Optimal Output Regulation of Partially Linear Discrete-time Systems Using Reinforcement Learning
-
摘要: 针对同时具有线性外部干扰与非线性不确定性下的离散时间部分线性系统的最优输出调节问题, 提出了仅利用在线数据的基于强化学习的数据驱动控制方法. 首先, 该问题可拆分为一个受约束的静态优化问题和一个动态规划问题, 第一个问题可以解出调节器方程的解. 第二个问题可以确定出控制器的最优反馈增益. 然后, 运用小增益定理证明了存在非线性不确定性离散时间部分线性系统的最优输出调节问题的稳定性. 针对传统的控制方法需要准确的系统模型参数用来解决这两个优化问题, 提出了一种数据驱动离线策略更新算法, 该算法仅使用在线数据找到动态规划问题的解. 然后, 基于动态规划问题的解, 利用在线数据为静态优化问题提供了最优解. 最后, 仿真结果验证了该方法的有效性.Abstract: A data-driven control method only using online data based on reinforcement learning is proposed for the optimal output regulation problem of discrete-time partially linear systems with both linear disturbance and nonlinear uncertainties. First, the problem can be split into a constrained static optimization problem and a dynamic one. The solution of the first problem is corresponding to the solution of the regulator equation. The second can determine the optimal feedback gain of the controller. Then the small-gain theorem is used to prove the stability of the optimal output regulation problem of discrete-time partially linear systems with nonlinear uncertainties. The traditional control method needs the dynamics of the system to solve the two problems. But for this problem, a data-driven off-policy algorithm is proposed using only the measured data to find the solution of the dynamic optimization problem. Then, based on the solution of the dynamic one, the solution of the static optimization problem can be found only using data online. Finally, simulation results verify the effectiveness of the proposed method.
-
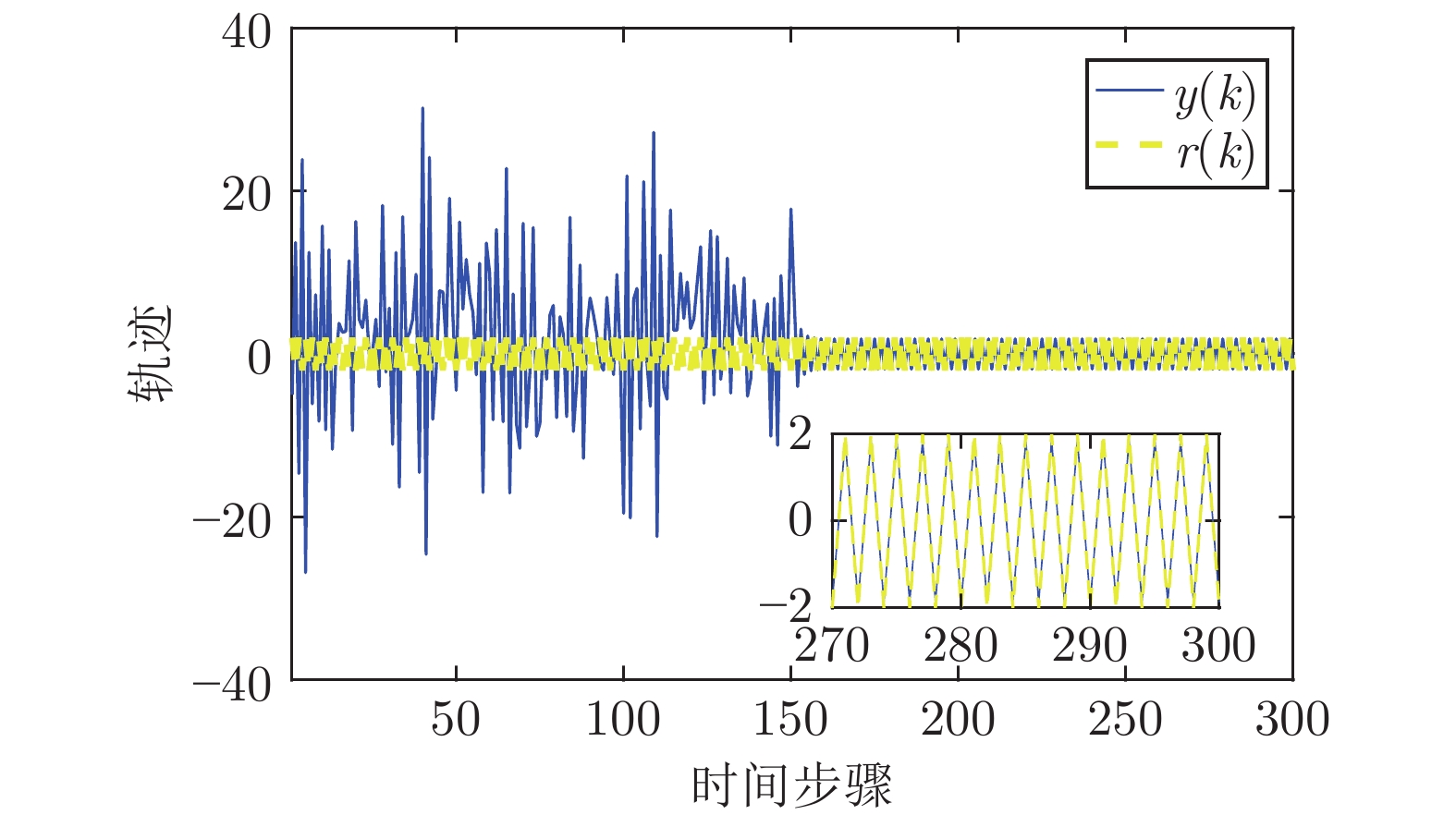
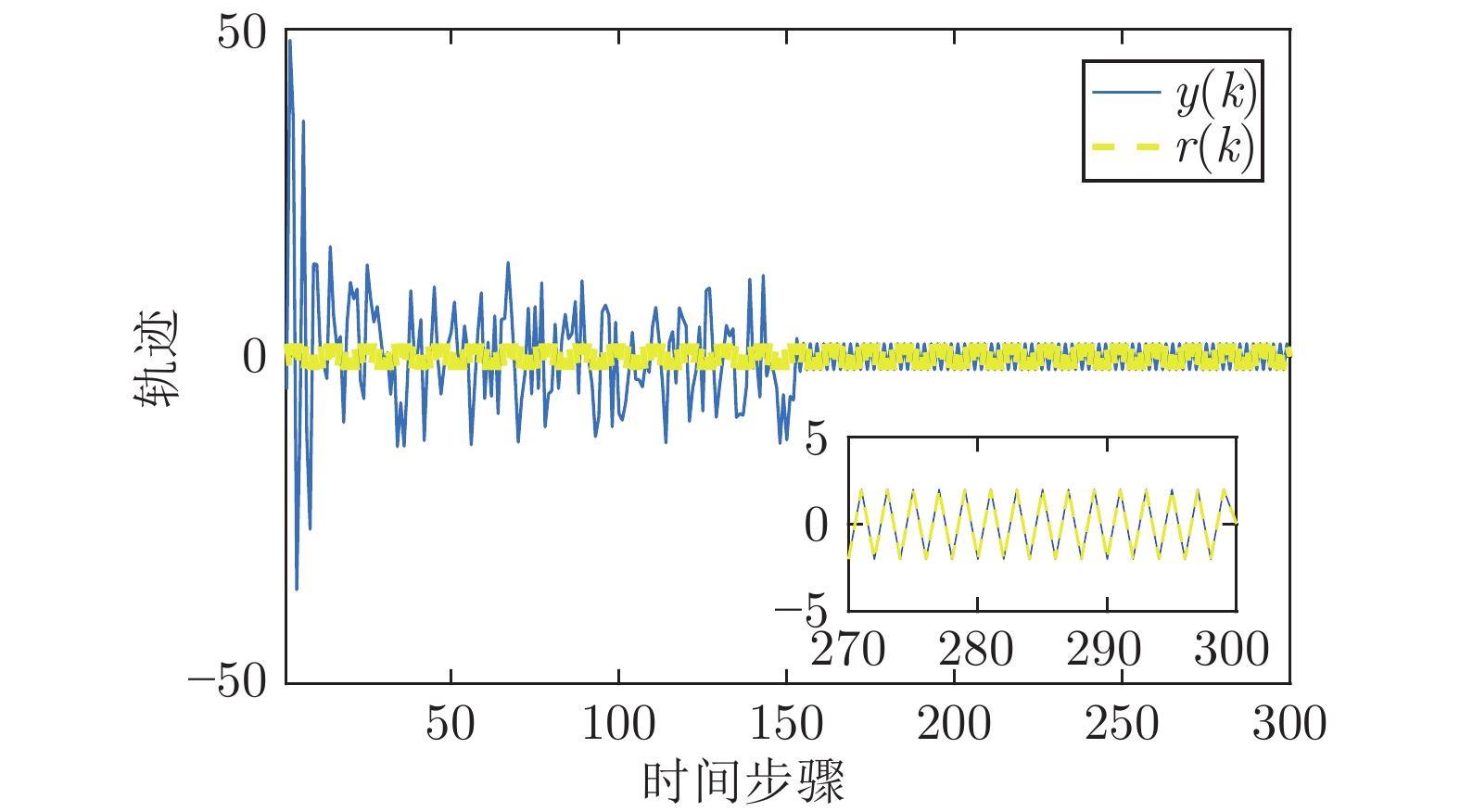
表 1 对比实验评价指标
Table 1 Performance index of comparison experiment
$220<k<280$ IAE RMSE 本文方法 1.8330×10−6 3.6653×10−8 对比方法 8.2293 0.1349 -
[1] Francis B A. The linear multivariable regulator problem. SIAM Journal on Control Optimization, 1977, 15(3): 486−505 doi: 10.1137/0315033 [2] Davison E, Goldenberg A. Robust control of a general servomechanism problem: The servo compensator. Automatica, 1975, 11(5): 461−471 doi: 10.1016/0005-1098(75)90022-9 [3] Davison E. The robust control of a servomechanism problem for linear time-invariant multivariable systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1976, 1(1): 25−34 [4] Sontag E D. Adaptation and regulation with signal detection implies internal model. System. & Control Letters, 2003, 50(2): 119−126 [5] Huang J. Nonlinear Output Regulation: Theory and Applications. Philadelphia: Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, 2004. [6] Saberi A, Stoorvogel A A, Sannuti P, Shi G Y. On optimal output regulation for linear systems. International Journal of Control, 76(4): 2003, 319−333 doi: 10.1080/0020717031000073054 [7] Gao W N, Jiang Z P. Global optimal output regulation of partially linear systems via robust adaptive dynamic programming. IFAC-Papers OnLine, 2015, 48(11): 742−747 doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2015.09.278 [8] Gao W N, Jiang Z P. Adaptive dynamics programming and adptive optimal output regulation of linear systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2016, 61(12): 4164−4169 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2016.2548662 [9] Kiumarsi B, Vamvoudakis K G, Modares H, Lewis F L. Optimal and autonomous control using reinforcement learning: a survey. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2018, 29(6): 2042−2062 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2017.2773458 [10] 李臻, 范家璐, 姜艺, 柴天佑. 一种基于Off-policy的无模型输出数据反馈H∞控制方法. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(9): 2182−2193Li Zhen, Fan Jia-Lu, Jiang Yi, Chai Tian-You. A model-free H∞ method based on off-policy with output data feedback. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021,47(9): 2182−2193 [11] 姜艺. 数据驱动的复杂工业过程运行优化控制方法研究[博士论文], 东北大学, 中国, 2020Jiang Yi. Research on Data-driven Operational Optimization Control Approach for Complex Industrial Processes[Ph.D. disse-rtation], Northeastern University, China, 2020 [12] Kiumarsi B, Lewis F L, Modares H, Karimpour A, Naghibi M B. Reinforcement Q-learning for optimal tracking control of linear discrete-time systems with unknown dynamics. Automatica, 2014, 50(4): 1167−1175 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2014.02.015 [13] Kiumarsi B, Lewis F L, Naghibi M B, Karimpour A. Optimal tracking control of unknown discrete-time linear systems using input-output measured data. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2015, 4(12): 2770−2779 [14] Kiumarsi B, Lewis F L. Actor-critic-based optimal tracking for partially unknown nonlinear discrete-time systems. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2015, 26(1): 140−151 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2014.2358227 [15] Kiumarsi B, Lewis F L, Jiang Z P. H∞ control of linear discrete-time systems: off-policy reinforcement learning. Automatica A Journal of Ifac the International Federation of Automatic Control, 2017, 78: 144−152 [16] Modares H, Lewis F L, Jiang Z P. H∞ tracking control of completely unknown continuous-time systems via off-policy reinforcement learning. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and learning systems, 2015, 26(10): 2550−2562 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2015.2441749 [17] Jiang Y, Fan J L, Chai T Y, Lewis F L, Li J N. Tracking control for linear discrete-time networked control systems with unknown dynamics and dropout. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2018, 29(10): 4607-4620 [18] Jiang Y, Kiumarsi B, Fan J L, Chai T Y, Li J N, Lewis F L. Optimal output regulation of linear discrete-time system with unknow dynamics using reinforcement learning. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2020, 50(4): 3147−3156 [19] Khalil H K, Grizzle J W. Nonlinear Systems. Upper Saddle Riv-er: Prentice hall, 2002. [20] Lan W Y, Huang J. Robust output regulation for discrete-time nonlinear systems. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2005, 15(2):63−81 doi: 10.1002/rnc.970 [21] Hewer G. An iterative technique for the computation of the steady state gains for the discrete optimal regulator. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1971, 16(4): 382−384 doi: 10.1109/TAC.1971.1099755 [22] Werbos P J. Neural network for control and system identification. In: Proceedings of the 28th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control. Tampa, USA: 1989, 260−265 [23] Jiang Z P, Wang Y. Input-to-state stability for discrete-time nonlinear systems. Automatica, 2001, 37: 857−869. doi: 10.1016/S0005-1098(01)00028-0 [24] Jiang Z P, Teel A R, Praly L. Small-gain theorem for ISS systems and applications. Mathematics of Control Signals and Systems, 1994, 7(2):95−120 doi: 10.1007/BF01211469 [25] 刘腾飞, 姜钟平. 信息约束下的非线性控制, 北京: 科学出版社, 2018.Liu Teng-Fei, Jiang Zhong-Ping. Nonlinear Control Under Information Constraints, Beijing: Science Press, 2018. [26] Jiang Y, Fan J L, Chai T Y, Lewis F L. Dual-rate operational optimal control for flotation industrial process with unknown operational model. IEEE Transaction on Industrial Electronics, 2019, 66(6): 4587−4599 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2018.2856198 [27] Jiang Y, Fan J L, Chai T Y, Li J N, Lewis F L. Data driven flotation industrial process operational optimal control based on reinforcement learning. IEEE Transcations on Industrial Informatics, 2018, 66(5): 1974−1989 [28] 吴倩, 范家璐, 姜艺, 柴天佑. 无线网络环境下数据驱动混合选别浓密过程双率控制方法. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(6): 1128−1141Wu Qian, Fan Jia-Lu, Jiang Yi, Chai Tian-You. Data-Driven Dual-Rate Control for Mixed Separation Thickening Process in a Wireless Network Environment. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(6): 1128−1141. [29] 姜艺, 范家璐, 贾瑶, 柴天佑. 数据驱动的浮选过程运行反馈解耦控制方法. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(4): 759−770Jiang Yi, Fan Jia-Lu, Jia Yao, Chai Tian-You. Data-driven flotation process operational feedback decoupling control. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(4): 759−770 -





 下载:
下载: