-
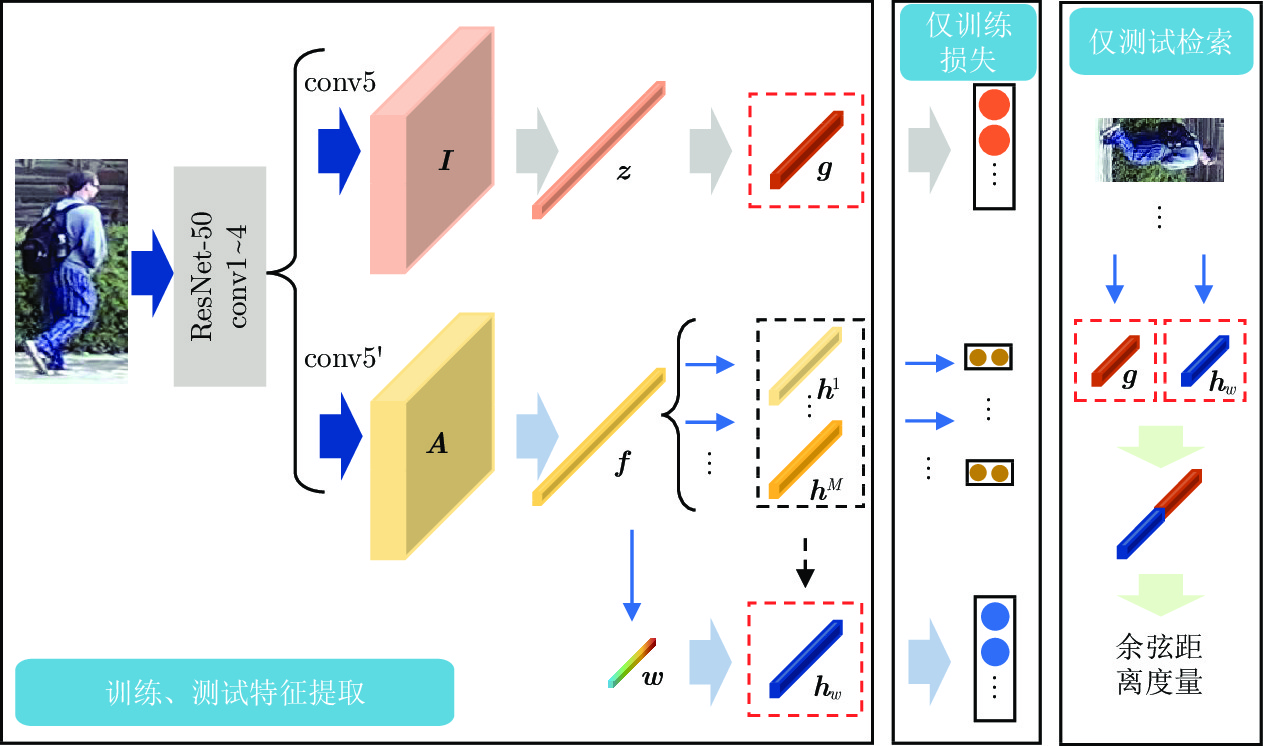
摘要: 行人重识别旨在跨监控设备下检索出特定的行人目标. 由于不同的行人可能具有相似的外观, 因此要求行人重识别模型能够捕捉到充足的细粒度特征. 本文提出一种融合属性特征的行人重识别的深度网络方法, 将行人重识别和属性识别集成在分类网络中, 进行端到端的多任务学习. 此外, 对于每张输入图片, 网络自适应地生成对应于每个属性的权重, 并将所有属性的特征以加权求和的方式结合起来, 与全局特征一起用于行人重识别任务. 全局特征关注行人的整体外观, 而属性特征关注细节区域, 两者相互补充可以对行人进行更全面的描述. 在行人重识别的主流数据集DukeMTMC-reID和Market-1501上的实验结果表明了本文方法的有效性, 平均精度均值(Mean average precision, mAP)分别达到了74.2%和83.5%, Rank-1值分别达到了87.1%和93.6%. 此外, 在这两个数据集上的属性识别也得到了比较好的结果.Abstract: Person re-identification aims to retrieve specific pedestrian target across surveillance devices. Since different pedestrians may have a similar appearance, it requires the person re-identification model to capture sufficient fine-grained features. This paper proposes a new deep network method for person re-identification based on fused attribute features. Person re-identification and attribute recognition are integrated into the classification network for end-to-end multi-task learning. In addition, for each input image, the network adaptively generates weights corresponding to each attribute. Features of all attributes are combined in a weighted summation way, and together with the global feature for person re-identification task. Global feature focuses on the overall appearance of the pedestrian, while the attribute feature focuses on the detail area, and they can complement each other to provide a more comprehensive description of the pedestrian. Experimental results on the DukeMTMC-reID and Market-1501 datasets, two popular datasets of person re-identification, show the effectiveness of the proposed method. The mean average precision (mAP) values reach 74.2% and 83.5% respectively, and the Rank-1 values reach 87.1% and 93.6% respectively. In addition, attribute recognition on these two datasets also achieved better results.
-
Key words:
- Person re-identification /
- attribute recognition /
- deep learning /
- adaptive weight
-
表 1 与相关方法的性能比较(%)
Table 1 Performance comparison with related methods (%)
表 2 使用不同损失函数的性能比较(%)
Table 2 Performance comparison using different loss functions (%)
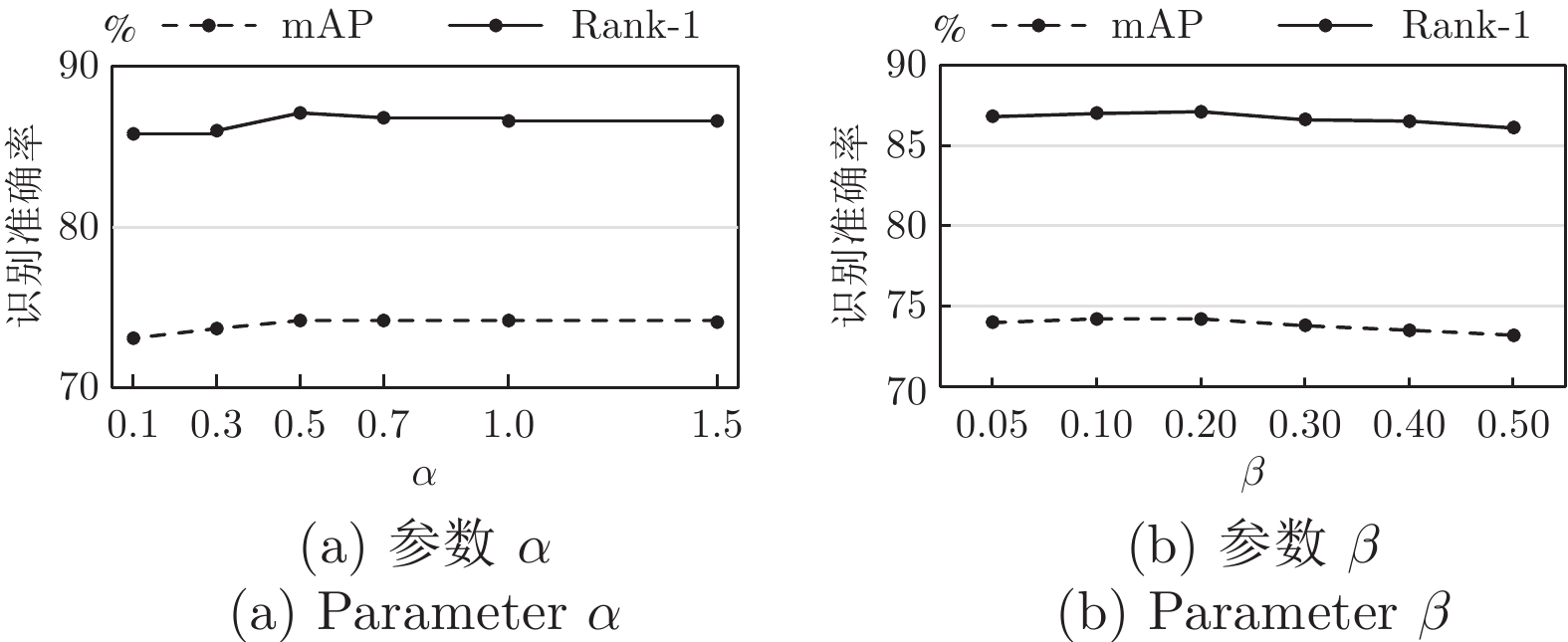
损失函数 mAP Rank-1 $L_{{\rm{id}}}$ 70.5 84.1 $L_{{\rm{id}}}+\beta L_{{\rm{att}}}$ 71.1 85.8 $L_{{\rm{id}}}+\alpha L_{{\rm{local}}}+\beta L_{{\rm{att}}}$ 74.2 87.1 ${L_{ {\rm{id} } }+\alpha L_{ {\rm{local} } }+\beta L^{*}_{ {\rm{att} } } }$ 73.0 86.0 $L_{ {\rm{id} } }\,({\rm{no} } \ {\rm{LS} })$ 66.8 83.3 表 3 使用不同特征融合方式的性能比较(%)
Table 3 Performance comparison using different feature fusion methods (%)
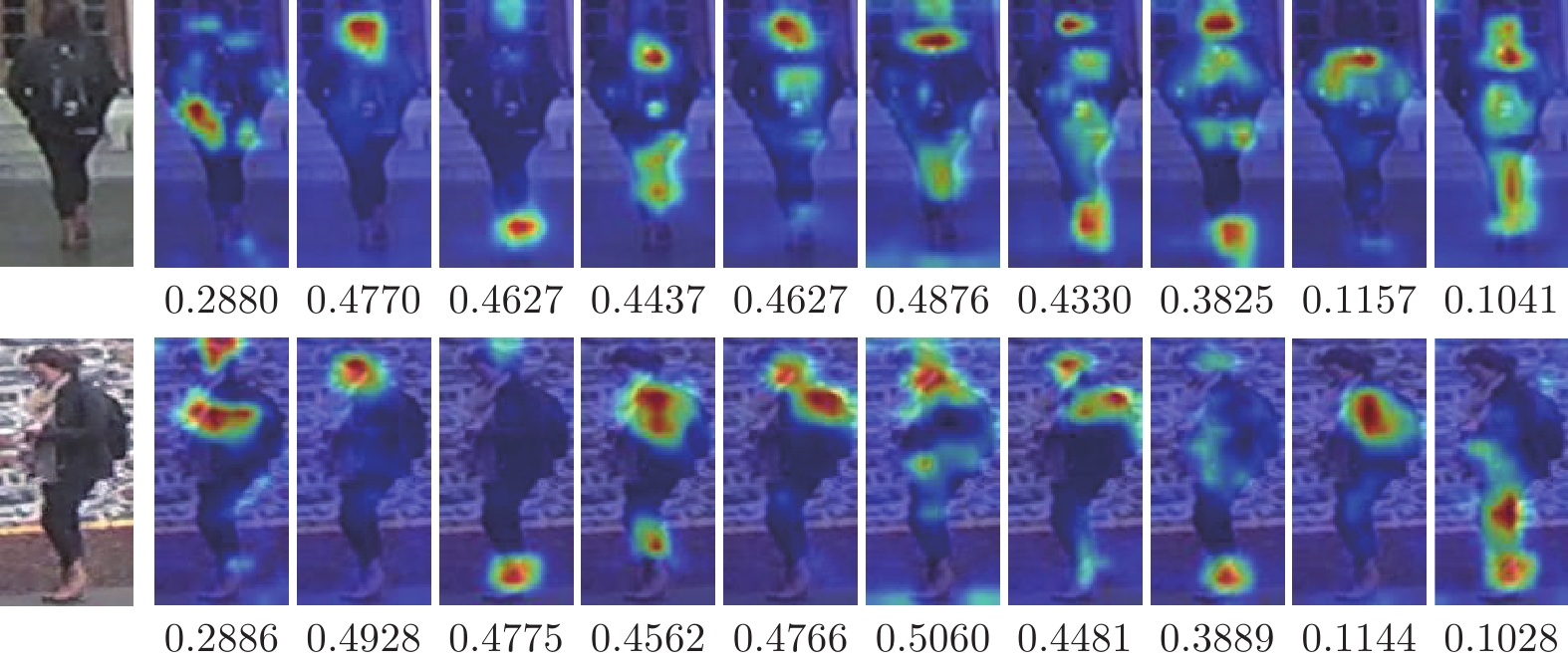
方法 特征维度 mAP Rank-1 var1 1024 71.6 84.6 var2 1024 72.5 85.7 var3 1024 74.1 86.3 本文 1024 74.2 87.1 特征${\boldsymbol g}$ 512 72.4 86.1 特征${\boldsymbol h}_{w}$ 512 71.8 85.1 表 4 DukeMTMC-reID上属性识别的准确率(%)
Table 4 Accuracy of attribute recognition on DukeMTMC-reID (%)
方法 gender hat boots l.up b.pack h.bag bag c.shoes c.up c.low 平均值 APR[22] 84.2 87.6 87.5 88.4 75.8 93.4 82.9 89.7 74.2 69.9 83.4 B2 85.94 89.75 89.92 88.64 84.35 93.61 83.06 90.70 74.62 66.81 84.74 本文 86.07 90.74 89.72 88.78 84.47 93.28 82.04 91.79 75.53 68.14 85.06 表 5 Market-1501上属性识别的准确率(%)
Table 5 Accuracy of attribute recognition on Market-1501 (%)
方法 gender age hair l.slv l.low s.clth b.pack h.bag bag hat c.up c.low 平均值 APR[22] 88.9 88.6 84.4 93.6 93.7 92.8 84.9 90.4 76.4 97.1 74.0 73.8 86.6 AANet-50[25] 92.31 88.21 86.58 94.45 94.24 94.83 87.77 89.61 79.72 98.01 77.08 70.81 87.80 B2 93.05 85.82 88.97 93.56 94.18 94.53 88.80 88.08 79.24 98.28 74.95 68.64 87.34 本文 93.69 86.16 89.00 94.11 94.80 94.81 89.33 88.68 79.03 98.33 76.52 70.68 87.93 -
[1] Dalal N, Triggs B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In: Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. San Diego, CA, USA: IEEE, 2005. 886−893 [2] Weinberger K Q, Saul L K. Fast solvers and efficient implementations for distance metric learning. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Machine Learning. Helsinki, Finland: ACM, 2008. 1160−1167 [3] Liao S C, Hu Y, Zhu X Y, Li S Z. Person re-identification by local maximal occurrence representation and metric learning. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Boston, MA, USA: IEEE, 2015. 2197−2206 [4] Ma F, Jing X Y, Zhu X K, Tang Z M, Peng Z P. True-color and grayscale video person re-identification. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2020, 15: 115−129 doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2019.2917160 [5] Ma F, Zhu X K, Zhang X Y, Yang L, Zuo M, Jing X Y. Low illumination person re-identification. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2019, 78(1): 337−362 doi: 10.1007/s11042-018-6239-3 [6] Ma F, Zhu X K, Liu Q L, Song C F, Jing X Y, Ye D P. Multi-view coupled dictionary learning for person re-identification. Neurocomputing, 2019, 348: 16−26 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2018.07.081 [7] (罗浩, 姜伟, 范星, 张思朋. 基于深度学习的行人重识别研究进展. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(11): 2032−2049)Luo Hao, Jiang Wei, Fan Xing, Zhang Si-Peng. A survey on deep learning based person re-identification. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(11): 2032−2049 [8] Jing X Y, Zhu X K, Wu F, Hu R M, You X G, Wang Y H, et al. Super-resolution person re-identification with semi-coupled low-rank discriminant dictionary learning. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(3): 1363−1378 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2651364 [9] Hermans A, Beyer L, Leibe B. In defense of the triplet loss for person re-identification. arXiv preprint, arXiv: 1703.07737, 2017. [10] Chen W H, Chen X T, Zhang J G, Huang K Q. Beyond triplet loss: A deep quadruplet network for person reidentification. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, Hawaii, USA: IEEE, 2017. 403−412 [11] Chen D P, Xu D, Li H S, Sebe N, Wang X G. Group consistent similarity learning via deep crf for person reidentification. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, Utah, USA: IEEE, 2018. 8649−8658 [12] Zhu X K, Jing X Y, Zhang F, Zhang X Y, You X G, Cui X. Distance learning by mining hard and easy negative samples for person re-identification. Pattern Recognition, 2019, 95: 211−222 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2019.06.007 [13] Sun Y F, Zheng L, Yang Y, Tian Q, Wang S J. Beyond part models: Person retrieval with refined part pooling (and a strong convolutional baseline). In: Proceedings of the 2018 European Conference on Computer Vision. Cham: Springer, 2018. 480−496 [14] Su C, Li J N, Zhang S L, Xing J L, Gao W, Tian Q. Pose-driven deep convolutional model for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 3960−3969 [15] Sarfraz M S, Schumann A, Eberle A, Stiefelhagen R. A pose-sensitive embedding for person re-identification with expanded cross neighborhood re-ranking. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, Utah, USA: IEEE, 2018. 420−429 [16] Kalayeh M M, Basaran E, Gökmen M, Kamasak M E, Shah M. Human semantic parsing for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, Utah, USA: IEEE, 2018. 1062−1071 [17] Gong K, Liang X D, Zhang D Y, Shen X H, Lin L. Look into person: Self-supervised structure-sensitive learning and a new benchmark for human parsing. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, Hawaii, USA: IEEE, 2017. 932−940 [18] Layne R, Hospedales T, Gong S G. Person re-identification by attributes. In: Proceedings of the 23rd British Machine Vision Conference. Guildford, UK: BMVA, 2012. [19] Zhu J Q, Liao S C, Lei Z, Li S Z. Multi-label convolutional neural network based pedestrian attribute classification. Image and Vision Computing, 2017, 58: 224−229 doi: 10.1016/j.imavis.2016.07.004 [20] Deng Y B, Luo P, Loy C C, Tang X O. Pedestrian attribute recognition at far distance. In: Proceedings of the 22nd ACM International Conference on Multimedia. Orlando, Florida, USA: ACM, 2014. 789−792 [21] Schumann A, Stiefelhagen R. Person re-identification by deep learning attribute-complementary information. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. Honolulu, Hawaii, USA: IEEE, 2017. 20−28 [22] Lin Y T, Zheng L, Zheng Z D, Wu Y, Hu Z L, Yan C G, et al. Improving person re-identification by attribute and identity learning. Pattern Recognition, 2019, 95: 151−161 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2019.06.006 [23] Ristani E, Solera F, Zou R, Cucchiara R, Tomasi C. Performance measures and a data set for multi-target, multi-camera tracking. In: Proceedings of the 2016 European Conference on Computer Vision Workshops. Cham: Springer, 2016. 17−35 [24] Zheng L, Shen L Y, Tian L, Wang S J, Wang J D, Tian Q. Scalable person re-identification: A benchmark. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Santiago, Chile: IEEE, 2015. 1116−1124 [25] Tay C P, Roy S, Yap K H. AANet: Attribute attention network for person re-identifications. In: Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, California, USA: IEEE, 2019. 7134−7143 [26] Zhao X Y, Li H X, Shen X H, Liang X D, Wu Y. A modulation module for multi-task learning with applications in image retrieval. In: Proceedings of the 2018 European Conference on Computer Vision. Cham: Springer, 2018. 401−416 [27] Szegedy C, Vanhoucke V, Ioffe S, Shlens J, Wojna Z. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, NV, USA: IEEE, 2016. 2818−2826 [28] Lin T Y, Goyal P, Girshick R, He K M, Dollar P. Focal loss for dense object detection. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 2980−2988 [29] Deng J, Dong W, Socher R, Li L J, Li K, Li F F. Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In: Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Miami, Florida, USA: IEEE, 2009. 248−255 [30] Zhou B L, Khosla A, Lapedriza A, Oliva A, Torralba A. Learning deep features for discriminative localization. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, NV, USA: IEEE, 2016. 2921−2929 [31] Selvaraju R R, Cogswell M, Das A, Vedantam R, Parikh D, Batra D. Grad-CAM: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 618−626 -




 下载:
下载: