Fuzzy Threshold Optical Remote Sensing Image Segmentation With Variable Class Number Based on Local Spatial Information
-
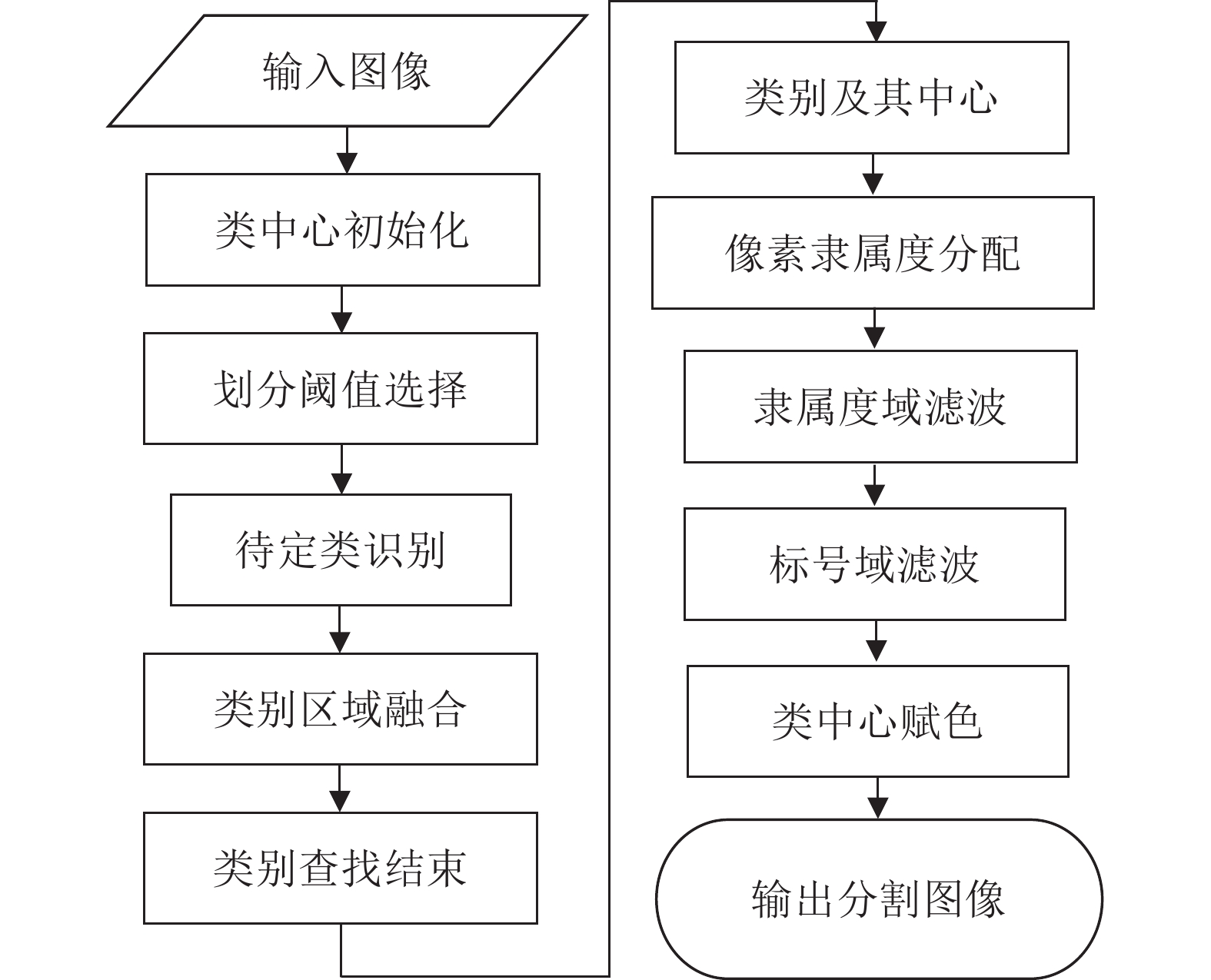
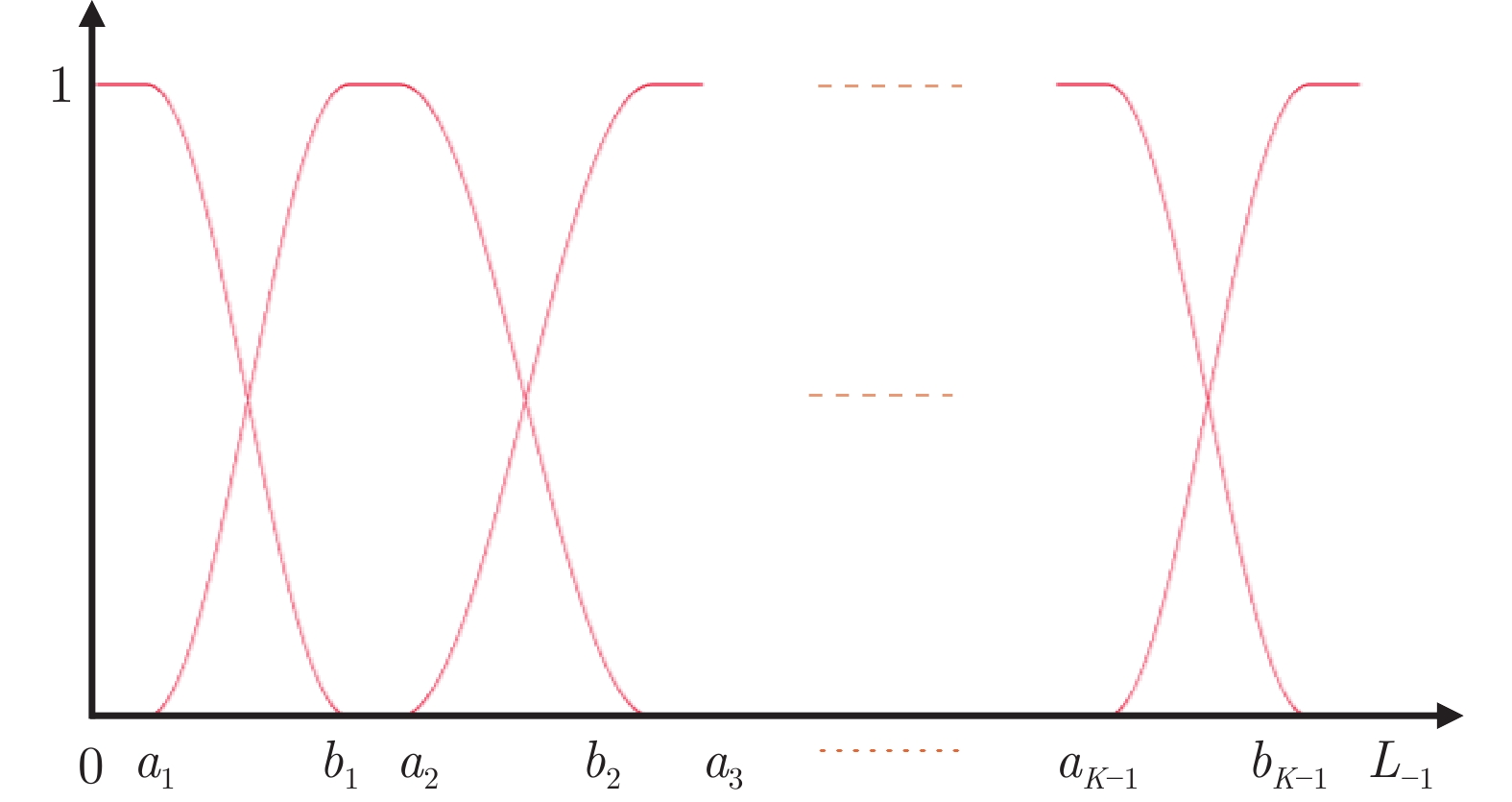
摘要: 阈值法分割在光学遥感图像分析中被得到广泛的应用, 然而传统阈值法也存在诸多局限性, 如对噪声敏感, 需人为设定类别数, 计算复杂度高等. 针对传统阈值法的局限性, 提出一种基于局部空间信息的可变类模糊阈值光学遥感图像分割方法. 首先, 以图像光谱的一阶矩为初始类中心, 利用二分法原理和区域间最大相似度准则来快速确定类别数及其中心. 然后, 通过岭形模糊隶属函数计算各像素点对不同类的隶属程度, 同时考虑到像素点的隶属度局部空间信息, 在隶属度域中定义一个模糊加权滤波器对各类的隶属度矩阵进行滤波, 以滤波后的隶属度集合为依据, 按照最大隶属原则确定图像的标号场. 最后, 对标号场中的局部异常标号进行替换, 将修正后的标号场由对应的类中心赋色得到分割图像. 视觉和统计分析评价结果表明, 与传统阈值法相比, 该方法能在减少计算时间的同时获得更好的分割结果, 可适用于光学遥感图像的多阈值分割.Abstract: Threshold segmentation has been widely used in optical remote sensing image analysis. However, traditional threshold methods also have many limitations, such as sensitivity to noise, artificially setting the number of classes, high computational complexity and so on. Aiming at the limitation of traditional threshold methods, a fuzzy threshold optical remote sensing image segmentation method with variable class numbers based on local spatial information is proposed. Firstly, taking the one-order moment of the image spectrum as the initial class center, the dichotomy principle and the maximum similarity criterion between regions are used to quickly determine the number of classes and their centers. Then, through the ridge-shaped fuzzy membership function, the degree of membership of each pixel to different classes is calculated. Meanwhile, considering the local spatial information of the membership of each pixel, a fuzzy weighted filter is defined in the membership domain to filter the membership matrix of each class. Based on the filtered membership set, the label field of the image is determined according to the maximum membership principle. Finally, the local abnormal labels in the label field are replaced, and the corrected label field is colored by the corresponding class center to obtain the segmented image. The results of visual and statistical analysis show that compared with the traditional threshold method, the proposed method can obtain better segmentation results while reducing the computation time. It can be applied to multi-threshold segmentation of optical remote sensing images.
-
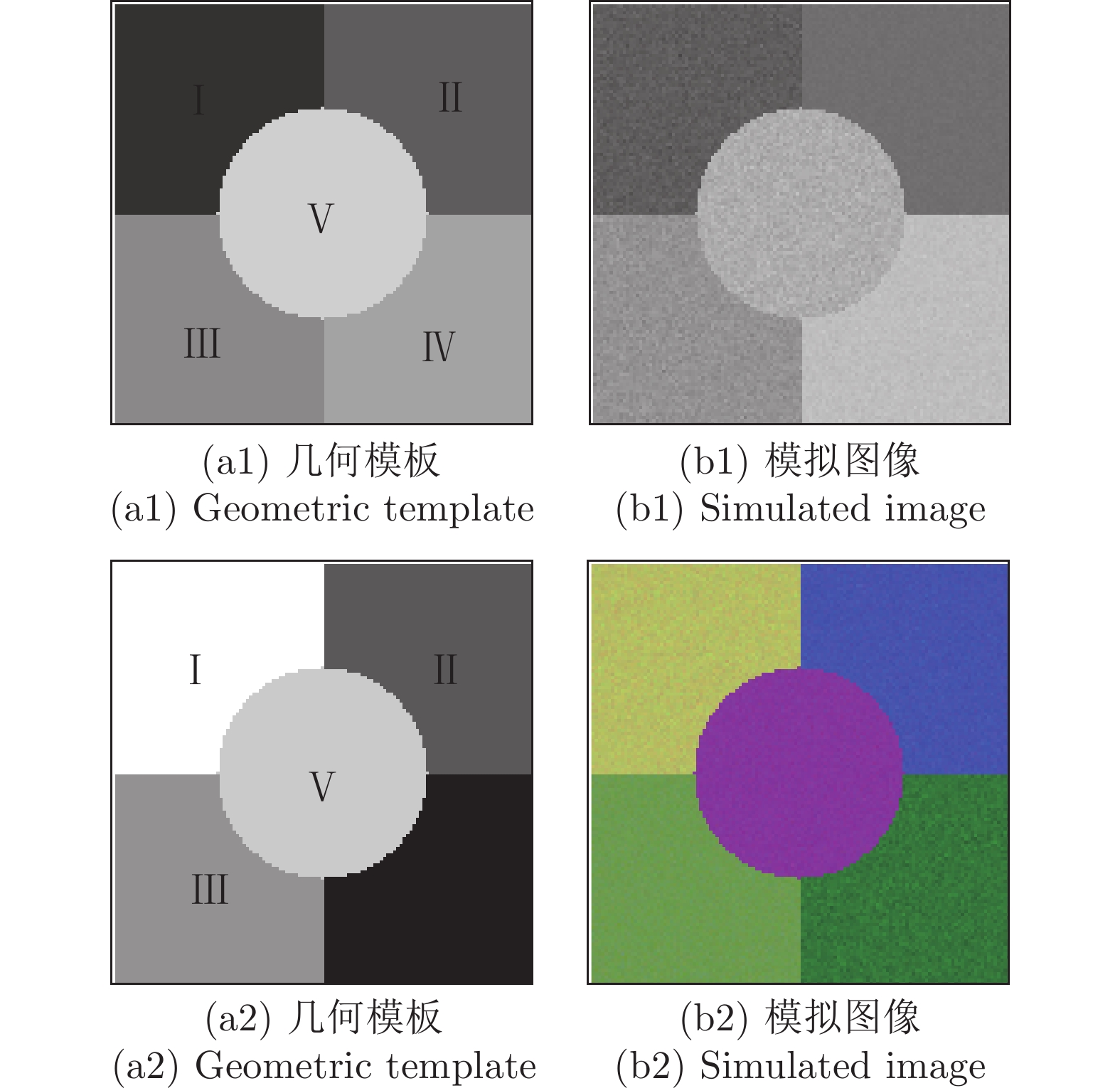
表 1 各同质区域的高斯分布参数
Table 1 Gaussian distribution parameters of homogeneous regions
表 2 模拟图像分割的定量评价结果
Table 2 Quantitative evaluation results of simulated image segmentation
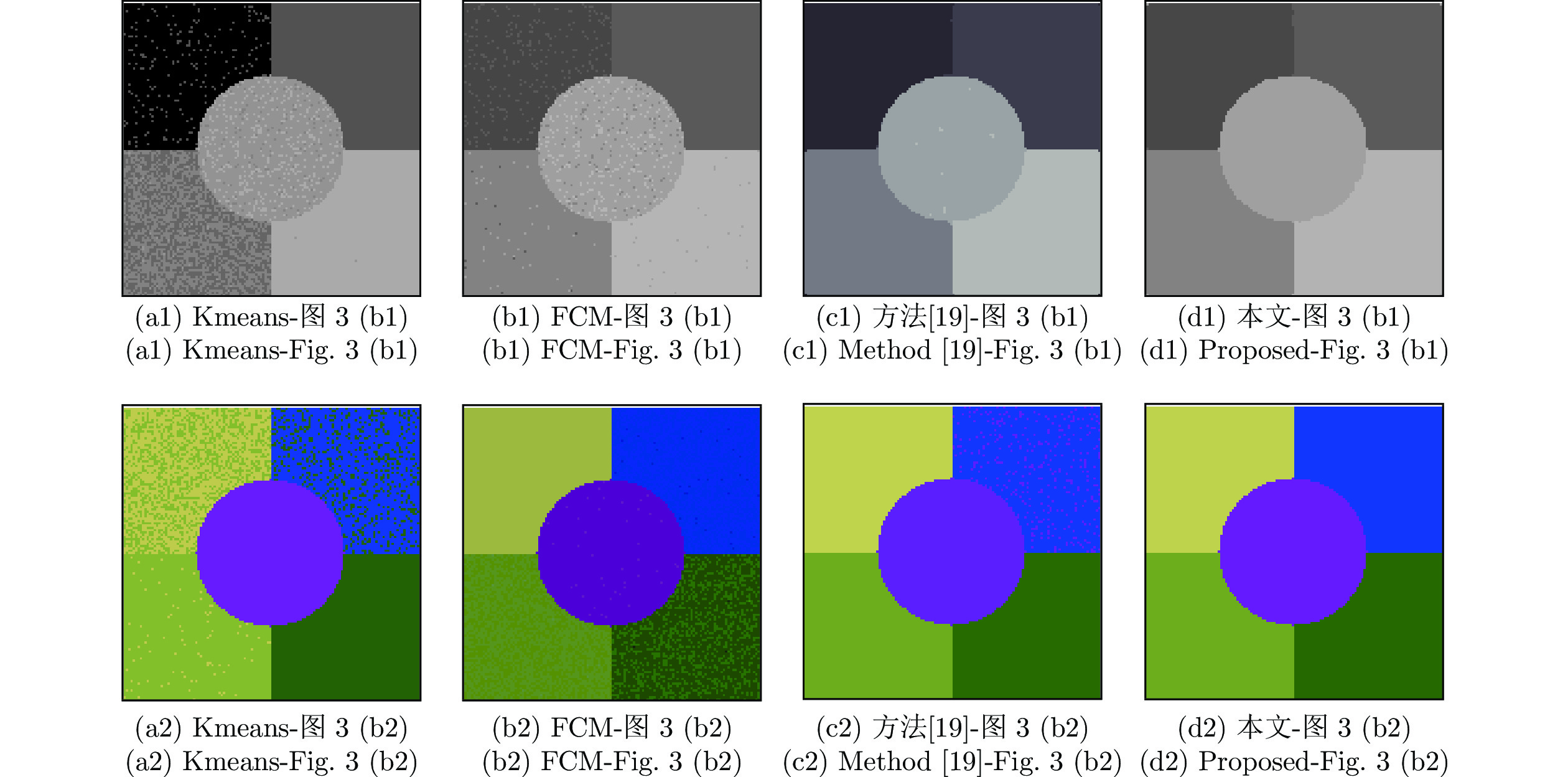
图像 指标 区域 Kmeans FCM 文献 [19] 本文方法 图 3 (b1) 用户精度 (%) Ⅰ 69.8 72.1 96.9 99.9 Ⅱ 92.2 90.1 98.6 99.9 Ⅲ 44.7 81.7 98.1 99.9 Ⅳ 90.4 80.4 97.0 99.8 Ⅴ 58.8 69.7 94.5 99.3 产品精度 (%) Ⅰ 56.3 66.5 99.6 99.7 Ⅱ 88.5 86.1 78.3 100 Ⅲ 33.9 75.6 98.5 99.5 Ⅳ 86.5 86.5 97.1 100 Ⅴ 63.3 71.7 90.4 99.6 总精度 (%) 55.4 75.2 88.6 99.4 Kappa 系数 (%) 53.9 74.6 85.3 99.7 图 3 (b2) 用户精度 (%) Ⅰ 42.4 96.5 97.5 99.5 Ⅱ 38.9 84.5 70.6 96.0 Ⅲ 63.2 96.1 96.6 99.5 Ⅳ 85.6 59.6 95.9 99.0 Ⅴ 88.4 86.7 88.3 97.2 产品精度 (%) Ⅰ 55.3 69.7 90.4 98.7 Ⅱ 55.3 90.5 76.8 99.9 Ⅲ 48.7 81.7 88.4 93.7 Ⅳ 78.3 71.4 69.5 98.5 Ⅴ 90.1 73.8 90.3 99.2 总精度 (%) 53.2 81.2 89.7 98.3 Kappa 系数 (%) 48.9 80.0 88.1 98.6 表 3 全色遥感图像分割质量评价指标
Table 3 Quality evaluation of panchromatic remote sensing image segmentation
表 4 计算复杂度对比
Table 4 Computational complexity comparison
方法 计算复杂度 Kmeans ${\rm{O }}((K+M \times N / K) \times t)$ FCM ${\rm{O }} ((M \times N \times K \times t)$ 文献 [19] ${\rm{O } }((1+M \times N) \times K \times t \times \omega^{2})$ 本文方法 ${\rm{O } }(M \times N \times K+2 \times M \times N \times \omega^{2})$ 表 5 全色图像分割时间对比(s)
Table 5 Panchromatic images segmentation time comparison (s)
表 6 多光谱遥感图像分割质量评价
Table 6 Quality evaluation of multispectral remote sensing image segmentation
指标 方法 图 6 (a1) 图 6 (b1) 图 6 (c1) 图 6 (d1) MV Kmeans 1.971 1.613 2.316 2.146 FCM 1.813 1.404 1.833 1.799 文献 [19] 1.570 1.071 1.279 1.344 本文方法 1.376 0.796 0.941 1.001 JM Kmeans 0.832 0.797 0.774 0.808 FCM 0.748 0.624 0.647 0.734 文献 [19] 0.662 0.588 0.541 0.631 本文方法 0.575 0.534 0.532 0.565 E Kmeans 0.671 0.572 0.607 0.632 FCM 0.524 0.466 0.573 0.597 文献 [19] 0.456 0.403 0.434 0.463 本文方法 0.347 0.332 0.293 0.306 -
[1] Min Wang, Jiru Huang, Dongping Ming. Region-line association constraints for high-resolution image segmentation. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations & Remote Sensing, 2016, 10(2): 1-10 [2] Andrés Troya-Galvis, Gancarski P, Berti-Equille L. Remote sensing image analysis by aggregation of segmentation-classification collaborative agents. Pattern Recognition, 2018, 73: 259-274 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2017.08.030 [3] 李修霞, 荆林海, 李慧, 唐韵玮, 戈文艳. 参考1维光谱差异的区域生长种子点选取方法. 中国图象图形学报, 2016, 21(9): 1256-1264 doi: 10.11834/jig.20160915Li Xiu-Xia, Jing Lin-Hai, Li Hui, Tang Yun-Wei, Ge Wen-Yan. Seed extraction method for seeded region growing based on one-dimensional spectral differences. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2016, 21(9): 1256-1264 doi: 10.11834/jig.20160915 [4] 游江, 唐力伟, 邓士杰, 苏续军. 完全基于边缘信息的目标靶快速分割算法. 激光与红外, 2017, 47(3): 372-378 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2017.03.023You Jiang, Tang Li-Wei, Deng Shi-Jie, Su Xue-jun. Fast target segmentation algorithm fully based on edge information. Laser & Infrared, 2017, 47(3): 372-378 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2017.03.023 [5] Funke J, Tschopp F D, Grisaitis W, Sheridan A, Singh C, Saalfeld Se. Large scale image segmentation with structured loss based deep learning for connectome reconstruction. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 2018, 41(7): 1669-1680 [6] 李擎, 唐欢, 迟健男, 邢永跃, 李华通. 基于改进最大类间方差法的手势分割方法研究. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(4): 528-537Li Qing, Tang Huan, Chi Jian-Nan, Xing Yong-Yue, Li Hua-Tong. Gesture segmentation with improved maximum between-cluster variance algorithm. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(4): 528-537 [7] Zeggada A, Melgani, Farid, Bazi, Yakoub. A deep learning approach to UAV image multilabeling. IEEE Geoscience & Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(5): 694-698 [8] 田娟秀, 刘国才, 谷珊珊, 鞠忠建, 刘劲光, 顾冬冬. 医学图像分析深度学习方法研究与挑战. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(3): 401-424Tian Juan-Xiu, Liu Guo-Cai, Gu Shan-Shan, Ju Zhong-Jian, Liu Jin-Guang, GU Dong-Dong. Deep learning in medical image analysis and its challenges. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(3): 401-424 [9] Fredo A R J, Abilash R S, Kumar C S. Segmentation and analysis of damages in composite images using multi-level threshold methods and geometrical features. Measurement, 2017, 100(100): 270-278 [10] Yamini B, Sabitha R. Image steganalysis: adaptive color image segmentation using Otsu’s method. Journal of Computational & Theoretical Nanoscience, 2017, 14(9): 4502-4507 [11] 黄扬, 郭立君, 张荣. 融合全局和局部相关熵的图像分割. 中国图象图形学报, 2018, 20(12): 1619-1628Huang Yang, Guo Li-Jun, Zhang Rong. Integration of global and local correntropy image segmentation algorithm. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2018, 20(12): 1619-1628 [12] Choy S K, Shu Y L, Yu K W, Lee W Y, Leung K T. Fuzzy model-based clustering and its application in image segmentation. Pattern Recognition, 2017, 100(68): 141-157 [13] Kurt B, Nabiyev V V, Turhan K. A novel automatic suspicious mass regions identification using Havrda & Charvat entropy and Otsu's N thresholding. Computer Methods & Programs in Biomedicine, 2014, 114(3): 349-360 [14] Mousavirad S J, Ebrahimpour-Komleh H. Multilevel image thresholding using entropy of histogram and recently developed population-based metaheuristic algorithms. Evolutionary Intelligence, 2017, 10(1): 45-75 [15] 产思贤, 周小龙, 张卓, 陈胜勇. 一种基于超像素的肿瘤自动攻击交互式分割算法. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(10): 1829-1840Chan Si-Xian, Zhou Xiao-Long, Zhang Zhuo, Chen Sheng-Yong. Interactive multi-label image segmentation with multi-layer tumors automata. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(10): 1829-1840 [16] 姜枫, 顾庆, 郝慧珍, 李娜, 郭延文, 陈道蓄. 基于内容的图像分割方法综述. 软件学报, 2017, 28(1): 160-183Jiang Feng, Gu Qing, Hao Hui-Zhen, Li Na, Guo Yan-Wen, Chen Dao-Xu. Survey on content-based image segmentation methods. Journal of Software, 2017, 28(1): 160-183 [17] 肖满生, 文志诚, 张居武, 汪新凡. 一种改进隶属度函数的FCM聚类算法. 控制与决策, 2015, 30(12): 2270-2274Xiao Man-Sheng, Wen Zhi-Cheng, Zhang Ju-Wu, Wan Xin-Fan. An FCM clustering algorithm with improved membership function. Control and Decision, 2015, 30(12): 2270-2274 [18] Meena Prakash R, Shantha S K R. Fuzzy C means integrated with spatial information and contrast enhancement for segmentation of MR brain images. International Journal of Imaging Systems & Technology, 2016, 26(2): 116-123 [19] 赵雪梅, 李玉, 赵泉华. 参数自适应的可变类FLICM灰度图像分割算法. 控制与决策, 2017, 32(2): 262-268Zhao Xue-Mei, Li Yu, Zhao Quan-Hua. Self-adaptive FLICM algorithm for gray image segmentation with unknown number of clusters. Control and Decision, 2017, 32(2): 262-268 [20] Ning J, Zhang L, Zhang D, Chengke W. Interactive image segmentation by maximal similarity based region merging. Pattern Recognition, 2010, 43(2): 445-456 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2009.03.004 [21] 杜茂康, 王忠思, 宋强. 基于Bhattacharyya系数的改进相似度度量方法. 重庆邮电大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 30(05): 115-120Du Mao-Kang, Wang Zhong-Si, Song Qiang. Research of improving similarity measure based on Bhattacharyya coefficient. Journal of Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 30(05): 115-120 [22] Choi S H, Jung H Y, Kim H. Ridge fuzzy regression model. International Journal of Fuzzy Systems, 2019, 21(7): 2077-2090 doi: 10.1007/s40815-019-00692-0 [23] Mansoori G, Zolghadri J, Katebi D. A weighting function for improving fuzzy classification systems performance. Fuzzy Sets & Systems, 2007, 158(5): 583-591 [24] Wang Y, Qi Q, Liu Y. Unsupervised segmentation evaluation using area-weighted variance and Jeffries-Matusita distance for remote sensing images. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(8): 1193-1217 doi: 10.3390/rs10081193 [25] Chen H C, Wang S J. Visible colour difference-based quantitative evaluation of colour segmentation. IEE Proceedings-Vision, Image and Signal Processing, 2006, 153(5): 598-609 doi: 10.1049/ip-vis:20045221 [26] 李玉, 徐艳, 赵雪梅, 赵泉华. 利用高斯混合模型的多光谱图像模糊聚类分割. 光学精密工程, 2017, 25(2): 509-518 doi: 10.3788/OPE.20172502.0509Li Yu, Xu Yan, Zhao Xue-Mei, Zhao Quan-Hua. Multispectral image segmentation by fuzzy clustering algorithm used Gaussian mixture model. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2017, 25(2): 509-518 doi: 10.3788/OPE.20172502.0509 [27] Yellamraju T, Boutin M. Clusterability and clustering of images and other “real” high-dimensional data. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(4): 1927-1938 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2789327 -




 下载:
下载: