Relevance Vector Machine Based Remaining Useful Life Prediction for Traction Systems of High-speed Trains
-
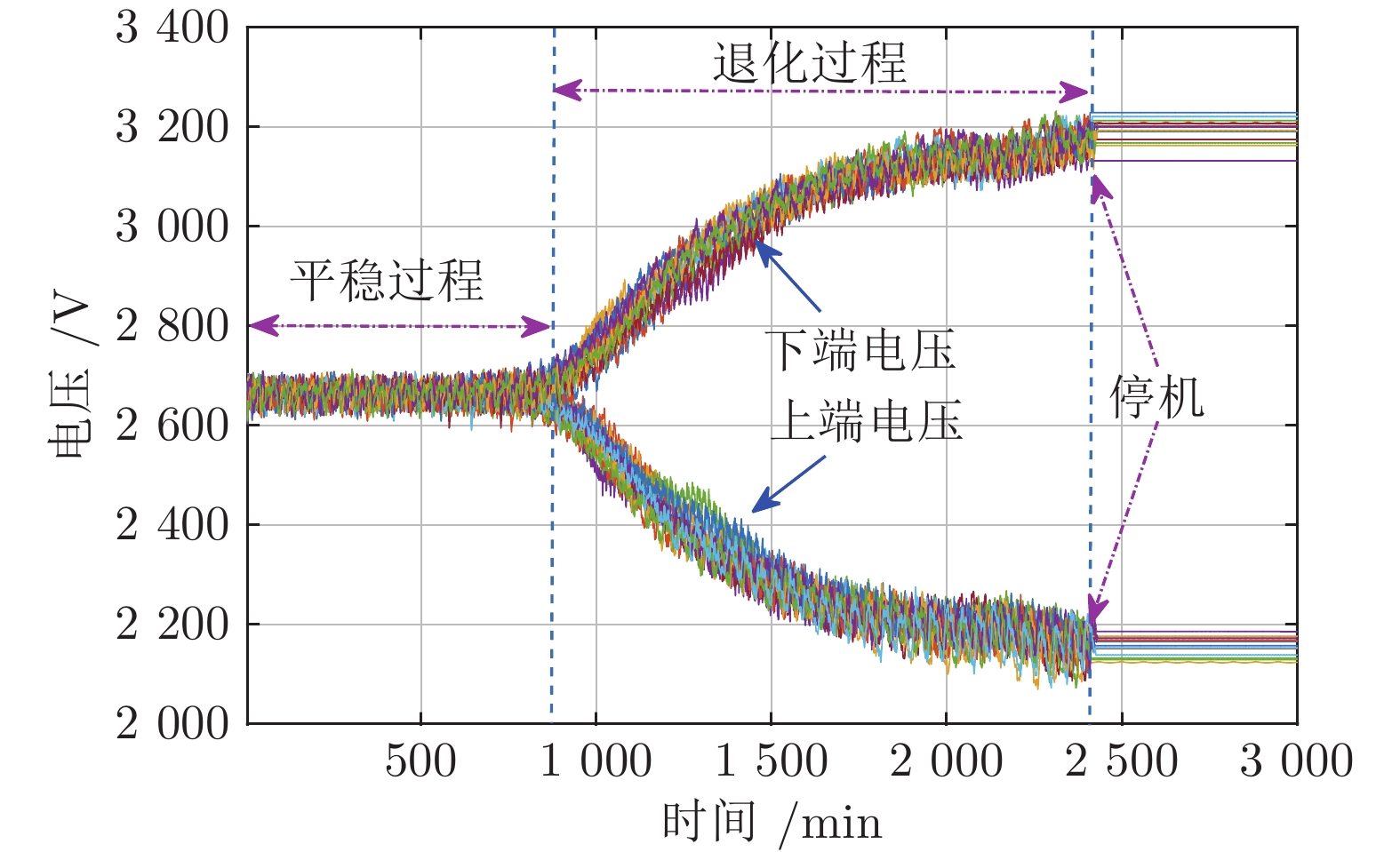
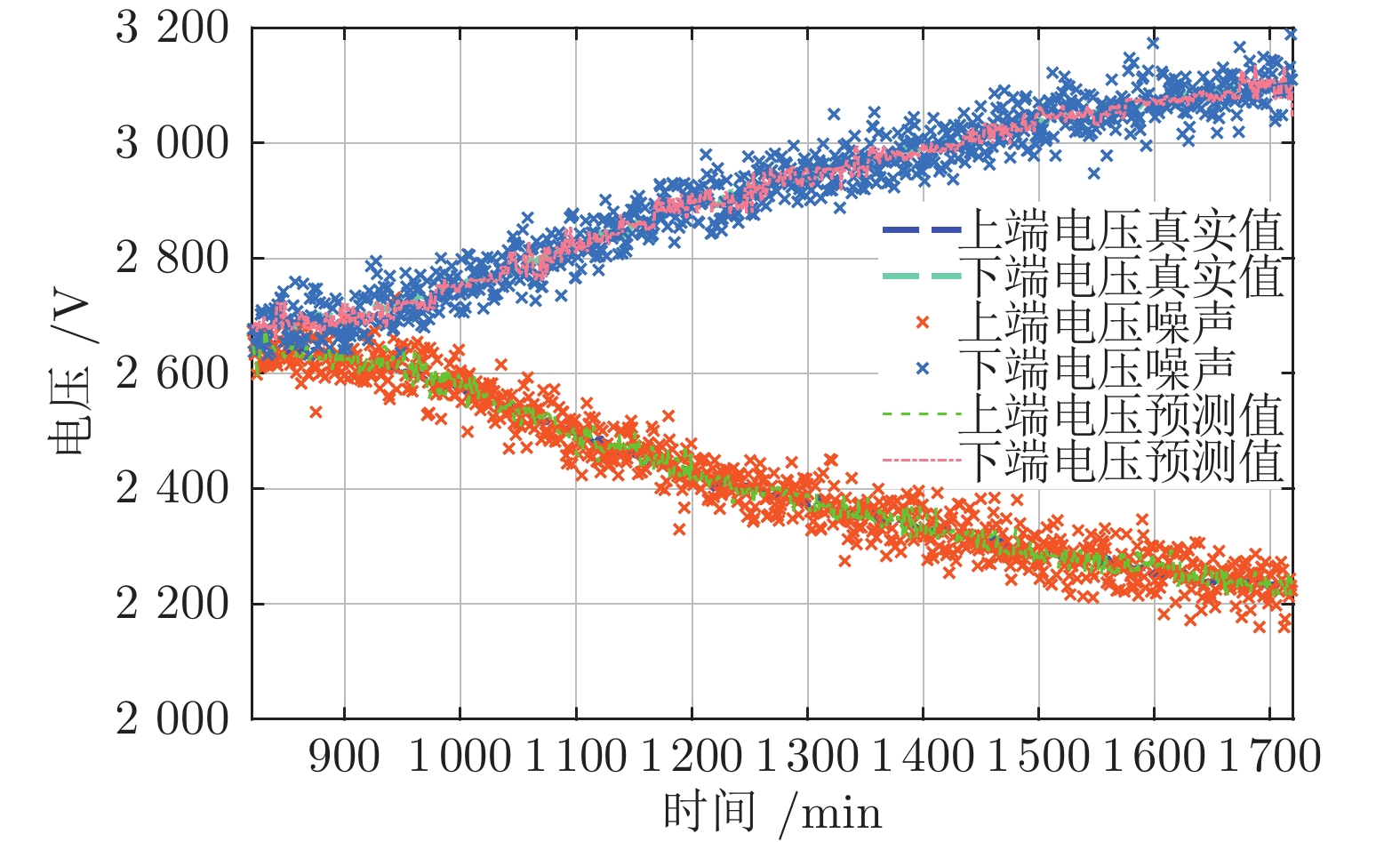
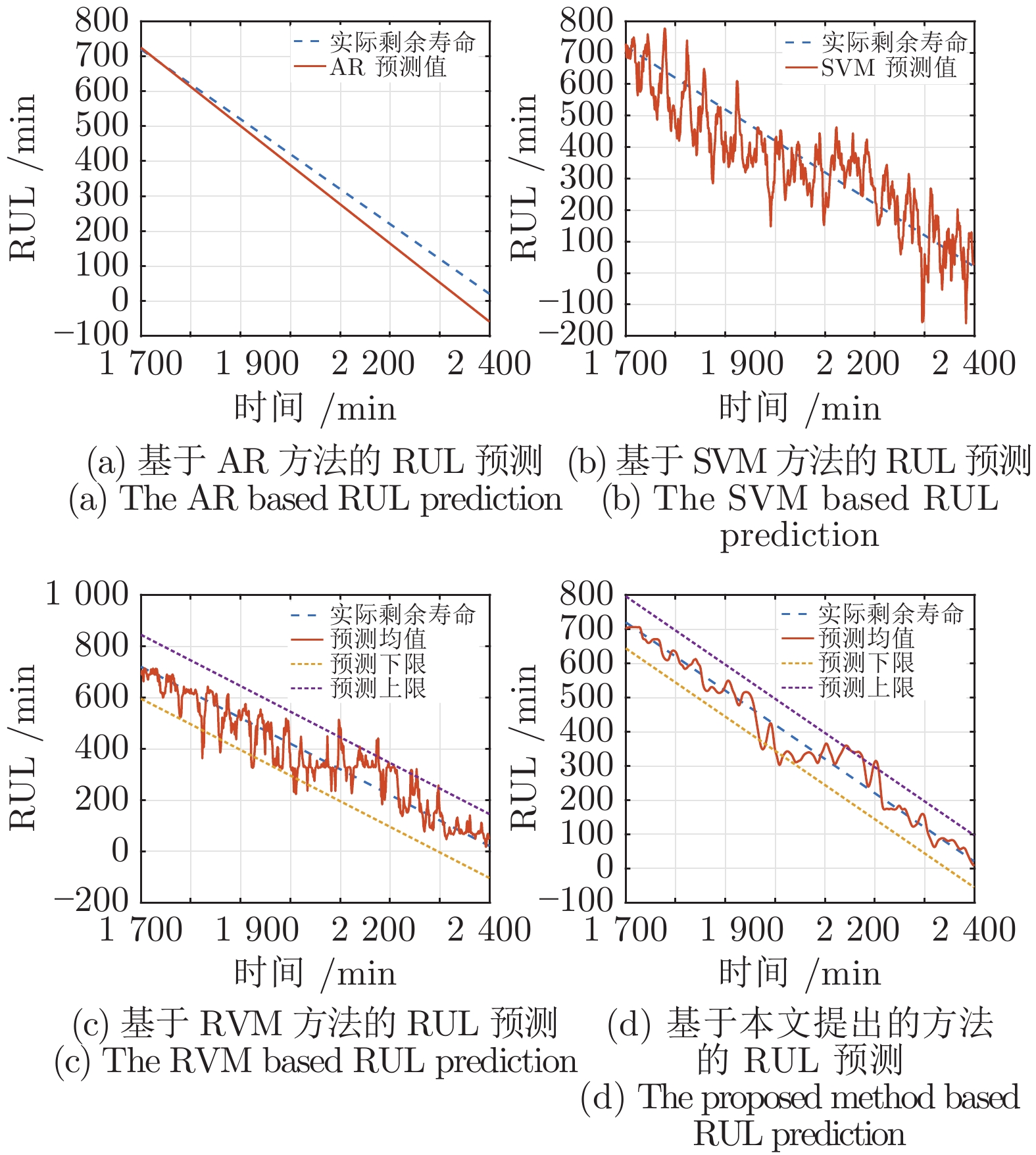
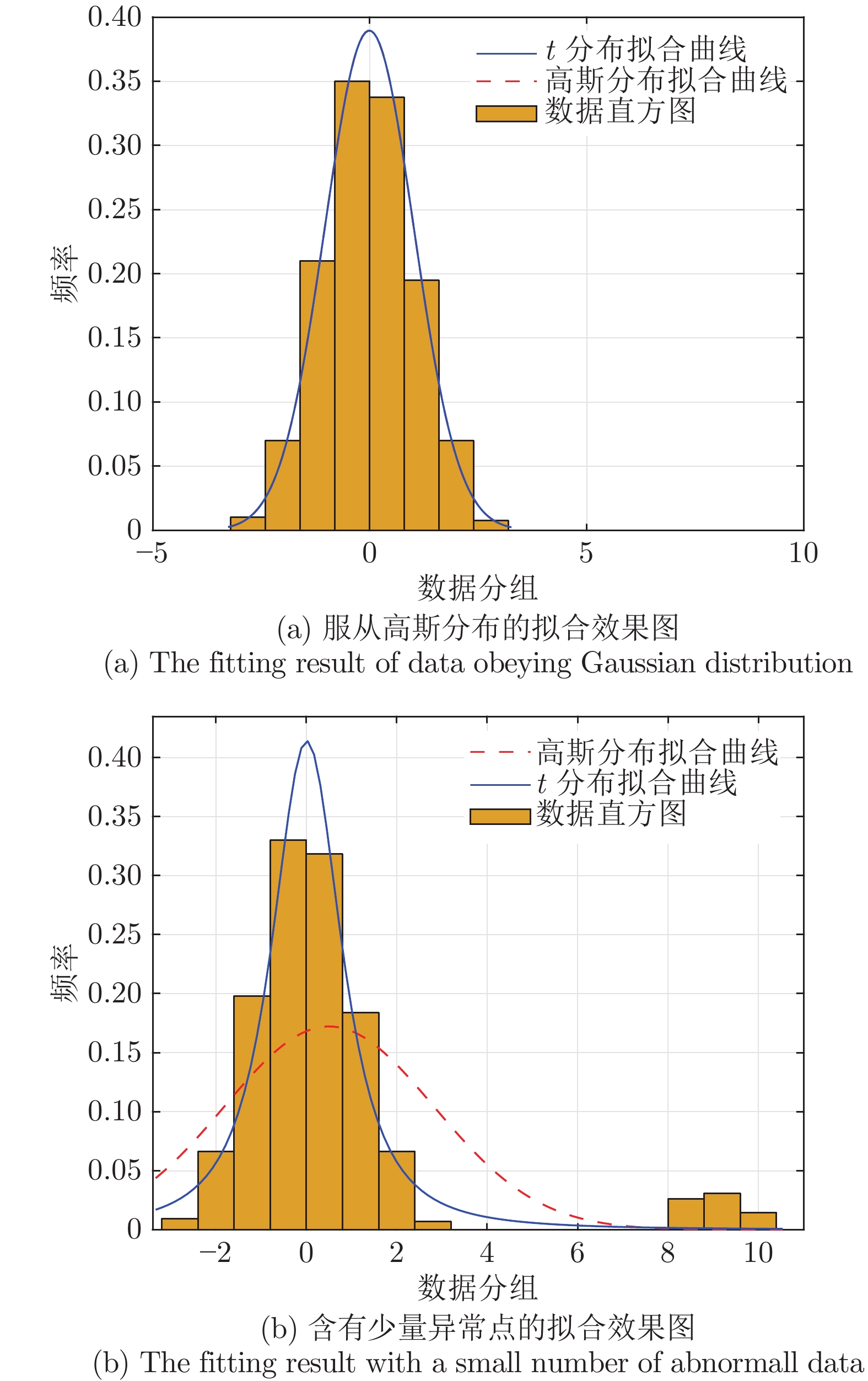
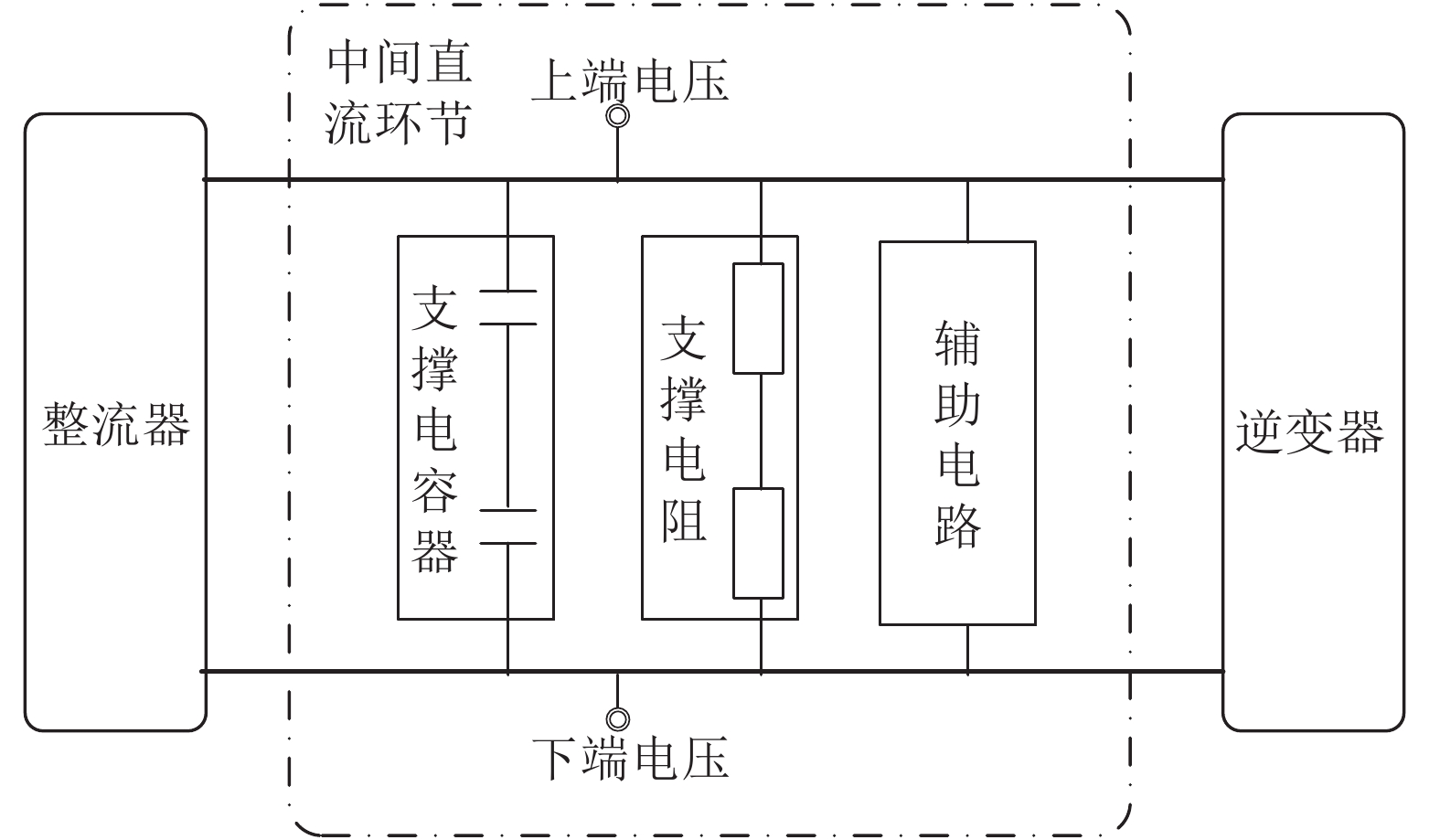
摘要: 高速列车牵引系统在运行过程中总是受到诸多不确定因素的影响, 例如, 由于列车的负载、运行环境及元器件的老化引起的不确定性, 不确定因素不可避免地影响牵引系统剩余寿命的预测精度. 为了提高不确定情景下剩余寿命预测的准确性, 本文首先采用改进的相关向量机(Relevance vector machine, RVM)方法, 建立鲁棒性能良好的多步回归模型, 由于t分布比常用的高斯分布更具有鲁棒性, 通过权重和随机误差服从t分布而非高斯分布, 改进了相关向量机回归模型, 随后将超参数的先验一并融入似然函数, 通过最大化似然函数估计未知的超参数, 此外, 利用首达时间方法从概率角度对剩余寿命进行了预测, 最后通过牵引系统中电容器退化的案例, 与传统的相关向量机方法、自回归方法和支持向量机方法进行对比, 验证了所提算法的有效性.Abstract: Traction systems often suffer from many uncertainties during their running processes, such as the inevitable uncertainties caused by the change of loading, operation and usage conditions. In order to improve the accuracy of remaining useful life (RUL) prediction under the uncertain scenario, a robust multi-step regression model is established by the improved relevance vector machine (RVM) method, in which weights and random errors are t distributed rather than Gaussian distributed. Then, unknown hyperparameters are estimated by taking priors of the hyperparameters into consideration. Moreover, the RUL is predicted by the first hitting time (FHT) method in probability perspective. The proposed method is demonstrated by a case study of capacitors degradation in traction systems. The results show the effectiveness of the proposed method.
-
表 1 退化趋势模型中的参数取值
Table 1 The parameter values in the degradation model
SVM RVM 改进RVM 核函数 径向基 高斯 高斯 $ \alpha_i $ / $ 1.0\times 10^{12} $ $ 1.2\times 10^{-6} $ $ \beta $ / $ 2.47\times 10^{-4} $ $ 6.62\times 10^{-4} $ 表 2 剩余寿命均方根误差(RMSE)及相对平均偏差(RAD)比较
Table 2 The RMSE and RAD comparison of RUL between different methods
AR SVM RVM 改进RVM RMSE (min) 1.6860 3.5654 2.3905 1.4586 RAD (%) 29.6802 35.8900 20.3468 11.3533 -
[1] 姜斌, 吴云凯, 陆宁云, 冒泽慧. 高速列车牵引系统故障诊断与预测技术综述. 控制与决策, 2018, 33(5): 841−8551 Jiang Bin, Wu Yun-Kai, Lu Ning-Yun, Mao Ze-Hui. Review of fault diagnosis and prognosis techniques for high-speed railway traction system. Control and Decision, 2018, 33(5): 841−855 [2] 2 Shang J, Chen M Y, Ji H Q, Zhou D H. Recursive transformed component statistical analysis for incipient fault detection. Automatica, 2017, 80: 313−327 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2017.02.028 [3] 3 Lei Y G, Qiao Z J, Xu X F, Liu J, Niu S T. An underdamped stochastic resonance method with stable-state matching for incipient fault diagnosis of rolling element bearings. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2017, 94: 148−164 doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2017.02.041 [4] 周东华, 纪洪泉, 何潇. 高速列车信息控制系统的故障诊断技术. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(7): 1153−11644 Zhou Dong-Hua, Ji Hong-Quan, He Xiao. Fault diagnosis techniques for the information control system of high-speed trains. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(7): 1153−1164 [5] 5 Tobon-Mejia D A, Medjaher K, Zerhouni N, Tripot, G. A data-driven failure prognostics method based on mixture of Gaussians hidden Markov models. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2012, 61(2): 491−503 doi: 10.1109/TR.2012.2194177 [6] 6 Haque M S, Choi S, Baek J. Auxiliary particle filtering-based estimation of remaining useful life of IGBT. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2018, 65(3): 2693−2703 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2017.2740856 [7] 7 Tseng S T, Balakrishnan N, Tsai C C. Optimal step-stress accelerated degradation test plan for gamma degradation processes. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2009, 58(4): 611−618 doi: 10.1109/TR.2009.2033734 [8] 8 Zhai Q, Ye Z S. RUL prediction of deteriorating products using an adaptive wiener process model. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2017, 13(6): 2911−2921 doi: 10.1109/TII.2017.2684821 [9] 9 Si X S, Wang W B, Hu C H, Zhou D H. Remaining useful life estimation-a review on the statistical data driven approaches. European Journal of Operational Research, 2011, 213(1): 1−14 doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2010.11.018 [10] 10 Lu N Y, Yao Y, Gao F R. Two-dimensional dynamic PCA for batch process monitoring. AIChE Journal, 2005, 51(12): 3300−3304 doi: 10.1002/aic.10568 [11] 11 Zhao C H, Gao F R. Online fault prognosis with relative deviation analysis and vector autoregressive modeling. Chemical Engineering Science, 2015, 138(22): 531−543 [12] 12 Zhao C H, Gao F R. Critical-to-fault-degradation variable analysis and direction extraction for online fault prognostic. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2017, 25(3): 842−854 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2016.2576018 [13] 13 Li Y, Lu N Y, Wang X L, Jiang B. Islanding fault detection based on data-driven approach with active developed reactive power variation. Neurocomputing, 2019, 337(14): 97−109 [14] 14 Pham H T, Yang B S, Nguyen T T. Machine performance degradation assessment and remaining useful life prediction using proportional hazard model and support vector machine. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2012, 32: 320−330 doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2012.02.015 [15] 15 Huang H Z, Wang H K, Li Y F, Zhang L L, Liu Z L. Support vector machine based estimation of remaining useful life: current research status and future trends. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 2015, 29(1): 151−163 doi: 10.1007/s12206-014-1222-z [16] 16 Tipping M E. Sparse bayesian learning and the relevance vector machine. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2001, 1(3): 211−44 [17] 17 Yu H Y, Wu Z H, Chen D W, Ma X L. Probabilistic prediction of bus headway using relevance vector machine regression. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2017, 18(7): 1772−1781 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2016.2620483 [18] 18 Wu Y M, Breaz E, Gao F, Miraoui A. A modified relevance vector machine for PEM fuel-cell stack aging prediction. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2016, 52(3): 2573−2581 doi: 10.1109/TIA.2016.2524402 [19] 19 Saha B, Goebel K, Poll S, Christophersen J. Prognostics methods for battery health monitoring using a Bayesian framework. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2009, 58(2): 291−296 doi: 10.1109/TIM.2008.2005965 [20] 20 Widodo A, Kim, E Y, Son J D, Yang B S, Tan A C, Gu D S, Choid B K, Mathew J. Fault diagnosis of low speed bearing based on relevance vector machine and support vector machine. Expert Systems with Applications, 2009, 36(3): 7252−7261 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2008.09.033 [21] 21 Zio E, Di Maio F. Fatigue crack growth estimation by relevance vector machine. Expert Systems with Applications, 2012, 39(12): 10681−10692 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2012.02.199 [22] 22 Widodo A, Yang B S. Application of relevance vector machine and survival probability to machine degradation assessment. Expert Systems with Applications, 2011, 38(3): 2592−2599 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2010.08.049 [23] Wang X L, Jiang B, Lu N Y. Adaptive relevant vector machine based RUL prediction under uncertain conditions. ISA Transactions, 2018, DOI: 10.1016/j.isatra. 2018.11.024 [24] 24 Yang C H, Yang C, Peng T, Yang X Y, Gui W H. A fault-injection strategy for traction drive control systems. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2017, 64(7): 5719−5727 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2017.2674610 [25] 25 Yang X Y, Yang C H, Peng T, Chen Z W, Liu B, Gui W H. Hardware-in-the-loop fault injection for traction control system. IEEE Journal of Emerging and Selected Topics in Power Electronics, 2018, 6(2): 696−706 doi: 10.1109/JESTPE.2018.2794339 -




 下载:
下载: