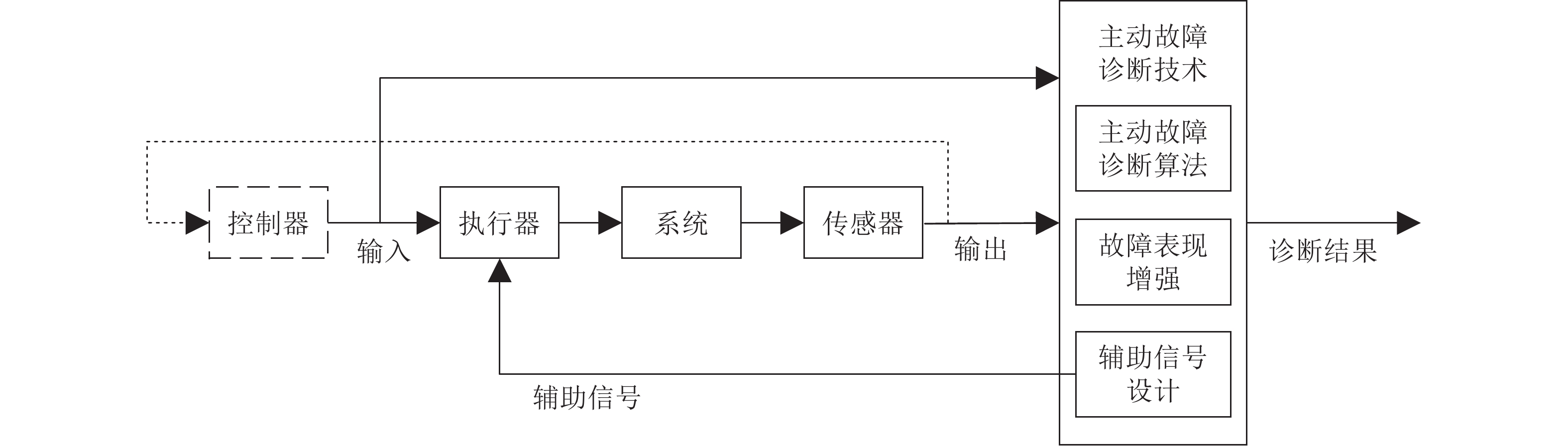
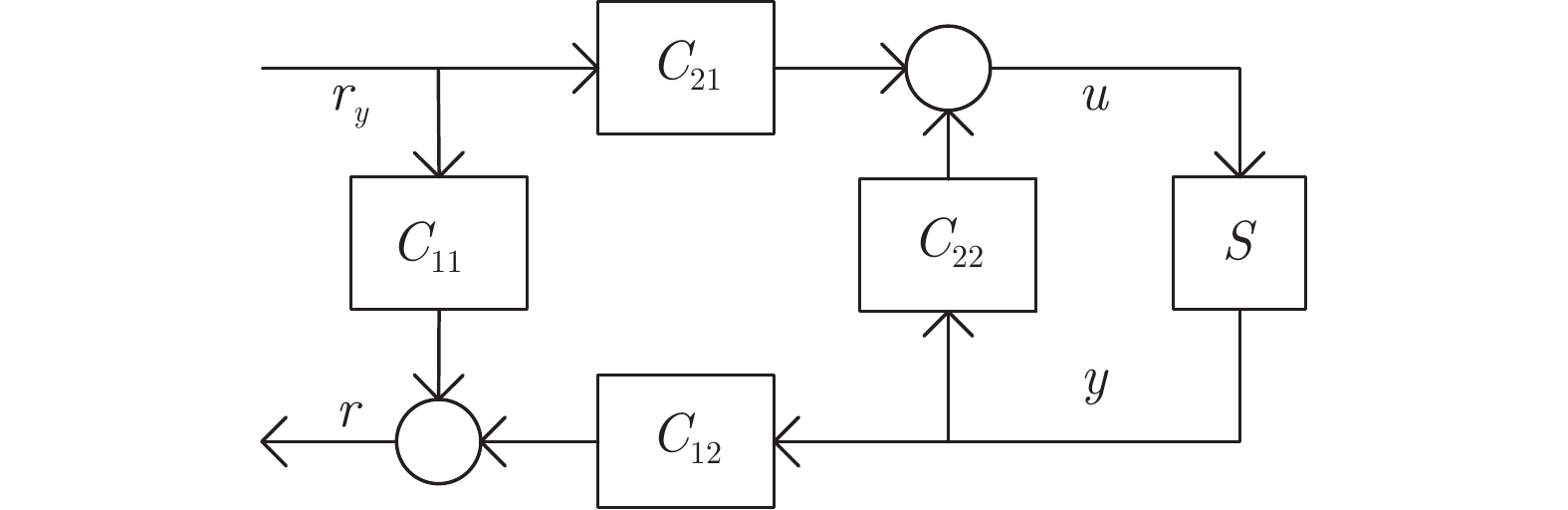
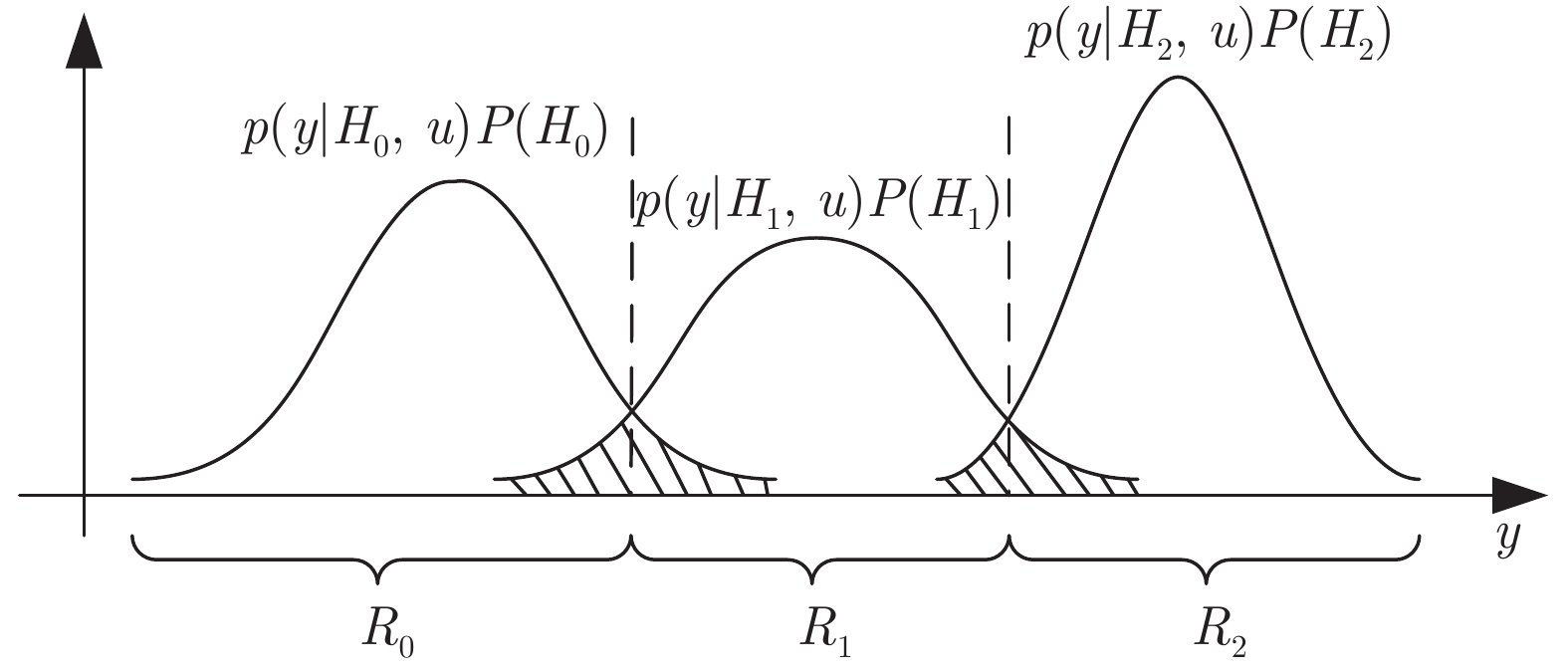
Active Fault Diagnosis for Dynamic Systems
-
摘要: 目前, 绝大多数动态系统的故障诊断方法仅利用系统的输入输出数据, 当数据中包含的故障特征不明显时, 诊断效果不佳. 动态系统的主动故障诊断方法通过向系统注入适当的辅助信号, 增强输入输出数据中特定故障的表现来提高对该故障的诊断能力. 主动故障诊断的研究不仅对于丰富与发展动态系统故障诊断理论具有重要价值, 还对故障诊断技术在实际中的推广应用具有重要意义. 本文阐述了主动故障诊断的思想, 介绍了用于增强故障表现的辅助信号所具有的特征, 分类概述了现有文献中的辅助信号设计方法, 分析了故障表现增强的形式与主动故障诊断技术的实现方式, 探讨了主动故障诊断中亟待解决的问题与未来的发展方向.Abstract: Most existing fault diagnosis techniques for dynamic systems only utilize the original input and output data of the system, which consequently can be regarded as the passive fault diagnosis approaches. This kind of methods limits the diagnosis capacity in the case that fault features can not be fully reflected by the input and output data. Within an alternative framework, active fault diagnosis (AFD) approaches inject appropriate auxiliary signals to the system and enhance the fault features that can be captured by analyzing the input and output data. Research of AFD is important to enrich the theory of fault diagnosis, and it is also of great significance to promote the application level of fault diagnosis approaches. This paper expounds the idea of AFD and summarizes the characteristics of auxiliary signals that need to be satisfied. An overview of state-of-the-art methods for auxiliary signals design is provided. Fault symptom enhancement as well as the active fault diagnosis techniques is discussed. We conclude this paper by pointing out several promising research topics on AFD.
-
表 1 两类故障诊断技术对比
Table 1 Comparison of two types of fault diagnosis techniques
被动故障诊断 主动故障诊断 是否利用系统输入输出信息 是 是 是否存在额外辅助信号输入 否 是 是否影响原系统演化规律 否 是 现有理论研究成果 多 极少 故障诊断能力 弱 强 实际应用潜力 小 大 表 2 系统友好型与系统侵入型辅助信号设计
Table 2 “System-friendly”and“System-intrusive”auxiliary signals design
类型 参考文献 系统友好型辅助信号设计 Nett et al. (1988)[13], Niemann (2006)[40], Niemann and Poulsen (2014)[45], Jacobson and Nett (1991)[51], Niemann (2012)[54], Niemann and Poulsen (2005)[56], Niemann (2006)[57], Poulsen and Niemann (2008)[58], Niemann and Poulsen (2015)[59] etc. 系统侵入型−随机性辅助信号设计 Zhang and Zarrop (1988)[12], Zhang (1989)[27], Paulson et al. (2018)[29], Mesbah et al. (2014)[30], Kerestecioğlu (1993)[33], Kim and Braatz (2013)[43], Punčochář et al. (2015)[62], Blackmore et al. (2008)[63], Heirung and Mesbah (2017)[64], Hatanaka and Uosaki (1999)[66], Hatanaka and Uosaki (1996)[68], Škach et al. (2017)[69] etc. 系统侵入型−确定性辅助信号设计 Raimondo et al. (2016)[14], Scott et al. (2014)[15], Ashari et al. (2012)[20], Choe et al. (2009)[23], Nikoukhah and Campbell (2006)[70], Marseglia et al. (2014)[71], Marseglia and Raimondo (2017)[73], Nikoukhah and Campbell (2008)[76] etc. 表 3 在线与离线辅助信号设计
Table 3 On-line and off-line auxiliary signals design
类型 参考文献 在线辅助信号设计 Ashari et al. (2012)[20], Zhang (1989)[27], Paulson et al. (2018)[29], Šimandl et al. (2005)[49], Nikoukhah et al. (2010)[77], Raimondo et al. (2013)[78], Heirung et al.(2019)[79], Paulson et al. (2017)[80], Wang et al.(2019)[81], Lin et al.(2017)[82] etc. 离线辅助信号设计 Blackmore and Williams (2006)[26], Mesbah et al. (2014)[30], Paulson et al. (2014)[31], Andjelkovic et al. (2008)[47], Blackmore et al. (2008)[63], Nikoukhah and Campbell (2006)[70], Fair and Campbell (2009)[84], Blackmore and Williams (2005)[92] etc. 表 4 主动故障诊断典型实例
Table 4 Typical examples of active fault diagnosis
系统 参考文献 飞行器 Kim and Braatz (2013)[43], Jacobson and Nett (1991)[51], Blackmore et al. (2008)[63], Blackmore and Williams (2005)[92] 电机 Campbell et al. (2006)[50], Nikoukhah et al. (2010)[77], Yang et al. (2014)[88] 水箱系统 Mesbah et al. (2014)[30], Paulson et al. (2014)[31], Palmer and Bollas (2019)[90] 钟摆系统 Škach et al. (2017)[69], Punčochář and Šimandl (2014)[83] 弹簧系统 Niemann (2006)[40], Blanchini et al. (2017)[42], Niemann and Poulsen (2014)[45] 化工过程 Zhang (1989)[27], Paulson et al. (2017)[80], Martin-Casas and Mesbah (2018)[91] -
[1] Gao Z W, Cecati C, Ding S X. A survey of fault diagnosis and fault-tolerant techniques — Part I: Fault diagnosis with model-based and signal-based approaches. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2015, 62(6): 3757−3767 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2015.2417501 [2] 周东华, 叶银忠. 现代故障诊断与容错控制. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2000.Zhou Dong-Hua, Ye Yin-Zhong. Fault Diagnosis and Fault-Tolerant Control. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2000. [3] 刘强, 卓洁, 郎自强, 秦泗钊. 数据驱动的工业过程运行监控与自优化研究展望. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(11): 1944−1956Liu Qiang, Zhuo Jie, Lang Zi-Qiang, Qin S. Joe. Perspectives on data-driven operation monitoring and self-optimization of industrial processes. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(11): 1944−1956 [4] 周东华, 纪洪泉, 何潇. 高速列车信息控制系统的故障诊断技术. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(7): 1153−1164Zhou Dong-Hua, Ji Hong-Quan, He Xiao. Fault diagnosis techniques for the information control system of high-speed trains. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(7): 1153−1164 [5] 吴高昌, 刘强, 柴天佑, 秦泗钊. 基于时序图像深度学习的电熔镁炉异常工况诊断. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(8): 1475−1485Wu Gao-Chang, Liu Qiang, Chai Tian-You, Qin S. Joe. Abnormal condition diagnosis through deep learning of image sequences for fused magnesium furnaces. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(8): 1475−1485 [6] 周东华, 胡艳艳. 动态系统的故障诊断技术. 自动化学报, 2009, 35(6): 748−758 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2009.00748Zhou Dong-Hua, Hu Yan-Yan. Fault diagnosis techniques for dynamic systems. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2009, 35(6): 748−758 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2009.00748 [7] Mehra R K, Peschon J. An innovations approach to fault detection and diagnosis in dynamic systems. Automatica, 1971, 7(5): 637−640 doi: 10.1016/0005-1098(71)90028-8 [8] Patton R J, Frank P M, Clark R N. Issues of Fault Diagnosis for Dynamic Systems. London: Springer-Verlag, 2000. [9] He X, Wang Z D, Zhou D H. Robust fault detection for networked systems with communication delay and data missing. Automatica, 2009, 45(11): 2634−2639 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2009.07.020 [10] He X, Wang Z D, Liu Y, Zhou D H. Least-squares fault detection and diagnosis for networked sensing systems using a direct state estimation approach. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2013, 9(3): 1670−1679 doi: 10.1109/TII.2013.2251891 [11] Zhou D H, He X, Wang Z D, Liu G P, Ji Y D. Leakage fault diagnosis for an Internet-based three-tank system: An experimental study. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2012, 20(4): 857−870 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2011.2154383 [12] Zhang X J, Zarrop M B. Auxiliary signals for improving on-line fault detection. In: Proceedings of the 1988 International Conference on Control. Oxford, UK: IET, 1988. [13] Nett C N, Jacobson C A, Miller A T. An integrated approach to controls and diagnostics: The 4-parameter controller. In: Proceedings of the 1988 American Control Conference. Atlanta, United States: IEEE, 1988. 824−835 [14] Raimondo D M, Marseglia G R, Braatz R D, Scott J K. Closed-loop input design for guaranteed fault diagnosis using set-valued observers. Automatica, 2016, 74: 107−117 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2016.07.033 [15] Scott J K, Findeisen R, Braatz R D, Raimondo D M. Input design for guaranteed fault diagnosis using zonotopes. Automatica, 2014, 50(6): 1580−1589 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2014.03.016 [16] Šimandl M, Punčochář I. Active fault detection and control: unified formulation and optimal design. Automatica, 2009, 45(9): 2052−2059 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2009.04.028 [17] Ashari A E, Nikoukhah R, Campbell S L. Auxiliary signal design for robust active fault detection of linear discrete-time systems. Automatica, 2011, 47(9): 1887−1895 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2011.06.009 [18] Heirung T A N, Mesbah A. Input design for active fault diagnosis. Annual Reviews in Control, 2019, 47: 35−50 doi: 10.1016/j.arcontrol.2019.03.002 [19] Punčochář I, Škach J. A survey of active fault diagnosis methods. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2018, 51(24): 1091−1098 doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2018.09.726 [20] Ashari A E, Nikoukhah R, Campbell S L. Effects of feedback on active fault detection. Automatica, 2012, 48(5): 866−872 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2012.02.020 [21] Campbell S L, Scott J R. Asynchronous auxiliary signal design for failure detection. In: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC). San Diego, USA: IEEE, 2014. 2727−2732 [22] Campbell S L, Horton K G, Nikoukhah R. Auxiliary signal design for rapid multi-model identification using optimization. Automatica, 2002, 38(8): 1313−1325 doi: 10.1016/S0005-1098(02)00040-7 [23] Choe D, Campbell S L, Nikoukhah R. Optimal piecewise-constant signal design for active fault detection. International Journal of Control, 2009, 82(1): 130−146 doi: 10.1080/00207170801993587 [24] Fair M, Campbell S L. Active incipient fault detection with more than two simultaneous faults. In: Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics. San Antonio, USA: IEEE, 2009. 3322−3327 [25] Nikoukhah R, Campbell S L, Horton K G, Delebecque F. Auxiliary signal design for robust multimodel identification. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2002, 47(1): 158−164 doi: 10.1109/9.981737 [26] Blackmore L, Williams B. Finite horizon control design for optimal discrimination between several models. In: Proceedings ofthe 45th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control. San Diego,USA: IEEE, 2006: 1147−1152 [27] Zhang X J. Auxiliary Signal Design in Fault Detection and Diagnosis. Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag, 1989 [28] Kim K K K, Raimondo D M, Braatz R D. Optimum input design for fault detection and diagnosis: model-based prediction and statistical distance measures. In: Proceedings of the 2013 European Control Conference (ECC). Zurich, Switzerland: IEEE, 2013. 1940−1945 [29] Paulson J A, Heirung T A N, Braatz R D, Mesbah A. Closed-loop active fault diagnosis for stochastic linear systems. In: Proceedings of the 2018 Annual American Control Conference (ACC). Milwaukee, USA: IEEE, 2018. 735−741 [30] Mesbah A, Streif S, Findeisen R, Braatz R D. Active fault diagnosis for nonlinear systems with probabilistic uncertainties. IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 2014, 47(3): 7079−7084 doi: 10.3182/20140824-6-ZA-1003.01594 [31] Paulson J A, Raimondo D M, Findeisen R, Braatz R D, Streif S. Guaranteed active fault diagnosis for uncertain nonlinear systems. In: Proceedings of the 2014 European Control Conference (ECC). Strasbourg, France: IEEE, 2014. 926−931 [32] Busch R, Peddle I K. Active fault detection for open loop stable LTI SISO systems. International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems, 2014, 12(2): 324−332 doi: 10.1007/s12555-012-0500-8 [33] Kerestecioğlu F. Change Detection and Input Design in Dynamical Systems. Baldock, Hertfordshire: Research Studies Press, 1993. [34] Uosaki K, Takata N, Hatanaka T. Optimal auxiliary input for on-line fault detection and fault diagnosis. IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 1993, 26(2): 441−446 [35] Kerestecioğlu F, Çetin İ. Auxiliary signal design for detecting changes towards unknown hypotheses. In: Proceedings of the 12th IEEE International Symposium on Intelligent Control. Istanbul, Turkey: IEEE, 1997. 297−302 [36] Kerestecioğlu F, Zarrop M B. Input design for detection of abrupt changes in dynamical systems. International Journal of Control, 1994, 59(4): 1063−1084 doi: 10.1080/00207179408923118 [37] Kerestecioğlu F, Çetin İ. Auxiliary input design for detecting changes towards partially known hypotheses. IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 1997, 30(18): 1023−1028 doi: 10.1016/S1474-6670(17)42535-3 [38] Kerestecioğlu F, Çetin İ. Optimal input design for the detection of changes towards unknown hypotheses. International Journal of Systems Science, 2004, 35(7): 435−444 doi: 10.1080/00207720410001734219 [39] Nikoukhah R, Campbell S L, Delebecque F. Detection signal design for failure detection: A robust approach. International Journal of Adaptive Control and Signal Processing, 2000, 14(7): 701−724 doi: 10.1002/1099-1115(200011)14:7<701::AID-ACS617>3.0.CO;2-6 [40] Niemann H. A setup for active fault diagnosis. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2006, 51(9): 1572−1578 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2006.878724 [41] Ashari A E, Nikoukhah R, Campbell S L. Active robust fault detection in closed-loop systems: Quadratic optimization approach. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2012, 57(10): 2532−2544 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2012.2188430 [42] Blanchini F, Casagrande D, Giordano G, Miani S, Olaru S, Reppa V. Active fault isolation: A duality-based approach via convex programming. SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization, 2017, 55(3): 1619−1640 doi: 10.1137/15M1046046 [43] Kim K K K, Braatz R D. Semidefinite programming relaxation of optimum active input design for fault detection and diagnosis: model-based finite horizon prediction. In: Proceedings of the 2013 European Control Conference (ECC). Zurich, Switzerland: IEEE, 2013. 1934−1939 [44] Ashari A E, Nikoukhah R, Campbell S L. Active robust fault detection of closed-loop systems: General cost case. IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 2009, 42(8): 585−590 doi: 10.3182/20090630-4-ES-2003.00097 [45] Niemann H, Poulsen N K. Active fault detection in MIMO systems. In: Proceedings of the 2014 American Control Conference. Portland, USA: IEEE, 2014. 1975−1980 [46] Hatanaka T, Uosaki K. Frequency domain approach to optimal auxiliary input design for fault diagnosis. In: Proceedings of the 1999 European Control Conference (ECC). Karlsruhe, Germany: IEEE, 1999. 1717−1722 [47] Andjelkovic I, Sweetingham K, Campbell S L. Active fault detection in nonlinear systems using auxiliary signals. In: Proceedings of the 2008 American Control Conference. Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2008. 2142−2147 [48] Campbell S L, Drake K, Nikoukhah R. Analysis of spline based auxiliary signal design for failure detection in delay systems. In: Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics. Washington, DC, USA: IEEE, 2003. 2551−2556 [49] Šimandl M, Punčochář I, Královec J. Rolling horizon for active fault detection. In: Proceedings of the 44th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control. Seville, Spain: IEEE, 2005. 3789−3794 [50] Campbell S L, Drake K J, Andjelkovic I, Sweetingham K, Choe D. Model based failure detection using test signals from linearizations: a case study. In: Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE Conference on Computer Aided Control System Design, 2006 IEEE International Conference on Control Applications, 2006 IEEE International Symposium on Intelligent Control. Munich, Germany: IEEE, 2006. 2659−2664 [51] Jacobson C A, Nett C N. An integrated approach to controls and diagnostics using the four parameter controller. IEEE Control Systems Magazine, 1991, 11(6): 22−29 doi: 10.1109/37.92987 [52] Jacobson C A, Valavanis K P. Review of the four parameter controller approach for FDI problems. In: Proceedings of the 5th IEEE International Symposium on Intelligent Control 1990. Philadelphia, USA: IEEE, 1990. 577−582 [53] Niemann H. Fault tolerant control based on active fault diagnosis. In: Proceedings of the 2005 American Control Conference. Portland, USA: IEEE, 2005. 2224−2229 [54] Niemann H. A model-based approach to fault-tolerant control. International Journal of Applied Mathematics and Computer Science, 2012, 22(1): 67−86 doi: 10.2478/v10006-012-0005-x [55] Wang J, Zhang J J, Qu B, Wu H Y, Zhou J L. Unified architecture of active fault detection and partial active fault-tolerant control for incipient faults. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2017, 47(7): 1688−1700 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2017.2667683 [56] Niemann H, Poulsen N K. Active fault diagnosis in closed-loop systems. IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 2005, 38(1): 448−453 [57] Niemann H. Active fault diagnosis in closed-loop uncertain systems. IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 2006, 39(13): 587−592 doi: 10.3182/20060829-4-CN-2909.00097 [58] Poulsen N K, Niemann H. Active fault diagnosis based on stochastic tests. International Journal of Applied Mathematics and Computer Science, 2008, 18(4): 487−496 doi: 10.2478/v10006-008-0043-6 [59] Niemann H, Poulsen N K. Active fault diagnosis in sampled-data systems. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2015, 48(21): 883−888 doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2015.09.638 [60] Nikoukhah R. Guaranteed active failure detection and isolation for linear dynamical systems. Automatica, 1998, 34(11): 1345−1358 doi: 10.1016/S0005-1098(98)00079-X [61] Scott J K, Marseglia G R, Magni L, Braatz R D, Raimondo D M. A hybrid stochastic-deterministic input design method for active fault diagnosis. In: Proceedings of the 52nd IEEE Conference on Decision and Control. Florence, Italy: IEEE, 2013. 5656−5661 [62] Punčochář I, Škach J, Šimandl M. Infinite time horizon active fault diagnosis based on approximate dynamic programming. In: Proceedings of the 54th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC). Osaka, Japan: IEEE, 2015. 4456−4461 [63] Blackmore L, Rajamanoharan S, Williams B C. Active estimation for jump markov linear systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2008, 53(10): 2223−2236 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2008.2006100 [64] Heirung T A N, Mesbah A. Stochastic nonlinear model predictive control with active model discrimination: A closed-loop fault diagnosis application. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2017, 50(1): 15934−15939 doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2017.08.1745 [65] Kerestecioğlu F, Zarrop M B. Bayesian approach to optimal input design for failure detection and diagnosis. Adaptive Systems in Control and Signal Processing 1989. Glasgow, UK: Elsevier, 1990. 525−529 [66] Hatanaka T, Uosaki K. Optimal auxiliary input design for fault diagnosis. IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 1999, 32(2): 3862−3867 doi: 10.1016/S1474-6670(17)56659-8 [67] Hatanaka T, Uosaki K. Optimal auxiliary input for fault detection-frequency domain approach. IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 1994, 27(8), 1069−1074 [68] Hatanaka T, Uosaki K. Optimal auxiliary input for fault detection and fault diagnosis. In: Proceedings of the 1996 Joint Conference on Control Applications Intelligent Control and Computer Aided Control System Design. Dearborn, USA: IEEE, 1996. 117−122 [69] Škach J, Punčochář I, Straka O. Active fault diagnosis for jump markov nonlinear systems. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2017, 50(1): 7308−7313 doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2017.08.1465 [70] Nikoukhah R, Campbell S L. Auxiliary signal design for active failure detection in uncertain linear systems with a priori information. Automatica, 2006, 42(2): 219−228 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2005.09.011 [71] Marseglia G R, Scott J K, Magni L, Braatz R D, Raimondo D M. A hybrid stochastic-deterministic approach for active fault diagnosis using scenario optimization. IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 2014, 47(3): 1102−1107 doi: 10.3182/20140824-6-ZA-1003.02590 [72] Scott J K, Findeisen R, Braatz R D, Raimondo D M. Design of active inputs for set-based fault diagnosis. In: Proceedings of the 2013 American Control Conference. Washington, USA: IEEE, 2013. 3561−3566 [73] Marseglia G R, Raimondo D M. Active fault diagnosis: A multi-parametric approach. Automatica, 2017, 79: 223−230 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2017.01.021 [74] Scott J K, Raimondo D M, Marseglia G R, Braatz R D. Constrained zonotopes: A new tool for set-based estimation and fault detection. Automatica, 2016, 69: 126−136 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2016.02.036 [75] Rego B S, Raffo G V, Scott J K, Raimondo D M. Guaranteed methods based on constrained zonotopes for set-valued state estimation of nonlinear discrete-time systems. Automatica, 2020, 111: 1−14 [76] Nikoukhah R, Campbell S L. On the detection of small parameter variations in linear uncertain systems. European Journal of Control, 2008, 14(2): 158−171 doi: 10.3166/ejc.14.158-171 [77] Nikoukhah R, Campbell S L, Drake K. An active approach for detection of incipient faults. International Journal of Systems Science, 2010, 41(2): 241−257 [78] Raimondo D M, Braatz R D, Scott J K. Active fault diagnosis using moving horizon input design. In: Proceedings of the 2013 European Control Conference (ECC). Zurich, Switzerland: IEEE, 2013. 3131−3136 [79] Heirung T A N, Santos T L M, Mesbah A. Model predictive control with active learning for stochastic systems with structural model uncertainty: Online model discrimination. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2019, 128(SEP.2): 128−140 [80] Paulson J A, Martin-Casas M, Mesbah A. Input design for online fault diagnosis of nonlinear systems with stochastic uncertainty. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2017, 56(34): 9593−9605 [81] Wang Y, Olaru S, Valmorbida G, Puig V, Cembrano G. Set-invariance characterizations of discrete-time descriptor systems with application to active mode detection. Automatica, 2019, 107: 255−263 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2019.05.053 [82] Lin F, Wang L Y, Chen W, Han L T, Shen B. N-diagnosability for active on-line diagnosis in discrete event systems. Automatica, 2017, 83: 220−225 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2017.06.004 [83] Punčochár I, Šimandl M. On infinite horizon active fault diagnosis for a class of non-linear non-Gaussian systems. International Journal of Applied Mathematics and Computer Science, 2014, 24(4): 795−807 doi: 10.2478/amcs-2014-0059 [84] Fair M, Campbell S L. Active incipient fault detection with two simultaneous faults. IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 2009, 42(8): 573−578 doi: 10.3182/20090630-4-ES-2003.00095 [85] Scola H R, Nikoukhah R, Delebecque F. Test signal design for failure detection: A linear programming approach. International Journal of Applied Mathematics and Computer Science, 2003, 13(4): 515−526 [86] Tabatabaeipour S M. Active fault detection and isolation of discrete-time linear time-varying systems: A set-membership approach. International Journal of Systems Science, 2015, 46(11): 1917−1933 doi: 10.1080/00207721.2013.843213 [87] Wang J D, Wang J, Zhou J L. On-line active fault detection based on set-membership ellipsoid and moving window. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 7th Data Driven Control and Learning Systems Conference (DDCLS). Hubei, China: IEEE, 2018. 420−425 [88] Yang J W, Hamelin F, Sauter D. Active fault diagnosis based on a framework of optimization for closed loop system. In: Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Control, Decision and Information Technologies (CoDIT). Metz, France: IEEE, 2014. 387−392 [89] 周东华, 刘洋, 何潇. 闭环系统故障诊断技术综述. 自动化学报, 2013, 39(11): 1933−1943Zhou Dong-Hua, Liu Yang, He Xiao. Review on fault diagnosis techniques for closed-loop systems. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(11): 1933−1943 [90] Palmer K A, Bollas G M. Optimal sensor selection for active fault diagnosis using test information criteria. IFAC-PapersOnline, 2019, 52(1): 382−387 doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2019.06.092 [91] Martin-Casas M, Mesbah A. Active fault diagnosis for stochastic nonlinear systems: Online probabilistic model discrimination. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2018, 51(18): 702−707 doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2018.09.281 [92] Blackmore L, Williams B. Finite horizon control design for optimal model discrimination. In: Proceedings of the 44th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, and the European Control Conference 2005. Seville Spain: IEEE, 2005. 3795−3802 -




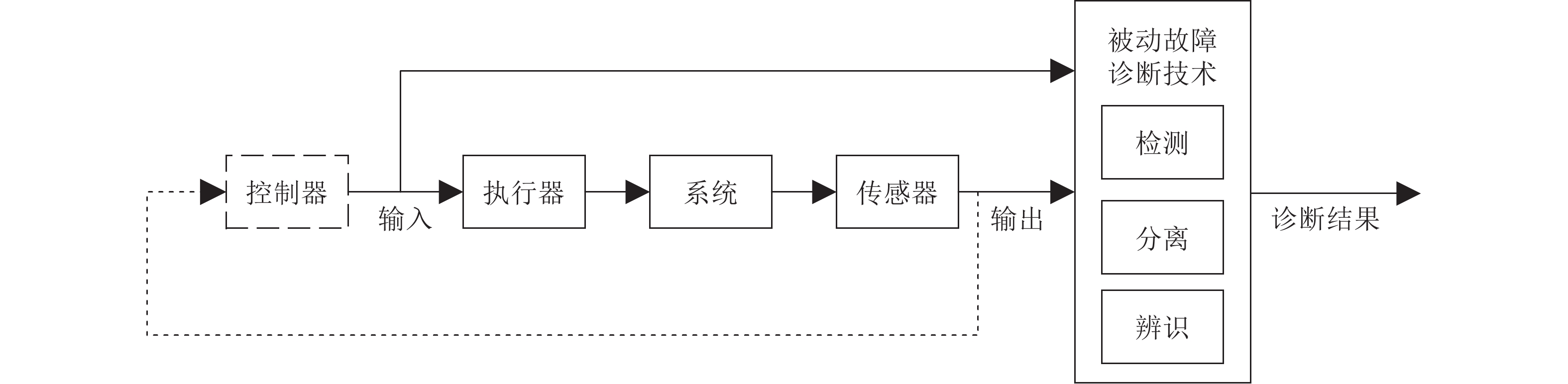
 下载:
下载: