-
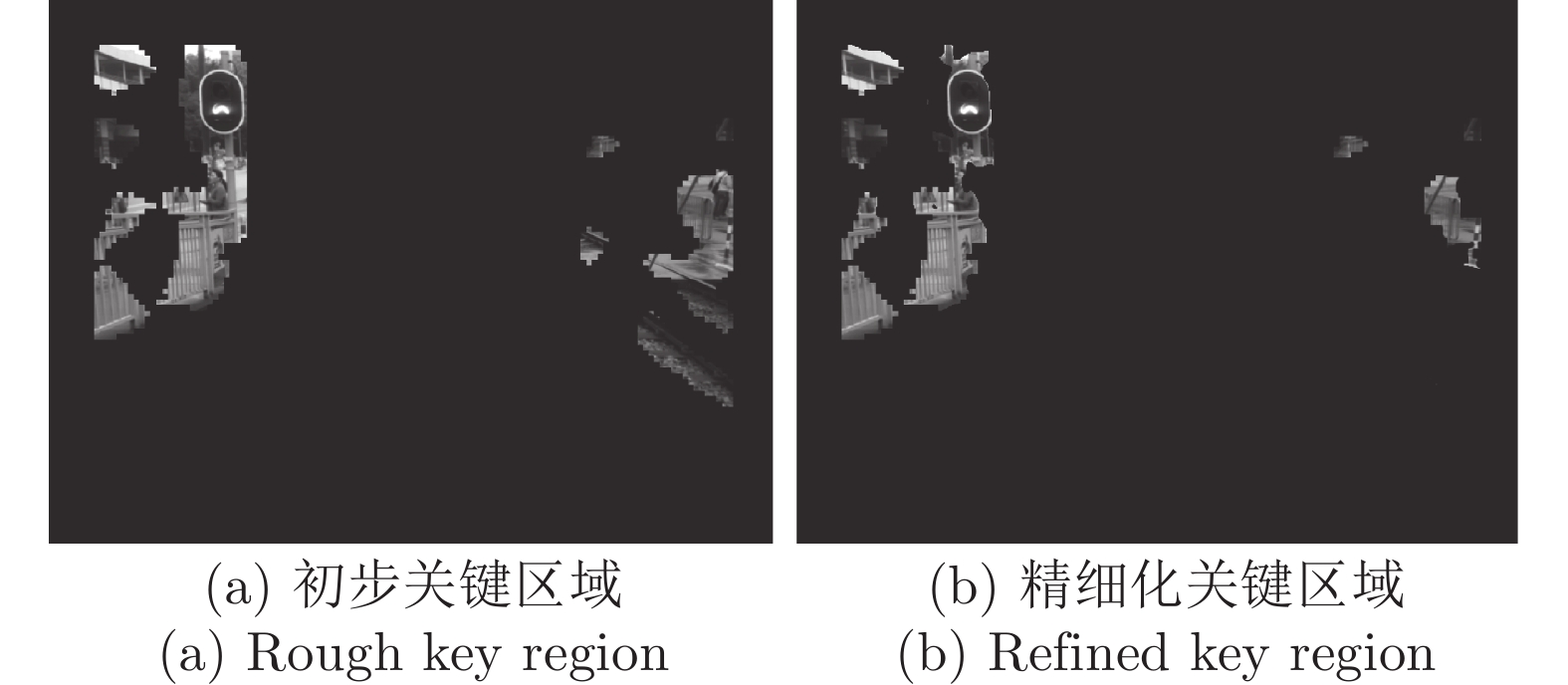
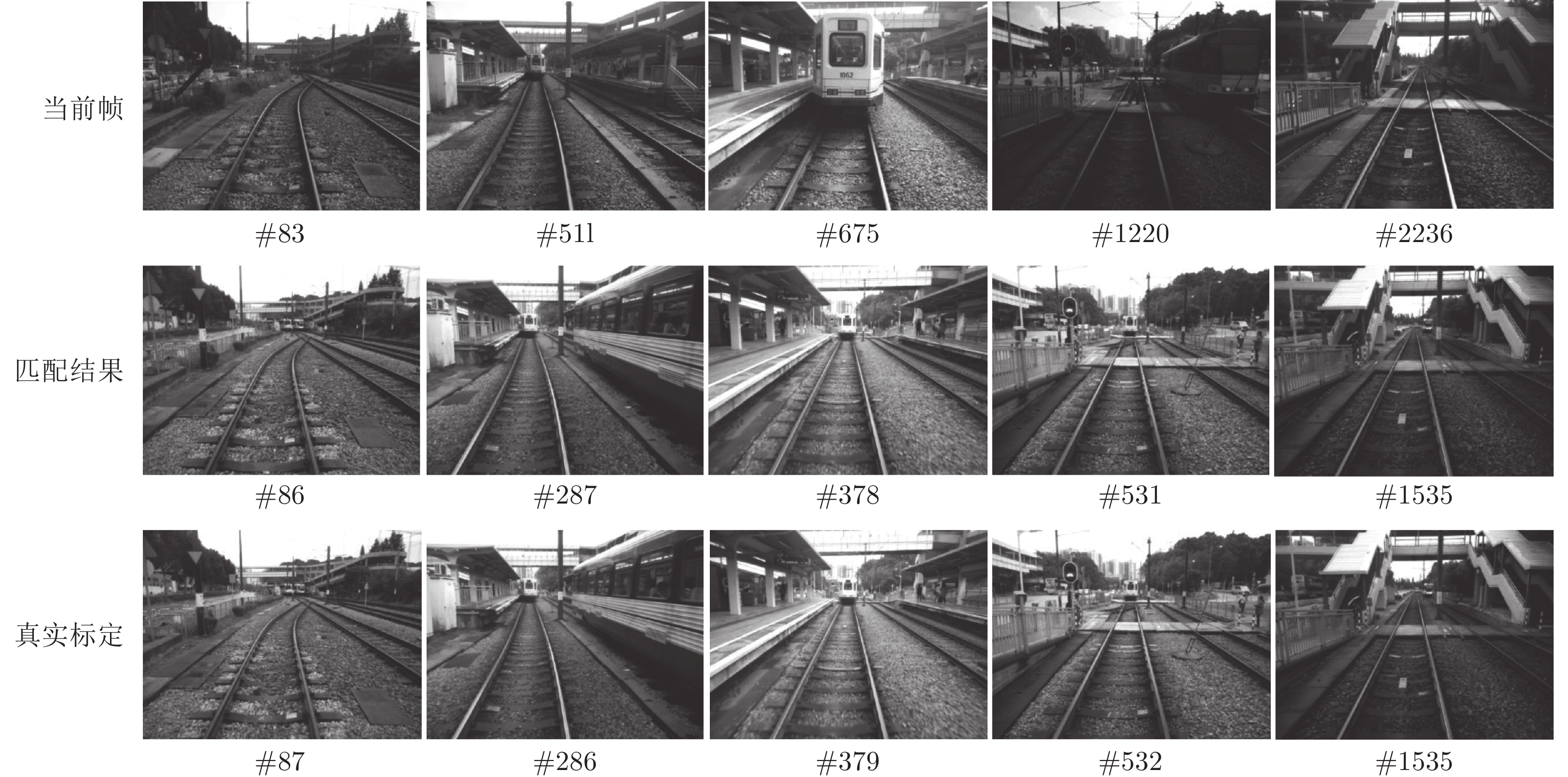
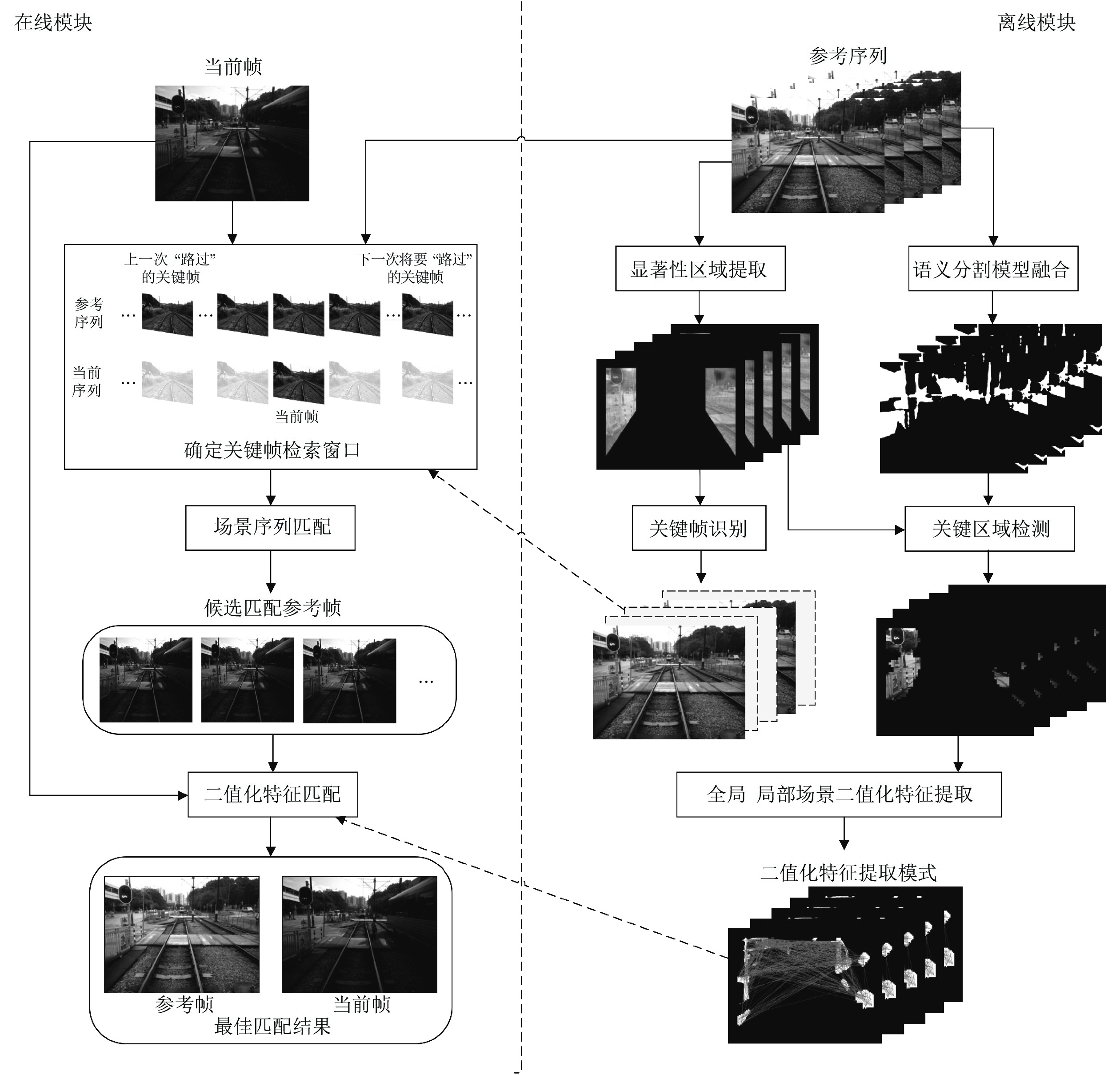
摘要: 轻轨作为城市公共交通系统的重要组成部分, 对其实现智能化的管理势在必行. 针对城市轻轨定位系统要求精度高、实时强且易于安装等特点, 本文提出一种基于全局−局部场景特征与关键帧检索的定位方法. 该方法在语义信息的指导下, 从单目相机获取的参考帧中提取区别性高的区域作为关键区域. 并结合像素点位置线索利用无监督学习的方式筛选关键区域中描述力强的像素对生成二值化特征提取模式, 不仅能够提升匹配精度还显著提高了在线模块场景特征提取与匹配的速度. 其次, 以场景显著性分数为依据获取的关键帧避免了具有相似外观的场景给定位带来的干扰, 并能辅助提高场景在线匹配的精度与效率. 本文使用公开测试数据集以及具有挑战性的轻轨数据集进行测试. 实验结果表明, 本系统在满足实时性要求的同时, 其定位准确率均可达到90%以上.Abstract: As an important part of the urban public transportation system, it is imperative to realize the intelligent management of light rail. By considering the practical requirements like high accuracy, real-time performance, and easy installation, this paper proposes a visual localization method based on global-local features and keyframe retrieval. Under the guidance of semantic information, the region with high significance in each reference frame obtained by the monocular camera is extracted as the key region. Combined with the location cues of pixels, unsupervised learning is used to filter the pixel pairs with strong description force in the key region to generate the binary pattern, which greatly reduces the computation of feature extraction and matching in the online module while improving the matching accuracy. Secondly, the keyframes obtained based on the discrimination score can effectively avoid the interference caused by the scene with analogous appearance, and assist to improve the accuracy and efficiency of online scene matching. The Nordland dataset and the challenging light rail dataset are used for testing. The experimental results show that the precision of the system can reach more than 90% while meeting real-time requirements.
-
Key words:
- Visual localization /
- place recognition /
- keyframe retrieval /
- key region detection /
- sequence matching
-
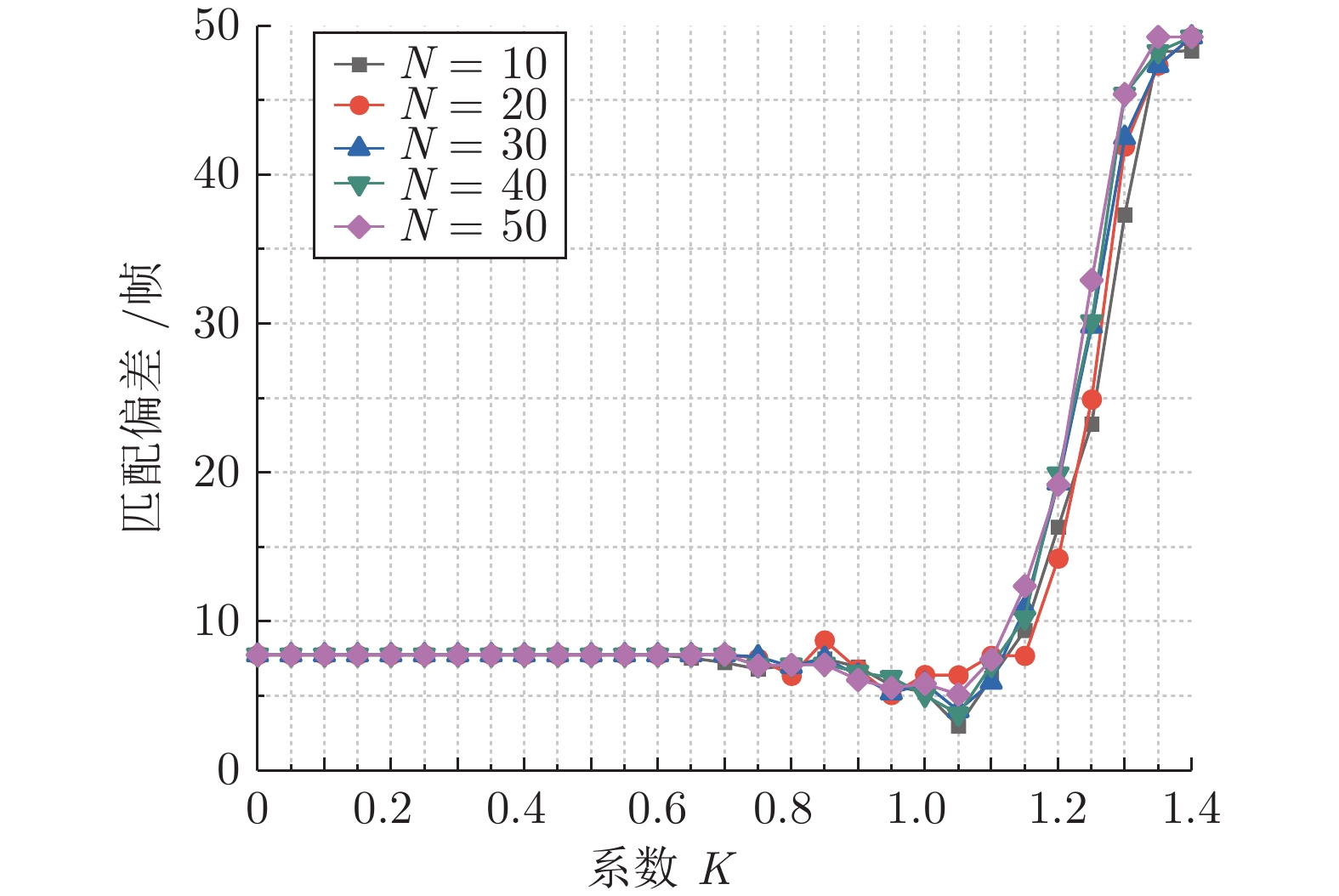
表 1 Nordland和MTRHK数据集中所需参数设置
Table 1 Parameter settings for Norland and MTRHK datasets
参数符号 参数定义 参数值 (Nordland) 参数值 (MTRHK) Vmin 最小路径拟合速度 0.8 0 Vmax 最大路径拟合速度 1.2 1.5 Vstep 路径拟合速度步长 0.1 0.1 Nc 像素对提取个数 512 512 K 关键区域检测系数 1.05 1.05 TL 最佳匹配距离阈值 175 175 表 2 不同语义分割模型间的精度对比
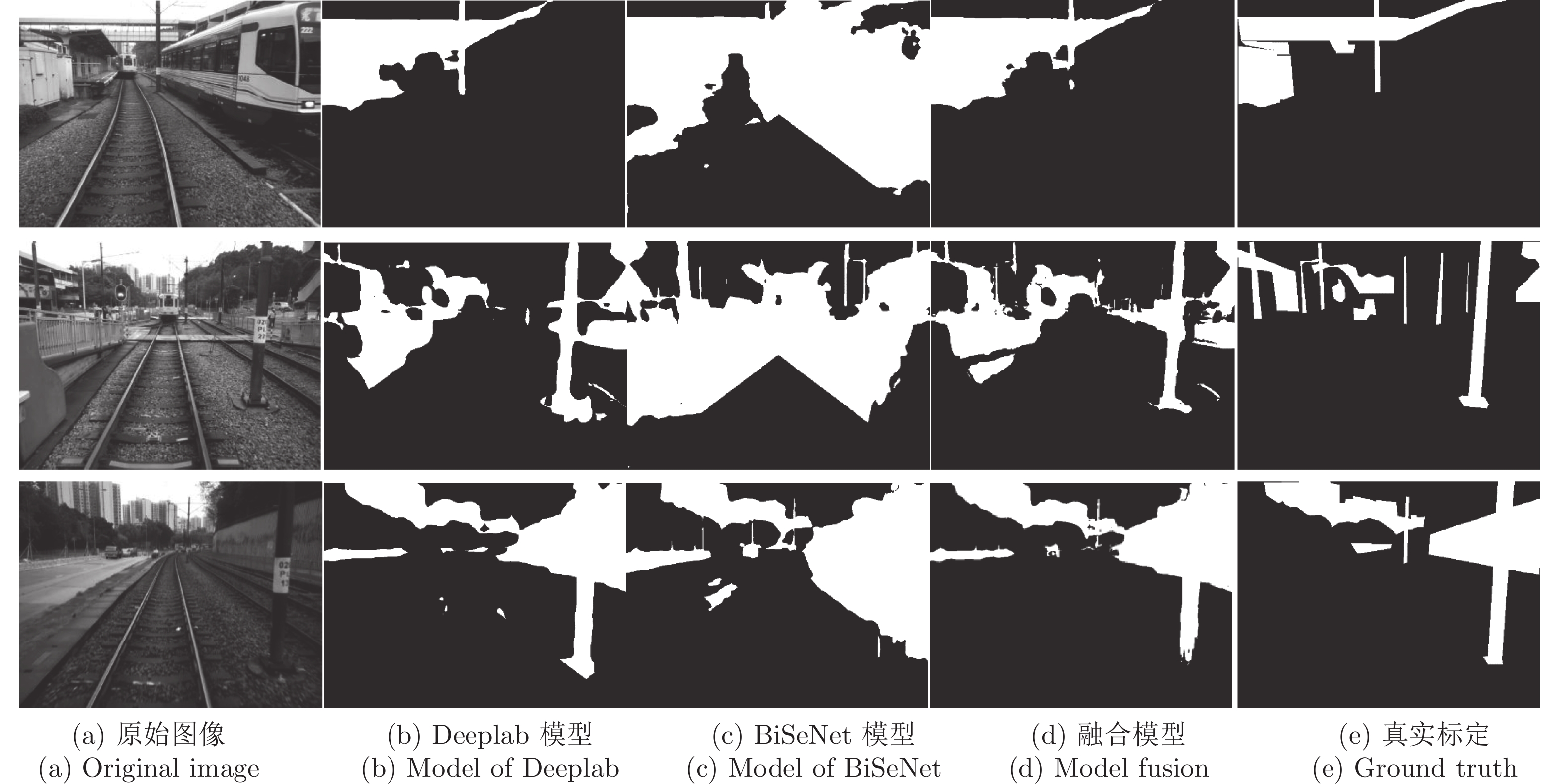
Table 2 Accuracy comparison of different semantic segmentation network
语义分割网络 平均交并比 (%) Nordland MTRHK FCN 67.9 54.9 PSPNet 70.8 32.7 Deeplab 71.7 55.8 RefineNet 72.5 59.2 DFN 73.0 48.2 BiSeNet 72.2 36.2 融合模型 78.0 64.6 表 3 不同方法对每帧图像的平均描述时间对比(s)
Table 3 Comparison of average describing time for each image by different methods (s)
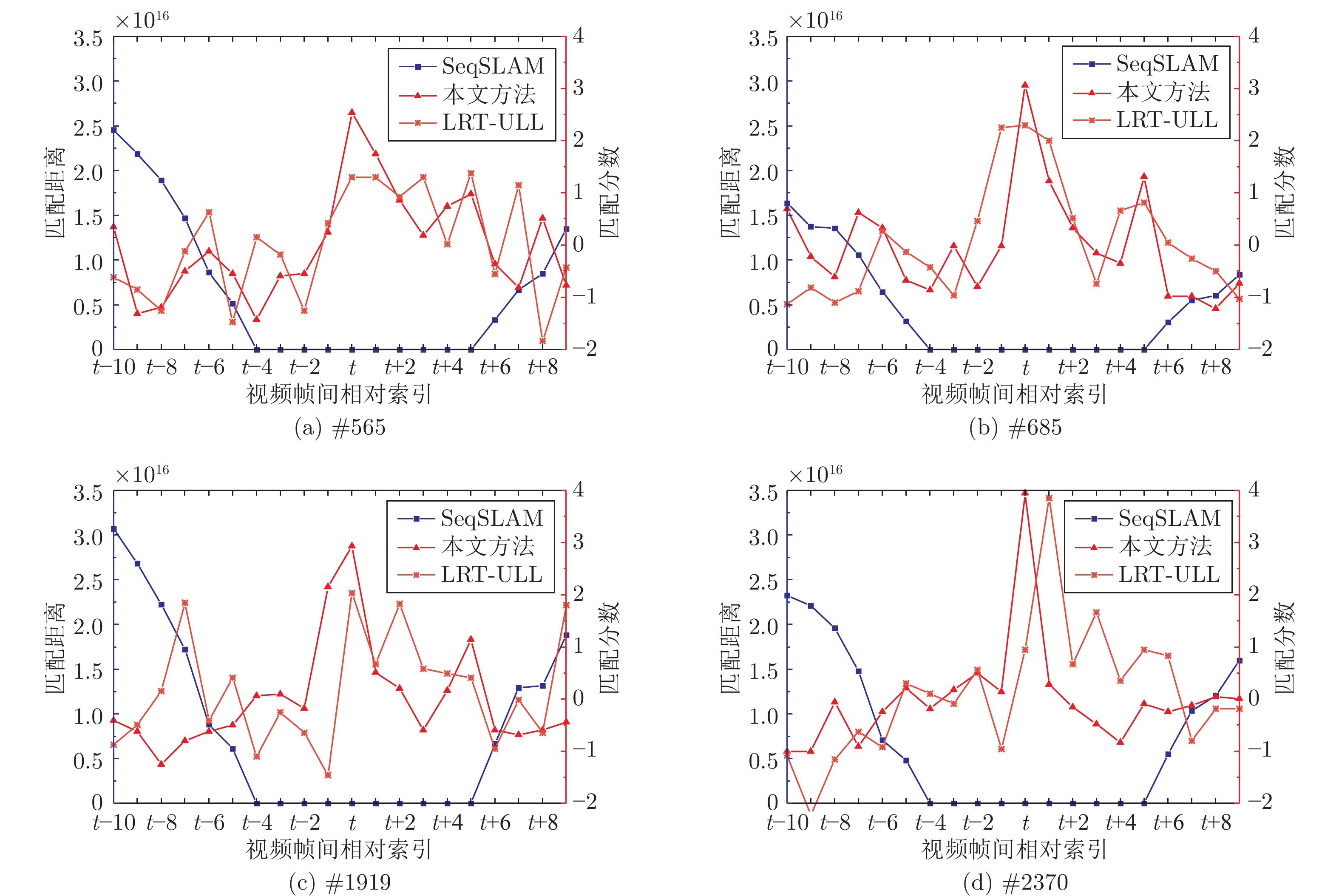
方法 SeqSLAM LRT-ULL 本文方法 时间 0.1327 1.2791 0.1238 表 4 不同场景跟踪算法的准确率(%)与召回率(%)
Table 4 Precision (%) and recall (%) of different scene tracking methods
数据集 准确率 (召回率) SeqSLAM SeqCNNSLAM 本文方法 Nordland 89.56 (100) 99.67 (100) 99.24 (100) MTRHK 39.71 (100) 60.72 (100) 90.20 (100) 表 5 在Nordland数据集和MTRHK数据集中不同场景跟踪算法的消耗时间(s)
Table 5 The consumption time of different scene tracking methods in the Nordland and the MTRHK dataset (s)
数据集 平均消耗时间 SeqSLAM SeqCNNSLAM 本文方法 Nordland 0.67×10−1 6.51×10−3 3.17×10−3 MTRHK 0.50×10−1 4.90×10−3 2.37×10−3 -
[1] Martinez C M, Heucke M, Wang F Y, Gao B, Cao D P. Driving style recognition for intelligent vehicle control and advanced driver assistance: A survey. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2018, 19(3): 666−676 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2017.2706978 [2] 俞毓锋, 赵卉菁, 崔锦实, 査红彬. 基于道路结构特征的智能车单目视觉定位. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(5): 725−734Yu Yu-Feng, Zhao Hui-Jing, Cui Jin-Shi, Zha Hong-Bin. Road structural feature based monocular visual localization for intelligent vehicle. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(5): 725−734 [3] Bresson G, Alsayed Z, Yu L, Glaser S. Simultaneous localization and mapping: A survey of current trends in autonomous driving. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles, 2017, 2(3): 194−220 doi: 10.1109/TIV.2017.2749181 [4] 丁文东, 徐德, 刘希龙, 张大朋, 陈天. 移动机器人视觉里程计综述. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(3): 385−400Ding Wen-Dong, Xu De, Liu Xi-Long, Zhang Da-Peng, Chen Tian. Review on visual odometry for mobile robots. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(3): 385−400 [5] Cadena C, Carlone L, Carrillo H, Latif Y, Scaramuzza D, Neira J, et al. Past, present, and future of simultaneous localization and mapping: Toward the robust-perception age. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2016, 32(6): 1309−1332 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2016.2624754 [6] 姚萌, 贾克斌, 萧允治. 基于单目视频和无监督学习的轻轨定位方法. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(9): 2127−2134 doi: 10.11999/JEIT171017Yao Meng, Jia Ke-Bin, Siu Wan-Chi. Learning-based localization with monocular camera for light-rail system. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2018, 40(9): 2127−2134 doi: 10.11999/JEIT171017 [7] Piasco N, Sidibé D, Demonceaux C, Gouet-Brunet V. A survey on visual-based localization: On the benefit of heterogeneous data. Pattern Recognition, 2018, 74: 90−109 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2017.09.013 [8] Lowry S, Sünderhauf N, Newman P, Leonard J J, Cox D, Corke P, et al. Visual place recognition: A survey. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2016, 32(1): 1−19 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2015.2496823 [9] Cummins M, Newman P. Appearance-only SLAM at large scale with FAB-MAP 2.0. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2011, 30(9): 1100−1123 doi: 10.1177/0278364910385483 [10] Mur-Artal R, Montiel J M M, Tardós J D. ORB-SLAM: A versatile and accurate monocular slam system. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2015, 31(5): 1147−1163 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2015.2463671 [11] Naseer T, Burgard W, Stachniss C. Robust visual localization across seasons. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2018, 34(2): 289−302 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2017.2788045 [12] Qiao Y L, Cappelle C, Ruichek Y. Visual localization across seasons using sequence matching based on multi-feature combination. Sensors, 2017, 17(11): 2442 doi: 10.3390/s17112442 [13] Zhang X M, Zhao Z H, Zhang H J, Wang S Z, Li Z J. Unsupervised geographically discriminative feature learning for landmark tagging. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2018, 149: 143−154 doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2018.03.005 [14] Hou Y, Zhang H, Zhou S L. Convolutional neural network-based image representation for visual loop closure detection. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Information and Automation. Lijiang, China: IEEE, 2015. 2238−2245 [15] 刘丽, 赵凌君, 郭承玉, 王亮, 汤俊. 图像纹理分类方法研究进展和展望. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(4): 584−607Liu Li, Zhao Ling-Jun, Guo Cheng-Yu, Wang Liang, Tang Jun. Texture classification: State-of-the-art methods and prospects. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(4): 584−607 [16] Sünderhauf N, Shirazi S, Dayoub F, Upcroft B, Milford M. On the performance of ConvNet features for place recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Hamburg, Germany: IEEE, 2015. 4297−4304 [17] Kong Y G, Liu W, Chen Z P. Robust ConvNet landmark-based visual place recognition by optimizing landmark matching. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 30754−30767 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2901984 [18] Bai D D, Wang C Q, Zhang B, Yi X D, Yang X J. Sequence searching with CNN features for robust and fast visual place recognition. Computers & Graphics, 2018, 70: 270−280 [19] Arroyo R, Alcantarilla P F, Bergasa L M, Romera E. Fusion and binarization of CNN features for robust topological localization across seasons. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Daejeon, Korea (South): IEEE, 2016. 4656−4663 [20] Milford M J, Wyeth G F. SeqSLAM: Visual route-based navigation for sunny summer days and stormy winter nights. In: Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Saint Paul, MN, USA: IEEE, 2012. 1643−1649 [21] Milford M. Vision-based place recognition: How low can you go?. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2013, 32(7): 766−789 doi: 10.1177/0278364913490323 [22] Pepperell E, Corke P I, Milford M J. All-environment visual place recognition with SMART. In: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Hong Kong, China: IEEE, 2014. 1612−1618 -




 下载:
下载: