-
摘要: 利用无人机载的热红外图像开展行人及车辆检测, 在交通监控、智能安防、防灾应急等领域中, 具有巨大的应用潜力. 热红外图像能够在夜间或者光照条件不理想的情况对场景目标清晰成像, 但也往往存在对比度低、纹理特征弱的缺点. 为此, 本文提出使用热红外图像的显著图来进行图像增强, 作为目标检测器的注意力机制, 并研究仅使用热红外图像和其显著图提高目标检测性能的方法. 此外, 针对无人机内存不足、算力有限的特点, 设计使用轻量化网络YOLOv3-MobileNetv2作为目标检测模型. 在实验中, 本文训练了YOLOv3网络作为检测的评价基准网络. 使用BASNet生成显著图, 通过通道替换和像素级加权融合两种方案将热红外图像与其对应的显著图进行融合增强, 比较了不同方案下YOLOv3-MobileNetv2模型的检测性能. 统计结果显示, 行人及车辆的平均精确度(Average precision, AP)相对于基准分别提升了6.7%和5.7%, 同时检测速度提升了60%, 模型大小降低了58%. 该算法模型为开拓无人机载热红外图像的应用领域提供了可靠的技术支撑.
-
关键词:
- 显著图 /
- 无人机 /
- 热红外图像 /
- 目标检测 /
- YOLOv3-MobileNetv2
Abstract: Using thermal images obtained from unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) for pedestrian and vehicle detection has great potential in the fields of traffic monitoring, intelligent security, disaster prevention, and emergency response. Thermal images can clearly observe objects at night or under bad lighting conditions, but they also have the disadvantages of low contrast and weak texture features. For these reasons, this paper proposes to use the saliency map of the thermal image for image enhancement as the attention mechanism of the object detector. The technology to improve the performance of object detection using only thermal images and their saliency maps is studied. In addition, considering the computing power of UAV platforms, a lightweight network YOLOv3-MobileNetv2 was designed as the object detection model. In the paper, YOLOv3 network is trained as a detection benchmark; BASNet is used to generate saliency maps. We fuse thermal images with their corresponding saliency maps through channel replacement and pixel-level weighted fusion schemes. In our experiments, the detection performances of YOLOv3-MobileNetv2 model with different schemes are compared. The statistical results show that the average precision (AP) of pedestrians and vehicles are increased by 6.7% and 5.7% respectively, compared with the benchmark. The detection speed is increased by 60%, while the model size is reduced by 58%. This model provides reliable technical support for the application of thermal images with UAV platforms.-
Key words:
- Saliency map /
- unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) /
- thermal image /
- object detection /
- YOLOv3-MobileNetv2
-
近年来, 以无人机(Unmanned aerial vehicles, UAV)为平台的图像获取和处理技术在交通、安防和环保等领域得到快速发展. 彩色图像在理想光照条件下, 对目标检测有很好的效果, 可以较容易地利用深度学习技术找到图像中兴趣目标的具体位置并识别其类别. 然而, 在夜间或缺乏足够光照的情况下, 基于彩色图像的目标检测往往难以达到预期效果, 容易造成漏检或误检. 红外相机非常适合在这种条件下成像, 因为它们能感应到目标物发出的辐射且不受光照条件的限制. 面向行人和车辆检测的需求, 本文研究一种适用于以无人机为平台获取的热红外图像数据智能处理算法.
相比于彩色图像, 热红外图像有着对比度低、纹理特征弱等缺点. 因此, 在彩色图像和热红外图像之间存在明显的互补. 为了开发这种互补的潜力, 相关学者做了大量的工作来构建融合彩色和热红外图像的数据结构[1]. 但是彩色−热红外图像对并不总是可用的, 因为它们实时同步成像的成本很高, 而且数据处理前还需要图像配准准确, 图像错位还会降低检测器的性能. 这些原因促使本文探索只使用热红外图像来进行目标检测的机制. 为了解决热红外图像中目标检测的难题, 本文提出使用显著图来进行图像增强. 文献[2]通过在颜色、方向、运动和深度上与周围环境的不同来定义特定位置的显著性. 在一个场景中寻找显著物体可以理解为一种视觉注意机制, 它突出了给定场景中属于显著物体的像素. 因此, 本文假设显著图和热红外图像结合将帮助提升目标检测模型的性能. 为验证此假设, 首先通过训练一个YOLOv3目标检测模型[3]来建立评价参考基准, 它仅使用制作的热红外图像数据集来检测目标. 然后, 使用BASNet[4]生成显著图融合热红外图像, 在此基础上训练目标检测模型. 此外, 由于深度显著性网络需要对显著性对象进行像素级标注, 因此实验中使用行人及车辆的像素级掩膜对制作的热红外图像数据集进行标注, 以方便对显著性目标检测的研究.
针对无人机平台内存和算力的局限性, 本文设计了YOLOv3-MobileNetv2网络, 利用轻量化网络MobileNetv2[5]替代YOLOv3原有的特征提取网络DarkNet53, 在大量减少网络参数的同时显著提升运行速度. 此外, 使用Focal loss[6]改进YOLOv3原有的损失函数, 解决正负样本不均衡问题, 使得网络专注于困难样本的计算.
本文的主要贡献如下:
1)首次将显著图用于提高无人机视角下的热红外图像目标检测性能, 通过设计不同的融合方案, 深入分析了显著图对热红外图像中行人及车辆目标检测的影响.
2)以轻量化网络YOLOv3-MobileNetv2改进原有模型, 在平均精确度、模型尺寸和检测速度方面取得了很好的平衡, 即在计算资源和存储资源有限的情况下实现了最优的精度, 将卷积神经网络(Convolutional neural network, CNN)[7]更好地应用于无人机场景中.
1. 相关工作
目前, 较少有论文探讨利用无人机结合热成像技术进行目标检测的深度学习方法. 本节回顾了在目标检测、显著性检测以及模型压缩和加速等领域的相关工作.
1.1 目标检测
在过去的20年里, 大量的研究工作致力于彩色图像中的行人及车辆检测. 于雪松等[8]针对人体运动跟踪领域中的自遮挡现象, 提出了一种基于概率模型的行人四肢自遮挡检测算法. 该算法通过马尔科夫模型和椭圆肤色模型将行人四肢自遮挡状态的识别转换为计算自遮挡状态转换概率的过程. 实验表明, 该方法具有较高的准确性. Dollár等[9]提出了采用积分通道特征(Integral channel feature, ICF)和Boosting算法相结合的方法, 提升了车辆检测的效果. 与传统的检测算法相比, 近几年CNN在目标检测上取得了重大的突破. 基于CNN的目标检测算法主要分为两大类: 一阶和二阶目标检测算法. 它们之间的主要区别在于是否存在提取候选区域的级联模块. 二阶目标检测算法中具有代表性的是R-CNN (Region CNN)系列检测算法[10-12], 它们通过使用级联模块可以使网络有针对性地检测疑似目标区域的物体, 但由于多了这样的级联模块, 提升精度的同时会使得模型的复杂度升高, 在检测速度上低于一阶检测算法, 不适用于无人机上的实时目标检测. 一阶目标检测算法虽然在检测精度上表现欠佳, 但其检测速度非常快. 其中最具有代表性的是Redmon等[13-14]提出的YOLO (You only look once)系列目标检测算法, 该算法将图像划分成
$S\times S$ 的格子, 每个格子负责目标中心在该格子的目标检测, 利用回归思想同时完成检测与识别. 基于此, 本文采用YOLOv3算法作为无人机载热红外图像中行人及车辆目标检测识别的基础模型.近年来, 基于无人机的交通监控系统研究十分活跃. Ruhé 等[15]使用无人机采集了城市道路车辆信息, 结合地理信息系统(Geographic information system, GIS)平台, 对地面交通状况进行预测, 完成流量、车速等信息的提取. 文献[16]通过安装在高架平台上的摄像机模拟无人机的视角, 提出一种基于Haar特征的人体部位检测器. 为提高无人机道路检测的实时性和鲁棒性, 文献[17]提出一种基于改进的图割(Graph cut)算法的道路检测方法, 针对航拍图像各个区域具有不同对比度的特点, 将单一的图像全局对比度矩阵替换为局部对比度矩阵.
随着热红外成像技术的广泛应用, 越来越多的研究专注于利用热红外图像实现对行人及车辆的有效检测. 热红外图像与普通的可见光图像相比差异明显, 热红外图像有着纹理特征不明显、成像对比度低、噪声较多等特点, 这些物理特性使得热红外场景下的目标检测一直都具有挑战性. 针对这一问题, 目前的主流方法是将热红外图像和可见光图像融合, 结合两种图像互补性优势, 获得对于场景全面准确的图像描述. 张秀伟等[18]提出了一种基于Co-motion的可见光与热红外图像序列自动融合方法, 引入Co-motion运动统计特征来解决异源图像序列融合问题, 从而避开了异源图像相似图像特征提取和精确运动检测的难题. Li等在文献[19]中设计了光照感知的神经网络, 它自适应地融合了彩色和热红外子网络, 并根据光照条件采用加权方案融合结果. 在文献[20]中, 作者引入了区域重建网络, 利用CNN对可见光与热红外数据之间的关系进行建模, 然后将这些特征输入到多尺度检测网络中进行鲁棒的目标检测.
然而, 可见光对光照变化以及其他环境影响较为敏感, 尤其是在夜间, 采用可见光获取图像的方法将完全不可用, 故可见光与热红外图像融合也无从谈起. 此外, 同时获取同一场景的可见光与热红外图像需要两种不同的传感器, 图像采集过程较为复杂, 对设备要求较高. 在此背景下, 本文研究仅使用热红外图像进行目标检测, 在克服夜间低能见度并实现全天候检测的同时, 简化检测过程, 通过算法的优化提高检测效果.
1.2 显著性检测
显著性目标检测的目的是突出图像中最明显的目标区域, 它可以引导机器视觉系统将有限的资源分配给少数几个显著区域, 为后续的视觉处理提供极大的便利. 从理论研究的层面来说, 可以把图像的显著性检测研究分为两大方向, 即数据驱动的显著性检测和目标驱动的显著性检测. 数据驱动的图像显著性区域检测算法主要关注由图像底层特征本身所引起的视觉刺激, 这类算法由内部数据驱动, 与目标任务无关. 与此相反, 目标驱动的显著性检测算法主要关注与任务相关的图像内容, 显著性检测的结果受到检测任务的决定性支配.
Itti等[21]最早提出认知视觉注意模型, 该模型提取场景中的特征显著图并采用线性合并的方式整合为总显著图, 以赢者通吃(Winner takes all)和返回抑制相结合的方式来引导视觉注意焦点的选择和转移. Hou等[22]提出基于频域的谱残差法, 对图像进行二维傅里叶变换后得到频域的相位谱和幅度谱, 作者认为频谱域上的统计奇异对应图像的异常区域, 因此该区域的物体显著性高. 利用深度学习技术进行显著性检测是近年来的研究趋势. He等[23]提出了一种新的超像素方法, 称为Super-CNN, 可以有效地学习显著性的内部表示. 与传统的卷积网络相比, 该网络能够学习分层对比度特征, 通过多尺度网络结构检测显著性区域. Hou等[24]提出了一种快速的显著性检测方法, 在整体嵌套边缘检测的基础上, 增加了一种高层信息指导低层信息的跳层连接结构, 从而构建了一种简单、有效、快速的端对端的显著性物体检测网络. 张芳等[25]设计实现了一种全卷积神经网络与低秩稀疏分解相结合的显著性检测方法, 将图像分解为代表背景的低秩矩阵和对应显著区域的稀疏噪声, 结合利用全卷积神经网络学习得到的高层语义先验知识, 检测图像中的显著区域. 本文使用了目前最先进的网络BASNet生成热红外图像的显著图, 并在第3.3.1节中进行结果评估.
1.3 模型压缩和加速
虽然现在CNN的特征提取能力随着网络层数的加深正在不断地提升, 但在实际工程中还需要考虑模型尺寸和模型预测速度. 深度CNN结构包含几十层甚至上百层的网络, 有着大量的权重参数, 如何调整其结构以在准确度、尺寸和速度之间实现最佳平衡已经成为一个很受关注的研究领域.
为了解决这个问题, 众多轻量化网络结构纷纷被提出. SqueezeNet[26]提出了一种称作Fire的模块, 它分为两个部分: 一个由1×1卷积核构成的压缩层以及一个由1×1和3×3卷积核组成的扩张层. 通过使用这种模块, SqueezeNet能在保持模型精度不损失的情况下达到50倍压缩率. ShuffleNet[27]充分利用了分组卷积和通道混洗进一步提高模型效率, 在减少计算量的同时解决了组间信息流通问题. 而Google提出的MobileNet系列模型[28-29]是专门针对移动和嵌入式设备开发的轻量级CNN结构. MobileNetv1采用一种深度可分离卷积的高效卷积方法来提升运算速度. 深度可分离卷积将一个标准卷积分解成两步来实现, 第1步是深度卷积, 即对每个输入通道用单个卷积核进行卷积运算; 第2步是一个1×1卷积, 即逐点卷积, 负责通过计算输入通道间的线性组合来构建新的特征. 通过深度卷积和逐点卷积两个步骤实现卷积层, 其参数仅约为普通卷积的1/9. 在此基础上, MobileNetv2加入了反向残差和线性瓶颈模块构成了更高效的基本模块. 传统的残差结构特征通道维度先缩减后扩展, 即先用一个1×1卷积来降低通道维度, 目的是减小计算量. 而 MobileNetv2 使用深度卷积替换了3×3标准卷积, 虽然极大地减少了计算量和参数量, 但提取的特征也会相对减少, 如果再进行压缩, 能提取的特征将更少, 影响模型的准确度. 因此采用反向残差结构, 先对通道进行扩展, 深度卷积能提取更多特征, 保证模型准确度. 线性瓶颈就是去掉了低维度输出层后面的非线性激活层, 目的也是为了在兼顾参数量和计算复杂度的同时实现较高的准确度. MobileNetv3采用了新的非线性激活层h-swish, 使用互补的网络搜索方法搜索得到轻量级的网络. 相较于之前的版本, MobileNetv3虽然实现了性能提升, 但设计及训练过程复杂. 本文使用MobileNetv2改进原有的YOLOv3模型, 满足无人机场景下的应用需要.
2. 算法
2.1 使用YOLOv3检测结果作为评价基准
本文采用的目标检测基础模型是YOLOv3模型, 首先用它来仅处理热红外图像, 进行行人及车辆的检测任务, 将这类检测的结果作为后续模型改进的评价基准. YOLOv3将图片划分为
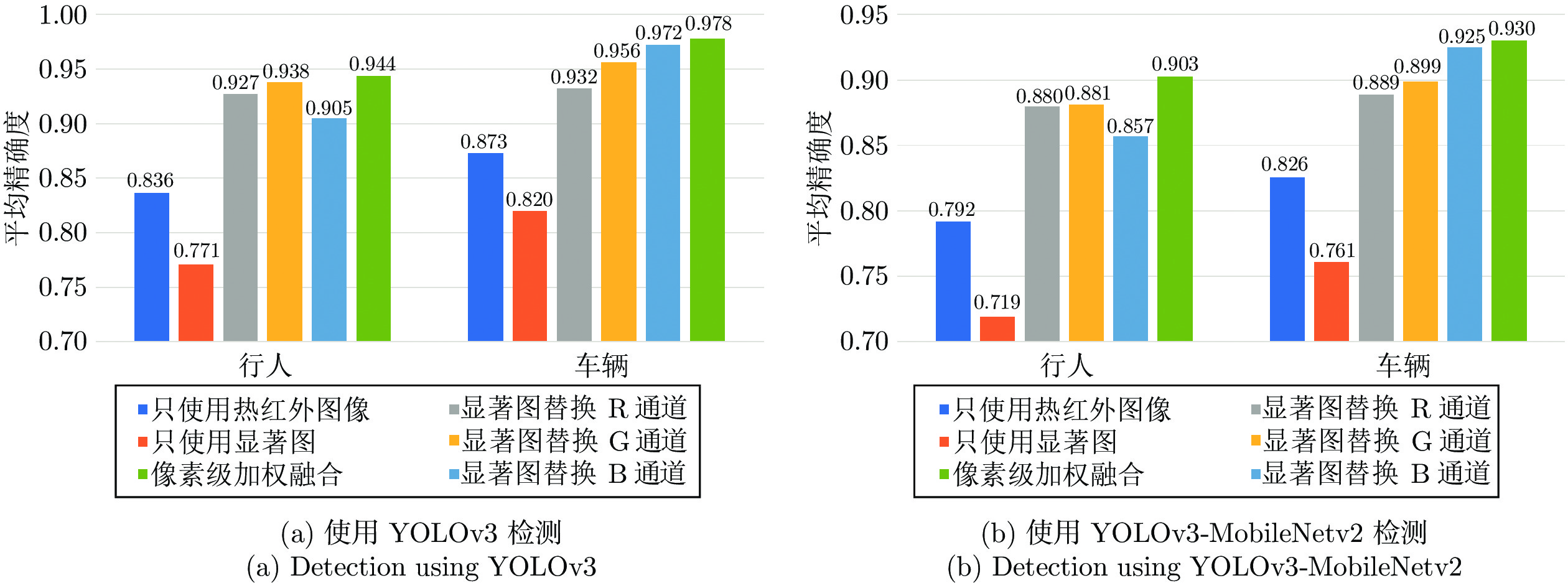
$S\times S $ 的网格, 各网格只负责检测中心落在该网格的目标, 每个网格需要预测三个尺度的边界框和类别信息, 一次性预测所有区域所含目标的边界框、目标置信度以及类别概率. 与之前的YOLO算法相比, YOLOv3采用了精度更高的DarkNet53作为图像特征提取网络, 设计了目标多尺度检测结构, 对无人机视角下小目标的检测具有很好的效果. 本文在采集制作的热红外图像数据集上训练YOLOv3模型作为行人及车辆检测基准, 结果如表1所示.表 1 采用不同方法所得到结果的比较Table 1 Comparison of results from different techniques类别 指标 行人 车辆 模型大小 (MB) AP FPS AP FPS 使用的数据和方法 热红外图像 YOLOv3 0.836 20 0.873 20 235 YOLOv3-MobileNetv2 0.792 32 0.826 32 97 显著图 YOLOv3 0.771 21 0.820 21 235 YOLOv3-MobileNetv2 0.719 34 0.761 34 97 替换 R 通道融合 YOLOv3 0.927 20 0.932 20 235 YOLOv3-MobileNetv2 0.880 32 0.889 32 97 替换 G 通道融合 YOLOv3 0.938 18 0.956 18 235 YOLOv3-MobileNetv2 0.881 30 0.899 30 97 替换 B 通道融合 YOLOv3 0.905 19 0.972 19 235 YOLOv3-MobileNetv2 0.857 31 0.925 31 97 像素级加权融合 YOLOv3 0.944 20 0.978 20 235 YOLOv3-MobileNetv2 0.903 32 0.930 32 97 2.2 使用显著图融合热红外图像改进行人及车辆检测
本文提出从热红外图像中提取显著图来使行人及车辆检测器获得更丰富的像素间关系. 在无人机航拍图像中背景复杂的情况下, 显著图的使用会使行人及车辆在图像中与周围环境的差别更大. 然而, 显著图抛弃了热红外图像中所有可用的纹理信息. 为了解决这个问题, 本文将热红外图像与其对应的显著图融合.
2.2.1 深度显著性网络BASNet提取显著图
深度CNN结构在显著目标检测(即显著图生成)上已有应用, 并取得了不错的性能. 但是之前的绝大多数工作都关注在兴趣目标区域的准确率上, 而不是边界的质量上. 无人机视角下目标的形态与地面视角成像时的差异较大, 因而热红外图像具有边界几何特性弱的特点. 本文提出使用显著图进行的目标检测增强, 其边界将会对图像增强效果产生较大影响. 因此, 使用更关注边界质量的BASNet网络[4]作为生成显著目标的基础网络.
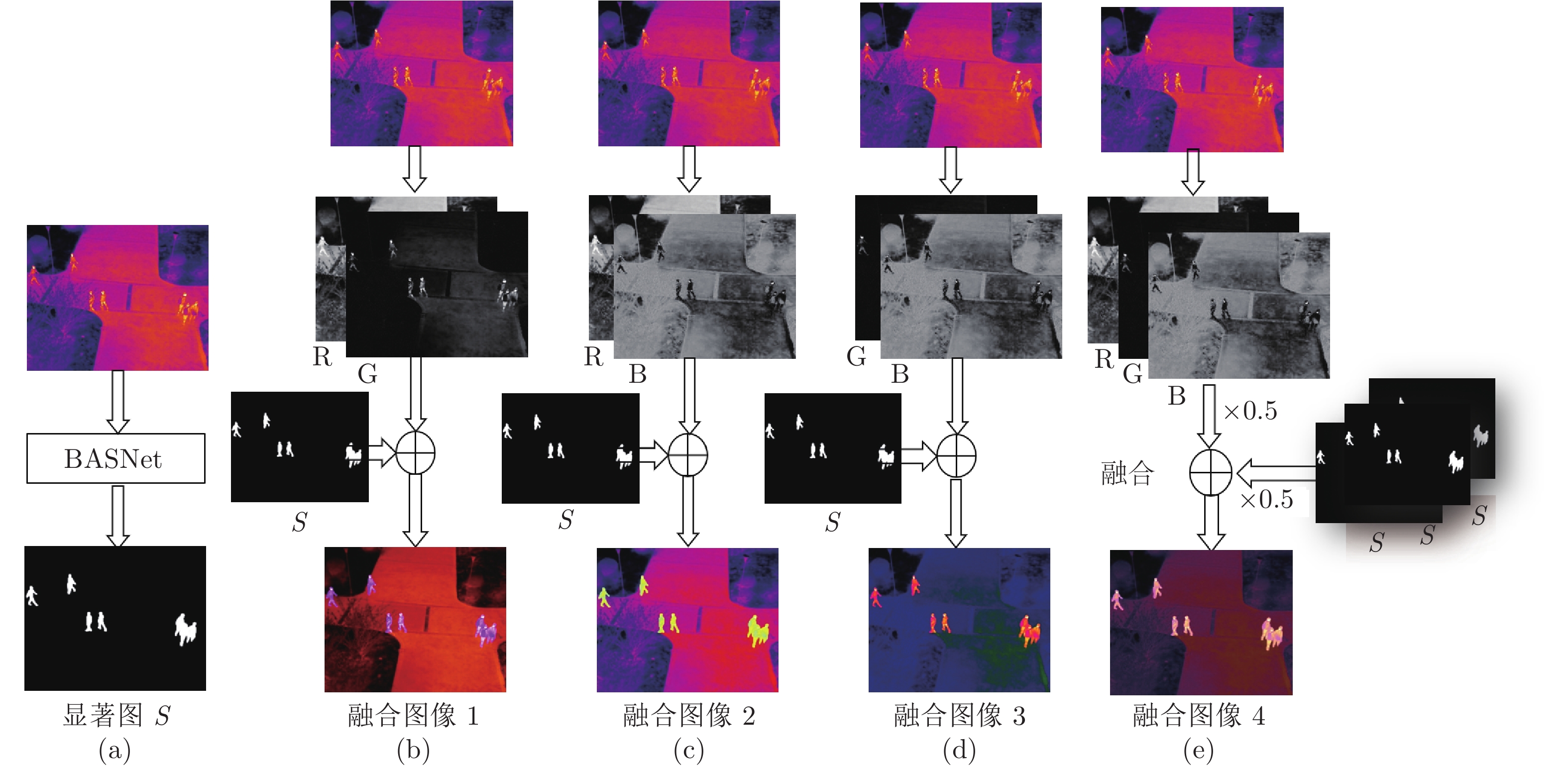
如图1所示, BASNet是一个新的预测−优化网络. 该架构由一个类似于U-Net的密集监督的编译码网络和一个额外的残差优化模块组成, 分别负责显著图预测和显著图优化. 在编码−解码网络中, 前面的编码网络对图像进行特征提取, 使用池化方法得到了分辨率逐步变小的高层语义特征; 后面的解码网络部分则负责将高层语义信息逐步还原放大, 从而逐步获得大分辨率的特征图, 最终输出和原图一样大小的粗糙的显著图. 在编码网络和解码网络之间有直连结构, 将相同分辨率的特征图相加, 从而让最终的输出的特征图能够同时兼顾低级和高级的特征. 此外, 为了优化粗糙的显著图中存在的区域和边界缺陷, BASNet设计了一个新的残差优化模块,该模块通过学习粗糙的显著图和真实值之间的残差来优化预测的输出. 这个优化模块的输出就是最终输出的显著图, 如图1中放大的视图展示了粗糙的和优化后的显著图.
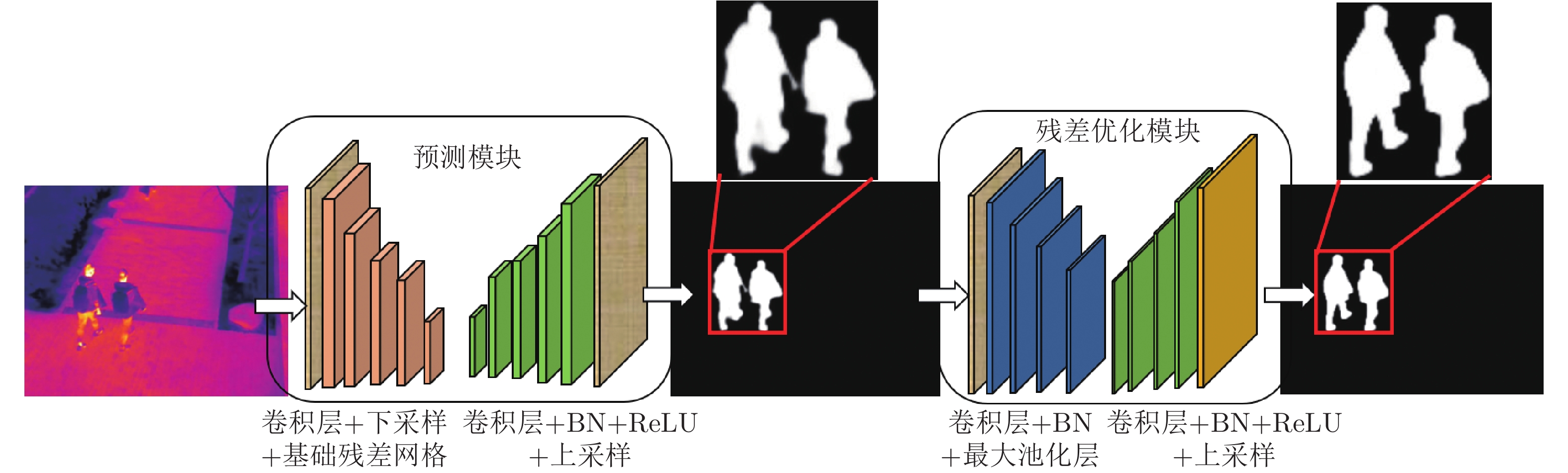
与其他的显著图预测网络不同, BASNet在每层损失函数的设计上, 使用了交叉熵、结构相似性损失、交并比(Intersection over union, IoU)损失这三种的混合损失
$ L $ , 使网络更关注于边界质量, 而不是像以前那样只关注区域精度. 损失函数的表达式为$$ L={L}_{{\rm{bce}}}+{L}_{{\rm{ssim}}}+{L}_{{\rm{iou}}} $$ (1) 其中,
${L}_{{\rm{bce}}}$ 代表交叉熵损失, 对应着像素级的监督.${L}_{{\rm{ssim}}}$ 是结构相似性损失, 对应着区域级的监督.${L}_{{\rm{iou}}}$ 是交并比损失, 对应着显著图级的监督. 各项损失的具体数学形式参见文献[4].2.2.2 使用显著图融合热红外图像
在获得显著图后(如图2(a)所示), 本文设计了两类图像融合方案, 即: 1)用显著图分别替换了热红外图像的红色(R)、绿色(G)、蓝色(B)三个通道中的一个通道, 如图2(b)~2(d)所示, 每个替换方式都对应了一个新的融合图像, 这些融合图像的目标检测性能也存在差异, 实验中将对其进行分析; 2)将显著图与热红外图像的三个通道亮度值分别在像素级别上直接按各自0.5的权重比例融合, 如图2(e)所示. 显著图与热红外图像的融合在突出图像中行人及车辆目标的同时保留了图像中的纹理信息, 如图3所示. 通道融合之后, 为比较显著图对行人及车辆检测的影响, 继续利用热红外图像中提取的显著图以及使用上述两类方法生成的与显著图融合的热红外图像分别训练没有改进的YOLOv3网络模型.
2.3 使用MobileNetv2改进YOLOv3模型
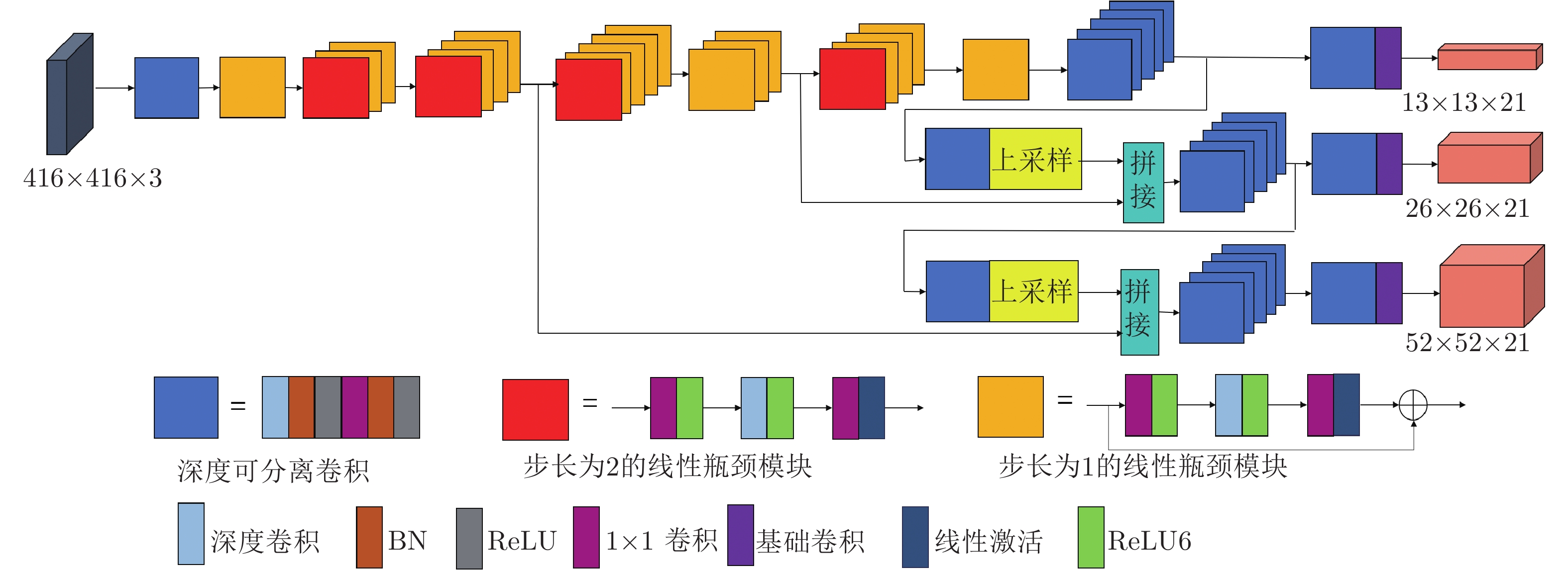
基于深度学习的目标检测算法计算开销和模型参数体量巨大, 难以部署在计算和存储资源有限的无人机平台上. 针对这一问题, 本文以轻量化目标分类网络MobileNetv2为基础, 提出了一种新型超轻量化目标检测网络模型. 将MobileNetv2的平均池化层和最后一个卷积层去掉, 使其替换YOLOv3网络中原有的DarkNet53网络. 同时, YOLOv3-MobileNetv2沿用了DarkNet53的连接规则, 即分别将MobileNetv2中分辨率为输入图像的8倍和16倍下采样的特征层中的最后一层作为细粒度特征与检测网络中上采样之后的高级语义特征融合, 增强网络的目标检测能力[30], 这对无人机航拍图像中的小目标检测具有重要意义. 深度可分离卷积可以使网络在保证准确度的同时获得较小的模型尺寸和较低的计算复杂度. 因此, 采用深度可分离卷积替换YOLOv3-MobileNetv2检测网络中占据大量参数的3×3卷积操作. 最后根据需要识别的目标类别和先验框的尺寸对模型进行了修改, 完成了轻量化模型YOLOv3-MobileNetv2的网络设计. 最终的YOLOv3-MobileNetv2结构中只有3个标准卷积, 采用了21个深度可分离卷积模块, 结构如图4所示.
此外, YOLOv3 检测过程会产生两个问题. 1) 极度不平衡的正负样本比例, 其候选样本生产方式会使正负样本相差巨大, 而且大部分的负样本都是易分样本; 2) 梯度被易分样本主导, 虽然这些样本的损失值很低, 但是数量众多, 对于损失依旧有很大贡献, 从而导致收敛效果不够好. 因此, 本文在损失函数中使用Focal loss改进原有的交叉熵, 如式(2)所示.
$$ Fl\left({p}_{t}\right)=-\alpha {\left(1-{p}_{t}\right)}^{\beta }\log\left({p}_{t}\right) $$ (2) 其中,
$ {p}_{t} $ 为预测的概率值,$ \alpha $ 与$ \beta $ 均为可以调节的超参数, 在本文中,$ \alpha $ 取0.5,$ \beta $ 取2.3. 实验
3.1 数据集及评估方法
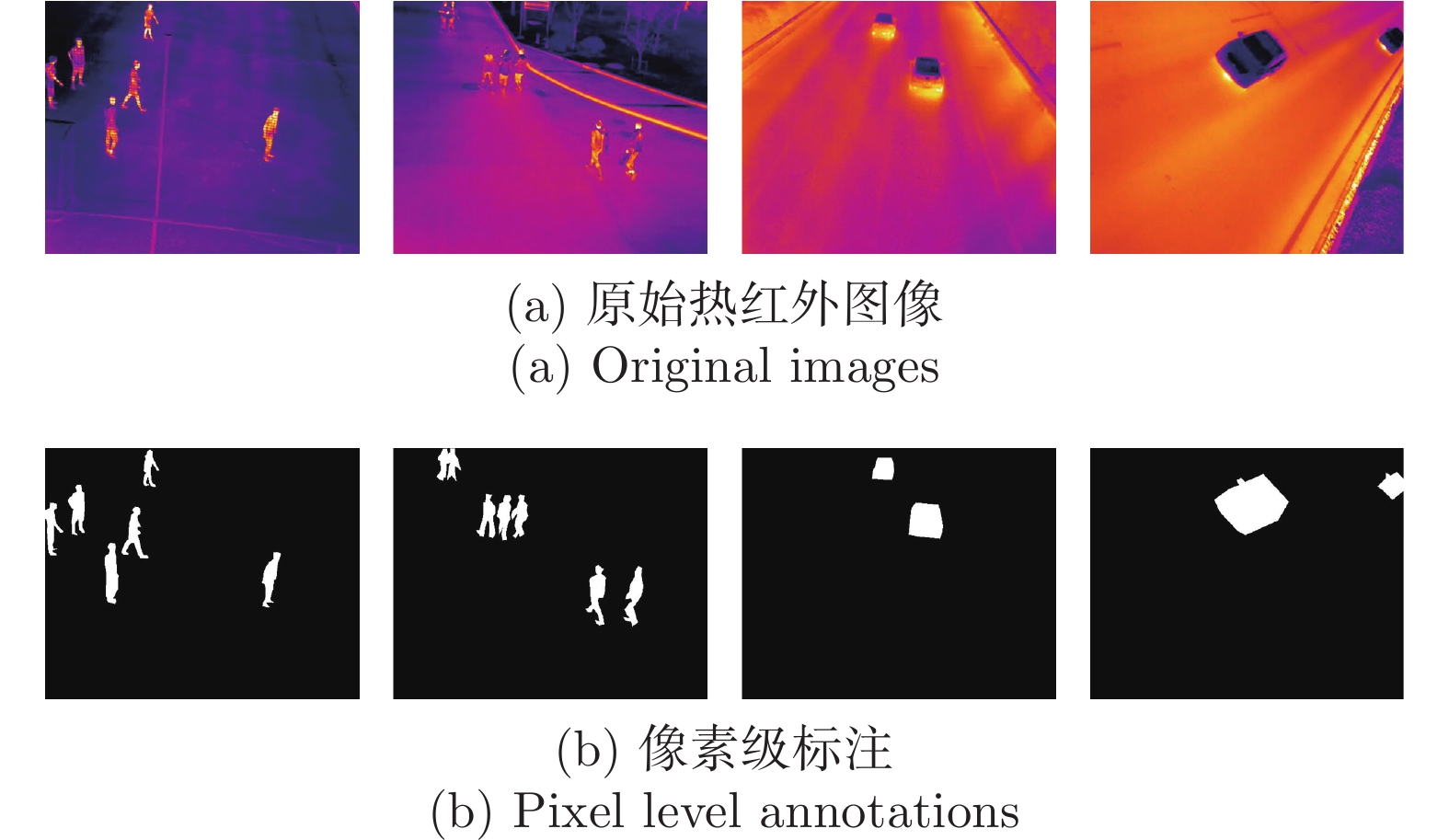
通常为了训练一个深度神经网络模型, 需要大量的数据样本. 然而, 目前并没有公开可用的针对无人机视角下行人及车辆的热红外数据集. 除此之外, 对图像进行显著性目标检测也需要对显著性对象进行像素级标注, 需要较大的工作量. 因此, 本文在实验环节采用现有设备制作了无人机载热红外图像行人及车辆数据集, 方便相关技术的进一步研究.
实验使用大疆无人机DJIM600 PRO搭载FLIR热红外相机Vue Pro采集行人及车辆热红外图像数据, 无人机飞行高度20 ~ 40 m, 图像分辨率640×512像素. 值得注意的是, 热红外相机接收到的原始图像只有亮度, 为单通道灰度图像. 为方便行人及车辆目标检测的研究, 将接收到的热红外图像经过温度映射后转换为RGB格式三通道伪彩色图像, 单通道灰度图像中像素值0映射为蓝色, 像素值255映射为红色, 中间平滑渐变, 即使用颜色的冷暖色调来显示低温和高温区域.
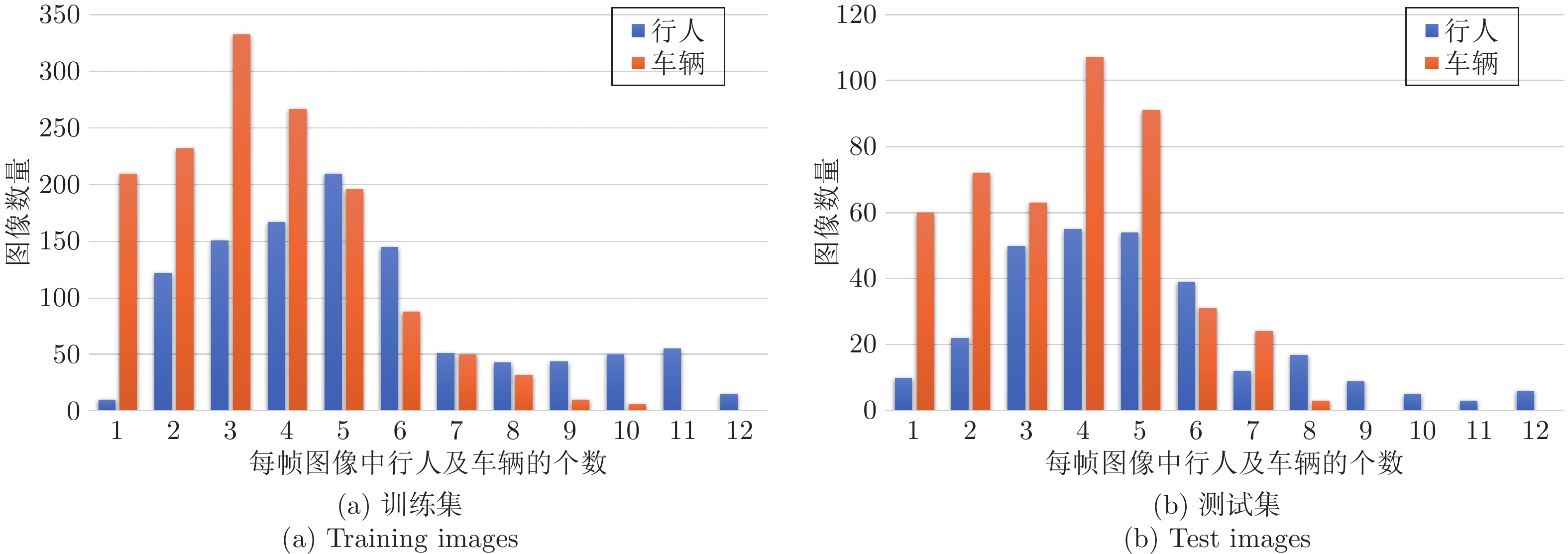
无人机携带热红外成像仪分别在白天和夜间采集数据, 共获得热红外图像2434幅, 其中包含3555个行人实例和3189个车辆实例. 使用图像标注工具Labelme手动标注这些图像, 用以生成训练BASNet所需要的显著性目标边缘像素级标注. 同时, 使用LabelImg标注图像, 用以生成训练YOLOv3及YOLOv3-MobileNetv2所需要的目标边框标注. 此外, 创建了541幅带有类似标注的图像, 用于验证本文的深度显著性检测网络和改进的目标检测网络, 其中包含1213个行人实例和667个车辆实例. 图5显示了4组所制作数据集的示例图像和标注. 训练集和测试集每帧图像中行人及车辆的分布如图6所示. 第3.3.1节的测试结果表明, 该数据集在行人及车辆显著性目标检测中可以取得相当好的效果.
为了对行人及车辆检测结果进行评估, 本文使用AP值和每秒帧率(Frame per second, FPS)分别作为精度和速度的评价指标. 此外, 使用F度量值(F-measure,
${F}_{\beta })$ 和平均绝对误差(Mean absolute error, MAE)来评估模型的显著性检测结果. 其中,$ {F}_{\beta } $ 是精确率(Precision)和召回率(Recall)在非负权重$ \beta $ 下的加权调和平均值,$ {F}_{\beta } $ 越高则模型越好, 具体计算为$$ {F}_{\beta }=\frac{\left(1+{\beta }^{2}\right)Precision\times Recall}{{\beta }^{2}Precision+Recall} $$ (3) 其中,
$ {\beta }^{2} $ 一般取值为0.3.MAE用来直接计算模型输出的显著图与其对应的真实值之间的像素误差
$$ MAE=\frac{1}{W\times H}\sum\limits_{x=1}^{W}\sum\limits_{y=1}^{H}\left|\bar{S}(x,y)-\bar{G}(x,y)\right| $$ (4) 其中,
$ W $ 和$ H $ 分别为图像的宽和高,$ \bar{S}(x,y) $ 和$ \bar{G}(x,y) $ 分别为输出的显著图和其对应的真实值二值化后的像素值.3.2 网络模型实现细节
3.2.1 使用YOLOv3及YOLOv3-MobileNetv2分别进行行人及车辆检测
本文在有8 GB内存的NVIDIA 1080ti GPU上对YOLOv3及YOLOv3-MobileNetv2模型进行训练, 使用双线性插值将图像尺寸由640×512像素调整为416×416像素后输入网络模型. 在Microsoft COCO数据集上预先训练YOLOv3及YOLOv3-MobileNetv2骨干网络, 并在3.1节中描述的热红外图像数据集上进行100个回合(Epoch)的微调. 此外, 设置批量大小(Batch size)为8, 初始学习率为0.001, 使用Adam优化器自适应调整学习率. IoU阈值设置为0.5, 经过非极大值抑制(Non-maximum suppression, NMS)操作后输出最终的预测结果.
3.2.2 深度显著性网络BASNet
本文使用像素级标注的热红外图像对BASNet进行训练, 并保持了与原始论文中相同的网络架构. 在训练阶段, 首先将训练集中每幅图像尺寸调整为256×256像素, 通过随机翻转和裁剪来对训练集图像做增强操作. 使用ResNet-34网络的权值来初始化特征提取网络的参数, 解码网络从0开始训练, 学习率为0.01. 在不使用验证集, 批量大小为8的情况下, 经过6万次迭代损失函数收敛, 整个训练过程耗时约7小时. 在测试阶段, 同样将输入图像尺寸调整为256×256像素, 并将其输入到网络中得到预测的显著图. 然后, 将降采样的显著图重新调整为原始输入图像的尺寸. 这两个调整过程都使用双线性插值.
3.3 结果和分析
3.3.1 深度显著性网络BASNet在热红外图像数据集上的检测效果
为了给接下来的图像显著图研究提供一个有效的支撑, 首先评估了BASNet在标注的无人机航拍热红外行人及车辆显著性数据集的测试集上的性能. 评估结果表明,
$ {F}_{\beta } $ 为0.767, MAE为0.008, 从中可以看出该模型的检测效果是十分优异的. BASNet对热红外图像进行处理, 检测提取出其中的行人及车辆目标, 目标像素值为255, 背景像素值为0, 以二值图像的形式输出. 使用该模型生成的掩膜可以在图3(b)中看到. 由于热红外图像以温度作为成像基础, 因此图像中部分与目标温度相近的物体不可避免地对检测结果造成影响, 形成显著目标的误判, 例如图3(b)第1幅图像最左边区域中的高温物体被误检为显著目标. 但此类现象在实际应用中产生频率较低, 且随着训练集样本的丰富由此对目标检测造成的影响可以忽略不计.3.3.2 目标检测的定量分析
在使用YOLOv3和YOLOv3-MobileNetv2分别训练热红外图像、显著图和通过不同的融合技术增强的热红外图像之后, 接下来对检测结果进行性能评估. 经过比较可以发现, 显著图对行人及车辆检测精度的提升有明显效果, 而YOLOv3-MobileNetv2网络则显著提高了模型的检测速度. 表1中总结了本文所提算法的检测性能, 下一节将对一些重要的结果做进一步的分析.
3.3.2.1 使用YOLOv3作为检测网络
1) 只使用热红外图像. 首先使用YOLOv3训练热红外图像作为检测基准, 模型大小为235 MB. 实验结果表明行人及车辆的AP值分别为83.6%和87.3%, 检测帧率为20 帧/s. 从实验结果中不难看出, 受限于无人机场景下内存不足、算力有限的特点, 现有的YOLOv3算法无论是模型尺寸还是检测速度、识别准确度都无法满足实际应用的需要, 由此证实了采用显著图融合增强热红外图像以及使用MobileNetv2改进YOLOv3算法的必要性. 此外, 由于场景中温度差别较大, 热红外图像中车辆的成像效果比行人更好, 这也是造成行人及车辆AP值差异的深层次原因.
 图 8 行人及车辆检测示例(1 ~ 3列为行人, 4、5列为车辆)Fig. 8 Sample results from pedestrian detection on images 1 ~ 3 and vehicle detection on images 4 and 5 from methods: ((a) Thermal images + YOLOv3; (b) Thermal images + YOLOv3-MobileNetv2; (c) Saliency maps + YOLOv3 -MobileNetv2; (d) ~ (f) represent replacing one of R, G, and B channel of thermal images by saliency maps + YOLOv3 -MobileNetv2; (g) Direct fusion of saliency maps and thermal images at pixel-level + YOLOv3-MobileNetv2)((a)原始热红外图像+YOLOv3; (b)原始热红外图像+YOLOv3-MobileNetv2; (c)显著图+YOLOv3-MobileNetv2; (d) ~ (f)分别是使用显著图替换热红外图像R、G、B通道+YOLOv3-MobileNetv2; (g)热红外图像与显著图进行像素级直接融合+YOLOv3-MobileNetv2)
图 8 行人及车辆检测示例(1 ~ 3列为行人, 4、5列为车辆)Fig. 8 Sample results from pedestrian detection on images 1 ~ 3 and vehicle detection on images 4 and 5 from methods: ((a) Thermal images + YOLOv3; (b) Thermal images + YOLOv3-MobileNetv2; (c) Saliency maps + YOLOv3 -MobileNetv2; (d) ~ (f) represent replacing one of R, G, and B channel of thermal images by saliency maps + YOLOv3 -MobileNetv2; (g) Direct fusion of saliency maps and thermal images at pixel-level + YOLOv3-MobileNetv2)((a)原始热红外图像+YOLOv3; (b)原始热红外图像+YOLOv3-MobileNetv2; (c)显著图+YOLOv3-MobileNetv2; (d) ~ (f)分别是使用显著图替换热红外图像R、G、B通道+YOLOv3-MobileNetv2; (g)热红外图像与显著图进行像素级直接融合+YOLOv3-MobileNetv2)2) 只使用显著图. 只使用显著图进行行人及车辆检测, 其AP值分别为77.1%和82.0%, 相较于基准下降了6.5%和5.3%, 检测帧率为21 帧/s. 此外, 实验中发现该方法导致了大量的误检和漏检, 影响了精度. 这表明, 虽然显著图具有一定的应用潜力, 但是它作为二值图像, 只是突出了图像中的显著物体, 并不具备任何纹理特征, 一方面使得深度卷积神经网络无法在图像中获取丰富的信息进行目标位置、大小和类别的判断; 另一方面容易造成形状大小相似的物体被错误检测为同一类目标. 尤其是当数据样本不足时, 提取显著图的误差与目标检测的误差累加, 将造成检测精度的大幅下降. 因此仅仅使用显著图来完成目标检测的任务往往达不到理想的精度要求.
3) 使用显著图增强的热红外图像. 本文设计了两种方案来完成热红外图像与显著图的融合增强. 实验结果表明, 方案1中使用显著图替换热红外图像的R通道后, 行人及车辆的AP值为92.7%和93.2%, 分别比基准提高了9.1%和5.9%, 检测帧率为20 帧/s. 使用显著图替换热红外图像的G通道后, 行人及车辆的AP值为93.8%和95.6%, 分别比基准提高了10.2%和8.3%, 检测帧率为18 帧/s. 使用显著图替换热红外图像的B通道后, 行人及车辆的AP值为90.5%和97.2%, 分别比基准提高了6.9%和9.9%, 检测帧率为19帧/s. 方案2中将热红外图像与显著图进行0.5比例的像素级加权融合后, 行人及车辆的AP值为94.4%和97.8%, 分别比基准提高了10.8%和10.5%, 检测帧率为20 帧/s. 更直观的比较如图7(a)所示.
这些提升可以用图8中的可视化示例来解释, 图8中, 使用显著图增强后的热红外图像突出了场景中的行人和车辆, 帮助检测器在低对比度的情况下识别目标. 此外, 不难看出, 使用像素级加权融合的方案要优于图像通道替换方案, 这是因为图像通道替换过程中损失了部分有用的像素信息, 破坏了图像原来的结构. 而像素级加权融合是在保留热红外图像和显著图通道结构的基础上, 对行人和车辆区域进行增强, 对非目标的背景区域进行抑制. 同时, 由于输入图像尺寸没有发生变化, 因此两种方案中检测帧率都与基准大致相同.
3.3.2.2 使用YOLOv3-MobileNetv2作为检测网络
实验结果表明, 改用YOLOv3-MobileNetv2网络后, 在保持平均精确度不发生明显变化的同时大幅提高了模型的检测速度, 而网络模型的大小得到了极大的精简. 这是因为YOLOv3-MobileNetv2沿用了YOLOv3多尺度预测、预测边框偏移量而不是直接预测边框的大小和位置、采用多重标签分类等优点, 以轻量化卷积替代原先数量多、参数量大的标准卷积, 从而取得速度、精度、模型大小的平衡. 在综合性能表现最好的像素级加权融合方案上, 行人及车辆的AP值为90.3%和93.0%, 相较于未改进的YOLOv3网络训练热红外图像的检测基准分别提升了6.7%和5.7%, 而检测帧率则由20 帧/s变为32 帧/s, 提升了60%, 模型大小由235 MB变为97 MB, 减小了58%. 其他各项方案的AP值及帧率、模型大小变化如表1和图7(b)所示.
3.3.3 融合显著图的目标检测分析
图8给出了使用上述技术在不同设置下对5组图像的检测结果. 通过图8 (a)与图8 (b)的比较, 可以看出YOLOv3-MobileNetv2在检测精度上与YOLOv3相近. 由图8可以看到, 用于图像增强的显著图8 (c)-1和图8 (c)-4有助于捕获原始热红外图像图8 (b)-1和图8 (b)-4中出现的行人及车辆的漏检, 这显示出显著图应用于复杂场景中目标检测的潜力. 在融合了热红外图像之后, 图8 (c)-2中漏检的行人在图8 (d)-2、图8 (e)-2和图8 (g)-2中被成功捕获. 在这里需要注意的是, 使用显著图替换热红外图像B通道的图8 (f)-2依然没有检测到行人, 表明此方法在行人检测性能上略低于其他方法, 这与在表1中得到的结果是一致的. 使用显著图分别替换热红外图像三个通道后显著物体在图像中的对比度及显著程度是不同的, 这也是造成检测结果出现些许差异的深层次原因. 利用图8 (b)-5中的热红外图像信息, 图8 (c)-5中漏检的车辆在图8 (d)-5 ~ 8 (g)-5中均被成功捕获. 以上结果显示出热红外图像与显著图之间的互补性, 从而证明了本文关于融合显著图提高热红外图像目标检测精度的假设.
在图8 (c)-3中, 可以看到显著图中最左边的行人被误检为车辆, 而图8 (b)-3中的热红外图像中很少发生这种误检. 因此, 将热红外图像与显著图结合后, 检测器能够排除这种错误. 在图8 (b)-3中, 由于与周围环境温度相近, 热红外图像中没有检测出最下方的行人, 而图8 (c)-3中的显著图很好地突出了这个区域, 帮助检测器将其成功捕获(参见图8 (d)-3 ~ 8 (g)-3). 尤其需要关注的是, 无论是热红外图像(图8 (b)-3)还是显著图像(图8 (c)-3), 都将左起第二处区域中两个相互重叠的行人检测为同一个人, 而通过将两种图像融合增强后, 在图8 (d)-3、图8 (f)-3和图8 (g)-3中成功地将这两个行人分别检测出来, 表明热红外图像与显著图的结合大大提高了重叠目标的检测性能.
4. 结论
面向行人和车辆两类典型目标, 本文利用无人机平台采集制作热红图像数据集, 并对其进行边界框标注和像素级标注. 利用深度学习的方法, 提取热红外图像的显著图. 将热红外图像与提取的显著图进行结合, 通过通道替换以及像素级加权等多种图像融合方案, 在热红外图像输入目标检测的深度神经网络之前进行图像增强. 融合图像为行人及车辆检测模型提供互补信息, 从而显著提高目标检测的性能. 此外, 通过使用轻量化网络YOLOv3-MobileNetv2替代原先的检测网络, 在保持平均精确度基本不变的前提下, 提升了模型的检测速度, 降低了模型的尺寸, 使其可以更好地应用于无人机场景下的行人及车辆检测.
-
图 2 使用显著图增强热红外图像的流程
((a)使用BASNet网络生成热红外图像的显著图; (b)~(d)分别是用显著图替换热红外图像三通道中的一个通道; (e)将显著图与热红外图像在三个通道分别进行像素级别上直接融合)
Fig. 2 The fusion of the thermal image and its saliency map
((a) Using BASNet to generate the saliency map of a thermal image; (b) to (d) replacing each of three channels of the thermal image with the saliency map; (e) Fusion of the thermal image and the duplicated saliency maps at pixel-level)
图 3 测试集中使用显著图增强的热红外行人(第1行和第2行)及车辆(第3行和第4行)图像
((a)原始热红外图像; (b)显著图; (c)使用显著图替换热红外图像R通道; (d)使用显著图替换热红外图像G通道; (e)使用显著图替换热红外图像B通道; (f)热红外图像与显著图的三个通道分别进行像素级直接融合)
Fig. 3 Thermal images and generated saliency maps for pedestrian (top 2 rows) and vehicle (bottom 2 rows) images from the test set
((a) Original thermal images; (b) Saliency maps; (c) Replacing red channel of thermal images with saliency maps; (d) Replacing green channel of thermal images with saliency maps; (e) Replacing blue channel of thermal images with saliency maps; (f) Direct fusion of saliency maps and thermal images at pixel-level)
图 8 行人及车辆检测示例(1 ~ 3列为行人, 4、5列为车辆)
((a)原始热红外图像+YOLOv3; (b)原始热红外图像+YOLOv3-MobileNetv2; (c)显著图+YOLOv3-MobileNetv2; (d) ~ (f)分别是使用显著图替换热红外图像R、G、B通道+YOLOv3-MobileNetv2; (g)热红外图像与显著图进行像素级直接融合+YOLOv3-MobileNetv2)
Fig. 8 Sample results from pedestrian detection on images 1 ~ 3 and vehicle detection on images 4 and 5 from methods: ((a) Thermal images + YOLOv3; (b) Thermal images + YOLOv3-MobileNetv2; (c) Saliency maps + YOLOv3 -MobileNetv2; (d) ~ (f) represent replacing one of R, G, and B channel of thermal images by saliency maps + YOLOv3 -MobileNetv2; (g) Direct fusion of saliency maps and thermal images at pixel-level + YOLOv3-MobileNetv2)
表 1 采用不同方法所得到结果的比较
Table 1 Comparison of results from different techniques
类别 指标 行人 车辆 模型大小 (MB) AP FPS AP FPS 使用的数据和方法 热红外图像 YOLOv3 0.836 20 0.873 20 235 YOLOv3-MobileNetv2 0.792 32 0.826 32 97 显著图 YOLOv3 0.771 21 0.820 21 235 YOLOv3-MobileNetv2 0.719 34 0.761 34 97 替换 R 通道融合 YOLOv3 0.927 20 0.932 20 235 YOLOv3-MobileNetv2 0.880 32 0.889 32 97 替换 G 通道融合 YOLOv3 0.938 18 0.956 18 235 YOLOv3-MobileNetv2 0.881 30 0.899 30 97 替换 B 通道融合 YOLOv3 0.905 19 0.972 19 235 YOLOv3-MobileNetv2 0.857 31 0.925 31 97 像素级加权融合 YOLOv3 0.944 20 0.978 20 235 YOLOv3-MobileNetv2 0.903 32 0.930 32 97 -
[1] 刘智嘉, 贾鹏, 夏寅辉, 林昱, 徐长彬. 基于红外与可见光图像融合技术发展与性能评价. 激光与红外, 2019, 49(5): 633-640 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2019.05.021Liu Zhi-Jia, Jia Peng, Xia Yin-Hui, Lin Yu, Xu Chang-Bin. Development and performance evaluation of infrared and visual image fusion technology. Laser & Infrared, 2019, 49(5): 633-640 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2019.05.021 [2] Koch C, Ullman S. Shifts in selective visual attention: Towards the underlying neural circuitry. Human Neurobiology, 1985, 4(4): 219-227 [3] Redmon J, Farhadi A. YOLOv3: An incremental improvement [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1804.02767, April 8, 2018 [4] Qin X B, Zhang Z C, Huang C Y, Gao C, Dehghan M, Jagersand M. BASNet: Boundary-aware salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 7479−7489 [5] Sandler M, Howard A, Zhu M L, Zhmoginov A, Chen L C. MobileNetV2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 4510−4520 [6] Lin T Y, Goyal P, Girshick R, He K M, Dollár P. Focal loss for dense object detection. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(2): 318-327 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2858826 [7] Lecun Y, Bottou L, Bengio Y, Haffner P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11): 2278-2324 doi: 10.1109/5.726791 [8] 于雪松, 刘家锋, 唐降龙, 黄剑华. 基于概率模型的行人四肢自遮挡的检测. 自动化学报, 2010, 36(4): 610-615 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2010.00610Yu Xue-Song, Liu Jia-Feng, Tang Xiang-Long, Huang Jian-Hua. Estimating the pedestrian 3D motion indoor via hybrid tracking model. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2010, 36(4): 610-615 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2010.00610 [9] Dollár P, Tu Z W, Perona P, Belongie S. Integral channel features. In: Proceedings of the 2009 British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC). London, UK: BMVA Press, 2009. 91.1−91.11 [10] Girshick R, Donahue J, Darrell T, Malik J. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Columbus, USA: IEEE, 2014. 580−587 [11] Girshick R. Fast R-CNN. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Santiago, Chile: IEEE, 2015. 1440−1448 [12] Ren S Q, He K M, Girshick R, Sun J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137-1149 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031 [13] Redmon J, Divvala S, Girshick R, Farhadi A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 779−788 [14] Redmon J, Farhadi A. YOLO9000: Better, faster, stronger [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1612.08242, December 25, 2016 [15] Ruhé M, Kühne R, Ernst I, Zuev S, Hipp E. Air borne systems and datafusion for traffic surveillance and forecast for the soccer world cup, In: Proceedings of the 86th Annual Meeting of Transportation Research Board (TRB 2017), Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [16] Portmann J, Lynen S, Chli M, Siegwart R. People detection and tracking from aerial thermal views. In: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Hong Kong, China: IEEE, 2014. 1794−1800 [17] 董培, 石繁槐. 基于小型无人机航拍图像的道路检测方法. 计算机工程, 2015, 41(12): 36-39 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3428.2015.12.007Dong Pei, Shi Fan-Huai. Road detection method based on small unmanned aerial vehicle image. Computer Engineering, 2015, 41(12): 36-39 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3428.2015.12.007 [18] 张秀伟, 张艳宁, 杨涛, 张新功, 邵大培. 基于co-motion的可见光-热红外图像序列自动配准算法. 自动化学报, 2010, 36(9): 1220-1231 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2010.01220Zhang Xiu-Wei, Zhang Yan-Ning, Yang Tao, Zhang Xin-Gong, Shao Da-Pei. Automatic visual-thermal image sequence registration based on co-motion. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2010, 36(9): 1220-1231 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2010.01220 [19] Li C Y, Song D, Tong R F, Tang M. Illumination-aware faster R-CNN for robust multispectral pedestrian detection. Pattern Recognition, 2019, 85: 161-171 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2018.08.005 [20] Xu D, Ouyang W L, Ricci E, Wang X G, Sebe N. Learning cross-modal deep representations for robust pedestrian detection. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 5363−5371 [21] Itti L, Koch C, Niebur E. A model of saliency-based visual attention for rapid scene analysis. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1998, 20(11): 1254-1259 doi: 10.1109/34.730558 [22] Hou X D, Zhang L Q. Saliency detection: A spectral residual approach. In: Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Minneapolis, USA: IEEE, 2007. 1−8 [23] He S F, Lau R W H, Liu W X, Huang Z, Yang Q X. SuperCNN: A superpixelwise convolutional neural network for salient object detection. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2015, 115(3): 330-344 doi: 10.1007/s11263-015-0822-0 [24] Hou Q B, Cheng M M, Hu X W, Borji A, Tu Z W, Torr P. Deeply supervised salient object detection with short connections. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 3203−3212 [25] 张芳, 王萌, 肖志涛, 吴骏, 耿磊, 童军, 等. 基于全卷积神经网络与低秩稀疏分解的显著性检测. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(11): 2148-2158Zhang Fang, Wang Meng, Xiao Zhi-Tao, Wu Jun, Geng Lei, Tong Jun, et al. Saliency detection via full convolution neural network and low rank sparse decomposition. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(11): 2148-2158 [26] Iandola F N, Han S, Moskewicz M W, Ashraf K, Dally W J, Keutzer K. SqueezeNet: AlexNet-level accuracy with 50x fewer parameters and < 0.5MB model size [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1602.07360, November 4, 2016 [27] Zhang X Y, Zhou X Y, Lin M X, Sun J. ShuffleNet: An extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1707.01083, December 7, 2017 [28] Howard A G, Zhu M L, Chen B, Kalenichenko D, Wang W J, Weyand T, et al. MobileNets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.04861, April 17, 2017 [29] Howard A, Sandler M, Chu G, Chen L C, Chen B, Tan M X, et al. Searching for MobileNetV3 [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.02244?context=cs, November 20, 2019 [30] 方青云, 王兆魁. 基于改进YOLOv3网络的遥感目标快速检测方法. 上海航天, 2019, 36(5): 21-27, 34Fang Qing-Yun, Wang Zhao-Kui. Efficient object detection method based on improved YOLOv3 network for remote sensing images. Aerospace Shanghai, 2019, 36(5): 21-27, 34 期刊类型引用(25)
1. 杨博然,蔺素珍,李大威,禄晓飞,崔晨辉. 基于信息补偿的红外弱小目标检测方法. 计算机应用. 2025(01): 284-291 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 刘鑫明,徐驰名,郭韩金,马三江. 螺栓状态无人机可见光图像目标检测方法. 信息技术. 2025(02): 104-109+115 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 黄年昌,杨阳,张强,韩军功. 基于深度学习的RGB-D图像显著性目标检测前沿进展. 计算机学报. 2025(02): 284-316 .  百度学术
百度学术4. 吴茜,魏晶鑫,陈中举. 选择性坐标注意力下红外图像无人机目标检测方法. 现代电子技术. 2025(07): 43-47 .  百度学术
百度学术5. 屈志坚,张博语,朱琳,梁家敏. 基于孪生多注意力网络的接触网侵限轻飘物跟踪. 铁道学报. 2024(02): 45-55 .  百度学术
百度学术6. 邵延华,张兴平,张晓强,楚红雨,吴亚东. 联合结构重参数和YOLOv5的航拍红外目标检测. 电子科技大学学报. 2024(03): 382-389 .  百度学术
百度学术7. 李游,毛文奇,李国栋,周云雅. 基于全卷积神经网络的无人机巡检图像边缘检测方法. 微型电脑应用. 2024(06): 91-95+108 .  百度学术
百度学术8. 邢顺翔,陈欣,王威振,薛鹏翔. 基于信息地图和改进蚁群算法的多无人机覆盖优化方法. 兵工自动化. 2024(10): 84-91+96 .  百度学术
百度学术9. 张兴平,邵延华,梅艳莹,张晓强,楚红雨. 融合视觉显著性的红外航拍行人检测. 红外技术. 2024(09): 1043-1050 .  百度学术
百度学术10. 卢佳佳,蔡坚勇. 基于增强视觉质量的图像感兴趣区域检测研究. 计算机仿真. 2023(01): 234-238 .  百度学术
百度学术11. 徐武,高寒,王欣达,张强. 基于LBP特征匹配算法的红外人脸图像表情识别技术. 激光杂志. 2023(03): 158-162 .  百度学术
百度学术12. 刘宇宸,李浩. 显著性特征融合的热红外图像光伏组件热斑检测. 水力发电. 2023(04): 96-101+112 .  百度学术
百度学术13. 叶裴雷,张大斌. 高速运动目标特征关联检测模型仿真. 计算机仿真. 2023(04): 208-212 .  百度学术
百度学术14. 林鹏,陈聪,徐盛秋,蔡富裕,廖华. 融合图像与红外传感的变电站异物入侵在线监测. 电子设计工程. 2023(15): 178-181+186 .  百度学术
百度学术15. 王文博,朱世豪,陈泽宇,张伟斌. 毫米波雷达与视觉融合在现代智慧交通目标检测中的研究综述. 现代交通与冶金材料. 2023(04): 2-14 .  百度学术
百度学术16. 王振平. 竞赛用投篮自动机器人目标识别方法研究. 机械设计与制造. 2023(10): 273-276+280 .  百度学术
百度学术17. 张睿,李允臣,王家宝,李阳,苗壮. 基于深度学习的红外目标检测综述. 计算机技术与发展. 2023(11): 1-8 .  百度学术
百度学术18. 梁晓,李俊. 基于改进YOLOv7的红外无人机目标检测方法. 电光与控制. 2023(12): 38-43+92 .  百度学术
百度学术19. 刘富,罗冰,裴峥. 一种基于区域权重平滑的弱监督目标定位方法. 西华大学学报(自然科学版). 2022(03): 1-7 .  百度学术
百度学术20. 蔺素珍,张海松,禄晓飞,李大威,李毅. RBNSM:一种复杂背景下红外弱小目标检测新方法. 红外技术. 2022(07): 667-675 .  百度学术
百度学术21. 陈永,卢晨涛,王镇. 红外弱光环境下多尺度密集注意力铁路异物检测. 铁道学报. 2022(07): 63-71 .  百度学术
百度学术22. 刘强,姚小良,尤帅,梅超君,刘尚东,季一木,亓晋. 一种轻量级网络模型的多尺度热红外行人检测方法. 南京邮电大学学报(自然科学版). 2022(05): 74-82 .  百度学术
百度学术23. 王子轩,汤健,夏恒,张晓晓,荆中岭,韩红桂. 基于并行差分进化–梯度特征深度森林的废旧手机识别方法. 控制理论与应用. 2022(11): 2137-2148 .  百度学术
百度学术24. 房良睿,王月明,李真如,刘浩楠,吴永刚. 基于YOLOv3算法的链箅机台车车轮故障检测系统. 烧结球团. 2021(01): 76-82 .  百度学术
百度学术25. 霍成军,史奕龙,武晓磊,李俊午,陆鑫,陈婧. 基于热成像技术的电气设备目标检测方法. 激光与红外. 2021(04): 530-536 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(23)
-





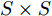
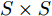
 下载:
下载:
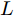
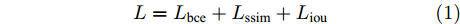
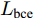
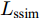
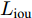

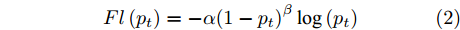

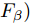
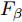
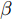

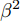
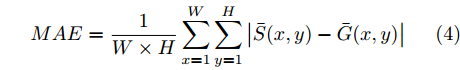
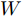
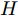
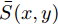
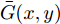
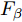
 下载:
下载:
