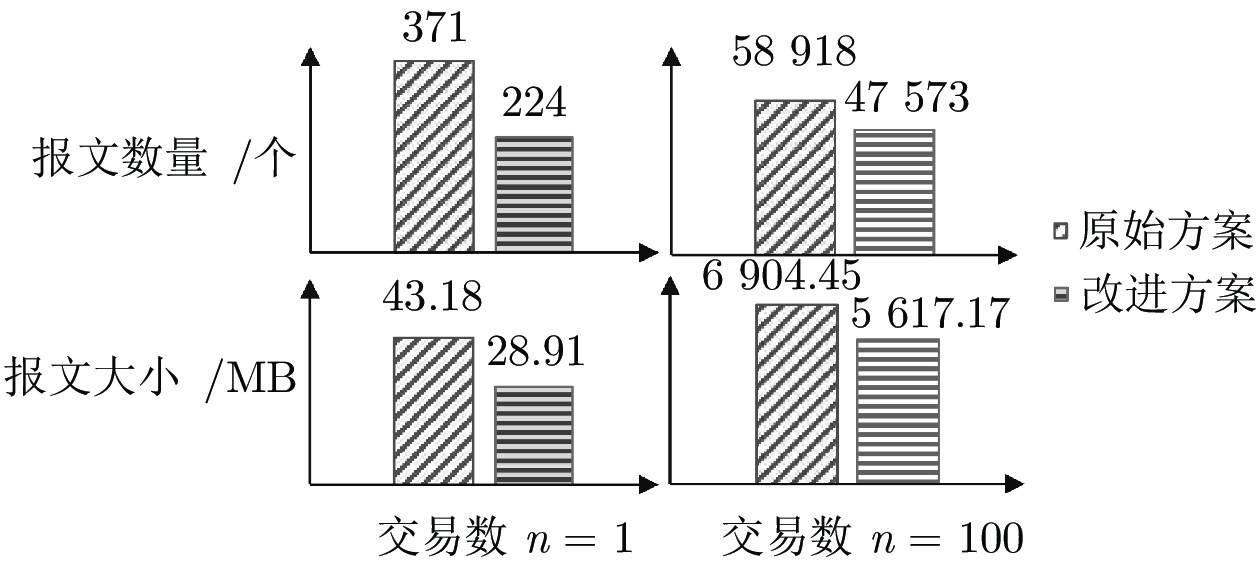
-
摘要:
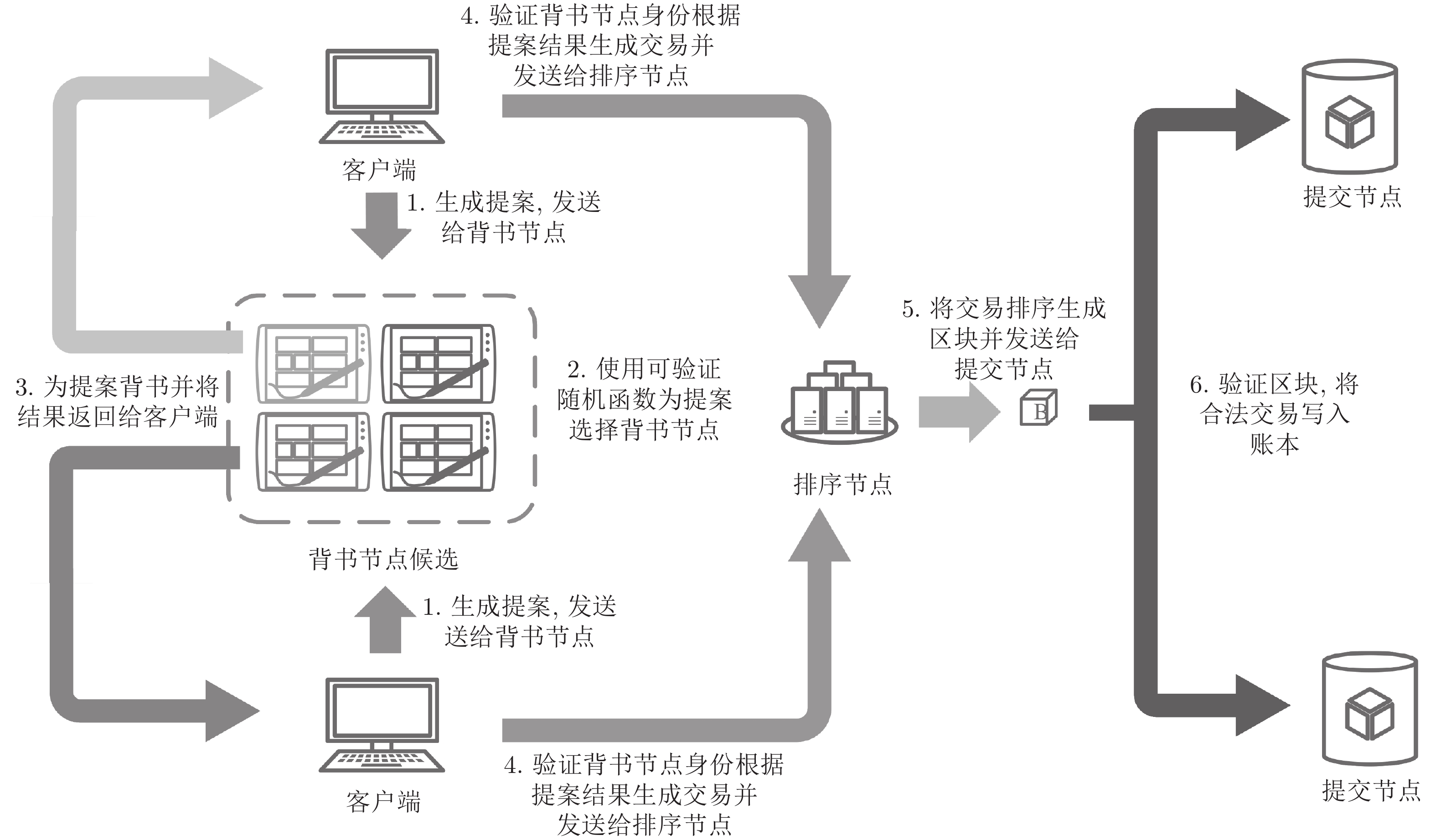
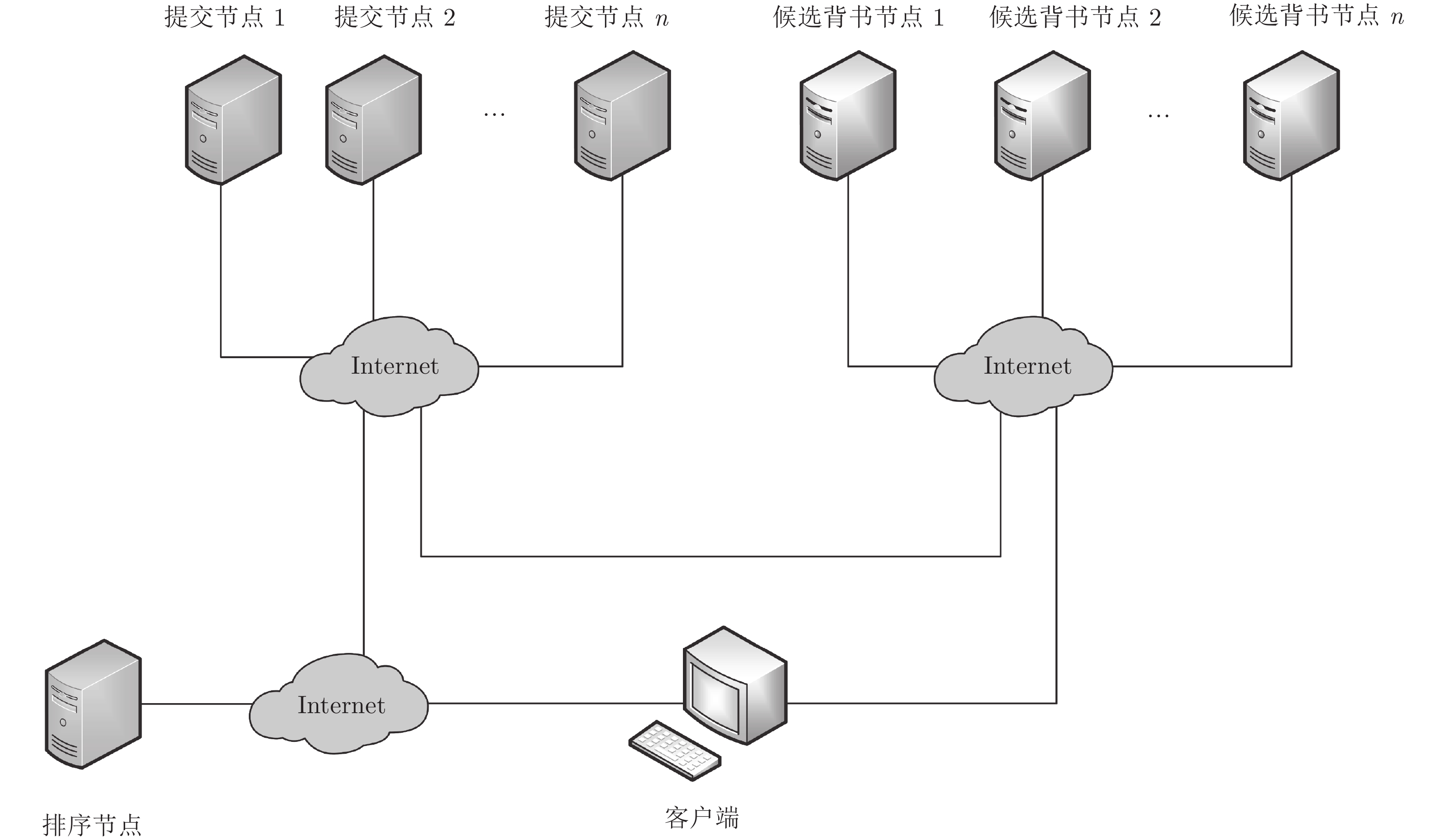
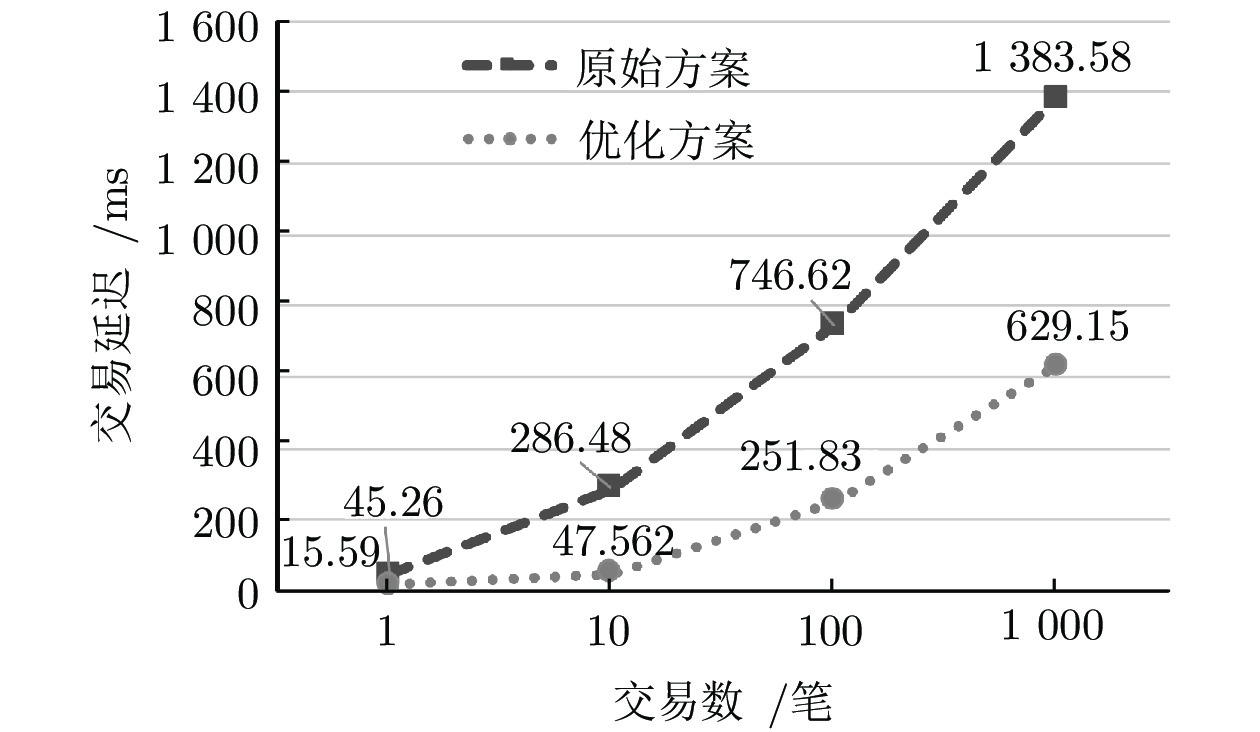
针对Hyperledger Fabric使用固定背书节点处理交易所带来的安全风险和性能瓶颈问题, 提出了一种非交互、可验证的随机化背书节点优化方案. 基于“背书−排序−验证”的Hyperledger fabric共识模型, 引入背书节点候选集, 使用可验证随机函数随机抽取背书节点进行交易背书, 实现了背书节点的非交互式可验证随机选取和背书过程的并行处理. 分析和实验表明, 优化后的共识机制具有更高的安全性和更快的交易处理速度.
-
关键词:
- 区块链 /
- 共识机制 /
- 可验证随机函数 /
- Hyperledger fabric
Abstract:To solve the problem of the security risk and processing bottleneck caused by handling all transactions with a fixed endorsement node in hyperledger fabric, a non-interactive and verifiable randomized endorsement scheme is proposed. On the basis of the “endorse-sort-verify” consensus mechanism, the non-interactive and verifiable random selection of the endorsement node and the parallel endorsement process are implemented by introducing the endorsement node candidate set and using the verifiable random function to randomly extract the endorsement node to endorse each transaction. Analysis and experiments show that the optimized consensus mechanism has higher security and faster transaction processing speed.
-
Key words:
- Blockchain /
- consensus mechanism /
- verifiable random function /
- hyperledger fabric
-
表 1 优化方案与其他共识机制的对比
Table 1 Comparison of optimization scheme with other consensus mechanisms
共识机制 VRF 的作用 共识原理 资源消耗 容错能力 Algorand 出块节点的选取 VRF + PBFT 低 $3f+1$ Definity 出块节点的选取 VRF + PoS 较高 $2f+1$ Ouroboros Praos 出块节点的选取 VRF + PoS 较高 $2f+1$ 优化方案 背书节点的选取 VRF + 背书 + 排序 + 验证 低 F($m,t$) 表 2 敌手攻击成功次数
Table 2 Number of successful attacks by adversary
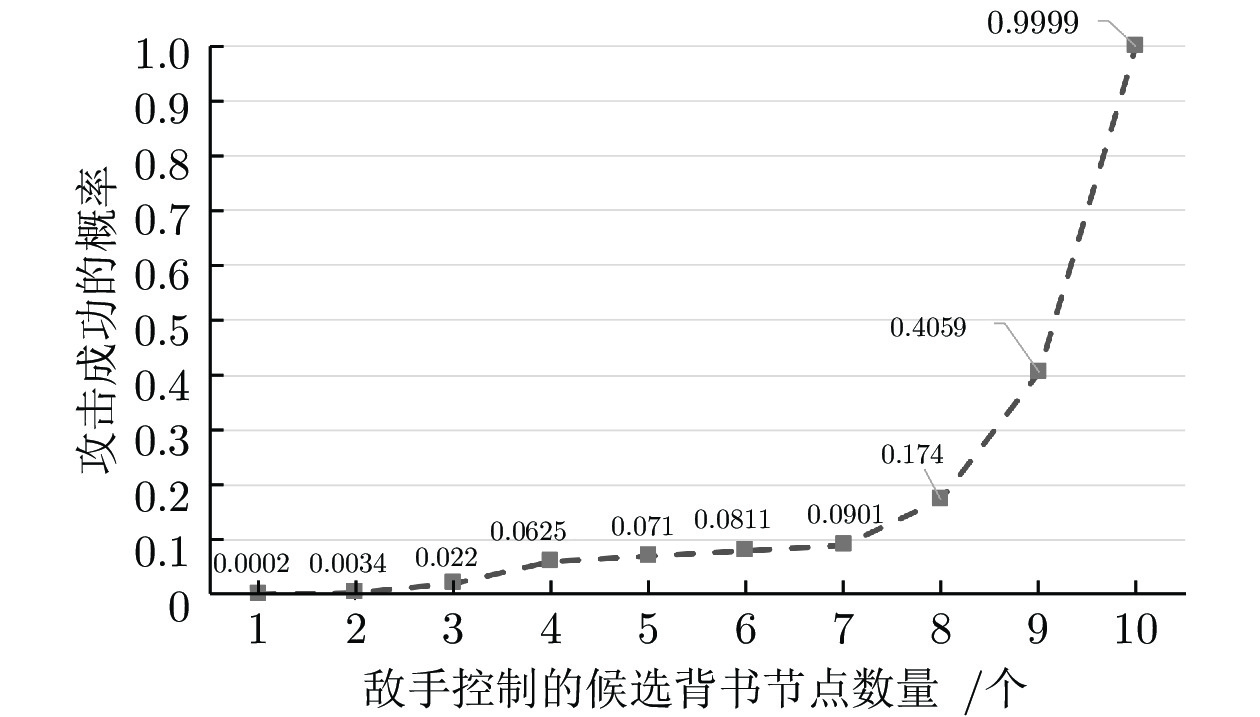
交易次数 敌手成功次数 攻击成功概率 原始方案 1 000 1 000 100 % 优化方案 100 000 686 6.86 % 表 3 无背书节点情况发生次数
Table 3 Frequency of nonoccurence of endorsing peer
交易次数 是否使用计时重传 无背书节点情况发生次数 1 000 否 2 100 000 否 17 1 000 是 0 100 000 是 0 表 4 可验证随机函数各部分算法运行时间
Table 4 Running time of each part of the VRF algorithm
算法 次数 总时间 (ms) 平均时间 (ms) 生成密钥 10000 2878.3546 0.2878 生成随机数和证明 10000 10395.3927 1.0395 验证随机数和证明 10000 12874.6190 1.2875 -
[1] Nakamoto S. Bitcoin: A peer-to-peer electronic cash system [Online], available: https://bitcoin.org/bitcoin.pdf, December 17, 2019 [2] 刘敖迪, 杜学绘, 王娜, 李少卓..区块链技术及其在信息安全领域的研究进展.软件学报, 2018, 29(7):2092-2115Liu Ao-Di, Du Xue-Hui, Wang Na, Li Shao-Zhuo. Research progress of blockchain technology and its application in information security. Journal of Software, 2018, 29(7):2092-2115 [3] 韩璇, 袁勇, 王飞跃. 区块链安全问题:研究现状与展望. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(1): 206-225Han Xuan, Yuan Yong, Wang Fei-Yue. Security problems on blockchain: the state of the art and future trends. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(1): 206-225. [4] Nguyen G T, Kim K. A survey about consensus algorithms used in blockchain. Journal of Information Processing Systems, 2018, 14(1). 101-128 [5] Elli A, Artem B, Vita B, Christian C, Konstantinos C, Angelo D. Hyperledger fabric: A distributed operating system for permissioned blockchains. In: Proceedings of the Thirteenth EuroSys Conference. Porto, Portugal: ACM, 2018. 1−15 [6] Vukolić M. Rethinking permissioned blockchains. In: Proceedings of the ACM Workshop on Blockchain, Cryptocurrencies and Contracts. Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates: ACM, 2017. 3−7 [7] Bessani A, Sousa J, Vukolić M. A byzantine fault-tolerant ordering service for the Hyperledger Fabric blockchain platform. In: Proceedings of the Workshop on Scalable & Resilient Infrastructures for Distributed Ledgers. Luxembourg City, Luxembourg: IEEE, 2018. 51−58 [8] 袁勇, 王飞跃. 区块链技术发展现状与展望. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(4): 481-494Yuan Yong, Wang Fei-Yue. Blockchain: The state of the art and future trends.Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(4):481-494 [9] Bach L M, Mihaljevic B, Zagar M. Comparative analysis of blockchain consensus algorithms. In: Proceedings of the 41st International Convention on Information and Communication Technology, Electronics and Microelectronics (MIPRO). Opatija, Croatia: IEEE, 2018. 1545−1550 [10] Lamport L, Shostak R, Pease M. The byzantine generals problem. Acm Transactions on Programming Languages & Systems, 1982, 4(3):382-401. [11] Lamport L. Paxos made simple. ACM Sigact News, 2001, 32(4): 18-25. [12] Ongaro D, Ousterhout J. In search of an understandable consensus algorithm. In: Proceedings of Usenix Conference on Usenix Technical Conference. Philadelphia, PA, USA: ACM, 2014. 305−319 [13] 范捷, 易乐天, 舒继武. 拜占庭系统技术研究综述[J]. 软件学报, 2013, 24(6):1346-1360Fan Jie, Yi Le-Tian, Shu Ji-Wu. Research on the technologies of byzantine system. Journal of Software. 2013, 24(6):1346-1360 [14] Castro M, Liskov B. Practical byzantine fault tolerance. In: Proceedings of the Third Symposium on Operating Systems Design and Implementation. New Orleans, Louisiana, USA: OSDI, 1999. 173−186 [15] 袁勇, 倪晓春, 曾帅, 王飞跃. 区块链共识算法的发展现状与展望. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(11), 2011-2022Yuan Yong, Ni Xiao-Chun, Zeng Shuai, Wang Fei-Yue. Blockchain consensus algorithms: the state of the art and future trends. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(11), 2011-2022 [16] Bentov I, Lee C, Mizrahi A, Rosenfeld M. Proof of activity: Extending bitcoin' s proof of work via proof of stake [Online], available: http://eprint.iacr.org/2014/452, December 16, 2019 [17] S King, S Nadal. PPCoin: Peer-to-peer crypto-currency with proofof-stake (whitepaper) [Online], available: https://bitcoin.peryaudo.org/vendor/peercoin-paper.pdf, December 17, 2019 [18] Li W, Andreina S, Bohli J M, Karame G. Securing proof-of-stake blockchain protocols. In: Proceedings of Cryptocurrencies and Blockchain Technology. Barcelona, Spain: Springer, 2017. 297−315 [19] Bitshares. Delegated proof of stake [Online], available: https://docs.bitshares.org/en/master/technology/dpos.html, December 17, 2019 [20] Silvio M, Salil V, Michael R. Verifiable random functions. In: Proceedings of the 40th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science. New York, USA : IEEE, 1999. 120−130 [21] Abdalla M, Catalano D, Fiore D. Verifiable random functions from identity-based key encapsulation. In: Proceedings of Annual International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques. Cologne, Germany: Springer, 2009. 554−571 [22] Gilad Y, Hemo R, Micali S, Vlachos G, Zeldovich K. Algorand: Scaling byzantine agreements for cryptocurrencies. In: Proceedings of the 26th Symposium on Operating Systems Principles. Shanghai, China: ACM, 2017. 51−68 [23] Hanke T, Movahedi M, Williams D. Dfinity technology overview series, consensus system. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2018, 1805. 04548 [24] Boneh D, Boyen X. Short signatures without random oracles. In: Proceedings of International conference on the theory and applications of cryptographic techniques. Interlaken, Switzerland: Springer, 2004. 56−73 [25] Kiayias A, Russell A, David B, Oliynykov R. Ouroboros: A provably secure proof-of-stake blockchain protocol. In: Proceedings of Annual International Cryptology Conference. Paris, France: Springer, 2017. 357−388 [26] David B, Gaži P, Kiayias A, Russell A. Ouroboros Praos: An adaptively-secure, semi-synchronous proof-of-stake blockchain. In: Proceedings of Annual International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques. Tel Aviv, Israel: Springer, 2018. 66−98 [27] Hearn M. Corda: A distributed ledger [Online], available: https://www.corda.net/content/corda-technical-whitepaper.pdf, December 17, 2019 [28] Yamashita K, Nomura Y, Zhou E, Pi B, Jun S. Potential risks of Hyperledger Fabric smart contracts. In: Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Workshop on Blockchain Oriented Software Engineering (IWBOSE). Hangzhou, China: IEEE, 2019. 1−10 [29] Manevich Y, Barger A, Tock Y. Endorsement in Hyperledger Fabric via service discovery. IBM Journal of Research and Development, 2019, 63(2):1-9 [30] Brandenburger M, Cachin C, Kapitza R, Sorniotti A. blockchain and trusted computing: Problems, pitfalls, and a solution for Hyperledger Fabric. arXiv preprint arXiv, 2018, 1805. 08541 [31] Sukhwani H, Wang N, Trivedi K S, Rindos A. Performance modeling of Hyperledger Fabric (permissioned blockchain network). In: Proceedings of the IEEE 17th International Symposium on Network Computing and Applications (NCA). Cambridge, MA, USA: IEEE, 2018. 1−8 [32] Sukhwani H, Martínez J M, Chang X, Trivedi K, Rindos A. Performance modeling of pbft consensus process for permissioned blockchain network (hyperledger fabric). In: Proceedings of the IEEE 36th Symposium on Reliable Distributed Systems (SRDS). Hong Kong, China: IEEE, 2017. 253−255 [33] Baliga A, Solanki N, Verekar S, Pednekar A, Kamat P, Chatterjee S. Performance characterization of Hyperledger Fabric. In: Proceedings of the 2018 Crypto Valley Conference on Blockchain Technology (CVCBT). Zug, Switzerland: IEEE, 2018. 65−74 [34] Goldberg S, Reyzin L, Papadopoulos D, Vcelak J. Verifiable random functions (VRFs) [Online], available: https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/draft-irtf-cfrg-vrf/, February 8, 2019 [35] Boneh D, Lynn B, Shacham H. Short signatures from the Weil pairing. In: Proceedings of International Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptology and Information Security. Gold Coast, Australia: Springer, 2001. 514−532 [36] Carter J L, Wegman M N. Universal classes of hash functions. Journal of computer and system sciences, 1979, 18(2): 143-154 doi: 10.1016/0022-0000(79)90044-8 [37] Nguyen T S L, Jourjon G, Potop-Butucaru M, Thai K L. Impact of network delays on Hyperledger Fabric. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2019. 1903. 08856 -




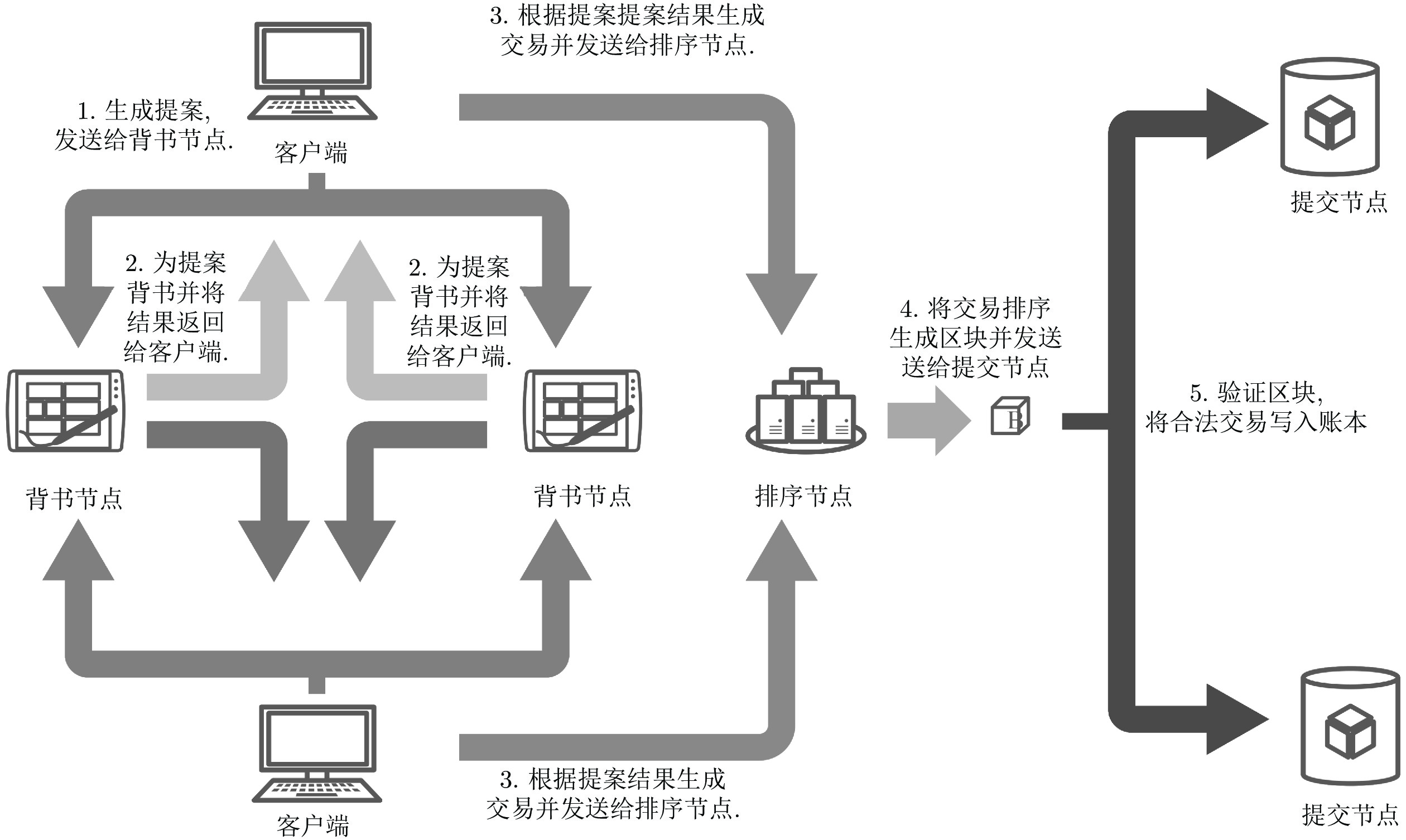
 下载:
下载: