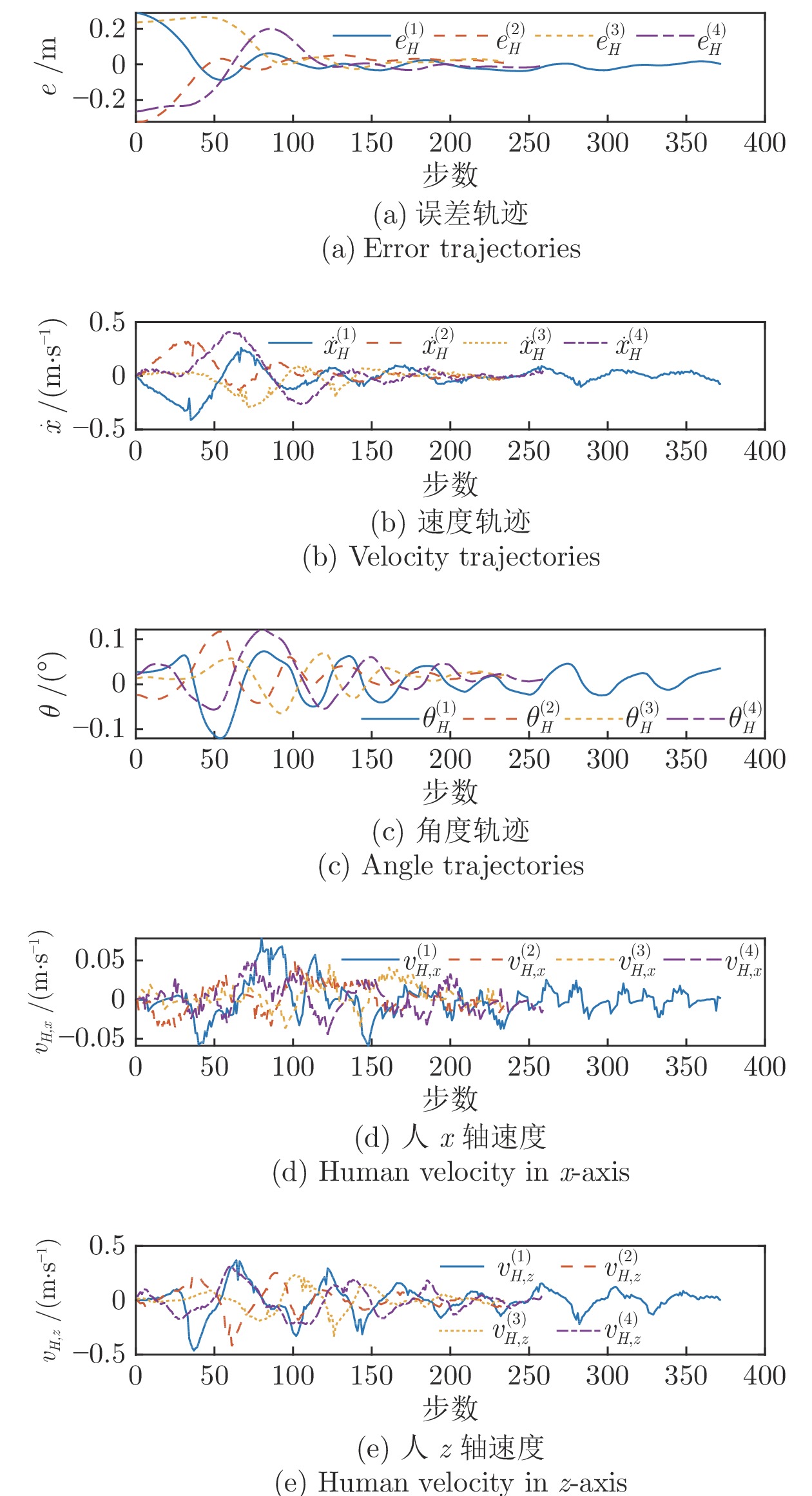
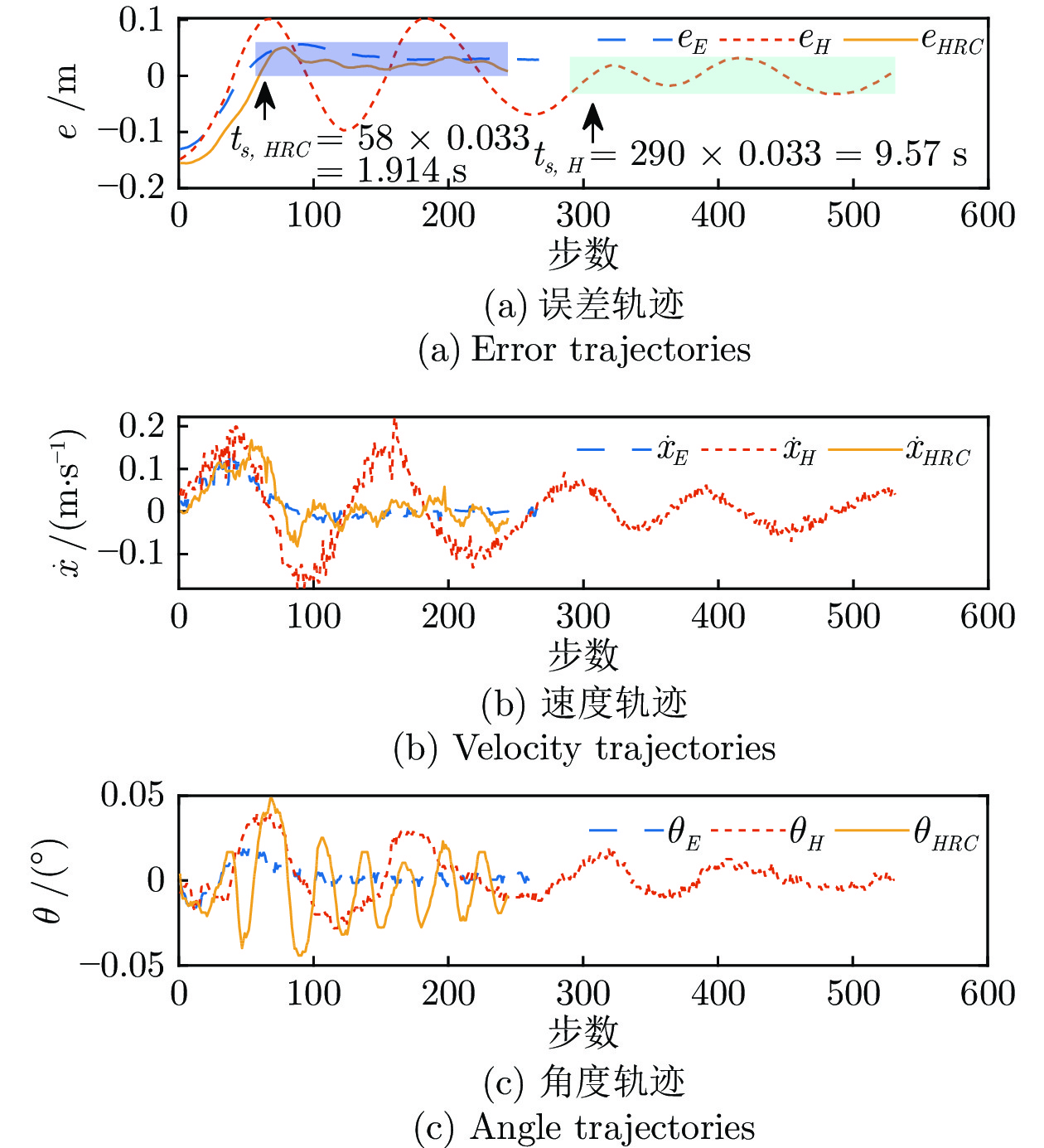
|
[1]
|
Amirshirzad N, Kumru A, Oztop E. Human adaptation to human–robot shared control. IEEE Transactions on Human-Machine Systems, 2019, 49(2): 126-136 doi: 10.1109/THMS.2018.2884719
|
|
[2]
|
Wojtara Y, Murayama H, Howard M, Shimoda S, Sakai S, Fujimoto H, et al. Human-robot collaboration in precise positioning of a three-dimensional object. Automatica, 2009, 45(2): 333-342 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2008.08.021
|
|
[3]
|
Dumora J, Geffard F, Bidard C, Brouillet T, Fraisse P. Experimental study on haptic communication of a human in a shared human-robot collaborative task. In: Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE/ RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Vilamoura, Portugal: IEEE, 2012. 5137−5144
|
|
[4]
|
Karayiannidis Y, Smith C, Kragic D. Mapping human intentions to robot motions via physical interaction through a jointly-held object. In: Proceedings of the 23rd IEEE International Symposium on Robot and Human Interactive Communication. Edinburgh, UK: IEEE, 2014. 391−397
|
|
[5]
|
Karayiannidis Y, Smith C, Vina F E, Kragic D. Online kinematics estimation for active human-robot manipulation of jointly held objects. In: Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Tokyo, Japan: IEEE, 2013. 4872−4878
|
|
[6]
|
Burdet E, Milner T E. Quantization of human motions and learning of accurate movements. Biological cybernetics, 1998, 78(4): 307-318 doi: 10.1007/s004220050435
|
|
[7]
|
Maeda Y, Hara T, Arai T. Human-robot cooperative manipulation with motion estimation. In: Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Maui, USA: IEEE, 2001. 2240−2245
|
|
[8]
|
Corteville B, Aertbelien E, Bruyninckx H, Schutter J D, Brussel H V. Human-inspired robot assistant for fast point-to-point movements. In: Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Roma, Italy: IEEE, 2007. 3639−3644
|
|
[9]
|
Miossec S, Kheddar A. Human motion in cooperative tasks: Moving object case study. In: Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics. Bangkok, Thailand: IEEE, 2009. 1509−1514
|
|
[10]
|
Sheng W H, Thobbi A, Gu Y. An integrated framework for human–robot collaborative manipulation. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2015, 45(10): 2030-2041 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2014.2363664
|
|
[11]
|
Thobbi A, Gu Y, Sheng W H. Using human motion estimation for human-robot cooperative manipulation. In: Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. San Francisco, USA: IEEE, 2011. 2873−2878
|
|
[12]
|
Deng Z, Mi J P, Han D, Huang R, Xiong X F, Zhang J W. Hierarchical robot learning for physical collaboration between humans and robots. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics. Macau, China: IEEE, 2017. 750−755
|
|
[13]
|
Agravante D J, Cherubini A, Bussy A, Kheddar A. Humanhumanoid joint haptic table carrying task with height stabilization using vision. In: Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Tokyo, Japan: IEEE, 2013. 4609−4614
|
|
[14]
|
Agravante D J, Cherubini A, Bussy A, Gergondet P, Kheddar A. Collaborative human-humanoid carrying using vision and haptic sensing. In: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Hong Kong, China: IEEE, 2014. 607−612
|
|
[15]
|
Mainprice J, Berenson D. Human-robot collaborative manipulation planning using early prediction of human motion. In: Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Tokyo, Japan: IEEE, 2013. 299−306
|
|
[16]
|
Maria K, Muhammad A H, Danijela R D, Axel G. Robot learning of industrial assembly task via human demonstrations. Autonomous Robots, 2019, 43(1): 239-257 doi: 10.1007/s10514-018-9725-6
|
|
[17]
|
Ghadirzadeh A, Butepage J, Maki A, Kragic D, Bjorkman M. A sensorimotor reinforcement learning framework for physical human-robot interaction. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Daejeon, South Korea: IEEE, 2016. 2682−2688
|
|
[18]
|
Wang P, Liu H Y, Wang L H, Gao R X. Deep learning-based human motion recognition for predictive context-aware human-robot collaboration. CIRP Annals - Manufacturing Technology, 2018, 67(1): 17-20 doi: 10.1016/j.cirp.2018.04.066
|
|
[19]
|
Wang Z, Peer A, Buss M. An HMM approach to realistic haptic human-robot interaction. In: Proceedings of the World Haptics 3rd Joint EuroHaptics Conference and Symposium on Haptic Interfaces for Virtual Environment and Teleoperator Systems. Teleoperator System. Salt Lake City, USA: 2016. 374−379
|
|
[20]
|
Mainprice J, Berenson D. Learning human-robot collaboration with POMDP. In: Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems. Gyeongju, South Korea: IEEE, 2013. 1238−1243
|
|
[21]
|
Hawkins K P, Vo N, Bansal S, Bobick A F. Probabilistic human action prediction and wait-sensitive planning for responsive human-robot collaboration. In: Proceedings of the 2013 13th IEEE-RAS International Conference on Humanoid Robots. Atlanta, USA: 2013. 499−506
|
|
[22]
|
Lillicrap T P, Hunt J J, Pritzel A, Heess N, Erez T, Silver D, et al. Continuous control with deep reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Learning Representations. San Juan, Puerto Rico: IEEE, 2016. 1−14
|
|
[23]
|
Mnih V, Kavukcuoglu K, Silver D, Rusu A A, Veness J, Bellemare M G, et al. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning. Nature, 2015, 518(7540): 529-533 doi: 10.1038/nature14236
|
|
[24]
|
Hado V H, Guez A, Silver D. Deep reinforcement learning with double Q-learning. In: Proceedings of the 2016 AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Arizona, USA: 2016. 2094−2100
|
|
[25]
|
Silver D, Lever G, Hess N, Degris T, Wierstra D, Riedmiller M. Deterministic policy gradient algorithms. In: Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Machine Learning. Beijing, China: 2014. 605−619
|
|
[26]
|
Espersson M. Vision Algorithms for Ball on Beam and Plate[Master thesis], Lund University, Sweden, 2010
|




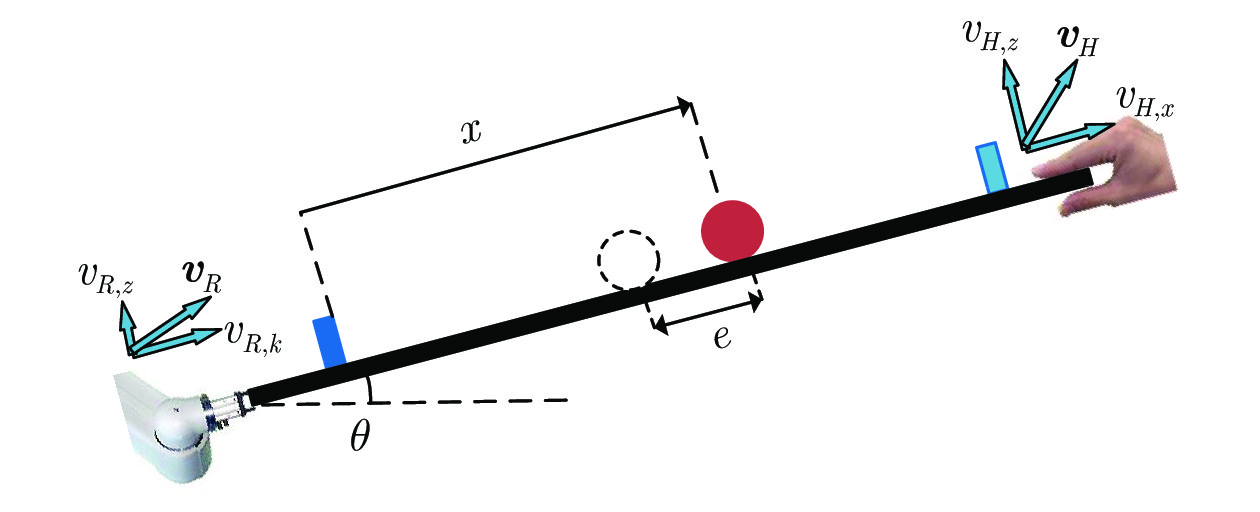
 下载:
下载: