Image Segmentation Based on Higher-order MRF Model With Multi-node Topological Overlap Measure
-
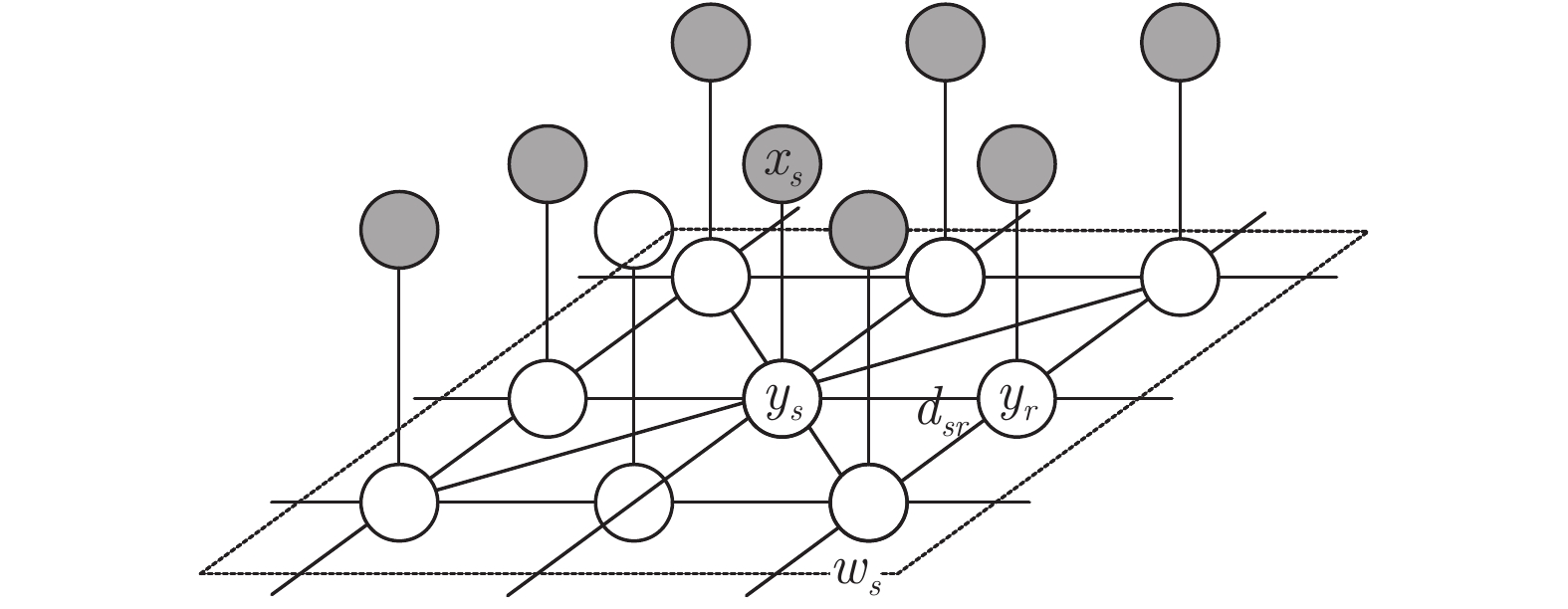
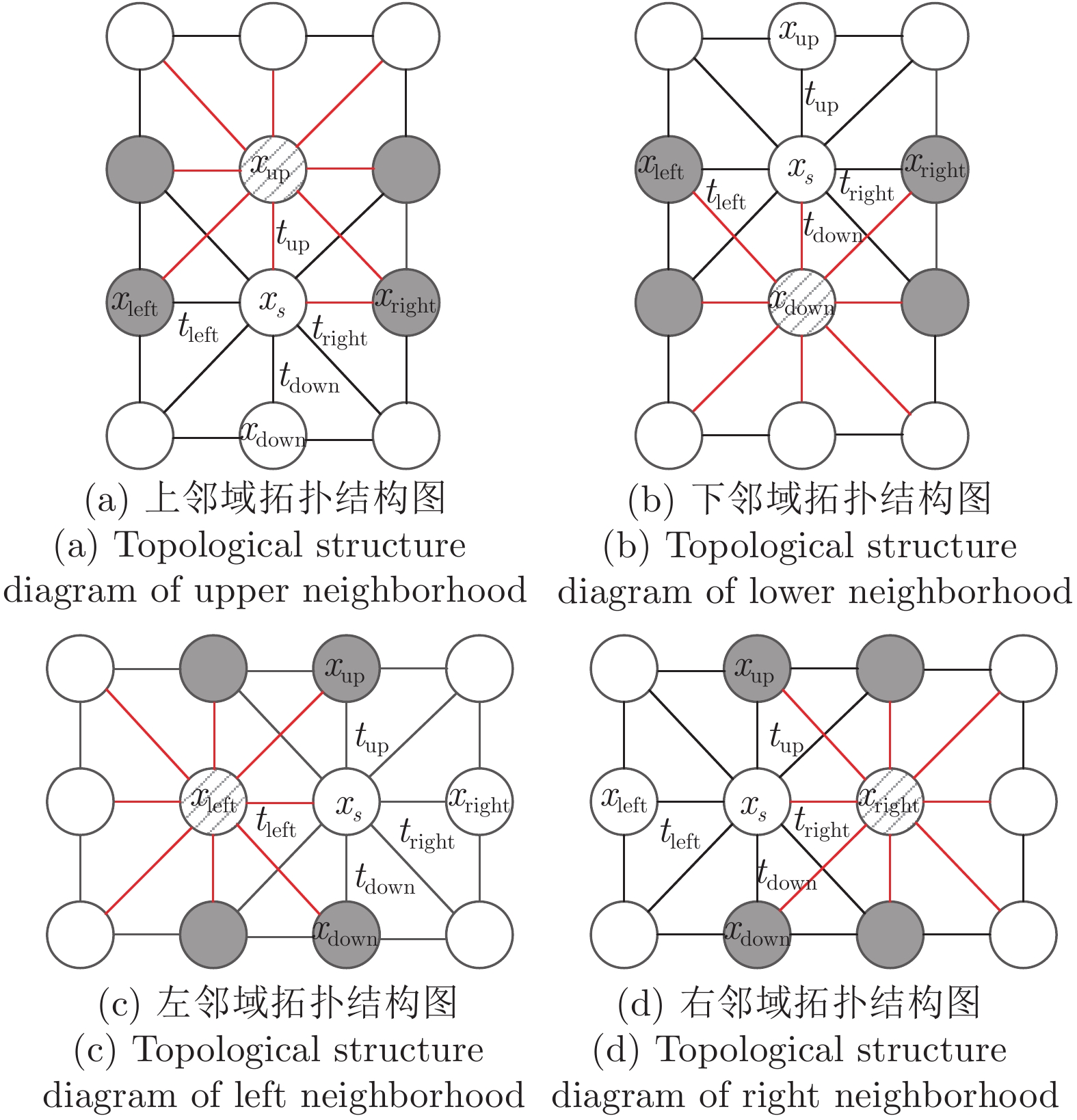
摘要: 针对低阶马尔科夫随机场(Markov random field, MRF)模型难以有效表达自然图像中复杂的先验知识而造成误分割问题, 提出一种基于多节点拓扑重叠测度高阶MRF模型(Higher-order MRF model with multi-node topological overlap measure, MTOM-HMRF)的图像分割方法. 首先, 为描述图像局部区域内多像素蕴含的复杂空间拓扑结构信息, 利用多节点拓扑重叠测度建立图像局部区域的高阶先验模型; 其次, 利用较大的局部区域包含更多的标签节点信息能力, 基于Pairwise MRF模型建立基于局部区域的部分二阶Potts先验模型, 提高分割模型的抗噪能力; 再次, 为有效描述观察图像场与其标签场的似然特征分布, 研究利用局部区域内邻接像素的Hamming距离引入图像局部空间相关性, 建立局部空间一致性约束的高斯混合分布; 最后, 基于MRF框架建立用于图像分割的多节点拓扑重叠测度高阶MRF模型, 采用Gibbs采样算法对提出模型进行优化. 实验结果表明, 提出模型不仅能有效抵抗图像强噪声和复杂的纹理突变干扰, 鲁棒性更好, 而且具有更准确的图像分割结果.Abstract: Aim at the problem that lower-order Markov random field (MRF) model is inefficient to capture the rich prior knowledge of nature images which may bring out error image segmentation results, a new image segmentation method is proposed based on higher-order MRF model with multi-node topological overlap measure (MTOM-HMRF). Firstly, to capture complex spatial topological structure information embedded in the local region of images, the proposed method utilizes the topological overlap measure among multi-image-pixels to build higher-order prior model for the local region of images. Secondly, according that larger local region contains more information in label nodes, a partial 2-order Potts model is built based on pairwise MRF model, which increases the anti-noise capability of the proposed model. Thirdly, to efficiently describe the likelihood distribution between observed image field and its label field, a local spatial consistency constraints Gaussian mixture distribution is constructed based on the Hamming distribution between neighbor pixels which incorporated image local spatial correlation. Finally, a topological overlap measure higher-order MRF model is proposed for image segmentation based on the MRF framework, and Gibbs sampling algorithm is used to optimize the proposed model. Experimental results on artificial synthesis images and nature images show that the proposed model is not only efficient to overcome the impact of strong noise and complex texture abrupt on image segmentation results, thus possesses more robustness, but also can provide more accurate edge segmentation results.
-
表 1 人工合成加噪图像在不同模型下的分割结果对比
Table 1 Synthetic image segmentation results of different models
Image Model Number of iterations Running time (s) CCR (均值 ± 标准差) 高斯白噪声方差 300 Pairwise MRF 46 12.496 0.9119 ± 0.0020 Robust ${{\cal{P}}^n}$ MRF 94 13.014 0.9483 ± 0.0019 不带 MTOM 项的提出模型 162 17.374 0.9793 ± 0.0012 提出模型 133 10.486 0.9977 ± 0.0002 高斯白噪声方差 900 Pairwise MRF 45 12.315 0.8854 ± 0.0039 Robust ${{\cal{P}}^n}$ MRF 83 11.588 0.9297 ± 0.0034 不带 MTOM 项的提出模型 149 11.853 0.9902 ± 0.0005 提出模型 120 9.521 0.9942 ± 0.0006 椒盐噪声 0.02 Pairwise MRF 44 11.917 0.8859 ± 0.0034 Robust ${{\cal{P}}^n}$ MRF 80 11.873 0.9386 ± 0.0019 不带 MTOM 项的提出模型 144 10.017 0.9883 ± 0.0004 提出模型 163 12.947 0.9978 ± 0.0001 椒盐噪声 0.05 Pairwise MRF 43 11.523 0.7463 ± 0.0025 Robust ${{\cal{P}}^n}$ MRF 77 11.955 0.9017 ± 0.0036 不带 MTOM 项的提出模型 94 8.925 0.9784 ± 0.0008 提出模型 160 12.605 0.9976 ± 0.0001 椒盐噪声 0.10 Pairwise MRF 41 10.997 0.5465 ± 0.0027 Robust ${{\cal{P}}^n}$ MRF 78 11.290 0.7915 ± 0.0047 不带 MTOM 项的提出模型 76 7.556 0.9440 ± 0.0012 提出模型 155 12.248 0.9962 ± 0.0003 表 2 自然图像在不同方法下的评价指标比较
Table 2 Comparison of evaluation indexes of natural image on different models
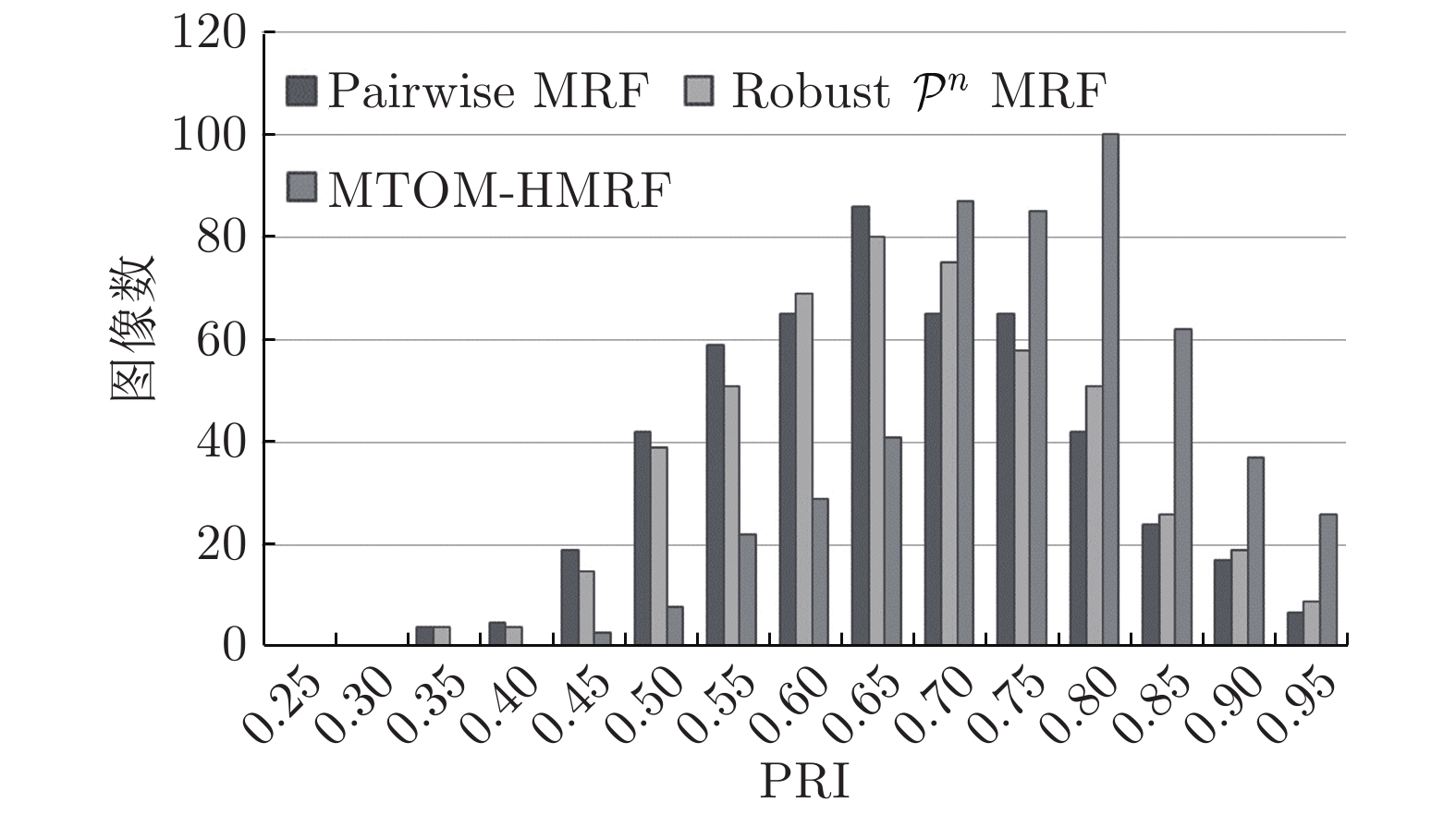
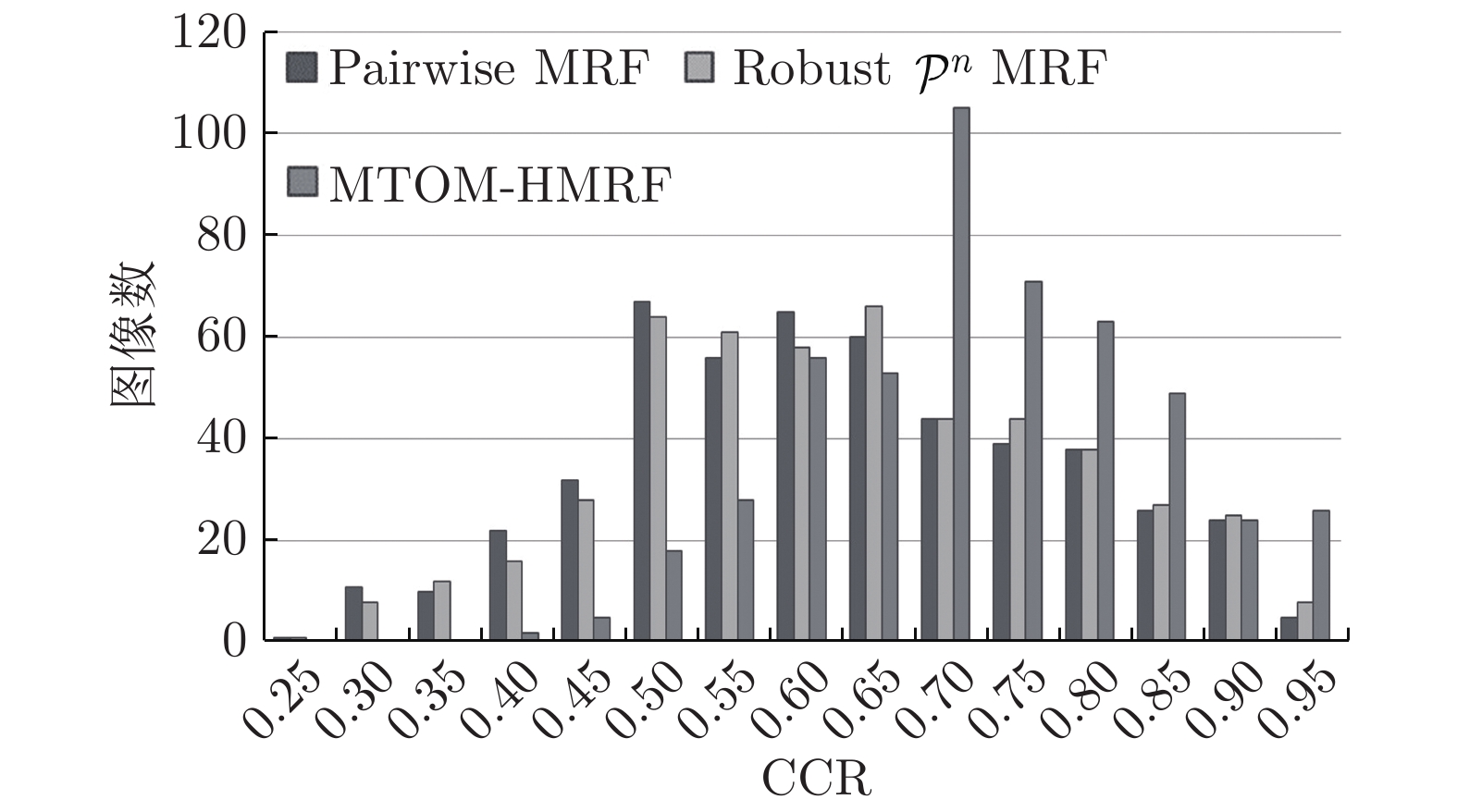
Image Evaluation index Pairwise MRF (均值 ± 标准差) Robust ${{\cal{P}}^n}$ MRF (均值 ± 标准差) MTOM-HMRF (均值 ± 标准差) 3 096 PRI 0.9159 ± 0.0008 0.9398 ± 0.0024 0.9456 ± 0.0004 CCR 0.9283 ± 0.0005 0.9431 ± 0.0003 0.9820 ± 0.0007 135 069 PRI 0.9635 ± 0.0003 0.9640 ± 0.0002 0.9652 ± 0.0004 CCR 0.9646 ± 0.0002 0.9649 ± 0.0001 0.9943 ± 0.0000 196 073 PRI 0.8598 ± 0.0019 0.8818 ± 0.0026 0.9522 ± 0.0005 CCR 0.9064 ± 0.0014 0.9186 ± 0.0016 0.9905 ± 0.0005 62 096 PRI 0.9331 ± 0.0006 0.9333 ± 0.0004 0.9451 ± 0.0006 CCR 0.8970 ± 0.0006 0.8978 ± 0.0006 0.9611 ± 0.0003 167 062 PRI 0.9529 ± 0.0009 0.9542 ± 0.0007 0.9705 ± 0.0001 CCR 0.9448 ± 0.0009 0.9464 ± 0.0007 0.9938 ± 0.0005 238 011 PRI 0.8631 ± 0.0001 0.8709 ± 0.0000 0.8711 ± 0.0001 CCR 0.8428 ± 0.0042 0.8429 ± 0.0000 0.9697 ± 0.0000 253 036 PRI 0.9571 ± 0.0004 0.9574 ± 0.0002 0.9600 ± 0.0005 CCR 0.9257 ± 0.0004 0.9286 ± 0.0008 0.9703 ± 0.0002 241 004 PRI 0.8758 ± 0.0002 0.8767 ± 0.0001 0.8801 ± 0.0005 CCR 0.8182 ± 0.0003 0.8212 ± 0.0003 0.9236 ± 0.0002 8 068 PRI 0.9093 ± 0.0006 0.9100 ± 0.0004 0.9182 ± 0.0007 CCR 0.9153 ± 0.0006 0.9154 ± 0.0005 0.9790 ± 0.0002 24 063 PRI 0.9043 ± 0.0003 0.9040 ± 0.0002 0.9076 ± 0.0035 CCR 0.8910 ± 0.0039 0.8906 ± 0.0003 0.9572 ± 0.0003 55 067 PRI 0.9205 ± 0.0002 0.9545 ± 0.0001 0.9552 ± 0.0002 CCR 0.8657 ± 0.0004 0.9072 ± 0.0002 0.9748 ± 0.0001 189 080 PRI 0.9009 ± 0.0002 0.9003 ± 0.0003 0.9066 ± 0.0014 CCR 0.9181 ± 0.0003 0.9174 ± 0.0002 0.9727 ± 0.0003 198 087 PRI 0.8200 ± 0.0004 0.8188 ± 0.0005 0.8249 ± 0.0009 CCR 0.8515 ± 0.0004 0.8493 ± 0.0003 0.9280 ± 0.0004 311 068 PRI 0.8688 ± 0.0017 0.6542 ± 0.0014 0.9265 ± 0.0016 CCR 0.8819 ± 0.0012 0.7264 ± 0.0013 0.9743 ± 0.0004 15 088 PRI 0.8944 ± 0.0007 0.8948 ± 0.0007 0.9170 ± 0.0015 CCR 0.9095 ± 0.0006 0.9096 ± 0.0006 0.9676 ± 0.0005 BSDS500数据集 PRI 0.6864 0.6962 0.7794 CCR 0.6478 0.6584 0.7452 表 3 自然图像在不同方法下的效率比较
Table 3 Comparison of the efficiency of natural image on different models
Image Pairwise MRF Robust ${{\cal{P}}^n}$ MRF MTOM-HMRF Number of iterations Running time (s) Number of iterations Running time (s) Number of iterations Running time (s) 3 096 44 13.356 84 26.084 112 9.578 135 069 33 10.192 60 18.440 140 12.045 196 073 47 14.184 87 26.472 134 11.559 62 096 44 17.130 83 33.516 139 15.443 167 062 40 15.558 88 33.239 109 12.082 238 011 9 3.466 74 22.964 101 11.919 253 036 42 16.144 74 29.421 171 19.248 241 004 46 21.275 80 32.993 197 25.981 8 068 43 13.405 89 27.509 154 19.192 24 063 73 29.401 74 29.421 197 32.271 55 067 38 19.117 34 17.517 146 31.874 189 080 38 12.476 72 22.266 189 23.924 198 087 41 12.927 79 25.239 177 23.081 311 068 44 18.138 88 36.111 153 26.101 15 088 42 12.881 87 27.319 116 15.346 -
[1] 余淼, 胡占义. 高阶马尔科夫随机场及其在场景理解中的应用. 自动化学报, 2015, 41(7): 1213--1234.Yu M, Hu Z Y. Higher-order Markov Random Fields and Their Applications in Scene Understanding. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(7): 1213--1234). [2] Kohli P, Kumar M P, Torr P H S. P3 & beyond: move making algorithms for solving higher order functions. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2009, 31(9): 1645--1656. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2008.217 [3] Kohli P, Kumar M P, Torr P H S. P3 & Beyond: Solving energies with higher order cliques. In: Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2007). Minneapolis, MN, USA : IEEE, 2007. 1−8 [4] Kohli P, Ladickµy L, Torr P H S. Robust higher order potentials for enforcing label consistency. In: Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2008). Anchorage, AK, USA: IEEE, 2008. 1−8 [5] 夏平, 施宇, 雷帮军, 龚国强, 胡蓉, 师冬霞.复小波域混合概率图模型的超声医学图像分割.自动化学报, 2021, 47(1): 185-196 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c180132Xia Ping, Shi Yu, Lei Bang-Jun, Gong Guo-Qiang, Hu Rong, Shi Dong-Xia. Ultrasound medical image segmentation based on hybrid probabilistic graphical model in complex-wavelet domain. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(1): 185-196 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c180132 [6] Li S, Ishfaq A, Alexander J A. Superpixel-enhanced pairwise conditional random field for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 25th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP). Athens, Greece: IEEE, 2018. 271−275 [7] 宋艳涛, 纪则轩, 孙权森. 基于图像片马尔科夫随机场的脑MR图像分割算法. 自动化学报, 2014(8): 1754--1763.Song Y T, Ji Z X, Sun Q S, Brain MR Image Segmentation Algorithm Based on Markov Random Field with Image Patch. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014(8): 1754--1763. [8] Kim S, Chang D Y, Nowozin S, Kohli P. Image Segmentation Using Higher-Order Correlation Clustering. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 2014, 36(9): 1761--1774. [9] Ji Z X, Huang Y B, Sun Q S, Guo C. A spatially constrained generative asymmetric Gaussian mixture model for image segmentation. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2016, 40(PB): 611--626. [10] Zhang H, Wen T, Zheng Y H, Xu D H. Two Fast and Robust Modified Gaussian Mixture Models Incorporating Local Spatial Information for Image Segmentation. Journal of Signal Processing Systems, 2015, 81(1): 45--58. doi: 10.1007/s11265-014-0898-8 [11] Ji Z X, Huang Y B, Xia Y, Zheng Y H. A robust modified Gaussian mixture model with rough set for image segmentation. Neurocomputing. 2017, 266, 550--565. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2017.05.069 [12] Niu S, Chen Q, Sisternes L D, et al. Robust noise region-based active contour model via local similarity factor for image segmentation. Pattern Recognition, 2017, 61: 104--119. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2016.07.022 [13] Bi H, Tang H, Yang G. Accurate image segmentation using Gaussian mixture model with saliency map. Pattern Analysis and Applications, 2018, 21: 869--878. doi: 10.1007/s10044-017-0672-1 [14] 徐胜军, 孟月波, 刘光辉, 等. 用于图像分割的局部区域一致性流形约束MRF模型. 控制与决策, 2019, 34(5): 997--1003.Xu S J, Meng Y B, Liu G H, et al. Local region consistency manifold constrained MRF model for image segmentation. Control and Decision, 2019, 34(5): 997--1003. [15] 冯宝, 陈业航, 刘壮盛, 等. 结合MRF 能量和模糊速度的乳腺癌图像分割方法. 自动化学报, DOI: 10.16383/j.aas.c180759.Feng B, Chen Y H, Liu Z S, et al. Segmentation of Breast Cancer on DCE-MRI Images with MRF Energy and Fuzzy Speed Function. Acta Automatica Sinica, DOI: 10.16383/j.aas.c180759. [16] Shao Y, Sang N, Gao C, Li M. Spatial and Class Structure Regularized Sparse Representation Graph for Semi-Supervised Hyperspectral Image Classification. Pattern Recognition, 2018, 81: 81--94. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2018.03.027 [17] Dornaika F, Weng L. Sparse graphs with smoothness constraints: Application to dimensionality reduction and semi-supervised classification, Pattern Recognition, 2019, 95: 285--295. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2019.06.015 [18] Ravasz E, Somera A, Mongru D, et al. Hierarchical organization of modularity in metabolic networks. Science, 2002, 297(5586): 1551--1555. doi: 10.1126/science.1073374 [19] Yip A M, Horvath S. Gene network interconnectedness and the generalized topological overlap measure. BMC Bioinformatics, 2007, 8(1): 22. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-8-22 [20] Li A. Generalizations of the Topological Overlap Measure for Neighborhood Analysis and Module Detection in Gene and Protein Networks [Ph. D. dissertation], University of California, USA, 2008 [21] Steuer R, Kurths J, Daub CO, et al. Themutual information: Detecting and evaluating dependencies between variables. Bioinformatics, 2002, 18(Suppl 2): S231--S240. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/18.suppl_2.S231 [22] Shi X, Wang X, Shajahan A. BMRF-MI: integrative identification of protein interaction network by modeling the gene dependency. BMC Genomics, 2015, 16 (7 Supplement): S10. [23] Lin S, Peter L, Steve H. Comparison of co-expression measures: mutual information, correlation, and model based indices. BMC Bioinformatics, 2012, 13: 328. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-13-328 [24] Langfelder P, Horvath S: WGCNA: an R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinformatics, 2008, 9: 559. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-9-559 [25] André V, Eivind A, Assessment of weighted topological overlap (wTO) to improve fidelity of gene co-expression networks. BMC Bioinformatics, 2019: 20: 58. doi: 10.1186/s12859-019-2596-9 [26] 徐胜军, 韩九强, 赵亮, 刘欣. 用于图像分割的局部区域能量最小化算法. 西安交通大学学报, 2011, 45(8): 7--12.Xu S J, Han J Q, Zhao L, Liu X. Algorithm of Minimizing Local Region Energy for Image Segmentation. Journal of Xi’an Jiao Tong University, 2011, 45(8): 7--12. [27] Shi J, Malik J. Normalized cuts and image segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2000, 22(8): 888--905. doi: 10.1109/34.868688 [28] Streib K, Davis J W. Using Ripley' s K-function to improve graph-based clustering techniques. In: Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2011). Providence, RI, USA: IEEE, 2011. 2305−2312 [29] Arbeláez P, Maire M, Fowlkes C. Contour detection and hierarchical image segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 2011, 33(5): 898--916. -




 下载:
下载:







.jpg)