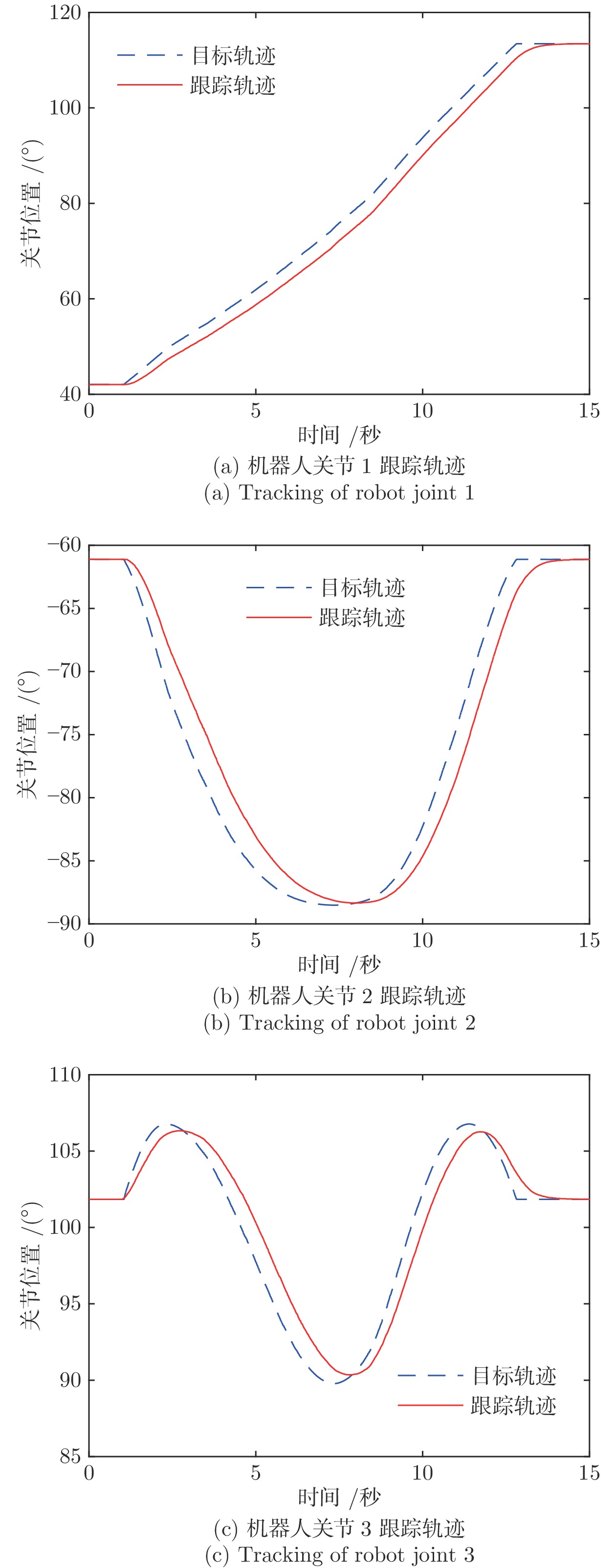
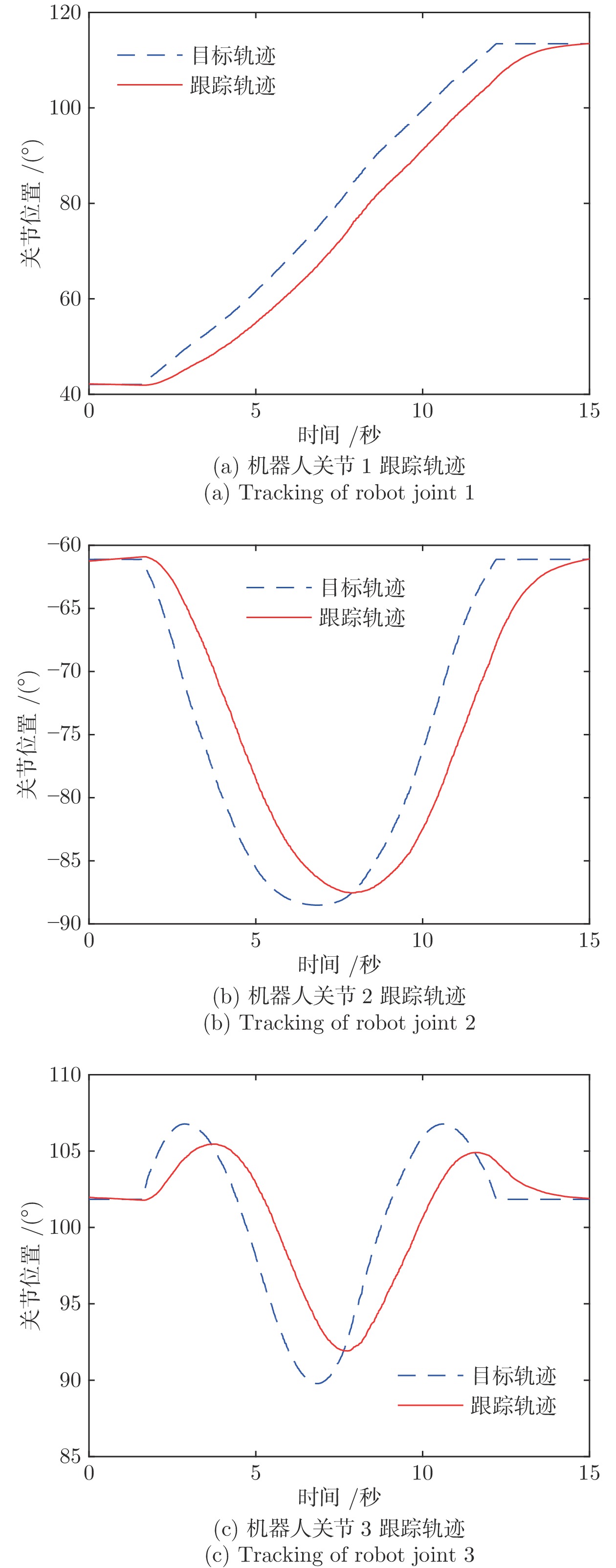
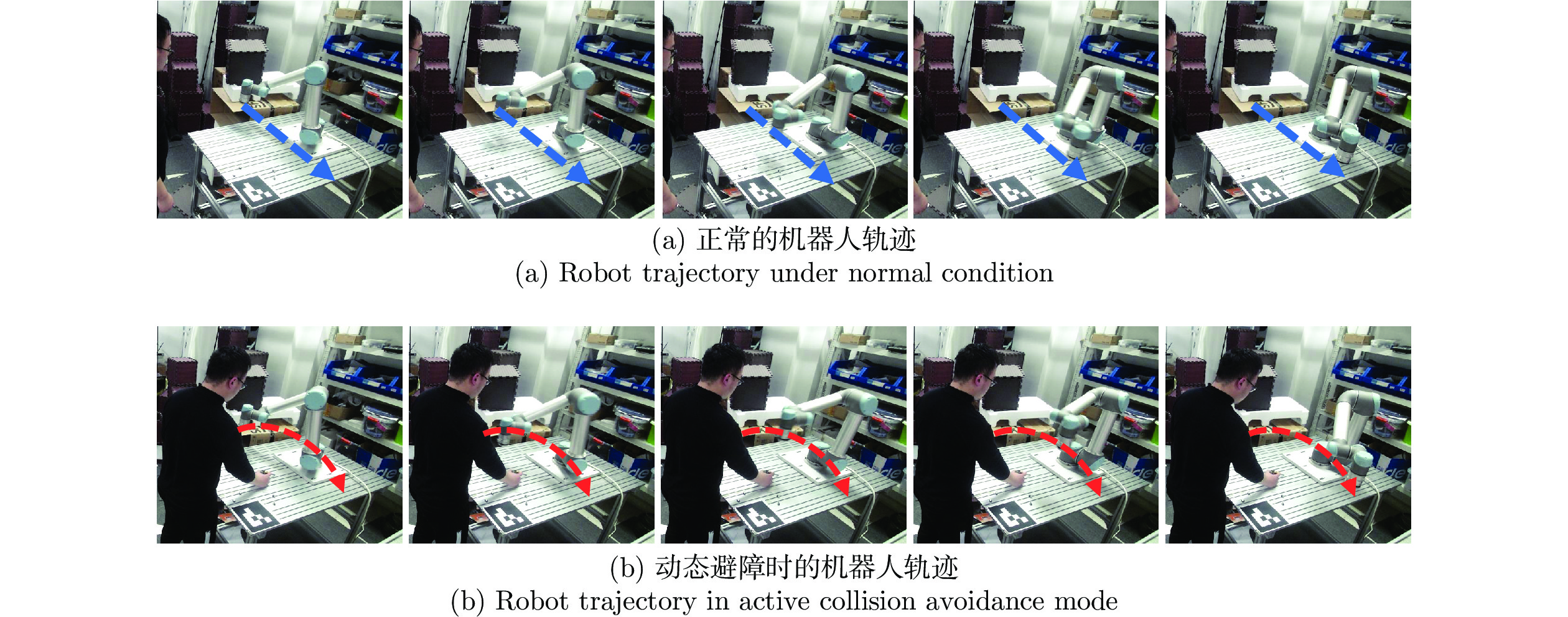
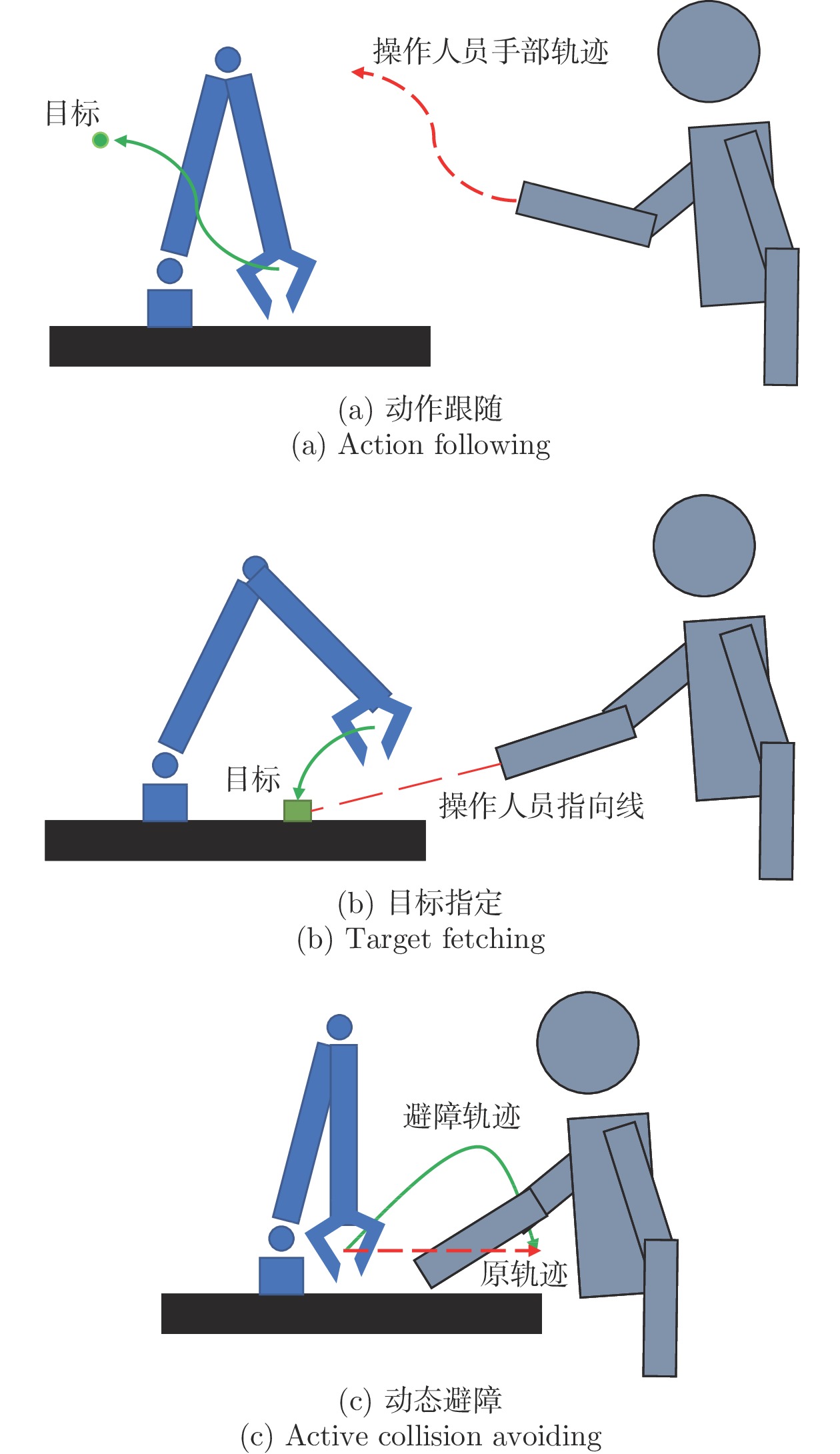
System Design for Human-robot Coexisting Environment Satisfying Multiple Interaction Tasks
-
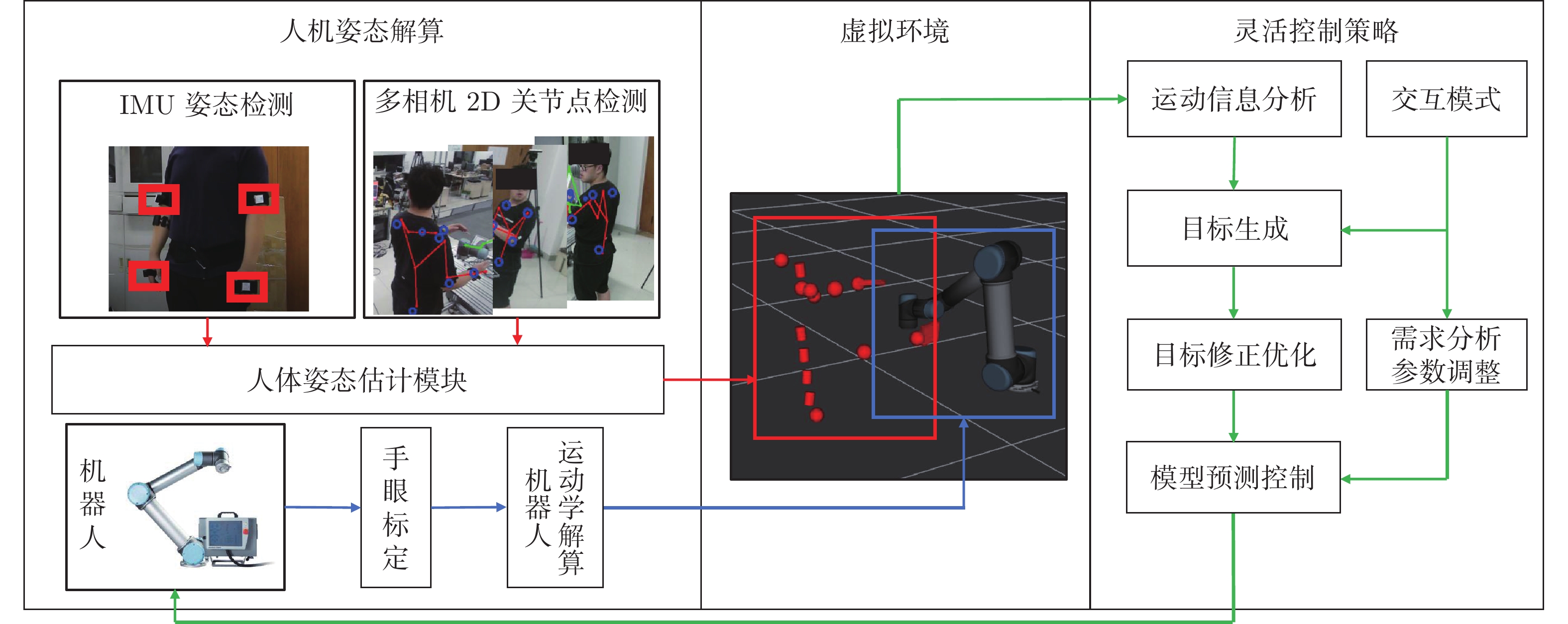
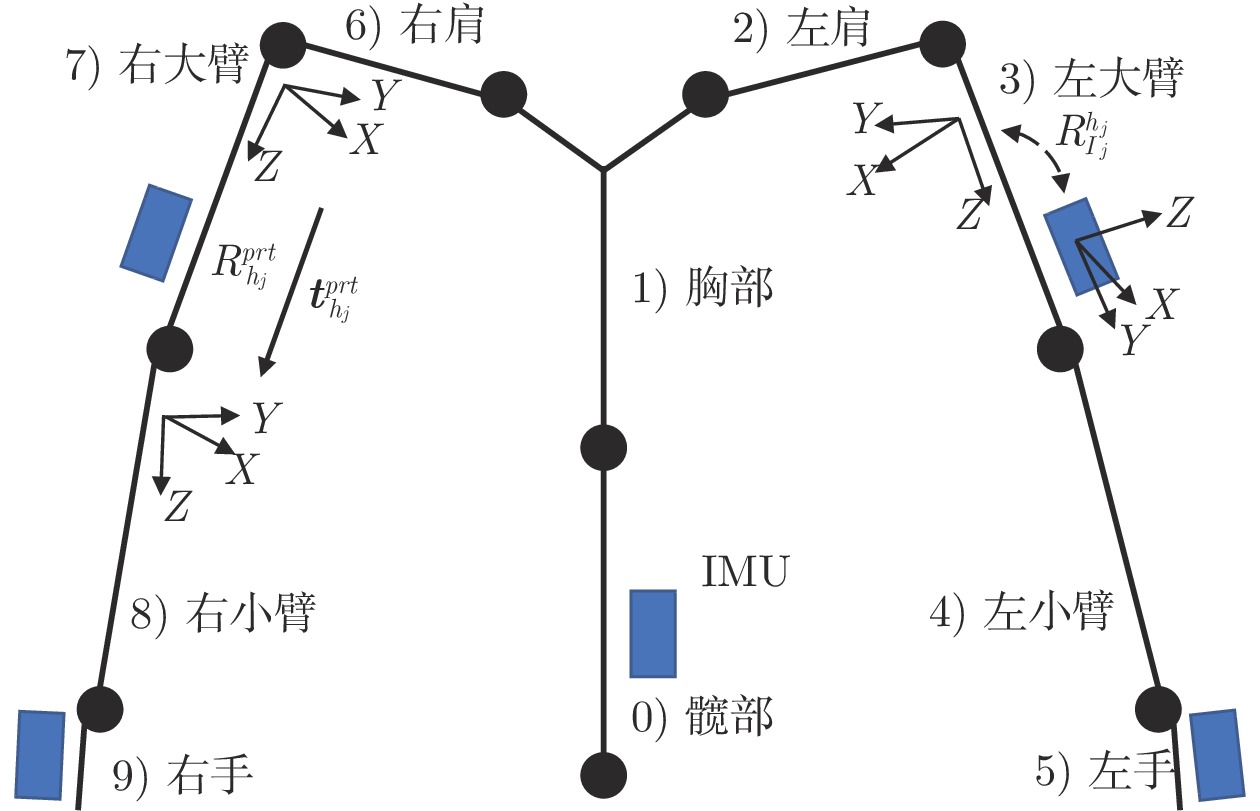
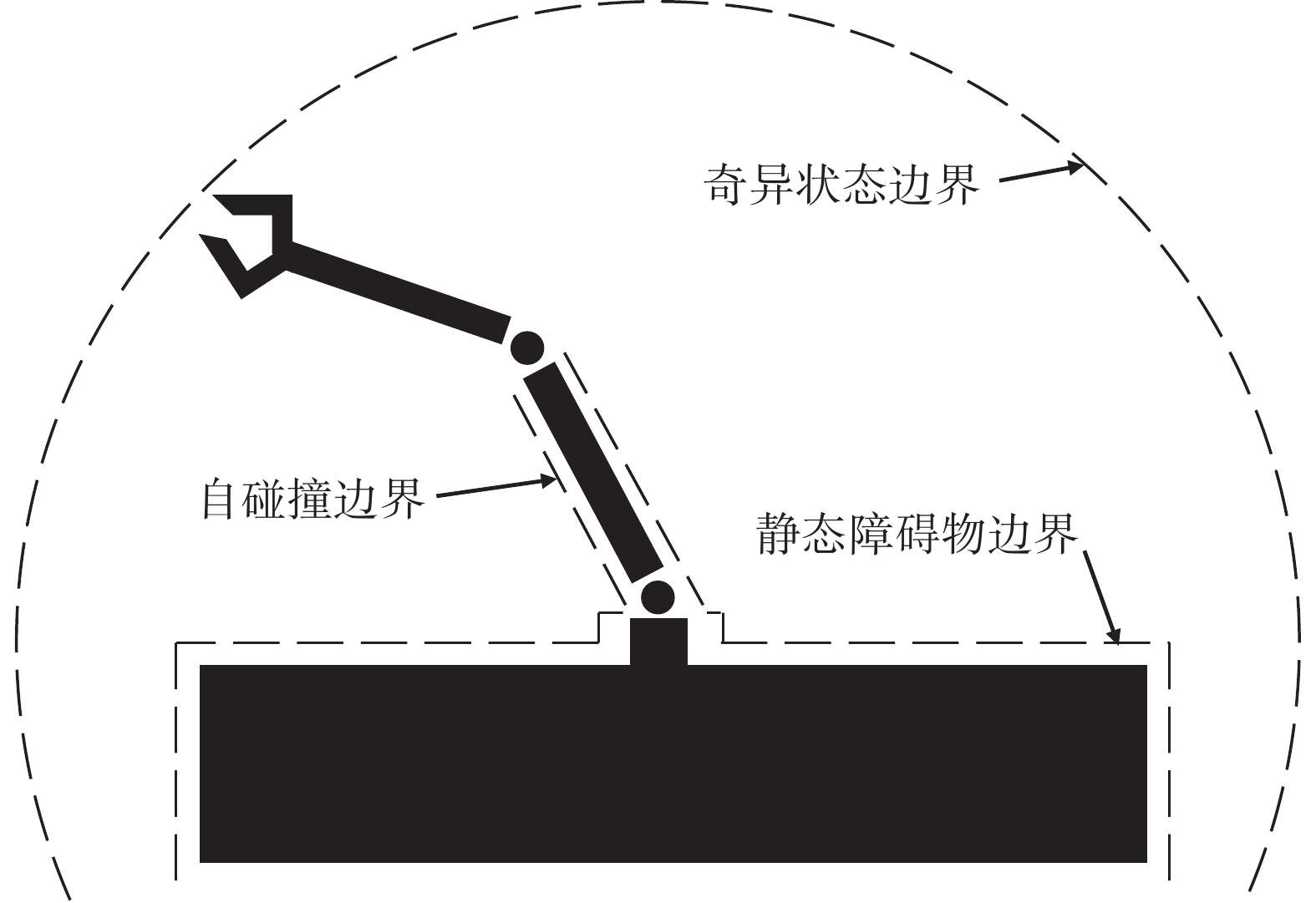
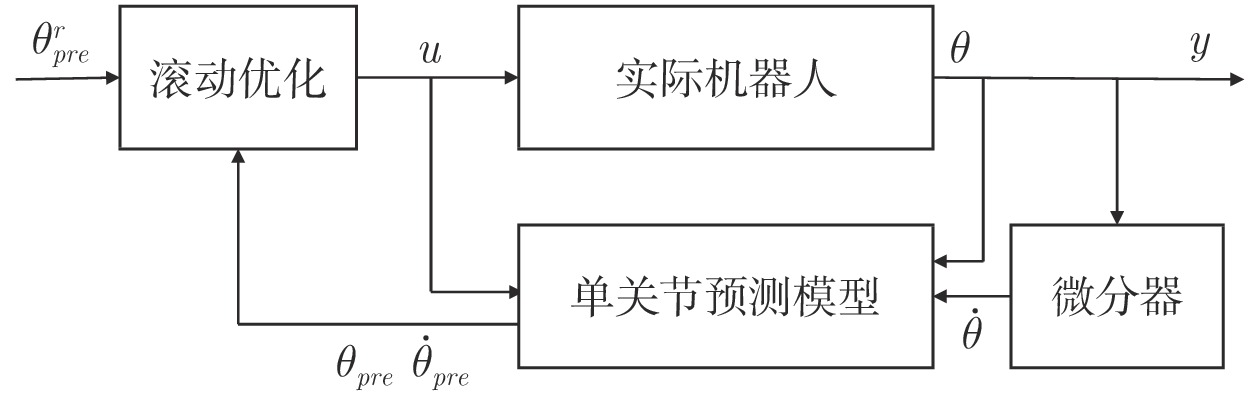
摘要: 人与机器人共同协作的灵活生产模式已经成为工业成产的迫切需求, 因此, 近年来人机共融系统方面的研究受到了越来越多关注. 设计并实现了一种满足不同交互任务的人机共融系统, 人体动作的估计和机器人的交互控制是其中的关键技术. 首先, 提出了一种基于多相机和惯性测量单元信息融合的人体姿态解算方法, 通过构造优化问题, 融合多相机下的2D关节检测信息和所佩戴的惯性测量单元测量信息, 对人体运动学姿态进行优化估计, 改善了单一传感器下, 姿态信息不全面以及对噪声敏感的问题, 提升了姿态估计的准确度. 其次, 结合机器人的运动学特性和人机交互的特点, 设计了基于目标点跟踪和模型预测控制的机器人控制策略, 使得机器人能够通过调整控制参数, 适应动态的环境和不同的交互需求, 同时保证机器人和操作人员的安全. 最后, 进行了动作跟随、物品传递、主动避障等人机交互实验, 实验结果表明了所设计的机器人交互系统在人机共融环境下的有效性和可靠性.Abstract: System design for human-robot coexisting environment has become a research hotspot due to great demand for applying robots as supportive tools in human workspaces for flexible industrial production. Recent researches have been focused on the problem of human pose estimation and flexible robot control. In this paper, a system for human-robot coexisting environment that adapts to multiple interaction tasks is designed. 2D human poses detected from multiple camera views and rotational measurements detected by wearable inertial measurement units on human limbs are fused by establishing optimization problem to estimate the 3D pose of human upper body, which surpasses the detection performance by using single module of sensors when dealing with obstacles and sensor noises. By considering the kinematics of the robots and the flexibility demands in human-robot interaction, a target-following based control strategy with motion target bounding and model predictive control is applied to enhance the motion flexibility of a robot while ensuring the safety of human operator and the robot itself. The designed system is tested by several interactive experiments including motion following, object fetching, active collision avoidance. The results show the validity and reliability of the system in human-robot coexisting environment.
-
Key words:
- Human-robot interaction /
- human pose estimation /
- sensor fusion /
- optimization /
- robot control
-
表 1 不同传感器配置下的人体姿态估计准确率
Table 1 Accuracy of human pose estimation under different sensor configurations
传感器配置 准确率 (%) 2 台相机 91.4 3 台相机 98.1 3 台相机 + IMU 98.7 -
[1] Halme R J, Lanz M, Kämäräinen J, Pieters R, Latokartano J, Hietanen A. Review of vision-based safety systems for human-robot collaboration. Procedia Cirp, 2018, 72: 111-116. doi: 10.1016/j.procir.2018.03.043 [2] Rosenstrauch M J, Kruger J. Safe human-robot-collaboration-introduction and experiment using ISO/TS 15066. In: Proceeding of the 2017 3rd International Conference on Control, Automation and Robotics (ICCAR). Nagoya, Japan: 2017. 740−744 [3] Marvel J A, Norcross R. Implementing speed and separation monitoring in collaborative robot workcells. Robotics Computer Integrated Manufacturing, 2017, 44: 144-155 doi: 10.1016/j.rcim.2016.08.001 [4] Bdiwi M, Pfeifer M, Sterzing A. A new strategy for ensuring human safety during various levels of interaction with industrial robots. CIRP Annals−Manufacturing Technology, 2017: 66(1), 453−456 [5] Bdiwi M. Integrated sensors system for human safety during cooperating with industrial robots for handing-over and assembling tasks. Procedia Cirp, 2014, 23: 65-70 doi: 10.1016/j.procir.2014.10.099 [6] Rakprayoon P, Ruchanurucks M, Coundoul A. Kinect-based obstacle detection for manipulator. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration. Kyoto, Japan: 2011. 68−73 [7] Windolf M, Götzen N, Morlock M. Systematic accuracy and precision analysis of video motion capturing systems-exemplified on the Vicon-460 system. Journal of Biomechanics, 2008, 41(12): 2776-2780 doi: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2008.06.024 [8] Von Marcard T, Rosenhahn B, Black M J, Pons-Moll G. Sparse inertial poser: automatic 3D human pose estimation from sparse IMUs. Computer Graphics Forum, 2017, 36(2): 349-360 doi: 10.1111/cgf.13131 [9] 张鋆豪, 何百岳, 杨旭升, 张文安. 基于可穿戴式惯性传感器的人体运动跟踪方法综述. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(8): 1439-1454Zhang Jun-Hao, He Bai-Yue, Yang Xu-Sheng, Zhang Wen-An. A Review on Wearable Inertial Sensor Based Human Motion Tracking. ACTA AUTOMATICA SINICA, 2019, 45(8): 1439-1454 [10] Cao Z, Simon T, Wei SE, Sheikh Y. Realtime multi-person 2D pose estimation using part affinity fields. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, USA: 2017. 1302-1310 [11] Mehta D, Sridhar S, Sotnychenko O, Rhodin H, Shafiei M, Seidel HP, Xu W, Dan C, Theobalt C. VNect: real-time 3D human pose estimation with a single RGB camera. Acm Transactions on Graphics, 2017, 36(4): 44 [12] Shotton J, Girshick R, Fitzgibbon A, Sharp T, Cook M, Finocchio M, Moore R, Kohli P, Criminisi A, Kipman A. Efficient human pose estimation from single depth images. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35(12): 2821-2840 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.241 [13] 贾丙西, 刘山, 张凯祥, 陈剑. 机器人视觉伺服研究进展: 视觉系统与控制策略. 自动化学报, 2015, 41(5): 861-873Jia Bing-Xi, Liu Shan, Zhang Kai-Xiang, Chen Jian. Survey on Robot Visual Servo Control: Vision System and Control Strategies. ACTA AUTOMATICA SINICA, 2015, 41(5): 861-873 [14] Flacco F, Kroeger T, De Luca A, Khatib O. A depth space approach for evaluating distance to objects. Journal of Intelligent Robotic Systems, 2015, 80(1): 7-22 [15] Tsai C S, Hu J S, Tomizuka M. Ensuring safety in human-robot coexistence environment. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots & Systems. Chicago, USA: IEEE. 2014. 4191−4196 [16] Mohammed A, Schmidt B, Wang L. Active collision avoidance for human-robot collaboration driven by vision sensors. International Journal of Computer Integrated Manufacturing, 2016:1-11. [17] Trumble M, Gilbert A, Malleson C, Hilton A, Collomosse J. Total Capture: 3D human pose estimation fusing video and inertial sensors. In: Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference. London, UK: 2017. 1−13 -




 下载:
下载: