-
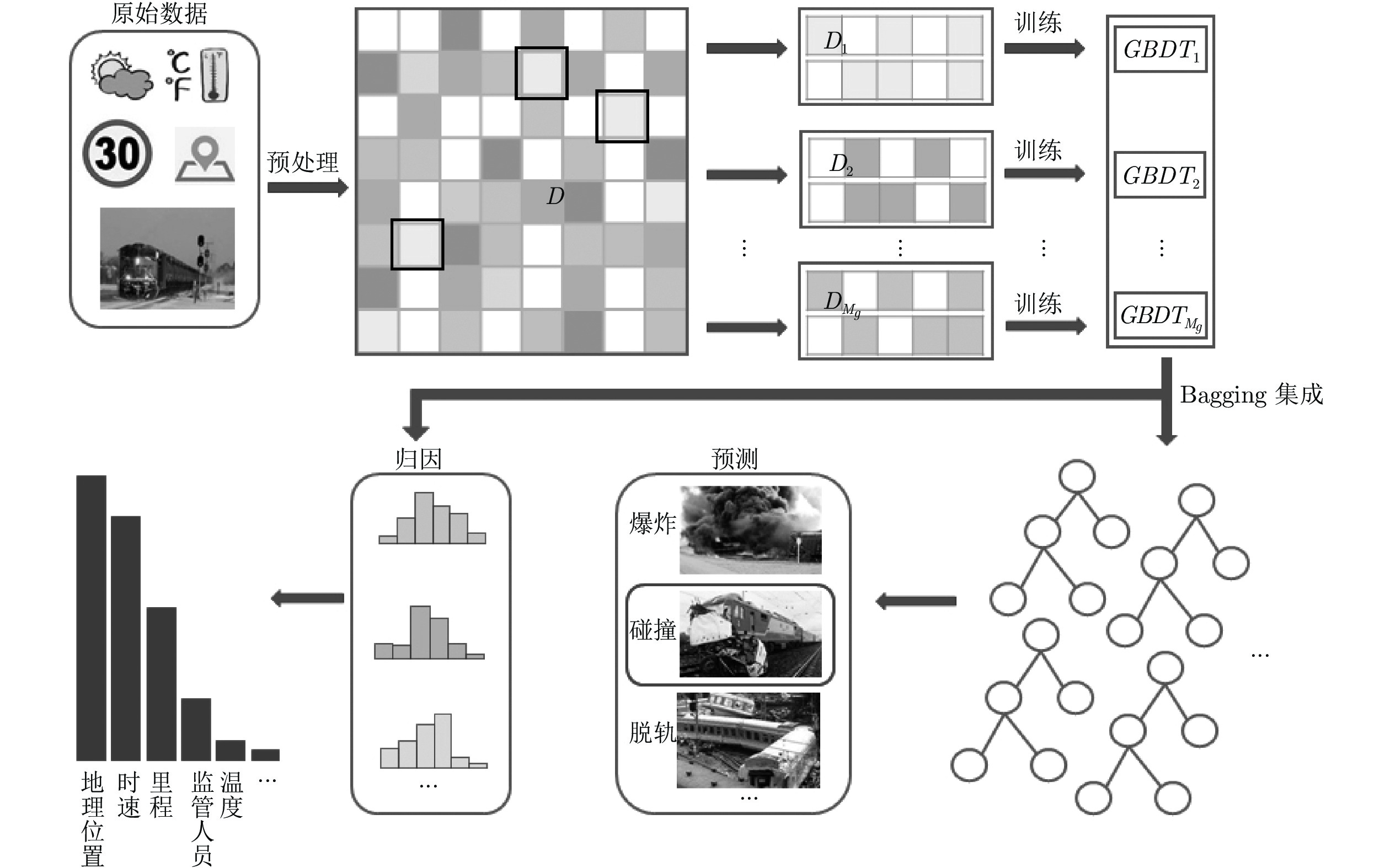
摘要: 运用数据挖掘技术进行铁路事故类型预测及成因分析, 对于建立铁路事故预警机制具有重要意义. 为此, 本文提出一种基于梯度提升决策树(Grandient boosting decision tree, GBDT)的铁路事故类型预测及成因分析算法. 针对铁路事故记录数据缺失的问题, 提出一种基于属性分布概率的补全算法, 最大程度保持原有数据分布, 从而降低数据缺失对事故类型预测造成的影响. 针对铁路事故记录数据类别失衡的问题, 提出一种集成的GBDT模型, 完成对事故类型的鲁棒性预测. 在此基础上, 根据GBDT预测模型中特征重要度排序, 实现事故成因分析. 通过在开放数据库上进行实验, 验证了本文模型的有效性.Abstract: The application of data mining technology in railway accident type prediction and cause analysis is of great significance to establish railway accident early warning mechanism. This paper proposes a gradient boosting decision tree (GBDT) based algorithm for railway accident type prediction and cause analysis. In order to solve the problem of data missing in railway accident record dataset, we propose a new data complement algorithm based on the attribute distribution probability, which can keep the distribution of original data as much as possible, thus reducing the impact of data missing on predicting railway accident type. To reduce the impact of unbalanced categories of data in railway accident dataset, an ensemble GBDT model is proposed to predict the types of accidents effectively and robustly. On these bases, according to the importance of features in GBDT prediction model, we complete the cause analysis of railway accidents. Experimental results on an open database show that our proposed method can predict the types and causes of railway accidents effectively.
-
表 1 原始数据描述
Table 1 Description of original data
Record Accident type Attribute Number 5 434 11 144 表 2 事故类型描述
Table 2 Description of accident types
Type Description 1 Derailment 2 Head on collision 3 Rearend collision 4 Side collision 5 Raking collision 6 Broken train collision 7 Hwy-rail crossing 8 RR grade crossing 9 Obstruction 10 Fire 11 Other impacts 表 3 数据集部分示例
Table 3 Examples of the dataset
Name Description Number Type RAILROAD Railroad code 5 434 Object CARS Num. of cars carrying hazmat 5 434 Int64 TYPSPD Train speed type 5 086 Object TRNDIR Train direction 5 161 Float64 TONS Gross tonnage, excluding power units 5 434 Int64 TYPEQ Type of consist 5 081 Object EQATT Equipment attended 5 074 Object CDTRHR Num. of hours conductors on duty 3 628 Int64 ENGHR Num. of hours engineers on duty 4 201 Int64 TRKNAME Track identification 5 434 Object 表 4 预处理后数据描述
Table 4 Description of preprocessed data
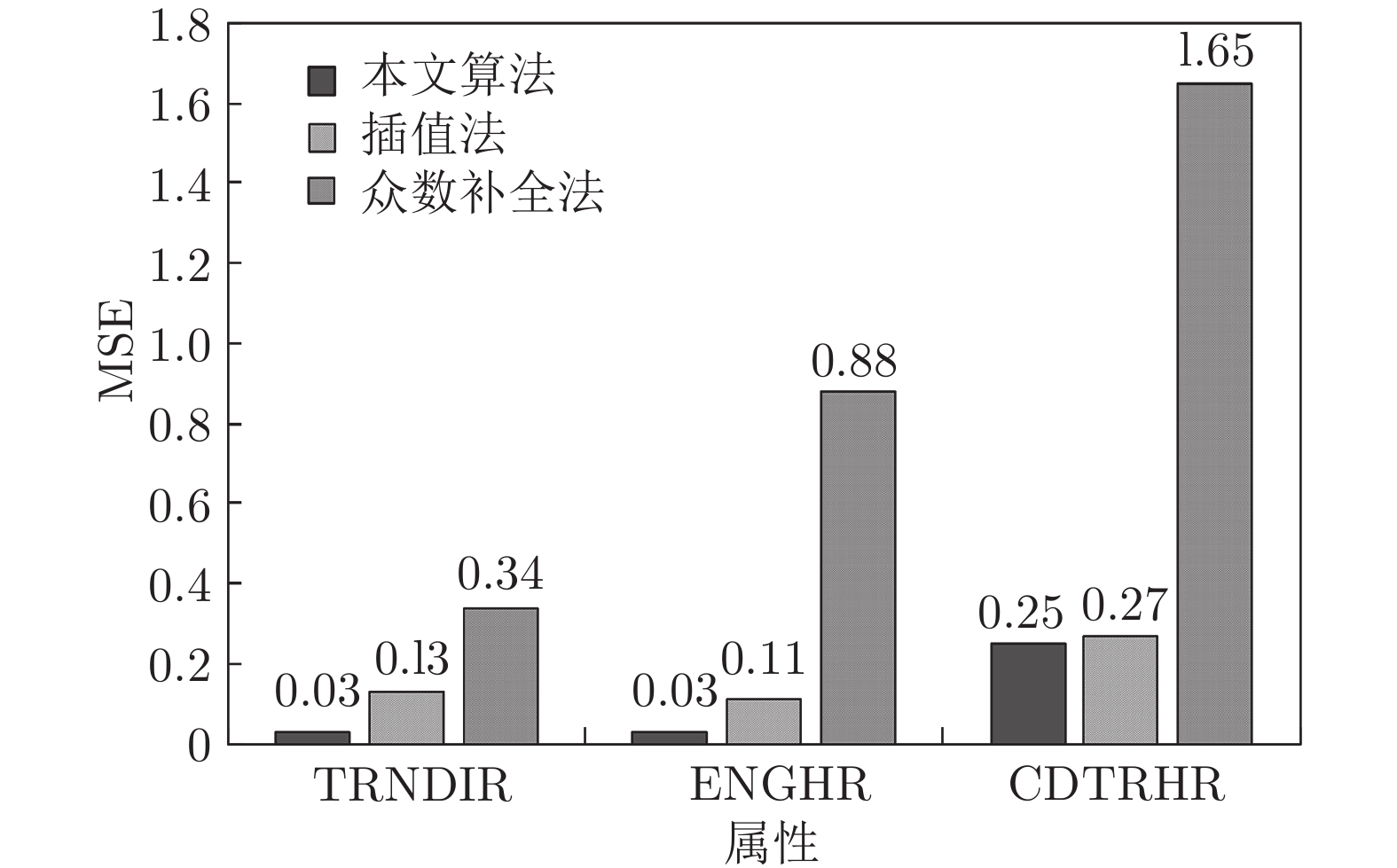
Record Accident type Attribute dimension Number 5 434 11 119 表 5 三种方法补全前后特征TRNDIR取值分布
Table 5 Distribution of the attribute TRNDIR values before and after three completion methods
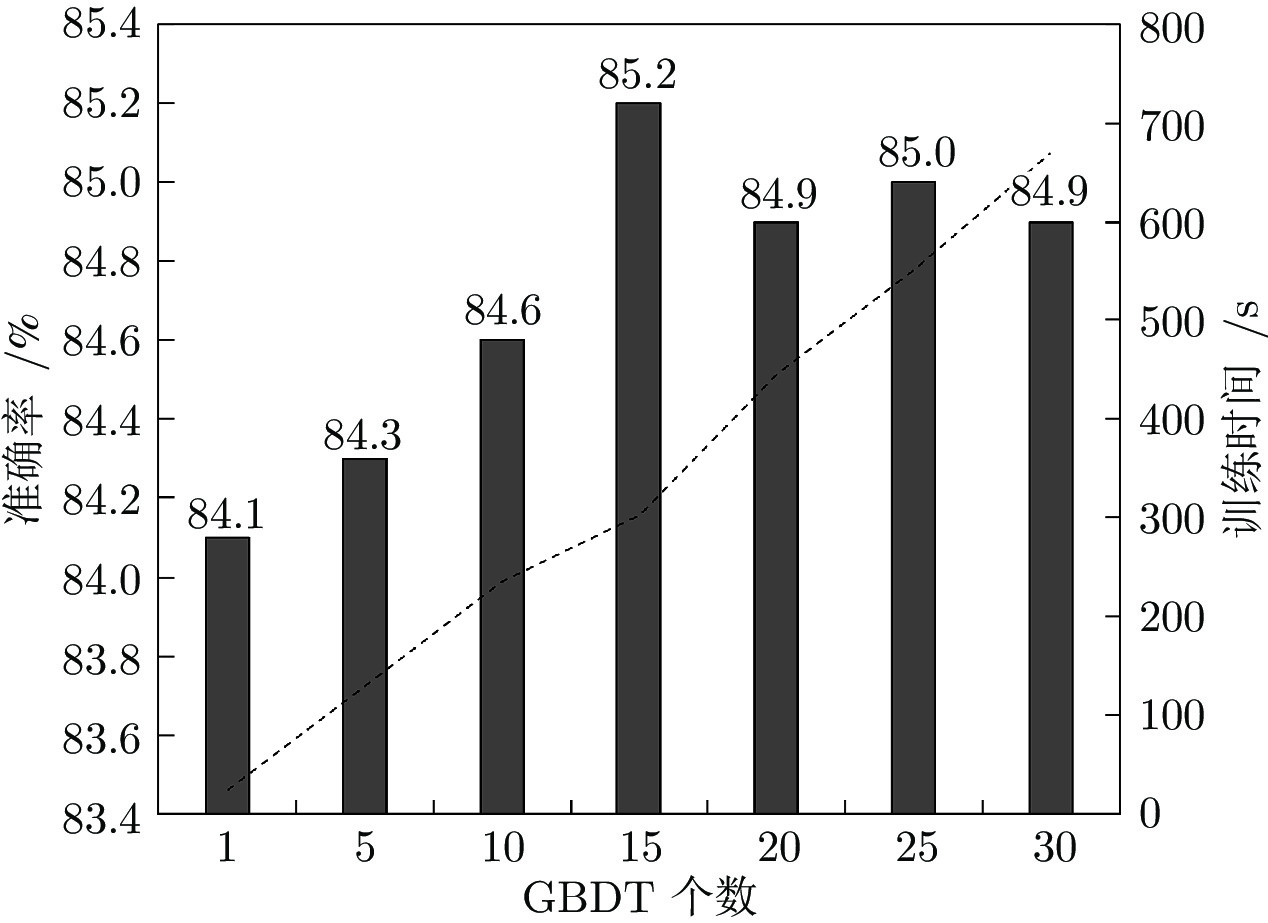
Algorithm $a_j=1$ $a_j=2$ $a_j=3$ $a_j=4$ Before completion 0.22 0.20 0.31 0.27 Interpolation 0.21 0.19 0.30 0.30 Mode 0.21 0.19 0.34 0.26 Our algorithm 0.22 0.20 0.31 0.27 表 6 不同采样率下集成GBDT分类准确率
Table 6 Accuracy of classifiers with different sampling rates
$\alpha$ 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0 Accuracy 0.841 0.846 0.845 0.852 0.848 表 7 各分类器性能对比
Table 7 Performance comparison of classifiers
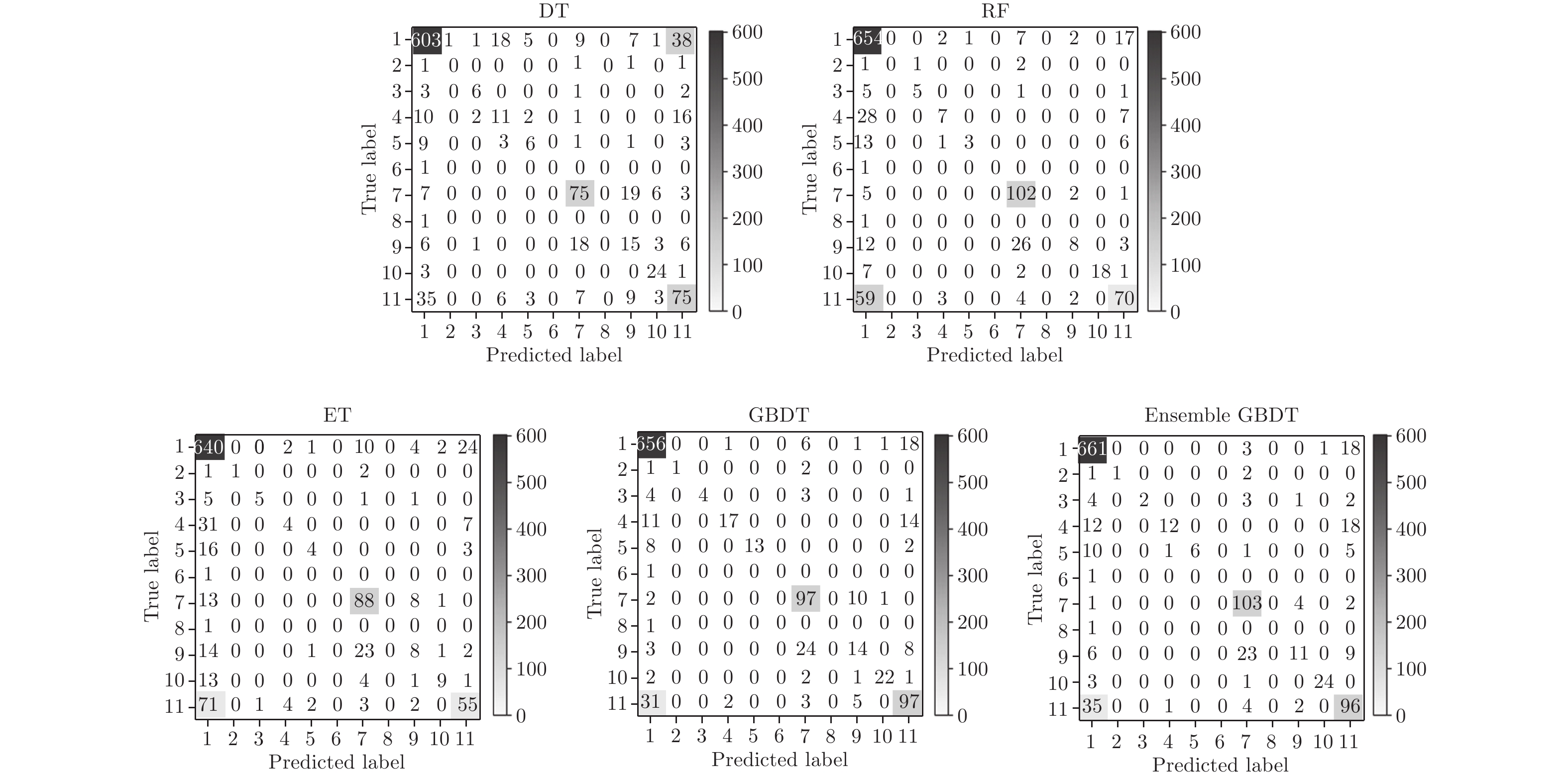
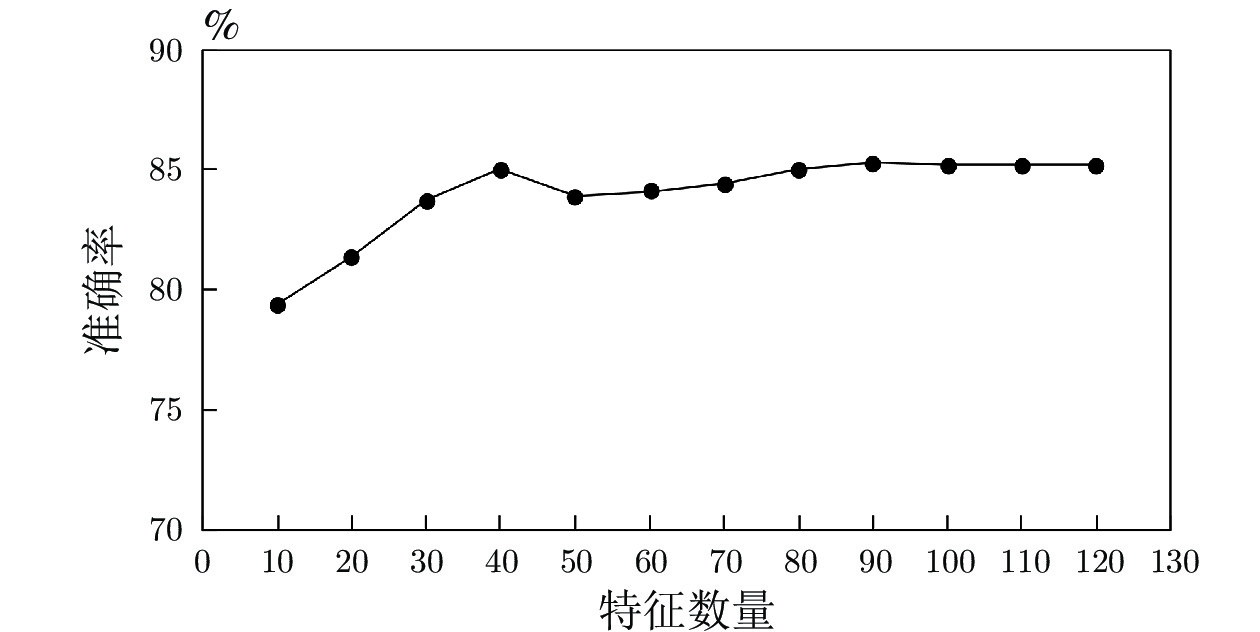
Classifier Accuracy Precision Recall F1 DT 0.728 0.73 0.73 0.73 RF 0.773 0.74 0.77 0.75 ET 0.734 0.70 0.73 0.71 GBDT 0.841 0.84 0.84 0.84 Ensemble GBDT 0.852 0.85 0.85 0.85 表 8 重要度排名前15的特征
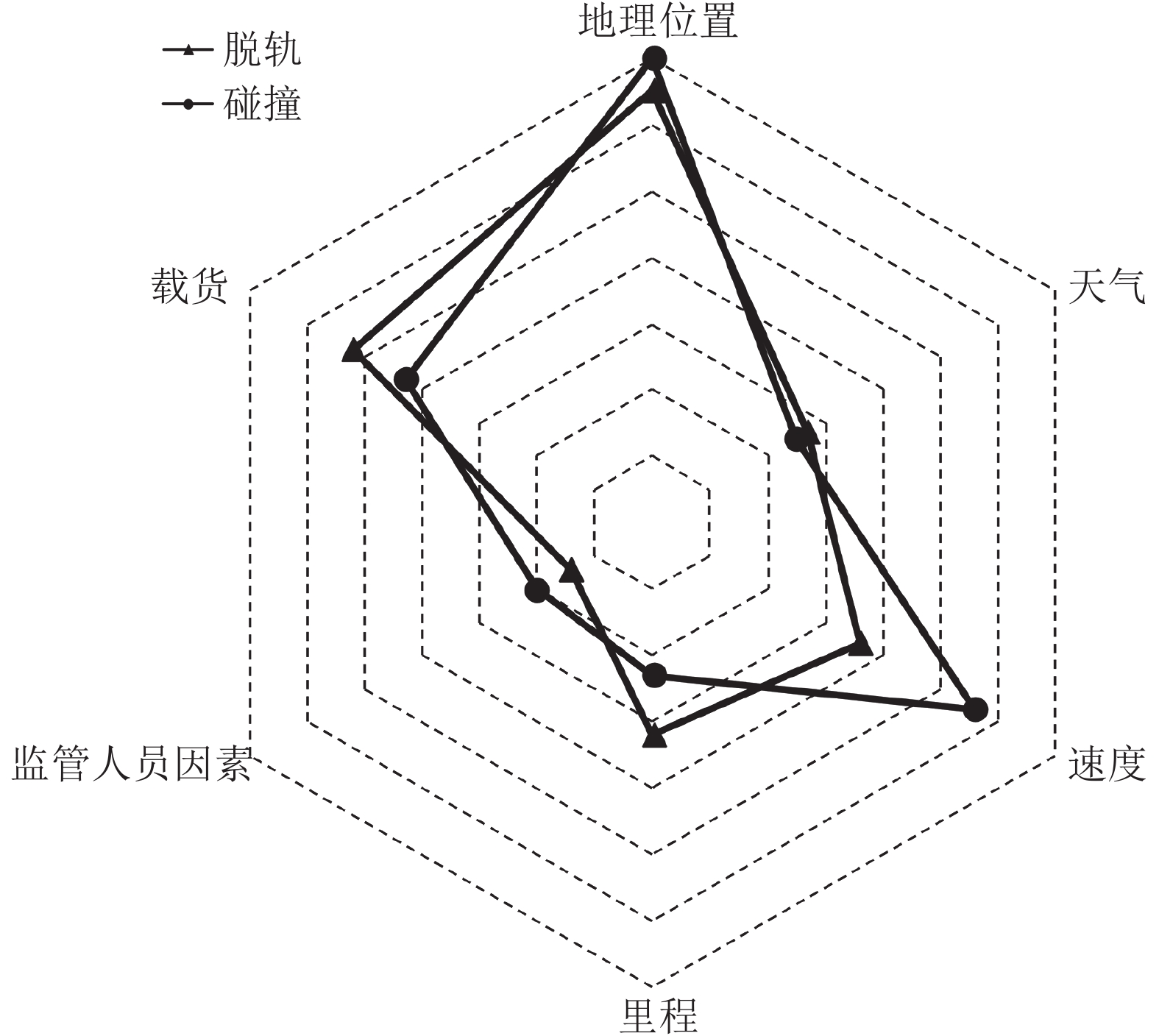
Table 8 Features of top 15 in importance
No. Name Description 1 Latitude Latitude in decimal degrees 2 Longitude Longitude in decimal degrees 3 CNTYCD FIPS county code 4 HIGHSPD Maximum speed 5 TRKNAME Track identification 6 RRCAR1 Car initials (fist involved) 7 TEMP Temperature in degrees fahrenheit 8 MILEPOST Milepost 9 STATION Nearest city and town 10 TRNSPD Speed of train in miles per hour 11 RRCAR2 Car initials (causing) 12 SUBDIV Railroad subdivision 13 ENGHR Num. of hours engineers on duty 14 CDTRHR Num. of hours conductors on duty 15 TONS Gross tonnage -
[1] Ming L. Data mining: concepts, models, methods, and algorithms. IIE Transaction, 2004, 36(5): 495-496 [2] 冯士雍. 回归分析方法. 北京: 科学出版社, 1974Feng Shi-Yong. Regression Analysis Method. Beijing: Science Press, 1974 [3] Rutkowski L, Jaworski M, Pietruczuk L, Duda P. Decision trees for mining data streams based on the gaussian approximation. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2014, 26(1): 108−119 doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2013.34 [4] 李定启, 程远平, 王海峰, 王亮, 周红星, 孙建华. 基于决策树ID3改进算法的煤与瓦斯突出预测. 煤炭学报, 2011, 36(4): 619−622Li Ding-Qi, Cheng Yuan-Ping, Wang Hai-Feng, Wang Liang, Zhou Hong-Xing, Sun Jian-Hua. . Coal and gas outburst prediction based on improved decision tree ID3 algorithm. Journal of China Coal Society, 2011, 36(4): 619−622 [5] Breiman L. Random forest. Machine Learning, 2001, 45(1): 5−32 doi: 10.1023/A:1010933404324 [6] Friedman J H. Greedy function approximation: a gradient boosting machine. The Annals of Statistics, 2001, 29(5): 1189−1232 [7] Friedman J H. Stochastic gradient boosting. Computational Statistics and Data Analysis, 2002, 38(4): 367−378 doi: 10.1016/S0167-9473(01)00065-2 [8] 周志华. 机器学习. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2016.Zhou Zhi-Hua. Machine Learning. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2016. [9] Schonlau M. Boosted regression (boosting): an introductory tutorial and a stata plugin. The Stata Journal, 2005, 5(3): 330−354. doi: 10.1177/1536867X0500500304 [10] 翁小雄, 吕攀龙. 基于 GBDT 算法的地铁 IC 卡通勤人群识别. 重庆交通大学学报 (自然科学版), 2019, 38(5): 8−12Weng Xiao-Xiong, Lv Pan-Long. Subway IC card commuter crowd identification based on GBDT algorithm. Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University(Natural Science), 2019, 38(5): 8−12 [11] Mursalin M, Zhang Yuan, Chen Yue-Hui, Chawla N V. Automated epileptic seizure detection using improved correlation-based feature selection with random forest classifier. Neurocomputing, 2017, 241: 204−214 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2017.02.053 [12] Cheng J, Li G, Chen X H. Research on travel time prediction model of freeway based on gradient boosting decision tree. IEEE Access, 2018, 7: 7466−7480 [13] Ma X, Ding C, Luan S, Wang Y, Wang Y P. Prioritizing influential factors for freeway incident clearance time prediction using the gradient boosting decision trees method. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2017, 18(9): 2303−2310 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2016.2635719 [14] Su H W, Zhang W J, Li Z H. Analysis and prediction of water traffic accidents in jingtang port based on improved GM(1, 1) model. In: Proceedings of the 37th Chinese Control Conference (CCC). New York, USA: IEEE, 2018.2212−2217 [15] Das S, Sun X D. Investigating the pattern of traffic crashes under rainy weather by association rules in data mining. In: Proceedings of the 93rd Transportation Research Board (TRB) Annual Meeting. Washington D.C., USA: Nation Academy of Sciences, 2014 [16] 金勇进. 缺失数据的统计处理, 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2009.Jin Yong-Jin. Statistical Processing of Missing Data. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2009. [17] 金勇进. 调查中的数据缺失及处理 (I)-缺失数据及其影响. 数理统计与管理, 2001, 20(4): 58−60 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1566.2001.04.012Jin Yong-Jin. Data loss and processing in survey(I)) data missing and impact. Journal of Applied Statistics and Management, 2001, 20(4): 58−60 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1566.2001.04.012 [18] Collell G, Prelec D, Patil K R. A simple plug-in bagging ensemble based on threshold-moving for classifying binary and multiclass imbalanced data. Neurocomputing, 2018, 275: 330−340 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2017.08.035 [19] Galar M, Fernandez A, Barrenechea E, Bustince H, Herrera F. A review on ensembles for the class imbalance problem: bagging-, boosting-, and hybrid-based approaches. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, Part C (Applications and Reviews), 2012, 42(4): 463−484 doi: 10.1109/TSMCC.2011.2161285 [20] 朱振峰, 汤静远, 常冬霞, 赵耀. 基于 GBDT 的商品分配层次化预测模型. 北京交通大学学报, 2018, 42(2): 9−13+45 doi: 10.11860/j.issn.1673-0291.2018.02.002Zhu Zhen-Feng, Tang Jing-Yuan, Chang Dong-Xia, Zhao Yao. GBDT based hierarchical model for commodity distribution prediction. Journal of Beijing Jiaotong University, 2018, 42(2): 9−13+45. doi: 10.11860/j.issn.1673-0291.2018.02.002 [21] 杨连报, 李平, 薛蕊, 马小宁, 吴艳华, 邹丹. 基于不平衡文本数据挖掘的铁路信号设备故障智能分类. 铁道学报, 2018, 40(2): 59−66 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2018.02.009Yang Lian-Bao, Li Ping, Xue Rui, Ma Xiao-Ning, Wu YanHua, Zou Dan. Intelligent classification of faults of railway signal equipment based on imbalancd text data mining. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2018, 40(2): 59−66 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2018.02.009 [22] Federal Railroad Administration Office of Safety Analysis [Online], available: https://safetydata.fra.dot.gov/OfficeofSafety/Default.aspx, June 1, 2019 -




 下载:
下载: