A Convex Hull Algorithm for Plane Point Sets Based on Region Normalization Segmentation
-
摘要: 为解决实际工程应用中具有超大规模的平面点集的凸包计算问题, 提出了一种基于点集所在区域正交化分割的新算法. 利用点集几何结构的部分极点对平面点集进行正交化分割, 以获取不相干的点集子集簇, 再对所有点集子集分别计算其凸包极点, 最后合并极点得到凸包点集. 在不同层级的正交化分割过程中, 根据已知极点的信息, 逐层舍去对于凸包极点生成没有贡献的无效点, 进而提高算法运行效率. 在与目前常用凸包算法的对比实验中, 该算法处理超大规模的平面点集时稳定性高且速度更快.Abstract: In order to solve the convex hull calculation problem of ultra-large scale planar point set in practical engineering applications, a new algorithm based on orthogonal segmentation of the region where the point set is located is designed. The partial point of the point set geometry is used to orthogonalize the plane point set to obtain the incoherent point set subset cluster, and then the convex hull poles are calculated for all the point set subsets, and finally the convex hull point set is obtained by combining the poles. In the process of orthogonalization and segmentation in different levels, according to the information of the existing convex hull poles, many of invalid points are discarded layer by layer, which improves the efficiency of the algorithm. In the comparison experiment with the commonly used convex hull algorithm, the proposed algorithm has high stability and speed when dealing with super large-scale planar point sets.
-
Key words:
- Planar point set /
- convex hull /
- orthogonal segmentation /
- parallel algorithm
-
表 1 点集不同层级分割的子集点数
Table 1 The number of points in the subset corresponding to different levels of segmentation
层级 5000 1 万 5 万 10 万 20 万 50 万 100 万 200 万 500 万 800 万 1000 万 1 438 873 4543 8893 17782 44541 88532 178749 449484 715181 885358 2 65 123 644 1213 2404 6120 11861 24559 61273 97727 120068 3 0 16 88 155 302 730 1398 3054 7967 12473 15307 4 0 0 12 22 44 85 175 403 1032 1630 2053 5 0 0 1 4 5 11 25 55 146 229 282 表 2 各算法运行时间 (s)
Table 2 Runtime for different algorithms (s)
点集点数 算法运行时间 Graham Jarvis 文献 [19] 算法 1 本文算法 5000 0.266 0.022 0.013 0.021 0.008 10000 1.067 0.045 0.027 0.047 0.011 50000 26.999 0.236 0.054 0.076 0.019 100000 108.645 0.539 0.102 0.448 0.028 150000 244.662 0.891 0.329 0.624 0.039 200000 435.077 1.296 0.585 0.752 0.047 表 3 不同数量级点集的运行时间 (s)
Table 3 Runtime comparison for different orders of magnitude point sets (s)
类别 20 万 50 万 100 万 200 万 500 万 0 0.586 0.048 1.574 0.102 3.315 0.197 6.964 0.384 18.509 0.989 1 0.580 0.046 1.575 0.104 3.317 0.194 6.962 0.383 18.510 0.965 2 0.589 0.047 1.574 0.103 3.312 0.201 6.962 0.386 18.506 1.021 3 0.579 0.047 1.568 0.107 3.321 0.200 6.960 0.396 18.518 0.949 4 0.581 0.045 1.574 0.106 3.312 0.202 6.963 0.392 18.509 0.959 5 0.589 0.048 1.579 0.108 3.313 0.190 6.958 0.386 18.511 0.962 6 0.585 0.048 1.573 0.105 3.317 0.197 6.988 0.390 18.513 0.970 7 0.585 0.046 1.570 0.103 3.313 0.199 6.966 0.391 18.509 0.957 8 0.591 0.050 1.574 0.105 3.315 0.200 6.963 0.405 18.518 0.959 9 0.586 0.047 1.582 0.105 3.315 0.198 6.968 0.398 18.499 0.961 10 0.584 0.046 1.575 0.105 3.313 0.196 6.962 0.385 18.510 1.019 -
[1] Barber C B, Dobkin D P, Huhdanpaa H. The quickhull algorithm for convex hulls. ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software, 1996, 22(4): 469−483 doi: 10.1145/235815.235821 [2] Kim Y, Kim J. Convex hull ensemble machine for regression and classification. Knowledge and Information Systems, 2004, 6(6): 645−663 doi: 10.1007/s10115-003-0116-7 [3] Ding S G, Nie X L, Qiao H, Zhang B. A fast algorithm of convex hull vertices selection for online classification. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2018, 29(4): 792−806 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2017.2648038 [4] Long P M, Servedio R A. Random classification noise defeats all convex potential boosters. Machine Learning, 2010, 78(3): 287−304 doi: 10.1007/s10994-009-5165-z [5] Chau A L, Li X O, Yu W. Convex and concave hulls for classification with support vector machine. Neurocomputing, 2013, 122: 198−209 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2013.05.040 [6] Sadahiro Y. Number of polygons generated by map overlay: the case of convex polygons. Transactions in Gis, 2001, 5(4): 345−353 doi: 10.1111/1467-9671.00087 [7] Chazelle B. An optimal convex hull algorithm in any fixed dimension. Discrete & Computational Geometry, 1993, 10(4): 377−409 [8] Yao A C. A lower bound to finding convex hulls. Journal of the ACM, 1981, 28(4): 780−787 doi: 10.1145/322276.322289 [9] Akl S G, Toussaint G T. A fast convex hull algorithm. Information Processing Letters, 1978, 7(5): 219−222 doi: 10.1016/0020-0190(78)90003-0 [10] Kim Y J, Lee J, Kim M S, Elber G. Efficient convex hull computation for planar freeform curves. Computers & Graphics, 2011, 35(3): 698−705 [11] Park M, Park C W, Park M, Lee C. Algorithm for detecting human faces based on convex-hull. Optics Express, 2002, 10(6): 274−279 doi: 10.1364/OE.10.000274 [12] Zhou X F, Jiang W H, Tian Y J, Shi Y. Kernel subclass convex hull sample selection method for SVM on face recognition. Neurocomputing, 2010, 73(10−12): 2234−2246 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2010.01.008 [13] Graham R L. An efficient algorith for determining the convex hull of a finite planar set. Information Processing Letters, 1972, 1(4): 132−133 doi: 10.1016/0020-0190(72)90045-2 [14] Jarvis R A. On the identification of the convex hull of a finite set of points in the plane. Information Processing Letters, 1973, 2(1): 18−21 doi: 10.1016/0020-0190(73)90020-3 [15] Andrew A M. Another efficient algorithm for convex hulls in two dimensions. Information Processing Letters, 1979, 9(5): 216−219 doi: 10.1016/0020-0190(79)90072-3 [16] Stein A, Geva E, El-Sana J. CudaHull: fast parallel 3D convex hull on the GPU. Computers & Graphics, 2012, 36(4): 265−271 [17] Tang M, Zhao J Y, Tong R F, Manocha D. GPU accelerated convex hull computation. Computers & Graphics, 2012, 36(5): 498−506 [18] Brönnimann H, Iacono J, Katajainen J, Morin P, Morrison J, Toussaint G. Space-efficient planar convex hull algorithms. Theoretical Computer Science, 2004, 321(1): 25−40 doi: 10.1016/j.tcs.2003.05.004 [19] 刘斌, 王涛. 一种高效的平面点集凸包递归算法. 自动化学报, 2012, 38(8): 1375−1379 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2012.01375Liu Bin, Wang Tao. An efficient convex hull algorithm for planar point set based on recursive method. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2012, 38(8): 1375−1379 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2012.01375 [20] Beltran A, Mendoza S. SymmetricHull: a convex hull algorithm based on 2D geometry and symmetry. IEEE Latin America Transactions, 2018, 16(8): 2289−2295 doi: 10.1109/TLA.2018.8528248 [21] 冯昌利, 张建勋, 梁睿, 代煜, 崔亮. 基于分形几何和最小凸包法的肺区域分割算法. 天津大学学报(自然科学与工程技术版), 2015, 48(10): 937−946Feng Chang-Li, Zhang Jian-Xun, Liang Rui, Dai Yu, Cui Liang. A lung region segmentation method based on the fractal theory and the minimal convex hull method. Journal of Tianjin University(Science and Technology), 2015, 48(10): 937−946 -




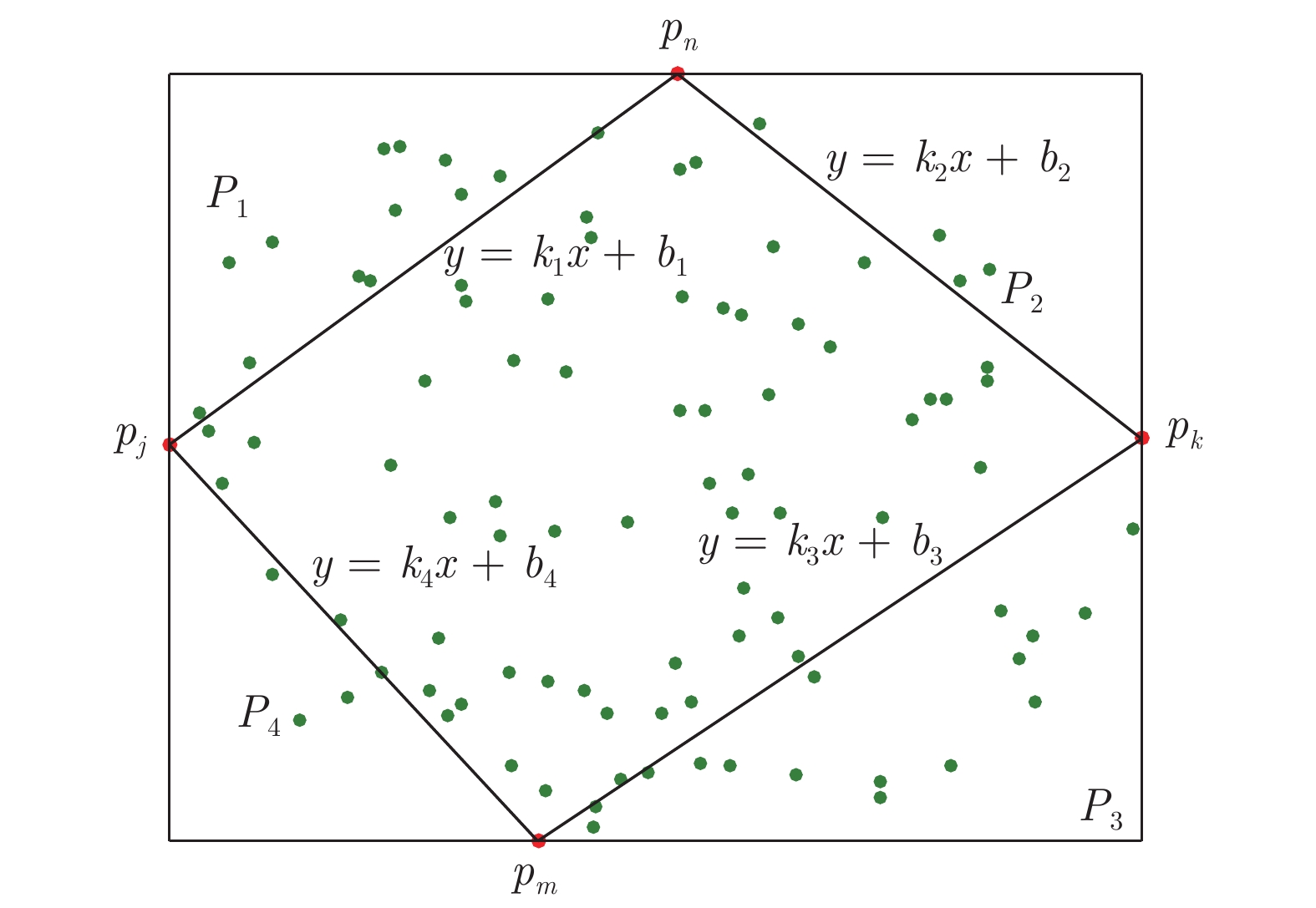
 下载:
下载: