Blackbody Temperature Control Based on Adaptive Double Output Function of PID Self-tuning
-
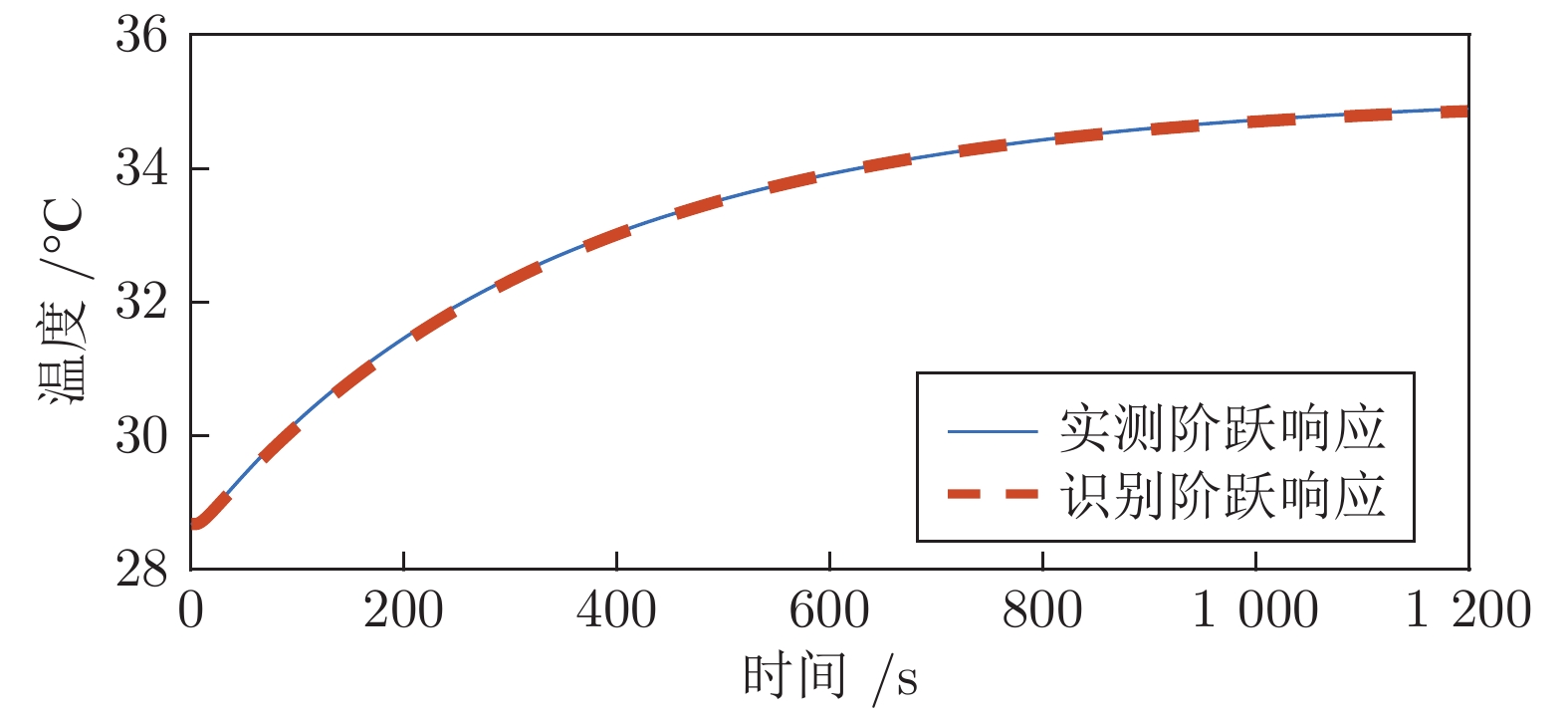
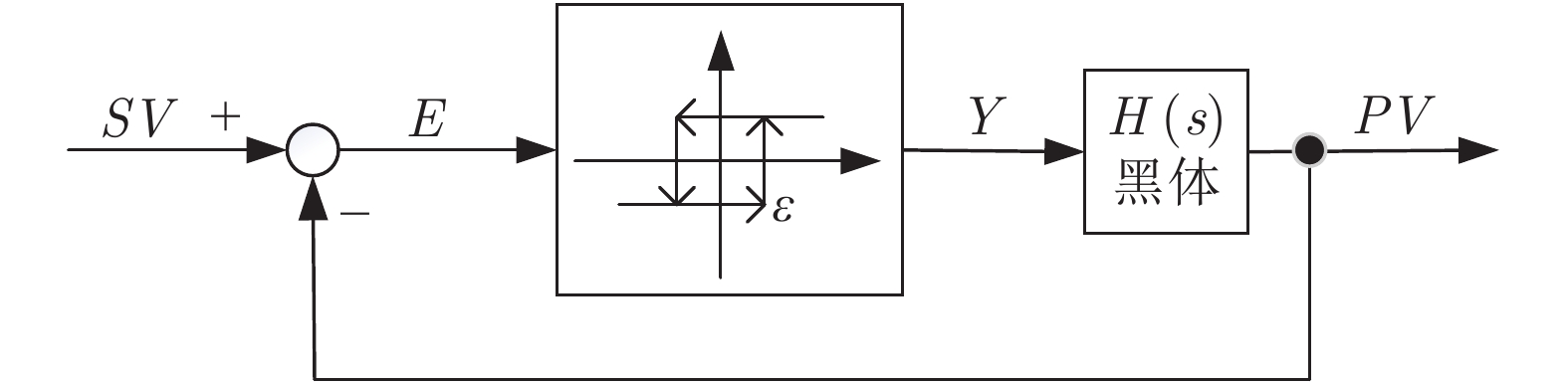
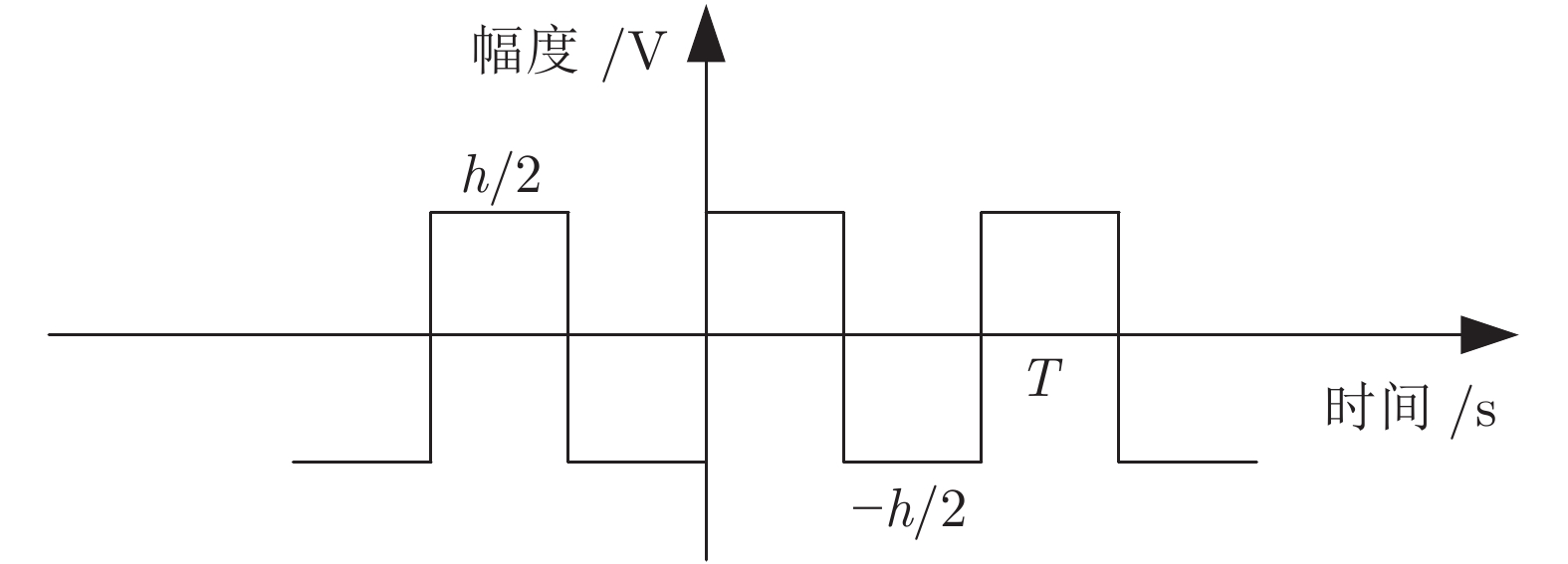
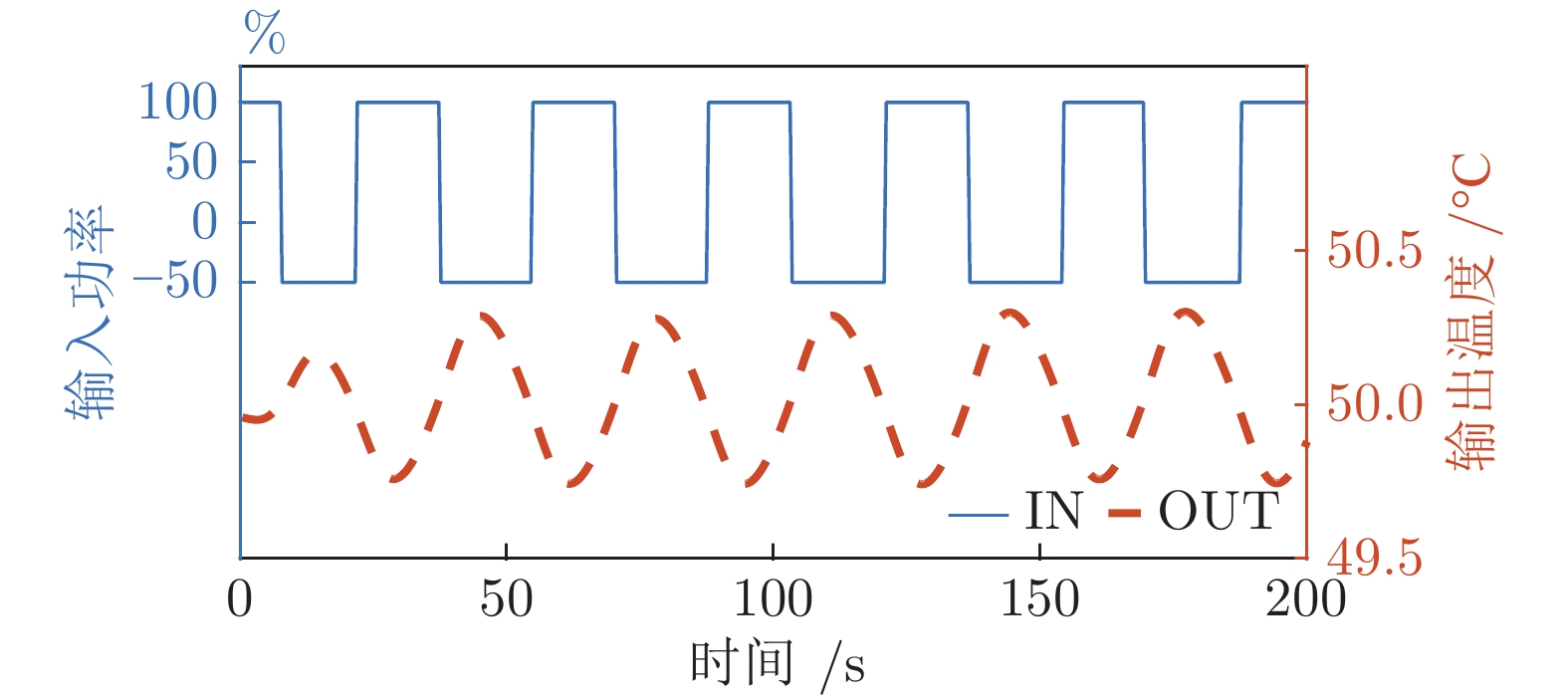
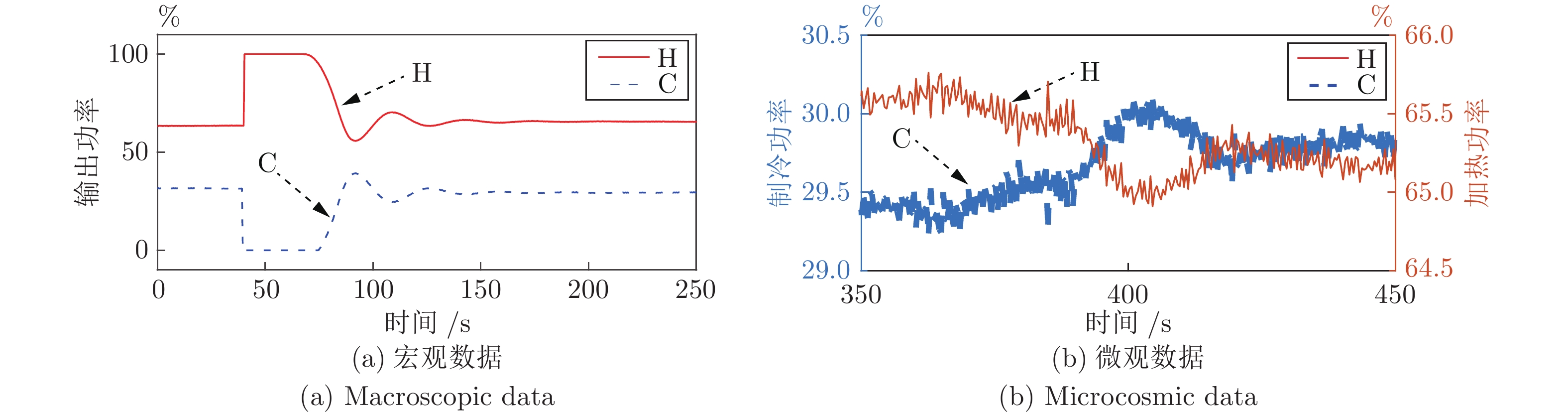
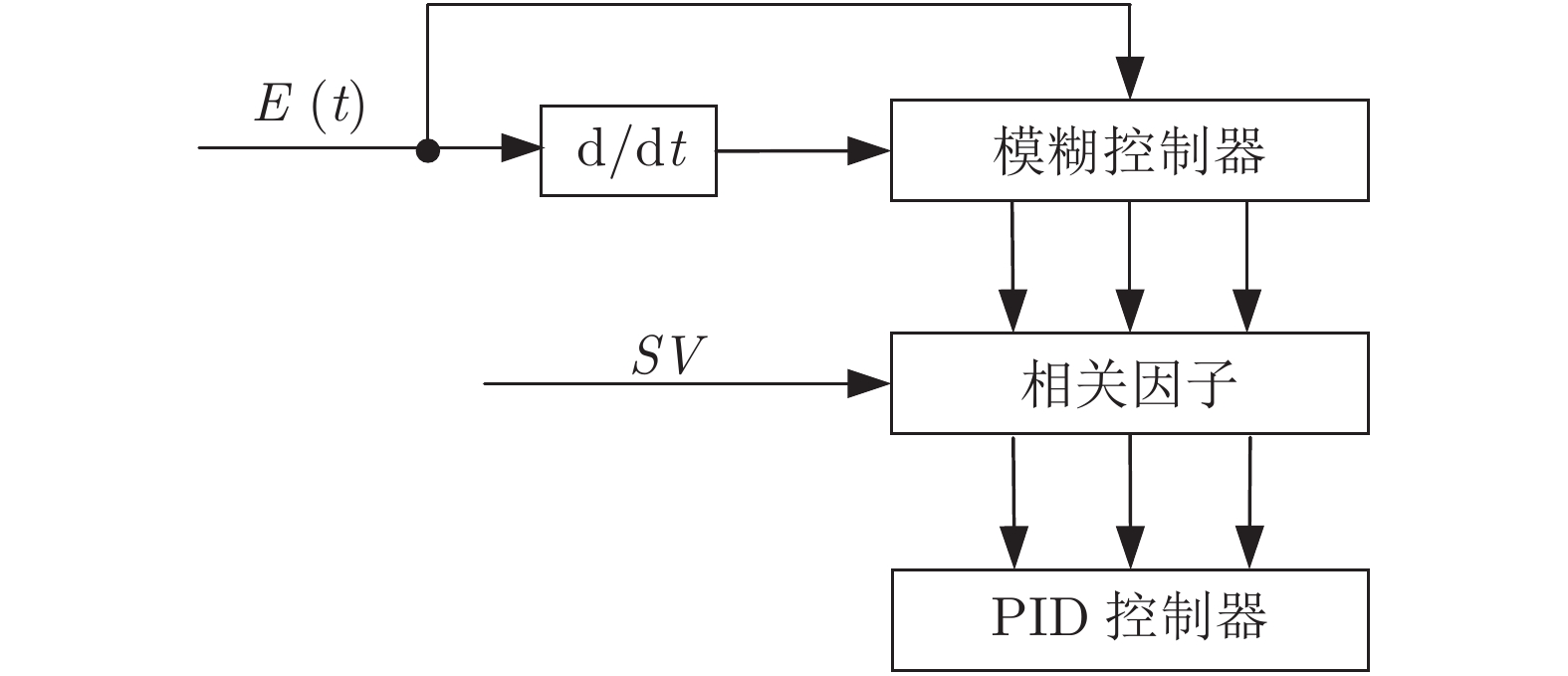
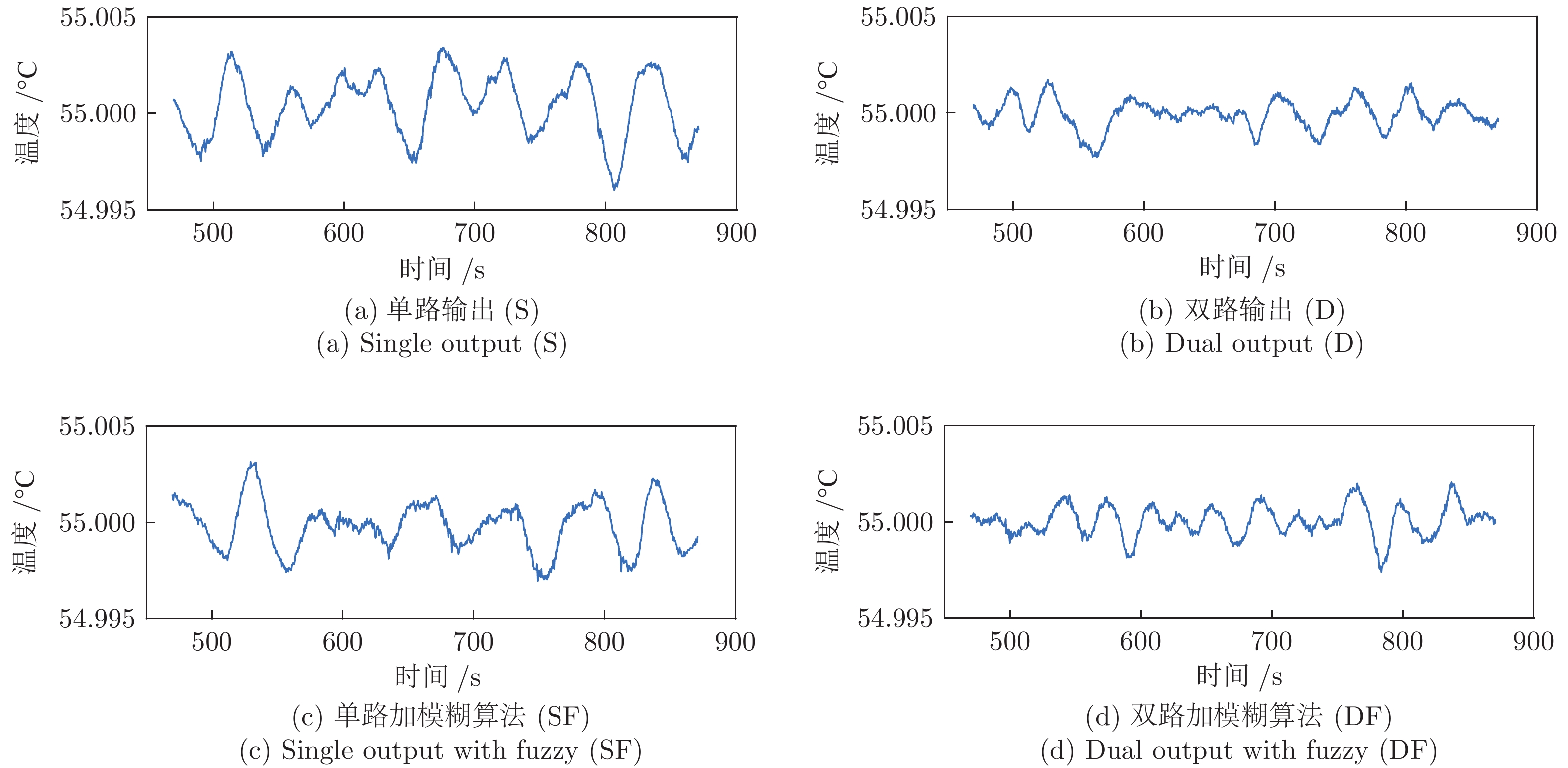
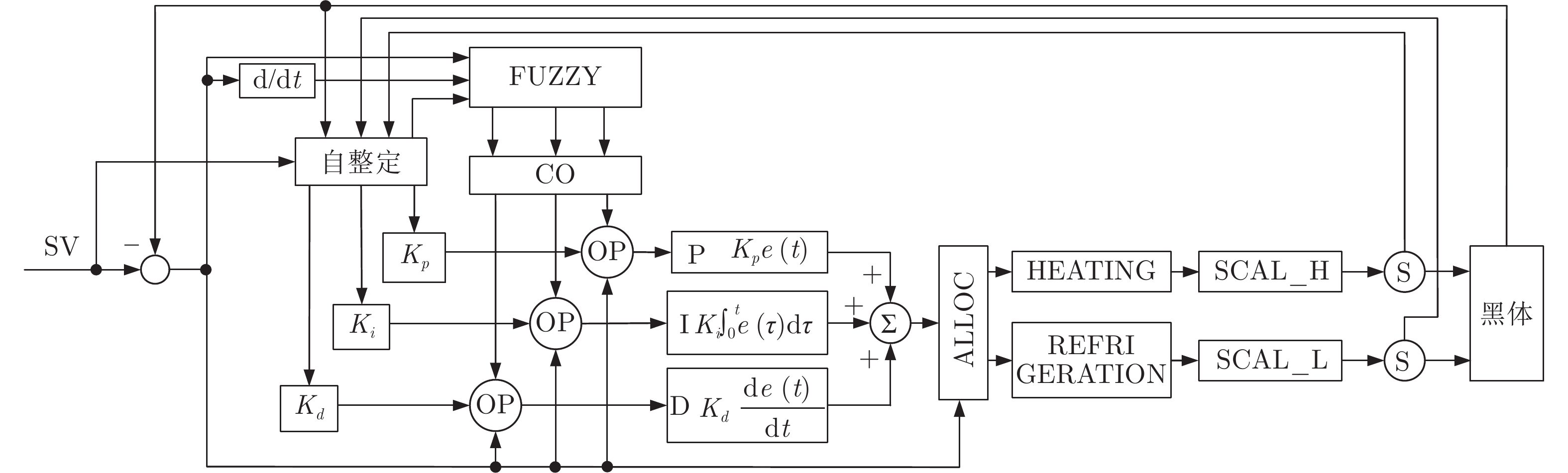
摘要: 首先, 通过分析黑体温度控制系统的物理模型, 推演出黑体传递函数的表达式.推演过程中得知黑体易受环境温度和空气散热的影响, 所以黑体温度控制系统是个非线性时变系统.结合实验黑体的阶跃响应数据, 采用阶跃响应法对传递函数进行近似计算, 得出黑体温控系统的传递函数是极点在左半轴的二阶系统, 该系统等效于二阶低通滤波器.经过低通滤波器的信号, 会滤除高频部分, 当用继电器法进行参数自整定时, 仅需计算能量较大的基波信号.通过对基波信号进行比较, 得出继电器法的整定公式, 并参照Ziegler-Nichols整定法则计算出PID参数.同时, 本文针对黑体加热器具有双路输出的特点, 提出了一种双路动态输出法, 通过理论分析了该方法可以消除环境对黑体温度的影响.对于环境温度变化较大的, 采用继电器法PID参数自整定的方式来消除; 对于黑体运行过程中环境温度变化较小的, 采用双路动态输出法来减少影响.最后, 结合实验数据, 引入性能指标, 验证了本文所述方法对黑体的温度控制性能有一定的提升.Abstract: Firstly, the expression of blackbody transfer function is deduced by analyzing the physical model of blackbody temperature control system. The blackbody temperature control system is a non-linear time-varying system. Based on the step response data of the experimental blackbody, the transfer function of the blackbody temperature control system is approximated by the step response method. It is concluded that the transfer function of the blackbody temperature control system is a second-order system with a left half axis, and the system is equivalent to a second-order low-pass filter. After low-pass filter, the high-frequency part will be filtered. When relay method is applied to parameter self-tuning, only the fundamental wave signal with large energy needs to be calculated. By comparing the fundamental wave signals, the setting formula of relay method is obtained, and the PID parameters are calculated according to Ziegler-Nichols setting rule. At the same time, aiming at the characteristics of double output of blackbody heater, a double dynamic output method is proposed, and the influence of environment on blackbody temperature can be eliminated by theoretical analysis. For the large change of ambient temperature, relay PID parameter self-tuning method can be used to eliminate; for the small change of ambient temperature during blackbody operation, dual dynamic output method can be used to reduce the impact. Finally, combined with the experimental data, the introduction of performance indicators verifies that the method described in this paper has a certain improvement in the control performance of blackbody temperature.
-
Key words:
- Parameter self-tuning /
- blackbody /
- two-way dynamic /
- second-order hysteresis system /
- PID
-
表 1 Ziegler-Nichols整定法则
Table 1 Ziegler-Nichols setting rule
控制器类型 Kp Tn Tv Ki Kd P 0.5· Kpcrit — — — — PD 0.8· Kpcrit — 0.12 Tcrit — Kp × Tv PI 0.45· Kpcrit 0.85 Tcrit — Kp/Tn — PID 0.6· Kpcrit 0.5 Tcrit 0.12 Tcrit Kp/Tn Kp × Tv 表 2 比例积分微分模糊规则
Table 2 Proportional integral differential fuzzy rule
P, I, D NB(EC) NM(EC) NS(EC) ZO(EC) PS(EC) PM(EC) PB(EC) NB(E) PB, NB, PS PB, NB, NS PM, NM, NB PM, NM, NB PS, NS, NB ZO, ZO, NM ZO, ZO, PS NM(E) PB, NB, PS PB, NB, NS PM, NM, NB PS, NS, NM PS, NS, NM ZO, ZO, NS NS, ZO, ZO NS(E) PM, NB, ZO PM, NM, NS PM, NS, NM PS, NS, NM ZO, ZO, NS NS, PS, PS NS, PS, ZO ZO(E) PM, NM, ZO PM, NM, NS PS, NS, PS ZO, ZO, NS NS, NS, NS NM, NM, NS NM, NM, ZO PS(E) PS, NM, ZO PS, NS, ZO ZO, ZO, ZO NS, PS, ZO NS, PS, ZO NM, PM, ZO NM, PB, ZO PM(E) PS, ZO, PB ZO, ZO, NS NS, PS, PS NM, PS, PS NM, PM, PS NM, PB, PS NB, PB, PB PB(E) ZO, ZO, PB ZO, ZO, PM NM, PS, PM NM, PM, PM NM, PM, PS NB, PB, PS NB, PB, PB 表 3 阶跃响应(抗干扰)性能指标
Table 3 Step response (anti-interference) performance index
条件 IAE ITAE PV TV 综合1 (综合2) S 1.000000 (1.000000) 1.000000 (1.000000) 1.000000 (1.000000) 1.000000 (1.000000) 1.000000 (1.000000) D 0.847483 (0.723668) 0.562693 (0.678478) 0.442698 (0.805442) 0.762998 (0.907009) 0.653968 (0.778649) SF 0.943743 (0.992518) 0.807751 (1.004470) 0.633536 (0.944839) 0.851171 (1.013720) 0.809050 (0.988887) DF 0.843329 (0.520340) 0.525302 (0.432016) 0.042592 (0.806038) 0.642354 (0.805883) 0.513394 (0.641069) 表 4 稳定精度测试(55 ℃)
Table 4 Stability accuracy testing (55 ℃)
条件 绝对误差 (℃) 绝对精度 均方差 TV 综合3 S 0.003979 0.0000723455 0.00163144 1.000000 1.000000 D 0.002308 0.0000419636 0.000764468 0.846146 0.844462 SF 0.003132 0.0000569455 0.00125763 0.954824 0.953850 DF 0.002628 0.0000477818 0.000786771 0.885582 0.884021 表 5 性能指标
Table 5 Performance index
条件 综合1 综合2 综合3 性能指标 S 1.000000 1.000000 1.000000 1.000000 D 0.653968 0.778649 0.844462 0.759026 SF 0.809050 0.988887 0.953850 0.917262 DF 0.513394 0.641069 0.884021 0.679495 -
[1] Oh H U, Shin S. Numerical study on the thermal design of on-board blackbody. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2012, 18(1): 25-34 doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2011.03.011 [2] Kim G J, Yoo Y S, Kim B H, Lim S D, Hyun Song J. A small-size transfer blackbody cavity for calibration of infrared ear thermometers. Physiological Measurement, 2014, 35(5): 753-762 doi: 10.1088/0967-3334/35/5/753 [3] Flambaum V V, Porsev S G, Safronova M S. Energy shift due to anisotropic blackbody radiation. Physical Review A, 2016, 93(2): 022508 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.93.022508 [4] Å ström K J, Hägglund T. The future of PID control. Control Engineering Practice, 2001, 9(11): 1163-1175 doi: 10.1016/S0967-0661(01)00062-4 [5] 黄大兴, 王景辉, 陈昱卓, 王志刚. 面黑体辐射源的温度自抗扰控制. 光电子·激光, 2017, 28(4): 376-381Huang Da-Xing, Wang Jing-Hui, Chen Yu-Zhuo, Wang Zhi-Gang. Temperature control of plane blackbody radiation source based on ADRC. Journal of Optoelectronics·laser, 2017, 28(4): 376-381 [6] Ramadan E A, El-Bardini M, Fkirin M A. Design and fpga-implementation of an improved adaptive fuzzy logic controller for dc motor speed control. Ain Shams Engineering Journal, 2014, 5(3): 803-816 doi: 10.1016/j.asej.2014.04.002 [7] Sahu B K, Pati S, Mohanty P K, Panda S. Teaching-learning based optimization algorithm based fuzzy-PID controller for automatic generation control of multi-area power system. Applied Soft Computing, 2015, 27: 240-249 doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2014.11.027 [8] 王维洲, 吴志伟, 柴天佑. 电熔镁砂熔炼过程带输出补偿的PID 控制. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(7): 1282-1292Wang Wei-Zhou, Wu Zhi-Wei, Chai Tian-You. PID control with output compensation for the fused magnesia smelting process. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(7): 1282-1292 [9] 杨天皓, 李健, 贾瑶, 刘腾飞, 柴天佑. 虚拟未建模动态补偿驱动的双率自适应控制. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(2): 299-310Yang Tian-Hao, Li Jian, Jia Yao, Liu Teng-Fei, Chai Tian-You. Dual-rate adaptive control driven by virtual unmodeled dynamics compensation in industrial heat exchange process. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(2): 299-310 [10] 李军, 陈世和, 万文军, 王越超, 黄卫剑. 一种内反馈控制器IFC 的研究与应用. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(9): 1706-1716Li Jun, Chen Shi-He, Wan Wen-Jun, Wang Yue-Chao, Huang Wei-Jian. An internal feedback controller. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(9): 1706-1716 [11] Alvarez J D, Redondo J L, Camponogara E, Normey-Rico J, Berenguel M, Ortigosa P M. Optimizing building comfort temperature regulation via model predictive control. Energy and Buildings, 2013, 57: 361-372 doi: 10.1016/j.enbuild.2012.10.044 [12] Boldbaatar E A, Lin C M. Self-learning fuzzy sliding-mode control for a water bath temperature control system. International Journal of Fuzzy Systems, 2015, 17(1): 31-38 doi: 10.1007/s40815-015-0015-6 [13] Zhang Y, Tang S, Guo J. Adaptive terminal angle constraint interception against maneuvering targets with fast fixed-time convergence. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2018, 28(8): 2996-3014 doi: 10.1002/rnc.4067 [14] 朱宇轩, 李少远. 双层模型预测控制系统的多包镇定域分析与系统设计. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(2): 262-269Zhu Yu-Xuan, Li Shao-Yuan. Analysis and system design of multi-convex hull stabilization domain for double-layered model predictive control system. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(2): 262-269 [15] Ding F, Xu L, Alsaadi F E, Hayat T. Iterative parameter identification for pseudo-linear systems with ARMA noise using the filtering technique. IET Control Theory & Applications, 2018, 12(7): 892-899 [16] 丁锋. 系统辨识新论. 北京: 科学出版社, 2013.Ding Feng. New Theory of System Identification. Beijing: Science Press, 2013. [17] Zhang X, Ding F, Xu L, Yang E F. State filtering-based least squares parameter estimation for bilinear systems using the hierarchical identification principle. IET Control Theory & Applications, 2018, 12(12): 1704-1713 [18] Huo X, Ma L, Zhao X D, Zong G D. Observer-based fuzzy adaptive stabilization of uncertain switched stochastic nonlinear systems with input quantization. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2019, 356(4): 1789-1809 doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2018.11.022 [19] Zhao X, Wang X, Zhang S, Zong G. Adaptive neural backstepping control design for a class of nonsmooth nonlinear systems. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2018, 99: 1-12 [20] Tan W, Fu C. Linear active disturbance-rejection control: analysis and tuning via IMC. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2016, 63(4): 2350-2359 [21] Guo B Z, Wu Z H, Zhou H C. Active disturbance rejection control approach to output-feedback stabilization of a class of uncertain nonlinear systems subject to stochastic disturbance. IEEE Transhactions on Automatic Control, 2016, 61(6): 1613-1618 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2015.2471815 [22] Jérôme Mendes, Luís Osório, Rui Araújo. Self-tuning PID controllers in pursuit of plug and play capacity. Control Engineering Practice, 2017, 69: 73-84 doi: 10.1016/j.conengprac.2017.09.006 [23] Ahmed S, Huang B, Shah S L. Identification from Step Responses with Transient Initial Conditions. Journal of Process Control, 2008, 18(2): 121-130 doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2007.07.009 [24] 王修中, 岳红, 高东杰. 二阶加滞后连续模型的直接辨识. 自动化学报, 2001, 27(5): 728-731Wang Xiu-Zhong, Yue Hong, Gao Dong-Jie. Direct identification of continuous second-order plus dead-time model. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2001, 27(5): 728-731 [25] 黄存坚, 尚群立, 余善恩, 张二青. 基于阶跃响应二阶加纯滞后模型的系统辨识. 机械制造, 2010, 48(10): 19-21 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4998.2010.10.006Huang Cun-Jian, Shang Qun-Li, Yu Shan-En, Zhang Er-Qin. System identification based on step response second-order plus pure delay model. Machinery, 2010, 48(10): 19-21 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4998.2010.10.006 -

计量
- 文章访问数: 1417
- HTML全文浏览量: 883
- 被引次数: 0



 下载:
下载: