botbol M, Canitano R, et al. Exploring self-consciousness from self- and other-image recognition in the mirror: concepts and evaluation. Frontiers in Psychology, 2019, 10: 719 doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.00719 [57] Nani A, Manuello J, Mancuso L, Liloia D, Costa T, Cauda F. The neural correlates of consciousness and attention: two sister processes of the brain. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 2019, 13: 1169 doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.01169 [58] Zhao T, Zhu Y Q, Tang H L, Xie R, Zhu J H, Zhang J H. Consciousness: new concepts and neural networks. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience, 2019, 13: 302 doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00302 [59] Shi Z Z, Ma G, Li J Q. Machine consciousness of mind model CAM. In: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Knowledge Management in Organizations. Cham, Switzerland: Springer Publishing, 2017. 16−26 [60] Diaz-Alvarez A, Higuchi R, Sanz-Leon P, Marcus I, Shingaya Y, Stieg A Z, et al. Emergent dynamics of neuromorphic nanowire networks. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9: 14920 doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-51330-6 [61] Wang Y X, Lu J H, Gavrilova M, Fiorini R A, Kacprzyk J. Brain-inspired systems (BIS): cognitive foundations and applications. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics. Miyazaki, Japan: IEEE Press, 2018. 995−1000 [62] Zeng Y, Zhao Y X, Bai J, Xu B. Toward robot self-consciousness (Ⅱ): brain-inspired robot bodily self model for self-recognition. Cognitive Computation, 2018, 10(2): 307−320 doi: 10.1007/s12559-017-9505-1 [63] Chella A, Macaluso I. The perception loop in CiceRobot, a museum guide robot. Neurocomputing, 2009, 72(4—6): 760−766 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2008.07.011 [64] Chella A, Pipitone A. A cognitive architecture for inner speech. Cognitive Systems Research, 2020, 59: 287−292 doi: 10.1016/j.cogsys.2019.09.010 [65] Samsonovich A V, De Jong K A, Kitsantas A. The mental state formalism of GMU-BICA. International Journal of Machine Consciousness, 2009, 1(1): 111−130 doi: 10.1142/S1793843009000116 [66] Subagdja B, Tan A H, Aaai. Towards a brain inspired model of self-awareness for sociable agents. In: Proceedings of the 31th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Palo Alto, USA: AAAI Press, 2017. 4452−4458 [67] Rodriguez I, Astigarraga A, Ruiz T, Lazkano E. Body self-awareness for social robots. In: Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Control, Artificial Intelligence, Robotics & Optimization. Prague, Czechoslovakia: IEEE Press, 2017. 69−73 [68] Garcia-Banos A. A computational theory of consciousness: qualia and the hard problem. Kybernetes, 2019, 48(5): 1078−1094 doi: 10.1108/K-10-2017-0387 [69] Koch C, Tononi G. Can we quantify machine consciousness? Brainlike circuitry might one day endow some computers with awareness-here's how we'd know. IEEE Spectrum, 2017, 54(6): 64−69 doi: 10.1109/MSPEC.2017.7934235 [70] Longinotti D. Agency, qualia and life: Connecting mind and body biologically. In: Proceedings of the 3rd Conference on Philosophy and Theory of Artificial Intelligence. Cham, Switzerland: Springer Publishing, 2018. 43−56 [71] Pandey S C. Can artificially intelligent agents really be conscious? Sādhanā, 2018, 43(7): 110 doi: 10.1007/s12046-018-0887-x [72] Aleksander I. Partners of humans: A realistic assessment of the role of robots in the foreseeable future. Journal of Information Technology, 2017, 32(1): 1−9 doi: 10.1057/s41265-016-0032-4 [73] Haikonen P O. Consciousness and Robot Sentience. 2nd Edition. Singapore: World Scientific, 2019 [74] Reggia J A, Monner D, Sylvester J. The computational explanatory gap. Journal of Consciousness Studies, 2014, 21(9-10): 153−178 [75] Blackmore S. Decoding the puzzle of human consciousness: the hardest problem. Scientific American, 2018, 319(3): 49−53 [76] Man K, Damasio A. Homeostasis and soft robotics in the design of feeling machines. Nature Machine Intelligence, 2019, 1(10): 446−452 doi: 10.1038/s42256-019-0103-7 [77] Chrisley R. Synthetic phenomenology. International Journal of Machine Consciousness, 2009, 1(01): 53−70 doi: 10.1142/S1793843009000074 [78] Tojo T, Ono O, Noh N B M, Yusof R. Interactive tutor robot for collaborative e-learning system. Electrical Engineering in Japan, 2018, 203(3): 22−29 doi: 10.1002/eej.23073 [79] Schweizer P. Could there be a turing test for qualia? In: Proceedings of the 2012 AISB/IACAP World Congress. Brighton, United Kingdom: The Society for the Study of Artificial Intelligence and the Simulation of Behaviour, 2012. 41−48 [80] Arrabales R, Ledezma A, Sanchis A. ConsScale: a pragmatic scale for measuring the level of consciousness in artificial agents. Journal of Consciousness Studies, 2010, 17(3—4): 131−164 [81] Takeno J. Creation of a Conscious Robot: Mirror Image Cognition and Self-awareness. Singapore: Pan Stanford Publishing, 2012 [82] Diaz J L. Self-consciousness: an I-World patterned process model. Adaptive Behavior, 2018, 26(5): 211−223 doi: 10.1177/1059712318783434 [83] Elamrani A, Yampolskiy R V. Reviewing tests for machine consciousness. Journal of Consciousness Studies, 2019, 26(5-6): 35−64 [84] Pennartz C M A, Farisco M, Evers K. Indicators and criteria of consciousness in animals and intelligent machines: an inside-out approach. Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience, 2019, 13: 25 doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2019.00025 [85] Nazri A, Abd Ghani A A, Hafez I, Ng K-Y. A new theoretical framework for testing consciousness in a machine. In: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Soft Computing and Data Mining. Cham, Switzerland: Springer Publishing, 2018. 330−339 [86] 吴朝晖, 俞一鹏, 潘纲, 王跃明. 脑机融合系统综述. 生命科学, 2014, 26(6): 645−649Wu Zhao-Hui, Yu Yi-Peng, Pan Gang, Wang Yue-Ming. Brain-machine integrated systems. Chinese Bulletin of Life Sciences, 2014, 26(6): 645−649 [87] Shanechi M M. Brain-machine interfaces from motor to mood. Nature Neuroscience, 2019, 22(10): 1554−1564 doi: 10.1038/s41593-019-0488-y [88] Wu Z H, Zhou Y D, Shi Z Z, Zhang C S, Li G L, Zheng X X, et al. Cyborg intelligence: recent progress and future directions. IEEE Intelligent Systems, 2016, 31(6): 44−50 doi: 10.1109/MIS.2016.105 [89] Dehaene S, Kerszberg M, Changeux J P. A neuronal model of a global workspace in effortful cognitive tasks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1998, 95(24): 14529−14534 doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.24.14529 [90] Whyte C J. Integrating the global neuronal workspace into the framework of predictive processing: towards a working hypothesis. Consciousness and Cognition, 2019, 73: 102763 doi: 10.1016/j.concog.2019.102763 [91] Shea N, Frith C D. The global workspace needs metacognition. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 2019, 23(7): 560−571 doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2019.04.007 [92] Jeczminska K. Global workspace theory and sensorimotor theory unified by predictive processing. Journal of Consciousness Studies, 2017, 24(7-8): 79−105 [93] Van Der Velde F. In situ representations and access consciousness in neural blackboard or workspace architectures. Frontiers in Robotics and AI, 2018, 5: 32 doi: 10.3389/frobt.2018.00032 [94] Franklin S, Madl T, D'mello S, Snaider J. LIDA: a systems-level architecture for cognition, emotion, and learning. IEEE Transactions on Autonomous Mental Development, 2014, 6(1): 19−41 doi: 10.1109/TAMD.2013.2277589 [95] Santos D H, Palar P S, Oliveira A S D, Fabro J A, Becker T. Adding conscious aspects and simulated emotions through facial expressions in virtual robot navigation with Baars-Franklins cognitive architecture. In: Proceedings of the 2018 Latin American Robotic Symposium, 2018 Brazilian Symposium on Robotics and 2018 Workshop on Robotics in Education. Joao Pessoa, Brazil: IEEE Press, 2018. 370−375 [96] Arrabales R, Muñoz J, Ledezma A, Gutierrez G, Sanchis A. A machine consciousness approach to the design of human-like bots, Hingston P, editor, Believable Bots: Can Computers Play Like People? Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Publishing, 2013: 171−191 [97] Oizumi M, Albantakis L, Tononi G. From the phenomenology to the mechanisms of consciousness: integrated information theory 3.0. Plos Computational Biology, 2014, 10(5): e1003588 doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003588 [98] McQueen K J. Illusionist integrated information theory. Journal of Consciousness Studies, 2019, 26(5—6): 141−169 [99] McQueen K J. Interpretation-neutral integrated information theory. Journal of Consciousness Studies, 2019, 26(1—2): 76−106 [100] Doerig A, Schurger A, Hess K, Herzog M H. The unfolding argument: Why ⅡT and other causal structure theories cannot explain consciousness. Consciousness and Cognition, 2019, 72: 49−59 doi: 10.1016/j.concog.2019.04.002 [101] Mayner W G P, Marshall W, Albantakis L, Findlay G, Marchman R, Tononi G. PyPhi: a toolbox for integrated information theory. Plos Computational Biology, 2018, 14(7): e1006343 doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006343 [102] Cleeremans A, Achoui D, Beauny A, Keuninckx L, Martin J-R, Munoz-Moldes S, et al. Learning to be conscious. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 2019, 24(2): 112−123 [103] Ledoux J E, Brown R. A higher-order theory of emotional consciousness. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2017, 114(10): E2016−E2025 doi: 10.1073/pnas.1619316114 [104] Sun R. The CLARION cognitive architecture: toward a comprehensive theory of mind, Chipman S F, editor, The Oxford Handbook of Cognitive Science, Oxford, United Kingdom: Oxford University Press, 2017: 117−134 [105] Samsonovich A V. Socially emotional brain-inspired cognitive architecture framework for artificial intelligence. Cognitive Systems Research, 2020, 60: 57−76 doi: 10.1016/j.cogsys.2019.12.002 [106] van den Boogaard E, Treur J, Turpijn M. A neurologically inspired network model for Graziano's attention schema theory for consciousness. In: Proceedings of the 2017 International Work-Conference on the Interplay Between Natural and Artificial Computation. Cham, Switzerland: Springer Publishing, 2017. 10−21 [107] Dolega K, Dewhurst J. Bayesian frugality and the representation of attention. Journal of Consciousness Studies, 2019, 26(3-4): 38−63 [108] Graziano M S A. The attention schema theory: a foundation for engineering artificial consciousness. Frontiers in Robotics and AI, 2017, 4: 60 doi: 10.3389/frobt.2017.00060 [109] Lanillos P, Ferreira J F, Dias J. Designing an artificial attention system for social robots. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Hamburg, Germany: IEEE Press, 2015. 4171−4178 [110] Da Silva Simoes A, Colombini E L, Ribeiro C H C. CONAIM: a conscious attention-based integrated model for human-like robots. IEEE Systems Journal, 2017, 11(3): 1296−1307 doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2015.2498542 [111] Simon C. Can quantum physics help solve the hard problem of consciousness? Journal of Consciousness Studies, 2019, 26(5-6): 204−218 [112] Woolf N J, Hameroff S R. A quantum approach to visual consciousness. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 2001, 5(11): 472−478 doi: 10.1016/S1364-6613(00)01774-5 [113] Hameroff S, Penrose R. Consciousness in the universe: a review of the 'Orch OR' theory. Physics of Life Reviews, 2014, 11(1): 39−78 doi: 10.1016/j.plrev.2013.08.002 [114] Pitkänen M. New results about microtubules as quantum systems. Journal of Nonlocality, 2014, 3(1): 1−18 [115] Tegmark M. Why the brain is probably not a quantum computer. Information Sciences, 2000, 128(3-4): 155−179 doi: 10.1016/S0020-0255(00)00051-7 [116] Baars B J, Edelman D B. Consciousness, biology and quantum hypotheses. Physics of Life Reviews, 2012, 9(3): 285−294 doi: 10.1016/j.plrev.2012.07.001 [117] Mahanti S, Das S, Behera B K, Panigrahi P K. Quantum robots can fly; play games: an IBM quantum experience. Quantum Information Processing, 2019, 18(7): 219 doi: 10.1007/s11128-019-2332-4 [118] Toffano Z, Dubois F. Quantum eigenlogic observables applied to the study of fuzzy behaviour of Braitenberg vehicle quantum robots. Kybernetes, 2019, 48(10): 2307−2324 doi: 10.1108/K-11-2018-0603 [119] Jeswal S K, Chakraverty S. Recent developments and applications in quantum neural network: A review. Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering, 2019, 26(4): 793−807 doi: 10.1007/s11831-018-9269-0 [120] Zhang W R. Programming the mind and decrypting the universe-a bipolar quantum-neuro-fuzzy associative memory model for quantum cognition and quantum intelligence. In: Proceedings of the 2017 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks. Anchorage, USA: IEEE Press, 2017. 1180−1187 [121] Adamski A G. Role of Bose-Einstein condensate and bioplasma in shaping consciousness. Neuroquantology, 2016, 14(1): 36−44 [122] Qazi W M, Ware J A, Bukhari S T S, Athar A. NiHA: a conscious agent. In: Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Advanced Cognitive Technologies and Applications. Wilmington, USA: IARIA XPS Press, 2018. 78−87 [123] Shi Z Z, Huang Z Q. Cognitive model of brain-machine integration. In: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Artificial General Intelligence. Cham, Switzerland: Springer Publishing, 2019. 168−177 [124] Schweizer P. Artificial brains and hybrid minds. In: Proceedings of the 3rd Conference on Philosophy and Theory of Artificial Intelligence. Cham, Switzerland: Springer Publishing, 2018. 81−91 [125] Romano D, Donati E, Benelli G, Stefanini C. A review on animal-robot interaction: from bio-hybrid organisms to mixed societies. Biological Cybernetics, 2019, 113(3): 201−225 doi: 10.1007/s00422-018-0787-5 [126] Lorrimar V. Mind uploading and embodied cognition: a theological response. Zygon, 2019, 54(1): 191−206 doi: 10.1111/zygo.12481 [127] Lee J. Brain-computer interfaces and dualism: a problem of brain, mind, and body. AI & Society, 2016, 31(1): 29−40 [128] Reggia J A. The rise of machine consciousness: studying consciousness with computational models. Neural Networks, 2013, 44: 112−131 doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2013.03.011 [129] Manzotti R, Chella A. Good old-fashioned artificial consciousness and the intermediate level fallacy. Frontiers in Robotics and AI, 2018, 5: 39 doi: 10.3389/frobt.2018.00039 [130] Tononi G, Boly M, Massimini M, Koch C. Integrated information theory: from consciousness to its physical substrate. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 2016, 17(7): 450−461 doi: 10.1038/nrn.2016.44 [131] Rosenthal D M. Higher-order thoughts and the appendage theory of consciousness. Philosophical Psychology, 1993, 6(2): 155−166 doi: 10.1080/09515089308573085 [132] Lau H, Rosenthal D. Empirical support for higher-order theories of conscious awareness. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 2011, 15(8): 365−373 doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2011.05.009 [133] Chella A, Frixione M, Gaglio S. A cognitive architecture for robot self-consciousness. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine, 2008, 44(2): 147−154 doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2008.07.003 [134] Chella A, Lanza F, Pipitone A, Seidita V. Knowledge acquisition through introspection in human-robot cooperation. Biologically Inspired Cognitive Architectures, 2018, 25: 1−7 doi: 10.1016/j.bica.2018.07.016 [135] Hameroff S, Penrose R. Orchestrated objective reduction of quantum coherence in brain microtubules: the “Orch OR” model for consciousness. Mathematics and Computer Simulation, 1996, 40(3-4): 453−480 doi: 10.1016/0378-4754(96)80476-9 [136] Majumder D D, Karan S. Quantum computing: a nano scale information processing in minds and machines. In: Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Recent Trends in Information Systems. Kolkata, India: IEEE Press, 2011. 1−6 [137] Yan F, Iliyasu A M, Jiao S H, Yang H M. Quantum structure for modelling emotion space of robots. Applied Sciences-Basel, 2019, 9(16): 3351 doi: 10.3390/app9163351 [138] Biamonte J, Wittek P, Pancotti N, Rebentrost P, Wiebe N, Lloyd S. Quantum machine learning. Nature, 2017, 549(7671): 195−202 doi: 10.1038/nature23474 [139] Abdulridha H M, Hassoun Z A. Control design of robotic manipulator based on quantum neural network. Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control, 2018, 140(6): 061002 doi: 10.1115/1.4038492 [140] Amoroso R. Engineering a conscious computer. In: Proceedings of the 4th Workshop on Physics and Computation. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier, 1996. 12−16 [141] Raghuvanshi A, Fan Y, Woyke M, Perkowski M. Quantum robots for teenagers. In: Proceedings of the 37th International Symposium on Multiple-Valued Logic. Oslo, Norway: IEEE Press, 2007. 18−25 [142] Kak S. On quantum neural computing. Information Sciences, 1995, 83(3—4): 143−160 doi: 10.1016/0020-0255(94)00095-S [143] Peruš M, Loo C K. Biological and Quantum Computing for Human Vision: Holonomic Models and Applications. Hershey, USA: IGI Global, 2011 [144] Mallakin A. An integration of deep learning and neuroscience for machine consciousness. Global Journal of Computer Science and Technology, 2019, 19(1): 21−29 [145] 林景栋, 吴欣怡, 柴毅, 尹宏鹏. 卷积神经网络结构优化综述. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(1): 24−37Lin Jing-Dong, Wu Xin-Yi, Chai Yi, Yin Hong-Peng. Structure optimization of convolutional neural networks: A survey. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(1): 24−37 [146] 林懿伦, 戴星原, 李力, 王晓, 王飞跃. 人工智能研究的新前线: 生成式对抗网络. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(5): 775−792Lin Yi-Lun, Dai Xing-Yuan, Li Li, Wang Xiao, Wang Fei-Yue. The new frontier of AI research: Generative adversarial networks. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(5): 775−792 [147] 张鲁宁, 左信, 刘建伟. 零样本学习研究进展. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(1): 1−23Zhang Lu-Ning, Zuo Xin, Liu Jian-Wei. Research and development on zero-shot learning. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(1): 1−23 [148] Kriegman S, Blackiston D, Levin M, Bongard J. A scalable pipeline for designing reconfigurable organisms. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2020, 117(4): 1853−1859 doi: 10.1073/pnas.1910837117 -




 下载:
下载: