Brain Functional Connection Classification Method Based on Prototype Learning and Deep Feature Fusion
-
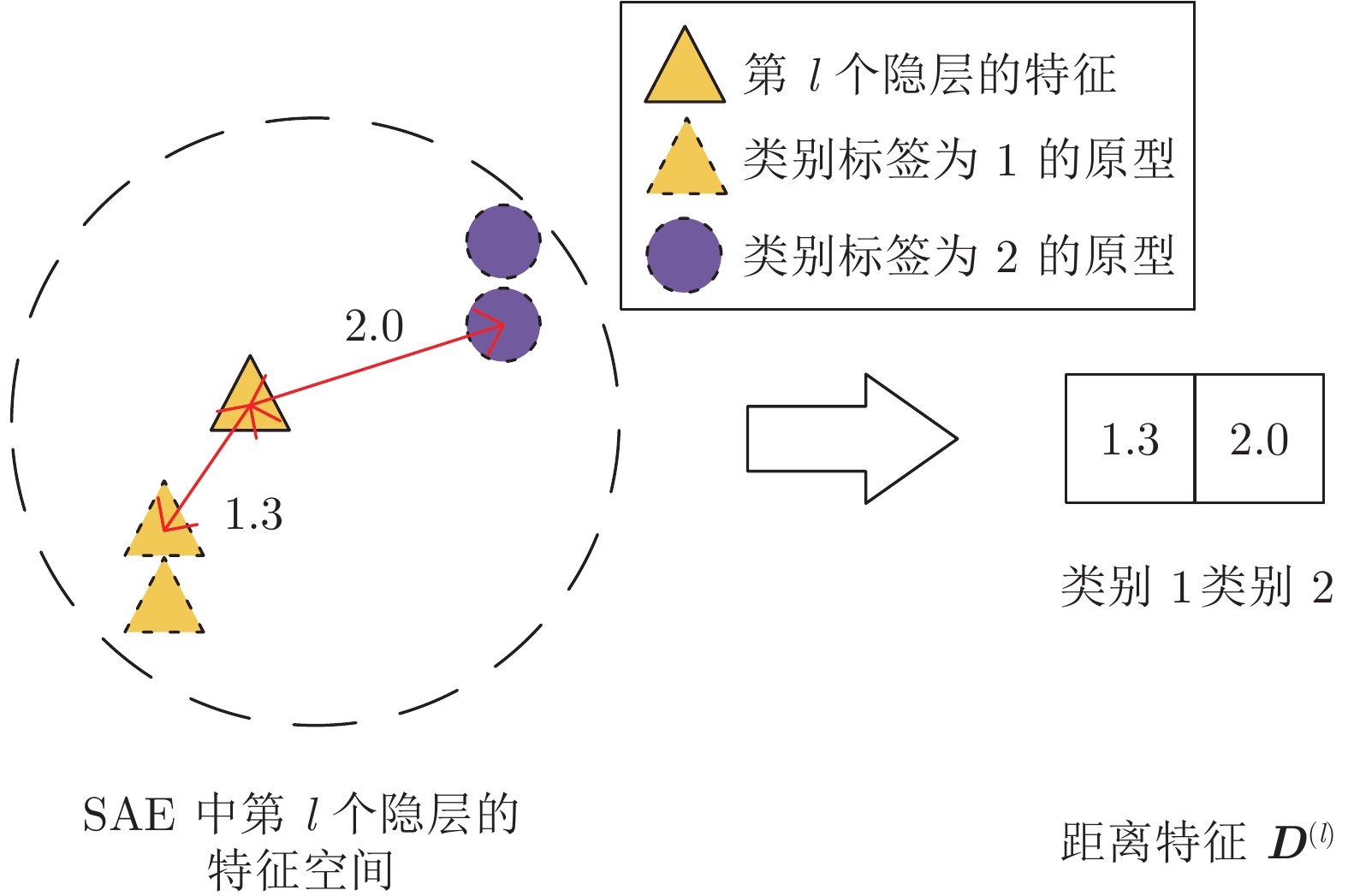
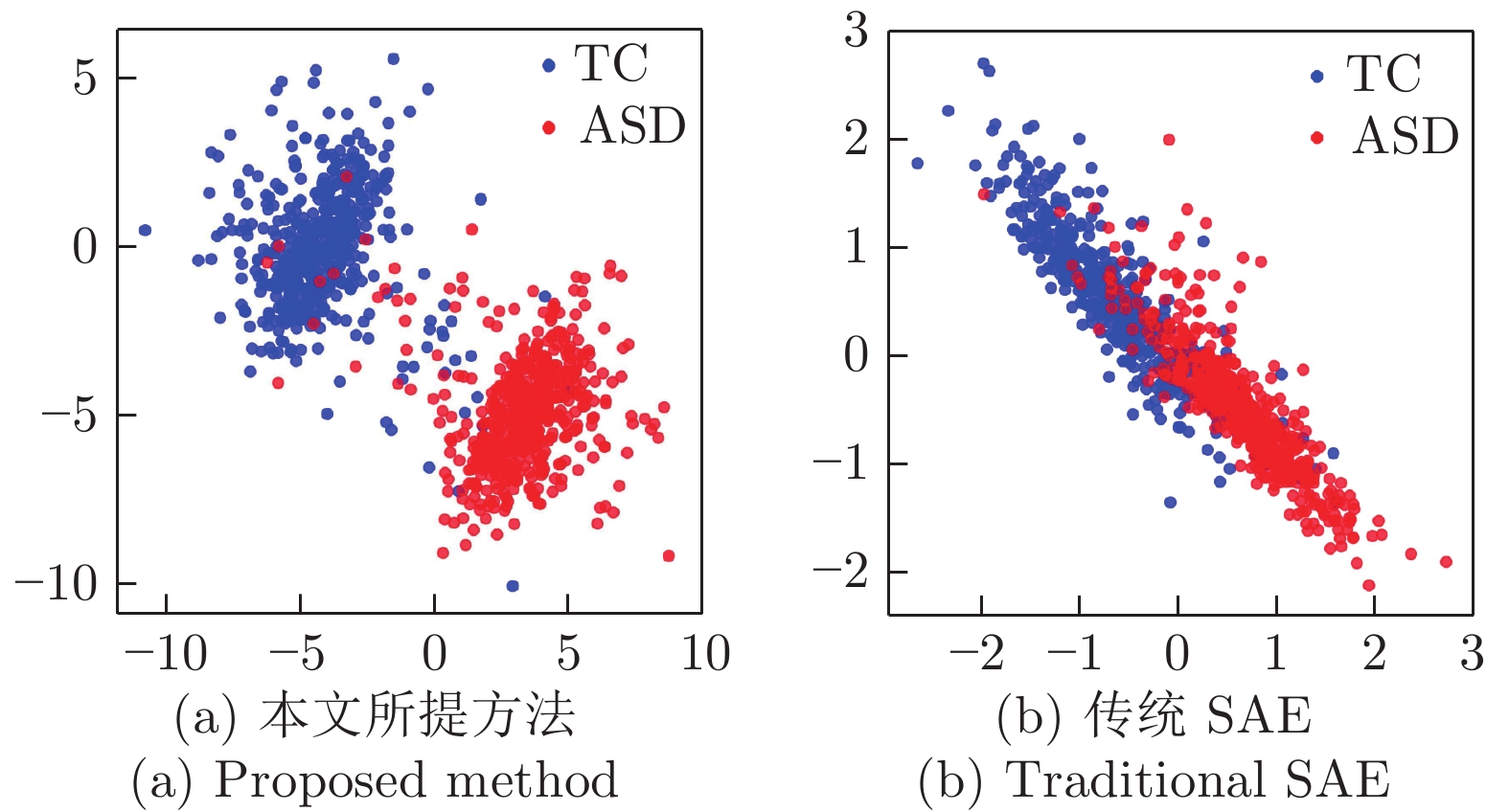
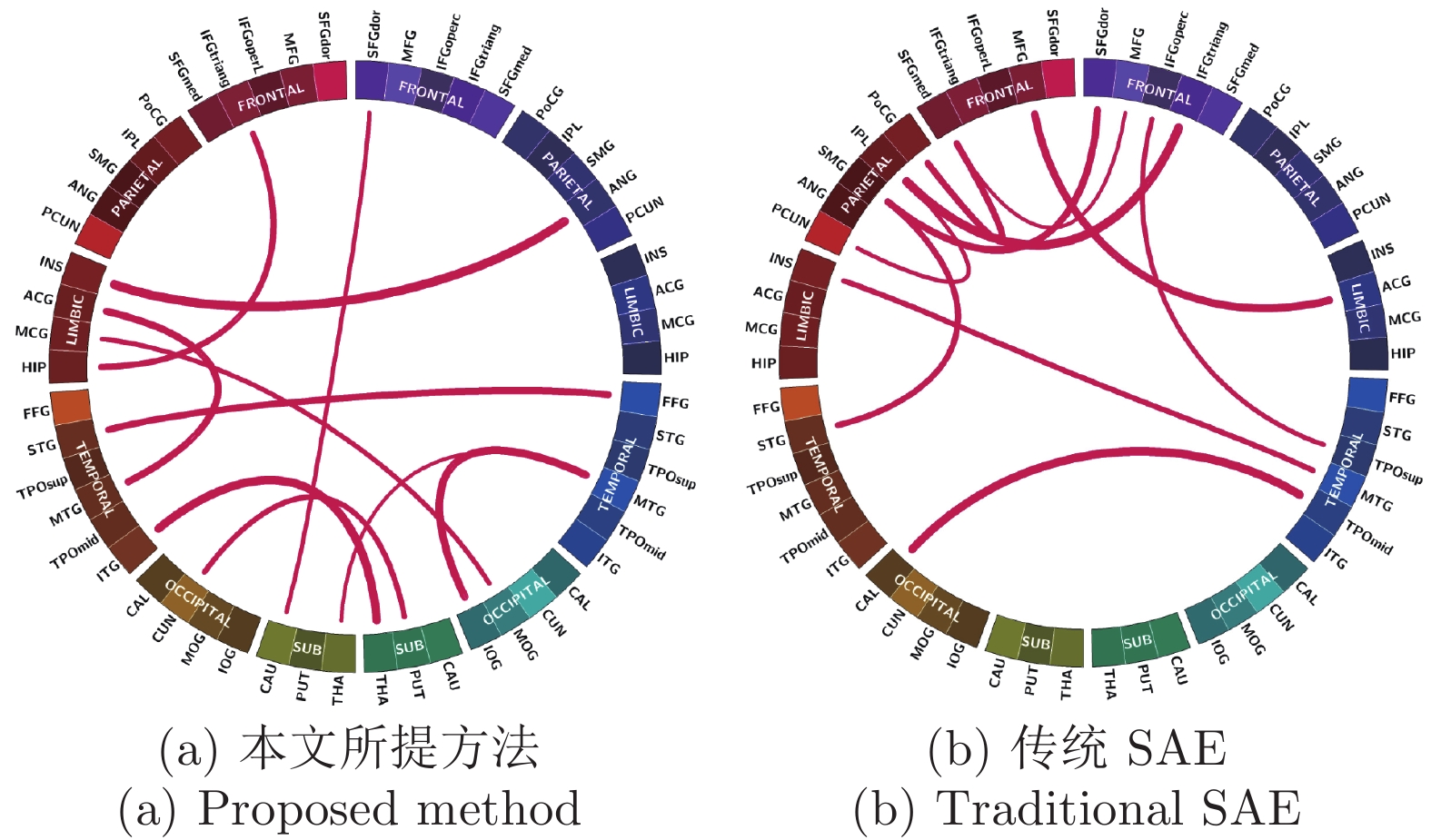
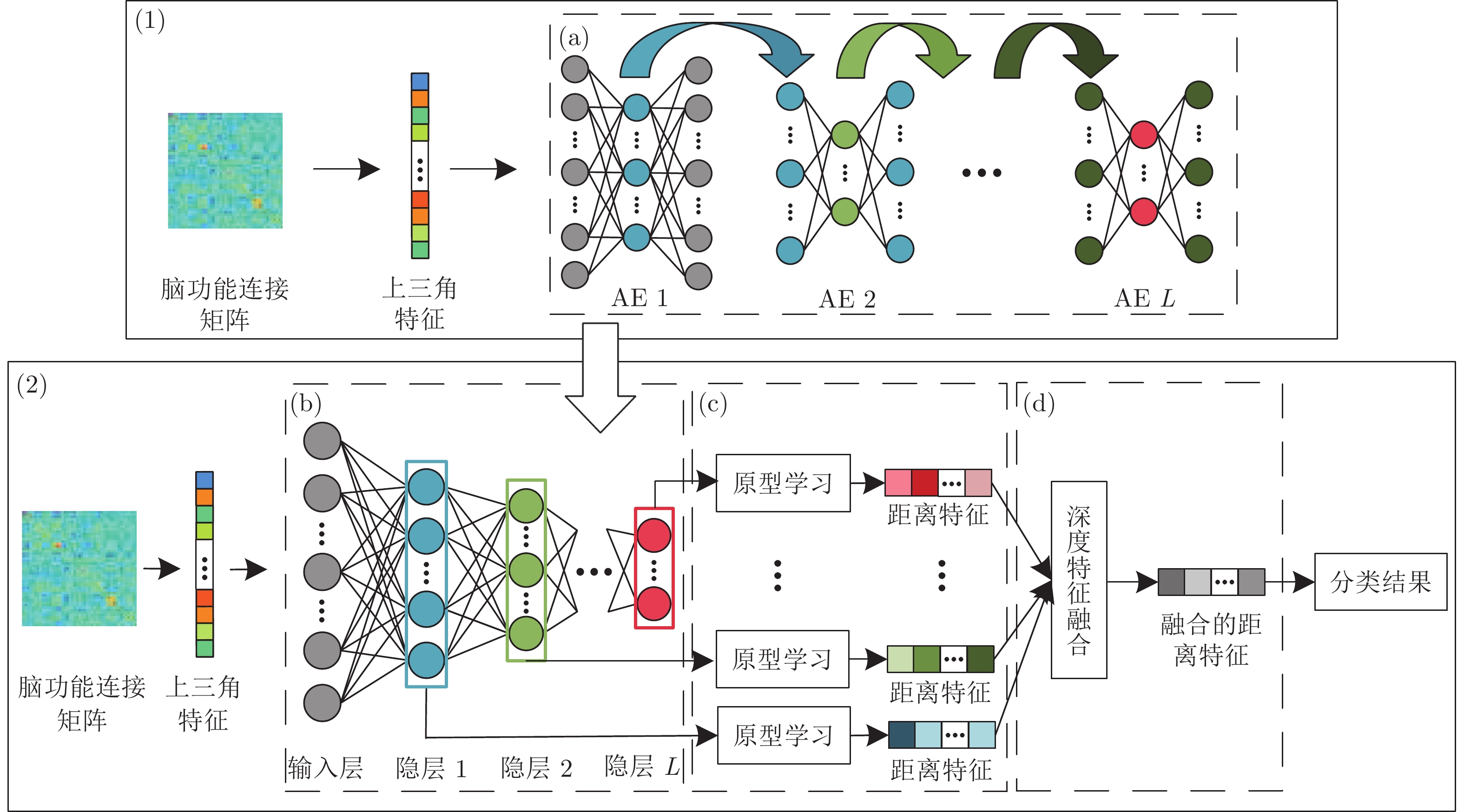
摘要: 近年来, 基于深度学习的脑功能连接分类方法已成为一个研究热点. 为了进一步提高脑功能连接的分类准确率, 获得与疾病相关的鉴别性特征, 本文提出了一种基于原型学习与深度特征融合的脑功能连接分类方法. 该方法首先使用栈式自编码器从脑功能连接中提取从低层次到高层次的深度特征; 然后利用原型学习在自编码器的各隐层中提取表示样本类别信息的距离特征; 最后采用深度特征融合策略将这些距离特征融合, 并将该融合特征用于脑功能连接的类别标签预测. 在ABIDE数据集上的实验结果表明, 与其他同类方法相比, 该方法不仅具有较高的分类准确率, 而且能够更加准确地定位与疾病相关的脑区.Abstract: In recent years, the brain functional connection classification method based on deep learning has become a hot research topic. In order to further improve the classification accuracy of brain functional connections and gain discriminative features associated with a disease, we propose a brain functional connection classification method based on prototype learning and deep feature fusion in this paper. Firstly, we use stacked autoencoders to extract lower-to-higher deep features from brain functional connections. Then the prototype learning is used to extract the distance features of the sample category from each hidden layer of the stacked autoencoders. Finally, the deep feature fusion strategy is adopted to fuse these distance features and the fused features are applied for the brain functional connection classification. The experimental results on the ABIDE dataset show that compared with other methods, the proposed method not only has a higher classification accuracy, but also can locate the brain areas related to the disease more precisely.
-
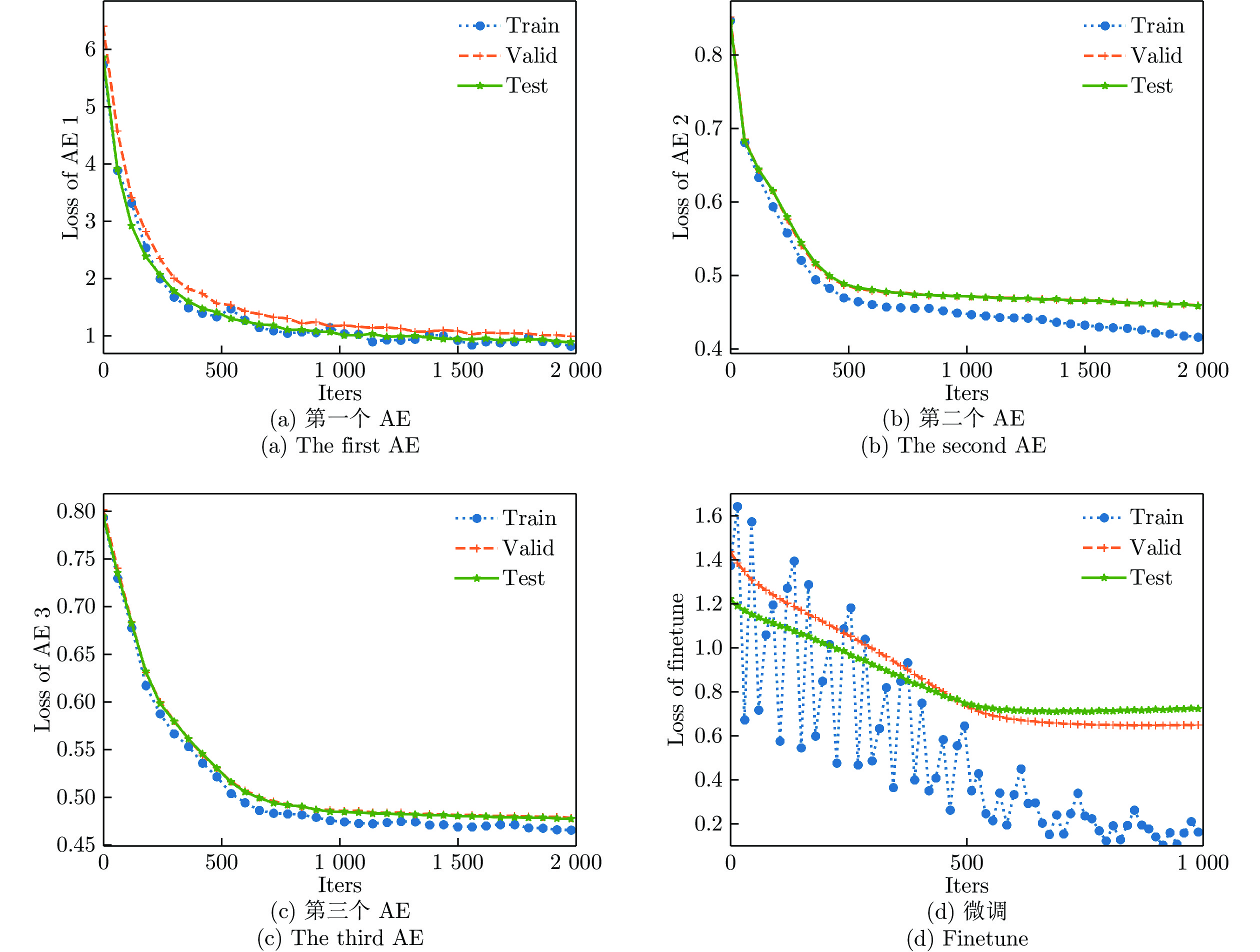
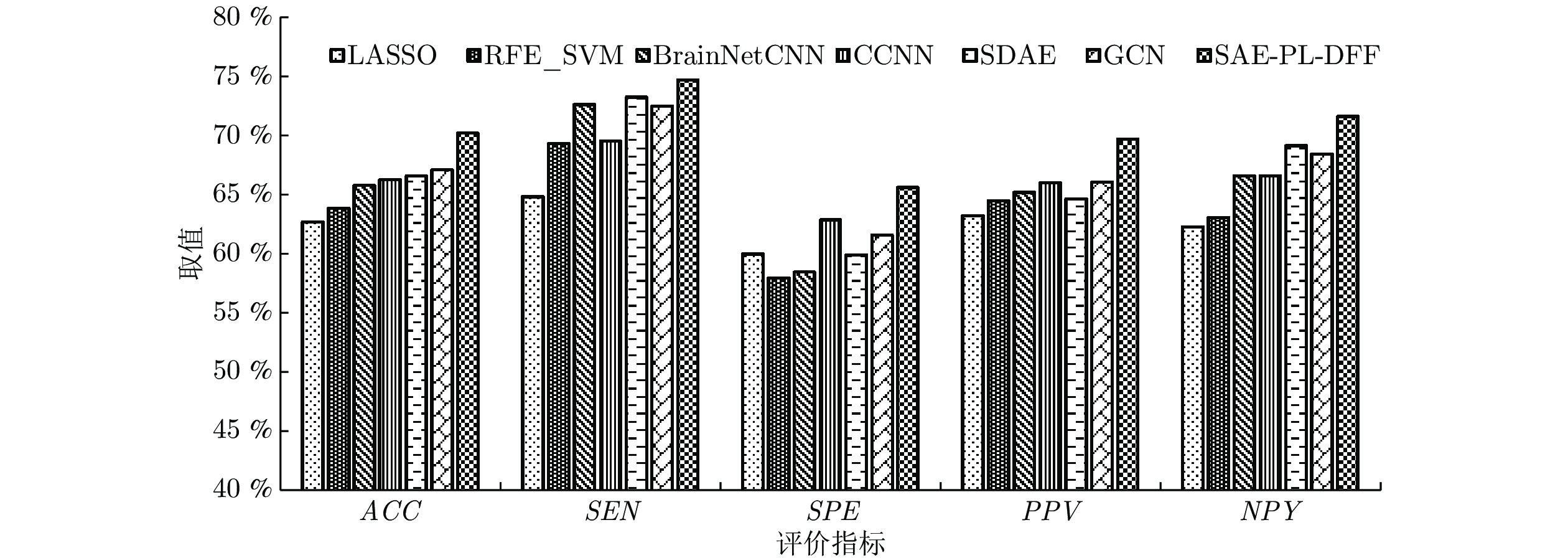
表 1 不同隐层数量下的实验结果(%)
Table 1 Experimental results of our method with different hidden layers (%)
隐层数量 ACC SEN SPE PPV NPV 1 68.03 70.97 65.00 67.69 68.42 2 68.75 74.00 63.04 68.51 69.05 3 69.30 73.60 65.30 68.97 69.90 4 68.42 71.43 65.22 68.63 68.18 5 68.23 72.73 63.41 68.08 68.42 表 2 不同原型数量下的实验结果(%)
Table 2 Experimental results of our method with different number of prototypes (%)
原型数量 ACC SEN SPE PPV NPV 1 69.30 73.60 65.30 68.97 69.90 2 69.23 71.11 67.39 68.10 70.45 3 69.28 73.40 64.98 68.94 70.21 4 69.18 73.10 64.52 68.70 70.22 5 69.13 71.87 66.29 69.24 69.39 表 3 不同深度特征融合方式下的实验结果(%)
Table 3 Experimental results of our method with different deep feature fusion modes (%)
融合方式 ACC SEN SPE PPV NPV DFF-3 69.30 73.60 65.30 68.97 69.90 DFF-1, 3 69.64 73.44 65.50 69.38 70.47 DFF-2, 3 69.95 75.02 64.63 69.26 71.40 DFF-all 70.30 74.80 65.68 69.80 71.70 -
[1] 梁夏, 王金辉, 贺永. 人脑连接组研究: 脑结构网络和脑功能网络. 科学通报, 2010, 55(16): 1565-1583. doi: 10.1360/972009-2150Liang Xia, Wang Jin-Hui, He Yong. Human connectome: Structural and functional brain networks. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2010, 55(16): 1565-1583. doi: 10.1360/972009-2150 [2] Craddock R C, Holtzheimer Ⅲ P E, Hu X P, Mayberg H S. Disease state prediction from resting state functional connectivity. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine: An Official Journal of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 2009, 62(6): 1619–1628. doi: 10.1002/mrm.22159 [3] Khazaee A, Ebrahimzadeh A, Babajani-Feremi A. Application of advanced machine learning methods on resting-state fMRI network for identification of mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease. Brain Imaging&Behavior, 2016, 10(3): 799-817. [4] Kim J, Calhoun V D, Shim E, Lee J H. Deep neural network with weight sparsity control and pre-training extracts hierarchical features and enhances classification performance: Evidence from whole-brain resting-state functional connectivity patterns of schizophrenia. Neuroimage, 2016, 124: 127-146. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.05.018 [5] Hailong L, Parikh N A, Lili H. A Novel Transfer Learning Approach to Enhance Deep Neural Network Classification of Brain Functional Connectomes. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 2018, 12: 491. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00491 [6] Meszlényi R, Buza K, Vidnyánszky Z. Resting State fMRI Functional Connectivity-Based Classification Using a Convolutional Neural Network Architecture. Frontiers in Neuroinformatics, 2017, 11: 61. doi: 10.3389/fninf.2017.00061 [7] Kawahara J, Brown C J, Miller S P, et al. BrainNetCNN: Convolutional Neural Networks for Brain Networks; Towards Predicting Neurodevelopment. Neuroimage, 2017, 146: 1038-1049. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.09.046 [8] Sun Y, Wang X G, Tang X O. Deep learning face representation from predicting 10 000 classes. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Columbus, OH, USA, IEEE. 2014: 1891−1898. [9] 张婷, 李玉鑑, 胡海鹤, 张亚红. 基于跨连卷积神经网络的性别分类模型. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(6): 858-865.Zhang T, Li Y J, Hu H H, Zhang Y H. A gender classification model based on cross-connected convolutional neural networks. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(6): 858-865. [10] 李勇, 林小竹, 蒋梦莹. 基于跨连接Lenet-5网络的面部表情识别. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(1): 176-182.Li Y, Lin X Z, Jiang M Y. Facial expression recognition with cross-connect LeNet-5 network. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(1): 176-182. [11] Yang H M, Zhang X Y, Yin F, Liu C L. Robust classification with convolutional prototype learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Salt Lake City, UT, USA, IEEE. 2018: 3474−3482 [12] Wang Z, Kong Z, Chang S, et al. Robust high dimensional stream classification with novel class detection. In: Proceedings of IEEE 35th International Conference on Data Engineering (ICDE). Macao, China, IEEE. 2019: 1418−1429 [13] Zhang C Q, Han Z B, Cui Y J, Hu Q. CPM-Nets: Cross partial multi-view networks. In: Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS). Vancouver, BC, Canada, Curran Associates, Inc. 2019: 4077−4087 [14] Wang S, Zhan Y, Zhang Y, et al. Abnormal long-and short-range functional connectivity in adolescent-onset schizophrenia patients: a resting-state fMRI study. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry, 2018, 81: 445-451. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2017.08.012 [15] Bi X A, Wang Y, Shu Q, Sun Q, Xu Q. Classification of autism spectrum disorder using random support vector machine cluster. Frontiers in genetics, 2018, 9: 18. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2018.00018 [16] Watanabe T, Kessler D, Scott C, Angstadt M, Sripada C. Disease prediction based on functional connectomes using a scalable and spatially-informed support vector machine. NeuroImage, 2014, 96: 183-202. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.03.067 [17] Anibal S H, Franco A R, Craddock R C, Buchweitz A, Meneguzzi F. Identification of autism spectrum disorder using deep learning and the ABIDE dataset. NeuroImage: Clinical, 2018, 17(C): 16-23. [18] Ju R, Hu C, Zhou P. Early Diagnosis of Alzheimer's Disease Based on Resting-State Brain Networks and Deep Learning. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Computational Biology and Bioinformatics, 2019, 16(1): 244-257. doi: 10.1109/TCBB.2017.2776910 [19] Parisot S, Ktena S I, Ferrante E, et al. Disease prediction using graph convolutional networks: Application to Autism Spectrum Disorder and Alzheimer's disease. Medical image analysis, 2018, 48: 117-130. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2018.06.001 [20] Brown C J, Kawahara J, Hamarneh G. Connectome priors in deep neural networks to predict autism. In: Proceedings of IEEE 15th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI). Washington, DC, USA, IEEE. 2018: 110−113 [21] Xing X, Ji J, Yao Y. Convolutional neural network with element-wise filters to extract hierarchical topological features for brain networks. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM). Madrid, Spain, IEEE. 2018: 780−783 [22] Kohonen T. The self-organizing map. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1990, 1(1–3): 1-6. [23] Kohonen T. Improved versions of learning vector quantization. In: Proceedings of International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN). San Diego, CA, USA, IEEE. 1990: 545−550 [24] Snell J, Swresky K, Zemel R. Prototypical networks for few-shot learning. In: Proceedings of Advances in neural information processing systems (NIPS). Long Beach, CA, USA, Curran Associates, Inc. 2017: 4077−4087 [25] Boney R, Alexander I. Semi-supervised and active few-shot learning with prototypical networks. arXiv: 1711.10856, 2017. [26] Craddock R C, James G A, Holtzheimer Ⅲ P E, Hu X P, Mayberg H S. A whole brain fMRI atlas generated via spatially constrained spectral clustering. Human Brain Mapping, 2012, 33(8): 1914-1928. doi: 10.1002/hbm.21333 [27] Wen Y, Zhang K, Li Z, Qiao Y. A Discriminative feature learning approach for deep face recognition. In: Proceedings of European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Amsterdam, The Netherlands, Springer. 2016: 499−515 [28] Simonyan K, Vedaldi A, Zisserman A. Deep inside convolutional networks: Visualising image classification models and saliency maps. arXiv: 1312.6034, 2013. [29] Meszlényi R J, Hermann P, Buza K, Gal V, Vidnyanszky Z. Resting state fmri functional connectivity analysis using dynamic time warping. Frontiers in neuroscience, 2017, 11: 75. -




 下载:
下载: